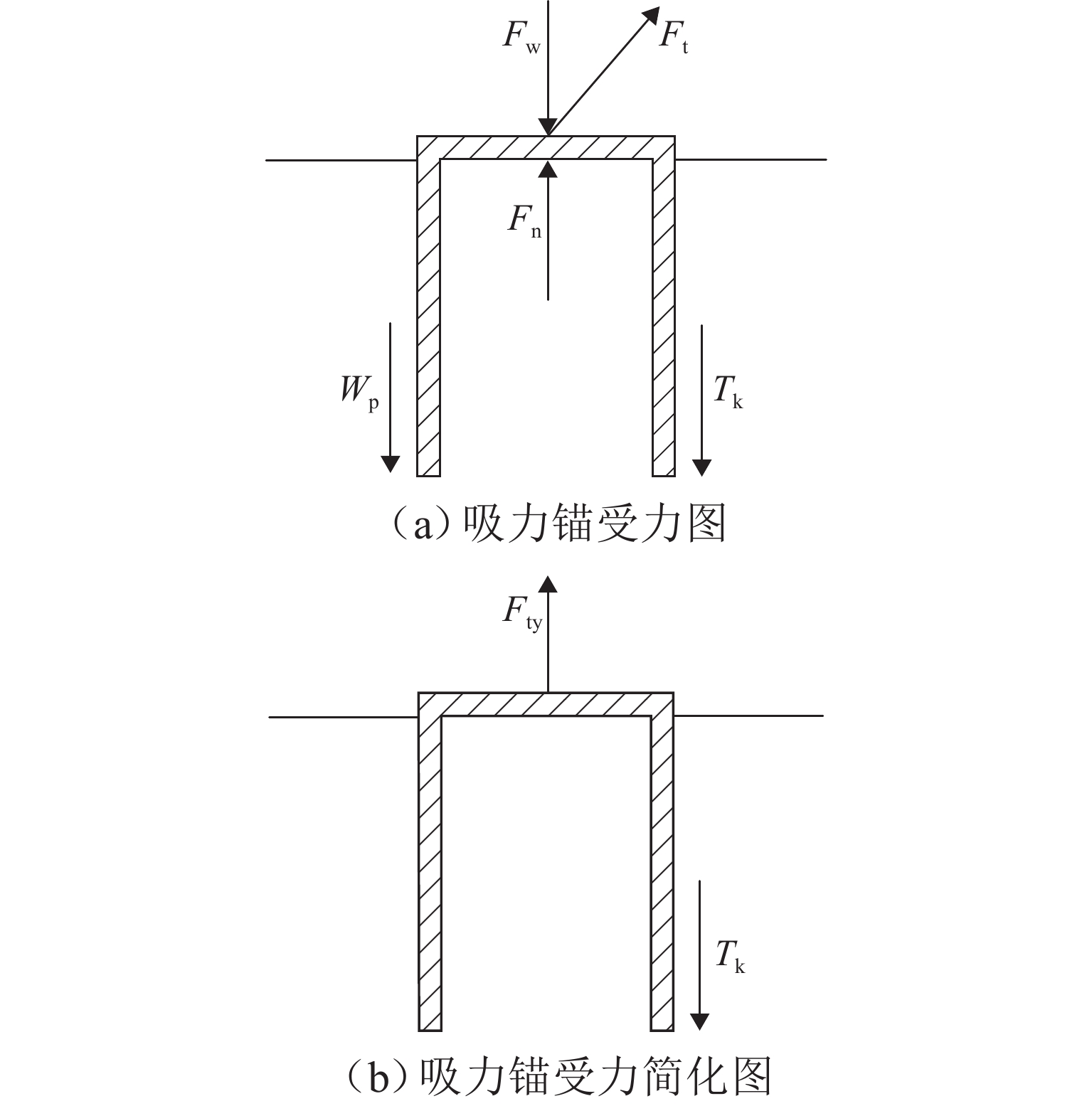
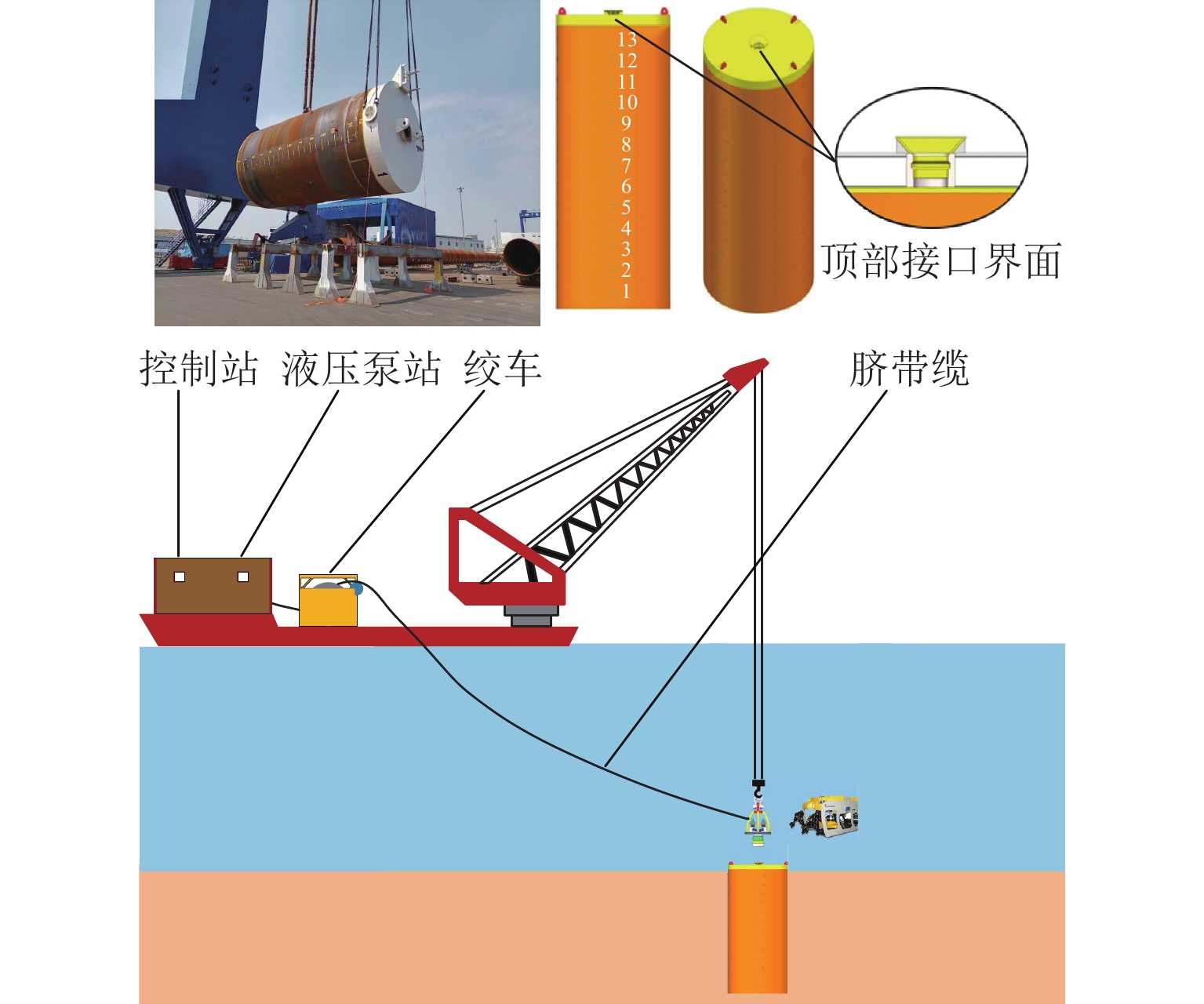
Time-Dependent Reliability Analysis of LS-FA-211001 Suction Anchor Under Cyclic Load
-
摘要:
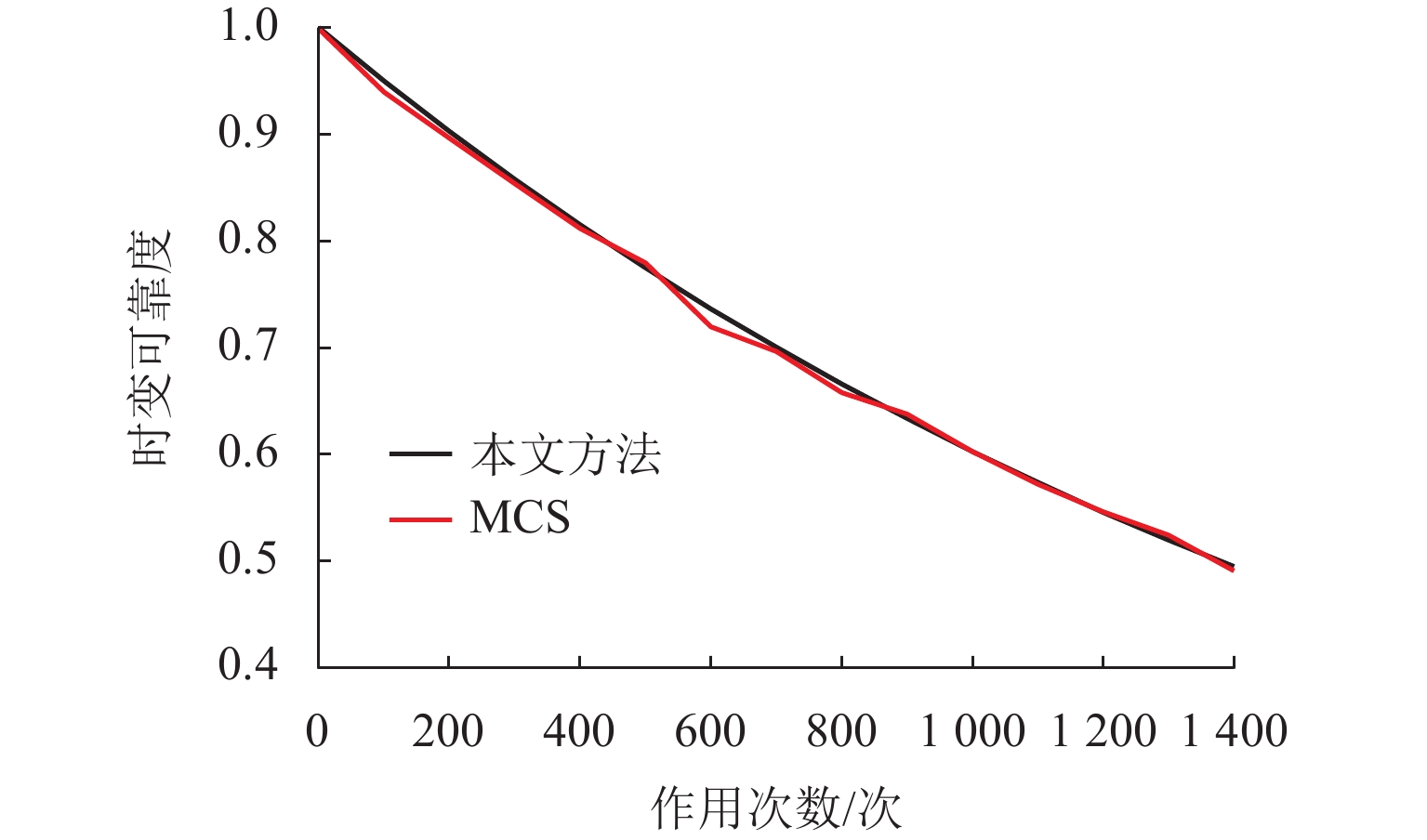
为有效评估在使用过程中LS-FA-211001吸力锚的可靠性水平,考虑外部载荷的累积效应,建立循环载荷作用下的时变可靠性模型;结合LS-FA-211001吸力锚的不确定性量化数据,对其展开时变可靠性分析;利用蒙特卡罗模拟(MCS)方法对吸力锚可靠度进行验证. 结果表明:在可靠度要求95%以上的条件下,LS-FA-211001吸力锚的寿命即使在恶劣勘探点也能达到100次;同时,在循环载荷不同作用次数下,本文建立的吸力锚时变可靠性模型与MCS方法评估出的可靠度结果相比,误差不超过2.15%,验证了本文方法的有效性.
Abstract:To effectively evaluate the reliability level of the LS-FA-211001 suction anchor during application, the cumulative effect of external loads was considered, and a time-dependent reliability model was established under cyclic loads. The time-dependent reliability analysis of the suction anchor was carried out based on the quantified uncertainty data. The Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) method was adopted to verify the reliability of the suction anchor. The results show that the life of LS-FA-211001 suction anchor can reach 100 times even in harsh exploratory points under the reliability of being over 95%. At the same time, under different cycles of load, the error of the time-dependent reliability model of the suction anchor established in this paper is less than 2.15% compared with the reliability results evaluated by the MCS method, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
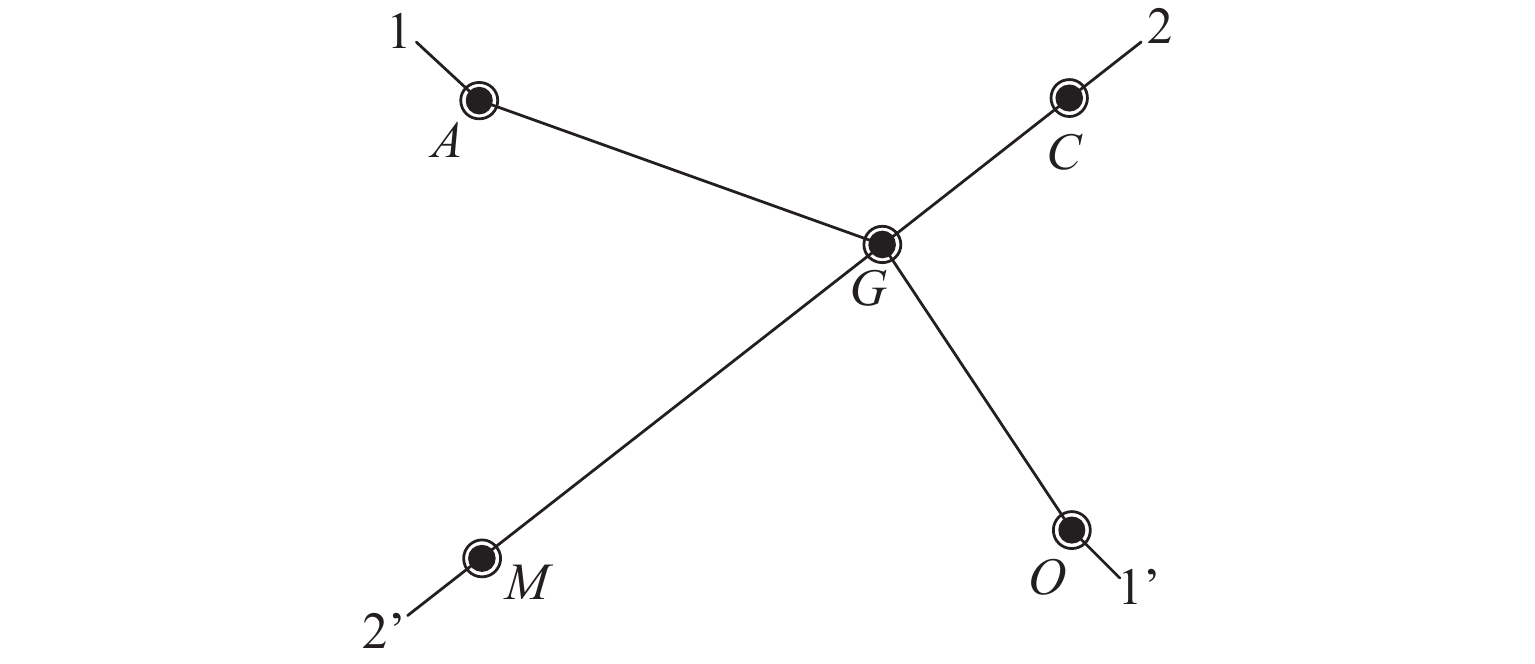
表 1 各勘探点附近的抗拔力值
Table 1. Pulling resistance values near each exploratory point
kN 组号 点 A 点 C 点 G 点 M 点 O 1 1330.9777 2007.6882 2247.3961 1826.8866 1835.3776 2 1339.7254 1998.8052 2261.1515 1820.1196 1840.0185 3 1336.7282 1982.7419 2274.1373 1814.4576 1843.6222 4 1330.8861 1964.7617 2286.1875 1809.4007 1846.4546 5 1323.8135 1947.6050 2297.1344 1804.6813 1848.9262 6 1319.7456 1954.0500 2191.5069 1800.0756 1851.5450 7 1319.9079 1970.4304 2187.9786 1795.7828 1854.8203 8 1322.8437 1987.0357 2182.8988 1792.0530 1859.1009 9 1328.1747 2003.6953 2176.1155 1791.3837 1864.3240 10 1338.2259 2020.2961 2167.4843 1791.0338 1869.6512 表 2 各勘探点附近抗拔力分布参数
Table 2. Parameters of pulling resistance distribution near each exploratory point
勘探点 均值 标准差 A 1329.1029 7.4612 C 1983.7110 24.2016 G 2227.1991 48.0464 M 1804.5875 12.7894 O 1851.3841 10.7934 -
[1] 王胤,朱兴运,杨庆. 考虑砂土渗透性变化的吸力锚沉贯及土塞特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(1): 184-190.WANG Yin, ZHU Xingyun, YANG Qing. Installation of suction caissons and formation of soil plug considering variation of permeability of sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(1): 184-190. [2] 霍知亮. 黏土地基中桶形基础模型试验及工作机理研究[D]. 天津:天津大学,2015. [3] 王胤,杨涵,庞子毅,等. 基于CFD-DEM流固耦合方法的吸力锚基础负压沉贯数值模拟[J]. 岩土工程学报,2023,45(2): 384-393,444. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211512WANG Yin, YANG Han, PANG Ziyi, et al. Numerical simulation of negative pressure penetration of suction anchor foundation based on CFD-DEM fluid solid coupling method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(2): 384-393,444. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211512 [4] 闫宏生,苑恒,李怀亮,等. 大抓力锚和吸力锚在CALM型单点系泊系统中的应用[J]. 中国海洋平台,2022,37(4): 31-36,42.YAN Hongsheng, YUAN Heng, LI Huailiang, et al. Application of fluke anchor and suction anchor in CALM single-point mooring system[J]. China Offshore Platform, 2022, 37(4): 31-36,42. [5] RICE S O. Mathematical analysis of random noise[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1944, 23(3): 282-332. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1944.tb00874.x [6] CRANDALL S H, CHANDIRAMANI K L, COOK R G. Some first-passage problems in random vibration[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1966, 33(3): 532-538. doi: 10.1115/1.3625118 [7] ANDRIEU-RENAUD C, SUDRET B, LEMAIRE M. The PHI2 method: a way to compute time-variant reliability[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2004, 84(1): 75-86. [8] SINGH A, MOURELATOS Z P. On the time-dependent reliability of non-monotonic, non-repairable systems[J]. SAE International Journal of Materials and Manufacturing, 2010, 3(1): 425-444. doi: 10.4271/2010-01-0696 [9] HU Z, DU X P. A sampling approach to extreme value distribution for time-dependent reliability analysis[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2013, 135(7): 071003.1-071003.8. [10] HU Z, DU X P. Time-dependent reliability analysis with joint upcrossing rates[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2013, 48(5): 893-907. doi: 10.1007/s00158-013-0937-2 [11] JIANG C, HUANG X P, HAN X, et al. A time-variant reliability analysis method based on stochastic process discretization[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2014, 136(9): 091009.1-091009.11. [12] LI C Y, ZHANG Y M. Time-variant reliability assessment and its sensitivity analysis of cutting tool under invariant machining condition based on gamma process[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012, 2012: 676923.1-676923.19. [13] CAZUGUEL M, RENAUD C, COGNARD J Y. Time-variant reliability of nonlinear structures: application to a representative part of a plate floor[J]. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2006, 22(1): 101-118. doi: 10.1002/qre.750 [14] KOPUSTINSKAS V, AUGUTIS J, RIMKEVIČIUS S. Dynamic reliability and risk assessment of the accident localization system of the Ignalina NPP RBMK-1500 reactor[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2005, 87(1): 77-87. [15] 张德权,韩旭,姜潮,等. 时变可靠性的区间PHI2分析方法[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学,2015,45(5):41-53.ZHANG D Q, HAN X, JIANG C, et al. The interval PHI2 analysis method for time-dependent reliability[J]. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 2015, 45(5):41-53. [16] TIAN L, NOORE A. Dynamic software reliability prediction: an approach based on support vector machines[J]. International Journal of Reliability, Quality and Safety Engineering, 2005, 12: 309-321. doi: 10.1142/S0218539305001847 [17] BECKER G, CAMARINOPOULOS L, KABRANIS D. Dynamic reliability under random shocks[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2002, 77(3): 239-251. [18] STREICHER H, RACKWITZ R. Time-variant reliability-oriented structural optimization and a renewal model for life-cycle costing[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 19(1/2): 171-183. [19] SUDRET B. Analytical derivation of the outcrossing rate in time-variant reliability problems[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2008, 4(5): 353-362. doi: 10.1080/15732470701270058 [20] 茆诗松,王静龙,濮晓龙. 高等数理统计[M]. 2版. 北京:高等教育出版社,2006:34-35. [21] 钟泽棋. 基于FMECA的吸力锚系统可靠性评估[D]. 成都:电子科技大学,2023. -




 下载:
下载: