Prediction Model for Water Film Thickness of Drainage Asphalt Pavement under Ultimate Rainfall Intensity
-
摘要:
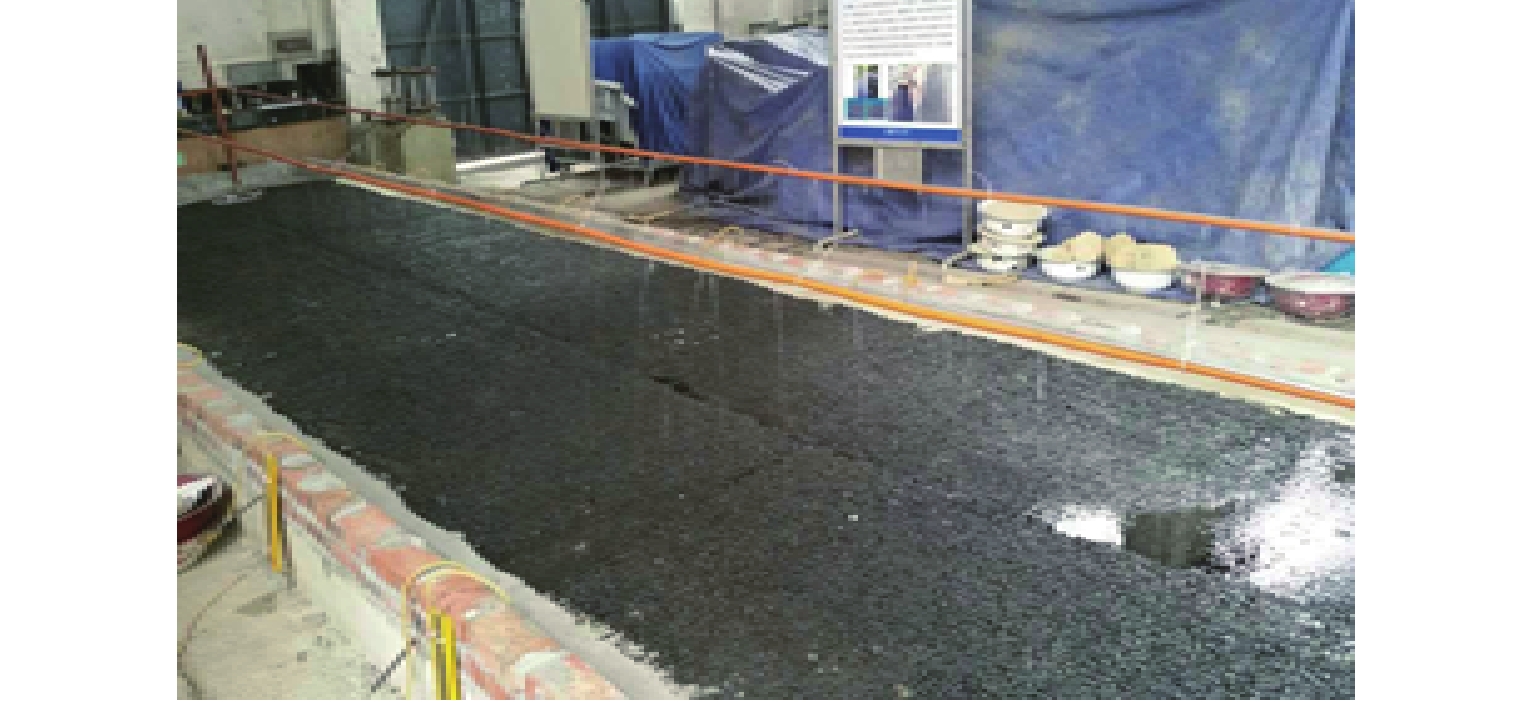
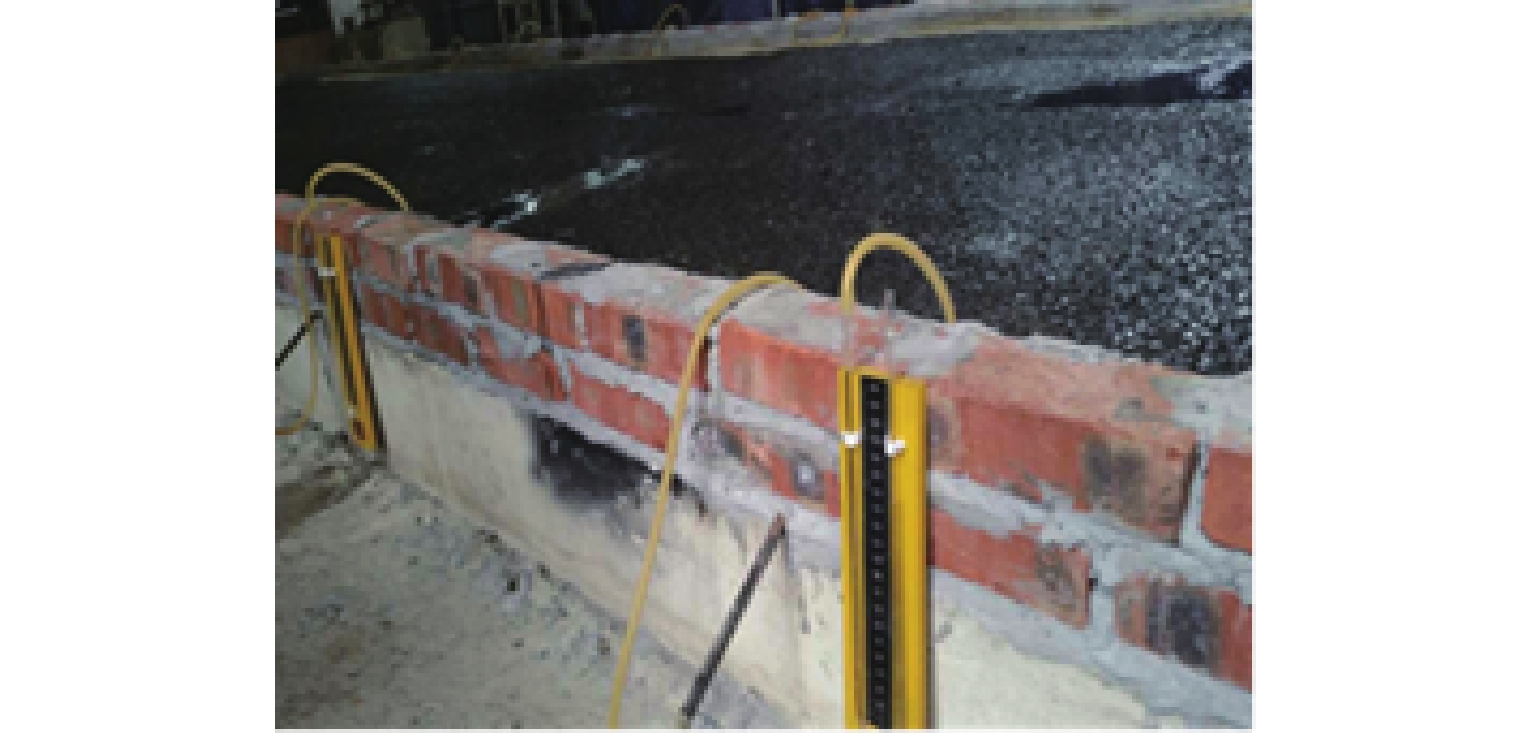
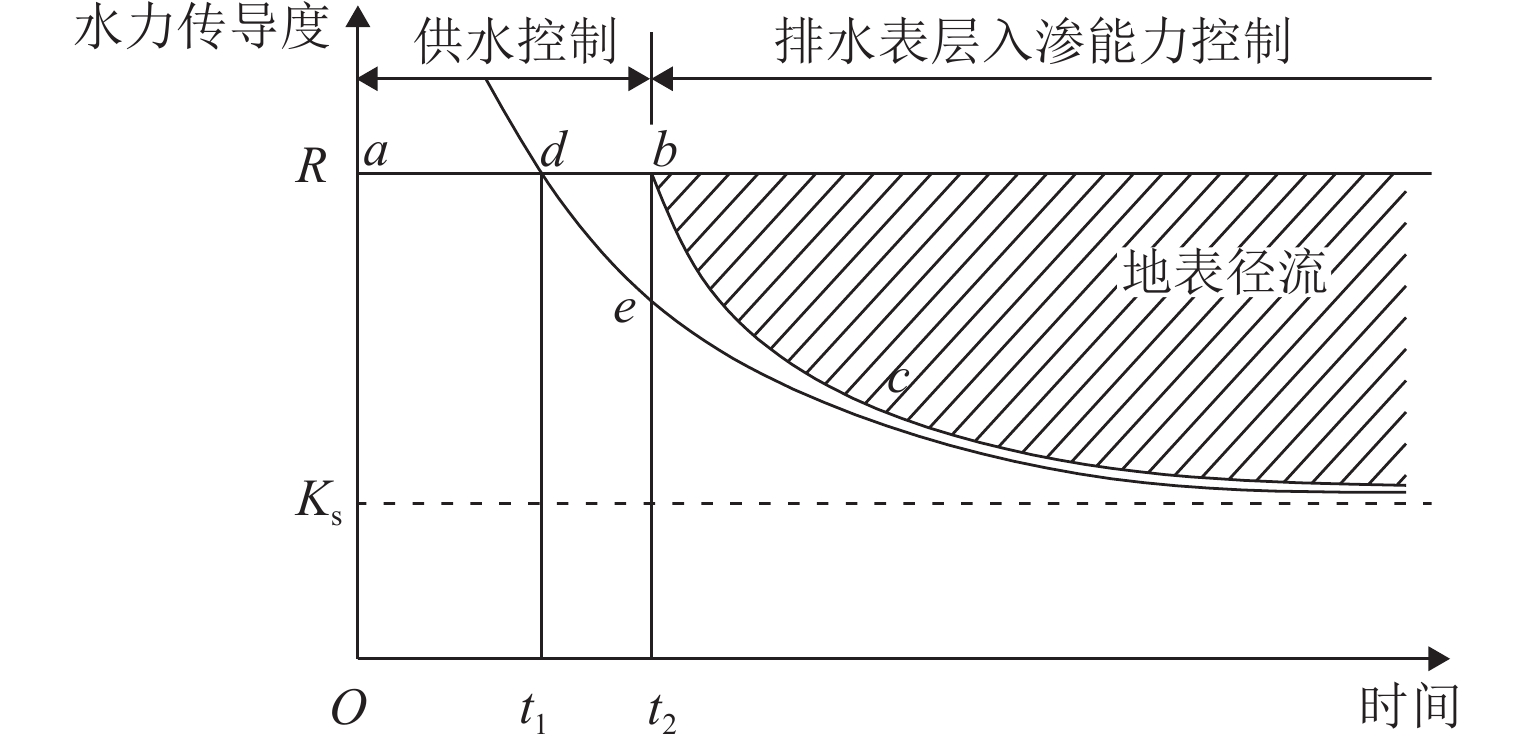
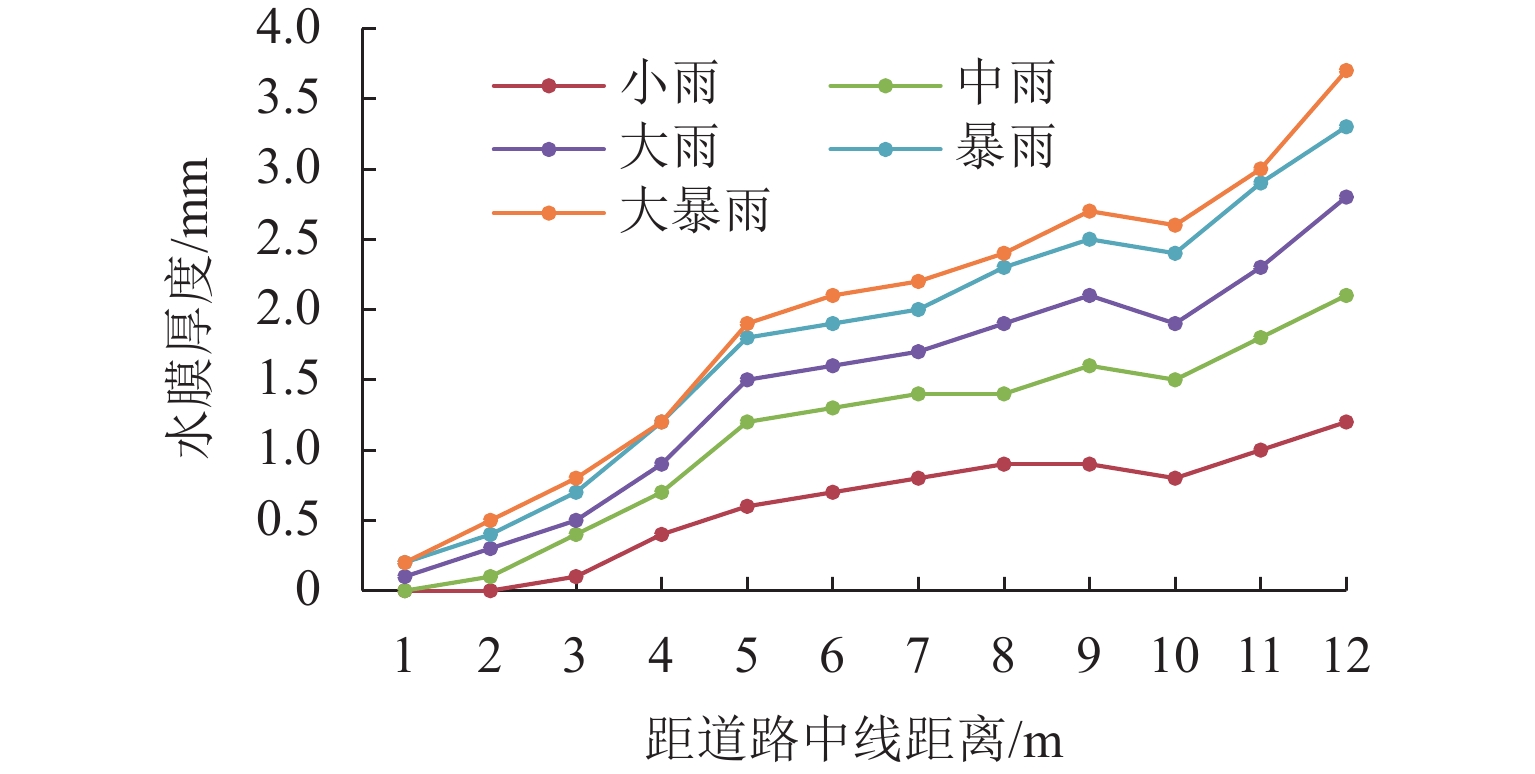
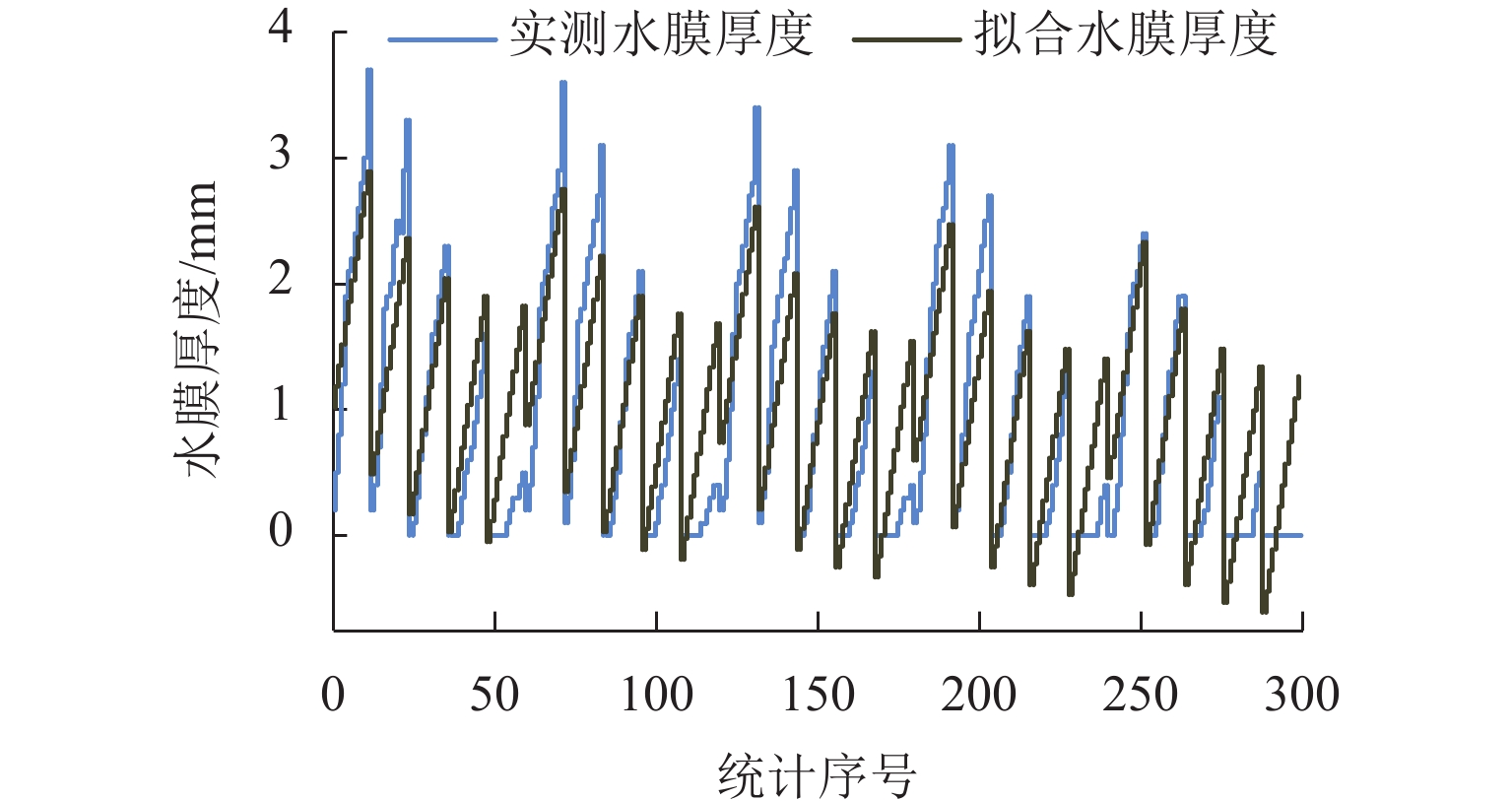
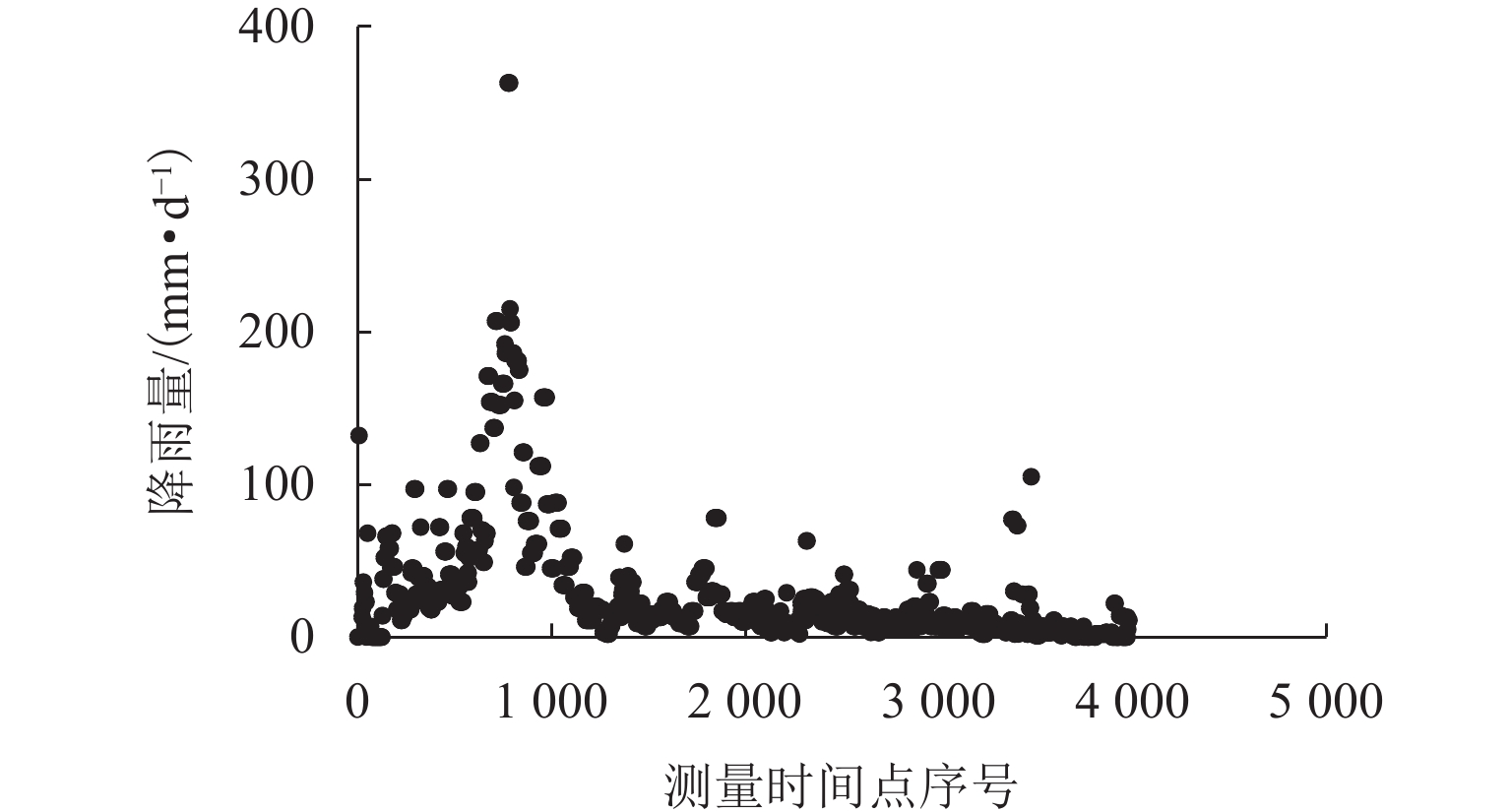
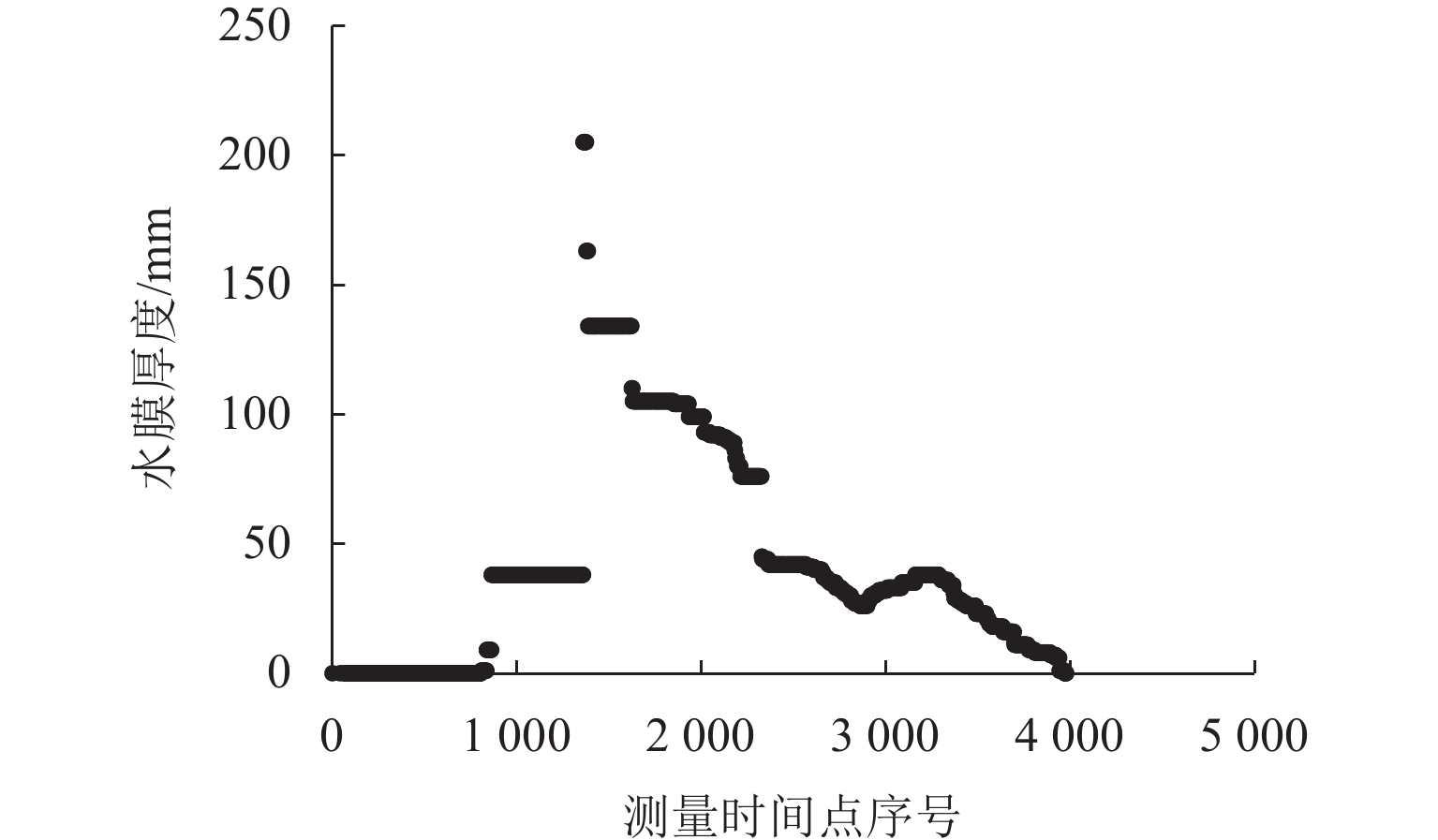
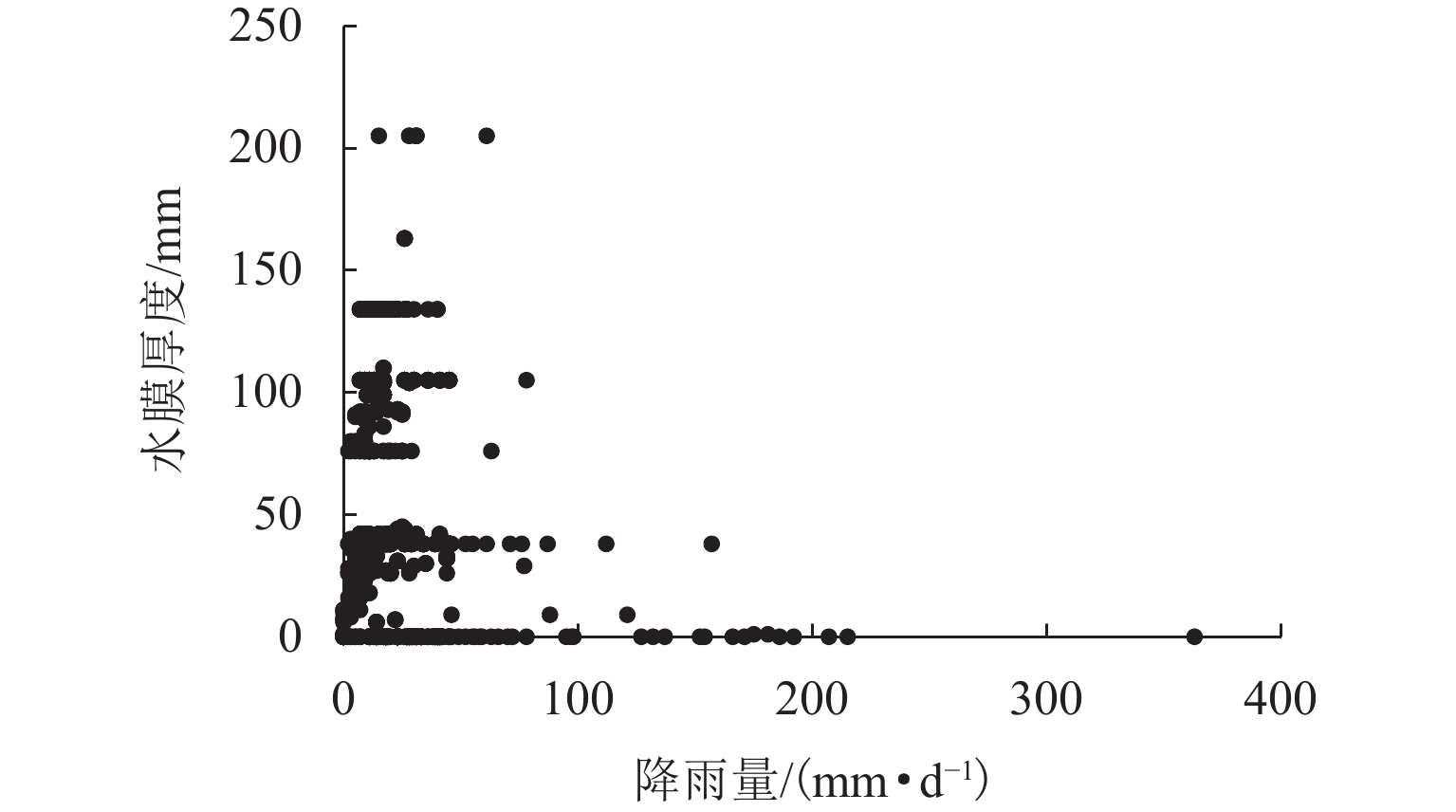
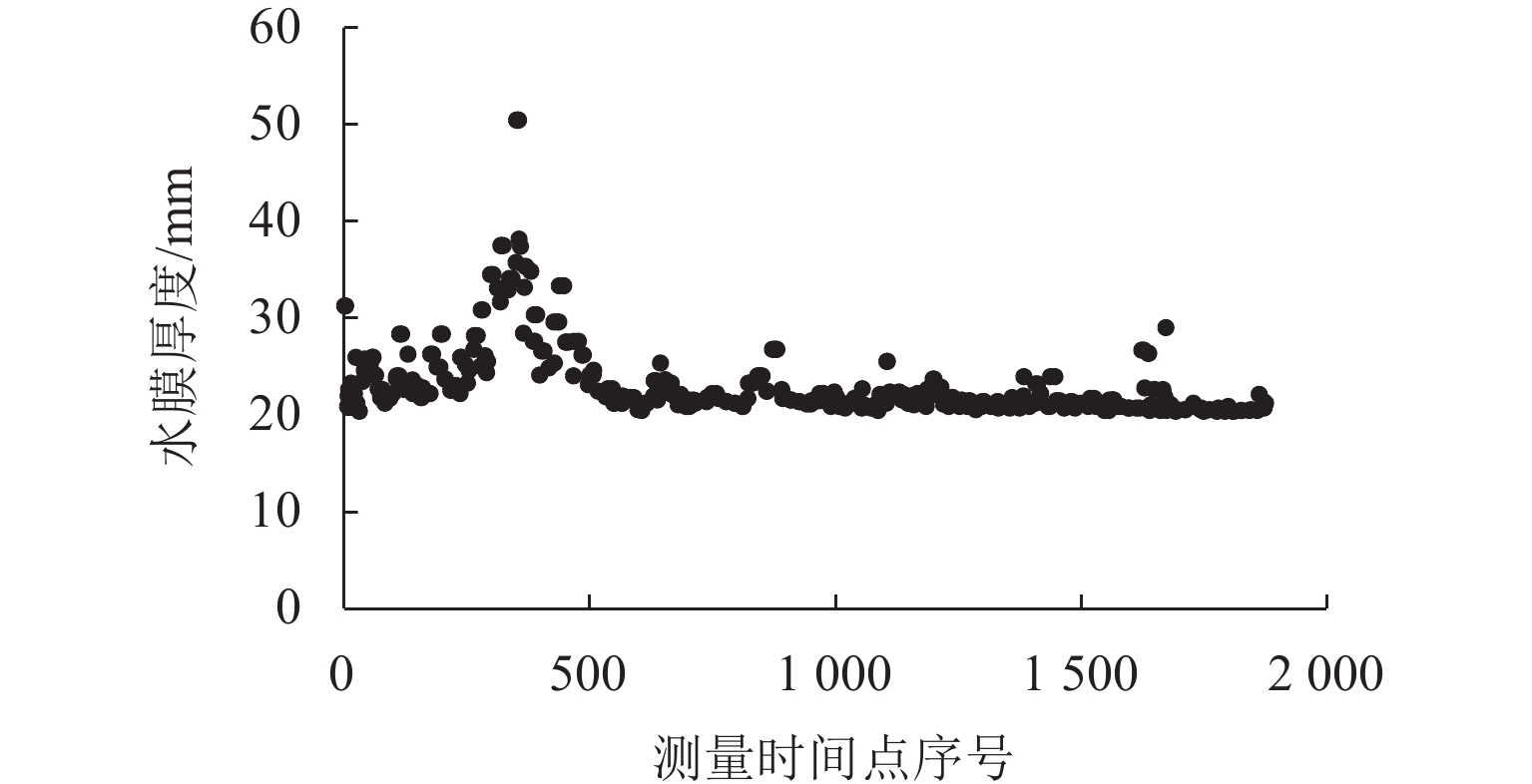
为研究多车道排水沥青路面在极限降雨强度下的水膜厚度变化规律,基于排水沥青路面渗流特性,在室内铺筑了多车道排水沥青路面足尺试验段,测量不同降雨强度下路表水膜厚度,分析水膜厚度随降雨强度和路面排水路径长度等影响因素的变化规律,构建强降雨下排水沥青路面水膜厚度预估模型,并在广西南宁绕城高速对预估模型进行现场验证;基于水膜厚度预估模型,提出排水沥青路面不出现水膜的极限降雨强度. 研究结果表明:排水沥青路面表面的实测水膜厚度随着路面排水路径变长而增加,且随降雨强度增大而急速增加,在雨量不大的中小雨阶段,在距道路中心3 m范围内不会出现水膜;水膜厚度随降雨量、排水路径长度增大而增大,而随路面厚度、坡度和空隙率增加而减小;在排水路径长度不超过2 m时,排水沥青路面可承受特大暴雨而不会出现水膜,当排水路径长度超过10 m后,降雨强度达到大雨等级会形成路表水膜.
Abstract:In order to study the variation law of water film thickness of multi-lane drainage asphalt pavement under ultimate rainfall intensity, a full-scale experimental section of multi-lane drainage asphalt pavement was constructed in the laboratory based on the seepage characteristics of drainage asphalt pavement. The water film thickness of the road surface was measured under different rainfall intensities, and the variation law of water film thickness with factors such as rainfall intensity and drainage path length of the pavement was analyzed. A model for predicting the water film thickness of drainage asphalt pavement under heavy rainfall was proposed, and on-site verification of the prediction model was conducted on the Nanning Ring Expressway in Guangxi Province. The ultimate rainfall intensity for drainage asphalt pavement without water film was determined based on a water film thickness prediction model. The research results indicate that the measured water film thickness of the drainage asphalt pavement increases with the drainage path length of the pavement and rapidly increases with the increase in rainfall intensity. During moderate to light rain periods with minimal rainfall, no water film will appear within 3 m of the road center; the water film thickness increases with the increase in rainfall and drainage path length, and it decreases with the increase in pavement thickness, slope, and porosity; when the drainage path length does not exceed 2 m, drainage asphalt pavement can withstand extremely heavy rainstorm without water film. When the drainage path length exceeds 10 m, the rainfall intensity reaches the level of heavy rain, which will form a water film on the road surface.
-
Key words:
- asphalt pavement /
- rainfall /
- traffic safety /
- water film /
- model structure
-
表 1 降雨强度试验模拟值换算
Table 1. Simulated value conversion in rainfall intensity experiment
降雨强度等级 q/(mm·d−1) 水表读数/(mm•s−1) 小雨 (0,10.0] 0.000423 中雨 (10.0,25.0] 0.000872 大雨 (25.0,50.0] 0.001256 暴雨 (50.0,100.0] 0.001718 大暴雨 (100.0,250.0] 0.001897 表 2 排水沥青路面试验段实测数据(大暴雨状态为例)
Table 2. Measured data of experimental section of drainage asphalt pavement (taking heavy rainstorm as an example)
l/m h/mm i/% V/% hq/mm q/mm 1 38.7 2.0 20.4 0.2 160 2 40.2 2.0 19.8 0.5 160 3 43.6 2.0 19.1 0.8 160 4 45.1 2.0 18.5 1.2 160 5 46.3 2.0 18.3 1.9 160 6 48.3 2.0 19.5 2.1 160 7 49.6 2.0 19.8 2.2 160 8 51.4 2.0 20.6 2.4 160 9 53.2 2.0 20.2 2.7 160 10 54.7 2.0 19.9 2.6 160 11 56.9 2.0 19.2 3.0 160 12 58.6 2.0 20.3 3.7 160 表 3 极限降雨强度的试算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of ultimate rainfall intensity
$ l $/m $ h $/m $ i $/% $ V $/% $ {q}_{{\mathrm{max}}} $/(mm•d−1) 承受降雨强度等级 1 0.04 2.0 21 282.491 特大暴雨 2 0.04 2.0 21 258.972 特大暴雨 3 0.04 2.0 21 235.334 大暴雨 4 0.04 2.0 21 211.577 大暴雨 5 0.04 2.0 21 187.700 大暴雨 6 0.04 2.0 21 163.704 大暴雨 7 0.04 2.0 21 139.586 大暴雨 8 0.04 2.0 21 115.347 大暴雨 9 0.04 2.0 21 90.985 暴雨 10 0.04 2.0 21 66.501 暴雨 11 0.04 2.0 21 41.894 大雨 -
[1] 郑彬双. 无人驾驶车辆制动过程沥青路面抗滑特性及感应需求研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021. [2] IVAN J N, RAVISHANKER N, JACKSON E, et al. A statistical analysis of the effect of wet-pavement friction on highway traffic safety[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety & Security, 2012, 4(2): 116-136. [3] CHARBENEAU R J, BARRETT M E. Drainage hydraulics of permeable friction courses[J]. Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(4): W04417.1-W04417.10. [4] ZHOU W, HUANG X M, WANG L B. Study on the void reduction behaviour of porous asphalt pavement based on discrete element method[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2017, 18(4): 285-291. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2015.1065987 [5] 张从友, 何兆益, 王东敏, 等. 基于排水沥青路面结构参数的排水能力研究[J]. 中外公路, 2019, 39(6): 43-47.ZHANG Congyou, HE Zhaoyi, WANG Dongmin, et al. Research on drainage performance based on structural parameters of drainage asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2019, 39(6): 43-47. [6] DREELIN E A, FOWLER L, RONALD CARROLL C. A test of porous pavement effectiveness on clay soils during natural storm events[J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(4): 799-805. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.12.002 [7] 丁永富. 透水沥青路面渗流特性与雨水控制效果模拟研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2019. [8] CHEN J, TANG T, ZHANG Y Q. Laboratory characterization of directional dependence of permeability for porous asphalt mixtures[J]. Materials and Structures, 2017, 50(5): 215.1-215.11. [9] 马翔, 倪富健, 李强. 排水面层渗流模型及参数[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(2): 381-385.MA Xiang, NI Fujian, LI Qiang. Seepage model and parameters of porous pavement layer[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 44(2): 381-385. [10] 肖鑫, 张肖宁. 基于排水沥青混合料细观结构的排水特性分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(6): 113-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2016.06.018XIAO Xin, ZHANG Xiaoning. Analysis of drainage characteristics based on microstructure of porous asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(6): 113-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2016.06.018 [11] 王旭波. 透水沥青路面透水性能及结构分析和应用研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2019. [12] 陈泽孔. 多车道排水沥青路面排水性能实验研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2016. [13] 王宏畅, 葛辉, 周明刚. 基于常水头渗透试验的 PAC 排水和抗堵塞能力[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(1): 209-214.WANG Hongchang, GE Hui, ZHOU Minggang. Drain and anti-clogging ability of porous asphalt concrete based on constant head permeability experiment[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46(1): 209-214. [14] TAN S A, FWA T F, CHAI K C. Drainage considerations for porous asphalt surface course design[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2004, 1868(1): 142-149. doi: 10.3141/1868-15 [15] KUANG X H, KIM J Y, GNECCO I, et al. Particle separation and hydrologic control by cementitious permeable pavement[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2007(2025): 111-117. [16] 罗京, 刘建蓓, 王元庆. 路面水膜深度预测模型验证试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2015, 28(12): 57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.008LUO Jing, LIU Jianbei, WANG Yuanqing. Validation test on pavement water film depth prediction model[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(12): 57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2015.12.008 -




 下载:
下载: