Vehicle to Grid Optimization Strategy from the Perspective of Supply and Demand Game
-
摘要:
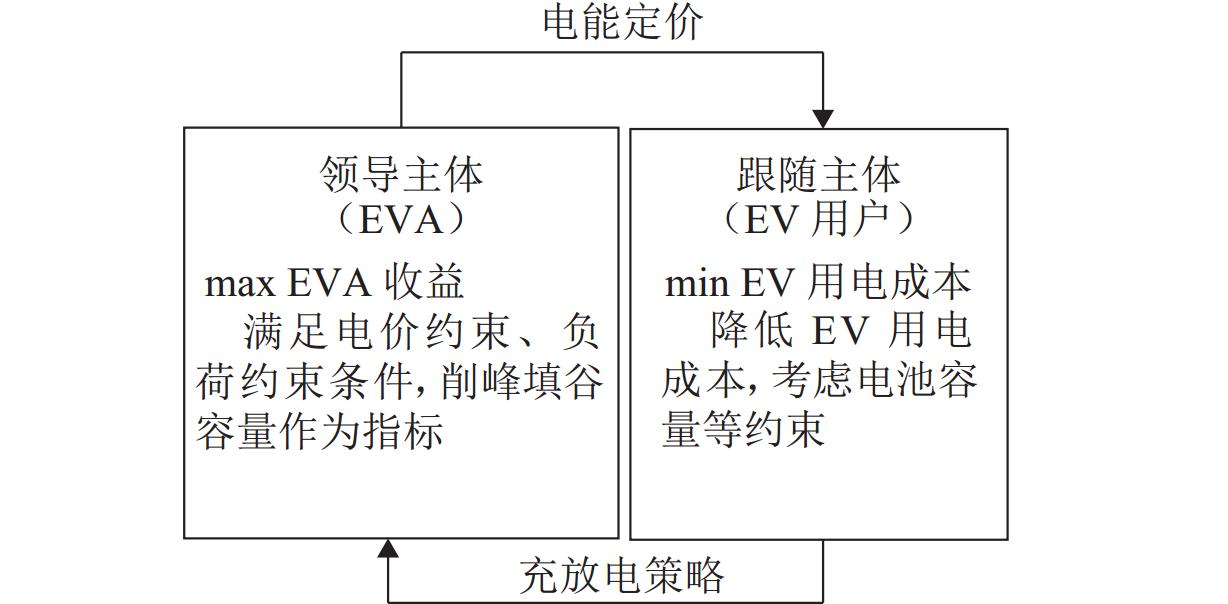
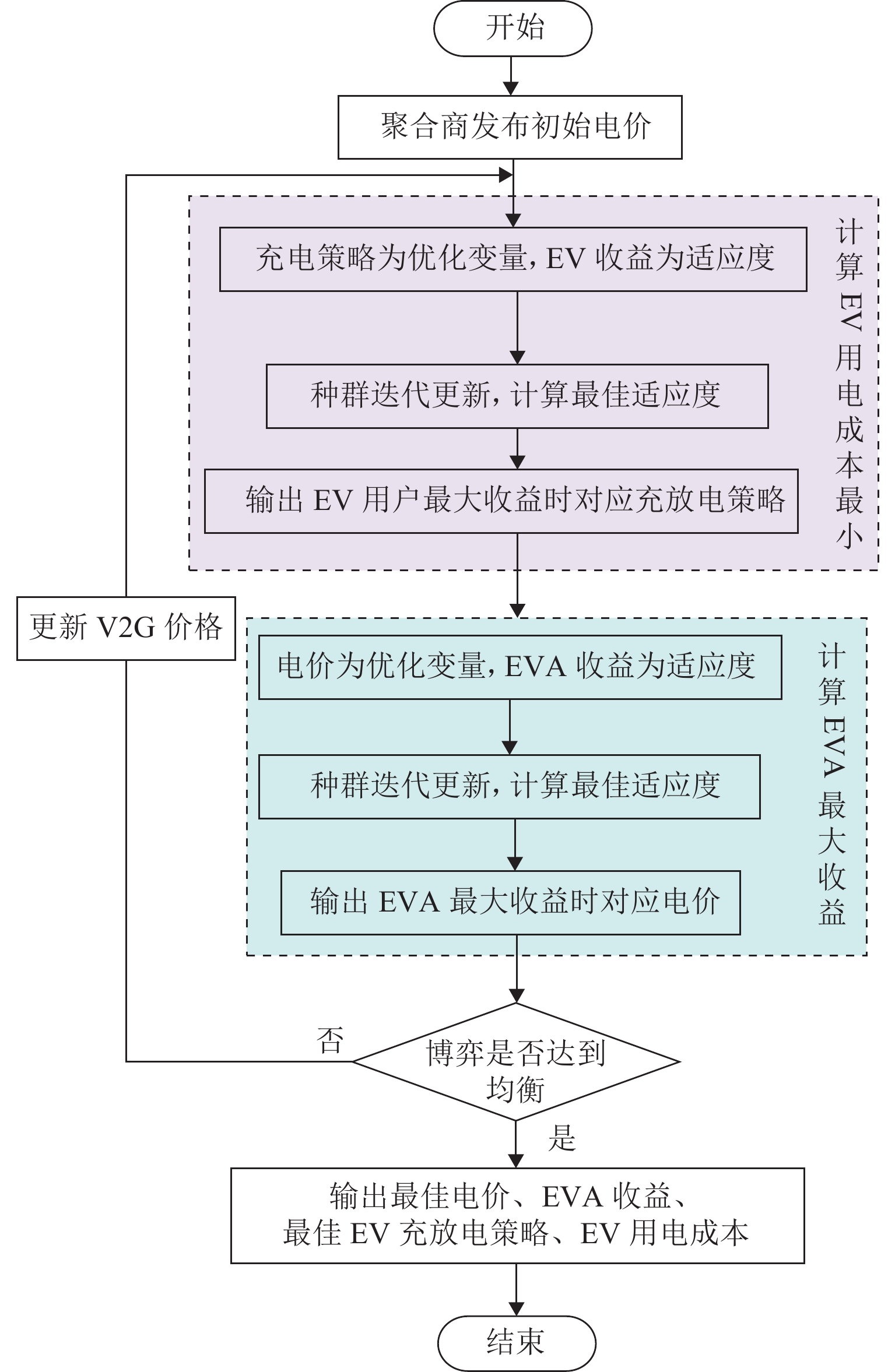
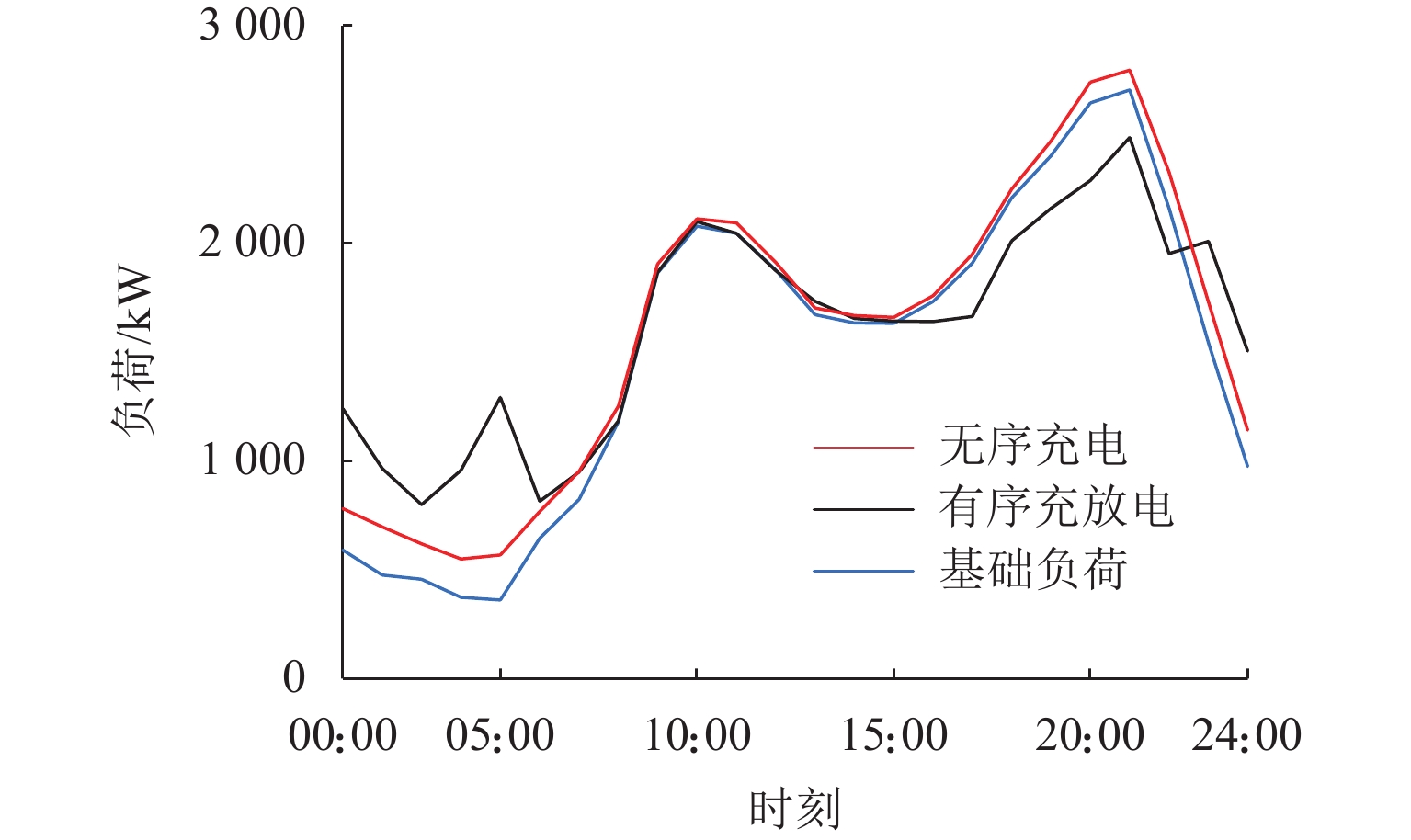
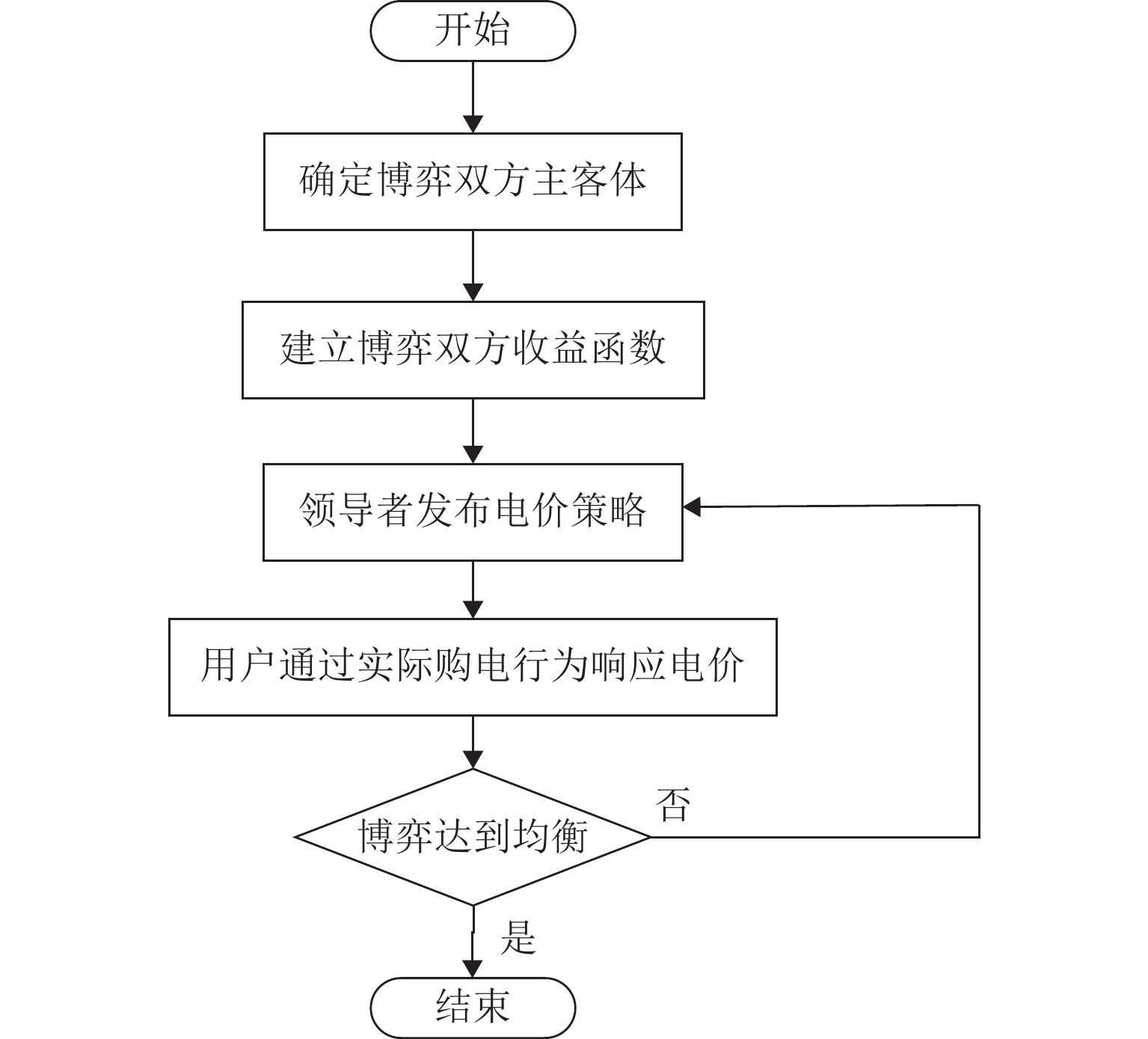
随着电动汽车爆发式发展,充电负荷的冲击性与电网支撑能力的矛盾突出. 为此,提出一种基于供需双方博弈视角的电动汽车充放电(vehicle to grid,V2G)优化策略. 首先,结合用户充放电行为特性,构建使电动汽车充放电与基础负荷互洽的电能价格分享机制;然后,针对聚合商电能定价与电动汽车用户充放电行为选择过程中的领导-追随者博弈关系,建立优化模型,领导者层面以聚合商收益最大化为目标,追随者层面以电动汽车用户用电成本最小化为目标;最后,利用搜寻者优化算法分别求解双方的优化目标,进行博弈循环直到均衡,从而得到最优的电能定价策略和电动汽车充放电策略. 仿真结果表明:所提出的充放电策略能使电动汽车充放电负荷对基础负荷曲线起到削峰填谷作用,使基础负荷曲线方差减小56.6%,峰谷差减少28.0%,同时,电动汽车用户的充放电成本减少40.4%,而聚合商收益增加约40.1%.
Abstract:With the explosive development of electric vehicles (EV), the contradiction between the impact of charging load and grid support capacity is highlighted. In response to this problem, an EV charging and discharging (vehicle to grid, V2G) optimization strategy was proposed from the perspective of the game between supply and demand. Firstly, a power price sharing mechanism was constructed to make EV charging and discharging mutually appropriate with base load by combining the characteristics of EV charging and discharging behaviors. Then, for the leader-follower game relationship between the aggregator’s pricing of electricity and the EV users’ charging and discharging behavior selection process, an optimization model was established, whose optimization objectives are maximizing the revenue of the aggregator on the leader level and minimizing the cost of electricity for EV users on the follower level. Finally, the seeker optimization algorithm was used to solve the optimization objectives of both sides separately, and the game cycle was carried out until the equilibrium, so that the optimal electricity pricing strategy and EV charging/discharging strategy were obtained. The simulation results show that the proposed charging and discharging strategy can realize the peak-cutting and valley-filling of the base load curve by the EV charging and discharging load. The variance of the base load curve is reduced by 56.6%, and the difference between peak and valley is decreased by 28.0%. Meanwhile, the charging and discharging cost of EV users is lowered by 40.4%, and the revenue of the aggregator is increased by 40.1%.
-
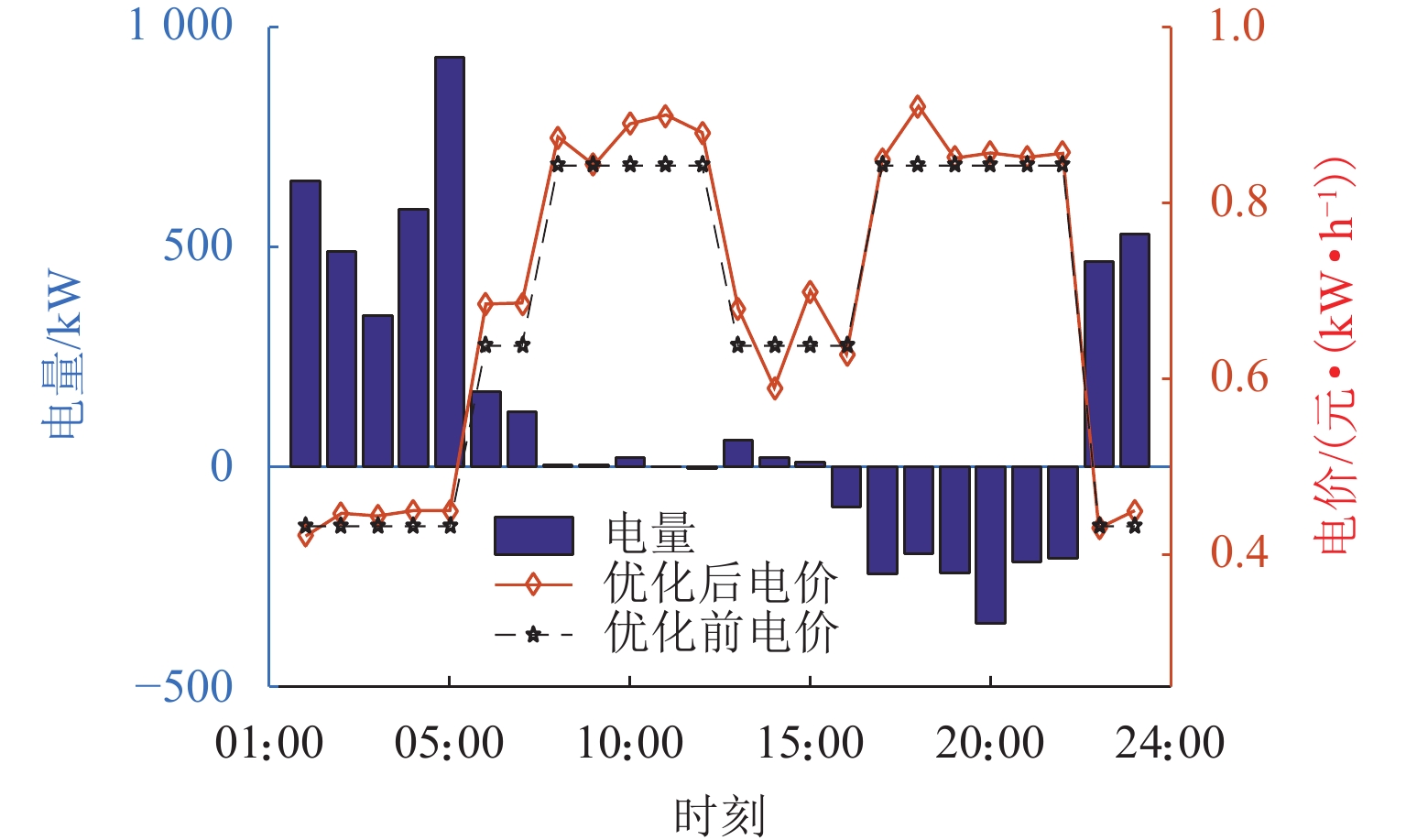
表 1 四川省某充电站分时电价
Table 1. Time-of-use tariff at a charging station in Sichuan Province
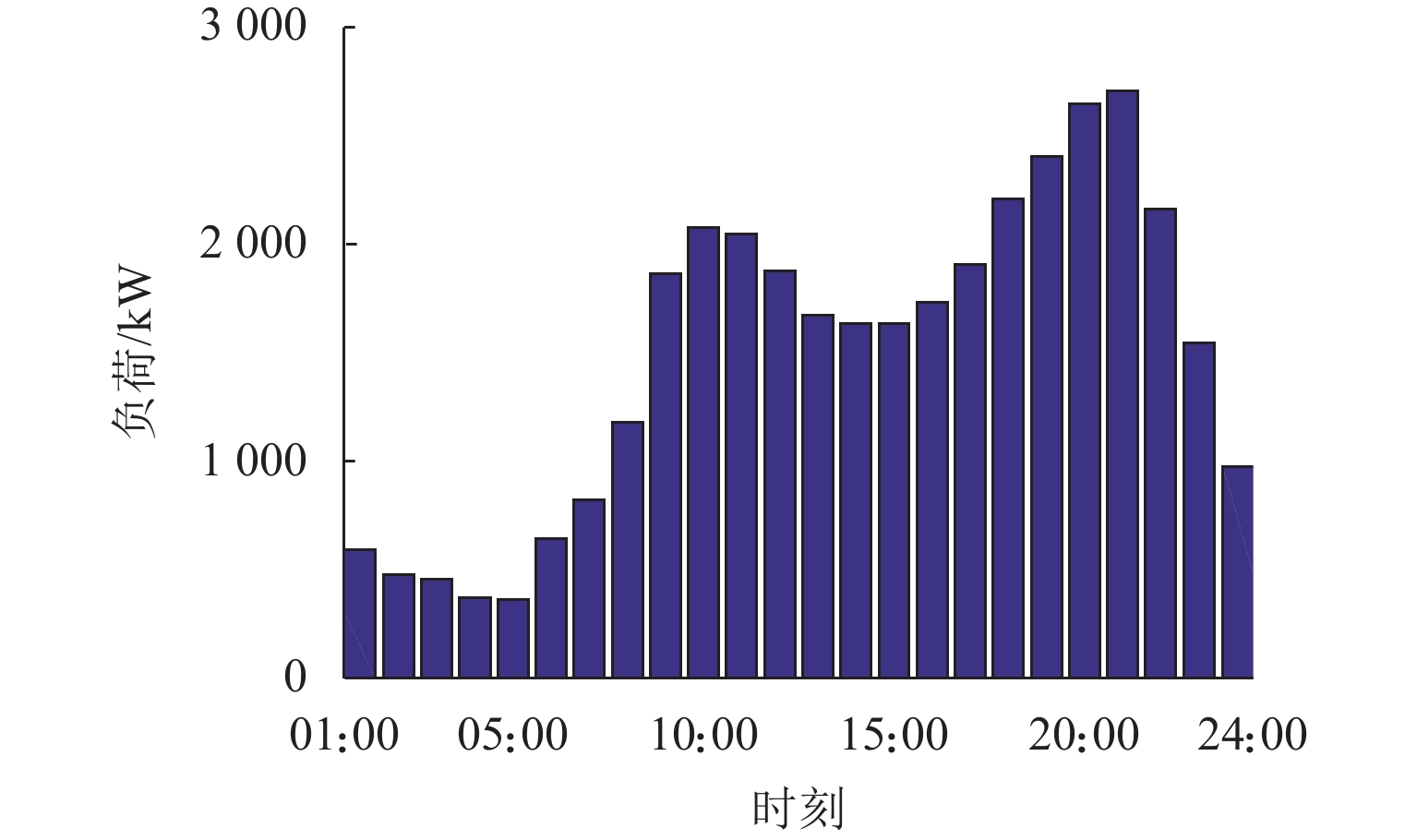
时段 电价/(元·(kW·h)−1) T1 0.84252 T2 0.63740 T3 0.42228 表 2 充放电优化与无序充电定量对比
Table 2. Quantitative comparison of charging and discharging optimization with disorderly charging
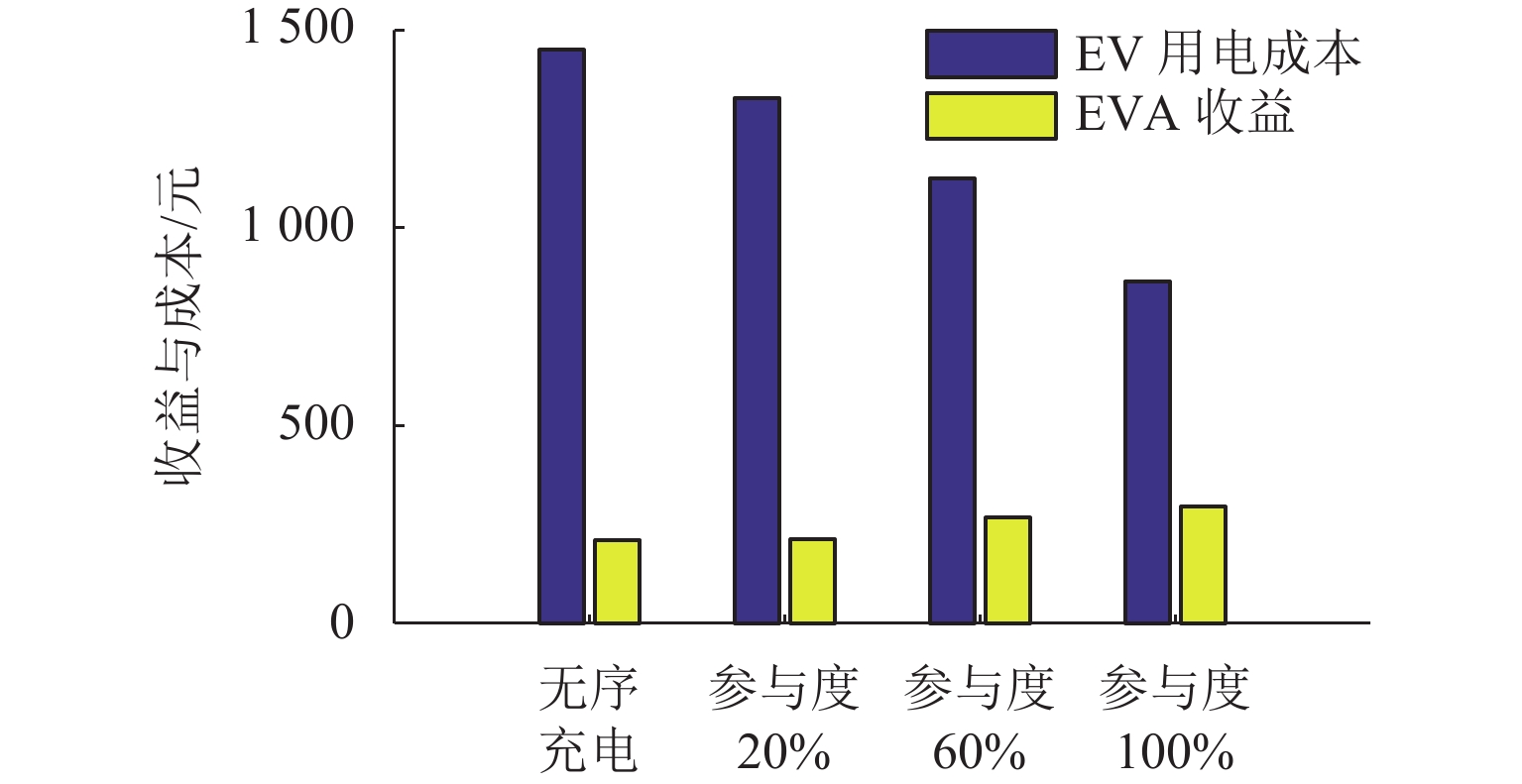
充电策略 峰谷差/
kW负荷
方差/kW2用户成本/
元EVA 收益/
元基础负荷 2344 557359.6 无序充电 2247 495058.3 1449.8 210.1 有序充放电 1688 241684.3 864.7 294.3 表 3 不同参与度有序充放电优化效果
Table 3. Optimization effect of orderly charging and discharging at different participation levels
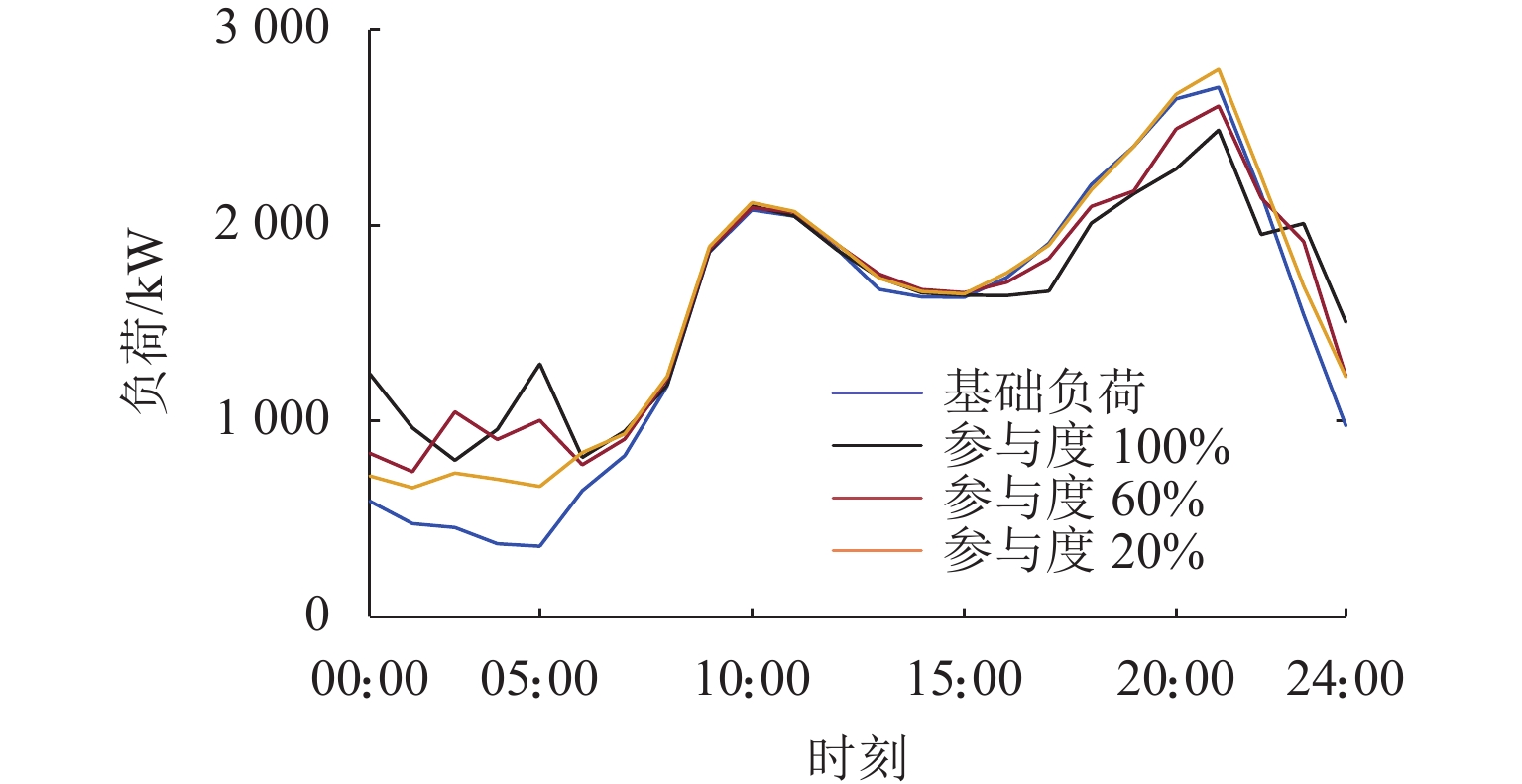
kW·h 参与度/% 削峰容量 填谷容量 峰值变化 谷值变化 100 1560.6 4409.8 −217.6 438.4 60 710.6 3369.4 −95.2 380.2 20 0 2424.2 91.8 298.6 -
[1] 陈琦. 大势所趋,企业加速在电动汽车领域的谋篇布局[J]. 汽车与配件,2022(21): 4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0162.2022.21.001CHEN Qi. The trend is to accelerate the layout of companies in the field of electric vehicles[J]. Automobile & Parts, 2022(21): 4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0162.2022.21.001 [2] KE S, CHEN L, YANG J, et al. Vehicle to everything in the power grid (V2eG): a review on the participation of electric vehicles in power grid economic dispatch[J]. Energy Conversion and Economics, 2022, 3(5): 259-286. doi: 10.1049/enc2.12070 [3] TIRUNAGARI S, GU M C, MEEGAHAPOLA L. Reaping the benefits of smart electric vehicle charging and vehicle-to-grid technologies: regulatory, policy and technical aspects[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 114657-114672. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3217525 [4] INALA K P, SAH B, KUMAR P, et al. Impact of V2G communication on grid node voltage at charging station in a smart grid scenario[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 3749-3758. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3007320 [5] 王鹤,冷贤达,潘禹含,等. 考虑时空特性及时间成本的电动汽车有序充放电策略[J]. 电力自动化设备,2022,42(10): 86-91,133.WANG He, LENG Xianda, PAN Yuhan, et al. Orderly charging and discharging strategy of electric vehicle considering spatio-temporal characteristic and time cost[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022, 42(10): 86-91,133. [6] YANG W H, WANG H, WANG Z J, et al. Optimization strategy of electric vehicles charging path based on “traffic-price-distribution” mode[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(12): 3208.1-3208.21. [7] 肖丽,谢尧平,胡华锋,等. 基于V2G的电动汽车充放电双层优化调度策略[J]. 高压电器,2022,58(5): 164-171.XIAO Li, XIE Yaoping, HU Huafeng, et al. Two-level optimization scheduling strategy for EV’s charging and discharging based on V2G[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2022, 58(5): 164-171. [8] 蔡国伟,姜雨晴,黄南天,等. 电力需求响应机制下基于多主体双层博弈的规模化电动汽车充放电优化调度[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2023,43(1): 85-99.CAI Guowei, JIANG Yuqing, HUANG Nantian, et al. Large-scale electric vehicles charging and discharging optimization scheduling based on multi-agent two-level game under electricity demand response mechanism[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(1): 85-99. [9] 冯小,张传林,崔承刚,等. 基于Stackelberg博弈的孤岛式光储充电站调度优化[J]. 电网技术,2022,46(10): 3989-4001.FENG Xiao, ZHANG Chuanlin, CUI Chenggang, et al. Scheduling optimization of islanded electric vehicle charging station based on Stackelberg game[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46(10): 3989-4001. [10] 程宏波,李明慧. 基于Stackelberg博弈的车-网双向互动策略研究[J]. 华东交通大学学报,2017,34(5): 49-55,80.CHENG Hongbo, LI Minghui. Study on bilateral interaction between vehicle and grid based on Stackelberg model[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2017, 34(5): 49-55,80. [11] 马英姿,马兆兴. 基于博弈算法的电动汽车有序充电优化及效益分析[J]. 电力工程技术,2021,40(5): 10-16. doi: 10.12158/j.2096-3203.2021.05.002MA Yingzi, MA Zhaoxing. Orderly charging optimization and benefit analysis of electric vehicles based on game algorithm[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2021, 40(5): 10-16. doi: 10.12158/j.2096-3203.2021.05.002 [12] 李东东,张凯,姚寅,等. 基于信息间隙决策理论的电动汽车聚合商日前需求响应调度策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2022,50(24): 101-111.LI Dongdong, ZHANG Kai, YAO Yin, et al. Day-ahead demand response scheduling strategy of an electric vehicle aggregator based on information gap decision theory[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50(24): 101-111. [13] 潘樟惠,高赐威,刘顺桂. 基于需求侧放电竞价的电动汽车充放电调度研究[J]. 电网技术,2016,40(4): 1140-1146.PAN Zhanghui, GAO Ciwei, LIU Shungui. Research on charging and discharging dispatch of electric vehicles based on demand side discharge bidding[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(4): 1140-1146. [14] WANG D, GAO J Y, LI P, et al. Modeling of plug-in electric vehicle travel patterns and charging load based on trip chain generation[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 359: 468-479. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.05.036 [15] 郭爱,叶涵昌,戴朝华,等. 考虑电网支撑能力的储换一体站容量优化配置[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(6): 1257-1266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220431GUO Ai, YE Hanchang, DAI Chaohua, et al. Capacity optimization configuration of electric vehicle swapping-storage integrated station considering support ability to grid[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(6): 1257-1266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220431 [16] 陈丽丹,聂涌泉,钟庆. 基于出行链的电动汽车充电负荷预测模型[J]. 电工技术学报,2015,30(4): 216-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.04.027CHEN Lidan, NIE Yongquan, ZHONG Qing. A model for electric vehicle charging load forecasting based on trip chains[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(4): 216-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2015.04.027 [17] 牛牧童,廖凯,杨健维,等. 考虑季节特性的多时间尺度电动汽车负荷预测模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2022,50(5): 74-85.NIU Mutong, LIAO Kai, YANG Jianwei, et al. Multi-time-scale electric vehicle load forecasting model considering seasonal characteristics[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50(5): 74-85. [18] 魏韡,陈玥,刘锋,等. 基于主从博弈的智能小区代理商定价策略及电动汽车充电管理[J]. 电网技术,2015,39(4): 939-945.WEI Wei, CHEN Yue, LIU Feng, et al. Stackelberg game based retailer pricing scheme and EV charging management in smart residential area[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39(4): 939-945. [19] 姜雨晴. 多主体博弈视角下的电动汽车充放电调度策略研究[D]. 吉林: 东北电力大学,2022. [20] CHAI B, CHEN J M, YANG Z Y, et al. Demand response management with multiple utility companies: a two-level game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2014, 5(2): 722-731. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2013.2295024 [21] 戴朝华. 搜寻者优化算法及其应用研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学,2009. -




 下载:
下载: