Overall Reliability Analysis of Transmission Towers with Asymmetrical Legs Based on Sample Moment and Maximum Entropy Method
-
摘要:
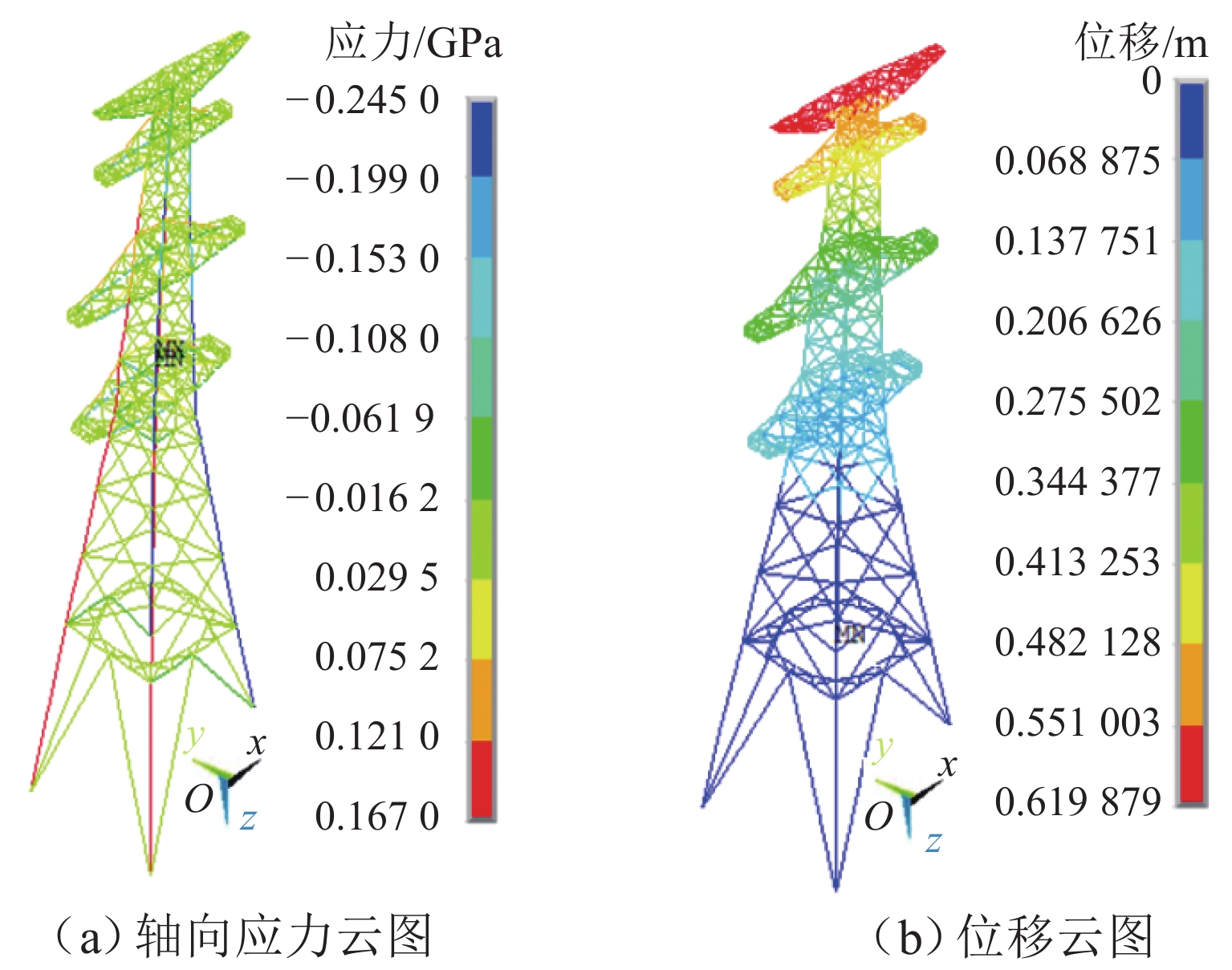
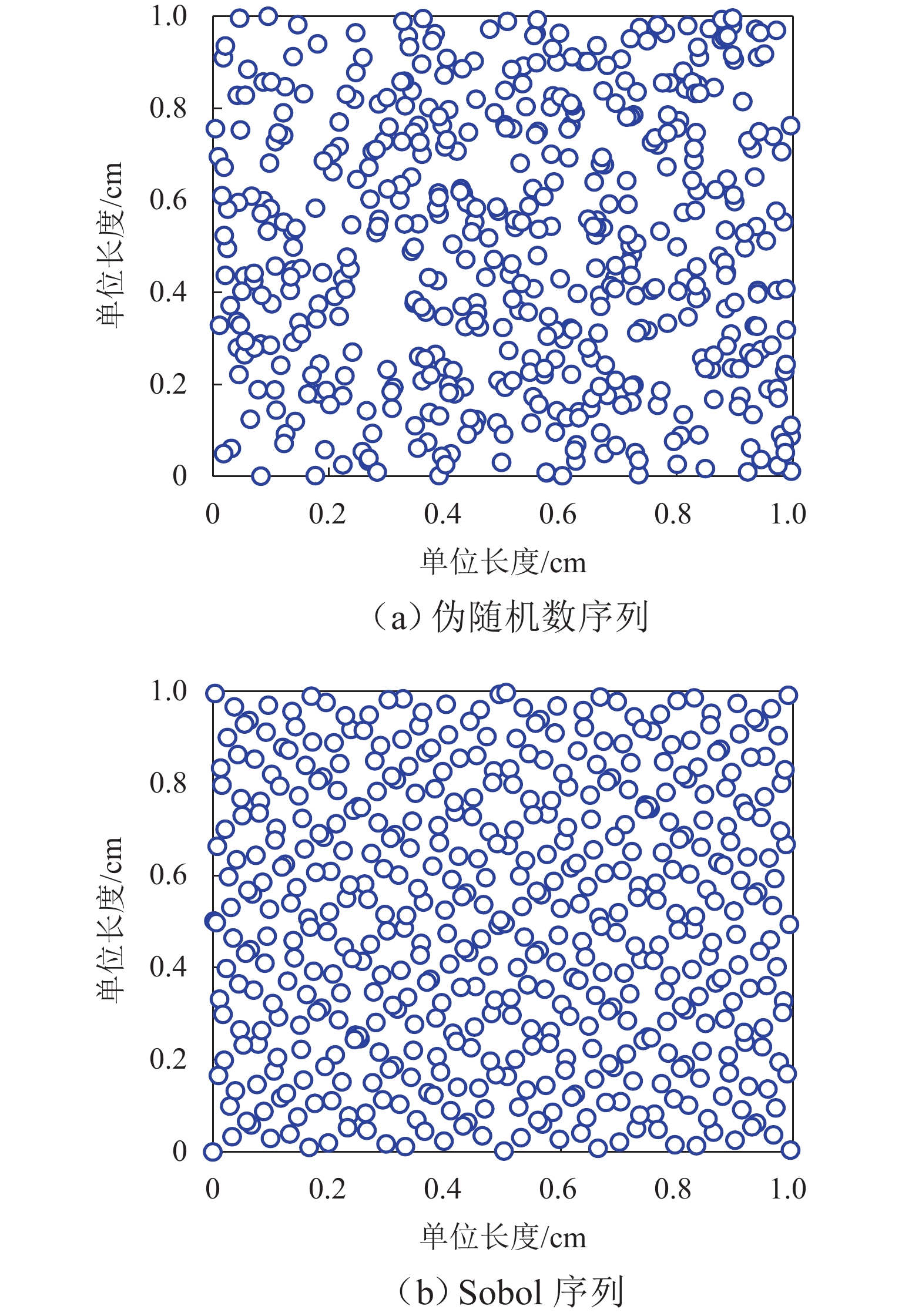
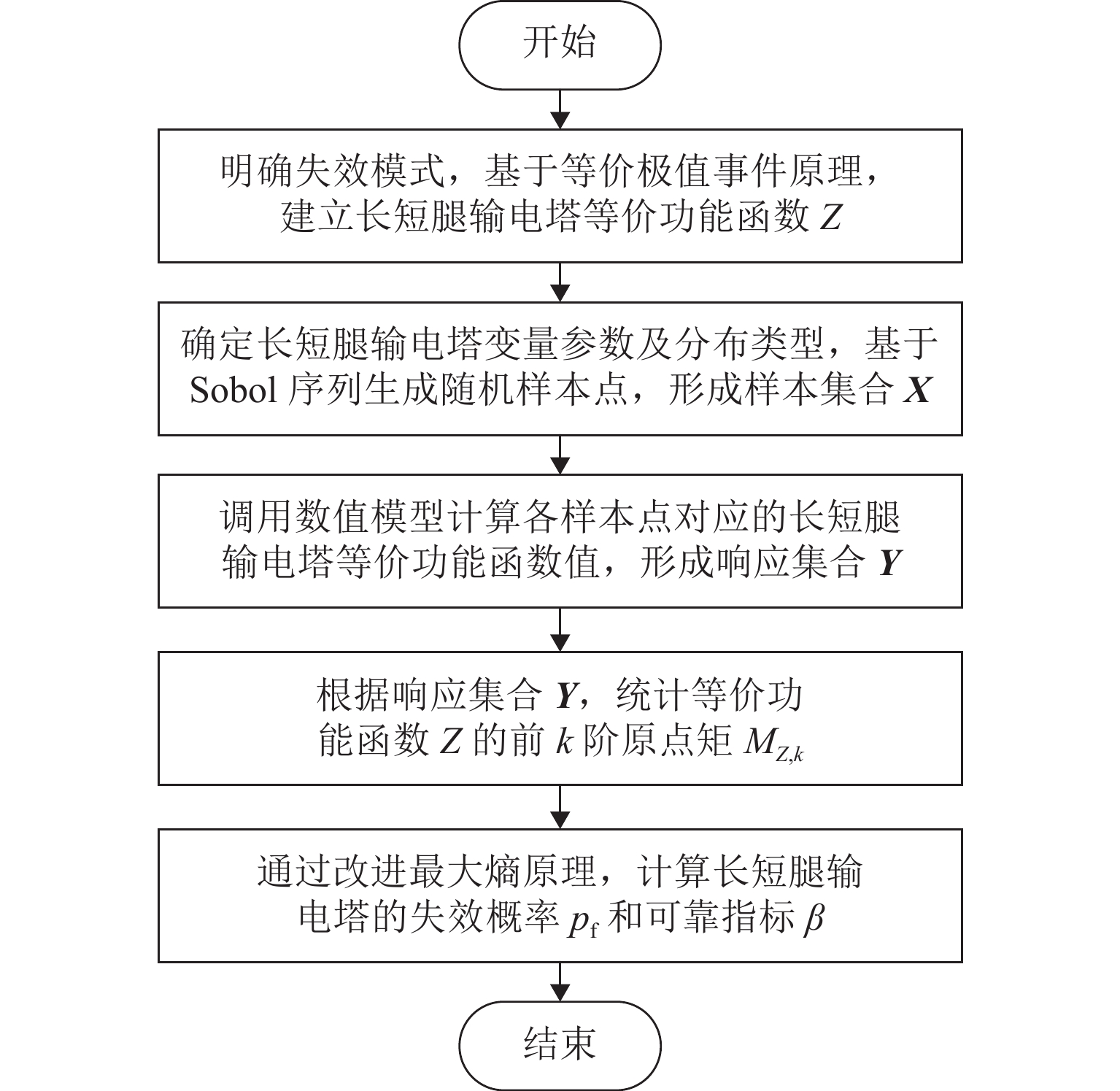
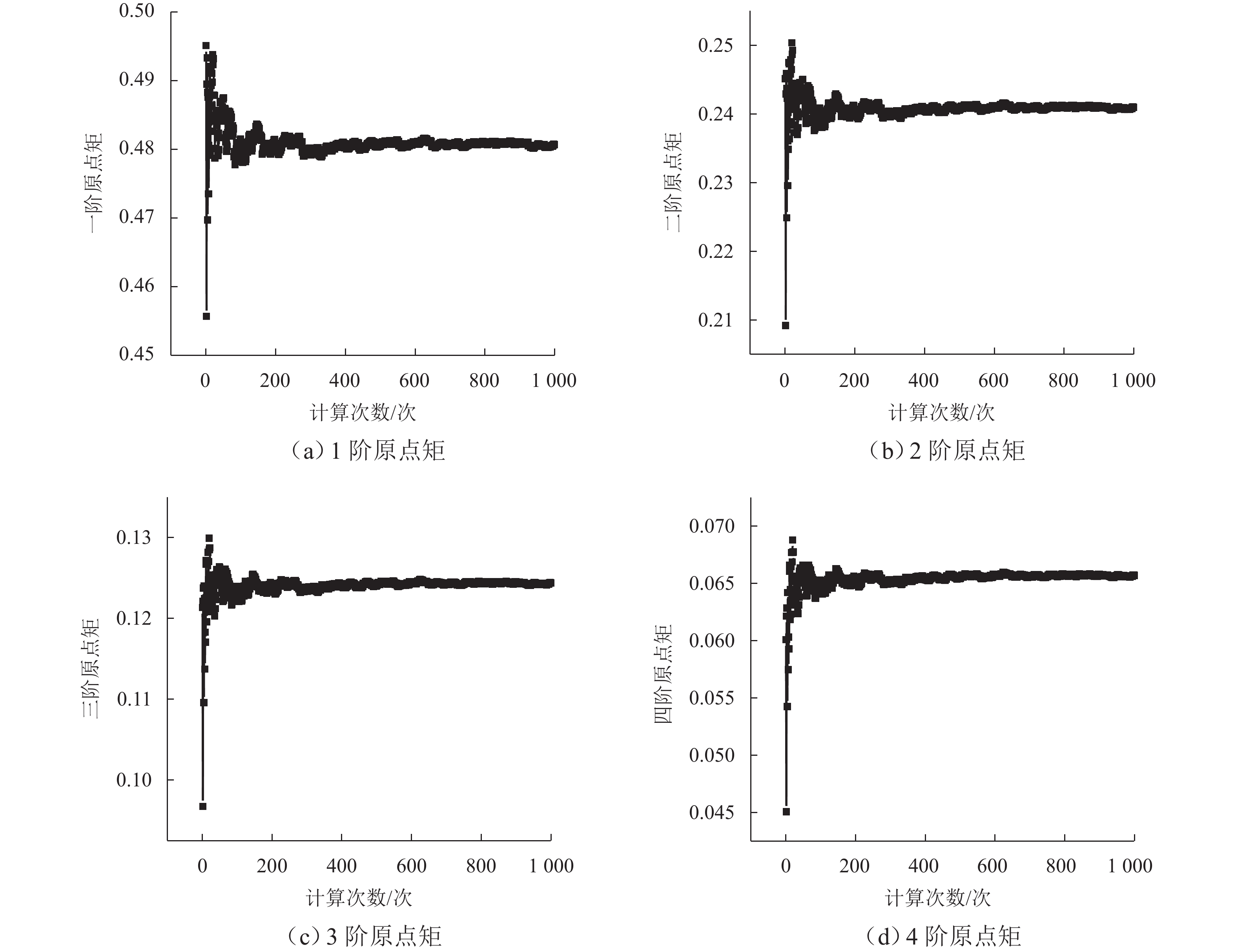
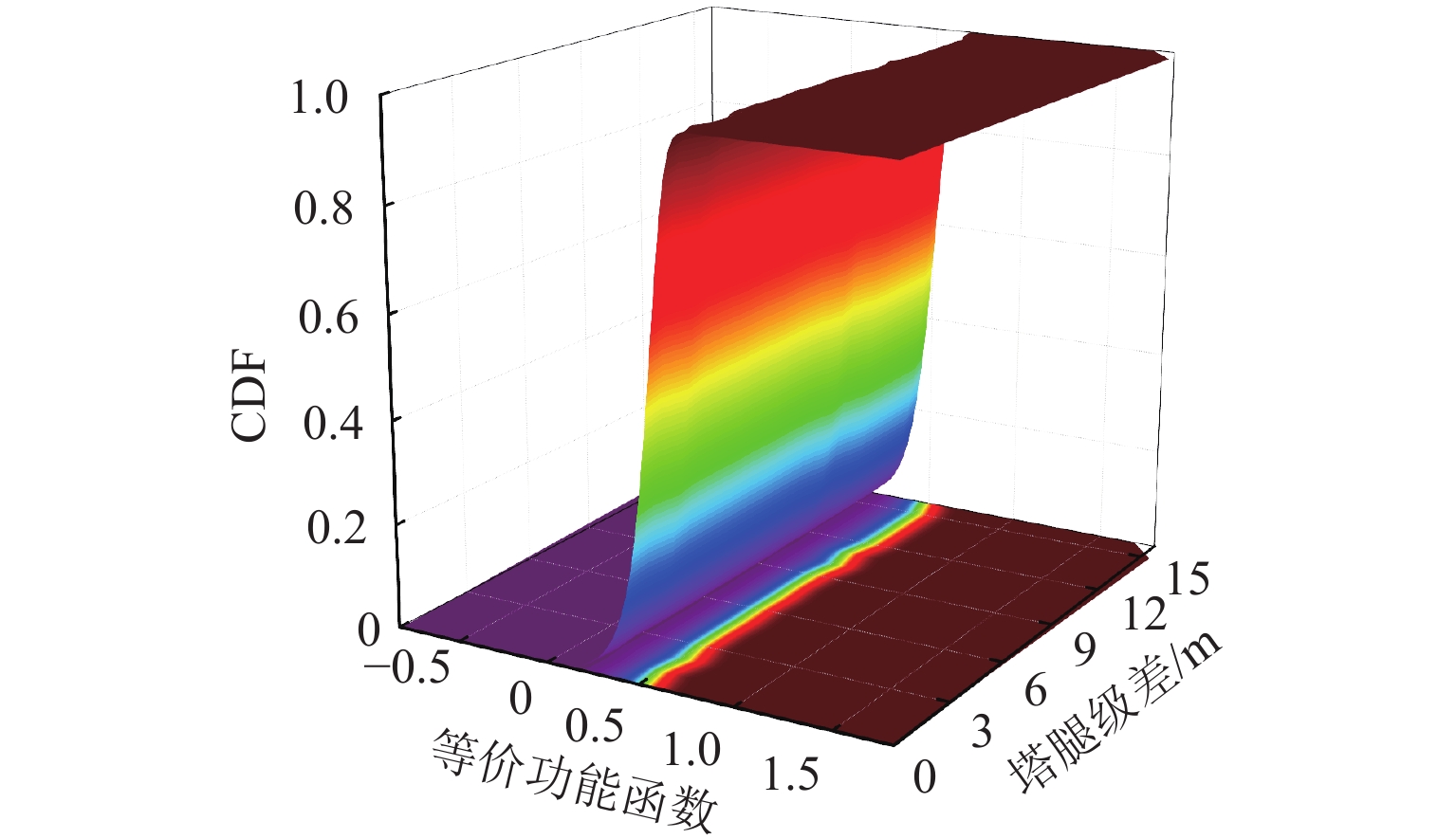
为准确评估长短腿输电塔整体安全水平,依托某500 kV输电线路工程,建立长短腿输电塔精细化数值模型,根据《架空输电线路杆塔结构设计技术规程》(DL/T 5486—2020)以及数值分析结果,给出长短腿输电塔不同失效模式下的功能函数,并结合等价极值事件原理加以等价描述;随后,基于低偏差序列方法生成随机样本点,计算样本响应并获得等价功能函数统计矩;最后,通过改进最大熵法计算长短腿输电塔整体可靠指标. 分析结果表明:本文方法所计算的长短腿输电塔整体可靠指标的相对误差和计算成本分别为Monte Carlo仿真(MCS)法的0.46%和0.05%;单一失效模式下得到的长短腿输电塔可靠指标较整体可靠指标偏低,建议采用整体可靠指标衡量长短腿输电塔的安全水平;塔腿级差和长短腿输电塔整体可靠指标成反比,16 m级差工况下的长短腿输电塔整体可靠指标较等长腿降低了15.72%,设计时应避免级差过大的情况.
Abstract:To accurately assess the overall safety of transmission towers with asymmetrical legs, a refined numerical model for a transmission tower with asymmetrical legs was established based on a 500 kV transmission line project. Based on the
Technical Specification for the Design of Steel Supporting Structures of Overhead Transmission Line (DL/T 5486—2020) and numerical results, functional expressions for different failure modes of the transmission tower with asymmetrical legs were derived, and these were equivalently described using the principle of equivalent extreme value events. Subsequently, random sample points were generated based on the low discrepancy sequence method, and the sample responses were calculated to obtain statistical moments of the equivalent functional expressions. Finally, the overall reliability index of the transmission tower with asymmetrical legs was calculated using the improved maximum entropy method. The results show that the relative error and computational cost of the overall reliability index of the transmission tower with asymmetrical legs obtained by this method are 0.46% and 0.05%, respectively, compared with the Monte Carlo simulation (MCS) method. The reliability index derived from a single failure mode is lower than the overall reliability index of the transmission tower with asymmetrical legs, suggesting that the latter is more accurate for the safety assessment of transmission towers with asymmetrical legs. Moreover, there is an inverse relationship between the difference in tower leg lengths and the overall reliability index of the transmission tower with asymmetrical legs. Specifically, the overall reliability index of a transmission tower with a 16-meter leg length difference is 15.72% lower than that of a transmission tower with equal-length legs. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid excessive leg length differences during the design phase. -
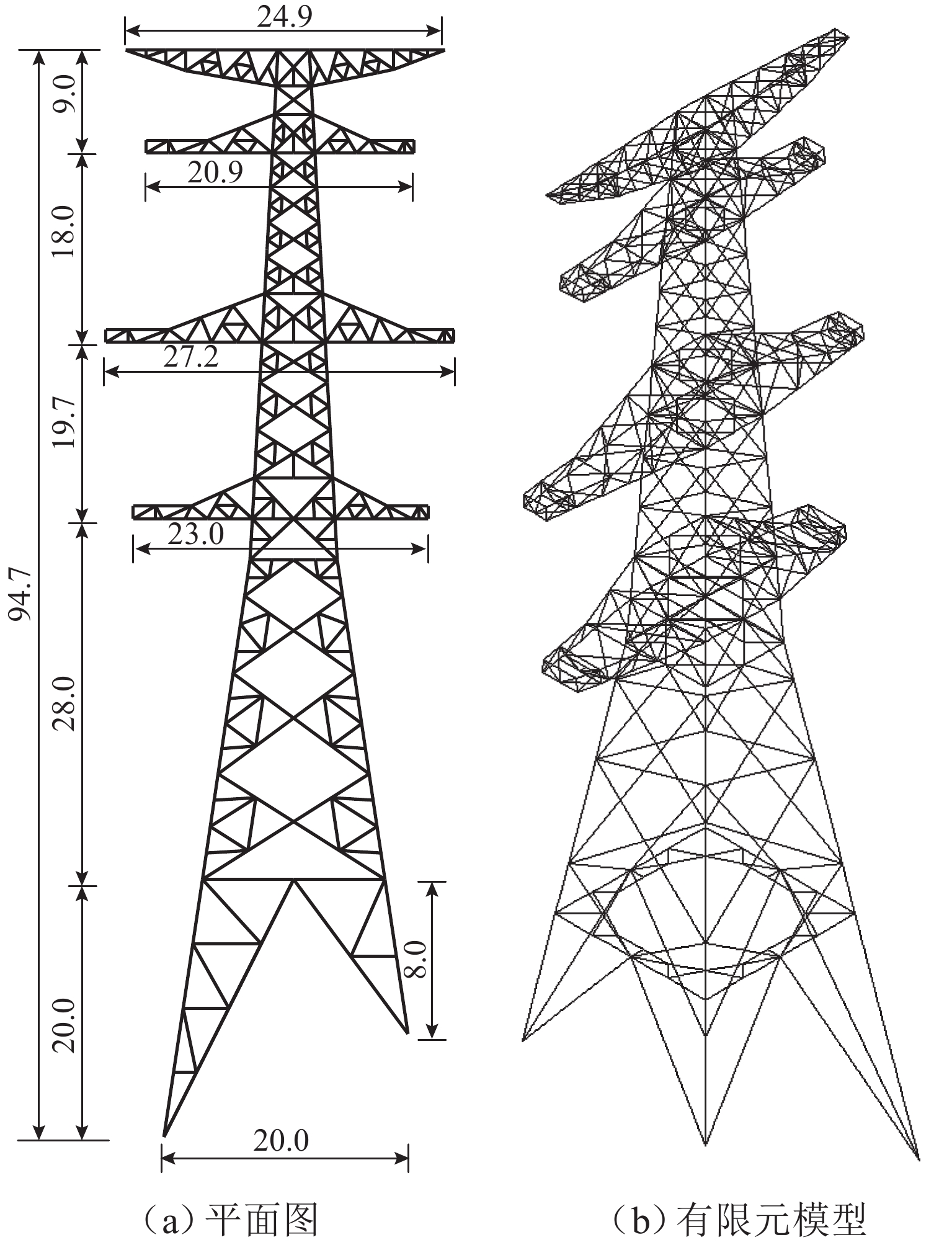
表 1 输电塔设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of transmission tower
设计参数 取值/m 设计参数 取值/m 塔高 94.7 呼高 48 对角半根开 12.3 水平档距 450 垂直档距 700 塔腿级差 12 表 2 材料随机变量及其概率分布参数
Table 2. Random variables of material and their probability distribution parameters
变量 均值 标准差 分布类型 弹性模量/MPa 2.06 × 105 6180 Lognormal 泊松比 0.3 0.009 Lognormal Q235 屈服强度/MPa 263.7 18.46 Lognormal Q355 屈服强度/MPa 387.1 27.10 Lognormal 表 3 整体可靠度计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of overall reliability
计算方法 pf β 分析次
数/次取值 相对误差/% 取值 相对误差/% MCS 法 9.97 × 10−5 3.7198 1×106 本文方法 9.32 × 10−5 6.52 3.7368 0.46 500 表 4 单失效可靠度计算结果
Table 4. Reliability calculation results under single failure mode
计算方法 应力失效 挠度失效 pf pf 相对误差/% β β 相对误差/% pf pf 相对误差/% β β 相对误差/% MCS 法 8.24 × 10−5 3.7678 6.28 × 10−5 3.8349 本文方法 8.94 × 10−5 8.50 3.7471 0.55 5.80 × 10−5 7.64 3.8543 0.51 表 5 不同级差下长短腿输电塔可靠指标
Table 5. Reliability indexes of transmission tower with asymmetrical legs under different leg length differences
塔腿级差/m β pf 变化率/% 0 4.213 1.26 × 10−5 1 4.192 1.38 × 10−5 0.50 2 4.158 1.60 × 10−5 1.30 3 4.124 1.87 × 10−5 2.13 4 4.089 2.16 × 10−5 2.94 5 4.054 2.52 × 10−5 3.78 6 4.028 2.81 × 10−5 4.39 7 3.996 3.22 × 10−5 5.16 8 3.974 3.53 × 10−5 5.67 9 3.943 4.02 × 10−5 6.41 10 3.913 4.56 × 10−5 7.13 11 3.872 5.41 × 10−5 8.11 12 3.810 6.96 × 10−5 9.58 13 3.737 9.32 × 10−5 11.31 14 3.680 1.17 × 10−4 12.65 15 3.625 1.44 × 10−4 13.95 16 3.551 1.92 × 10−4 15.72 注:级差为 0 表示等长腿. -
[1] 雷旭, 付兴, 肖凯, 等. 强风作用下输电塔结构不确定性倒塌分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(增1): 266-274.LEI Xu, FU Xing, XIAO Kai, et al. Failure analysis of a transmission tower subjected to wind load using uncertainty method[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(S1): 266-274. [2] 陈波, 李鹏, 乔婉风, 等. 小根开细柔输电杆塔抗风可靠性研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2020, 42(5): 58-62.CHEN Bo, LI Peng, QIAO Wanfeng, et al. Research on wind-resistant reliability of slender transmission tower with a small root span[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2020, 42(5): 58-62. [3] 鄢秀庆, 何松洋, 李正良, 等. 输电塔斜材不同节点型式下的受压承载力[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(3): 712-719. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220573YAN Xiuqing, HE Songyang, LI Zhengliang, et al. Compression bearing capacity of inclined members of transmission tower with different joint types[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(3): 712-719. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220573 [4] 刘树堂, 康丽萍. 长短腿耐张输电铁塔的静力及自振特性分析[J]. 广东电力, 2007, 20(10): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-290X.2007.10.006LIU Shutang, KANG Liping. Static and self-vibration characteristic analysis of strain towers with unequal legs[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2007, 20(10): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-290X.2007.10.006 [5] 王磊, 王涛, 李正良, 等. 考虑土-结构相互作用的输电塔-线耦合系统抗风整体可靠度分析[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024: 1-11. (2024-07-05). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20240704.1536.008.html.WANG Lei, WANG Tao, LI Zhengliang, et al. Overall reliability analysis of wind resistance of transmission tower-line coupling system considering soil-structure interaction[J/OL]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024: 1-11. (2024-07-05). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20240704.1536.008.html. [6] 贾玉琢, 汤彪. 长短腿输电塔的风振响应分析[J]. 工业建筑, 2010, 40(增1): 413-416, 426.JIA Yuzhuo, TANG Biao. Analysis of wind-induced dynamic response of electric transmission towers with unequal legs[J]. Industrial Construction, 2010, 40(S1): 413-416, 426. [7] SZAFRAN J, RYKALUK K. A full-scale experiment of a lattice telecommunication tower under breaking load[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 120: 160-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.01.006 [8] CHEN C C, SIAO S Y, JIANG C R, et al. Structural effects of unequal leg lengths in lattice steel towers with the D-type bracing system[J]. Structures, 2021, 34: 2801-2817. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2021.09.036 [9] 刘鸣, 孟梅, 张连法, 等. 覆冰条件下山区长短腿钢管输电塔的动力特性分析[C]//《工业建筑》2018年全国学术年会论文集(中册). 北京: [s.n.], 2018: 161-164. [10] 赵瑜, 张晓燕, 靳彩. 长短腿输电线路铁塔的优化分析[J]. 华北水利水电学院学报, 2004, 25(2): 22-25.ZHAO Yu, ZHANG Xiaoyan, JIN Cai. The optimization design of unequal legs transmission tower[J]. Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power, 2004, 25(2): 22-25. [11] 熊铁华, 侯建国, 安旭文, 等. 覆冰荷载下输电铁塔体系可靠度研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2010, 43(10): 8-13.XIONG Tiehua, HOU Jianguo, AN Xuwen, et al. System reliability of a transmission tower under ice load[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2010, 43(10): 8-13. [12] 李悦, 谢强, 张欣, 等. 强风作用下输电塔线体系连续性倒塌分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2024, 59(2): 423-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220619LI Yue, XIE Qiang, ZHANG Xin, et al. Cascading failure analysis of transmission tower–line system under strong wind[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(2): 423-430. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220619 [13] 姚瑶, 王凌旭, 张有佳. 高压输电塔主材的角钢并联加固轴压承载力[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2020, 55(3): 561-569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190370YAO Yao, WANG Lingxu, ZHANG Youjia. Axial bearing capacity of angle parallel reinforcement for high voltage transmission towers[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(3): 561-569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190370 [14] LI J, CHEN J B, FAN W L. The equivalent extreme-value event and evaluation of the structural system reliability[J]. Structural Safety, 2007, 29(2): 112-131. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2006.03.002 [15] DER KIUREGHIAN A, DAKESSIAN T. Multiple design points in first and second-order reliability[J]. Structural Safety, 1998, 20(1): 37-49. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4730(97)00026-X [16] HE J, GAO S B, GONG J H. A sparse grid stochastic collocation method for structural reliability analysis[J]. Structural Safety, 2014, 51: 29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2014.06.003 [17] 张文生, 罗强, 蒋良潍, 等. 小样本岩土参数下考虑矩估计偏差的土质边坡可靠度分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(1): 315-324.ZHANG Wensheng, LUO Qiang, JIANG Liangwei, et al. Reliability analysis of soil slope considering moment estimation bias using small sample geotechnical parameters[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 315-324. [18] WANG T, LI Z L, FAN W L, et al. Structural system reliability assessment using generalized factorized dimensional reduction method and iterative maximum entropy method[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2024, 20(5): 607-618. doi: 10.1080/15732479.2022.2119582 [19] 国家能源局. 架空输电线路荷载规范: DL/T 5551—2018[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019. [20] 国家能源局. 架空输电线路杆塔结构设计技术规程: DL/T 5486—2020[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2020. [21] 住房和城乡建设部. 建筑结构可靠性设计统一标准: GB 50068—2018[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018 [22] 孔伟, 刘玉龙. 输电塔在大风覆冰下的可靠度分析[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2015, 37(4): 59-64.KONG Wei, LIU Yulong. Reliability analysis of transmission tower under wind and ice cover[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2015, 37(4): 59-64. [23] SOBOL I M. On the distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals[J]. USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 1967, 7(4): 86-112. doi: 10.1016/0041-5553(67)90144-9 [24] RAJAN A, KUANG Y C, OOI M P, et al. Moment-constrained maximum entropy method for expanded uncertainty evaluation[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 4072-4082. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2787736 [25] 欧进萍, 段宇博, 叶骏. 等效随机静风荷载的模型及其参数确定[J]. 哈尔滨建筑工程学院学报, 1994(2): 1-8.OU Jinping, DUAN Yubo, YE Jun. A random equivalent static wind load model and its parameter determination[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 1994(2): 1-8. -




 下载:
下载: