Lane Selection of Automated Vehicle Groups Approaching Intersections Based on Vehicle–Infrastructure Cooperation
-
摘要:
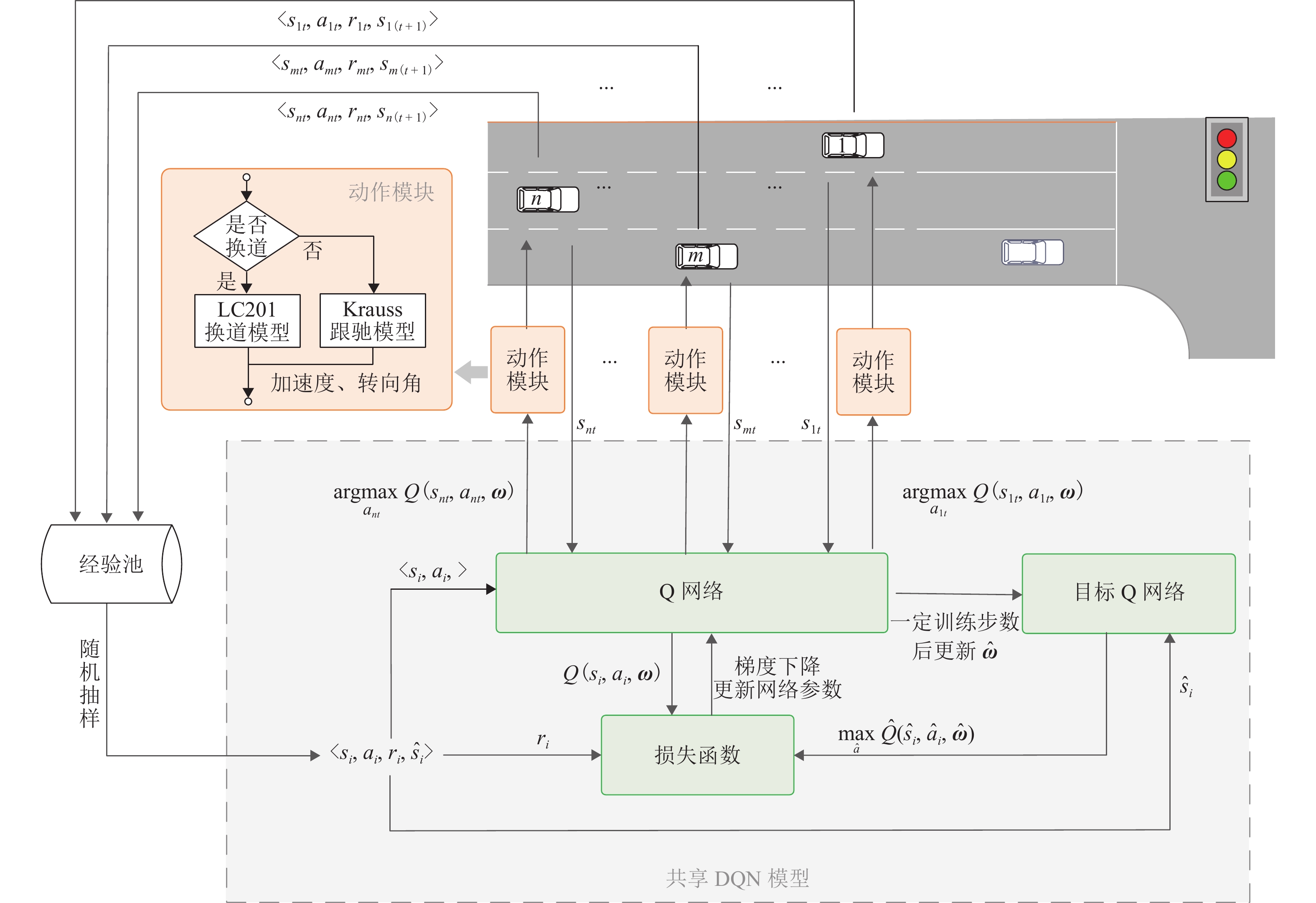
针对在信号交叉口前由于车辆转向和换道操作频繁容易引发冲突、降低通行效率的问题,构建基于深度强化学习(DQN)的车辆群体控制模型,优化车辆车道选择. 首先,利用传感器和网联设备等获取周围车辆及交叉口信号灯实时状态信息,基于共享DQN模型进行车道选择,并根据该结果计算下一时刻位置、速度和转向角;进一步以效率及安全性指标建立奖励函数对车道选择决策实施评价,将状态信息、决策信息及奖励评价信息整合形成经验,存入同一经验池用于共享DQN模型参数迭代更新;最后,使用SUMO (simulation of urban mobility)与Python联合仿真搭建不同交通流量环境对训练后的模型进行验证. 研究表明:相较于SUMO中的车道选择模型,基于共享DQN模型的信号交叉口前车辆群体车道选择模型,在低、中、高流量测试场景的平均速度均有提高,交叉口前排队长度分别减少了9.6%、22.5%和24.8%. 本文模型可以有效减少信号交叉口的排队长度、提高信号交叉口前的路段平均速度、增强车辆从上游到达交叉口的效率,为未来车路协同的应用提供理论借鉴和技术支持.
Abstract:In front of signalized intersections, frequent lane-changing and turning maneuvers often lead to conflict and reduced traffic efficiency. To address this issue, a shared deep Q-network (DQN)-based reinforcement learning framework was developed for vehicle group control, aiming to optimize lane selection. Firstly, real-time state information on surrounding vehicles and intersection signal lights was obtained using sensing and connected devices. Lane selection was then carried out based on the shared DQN model, and the vehicle’s next position, speed, and steering angle were calculated accordingly. A reward function incorporating efficiency and safety indicators was then constructed to evaluate lane selection decisions. The state, decision, and reward evaluation information were integrated into experience and stored in a shared experience pool to iteratively update the parameters of the shared DQN model. Finally, simulation of urban mobility (SUMO) and Python were used to simulate different traffic scenarios to verify the trained model. Experimental results show that, compared with the lane selection model in SUMO, the proposed shared DQN-based lane selection model for vehicle groups approaching signalized intersections improves average speeds in low, medium, and high traffic scenarios, while reducing queue lengths before intersections by 9.6%, 22.5%, and 24.8%, respectively. The model can effectively reduce the queue length at signal intersections, increase average speeds on road sections before signalized intersections, and improve the efficiency of vehicles arriving at the intersection from upstream, providing a theoretical reference and technical support for future application of vehicle–infrastructure cooperation.
-
表 1 多车共享的DQN学习过程
Table 1. DQN learning process shared by vehicle groups
步骤 指令 1 for 回合数 $ j = 1,2, \cdots ,D $ do: 2 for 时刻 $ t = 1,2, \cdots ,T $ do: 3 对于给定状态 $ {s_t} $,根据 Q 网络执行动作 $ {a_t} $ 4 转移到下一状态 $ {\hat s_t} $,得到奖励 $ {r_t} $ 5 将经验 $ \langle { {s_t},{a_t},{r_t},{\hat s_t} } \rangle $ 存入经验池中 6 从经验池中任取一组经验 $ \langle { {s_i},{a_i},{r_i},{\hat s_i} } \rangle $ 7 计算网络目标值 $ {y_i} $ 8 用梯度下降法更新 $ {\text{ω}} $, 使状态动作值函数 $ Q\left( {{s_i},{a_i}} \right) $趋近于 $ {y_i} $ 9 一定训练步数后更新 $ \hat {\text{ω}} $ 10 end for 11 end for 注:输入为Q网络参数$ {\text{ω}} $、目标Q网络参数$ \hat {\text{ω}} $,输出为训练后的DQN网络. 表 2 状态空间及动作空间
Table 2. State and action spaces
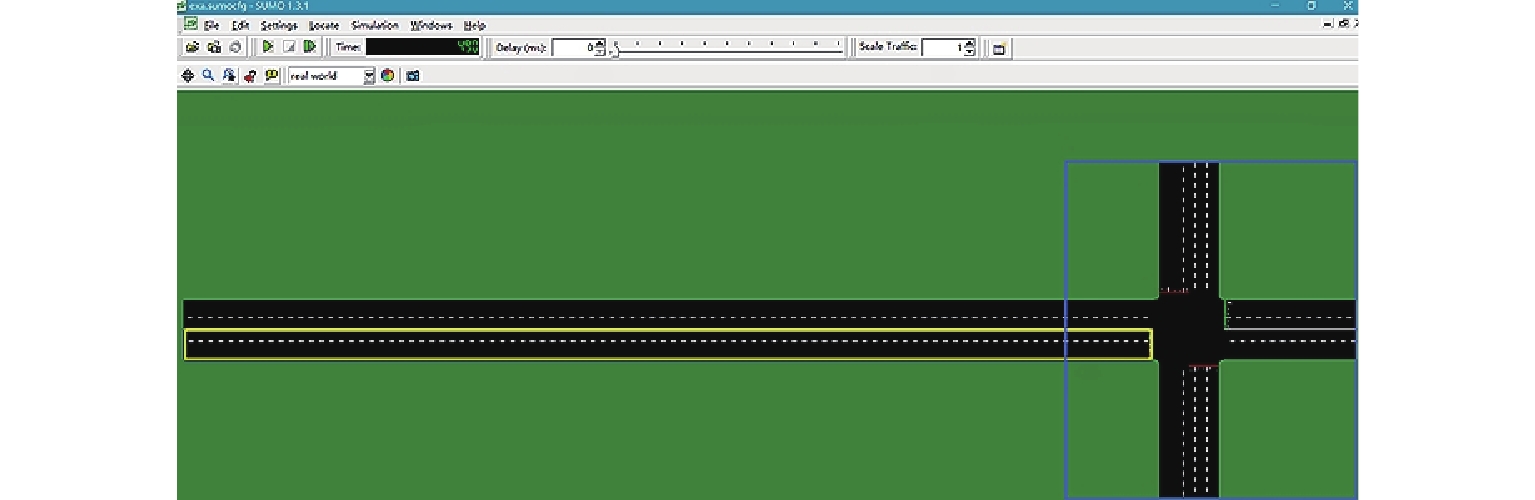
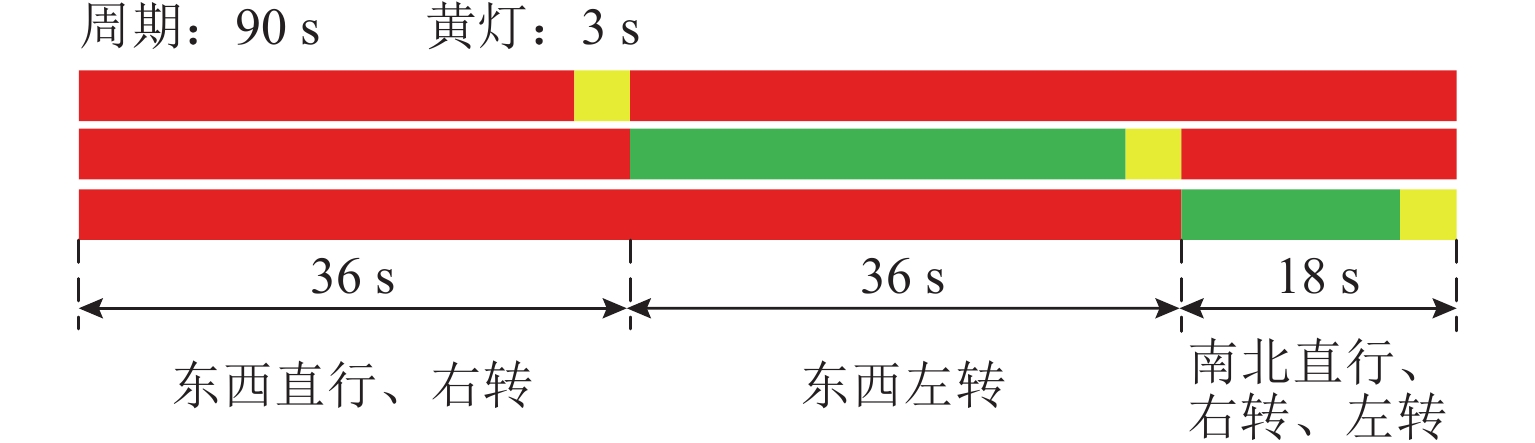
空间类型 符号 意义 取值范围 状态空间 $ {X_{\mathrm{d}}} $ 车辆目标转向车道编号 $ \left\{ {1,2,\cdots,x} \right\} $ $ {X_t} $ 车辆在时刻t所在车道编号 $ \left\{ {1,2,\cdots,x} \right\} $ $ {L_t} $ 车辆在时刻t到交叉口停止线纵向距离 $ \left[ {0,l} \right] $ $ {P_t} $ 时刻t交叉口信号灯相位 $ \left\{ {1,2,\cdots,p} \right\} $ $ {G_t} $ 时刻t交叉口信号灯到下一相位开始时间 $ \left( {0,g} \right] $ $ F_{{\mathrm{r}}t} $ 向右换道可行性信息(可换,不可换) $ \left\{ {0,1} \right\} $ $ F_{{\mathrm{l}}t} $ 向左换道可行性信息(可换,不可换) $ \left\{ {0,1} \right\} $ 动作空间 $ A $ 车道选择决策(向右换道,向左换道,保持车道) $ \left\{ {0,1,2} \right\} $ 表 3 仿真软件环境配置
Table 3. Simulation Software Environment Configuration
项目 信息 SUMO 1.3.1 Python 3.6 软件开发环境 PyCharm Tensorflow 2.3.0 Numpy 1.14.3 Matplotlib 2.2.2 Pandas 0.23.0 表 4 车流量设置
Table 4. Traffic flow settings
辆·h−1 场景 右转流量 直行流量 左转流量 场景 1 400 1000 400 场景 2 600 1400 600 场景 3 800 1800 800 表 5 群体决策模型在3种场景下与SUMO单车决策模型的比较
Table 5. Performance comparison between group decision model and SUMO single-vehicle model under three scenarios
场景 总排队长度 右转车道排队长度 直行车道排队长度 左转车道排队长度 路段平均速度 对比图 减量/% 对比图 减量/% 对比图 减量/% 对比图 减量/% 对比图 增量/% 场景 1 ① 16.7 ④ −8.5 ⑦ 27.1 ⑩ 3.0 ⑬ 3.0 场景 2 ② 27.2 ⑤ 2.6 ⑧ 37.9 ⑪ 22.3 ⑭ 4.1 场景 3 ③ 23.7 ⑥ 27.6 ⑨ 20.2 ⑫ 27.8 ⑮ 2.3 
-
[1] ZHANG H Y, DU L L. Platoon-centered control for eco-driving at signalized intersection built upon hybrid MPC system, online learning and distributed optimization part I: Modeling and solution algorithm design[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2023, 172: 174-198. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2023.02.006 [2] 金立生, 郭柏苍, 谢宪毅, 等. 基于行车安全场模型的交叉口车辆控制算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(4): 753-760. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200482JIN Lisheng, GUO Baicang, XIE Xianyi, et al. Cooperative control algorithm for vehicle at intersection based on driving safety field model[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(4): 753-760. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200482 [3] 张游, 潘福全, 张丽霞, 等. 车路协同环境下智能交叉口车速控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(6): 1057-1064. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10606ZHANG You, PAN Fuquan, ZHANG Lixia, et al. Speed control for intelligent intersection under vehicle-infrastructure cooperative environment[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(6): 1057-1064. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10606 [4] PARK C, KEE S C. Implementation of autonomous driving vehicle at an intersection with traffic light recognition and vehicle controls[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems. Greece: Science and Technology Publications (SCITEPRESS), 2019: 542-549. [5] ZHOU M F, YU Y, QU X B. Development of an efficient driving strategy for connected and automated vehicles at signalized intersections: a reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 21(1): 433-443. [6] TAJEDDIN S, EKHTIARI S, FAIEGHI M, et al. Ecological adaptive cruise control with optimal lane selection in connected vehicle environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 21(11): 4538-4549. [7] KUMAR A V S S B, MODH A, BABU M, et al. A novel lane merging framework with probabilistic risk based lane selection using time scaled collision cone[C]//2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). Changshu: IEEE, 2018: 1406-1411. [8] BAKER C R, DOLAN J M. Traffic interaction in the urban challenge: putting boss on its best behavior[C]// 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Nice: IEEE, 2008: 1752-1758. [9] MONTEMERLO M, BECKER J, BHAT S, et al. Junior: the stanford entry in the urban challenge[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2008, 25(9): 569-597. doi: 10.1002/rob.20258 [10] GINDELE T, JAGSZENT D, PITZER B, et al. Design of the planner of team AnnieWAY’s autonomous vehicle used in the DARPA Urban Challenge 2007[C]//2008 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. Eindhoven. Eindhoven: IEEE, 2008: 1131-1136. [11] 杨达, 杨果, 罗旭, 等. 考虑前车状态的智能网联车交叉口行为决策[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(2): 410-417, 433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200553YANG Da, YANG Guo, LUO Xu, et al. Behavior decision of intelligent connected vehicles considering status of preceding vehicles at intersections[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(2): 410-417, 433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200553 [12] KANARIS A, KOSMATOPOULOS E B, LOANNOU P A. Strategies and spacing requirements for lane changing and merging in automated highway systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 50(6): 1568-1581. [13] 裴晓飞, 莫烁杰, 陈祯福, 等. 基于TD3算法的人机混驾交通环境自动驾驶汽车换道研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(11): 246-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.11.020PEI Xiaofei, MO Shuojie, CHEN Zhenfu, et al. Lane changing of autonomous vehicle based on TD3 algorithm in human-machine hybrid driving environment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(11): 246-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.11.020 [14] 赵建东, 贺晓宇, 余智鑫, 等. 多网联范围下的智能网联车换道决策组合模型研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2023, 23(1): 77-85.ZHAO Jiandong, HE Xiaoyu, YU Zhixin, et al. A combination model for connected and autonomous vehicles lane-changing decision-making under multi connectivity range[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2023, 23(1): 77-85. [15] LIU K, WAN Q, LI Y J. A deep reinforcement learning algorithm with expert demonstrations and supervised loss and its application in autonomous driving[C]//2018 37th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Wuhan: IEEE, 2018: 2944-2949. [16] 李传耀, 张帆, 王涛, 等. 基于深度强化学习的道路交叉口生态驾驶策略研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2024, 24(1): 81-92.LI Chuanyao, ZHANG Fan, WANG Tao, et al. Signalized intersection eco-driving strategy based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2024, 24(1): 81-92. [17] CHEN Y L, DONG C Y, PALANISAMY P, et al. Attention-based hierarchical deep reinforcement learning for lane change behaviors in autonomous driving[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Changsha: IEEE, 2019: 3697-3703. [18] KRAUß S. Towards a unified view of microscopic traffic flow theories[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1997, 30(8): 901-905. doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)43936-X [19] KRAUSS S, WAGNER P, GAWRON C. Metastable states in a microscopic model of traffic flow[J]. Physical Review E, 1997, 55(5): 5597-5602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.55.5597 [20] BEHRISCH M, WEBER M. Modeling mobility with open data[C]//2nd SUMO Conference 2014 Berlin. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 102-111. [21] ERDMANN J. SUMO’s lane-changing model[M]. Cham: Springer, 2015: 105-123. [22] JIANG X, ZHANG J, LI D. Eco-driving at signalized intersections: a parameterized reinforcement learning approach[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2023, 11(1): 1406-1431. doi: 10.1080/21680566.2023.2215957 [23] PENG M, FENG P F, LIANG Z J, et al. The hardware in-loop simulation system based on SUMO for autonomous optimization control algorithm at intersection[C]//2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET). Chengdu: IEEE, 2020: 591-596. [24] YANG X X, XU Y S, KUANG L, et al. An information fusion approach to intelligent traffic signal control using the joint methods of multiagent reinforcement learning and artificial intelligence of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 9335-9345. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3105426 -




 下载:
下载: