Experimental Study on Steel-Concrete Joint of Integrated Track Beam for Medium and Low Speed Maglev
-
摘要:
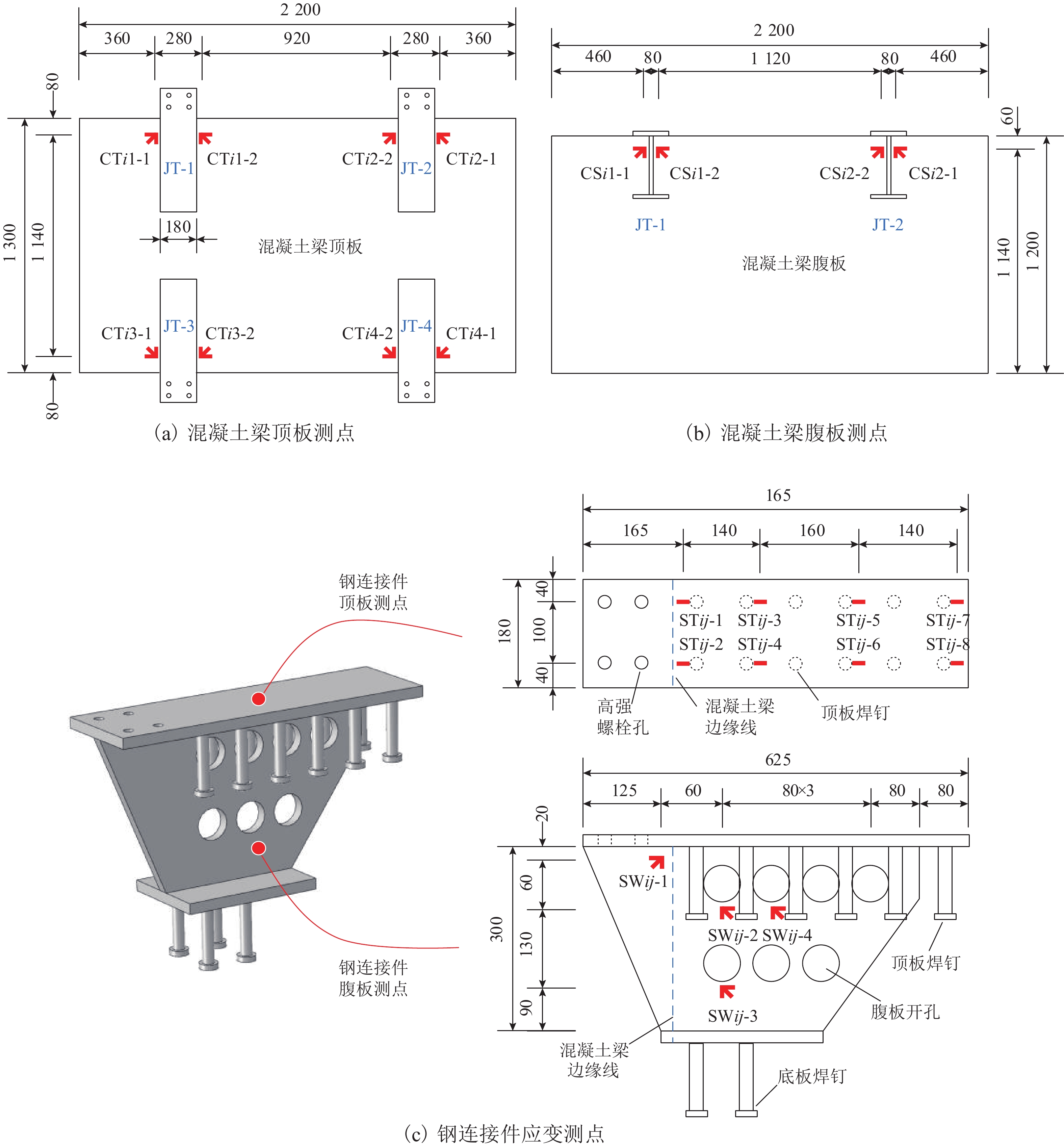
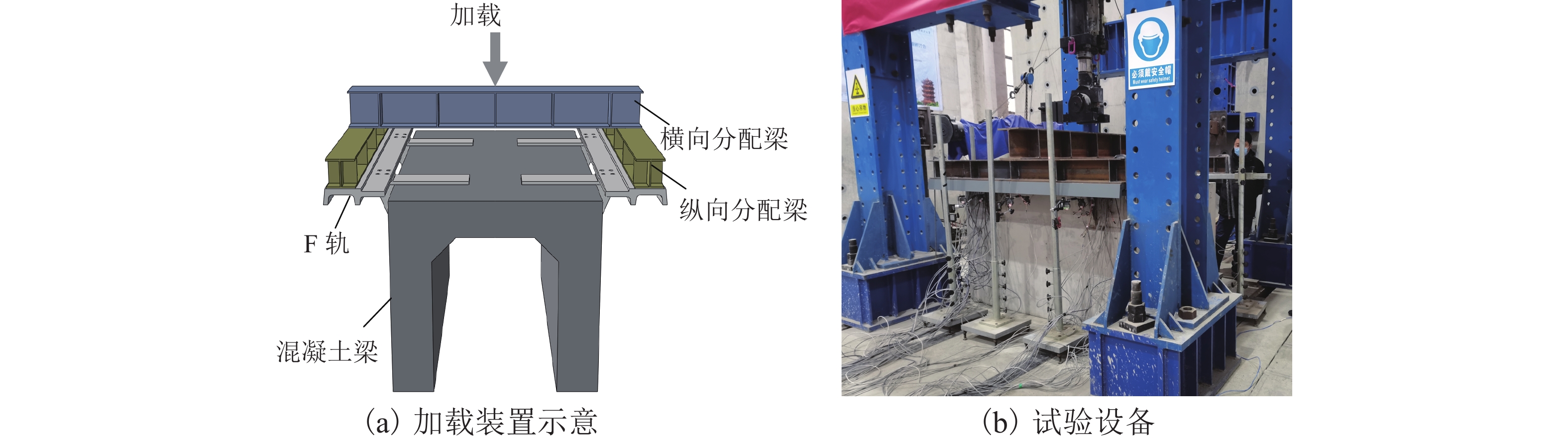
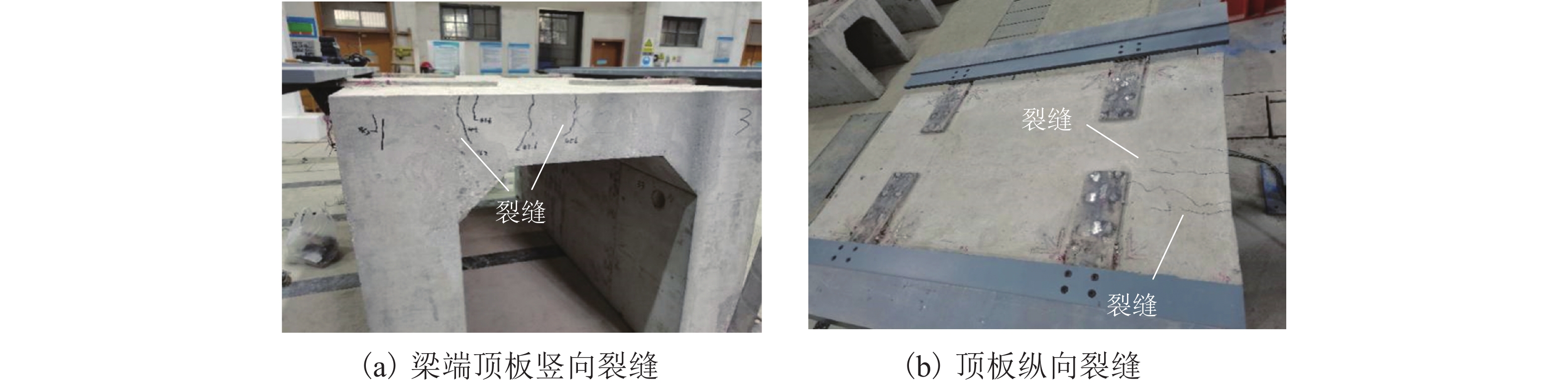
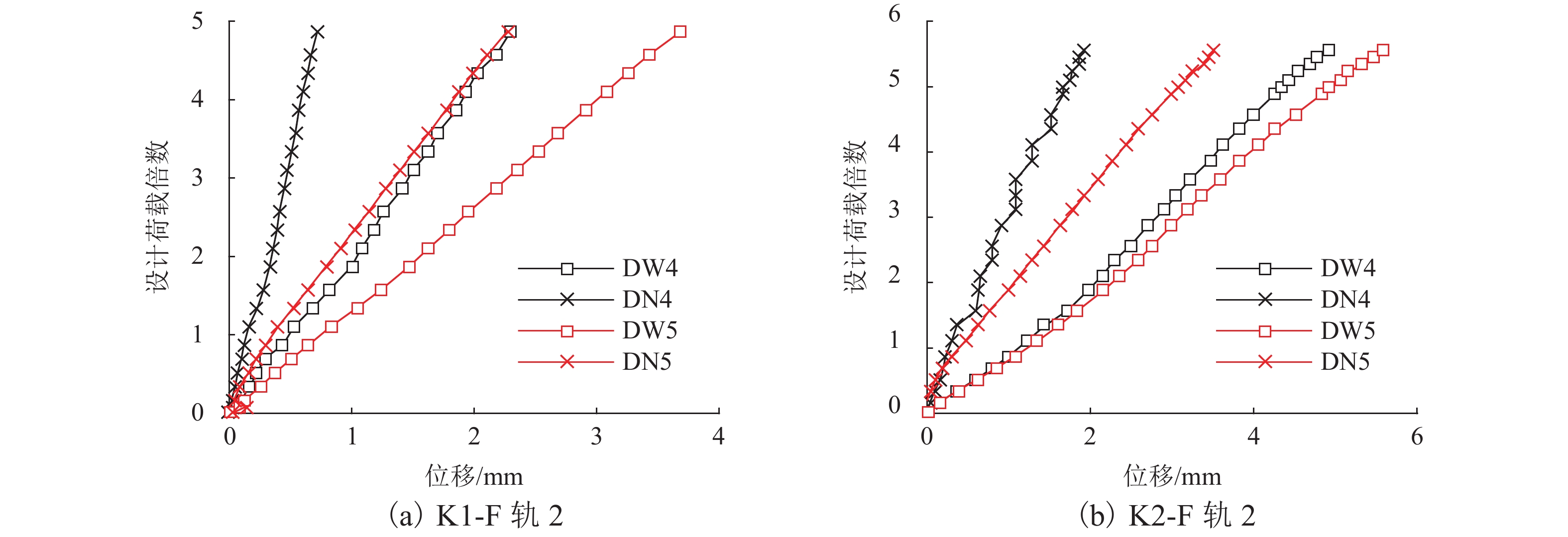
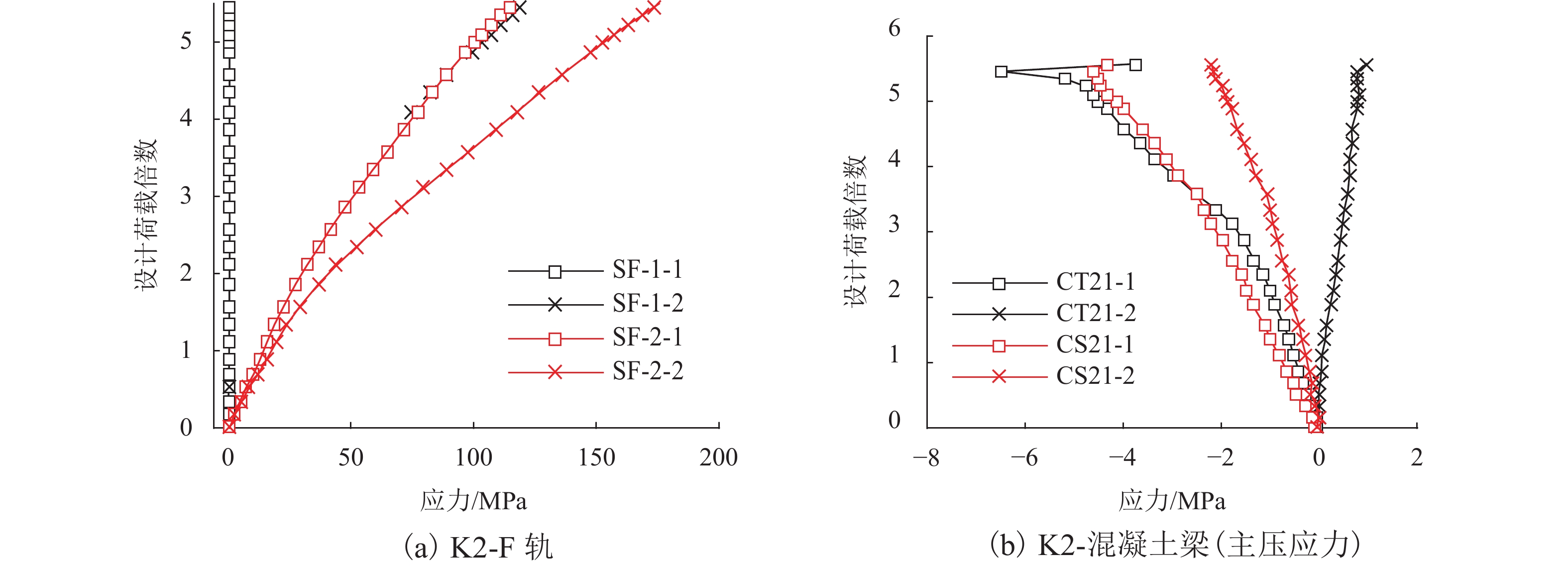
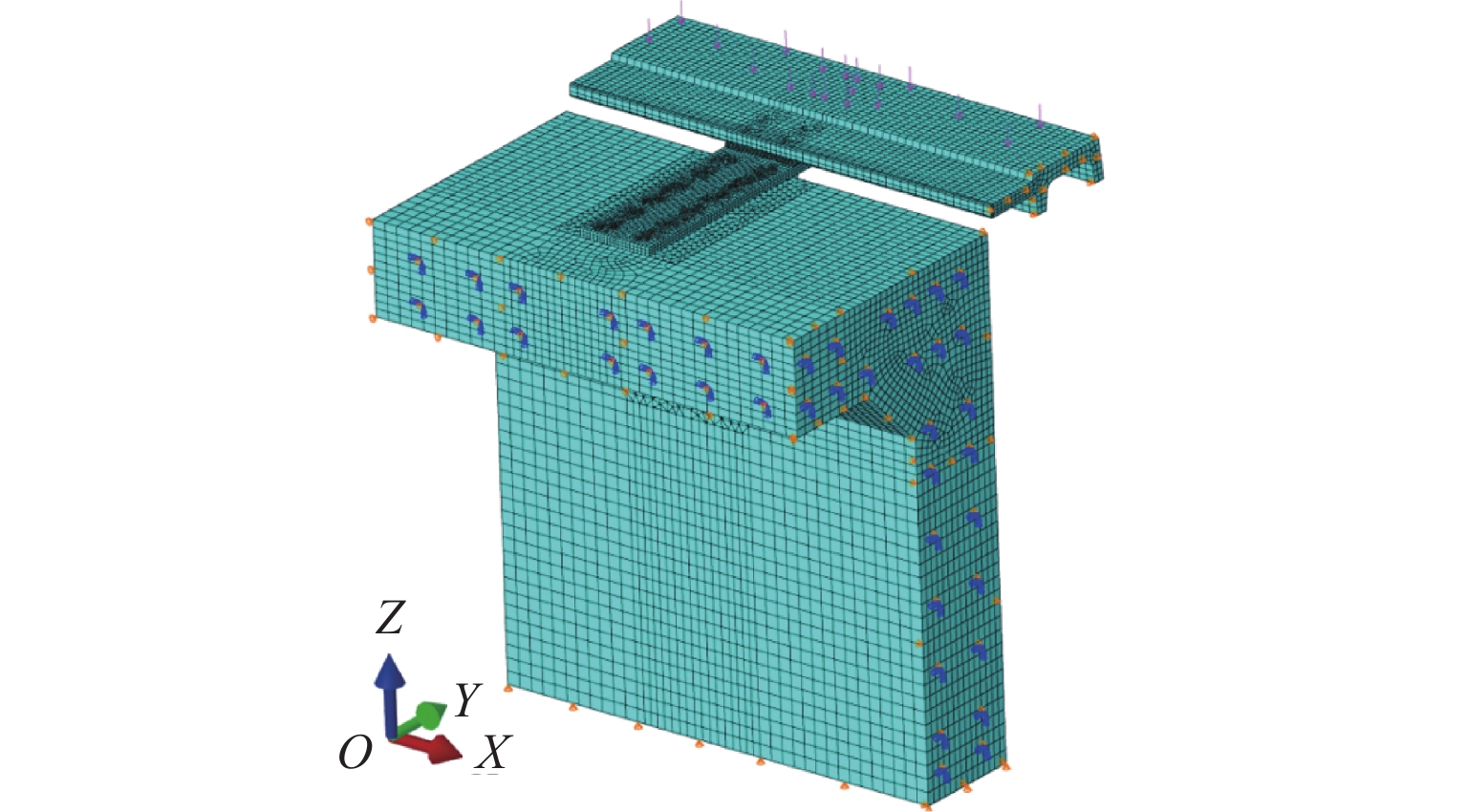
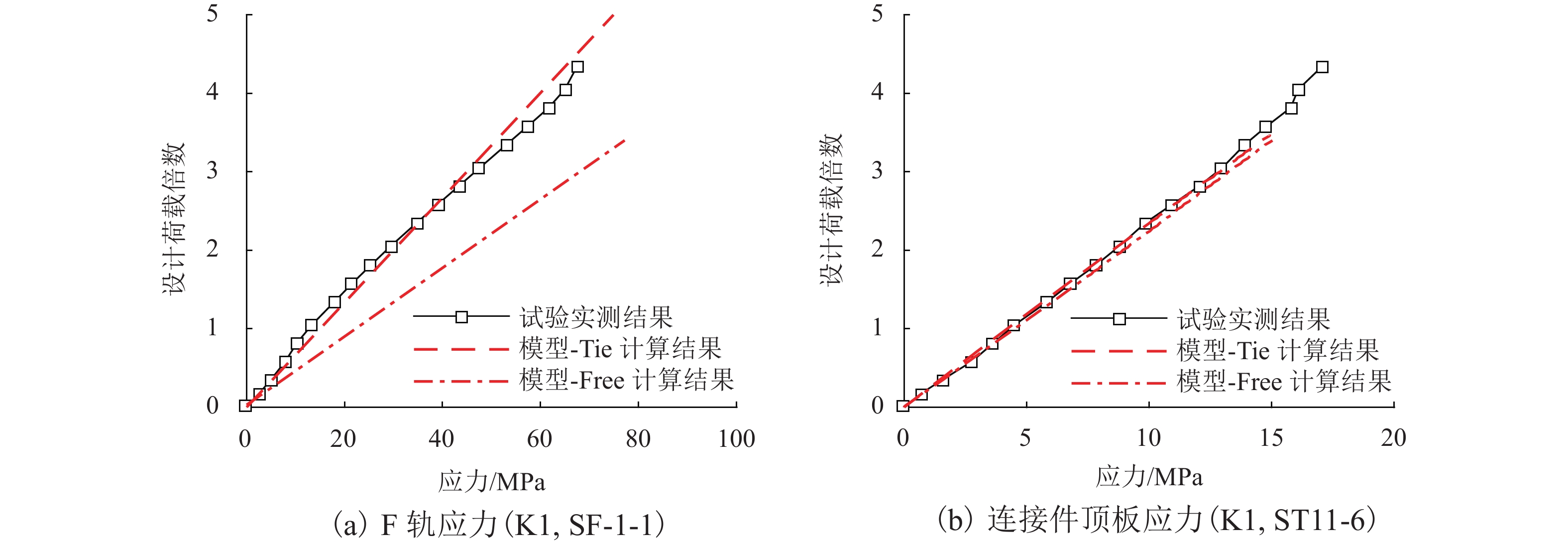
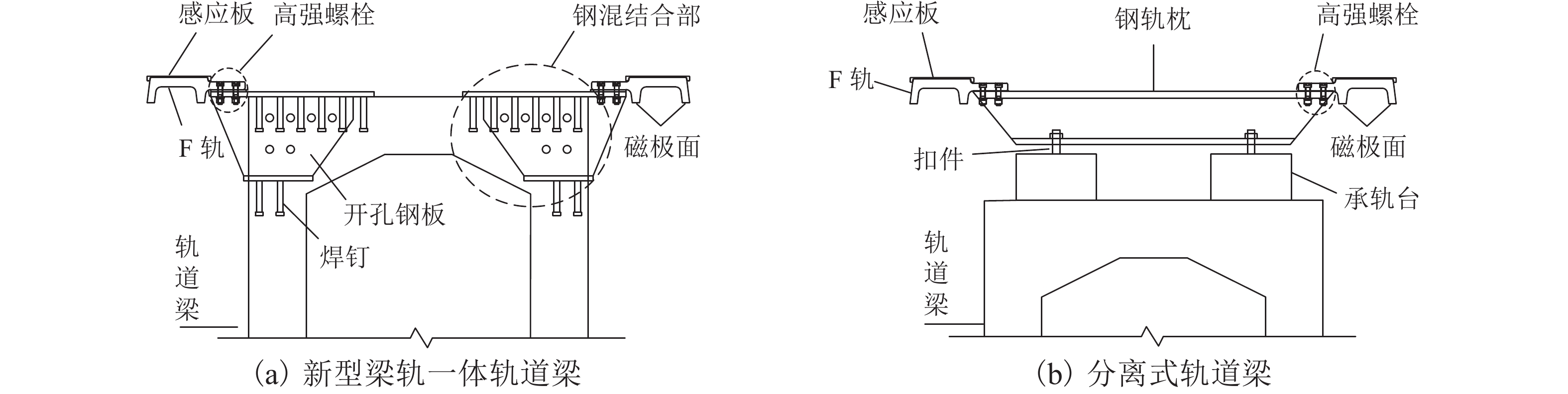
针对中低速磁浮分离式轨道梁建筑高度较大、无法考虑F轨刚度贡献等问题,提出了一种开孔钢板式梁轨一体轨道梁结构,并针对其钢-混结合部的静力性能开展足尺模型试验和有限元仿真计算分析. 首先,介绍了梁轨一体轨道梁工程背景以及钢-混结合部的结构特征;其次,设计了钢-混结合部静载模型试验,测试F轨、钢连接件和混凝土等构件在各级荷载下的应力和位移;最后,建立了钢-混结合部实体有限元模型,并结合试验数据分析了钢-混结合部的受力性能、传力机理以及设计参数影响. 研究结果表明:1) 在1.50倍设计荷载内,钢-混结合部基本处于弹性状态,连接件承载力满足设计要求;荷载继续增大时,F轨的荷载-应力曲线表现出一定的非线性; 5.47倍设计荷载下,混凝土梁体发生开裂破坏. 2) F轨内外磁极位移均较小,钢-混结合部刚度较大;F轨内外磁极位移差在设计荷载下满足设计限值;1.58倍设计荷载下内外磁极位移差达到0.54 mm,开始超过位移差限值;表明钢混结合部刚度的富裕量小于强度,钢连接件应以刚度控制设计. 3) 在正常运营状态,磁浮列车荷载主要由钢连件的钢板承压传递,焊钉与开孔钢板传力比例较小;钢连接件中开孔直径、贯穿钢筋直径对传力影响较小,钢连接件腹板厚度增加使得钢混结合部处传力更加平顺.
Abstract:To solve problems such as the large construction height of separated track beams for medium and low speed maglev and the inability to consider the stiffness contribution of F rail, an integrated track beam structure with a perforated steel plate was proposed. In addition, a full-scale model test and finite element simulation calculation were carried out to investigate the static performance of the steel-concrete joint. Firstly, the engineering background of the integrated track beam and the structural characteristics of the steel-concrete joint were introduced. Secondly, the static load model test of the steel-concrete joint was designed to test the stress and displacement of F rail, steel connector, and concrete components under various load scenarios. Finally, a solid finite element model of the steel-concrete joint was established, and the mechanical properties, force transmission mechanism, and design parameters of the steel-concrete joint were analyzed based on the test data. The results show that: 1) within 1.50 times the design load, the steel-concrete joint is basically in an elastic state, and the bearing capacity of the connector meets the design requirements. With the increase in load, the load–stress curve of F rail shows certain nonlinearity. Under 5.47 times the design load, the concrete beam cracks. 2) The displacements of the internal and external magnetic poles of F rail are small, and the stiffness of the steel-concrete joint is large. The displacement difference of the internal and external magnetic poles of F rail meets the design limit under the design load. Under 1.58 times the design load, the displacement difference reaches 0.54 mm, which begins to exceed the limit value. It shows that the stiffness abundance of the steel-concrete joint is less than the strength abundance, indicating that the design of the steel connector should be controlled by stiffness. 3) Under normal operational conditions, the maglev train load is mainly transmitted by the steel bearing plate of the steel connector, and the force transmission ratio between the welding nail and the perforated steel plate is small. The diameter of the hole and the diameter of the steel bar in the steel connector have little influence on the force transmission, and the increase in the thickness of the web of the steel connector makes the force transmission at the steel-concrete joint smooth.
-
表 1 不同开孔钢板厚度下钢混结合部受力
Table 1. Force on steel-concrete joint under different thicknesses of perforated steel plate
开孔钢板
厚度/mm位移最大
值/mm混凝土主拉
应力最大值/
MPa混凝土主压
应力最小值/
MPaF 轨 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa连接件 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa焊钉 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa钢筋 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa16 0.49 5.40 −5.87 41.66 69.30 8.13 1.52 20 0.47 5.73 −5.05 41.75 60.83 7.89 1.54 24 0.45 6.00 −4.30 41.79 55.00 7.92 1.53 表 2 不同开孔直径下钢混结合部受力
Table 2. Force on steel-concrete joint under different hole diameters
开孔钢板开孔
直径/mm位移最大
值/mm混凝土主拉
应力最大值/
MPa混凝土主压
应力最小值/
MPaF 轨 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa连接件 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa焊钉 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa钢筋 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa30 0.47 5.92 −4.95 41.75 60.89 7.92 1.54 40 0.47 5.73 −5.05 41.75 60.83 7.89 1.54 50 0.47 5.72 −4.97 41.75 61.09 7.91 1.54 60 0.47 5.92 −4.94 41.75 60.85 8.03 1.53 表 3 不同贯穿钢筋直径下钢混结合部受力
Table 3. Force on steel-concrete joint under different diameters of steel bar
穿孔钢筋
直径/mm位移最大
值/mm混凝土主拉
应力最大值/
MPa混凝土主压
应力最小值/
MPaF 轨 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa连接件 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa焊钉 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa钢筋 Mises 应
力最大值/
MPa16 0.47 5.73 −5.05 41.75 60.83 7.89 1.54 20 0.47 5.73 −5.05 41.75 60.83 7.89 1.54 -
[1] LEE H W, KIM K C, LEE J. Review of maglev train technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(7): 1917-1925. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.875842 [2] 梁潇,戴小冬,谭超,等. 既有长沙磁浮线路桥梁结构提速适用性研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(6): 1493-1498.LIANG Xiao, DAI Xiaodong, TAN Chao, et al. Study on the speed-increasing adaptation of the bridge structures in the existing maglev lines in Changsha[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(6): 1493-1498. [3] 杨平,刘德军,李小珍. 中低速磁浮简支轨道梁动力系数研究[J]. 桥梁建设,2016,46(4): 79-84.YANG Ping, LIU Dejun, LI Xiaozhen. Investigation of dynamic factors of low and medium speed maglev simply-supported guideway beam[J]. Bridge Construction, 2016, 46(4): 79-84. [4] 朱志辉,胡明勋,冯典瑾,等. 移动车辆荷载作用下中低速磁浮大跨度连续梁桥动力响应分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(7): 1695-1703.ZHU Zhihui, HU Mingxun, FENG Dianjin, et al. Dynamic response analysis of low and medium speed maglev long-span continuous beam bridge traversed by moving train load[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(7): 1695-1703. [5] 蔡文锋,颜华,杨平. 中低速磁浮轨道系统特点及工程适应性分析[J]. 铁道工程学报,2015,32(2): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2015.02.011CAI Wenfeng, YAN Hua, YANG Ping. Analysis of the characteristics and engineering adaptability of track system for medium and low speed maglev transit[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2015, 32(2): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2015.02.011 [6] 龚俊虎,谢海林,鄢巨平,等. 一种开孔钢板剪力键式梁轨一体化中低速磁浮轨道梁:CN210561504U[P]. 2020-05-19. [7] XIAO L, LI X Z, JOHN MA Z. Behavior of perforated shear connectors in steel–concrete composite joints of hybrid bridges[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 22(4): 04016135.1-04016135.15. [8] ZHANG Q H, JIA D L, BAO Y, et al. Analytical study on internal force transfer of perfobond rib shear connector group using a nonlinear spring model[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 22(10): 04017081.1-04017081.11. [9] 任晓博,赵春发,冯洋,等. 中低速磁浮车辆-轨道-桥梁垂向耦合振动仿真分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2019,63(2): 70-76.REN Xiaobo, ZHAO Chunfa, FENG Yang, et al. Numerical analysis on vertical coupled vibration of medium-low speed maglev vehicle-track-viaduct system[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2019, 63(2): 70-76. [10] 朱晓嘉,赵春发,庞玲,等. 低速磁浮交通轨道结构强度计算与分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2012,56(10): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2954.2012.10.002ZHU Xiaojia, ZHAO Chunfa, PANG Ling, et al. Strength calculation and analysis on track structure for low-speed maglev transit[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2012, 56(10): 4-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2954.2012.10.002 [11] XU X Q, LIU Y Q, HE J. Study on mechanical behavior of rubber-sleeved studs for steel and concrete composite structures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 53: 533-546. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.12.011 [12] 蒲黔辉,周阳,施洲. 铁路混合梁斜拉桥钢-混结合段受力及参数分析[J]. 桥梁建设,2016,46(1): 12-17.PU Qianhui, ZHOU Yang, SHI Zhou. Mechanical behavior and parametric analysis of steel and concrete joint section of railway hybrid girder cable-stayed bridge[J]. Bridge Construction, 2016, 46(1): 12-17. [13] 梁博文. 钢-混凝土混合箱梁结合段传力机理与设计方法研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学,2018. [14] YAO Y D, YAN M, SHI Z, et al. Mechanical behavior of an innovative steel–concrete joint for long-span railway hybrid box girder cable-stayed bridges[J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 239: 112358.1-112358.17. [15] 娄学全,武焕陵,崔冰,等. 悬索桥主缆分布传力锚固系统设计与施工[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社,2012. -




 下载:
下载: