Review of Research on Vehicle Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension Technology
-
摘要:
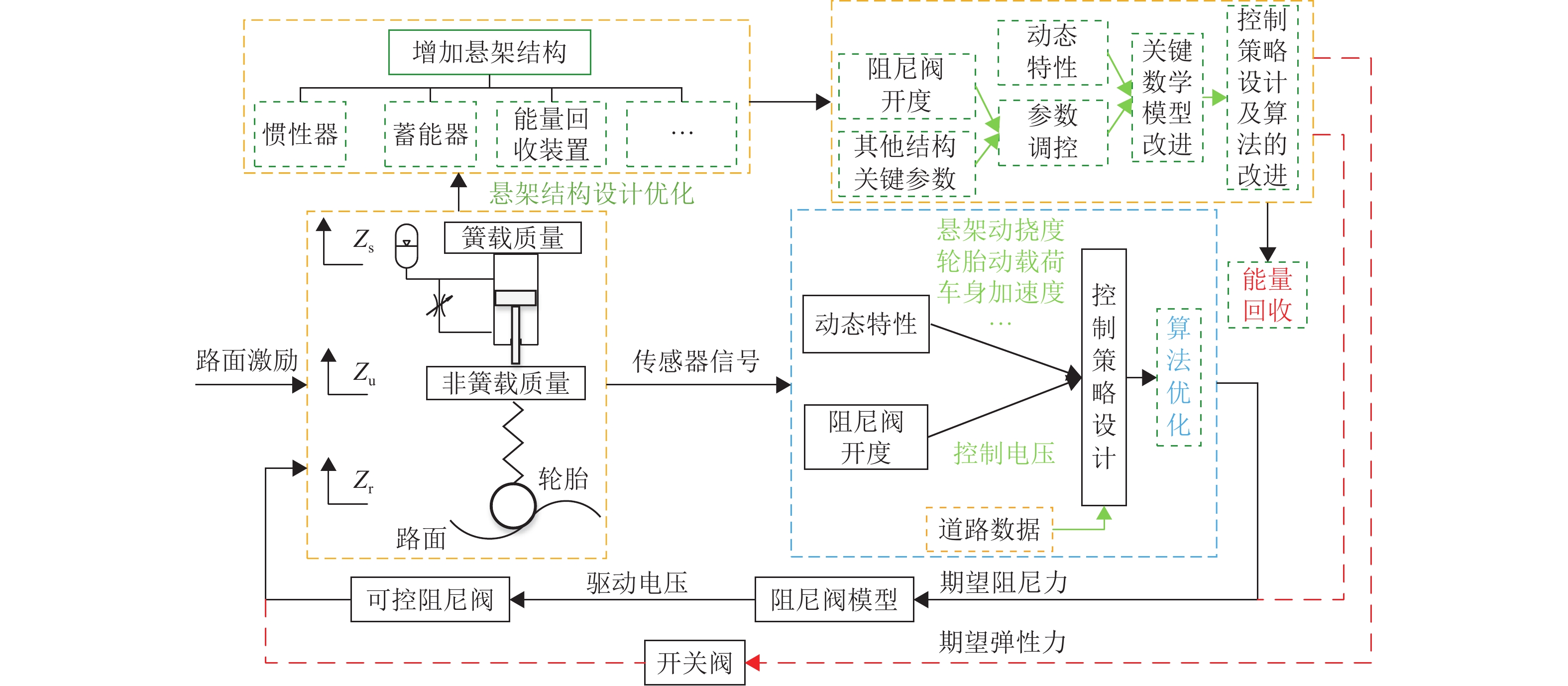
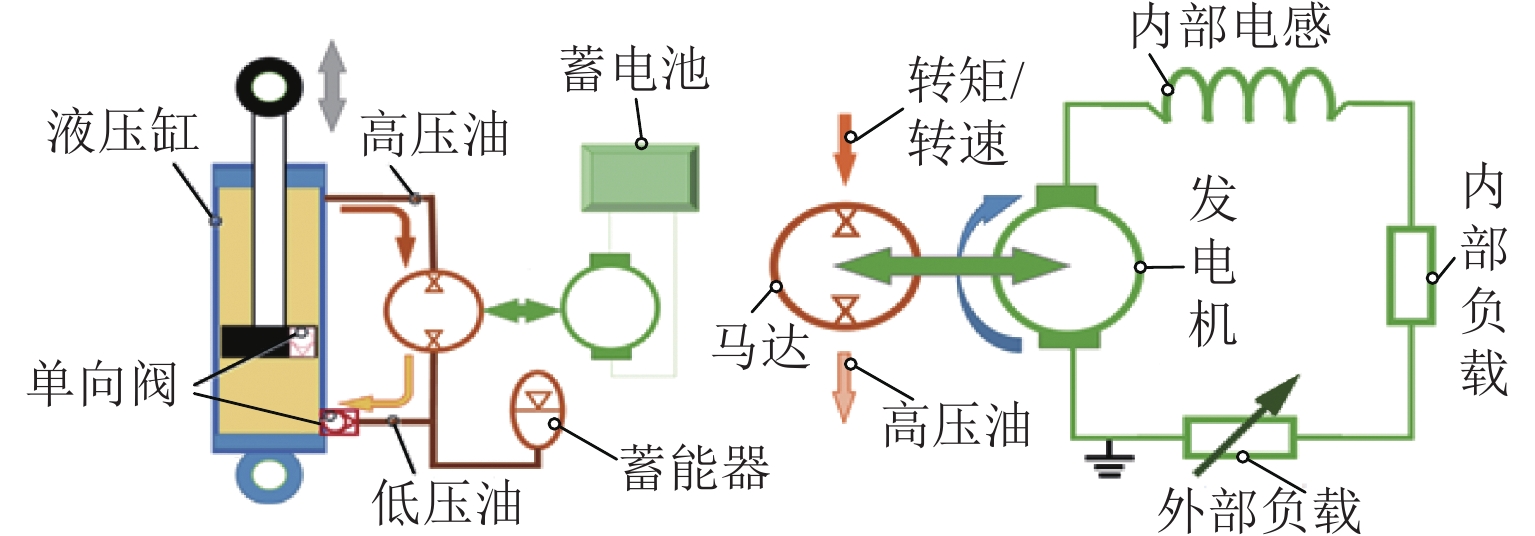
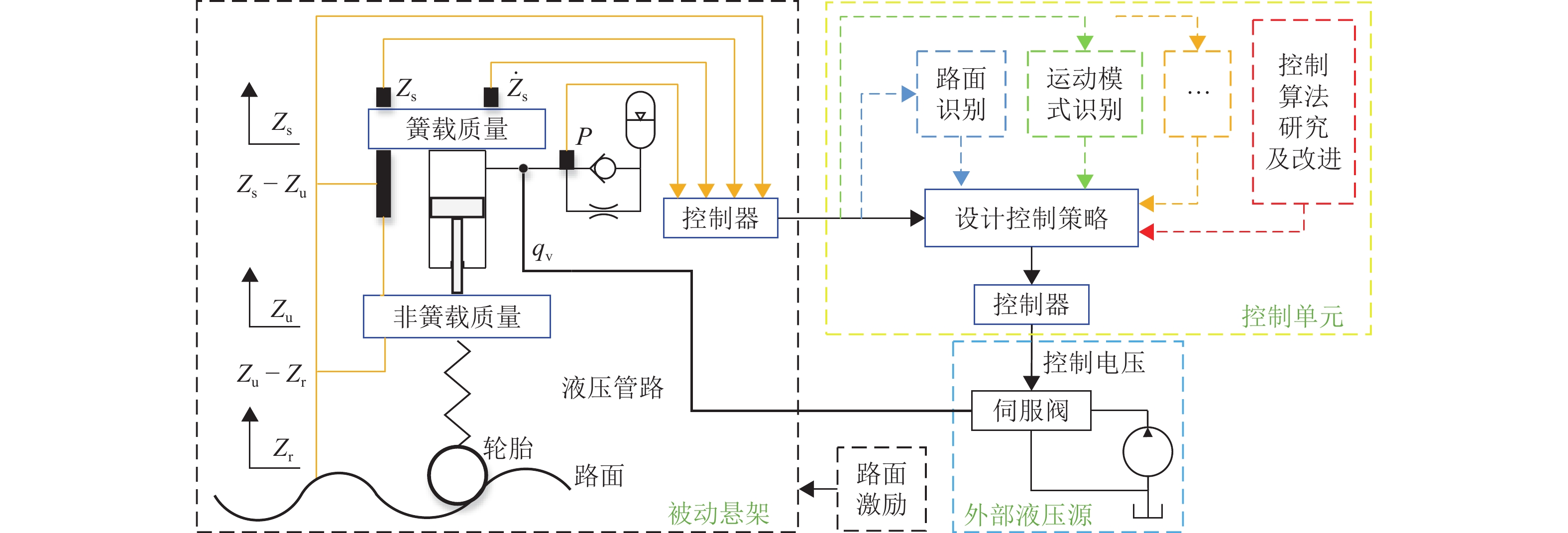
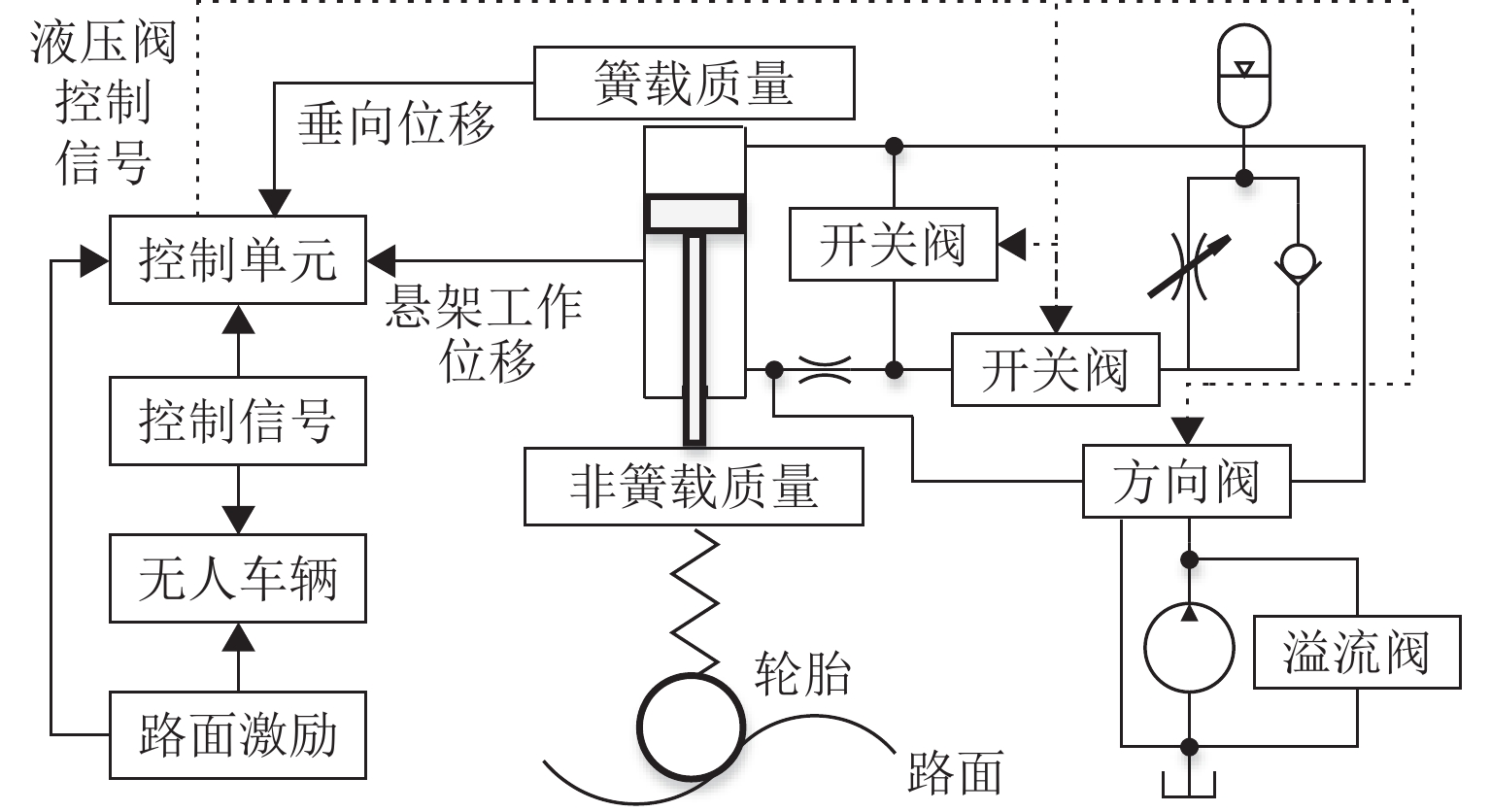
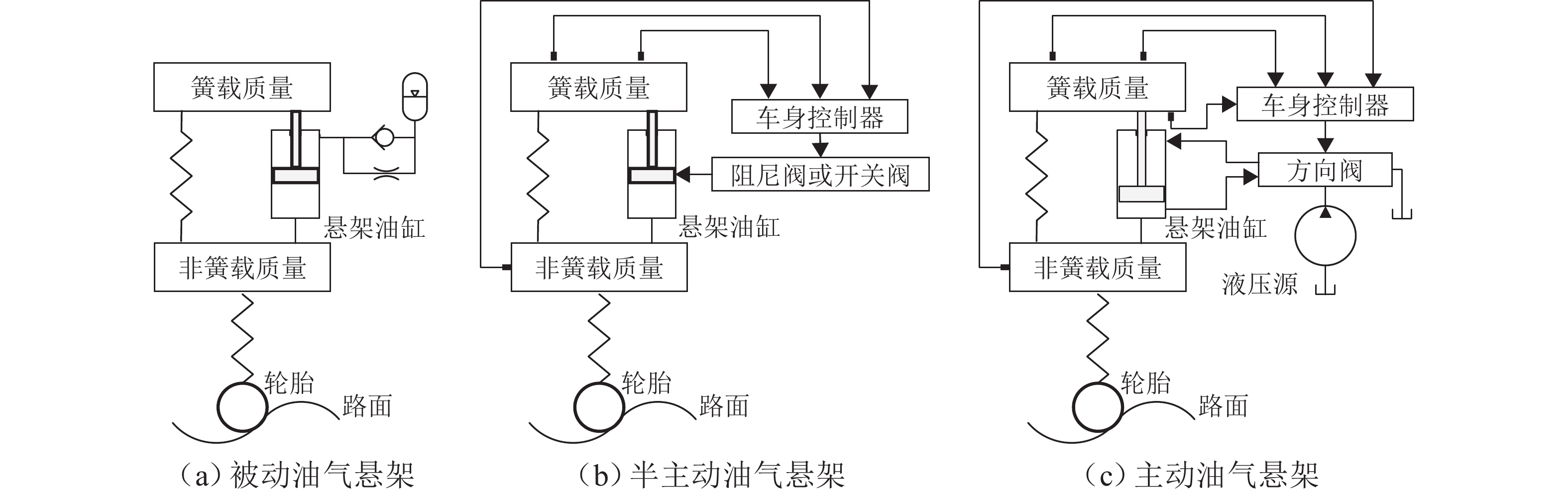
油气悬架具有缓冲减振、车身姿态调整等功能,其结构复杂、压力冲击大、耐磨性与密封性要求高. 优良的悬架油缸结构、油气悬架系统及控制方法是决定车辆行驶性能的重要条件. 从悬架结构、工作特性与控制方式等方面系统阐述了油气悬架的构成型式,归纳总结油气悬架的分类与原理;基于悬架可控制性角度,从油气悬架的结构设计与优化、数学建模、控制算法与策略等方面论述油气悬架技术,分析现有结构的特点与不足后得出:被动悬架结构简单、技术成熟,但缺乏自适应性;半主动悬架能耗小、成本较低、响应快、可靠性高,但自适应性有限;主动悬架性能优良,但能耗大、成本高、系统结构与控制策略复杂. 总结与展望3种悬架的发展现状和研究方向,为车辆油气悬架设计与控制方法的深入研究和发展提供参考.
Abstract:The hydro-pneumatic suspension has the functions of cushioning and damping, body attitude adjustment, etc., but its structure is complex, with large pressure impact and high wear resistance and sealing. The excellent suspension cylinder structure, hydro-pneumatic suspension system, and control method are the important conditions to determine the driving performance of the vehicle. The type of hydro-pneumatic suspension was analyzed, and the classification and principle of hydro-pneumatic suspension were summarized from the aspects of suspension structure, working characteristics, and control mode. From the perspective of suspension controllability, the hydro-pneumatic suspension technology was discussed in terms of structural design and optimization of hydro-pneumatic suspension, mathematical modelling, and control algorithm and strategy. By analyzing the characteristics and shortcomings of existing structures, it is concluded that passive suspension is simple in structure and mature in technology, but it lacks adaptability. The semi-active suspension has low energy consumption, low cost, fast response, and high reliability, but its adaptability is limited. Active suspension has excellent performance, but it has high energy consumption, high cost, and complex system structure and control strategy. The development status and research direction of the three types of suspension were summarized and prospected, so as to provide a reference for the further research and development of vehicle hydro-pneumatic suspension design and control methods.
-
表 1 悬架控制理论分类及特点
Table 1. Classification and characteristics of suspension control theories
控制理论 控制特点 天棚阻尼 根据簧载质量速度反馈实现阻尼控制,计算简便、响应快、鲁棒性强,广泛应用于半主动悬架,但只考虑幅频特性、忽略相频,致使传递函数评价悬架性能存在不确定性,在具体应用中存在局限性[17-18] 模糊控制 基于专家经验准则、模糊规则及隶属函数,以“if-then”为控制逻辑处理系统不确定性参数控制问题,对模型精度要求低、适应性强、鲁棒性好且易于理解,但精度低且因主观经验影响控制效果,对其实际应用造成局限性[19] 最优控制 在已知运动方程及控制范围前提下,通过性能指标参数优化实现其指标函数的最优调控,此方法目的明确且计算速度快,包括线性、非线性最优调控及H∞最优控制等,但实际悬架含有许多不确定因素,因而难以达到预期控制性能[20-21] 自适应控制 因路面工况、环境等不确定因素会影响油气悬架性能,而自适应控制基于数学模型,依据实际路面激励的变化对悬架系统参数进行实时合理地自动调节,以保持良好工作性能,但控制方案复杂、运算量大,有模型参考自适应和自校正控制两类[22] PID(proportional integral derivative)控制 控制器输入输出间无需精确数学模型,通过对输入量的比例、积分、微分参数修定可得合理的输出量,该方法简单实用,但控制效果较差且参数整定影响系统响应速度[23] 遗传算法 基于自然选择与遗传机理,通过选择、交叉与变异寻找问题最优解,搜索过程简单、覆盖面大,适应度函数选取不当易陷入局部最优解且容易过早收敛、效率低 神经网络 依据动物神经元的大规模信息处理、传递存储等特点而提出,具备信息并行处理、容错能力强与自适应学习等特点,多用于处理系统复杂非线性问题,可逼近任意连续函数[24] 变结构滑模控制 系统结构不固定,可依据系统当前的信息调整其结构,改变控制规则,具备操作简单、响应迅速、对干扰不敏感,通过调整滑模面或控制律参数可增强其控制性能[25] 复合控制 依据不同控制方法的特点以及被控对象的工作特性,通过各方法性能匹配,实现系统单个或者多目标控制,充分发挥各自优点并弥补其缺陷,具备优良控制性能及稳定性,常用模糊 PID、模糊滑模控制、模糊神经网络等 -
[1] 王连志,赵北,黎德才,等. 矿用宽体车油气悬架系统及整车动力学仿真[J]. 液压与气动,2020(11): 158-163.WANG Lianzhi, ZHAO Bei, LI Decai, et al. Simulation of hydro-pneumatic suspension and vehicle dynamics system of wide body truck for mine[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2020(11): 158-163. [2] 宋勇,刘林鑫,李占龙,等. 含圆弧形缓冲结构的仿袋鼠腿悬架建模与行为特性研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2021,55(9): 28-38.SONG Yong, LIU Linxin, LI Zhanlong, et al. Research on modeling and behavioral characteristics of bionic kangaroo leg suspension with circular arc-buffer structures[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(9): 28-38. [3] 周德成,王国强,刘玉臣,等. 油气悬挂缸参数对车辆平顺性影响的理论研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2004,35(5): 25-28.ZHOU Decheng, WANG Guoqiang, LIU Yuchen, et al. Effects of parameters of hydro-pneumatic suspension cylinder on vehicle ride comfort[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2004, 35(5): 25-28. [4] 苗明,方新,王欣,等. 连通式油气悬挂系统阻尼特性分析[J]. 中国工程机械学报,2012,10(1): 23-28.MIAO Ming, FANG Xin, WANG Xin. Damping property analysis on interconnecting oil-gas suspension system[J]. Chinense Journal of Construction Machinery, 2012, 10(1): 23-28. [5] 甄龙信,张文明. 单气室油气悬架的仿真与试验研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2009,45(5): 290-294. doi: 10.3901/JME.2009.05.290ZHEN Longxin, ZHANG Wenming. Research on simulation and experiment of hydro-pneumatic suspension with single gas cell[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(5): 290-294. doi: 10.3901/JME.2009.05.290 [6] 刘涛. 基于半主动油气悬架的车身姿态补偿控制研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学,2019. [7] 田文朋. 七桥登高车混连油气悬架系统特性研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2018. [8] 何淼. TLD110矿用自卸车前油气悬架系统研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2018. [9] 孙建民,刘祥,张帅,等. 重载工程车辆油气悬架系统控制技术研究现状分析[J]. 中国工程机械学报,2021,19(6): 482-486.SUN Jianmin, LIU Xiang, ZHANG Shuai, et al. Control technology analysis of hydro pneumatic suspension system for heavy duty engineering vehicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Construction Machinery, 2021, 19(6): 482-486. [10] 孙齐超. 油气悬架系统神经网络控制策略研究[D]. 太原:太原科技大学,2018. [11] 杨波,陈思忠,王勋,等. 双气室油气悬架特性研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2009,45(5): 276-280. doi: 10.3901/JME.2009.05.276YANG Bo, CHEN Sizhong, WANG Xun, et al. Research of twin-accumulator hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(5): 276-280. doi: 10.3901/JME.2009.05.276 [12] 刘伯庚. 非线性油气悬架参数优化设计[D]. 北京:北京理工大学,2016. [13] 刘刚,陈思忠,王文竹,等. 基于AMEsim和Simulink的油气悬架仿真与试验[J]. 振动. 测试与诊断,2016,36(2): 346-350.LIU Gang, CHEN Sizhong, WANG Wenzhu, et al. Simulation and test of hydro-pneumatic suspension based on AMEsim and Simulink[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2016, 36(2): 346-350. [14] 武德. 超大吨位全地面起重机油气悬架系统控制策略研究[D]. 太原:太原科技大学,2015. [15] 王亚曦. 磁流变液减振器CAD建模技术研究及应用[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2006. [16] Dave Crolla,喻凡. 车辆动力学及其控制[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社,2004. [17] 史文库,张曙光,陈志勇,等. 磁流变半主动座椅悬架建模及振动特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(2): 253-260.SHI Wenku, ZHANG Shuguang, CHEN Zhiyong, et al. Modeling and vibration analysis of semi-active seat suspension with magnetorheological damper[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 253-260. [18] 寇发荣,魏冬冬,梁津,等. 一种馈能型混合悬架的多模式协调控制[J]. 中国机械工程,2018,29(11): 1356-1363.KOU Farong, WEI Dongdong, LIANG Jin, et al. Multi-mode coordination control of a kind of regenerative energy hybrid suspensions[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(11): 1356-1363. [19] 张微敬,欧进萍. 基于粗糙集理论的结构振动模糊控制[J]. 振动工程学报,2005,18(4): 406-411.ZHANG Weijing, OU Jinping. Fuzzy control of structural vibration based on rough set theory[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2005, 18(4): 406-411. [20] SU X Y. Master-slave control for active suspension systems with hydraulic actuator dynamics[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 3612-3621. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2672598 [21] 孙凤,邢大壮,周冉,等. 考虑能耗的电磁主动悬架 LQR控制策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 754-760,798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220815SUN Feng, XING Dazhuang, ZHOU Ran, et al. LQR control for electromagnetic active suspension considering energy consumption[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4): 754-760,798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220815 [22] 郑玲,邓兆祥,李以农. 汽车半主动悬架的模型参考自适应控制[J]. 中国公路学报,2005,18(2): 99-102.ZHENG Ling, DENG Zhaoxiang, LI Yinong. Model reference adaptive control of semi-active suspensions[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2005, 18(2): 99-102. [23] 杨启耀,周孔亢,张文娜,等. 半主动空气悬架 Fuzzy-PID控制[J]. 农业机械学报,2008,39(9): 25-29.YANG Qiyao, ZHOU Kongkang, ZHANG Wenna, et al. Fuzzy-PID control on semi-active air suspension[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008, 39(9): 25-29. [24] 杨林,赵玉壮,陈思忠,等. 半主动油气悬架的神经网络模型参考控制[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2011,31(1): 24-28.YANG Lin, ZHAO Yuzhuang, CHEN Sizhong, et al. Neural network model reference control for semi-active hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2011, 31(1): 24-28. [25] 秦武,上官文斌,吕辉. 非线性二自由度主动悬架滑模控制方法的研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2020,56(1): 58-68. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.01.058QIN Wu, SHANGGUAN Wenbin, LÜ Hui. Research on sliding mode control for nonlinear active suspension system with two degrees of freedom[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(1): 58-68. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.01.058 [26] TAN B H, WU Y, ZHANG N, et al. Dynamic characteristics analysis of an ambulance with hydraulically interconnected suspension system[C]// SAE Technical Paper Series. Pennsylvania: SAE International, 2018: 1-5. [27] 汪若尘,叶青,孙泽宇,等. 液压互联ISD悬架系统模式切换研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2017,53(6): 110-115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.06.110WANG Ruochen, YE Qing, SUN Zeyu, et al. Study of mode switch of the hydraulically interconnected inerter-spring-damper suspension system[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(6): 110-115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.06.110 [28] ZHANG X L, LIU J C, NIE J M, et al. Simulation analysis and experiment research on hydro-pneumatic ISD suspension[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2021, 2021(1): 2095350.1-209535.14. [29] MARTINI A, BELLANI G, et al. Numerical assessment of a new hydro-pneumatic suspension system for motorcycles[J]. International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 15(2): 5308-5325. doi: 10.15282/ijame.15.2.2018.12.0409 [30] 张小江,闫振华. 准零刚度油气悬架系统设计与分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(11): 55-63,79.ZHANG Xiaojiang, YAN Zhenhua. Design and analysis of quasi-zero stiffness hydropneumatic suspension system[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 55-63,79. [31] 田文朋,窦建明,徐信芯. 七桥油气悬架耦连方案对车身姿态的影响[J]. 中国机械工程,2020,31(19): 2371-2378,2387.TIAN Wenpeng, DOU Jianming, XU Xinxin. Effects of seven-axle HPS coupling scheme on vehicle body attitude[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(19): 2371-2378,2387. [32] LUO R, LIU C D. Dynamics simulation of the high-speed train using interconnected hydro-pneumatic suspension as a self-steering system[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2022, 60(6): 2055-2074. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2021.1892156 [33] YANG F, DU Y F, LI W, et al. Innovative design method of hydro-pneumatic suspension for large high-clearance sprayer based on improved NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm[J]. Agriculture, 2023, 13(5): 1071.1-1071.27. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13051071 [34] ZHOU Q, GUO X X, XU L, et al. Simulation based evaluation of the Electro-Hydraulic Energy-Harvesting Suspension (EHEHS) for off-highway vehicles[C]// SAE Technical Paper Series. Pennsylvania: SAE International,2015: 1-1494. [35] ZOU J Y, GUO X X, ABDELKAREEM M A A, et al. Modelling and ride analysis of a hydraulic interconnected suspension based on the hydraulic energy regenerative shock absorbers[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 127: 345-369. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.02.047 [36] GUO S J, CHEN L, WANG X K, et al. Hydraulic integrated interconnected regenerative suspension: modeling and characteristics analysis[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(7): 733.1-733.22. doi: 10.3390/mi12070733 [37] 赵敬凯,谷正气,张沙,等. 矿用自卸车油气悬架力学特性研究与优化[J]. 机械工程学报,2015,51(10): 112-118,128. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.10.112ZHAO Jingkai, GU Zhengqi, ZHANG Sha, et al. Research and optimization on the mechanical property of mining dump truck’s hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(10): 112-118,128. doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.10.112 [38] 张军伟. 多轴重型车辆互连式油气悬架系统特性研究[D]. 北京:北京理工大学,2015. [39] ZHANG J W, CHEN S Z, ZHAO Y Z, et al. Research on modeling of hydropneumatic suspension based on fractional order[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015: 920279.1-920279.11. [40] CHEN Y J, HUANG L, XU L, et al. Modelling and simulation calculation of fixed-cylinder hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1965(1): 012048.1-012048.5. [41] VAN DER WESTHUIZEN S F, SCHALK ELS P. Comparison of different gas models to calculate the spring force of a hydropneumatic suspension[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2015, 57: 41-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2014.11.002 [42] LIN D Z, YANG F, LI R H. Experimental modelling and analysis of compact hydro-pneumatic interconnected suspension strut considering pneumatic thermodynamics and hydraulic inertial properties[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 172: 108988.1-108988.13. [43] LI Z X, WANG Y C, DU H, et al. Modelling and analysis of full-vehicle hydro-pneumatic suspension system considering real-gas polytropic process[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 165: 108406.1-108406.21. [44] YIN Y M, RAKHEJA S, YANG J, et al. Characterization of a hydro-pneumatic suspension strut with gas-oil emulsion[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 106: 319-333. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.12.040 [45] TAN B H, LIN X, ZHANG B J, et al. Nonlinear modeling and experimental characterization of hydraulically interconnected suspension with shim pack and gas-oil emulsion[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2023, 182: 109554.1-109554.18. [46] 索雪峰,焦生杰,张泽宇,等. 活塞导向长度对油气悬架减振性能的影响[J]. 液压与气动,2022,46(3): 120-127.SUO Xuefeng, JIAO Shengjie, ZHANG Zeyu, et al. Effect of hydro-pneumatic suspension piston guide length on its vibration reduction performance[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2022, 46(3): 120-127. [47] LIN D Z, YANG F, LI R H, et al. The dynamic analysis-effect of orifice- of roll-coupled compacted hydro-pneumatic suspension subjected to typical based excitation[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2022, 236(10/11): 2448-2458. [48] WANG Y L, WU T L, RAN Z H, et al. Modeling analysis and experiments of a novel hydro-pneumatic suspension with piezoelectric energy harvester[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2023, 32(7): 075005.1-075005.16. [49] KÜÇÜK K, YURT H K, ARıKAN K B, et al. Modelling and optimisation of an 8 × 8 heavy duty vehicle’s hydro-pneumatic suspension system[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2016, 71(1/2/3/4): 122-138. doi: 10.1504/IJVD.2016.078772 [50] KWON K, SEO M, KIM H, et al. Multi-objective optimisation of hydro-pneumatic suspension with gas-oil emulsion for heavy-duty vehicles[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(7): 1146-1165. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2019.1609050 [51] 周晨. 应急救援车辆油气悬架与主动前轮转向系统控制策略研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2021. [52] ZHAO H Y, WANG G Q, LV W D, et al. Optimization of hydropneumatic suspension for articulated wheel loader based on Kriging model and particle swarm algorithm[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 10(11): 1-10. [53] ZHAO Y Q, XU H, DENG Y J, et al. Multi-objective optimization for ride comfort of hydro-pneumatic suspension vehicles with mechanical elastic wheel[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2019, 233(11): 2714-2728. doi: 10.1177/0954407018804909 [54] XU H, ZHAO Y Q, YE C, et al. Integrated optimization for mechanical elastic wheel and suspension based on an improved artificial fish swarm algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2019, 137: 102722.1-102722.8. [55] TAN B H, WU Y, ZHANG N, et al. Improvement of ride quality for patient lying in ambulance with a new hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 11(4): 1-20. [56] TIAN W P, DOU J M, XU X X. Modelling and characteristics of hybrid coupling hydro-pneumatic suspension for a seven-axle vehicle[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2021, 235(7): 1892-1901. doi: 10.1177/0954407020983212 [57] YANG L, WANG R C, SUN Z Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization design of hydropneumatic suspension with gas-oil emulsion for ride comfort and handling stability of an articulated dumper truck[J]. Engineering Optimization, 2023, 55(2): 291-310. doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2021.2002314 [58] 杜甫,陈轶杰,万义强,等. 惯容式油气悬架力学建模和试验研究[J]. 汽车工程,2021,43(12): 1817-1824.DU Fu, CHEN Yijie, WAN Yiqiang, et al. Mechanical modeling and experimental study of inerter-based oil-gas suspension[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(12): 1817-1824. [59] MOAAZ A O, ALI A S, GHAZALY N M, et al. Performance evaluation of semi-active suspension for passenger vehicle through skyhook, groundhook and hybrid control strategies[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Structures and Systems, 2022, 14(5): 572-579. [60] SOLOMON U, PADMANABHAN C. Semi-active hydro-gas suspension system for a tracked vehicle[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2011, 48(3): 225-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2011.01.002 [61] 么鸣涛,曹锋,阙瑞义,等. 考虑汽车悬架动挠度的模糊PID控制[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2016,36(9): 929-934.YAO Mingtao, CAO Feng, QUE Ruiyi, et al. Fuzzy PID control considering vehicular suspension dynamic deflection[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016, 36(9): 929-934. [62] 刘涛. 车身姿态补偿半主动控制[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2020,34(7): 63-74.LIU Tao. Semi-active control for body attitude compensation[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science), 2020, 34(7): 63-74. [63] 孙建民,刘祥,赵国浩,等. 模糊反馈增量式比例积分微分油气悬架控制[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(34): 14814-14820.SUN Jianmin, LIU Xiang, ZHAO Guohao, et al. Incremental proportional-integral-derivative hydro pneumatic suspension control based on fuzzy feedback[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(34): 14814-14820. [64] 孙东,汪若尘,丁仁凯,等. 基于灰狼算法的矿用自卸车油气悬架半主动控制研究[J]. 中国机械工程,2023,34(4): 490-497.SUN Dong, WANG Ruochen, DING Renkai, et al. Research on semi-active control of hydro-pneumatic suspension for mining dump truck based on grey wolf algorithm[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(4): 490-497. [65] SIM K, LEE H, YOON J W, et al. Effectiveness evaluation of hydro-pneumatic and semi-active cab suspension for the improvement of ride comfort of agricultural tractors[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2017, 69: 23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2016.10.003 [66] ZHU Z H, WANG R C, YANG L, et al. Modelling and control of a semi-active dual-chamber hydro-pneumatic inerter-based suspension system[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2021, 235(9): 2355-2370. doi: 10.1177/0954407021990916 [67] WANG R C, LIU W, DING R K, et al. Switching control of semi-active suspension based on road profile estimation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2022, 60(6): 1972-1992. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2021.1889621 [68] 汪少华,翟旭辉,孙晓强,等. 车辆刚度阻尼多级可调式油气悬架系统分析及控制研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2022,41(12): 168-177.WANG Shaohua, ZHAI Xuhui, SUN Xiaoqiang, et al. Analysis and control of a vehicle hydro pneumatic suspension system with multistage adjustable stiffness and damping characteristics[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(12): 168-177. [69] ZHANG Y X, ZHANG X J, ZHAN M, et al. Study on a novel hydraulic pumping regenerative suspension for vehicles[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2015, 352(2): 485-499. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2014.06.005 [70] 周创辉,文桂林. 基于改进型天棚阻尼控制算法的馈能式半主动油气悬架系统[J]. 振动与冲击,2018,37(14): 168-174,207.ZHOU Chuanghui, WEN Guilin. Hydraulic-electrical energy regenerative semi-active hydro-pneumatic suspension system based on a modified skyhook damping control algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(14): 168-174,207. [71] AWAD M N, SOKAR M I, ABDRABBO S M, et al. Hydro-pneumatic energy harvesting suspension system using a PSO based PID controller[J]. SAE International Journal of Commercial Vehicles, 2018, 11(4): 223-234. doi: 10.4271/02-11-04-0018 [72] YANG L, WANG R C, DING R K, et al. Investigation on the dynamic performance of a new semi-active hydro-pneumatic inerter-based suspension system with MPC control strategy[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2021, 154: 107569.1-107569.21. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107569 [73] SUSATIO Y, OKTAVIANA L, RIZKI N K, et al. Design of half-car active suspension system for passenger riding comfort[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2018, 1075(1): 012030.1-012030.7. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1075/1/012030 [74] 张杰. 某无人战车主动油气悬架设计及控制的研究[D]. 南京:南京理工大学,2018. [75] SAGLAM F, UNLUSOY Y S. Adaptive ride comfort and attitude control of vehicles equipped with active hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2016, 71(1/2/3/4): 31-35. doi: 10.1504/IJVD.2016.078764 [76] QIAO C F, WEN H J, LIU X Y, et al. Damping control and experiment on active hydro-pneumatic suspension of sprayer based on genetic algorithm optimization[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2021, 15: 707390.1-707390.17. [77] NGUYEN D N, NGUYEN T A, DANG N D. A novel sliding mode control algorithm for an active suspension system considering with the hydraulic actuator[J]. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures, 2022, 19(1): 1-16. [78] OZER H O, HACIOGLU Y, YAGIZ N. High order sliding mode control with estimation for vehicle active suspensions[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2018, 40(5): 1457-1470. doi: 10.1177/0142331216685394 [79] WANG D Z, ZHAO D X, GONG M D, et al. Nonlinear predictive sliding mode control for active suspension system[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2018, 2018(1): 819405.1-819405.10. [80] HUANG Y B, NA J, WU X, et al. Approximation-free control for vehicle active suspensions with hydraulic actuator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(9): 7258-7267. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2798564 [81] CHEN G P, JIANG Y, TANG Y J, et al. Revised adaptive active disturbance rejection sliding mode control strategy for vertical stability of active hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. ISA Transactions, 2023, 132: 490-507. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.06.008 [82] ZHOU C, LIU X H, CHEN W, et al. Optimal sliding mode control for an active suspension system based on a genetic algorithm[J]. Algorithms, 2018, 11(12): 205.1-205.16. doi: 10.3390/a11120205 [83] WEI S W, SU X Y. Optimization of the new index reaching law of the active suspension sliding mode controller based on the cuckoo search algorithm[J]. Complexity, 2021, 2021(1): 1-10. [84] RIOFRIO A, SANZ S, BOADA M J L, et al. A LQR-based controller with estimation of road bank for improving vehicle lateral and rollover stability via active suspension[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(10): 2318.1-2318.20. [85] 曹玥. 轮式装载机油气悬架参数优化及主动控制[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2018. [86] WANG S, LU Z, LIU X H, et al. Active control of hydropneumatic suspension parameters of wheel loaders based on road condition identification[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2018, 15(6): 1-23. [87] SATHISHKUMAR P, WANG R C, YANG L, et al. Trajectory control for tire burst vehicle using the standalone and roll interconnected active suspensions with safety-comfort control strategy[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 142: 106776.1-106776.18. [88] ZHOU C, LIU X H, XU F X, et al. Sliding Mode Switch Control of Adjustable Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension based on Parallel Adaptive Clonal Selection Algorithm[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(5): 1852.1-1852.30. [89] GAO X, CHANG Y K, CAI T, et al. Analysis of suspension control strategy of wheel-track composite amphibious vehicle based on AMESim-simulink[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2417(1): 012033.1-012033.7. [90] GUO Q H, ZHAO D X, ZHAO X L, et al. Active suspension control strategy of multi-axle emergency rescue vehicle based on inertial measurement unit[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(20): 6877.1-6877.26. [91] ZHU J X, ZHAO D X, LIU S, et al. Integrated control of spray system and active suspension systems based on model-assisted active disturbance rejection control algorithm[J]. Mathematics, 2022, 10(18): 3391.1-3391.17. [92] SATHISHKUMAR P, WANG R C, YANG L, et al. Energy harvesting approach to utilize the dissipated energy during hydraulic active suspension operation with comfort oriented control scheme[J]. Energy, 2021, 224: 120124.1-120124.15. [93] XU F X, ZHOU C, LIU X H, et al. GRNN inverse system based decoupling control strategy for active front steering and hydro-pneumatic suspension systems of emergency rescue vehicle[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 167: 108595.1-108595.15. [94] 米承继,谷正气,伍文广,等. 基于参数辨识的矿用自卸车平顺性优化[J]. 机械工程学报,2012,48(6): 109-115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2012.06.109MI Chengji, GU Zhengqi, WU Wenguang, et al. Mining dump truck ride optimization based on parameter identification[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(6): 109-115. doi: 10.3901/JME.2012.06.109 [95] 刘大维,蒋荣超,朱龙龙,等. 基于遗传算法的路面有理函数功率谱密度参数识别[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(8): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.08.020LIU Dawei, JIANG Rongchao, ZHU Longlong, et al. Parameters identification of rational function power spectral density of pavement based on genetic algorithms[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(8): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.08.020 [96] 朱一帆,谷正气,张沙. 基于辨识路面的矿用自卸车平顺性优化[J]. 振动与冲击,2015,34(13): 24-30.ZHU Yifan, GU Zhengqi, ZHANG Sha. Mining dump truck’s ride comfort optimization based on road surface identification[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(13): 24-30. [97] LIU W, WANG R C, DING R K, et al. On-line estimation of road profile in semi-active suspension based on unsprung mass acceleration[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 135: 106370.1-106370.17. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106370 [98] 李以农,朱哲葳,郑玲,等. 基于路面识别的主动馈能悬架多目标控制与优化[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(2): 129-137.LI Yinong, ZHU Zhewei, ZHENG Ling, et al. Multi-objective control and optimization of active energy-regenerative suspension based on road recognition[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(2): 129-137. [99] WANG L F, ZHANG N, DU H P. Real-time identification of vehicle motion-modes using neural networks[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 50/51: 632-645. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.05.043 [100] ZHENG E L, ZHONG X Y, ZHU R, et al. Investigation into the vibration characteristics of agricultural wheeled tractor-implement system with hydro-pneumatic suspension on the front axle[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 186: 14-33. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.05.004 [101] ALI D, FRIMPONG S. Artificial intelligence models for predicting the performance of hydro-pneumatic suspension struts in large capacity dump trucks[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2018, 67: 283-295. doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2018.06.005 -




 下载:
下载: