Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication Multi-Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Network Assisted by Intelligent Reflecting Surface in Air
-
摘要:
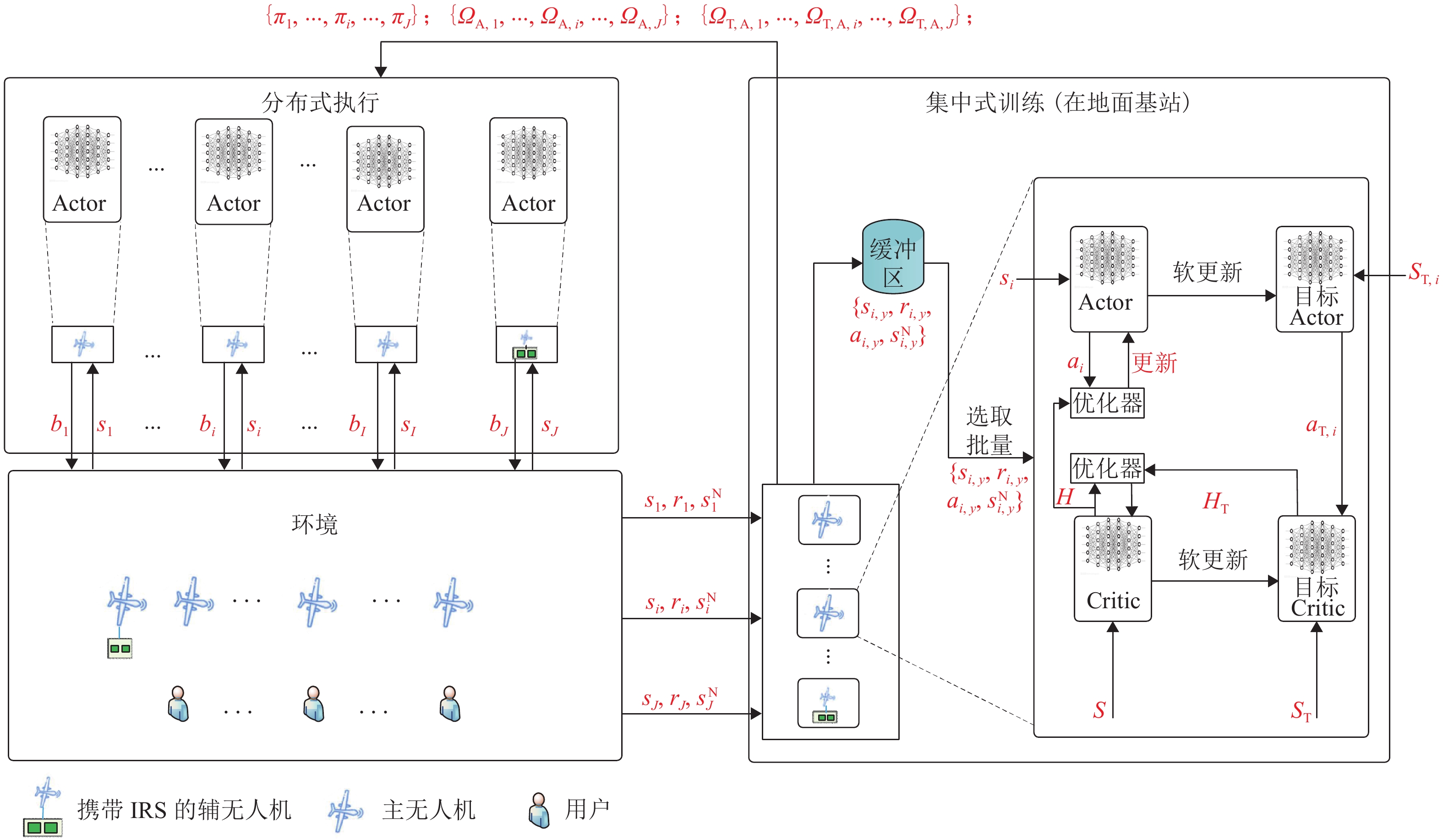
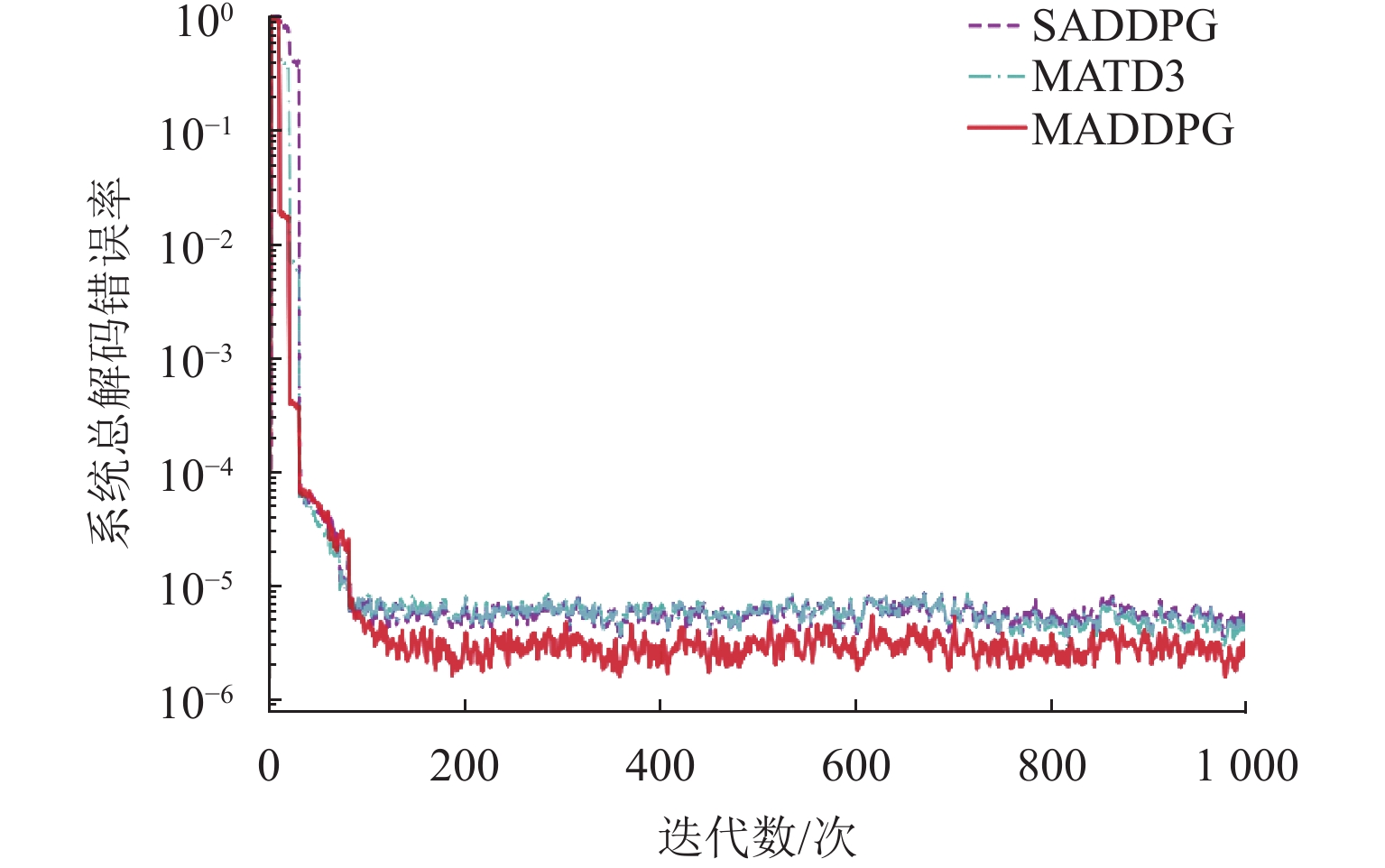
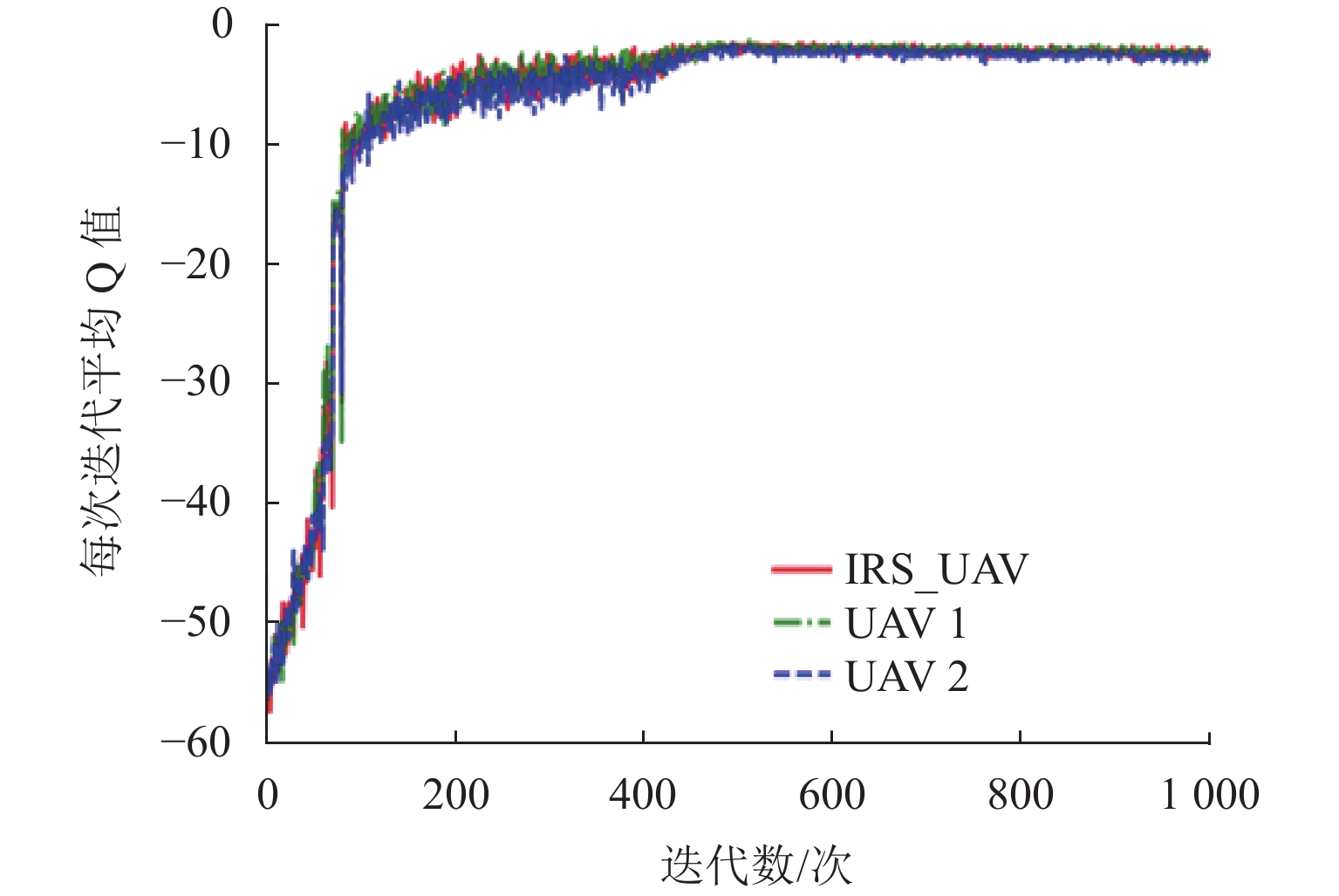
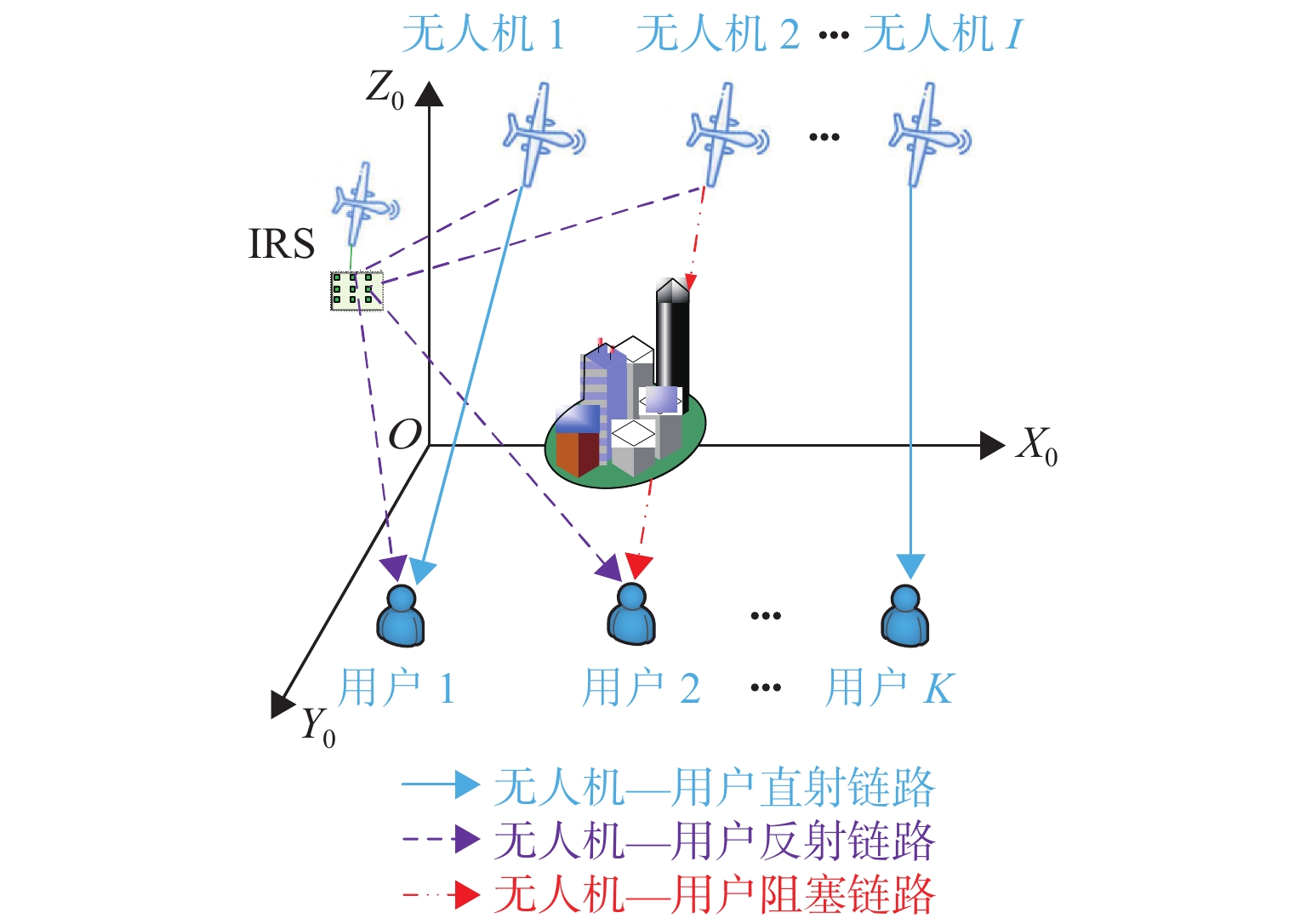
在多无人机超可靠低时延通信(ultra-reliable low-latency communications,URLLC)网络中,为满足超可靠低时延要求,引入空中智能反射面(intelligent reflecting surface,IRS)辅助通信,提出一种多智能体深度确定性策略梯度(multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient,MADDPG)方法. 首先,建立URLLC多无人机系统模型,其中,多架主无人机作为空中基站为多个地面用户提供服务,一架辅无人机携带IRS作为空中无源中继,辅助主无人机与地面用户通信;然后,考虑多种信道条件和能耗,分别建立复合信道模型和总能耗模型;接着,对问题进行分析,在满足有限块长、无人机能量以及IRS相移的约束下,通过联合优化通信调度、IRS相移以及块长,达到总解码错误率最小化的目标;最后,考虑集中式训练在URLLC场景下的时延敏感限制以及分布式训练在无人机资源限制下的能量限制,设计集中式训练、分布式执行的MADDPG框架. 研究结果表明:总解码错误率随着IRS反射单元的增加而急剧下降;同时,总解码错误率随着块长和发射功率的增大而减小,具体来说,块长每增加20 个符号,总解码错误率减小91.1%.
Abstract:In the ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC) multi-unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) network, to satisfy the ultra-reliable low-latency requirements, the intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) in the air was introduced to assist in communication, and a multi-intelligent deep deterministic policy gradient (MADDPG) method was proposed. First, the URLLC multi-UAV system model was established, in which multiple primary UAVs acted as airborne base stations to provide services for multiple ground users, and one auxiliary UAV carried an IRS as an airborne passive relay to assist the primary UAV in communicating with the ground users. The composite channel model and the total energy model were established respectively by considering multiple channel conditions and energy consumption. Second, the problem was analyzed to minimize the total decoding error rate by jointly optimizing the communication schedule, IRS phase shift, and block length while satisfying the constraints of finite block length, UAV energy, and IRS phase shift. Finally, the MADDPG framework with centralized training and distributed execution was designed by considering the delay-sensitive constraints of centralized training in URLLC scenarios and the energy constraints of distributed training under the resource limitations of UAVs. The results show that the total decoding error rate decreases sharply with the increase in IRS units. Meanwhile, the total decoding error rate decreases with the increase in block length and transmitted power. To be specific, the total decoding error rate decreases by 91.1% as every 20 symbols are added to the block length.
-
-
[1] HAYAT S, YANMAZ E, MUZAFFAR R. Survey on unmanned aerial vehicle networks for civil applications:a communications viewpoint[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(4): 2624-2661. [2] 王健,秦春霞,杨珂,等. 基于HSV透射率加权修正的机载视频去雾系统设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 160-167,205.WANG Jian, QIN Chunxia, YANG Ke, et al. Design of airborne video dehazing system for UCAV based on HSV transmission weighted correction[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 160-167,205. [3] SU Y H, PANG X W, CHEN S Z, et al. IRS-UAV relaying networks for spectrum and energy efficiency maximization[C]//IEEE International Conference on Communications. Seoul:IEEE,2022:2834-2839. [4] ZENG Y, WU Q Q, ZHANG R. Accessing from the sky:a tutorial on UAV communications for 5G and beyond[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(12): 2327-2375. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2952892 [5] HUANG C W, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157-4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [6] WU Q Q, ZHANG R. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394-5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025 [7] PANG X W, SHENG M, ZHAO N, et al. When UAV meets IRS:expanding air-ground networks via passive reflection[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(5): 164-170. doi: 10.1109/MWC.010.2000528 [8] WEI Z Q, CAI Y X, SUN Z, et al. Sum-rate maximization for IRS-assisted UAV OFDMA communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(4): 2530-2550. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3042977 [9] WANG F, ZHANG X. IRS/UAV-based edge-computing/traffic-offloading over RF-powered 6G mobile wireless networks[C]//IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC). Austin:IEEE,2022:1272-1277. [10] CHEN K H, WANG Y, ZHAO J W, et al. URLLC-oriented joint power control and resource allocation in UAV-assisted networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(12): 10103-10116. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3051322 [11] MA Z F, AI B, HE R S, et al. Multipath fading channel modeling with aerial intelligent reflecting surface[C]// IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). Madrid:IEEE,2021:1-6. [12] WU Q Q, ZHANG S W, ZHENG B X, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications:a tutorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313-3351. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051897 [13] GE L H, ZHANG H, WANG J B. Joint placement and beamforming design in multi-UAV-IRS assisted multiuser communication[C]//IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). Madrid:IEEE,2021:1-6. [14] SAMIR M, ELHATTAB M, ASSI C, et al. Optimizing age of information through aerial reconfigurable intelligent surfaces:a deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(4): 3978-3983. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3063953 [15] LIU X, YU Y F, LI F, et al. Throughput maximization for RIS-UAV relaying communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(10): 19569-19574. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3161698 [16] SU Y H, PANG X W, CHEN S Z, et al. Spectrum and energy efficiency optimization in IRS-assisted UAV networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(10): 6489-6502. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3201122 [17] YOU C S, ZHANG R. 3D trajectory optimization in rician fading for UAV-enabled data harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(6): 3192-3207. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2911939 [18] ZHANG J, ZHOU L, ZHOU F H, et al. Computation-efficient offloading and trajectory scheduling for multi-UAV assisted mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(2): 2114-2125. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2960103 [19] HUA M, YANG L X, WU Q Q, et al. UAV-assisted intelligent reflecting surface symbiotic radio system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5769-5785. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3070014 [20] XU Z C, YAN X Y, TANG W, et al. Maximizing sum rate by joint control and communication scheduling for RIS-assisted cellular connected UAV in THz communications[C]//IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops). Seoul:IEEE,2022:1207-1212. [21] SONG X K, ZHAO Y L, WU Z L, et al. Joint trajectory and communication design for IRS-assisted UAV networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(7): 1538-1542. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3179028 [22] LI Y B, ZHANG H J, LONG K P, et al. Exploring sum rate maximization in UAV-based multi-IRS networks:IRS association, UAV altitude, and phase shift design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(11): 7764-7774. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3206884 [23] MU X D, LIU Y W, GUO L, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced multi-UAV NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(10): 3051-3066. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3088679 [24] LI S X, DUO B, YUAN X J, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted UAV communication:joint trajectory design and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 716-720. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2966705 [25] TRAN D H, VU T X, CHATZINOTAS S, et al. Coarse trajectory design for energy minimization in UAV-enabled[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 9483-9496. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3001403 [26] ZENG Y, ZHANG R. Energy-efficient UAV communication with trajectory optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(6): 3747-3760. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2688328 [27] POLYANSKIY Y, POOR H V, VERDÚ S. Channel coding rate in the finite blocklength regime[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(5): 2307-2359. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2043769 [28] FENG R H, LI Z P, WANG Q, et al. An ADMM-based optimization method for URLLC-enabled UAV relay system[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(6): 1123-1127. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3153142 [29] RANJHA A, KADDOUM G, DEV K. Facilitating URLLC in UAV-assisted relay systems with multiple-mobile robots for 6G networks:a prospective of agriculture 4.0[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(7): 4954-4965. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3131608 [30] RANJHA A, KADDOUM G. Quasi-optimization of distance and blocklength in URLLC aided multi-hop UAV relay links[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(3): 306-310. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2953165 [31] PENG H X, SHEN X M. Multi-agent reinforcement learning based resource management in MEC- and UAV-assisted vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(1): 131-141. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3036962 [32] LI T X, ZHU K, LUONG N C, et al. Applications of multi-agent reinforcement learning in future Internet:a comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(2): 1240-1279. -




 下载:
下载: