Fine Urban Land Use Identification Based on Fusion of Multi-source Data
-
摘要:
我国土地利用类型复杂,为解决依靠单一遥感图像或POI(point of interest)数据而难以准确识别城市土地利用类型的困境,提出一种遥感图像和POI数据相结合的精细识别方法. 首先,为精细识别城市地块功能,选取500 m栅格为研究单位;其次,提取POI数据并生成各类土地利用的核密度分布图,对遥感、POI图像数据进行数据预处理、数据切分、数据增强以提取有效信息;最后,将POI核密度分布图和高分遥感影像数据融合,以现状土地利用数据为标签,构建UNet++网络对城市地块分类,并运用CA算法对模型参数进行优化. 以深圳市为实例开展实验,并在罗湖区和南山区进行迁移验证,结果表明:融合POI数据的城市土地利用精确识别模型平均精度为70.6%,比仅使用遥感数据识别模型精度高6.7%;使用CA算法后,模型精度提高1.5%;对模型进行迁移验证,模型平均精度为72.6%,表明模型具有较高的稳健性;此外,POI数据弥补了遥感影像仅涉及光谱、纹理和地物结构物理属性的不足,能较好识别商服用地、公共管理与公共服务用地,相较于单一数据识别模型精度分别高了7.5%、6.0%.
Abstract:Land use type in China is complex, and it is difficult to accurately identify urban land use type by relying on a single remote sensing image or point of interest (POI) data. To address this issue, a fine identification method combining remote sensing images and POI data was proposed. Firstly, to finely identify urban land parcel functions, a 500-meter grid was selected as the research unit; secondly, POI data were extracted, and kernel density distribution maps of various land uses were generated. Data preprocessing, data segmentation, and data enhancement were performed on remote sensing and POI image data to extract effective information. Finally, the POI kernel density distribution map and high-resolution remote sensing image data were fused together, and the current land use data was used as the label to construct the UNet++ network to classify urban land parcels. The model parameters were optimized using the cosine annealing (CA) algorithm, and the proposed method was tested in Shenzhen City. Migration verification was carried out in Luohu District and Nanshan District. The results show that the average accuracy of the urban land use identification model fused with POI data is 70.6%, which is 6.7% higher than that of the identification model using only remote sensing data; after using the CA algorithm, the model accuracy is increased by 1.5%. The migration verification of the model is carried out, and the average accuracy of the model is 72.6%. This shows that the model is robust. In addition, POI data makes up for the shortcomings of remote sensing images that only involve spectrum, texture, and physical attributes of ground structures, and it can better identify commercial land and public management and service land. The accuracy is 7.5% and 6.0% higher than that of a single data identification model.
-
Key words:
- traffic planning /
- land use /
- deep learning /
- multi-source data
-
表 1 深圳市土地利用现状类别
Table 1. Current land use types in Shenzhen City
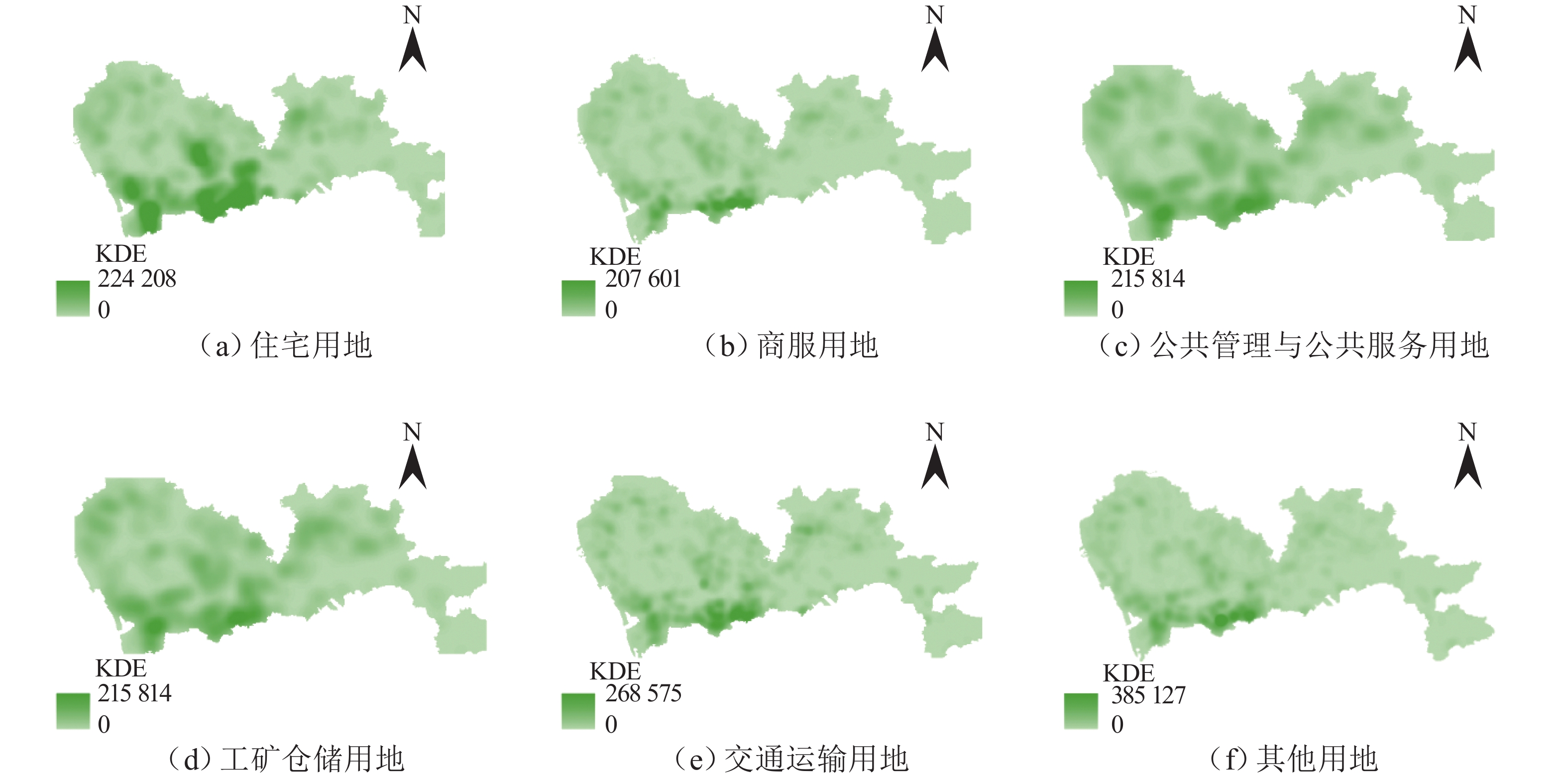
编码 用地属性 描述 总面积/km2 07 住宅用地 除配套的商务、服务业设施用地之外的用于居民生活和居住的各种类型的住宅以及周边的附属设施用地 211.75 05 商服用地 包括用于商务服务用地,以及办公场所具有经营性质的用地;居住用地中包含商业零售、服务、生产、批发、娱乐等功能为主的用地也包含在内 37.26 08 公共管理与公共服务用地 包括公用的文体设施用地,以及各种类型的教育、机关团体、医疗服务等用地 390.69 06 工矿仓储用地 指工厂、车间、手工业作坊等进行工业生产、产品加工制造活动用地,也包括直接服务于工业生产的附属设施用地 273.20 10 交通运输用地 包括直接用于交通运输和通行的地面线路;交通服务设施用地,例如火车场站、地铁站、汽运枢纽及其附属设施用地;军民合用机场、民用机场用地;港口及其附属建筑物用地 235.15 12 其他用地 裸地、水域等未利用和未开发用地 1084.64 表 2 高德POI和城市土地利用的映射关系
Table 2. Mapping relationship between AutoNavi POI and urban land use
类别编码 用地属性 高德 POI 类别编码 高德 POI 类别说明 07 住宅用地 中类: 1203 中类:住宅区 05 商服用地 大类:12,16,17 大类:商务住宅、金融保险服务,公司企业 08 公共管理与服务
服务用地大类:09,11,13,14;
中类:1410 ,1412 ,1413 ,1415 大类:医疗保健服务、风景名胜、政府机构及社会团体、科教文化服务
中类:文艺团体,学校、科研机构、驾校06 工矿仓储用地 中类:0705, 1703 ;
小类:170204 ,170205 中类:物流快递、工厂
小类:机械电子、冶金化工10 交通运输用地 大类:15 大类:交通设施服务 12 其他用地 表 3 输入数据通道概况
Table 3. Description of input data channels
数据类型 通道描述 通道数量/个 通道总和/个 遥感影像 全色 1 4 多光谱 3 NDVI 1 1 POI 映射编码为 07 1 6 映射编码为 05 1 映射编码为 08 1 映射编码为 06 1 映射编码为 10 1 映射编码为 12 1 表 4 POI特征交叉验证结果
Table 4. Results of cross-validation considering POI characteristics
验证折数序号 方法 是否融合 POI 通道特征 各用地类型准确度 mAcc 平均mAcc 07 05 08 06 10 12 1 UNet++ 是 0.660 0.467 0.523 0.679 0.644 0.835 0.635 0.639 2 0.676 0.451 0.515 0.691 0.637 0.830 0.633 3 0.720 0.472 0.519 0.712 0.661 0.864 0.658 4 0.675 0.450 0.493 0.639 0.660 0.863 0.630 5 0.689 0.417 0.484 0.677 0.684 0.877 0.638 1 UNet++ 否 0.714 0.581 0.591 0.720 0.681 0.865 0.692 0.706 2 0.729 0.616 0.645 0.735 0.674 0.847 0.708 3 0.735 0.605 0.674 0.723 0.708 0.865 0.718 4 0.720 0.594 0.635 0.684 0.704 0.871 0.701 5 0.735 0.586 0.628 0.712 0.720 0.881 0.710 表 5 CA算法优化前后结果
Table 5. Results of CA algorithm before and after optimization
验证折数序号 方法 CA 优化 各用地类别准确度 mAcc 平均mAcc 07 05 08 06 10 12 6 UNet++ 未使用 0.714 0.581 0.591 0.720 0.681 0.865 0.692 0.706 7 0.729 0.616 0.645 0.735 0.674 0.847 0.708 8 0.735 0.605 0.674 0.723 0.708 0.865 0.718 9 0.720 0.594 0.635 0.684 0.704 0.871 0.701 10 0.735 0.586 0.628 0.712 0.720 0.881 0.710 6 UNet++ 使用 0.726 0.599 0.600 0.736 0.708 0.864 0.706 0.721 7 0.742 0.641 0.647 0.754 0.700 0.852 0.723 8 0.744 0.628 0.670 0.733 0.735 0.876 0.731 9 0.733 0.625 0.644 0.705 0.732 0.873 0.719 10 0.748 0.607 0.639 0.729 0.741 0.878 0.724 表 6 迁移区域土地利用预测结果
Table 6. Predicted results of land use in migration area
土地利用
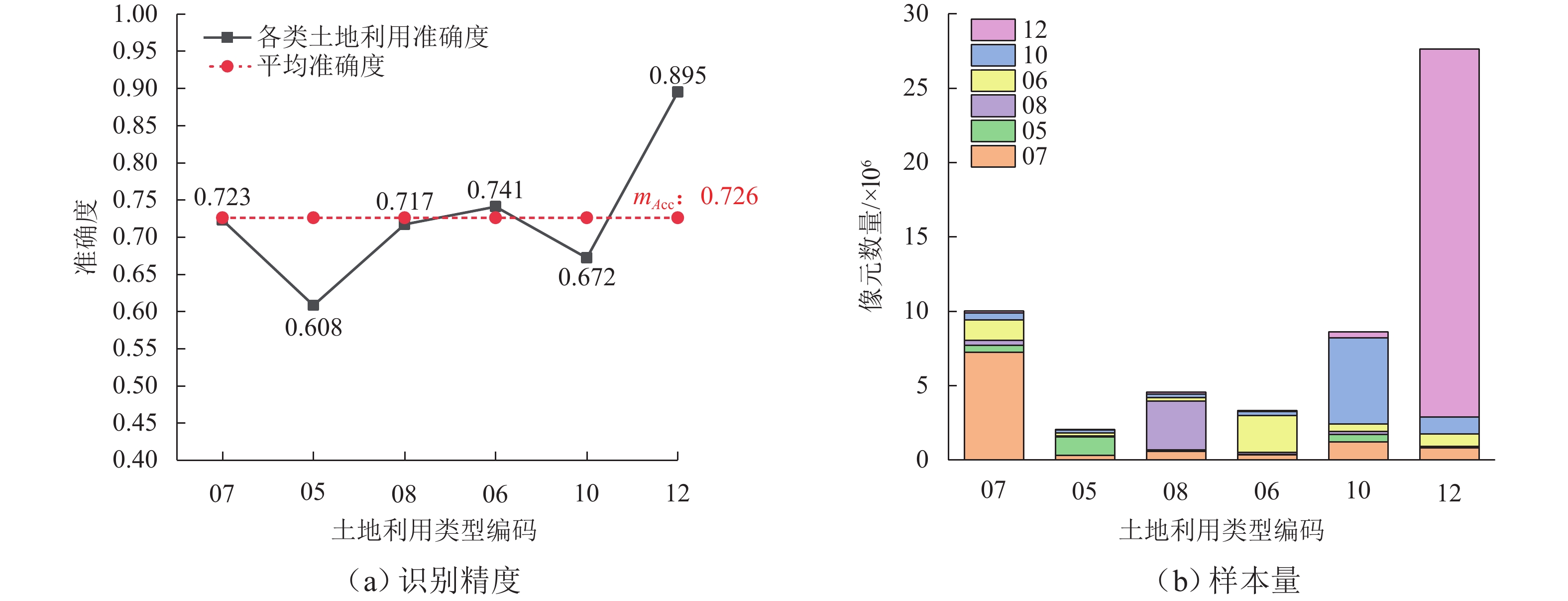
类型编码预测结果 准确度 mAcc 07 05 08 06 10 12 07 7254587 460884 331122 1373299 463604 150510 0.723 0.726 05 309627 1255023 45412 213230 199606 35091 0.608 08 592161 86457 3267402 256562 228235 126230 0.717 06 348281 35893 127925 2467265 289679 60600 0.741 10 1208635 504431 218529 498040 5776828 390006 0.672 12 824235 52864 32349 833590 1160088 24745690 0.895 -
[1] 钟鸣,董一鸣,汉特•道格拉斯,等. 面向新城的土地利用-交通整体规划建模方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21:13-25.ZHONG Ming, DONG Yi, JOHN-DOUGLAS H, et al. Development of a new town planning method using an integrated land use-transport model[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21: 13-25. [2] 武凯飞,钟鸣,王慧妮,等. 面向土地交通整体规划的土地利用精细分类模型研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版),2020,44:669-75.WU Kaifei, ZHONG Ming, WANG Huini, et al. Study on high-resolution classification model of land use for overall planning of land transportation[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 2020, 44: 669-75. [3] 赵锦焕,李文权. 居民出行调查中交通小区划分方法的改进[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报,2009,7(2): 110-115.ZHAO J, LI W. Improvement of the traffic district partition in resident trip investigation[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2009, 7(2): 110-115. [4] LI J X, HONG D F, GAO L R, et al. Deep learning in multimodal remote sensing data fusion: a comprehensive review[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2022, 112: 102926.1-102926.16. [5] CARRANZA-GARCÍA M, GARCÍA-GUTIÉRREZ J, RIQUELME J C. A framework for evaluating land use and land cover classification using convolutional neural networks[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 274.1-274.23. [6] ZHANG C, JIANG W S, ZHANG Y, et al. Transformer and CNN hybrid deep neural network for semantic segmentation of very-high-resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 3144894.1-3144894.20. [7] ZHENG H H, GONG M G, LIU T F, et al. HFA-Net: high frequency attention Siamese network for building change detection in VHR remote sensing images[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 129: 108717.1-108717.11. [8] CHENG G, WANG G X, HAN J W. ISNet: towards improving separability for remote sensing image change detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 3174276.1-3174276.11. [9] CAO R, ZHU J S, TU W, et al. Integrating aerial and street view images for urban land use classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1553.1-1553.23. [10] ZONG L L, HE S J, LIAN J T, et al. Detailed mapping of urban land use based on multi-source data: a case study of Lanzhou[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(12): 1987.1-1987.19. [11] LU W P, TAO C, LI H F, et al. A unified deep learning framework for urban functional zone extraction based on multi-source heterogeneous data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2022, 270: 112830.1-112830.16. [12] SUN J, WANG H, SONG Z L, et al. Mapping essential urban land use categories in Nanjing by integrating multi-source big data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(15): 2386.1-2386.18. [13] 季顺平,田思琦,张驰. 利用全空洞卷积神经元网络进行城市土地覆盖分类与变化检测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45:233-41.JI Shunping, TIAN Siqi, ZHANG Chi. Urban land cover classification and change detection using fully atrous convolutional neural network[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45: 233-41. [14] LIU X P, HE J L, YAO Y, et al. Classifying urban land use by integrating remote sensing and social media data[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2017, 31(8): 1675-1696. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2017.1324976 [15] PENG D F, ZHANG Y J, GUAN H Y. End-to-end change detection for high resolution satellite images using improved UNet + + [J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(11): 1382.1-1382.23. doi: 10.3390/rs11111382 [16] YUAN Y T, FANG F M, ZHANG G X. Superpixel-based seamless image stitching for UAV images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1565-1576. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2999404 [17] 禹文豪,艾廷华. 核密度估计法支持下的网络空间POI点可视化与分析[J]. 测绘学报,2015,44:82-90.YU Wenhao, AI Tinghua. The visualization and analysis of POI features under network space supported by kernel density estimation[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2015, 44: 82-90. [18] 侯越,陈逸涵,顾兴宇,等. 基于卷积自编码的沥青路面目标与裂缝智能识别[J]. 中国公路学报,2020,33:288-303.HOU Yue, CHEN Yihan, GU Xingyu, et al. Automatic identification of pavement objects and cracks using the convolutional auto-encoder[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33: 288-303. [19] 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局.土地利用现状分类 GB/T 21010—2017[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2017. [20] 中国资源卫星应用中心. 高分一号 [EB/OL]. [2023-06-01]. https://www.cresda.com. [21] 高德开放平台. POI数据[EB/OL]. [2023-06-01]. https://restapi.amap.com/v3/place. [22] DU S H, DU S H, LIU B, et al. Mapping large-scale and fine-grained urban functional zones from VHR images using a multi-scale semantic segmentation network and object based approach[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 261: 112480.1-112480.20. [23] DENG Y B, CHEN R R, YANG J, et al. Identify urban building functions with multisource data: a case study in Guangzhou, China[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2022, 36(10): 2060-2085. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2022.2046756 [24] ZHOU W, MING D P, LV X W, et al. SO-CNN based urban functional zone fine division with VHR remote sensing image[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 236: 111458.1-111458.20. -




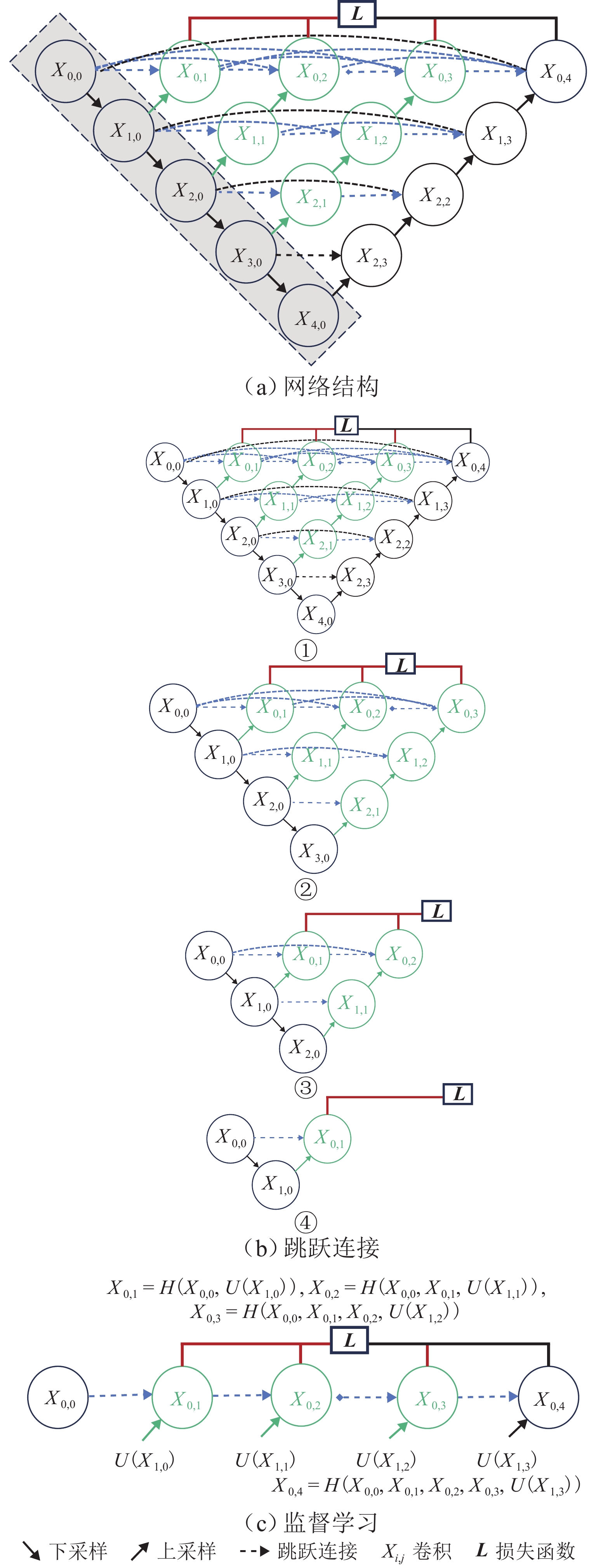
 下载:
下载: