Ride Comfort Analysis of Suspension System of Mining Dump Truck Based on AMESim
-
摘要:
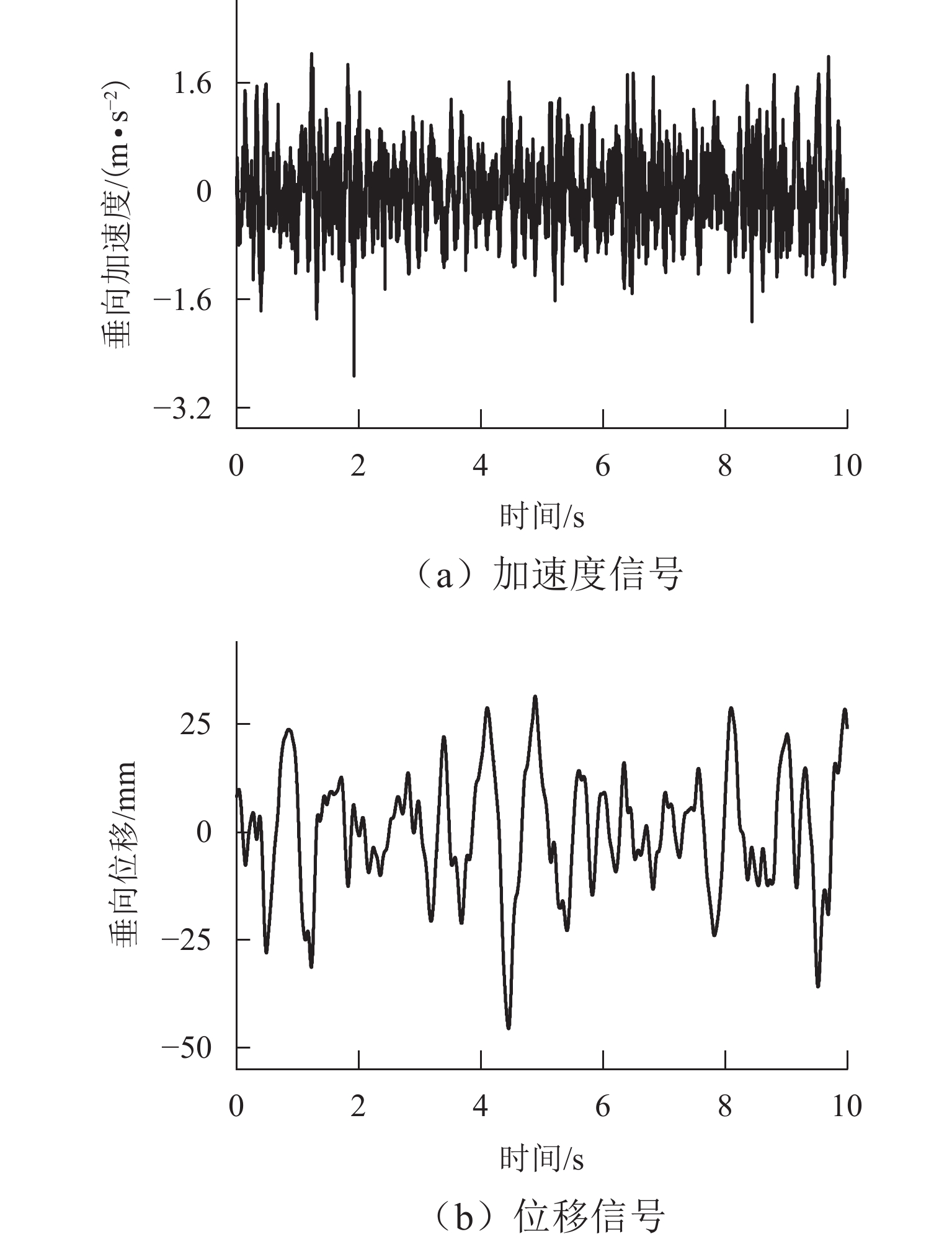
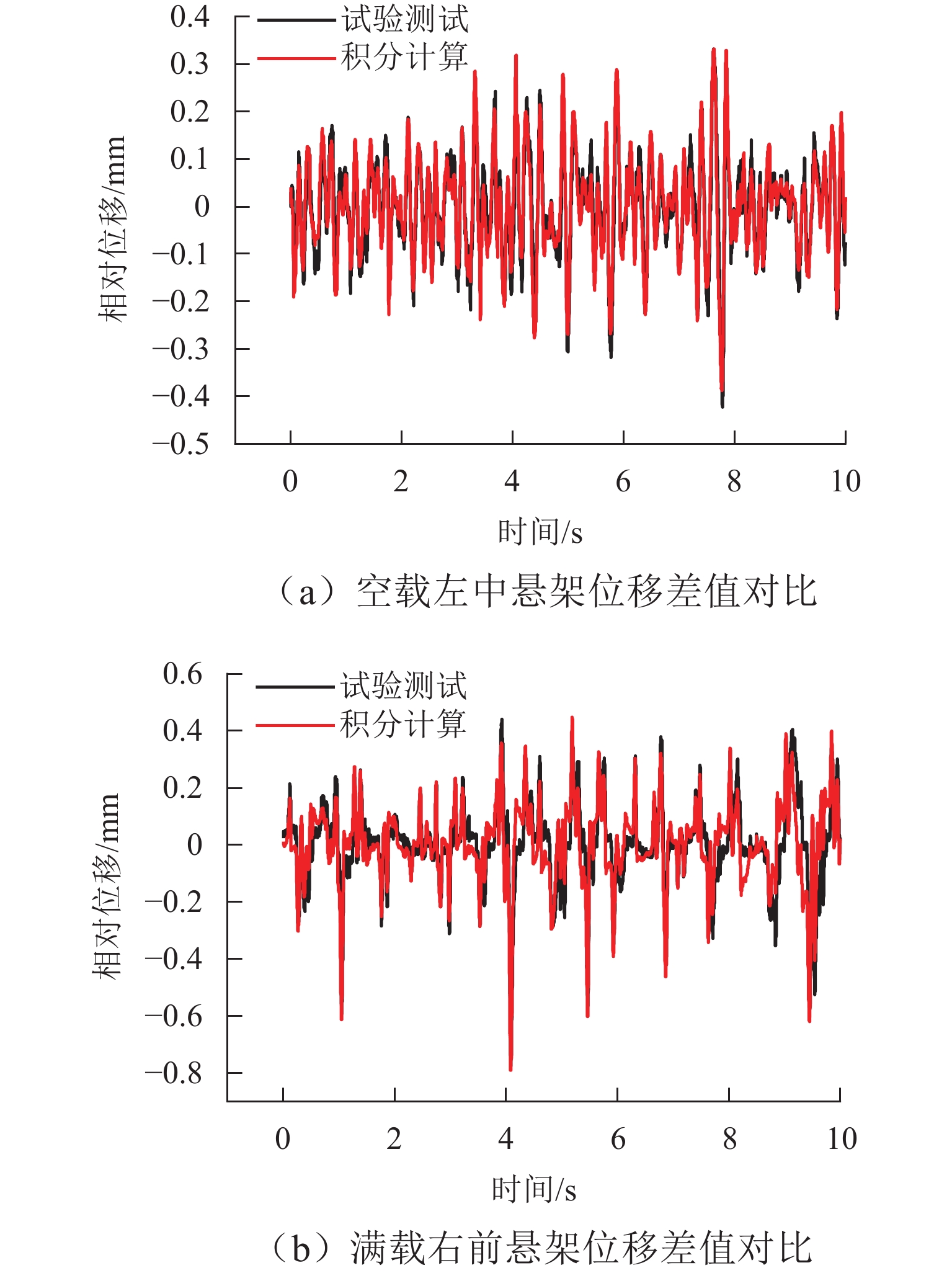
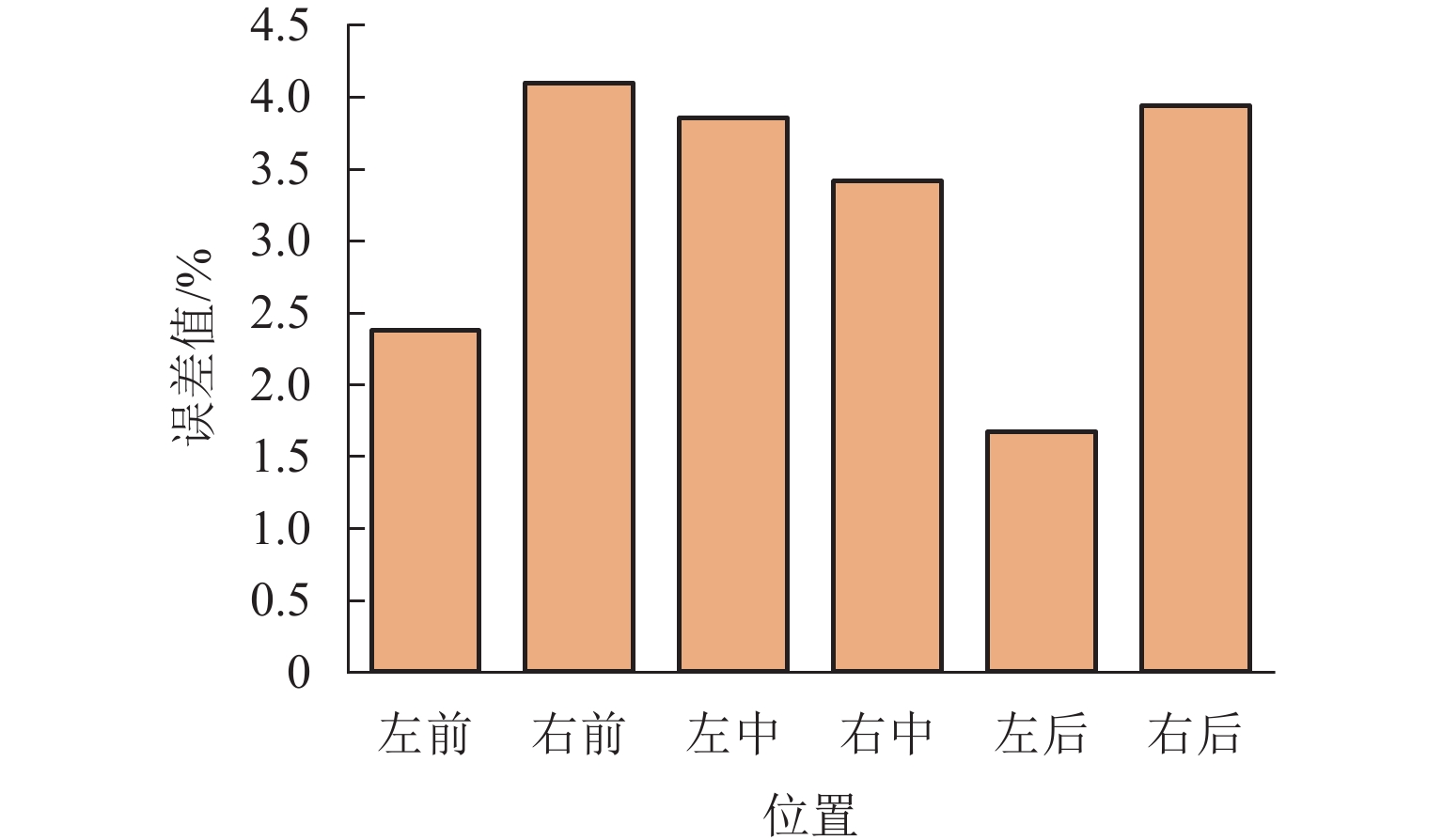
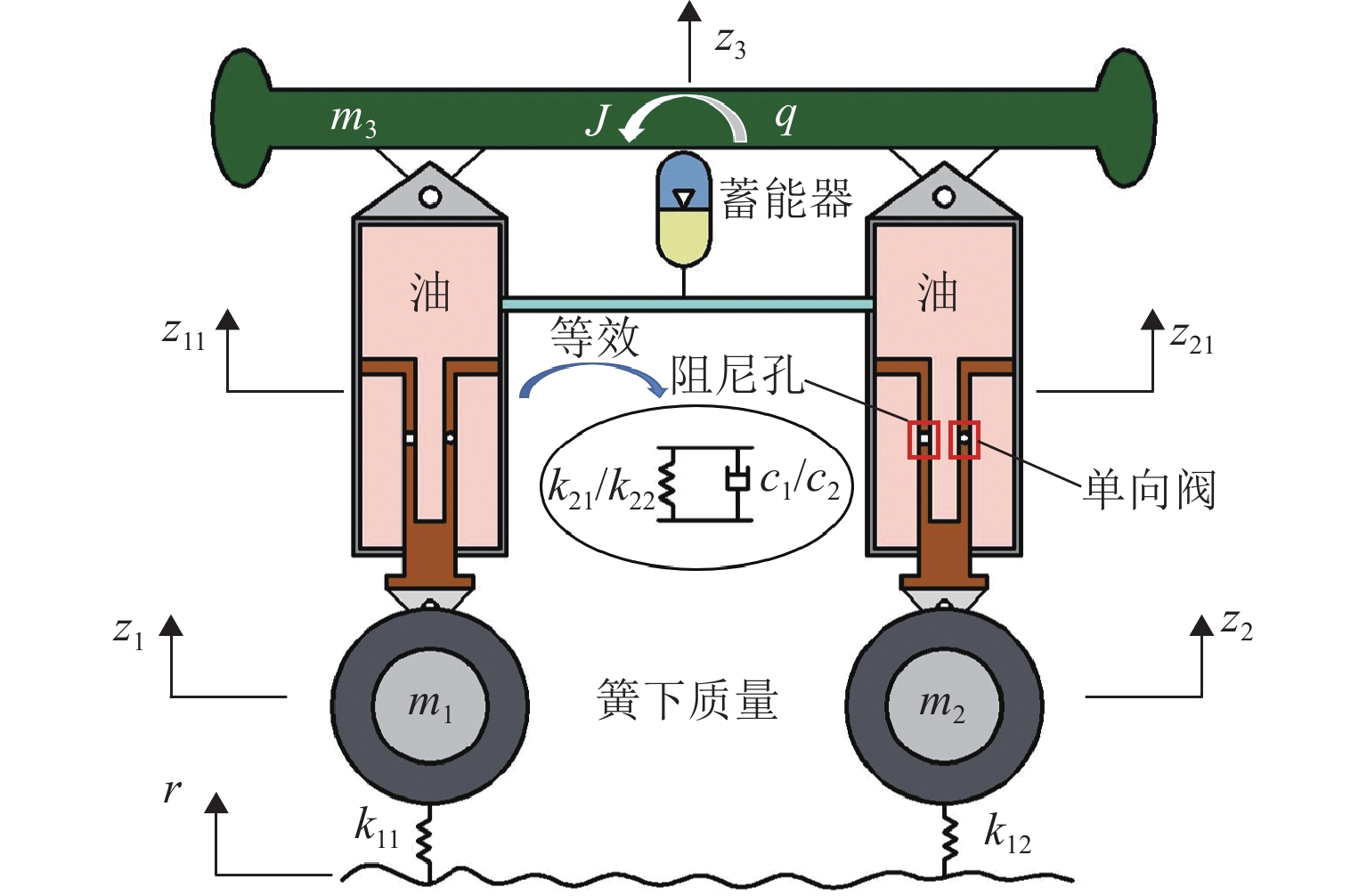
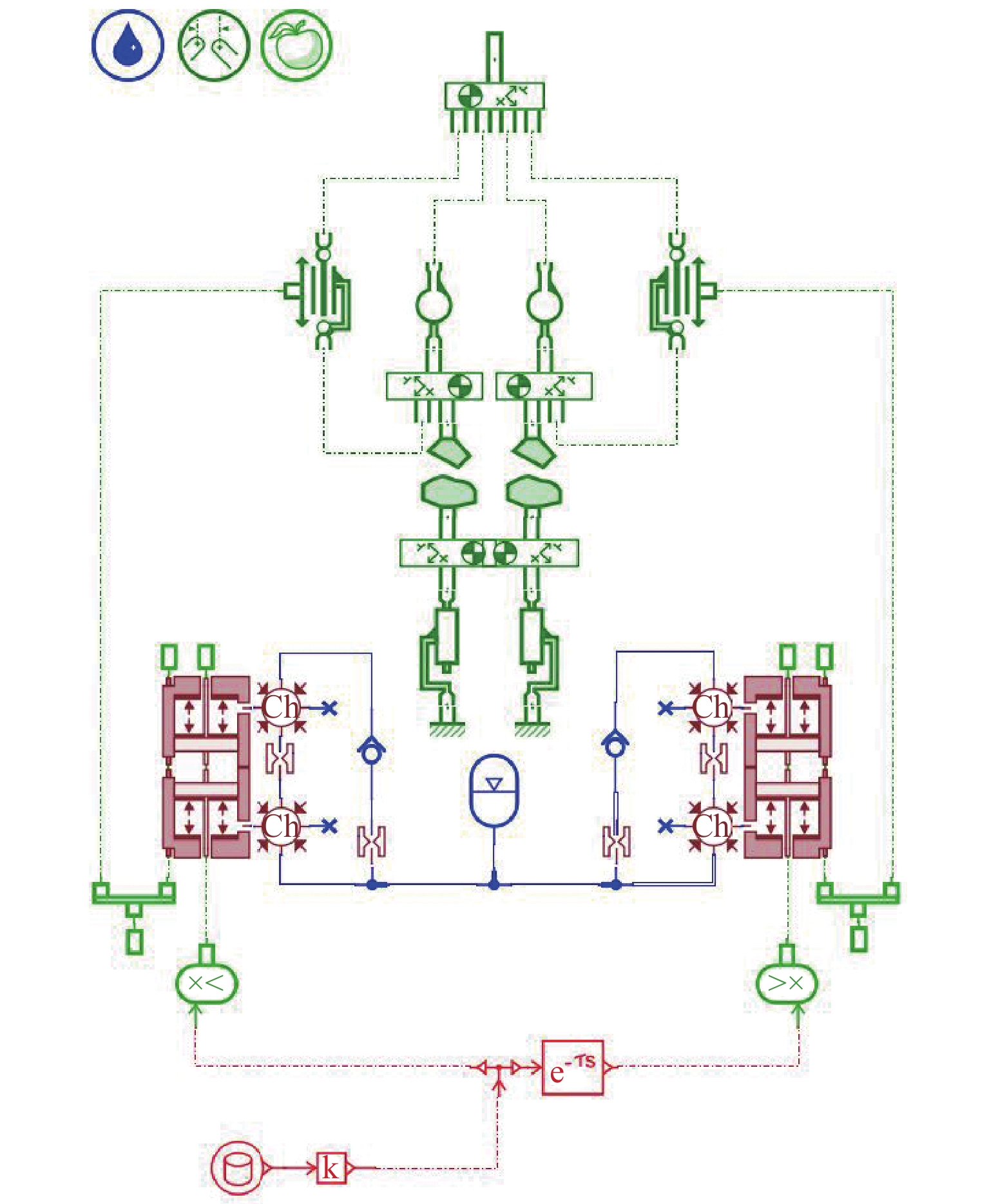
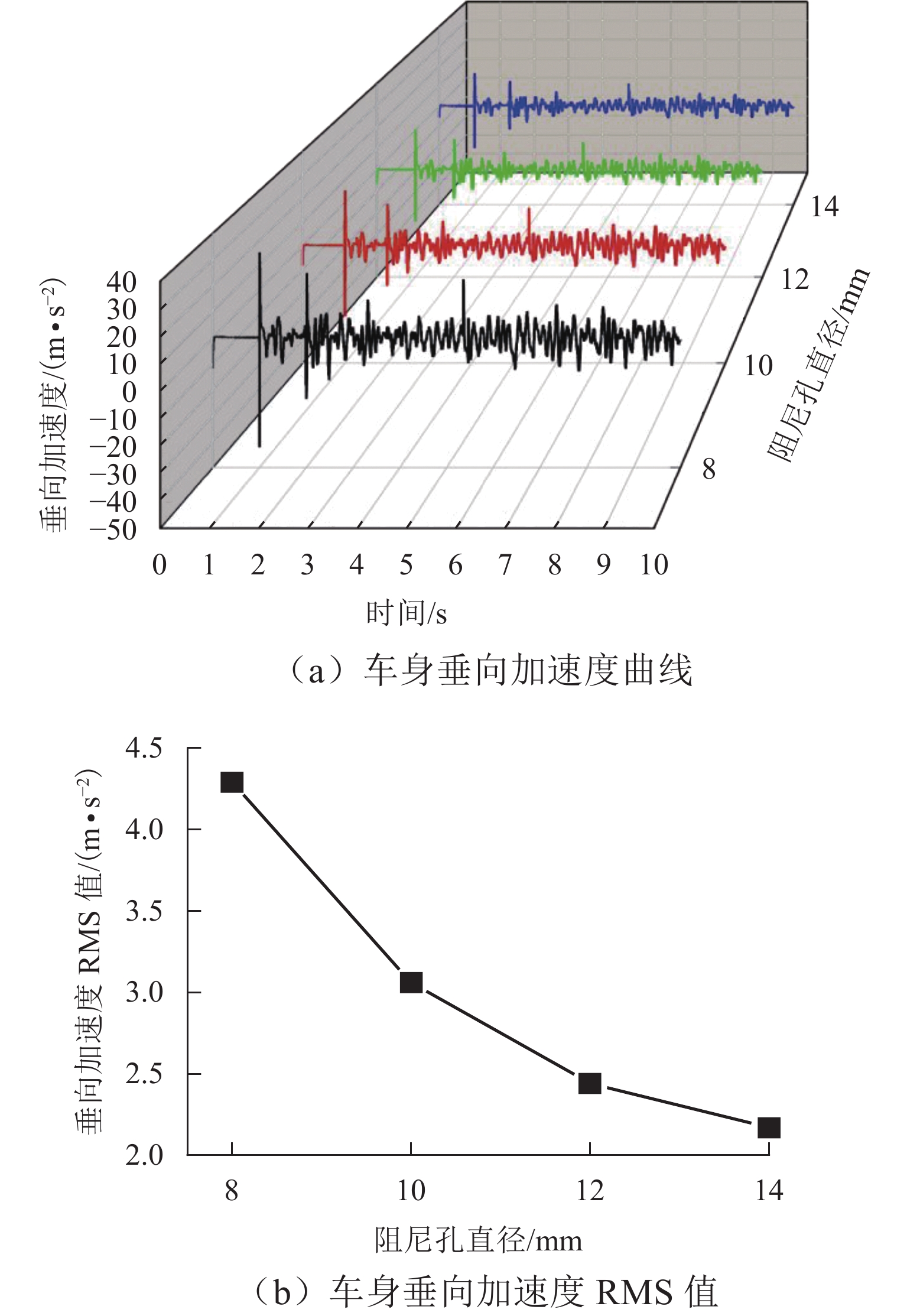
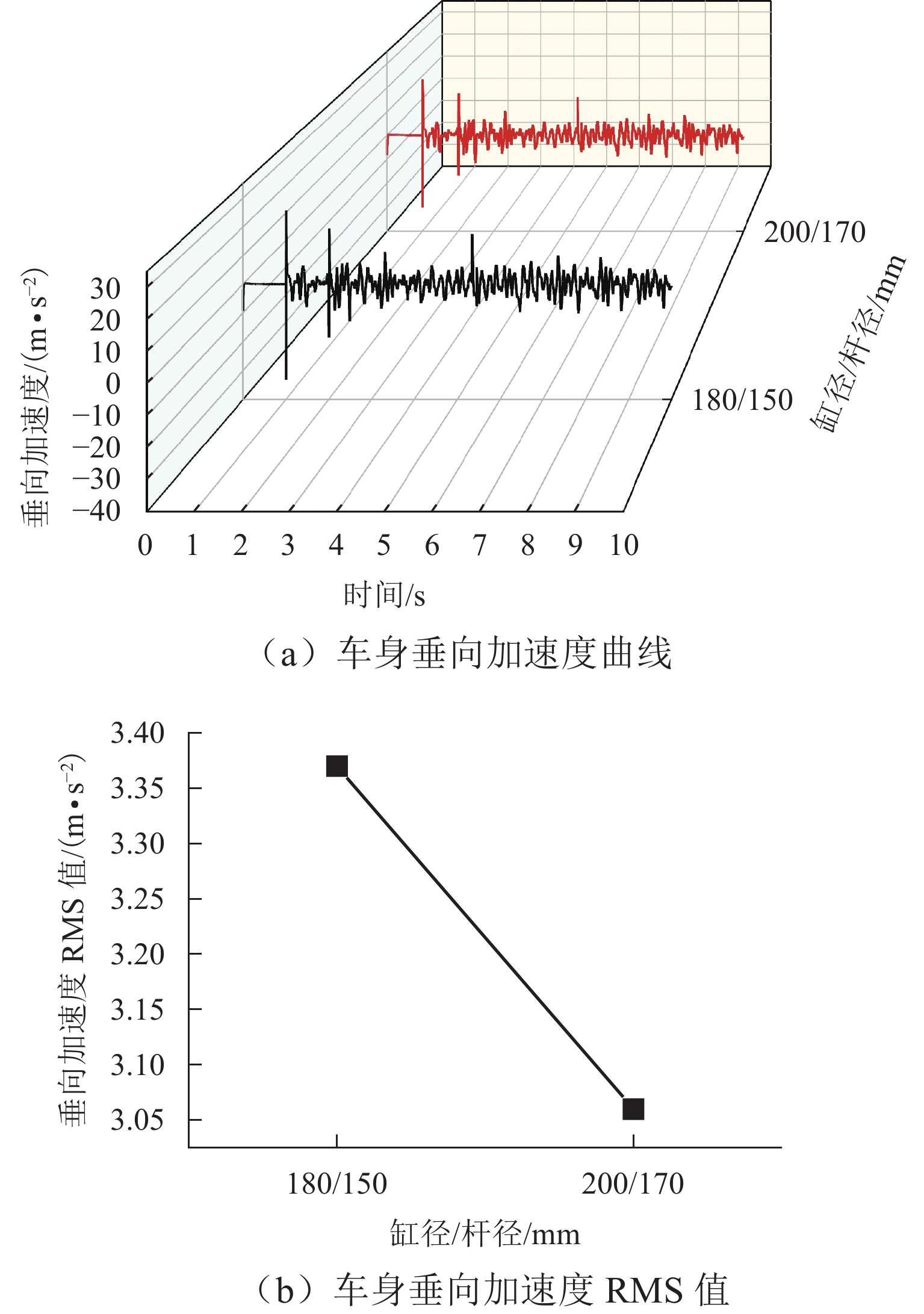
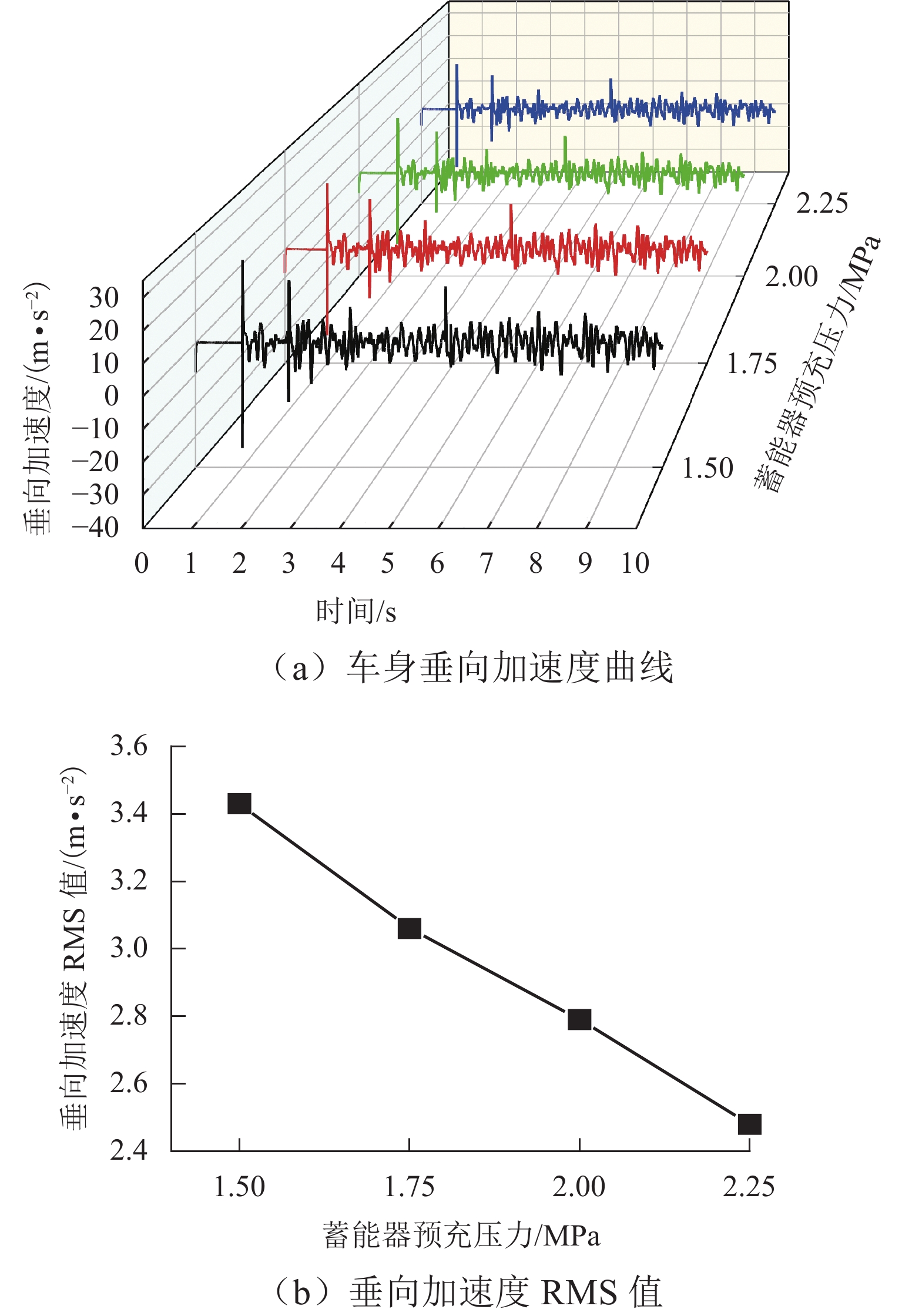
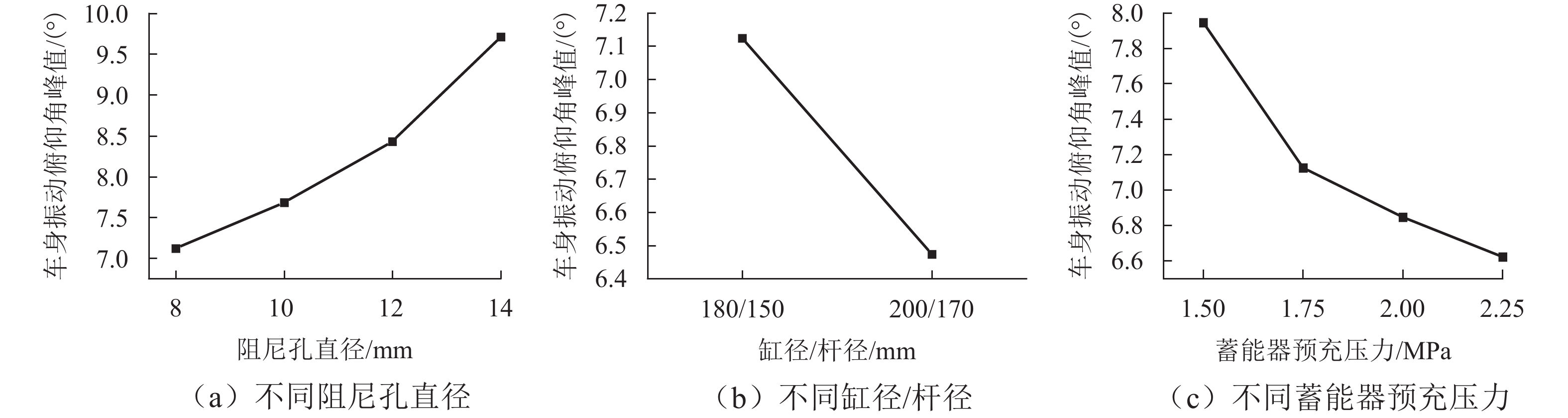
矿用自卸车主要用于小型矿山运输,常在道路条件恶劣、超载严重等工况下工作. 油气悬架因其刚度和阻尼的非线性特性,能较好适应外载荷激励变化,在大型工程车辆中广泛应用. 以徐工生产的XDR80t型矿用自卸车为研究对象,针对采集到的轮胎质心加速度以及车身加速度数据,利用频域积分的方法求解活塞杆相对位移量数据. 采用AMESim仿真平台建立机液联合仿真模型,研究了不同悬架结构参数下车身振动特性的变化趋势. 研究发现:阻尼孔直径对于车身振动状态影响较为明显,当阻尼孔直径由8 mm变化至14 mm时,加速度峰值减小约49.27%,均方根值RMS减少约49.42%,但相应的俯仰角却呈增加趋势;随着缸径/杆径由180/150 mm增加至200/170 mm,加速度峰值和RMS分别降低16.84%与18.62%;当预充压力从1.50 MPa增加至2.25 MPa时,加速度峰值及RMS均方根值分别减小27.67%及27.49%,俯仰角也减小.
-
关键词:
- 矿用自卸车 /
- 油气悬架系统 /
- 频域积分 /
- AMESim仿真平台
Abstract:Mining dump trucks are mainly used for small-scale mine transportation, often run on poor roads or with serious overloading and other conditions. Hydro-pneumatic suspension is widely used in large construction vehicles due to its nonlinear characteristics of stiffness and damping, which can better adapt to external load excitation changes. For the XDR80t mining dump truck produced by XCMG, the acceleration data of the tire center of mass and body were collected, and a method based on frequency domain integral was proposed to obtain the relative displacement data of the piston rod. AMESim simulation platform was used to establish a mechanical and hydraulic co-simulation model, and the variation trend of body vibration characteristics under different structural parameters of suspension was investigated. The results show that the damping hole diameter has a more obvious influence on the vibration state of the body. When the damping hole diameter is changed from 8 mm to 14 mm, the peak value of acceleration is reduced by about 49.27%, and the root mean square (RMS) value is reduced by about 49.42%. However, the pitch angle shows an increasing trend. With the increase in cylinder/rod diameter from 180/150 mm to 200/170 mm, the peak value of acceleration and RMS value decrease by 16.84% and 18.62%. When the pre-charge pressure is increased from 1.5 MPa to 2.25 MPa, the peak value of acceleration and RMS value decrease by 27.67% and 27.49%, and the pitch angle declines.
-
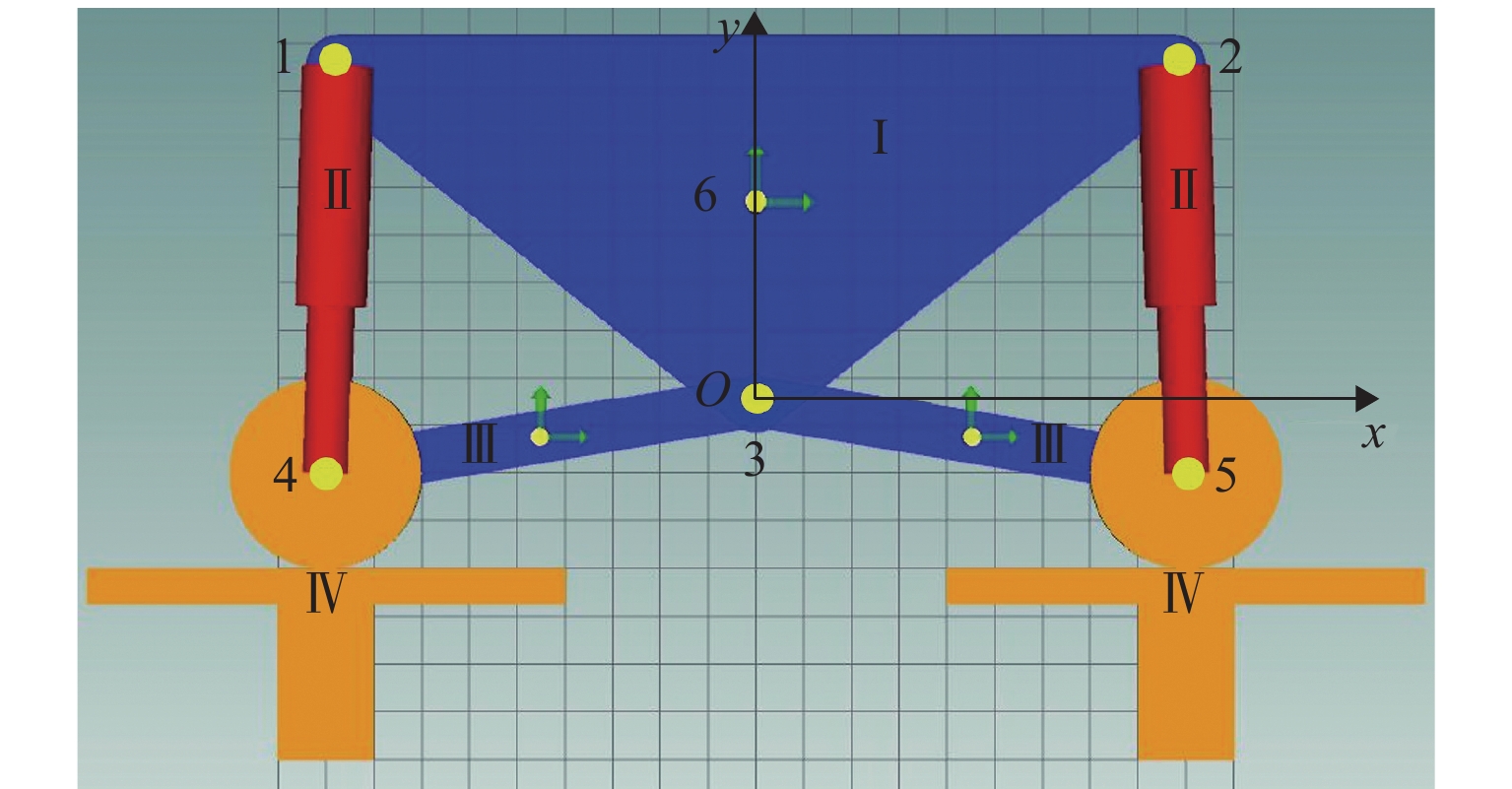
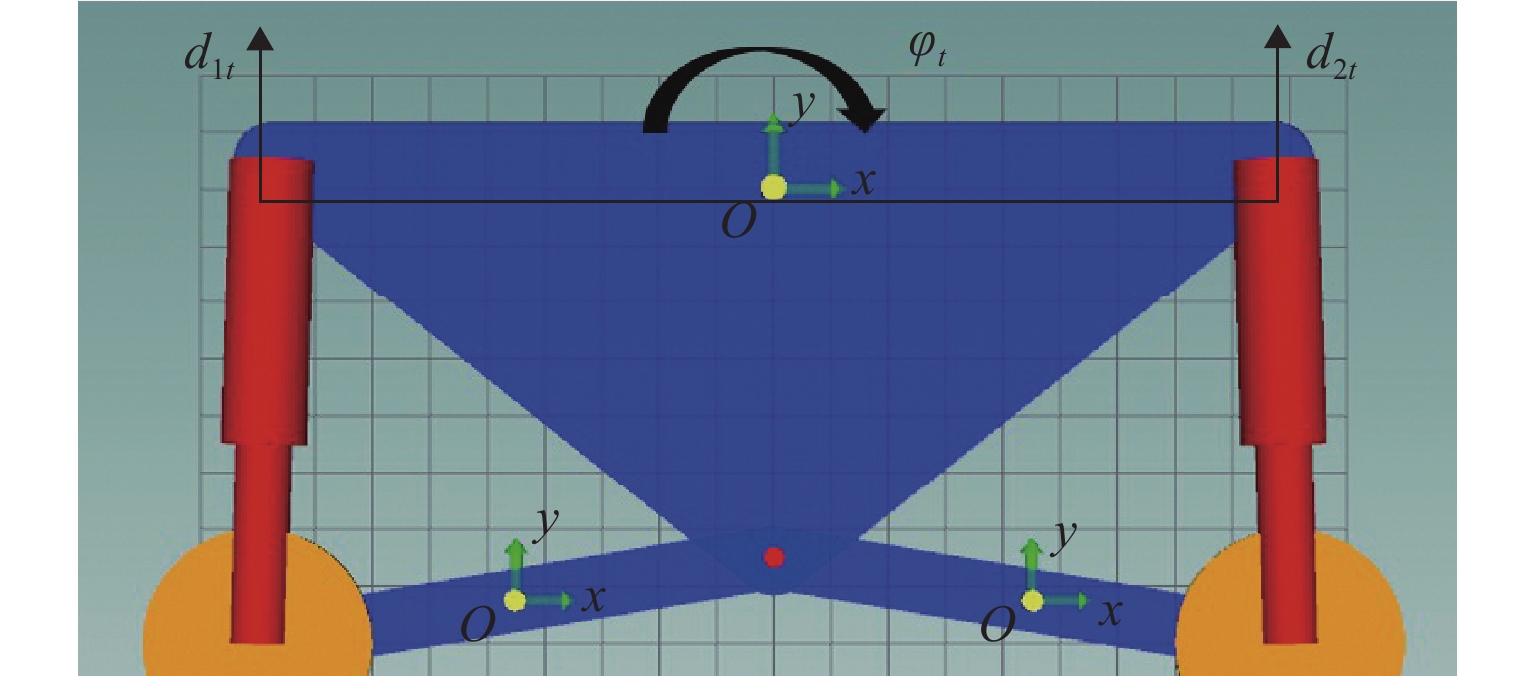
表 1 二维机械模型关键节点坐标
Table 1. Key node coordinates of two-dimensional mechanical model
序号 节点含义 坐标/m 1 中油缸-车架铰接点 (−0.875,0.85) 2 后油缸-车架铰接点 (0.875,0.85) 3 稳定连杆-车架铰接点 (0,0.15) 4 中油缸-稳定连杆铰接点 (−0.9,0) 5 后油缸-稳定连杆铰接点 (0.9,0) 6 车架质心点 (0,0.567) 表 2 油气悬架基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of hydro-pneumatic suspension
变量 取值 无杆腔直径*/mm 180 活塞杆直径*/mm 150 阻尼孔直径*/mm 10 蓄能器预充压力*/MPa 1.75 蓄能器体积/L 3.75 轴距/mm 1750 货物质量/t 15 车身质量/t 10 油液密度/(kg·m−3) 850 -
[1] 陈卫东. 矿用汽车的基本现状和发展趋势[J]. 中国水泥,2004(9): 70-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8321.2004.09.027CHEN Weidong. Basic status and development trend of mining vehicles[J]. China Building Material Equipment, 2004(9): 70-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8321.2004.09.027 [2] 何淼. TLD110矿用自卸车前油气悬架系统研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2018. [3] 刘志强. 基于主动悬架控制的电动汽车平顺性仿真研究[D]. 秦皇岛:燕山大学,2021. [4] BANERJEE S, BALAMURUGAN V, KRISHNAKUMAR R. Ride dynamics mathematical model for a single station representation of tracked vehicle[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2014, 53: 47-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2014.03.003 [5] SHELKE G D, MITRA A C, VARUDE V R. Validation of simulation and analytical model of nonlinear passive vehicle suspension system for quarter car[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(9): 19294-19302. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.288 [6] KONIECZNY Ł. Damping characteristics of hydropneumatic suspension strut in function of car static load[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2015, 17: 74-81. [7] KWON K, SEO M, KIM H, et al. Multi-objective optimisation of hydro-pneumatic suspension with gas–oil emulsion for heavy-duty vehicles[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2020, 58(7): 1146-1165. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2019.1609050 [8] 穆晓东. 55吨全地面起重机油气悬架系统设计与分析[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2015. [9] 张清郁. 基于Simulink单气室油气混合式悬架输出特性分析[J]. 机械设计与制造,2023(11): 140-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2023.11.030ZHANG Qingyu. Output characteristic analysis of the single chamber hydro-pneumatic suspension based on simulink[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2023(11): 140-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2023.11.030 [10] 陶建建. 矿用自卸车悬架系统设计与优化[D]. 长沙:湖南大学,2015. [11] 王靖岳,杨芳,王浩天. 两级压力式油气弹簧的非线性建模及其性能分析[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2020,40(4): 27-31,62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2020.04.005WANG Jingyue, YANG Fang, WANG Haotian. Nonlinear modeling of the double-stage pressure oil-gas spring and its performance analysis[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2020, 40(4): 27-31,62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2020.04.005 [12] SHA L, ZHANG H, CHEN G. Research on dynamic characteristics of oil and gas suspension cylinder[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 493: 012041.1-012041.8. [13] 刘同昊,石运序,曹常贞,等. 不同气室充气容积对油气弹簧动态特性影响分析[J]. 液压与气动,2021,45(9): 82-88. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2021.09.011LIU Tonghao, SHI Yunxu, CAO Changzhen, et al. Analysis of influence of different gas chamber volume on dynamic characteristics of hydro-pneumatic spring[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2021, 45(9): 82-88. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2021.09.011 [14] 陈林山. 基于Simulink油气悬架非线性特性影响因素分析[J]. 机床与液压,2017,45(19): 179-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2017.19.038CHEN Linshan. Analysis on influence factors of nonlinear characteristics of hydro-pneumatic suspension based on simulink[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2017, 45(19): 179-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2017.19.038 [15] 李阁强,崔国庆,毛波,等. 温升对油气悬架刚度的影响[J]. 液压与气动,2021,45(5): 127-131. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2021.05.018LI Geqiang, CUI Guoqing, MAO Bo, et al. Influence of temperature rise on stiffness of hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2021, 45(5): 127-131. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2021.05.018 [16] 王刚锋,刘湘,杜腾,等. 矿用自卸车两级压力式油气悬架特性分析[J]. 液压与气动,2022,46(9): 92-98. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2022.09.012WANG Gangfeng, LIU Xiang, DU Teng, et al. Characteristics analysis of a two-stage pressure hydro-pneumatic suspension for mining dump truck[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2022, 46(9): 92-98. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2022.09.012 [17] 索雪峰,焦生杰,张泽宇,等. 活塞导向长度对油气悬架减振性能的影响[J]. 液压与气动,2022,46(3): 120-127. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2022.03.015SUO Xuefeng, JIAO Shengjie, ZHANG Zeyu, et al. Effect of hydro-pneumatic suspension piston guide length on its vibration reduction performance[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2022, 46(3): 120-127. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2022.03.015 [18] WU W G, ZHANG S, ZHANG Z Y. Mathematical simulations and on-road experimentations of the vibration energy harvesting from mining dump truck hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019: 4814072.1-4814072.15. [19] SHAO X X, DU H P, NAGHDY F. Enhanced vehicle handling and ride through anti-pitch anti-roll hydraulically interconnected suspension[C]//SAE Technical Paper Series. Warrendale: SAE International, 2016, 1: 1561-1568. [20] 杜恒,魏建华. 基于遗传算法的连通式油气悬架平顺性与道路友好性参数优化[J]. 振动与冲击,2011,30(8): 133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.08.026DU Heng, WEI Jianhua. Parameters optimization of interconnected hydro-pneumatic suspension for road comfort and road-friendliness based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(8): 133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.08.026 [21] CAO D P, RAKHEJA S, SU C Y. Handling and braking analyses of a heavy vehicle with a cross-axle fluidically-coupled suspension[J]. SAE International Journal of Commercial Vehicles, 2008, 1(1): 406-415. doi: 10.4271/2008-01-2672 [22] 田玲玲,谷正气,李伟平,等. 非线性油气悬架系统平顺性仿真与参数优化设计[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2011,42(12): 3715-3721.TIAN Lingling, GU Zhengqi, LI Weiping, et al. Ride comfort simulation and parameters optimization design of nonlinear hydro-pneumatic suspension system[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2011, 42(12): 3715-3721. [23] 张德军,聂昕. 某电动车前悬架运动学分析与优化[J]. 汽车实用技术,2023,48(3): 1-4.ZHANG Dejun, NIE Xin. Kinematics analysis and optimization of front suspension of a electric vehicle[J]. Automobile Applied Technology, 2023, 48(3): 1-4. [24] 高荟超. 某战车油气悬架性能分析与优化[D]. 武汉:武汉科技大学,2022. [25] 崔阳文,张明,傅耀宇,等. 应用ISO 2631-1与ISO 2631-5评估某军用越野汽车振动水平[J]. 南京理工大学学报,2022,46(3):344-351.CUI Yangwen,ZHANG Ming,FU Yaoyu,et al. Apply ISO 2631-1 and ISO 2631-5 to evaluate vibration level of military off-road vehicle[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2022, 46(3):344-351. -





 下载:
下载: