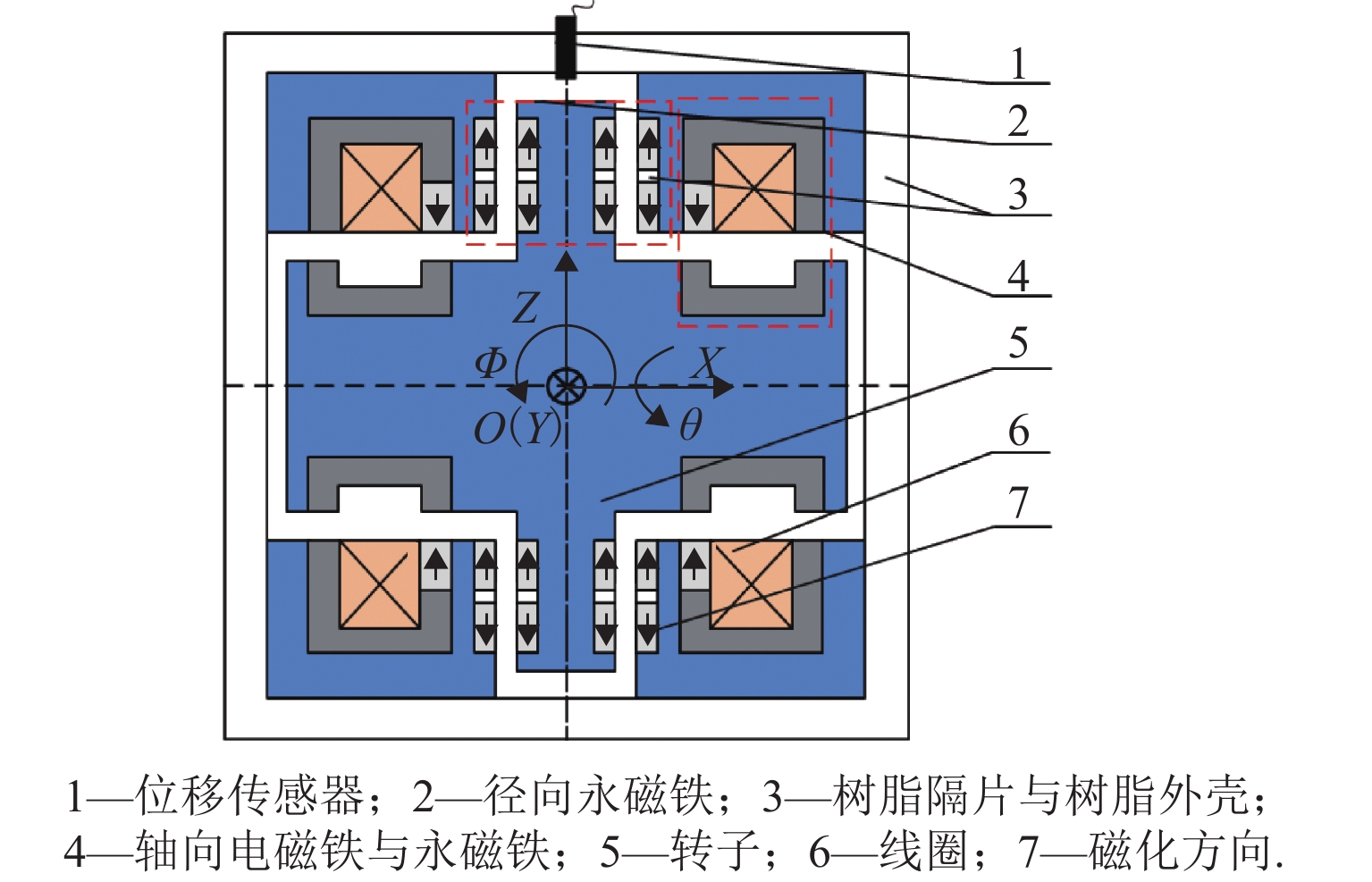
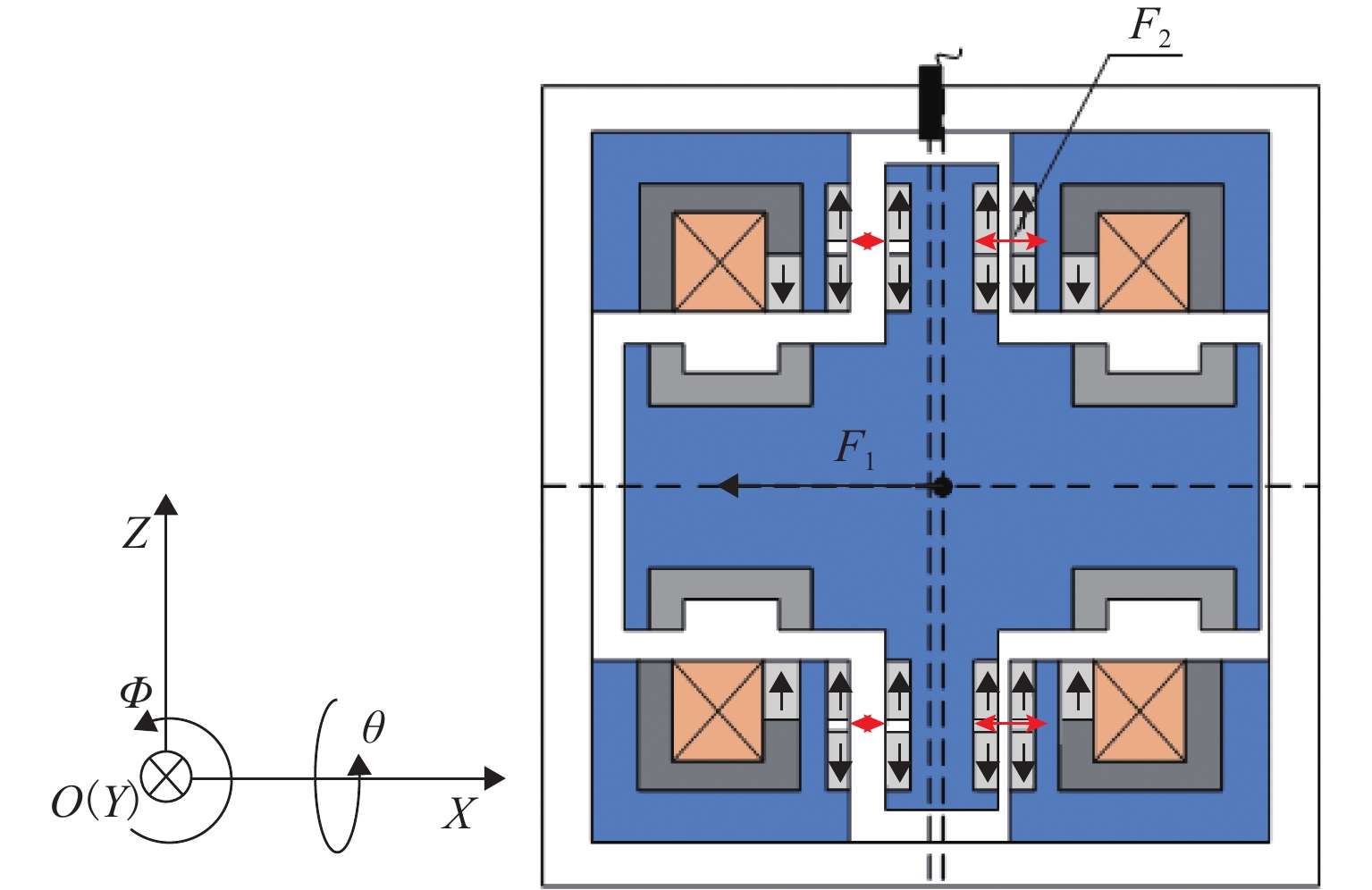
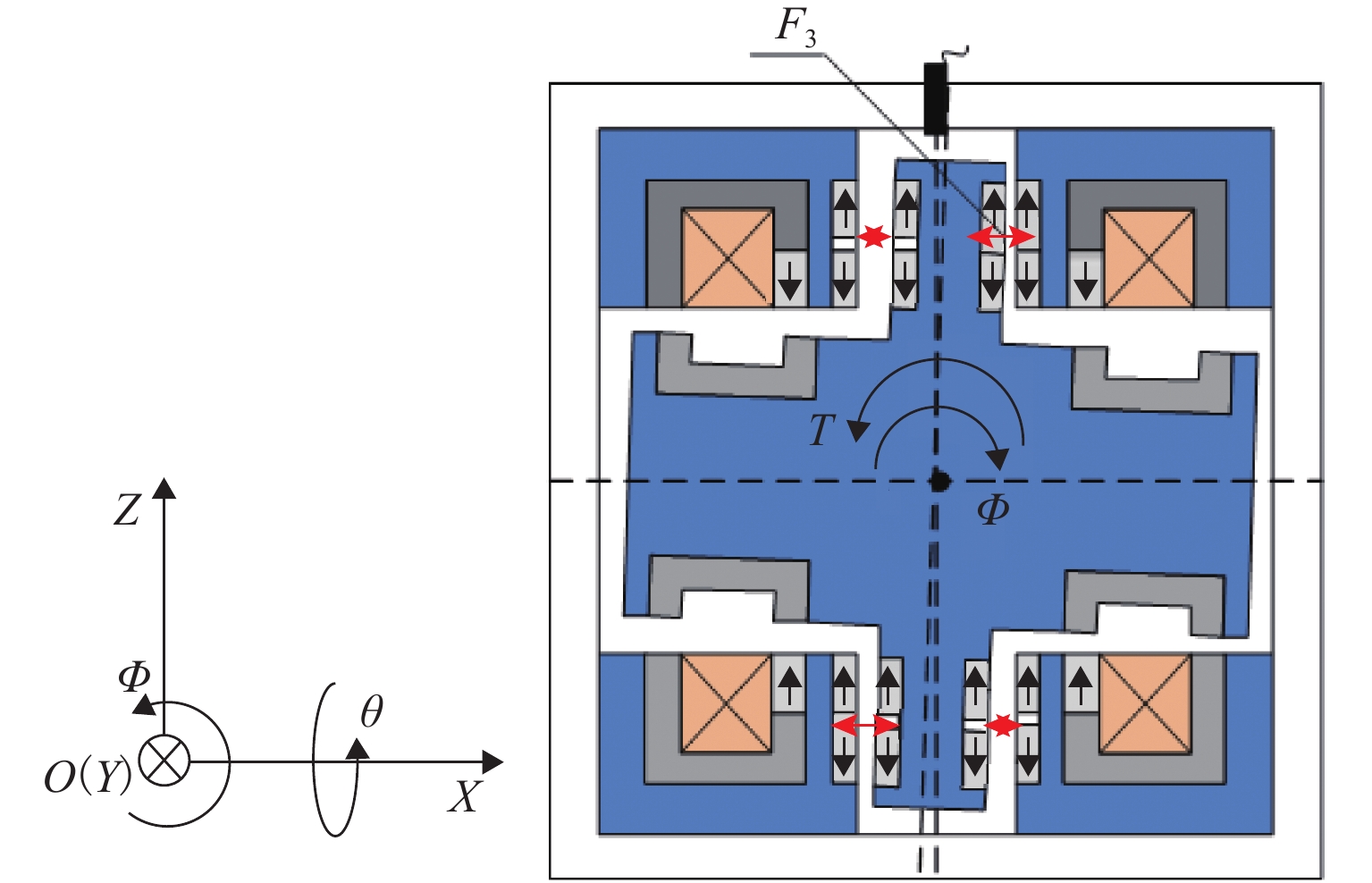
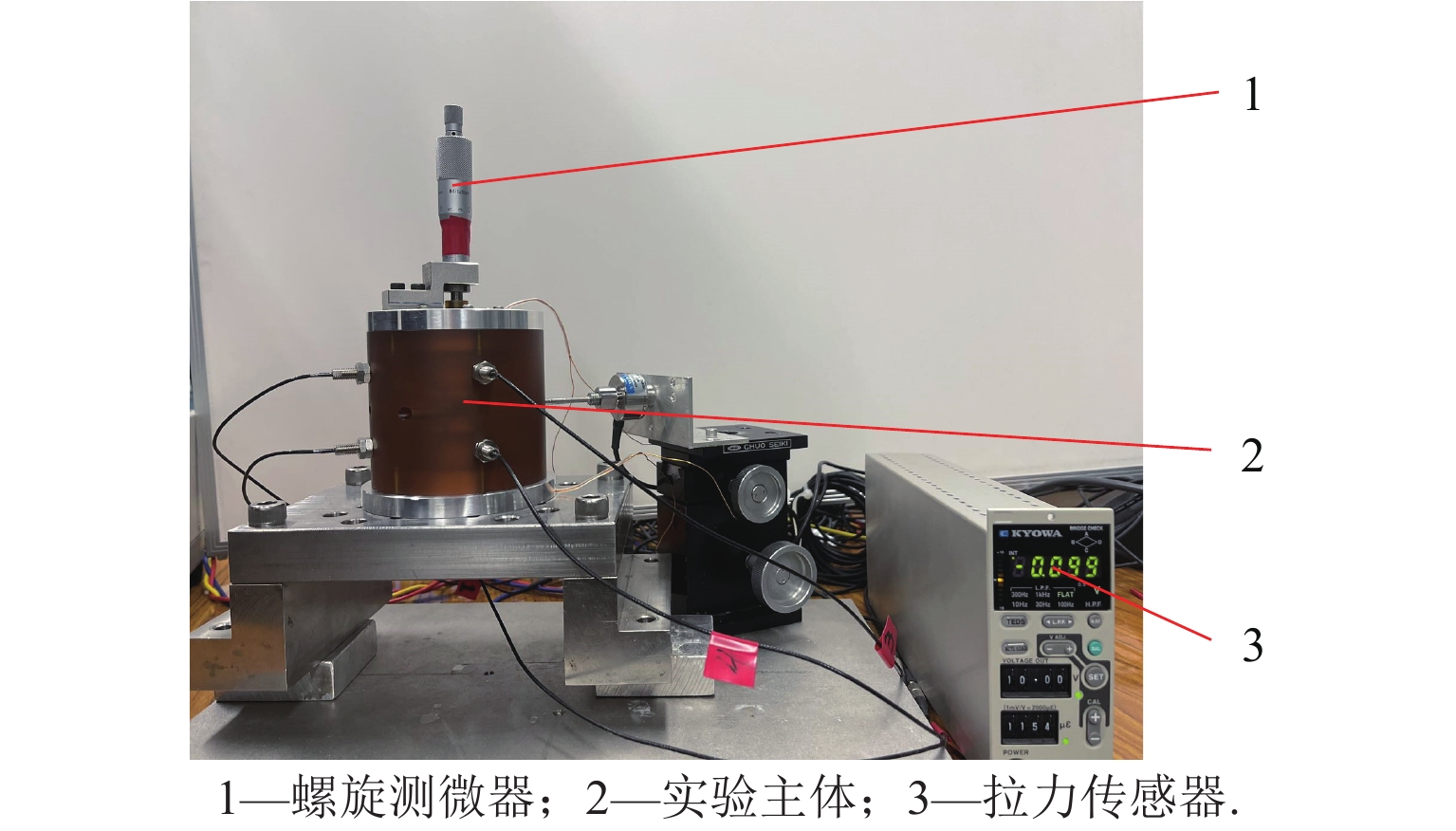
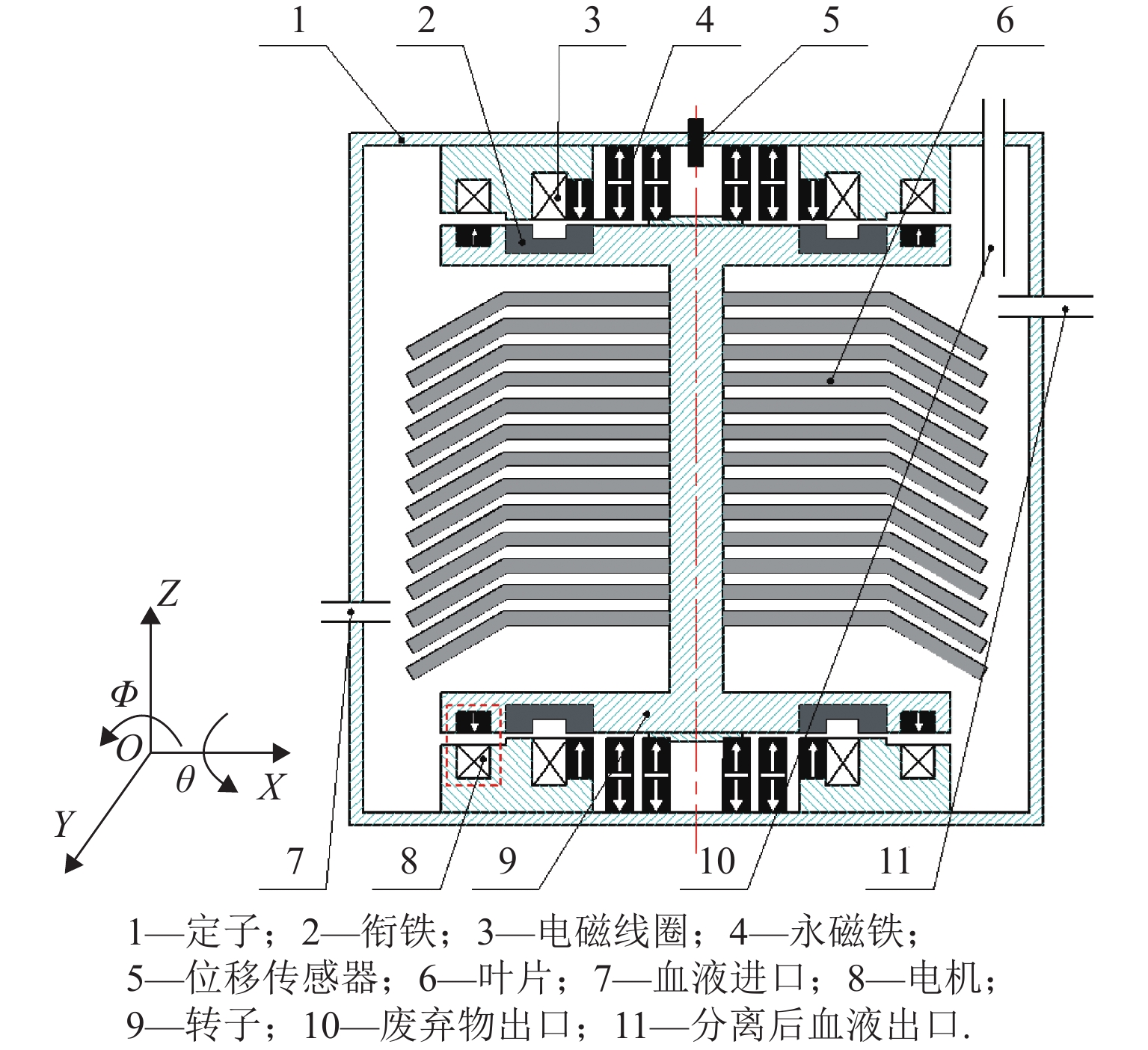
Design and Magnetic Force Characteristic Analysis of Magnetic Levitation Bearing for Artificial Kidney Pumps
-
摘要:
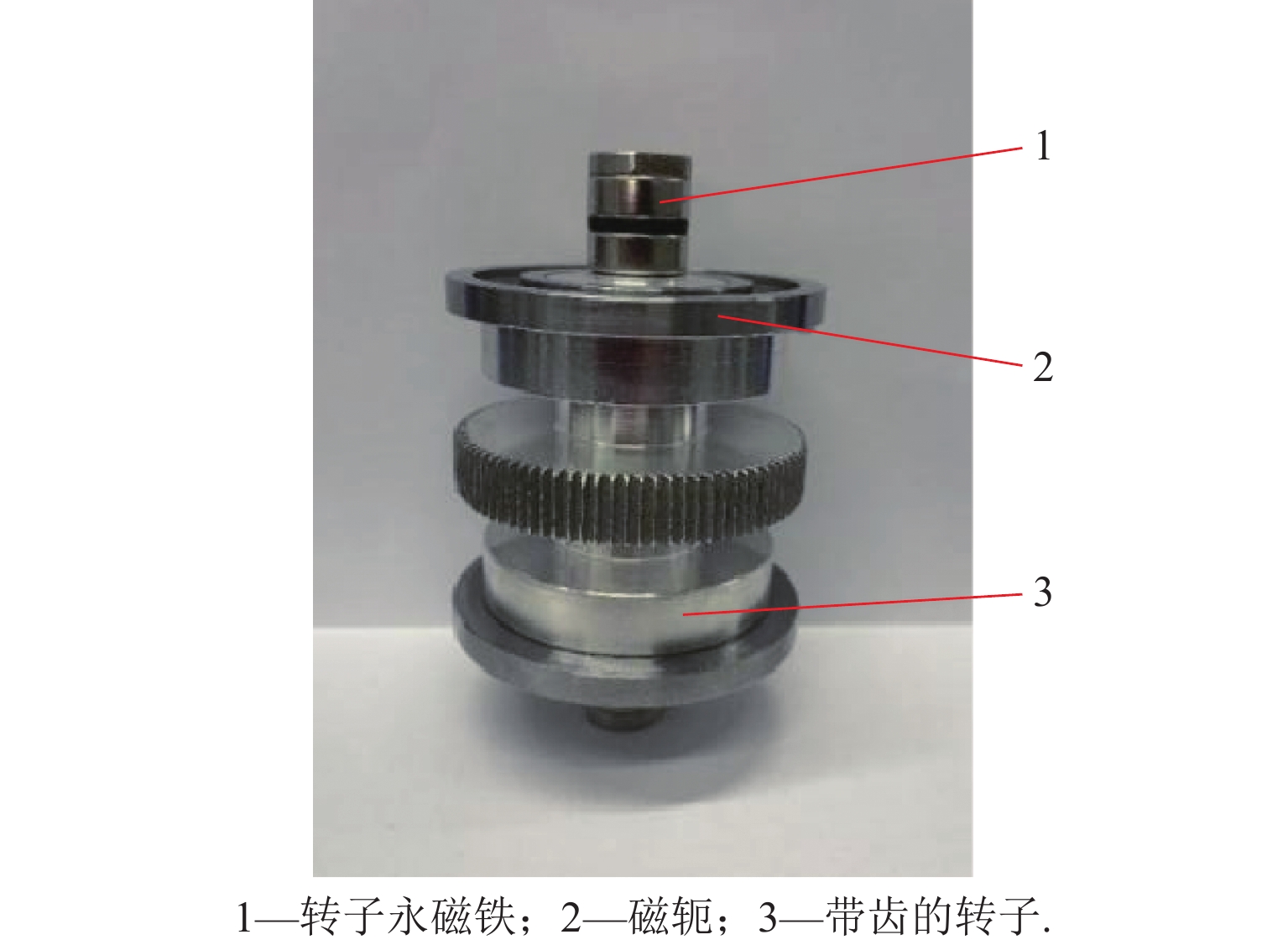
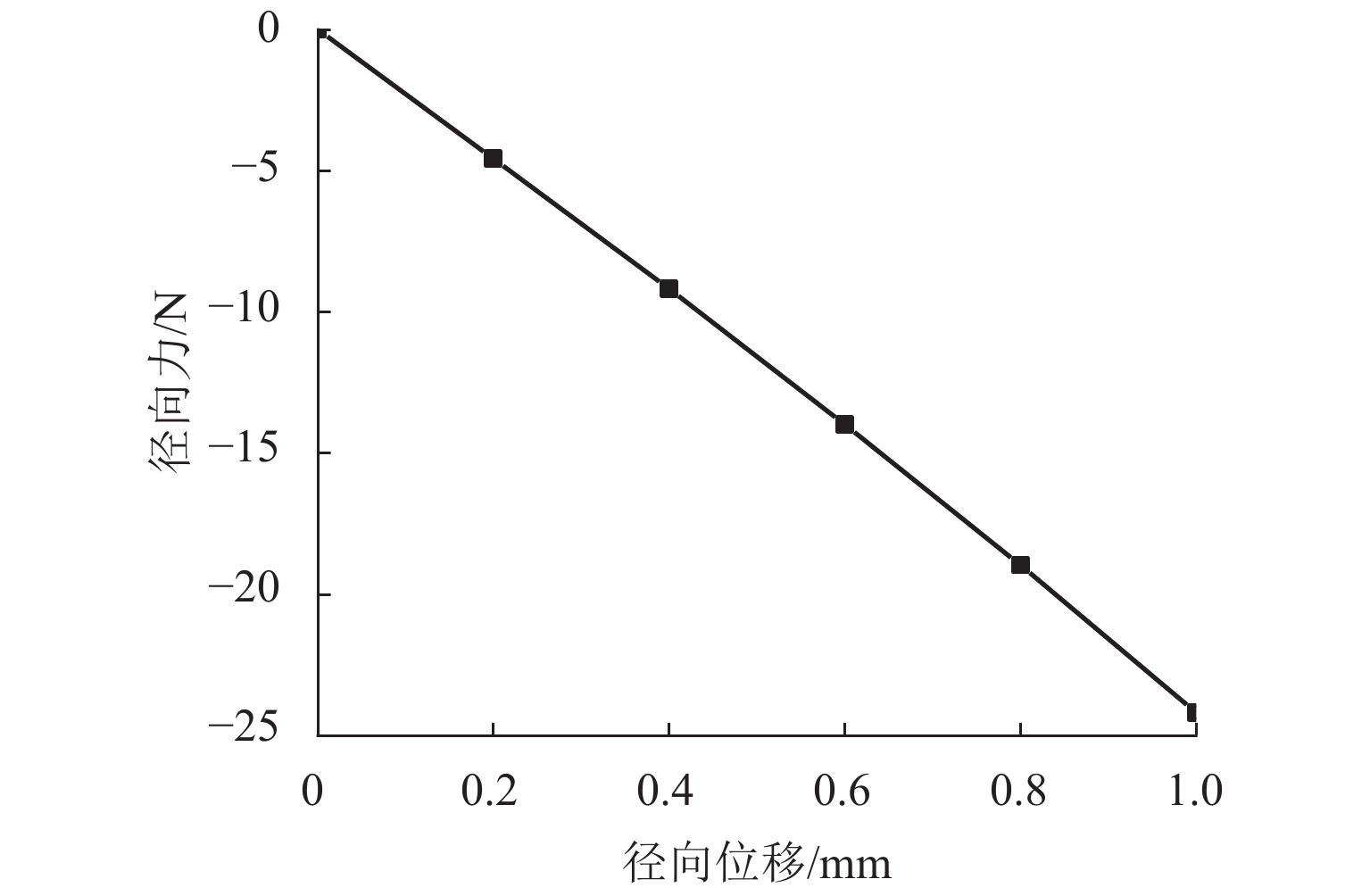
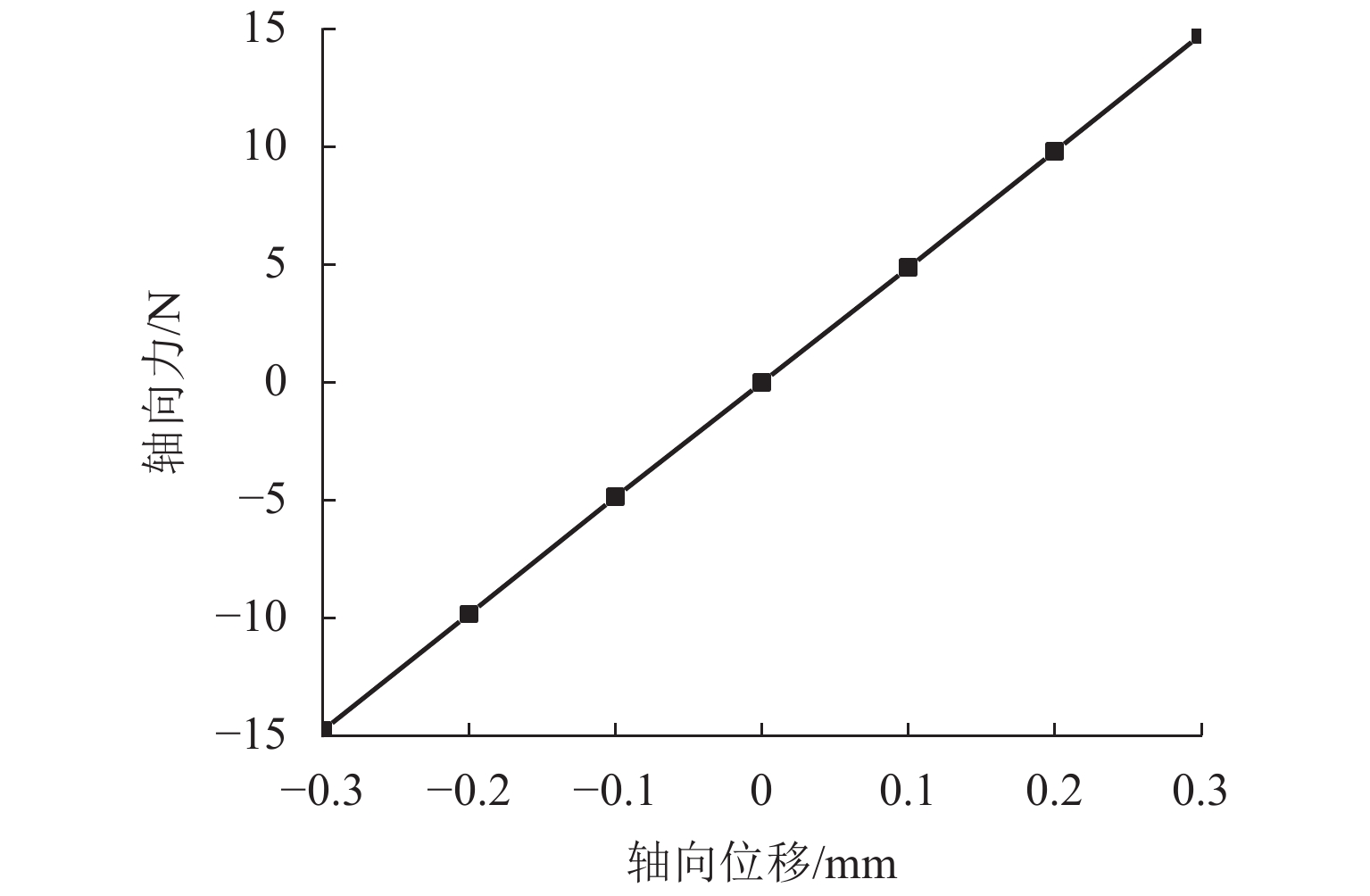
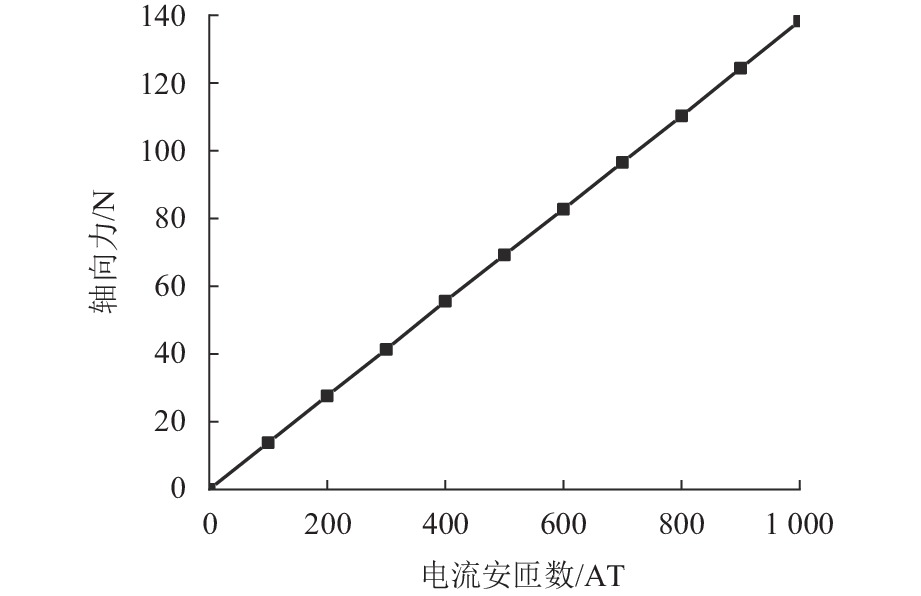
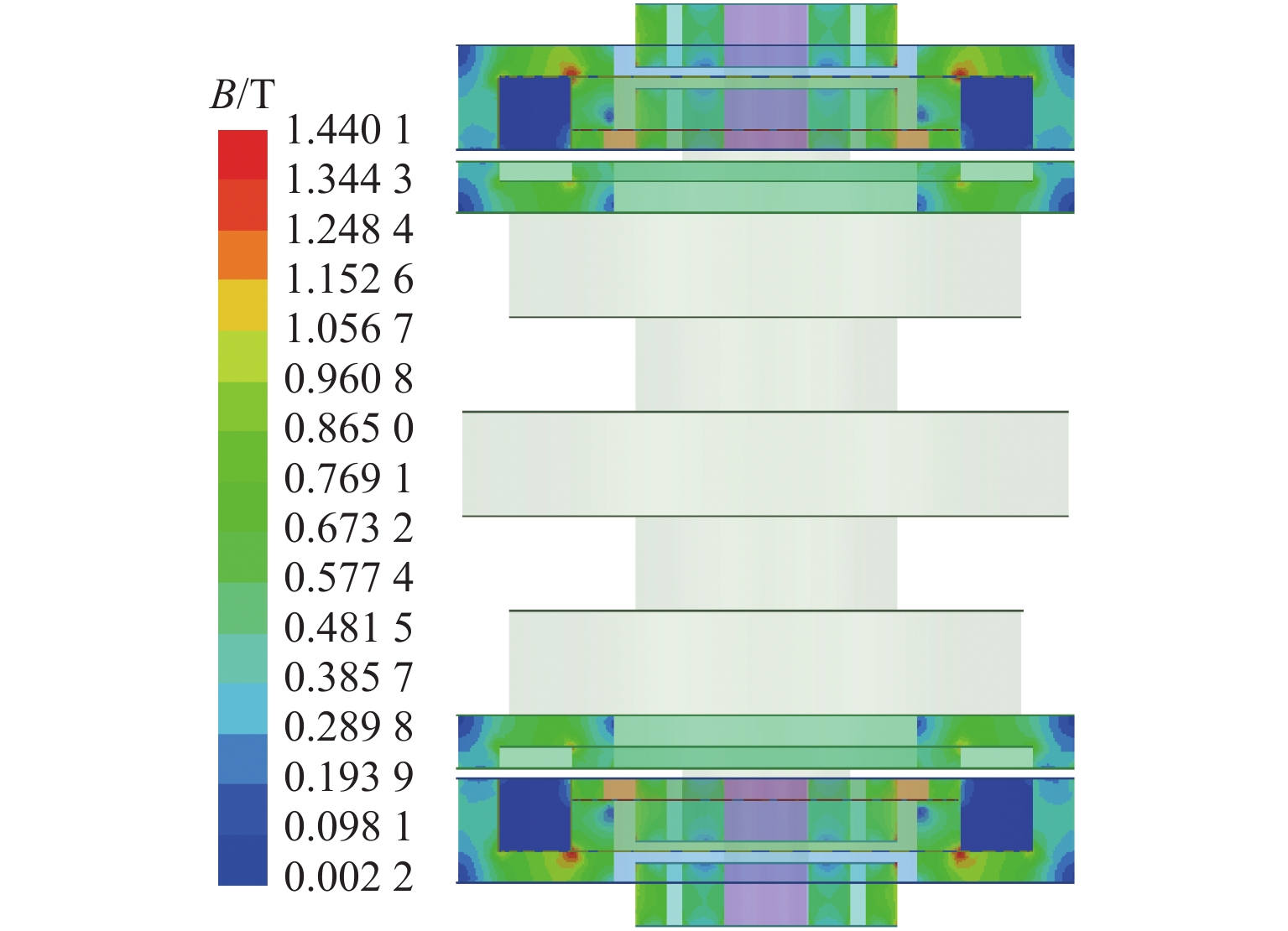
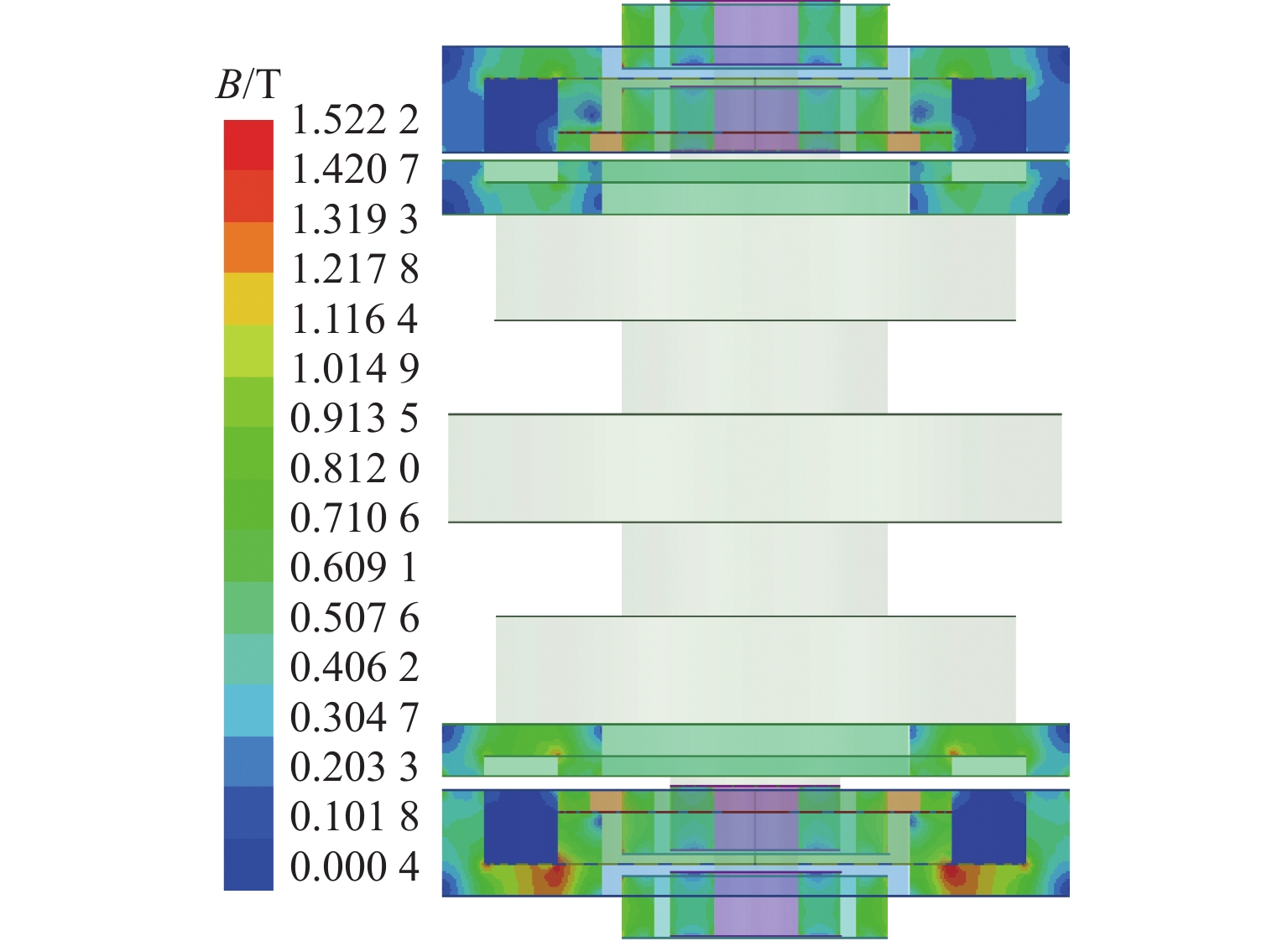
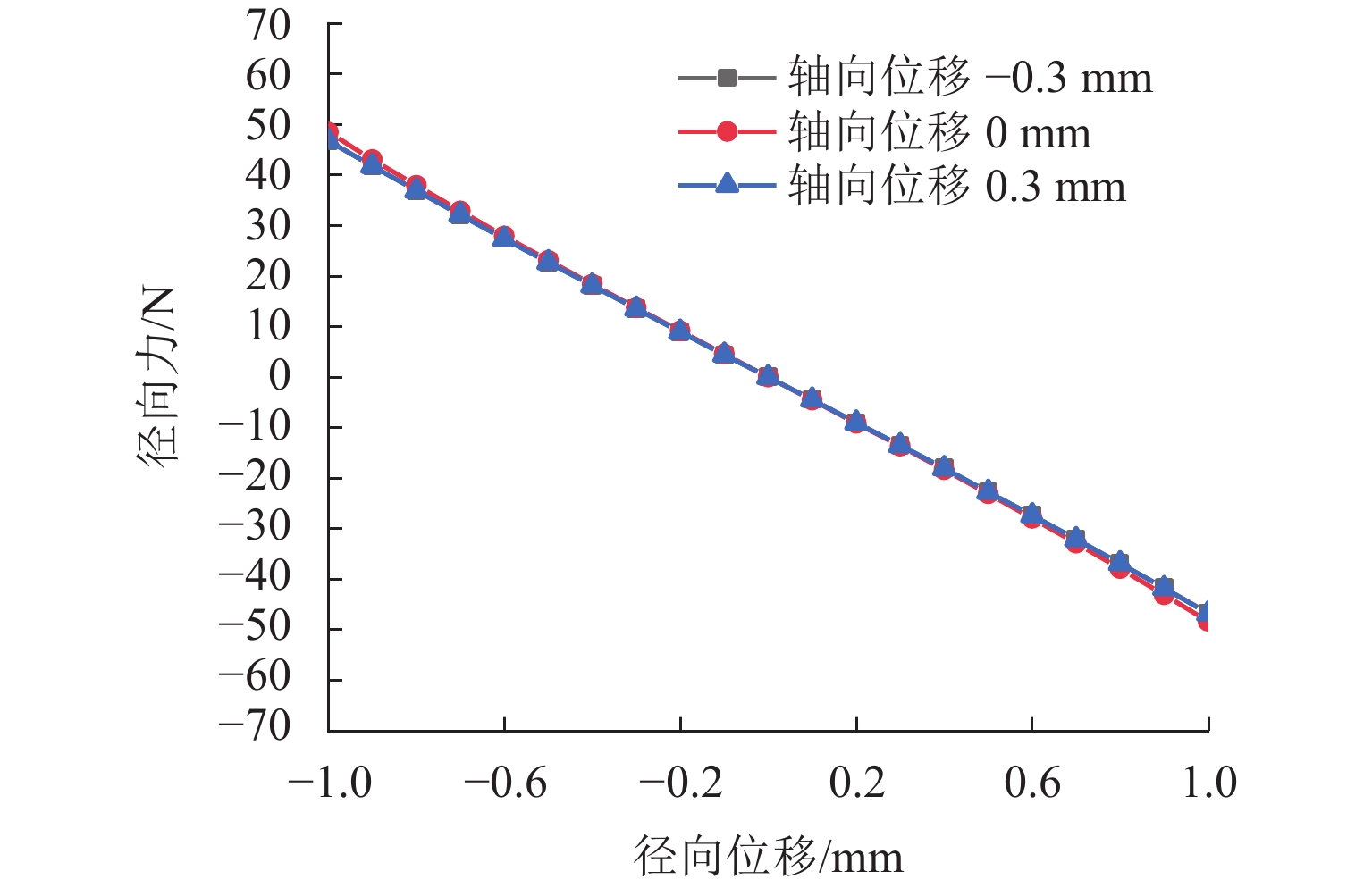
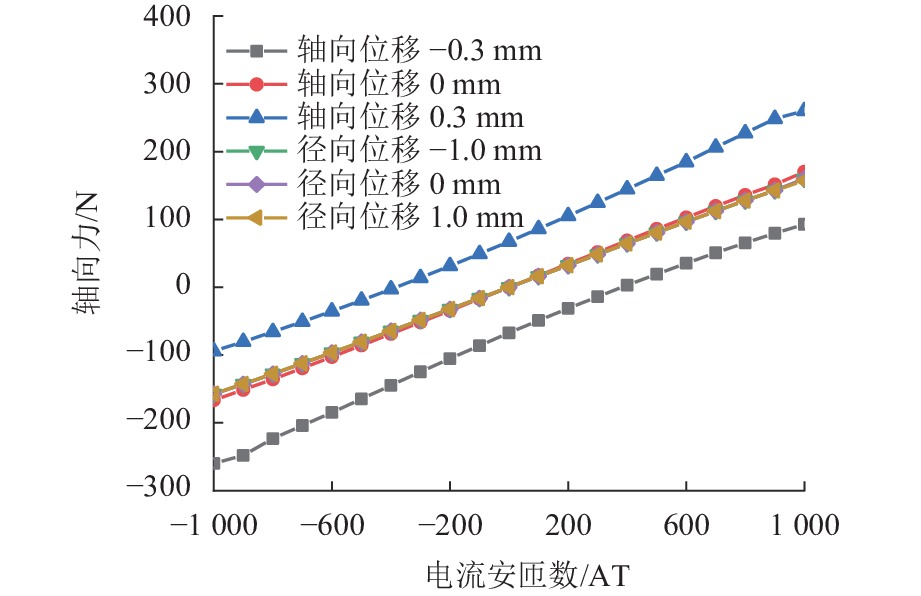
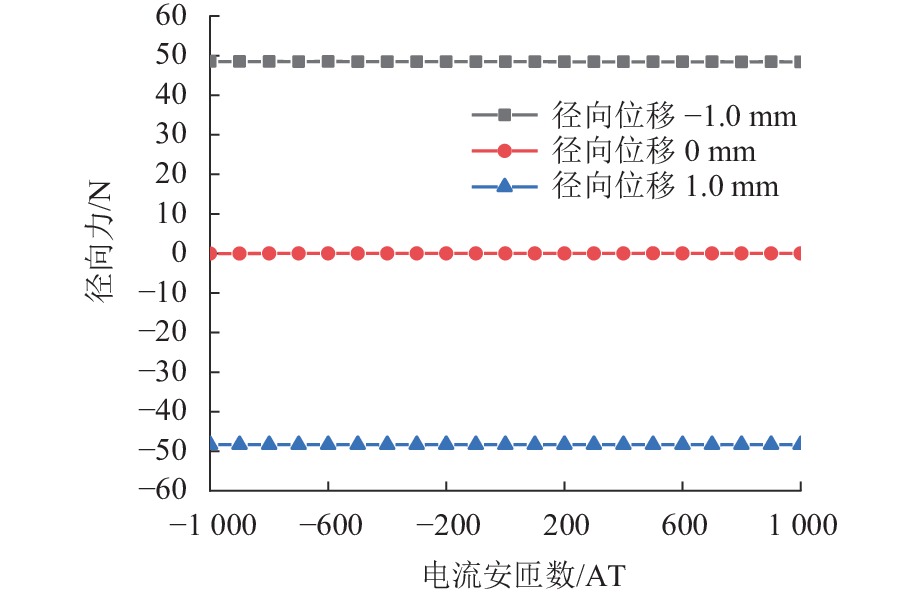
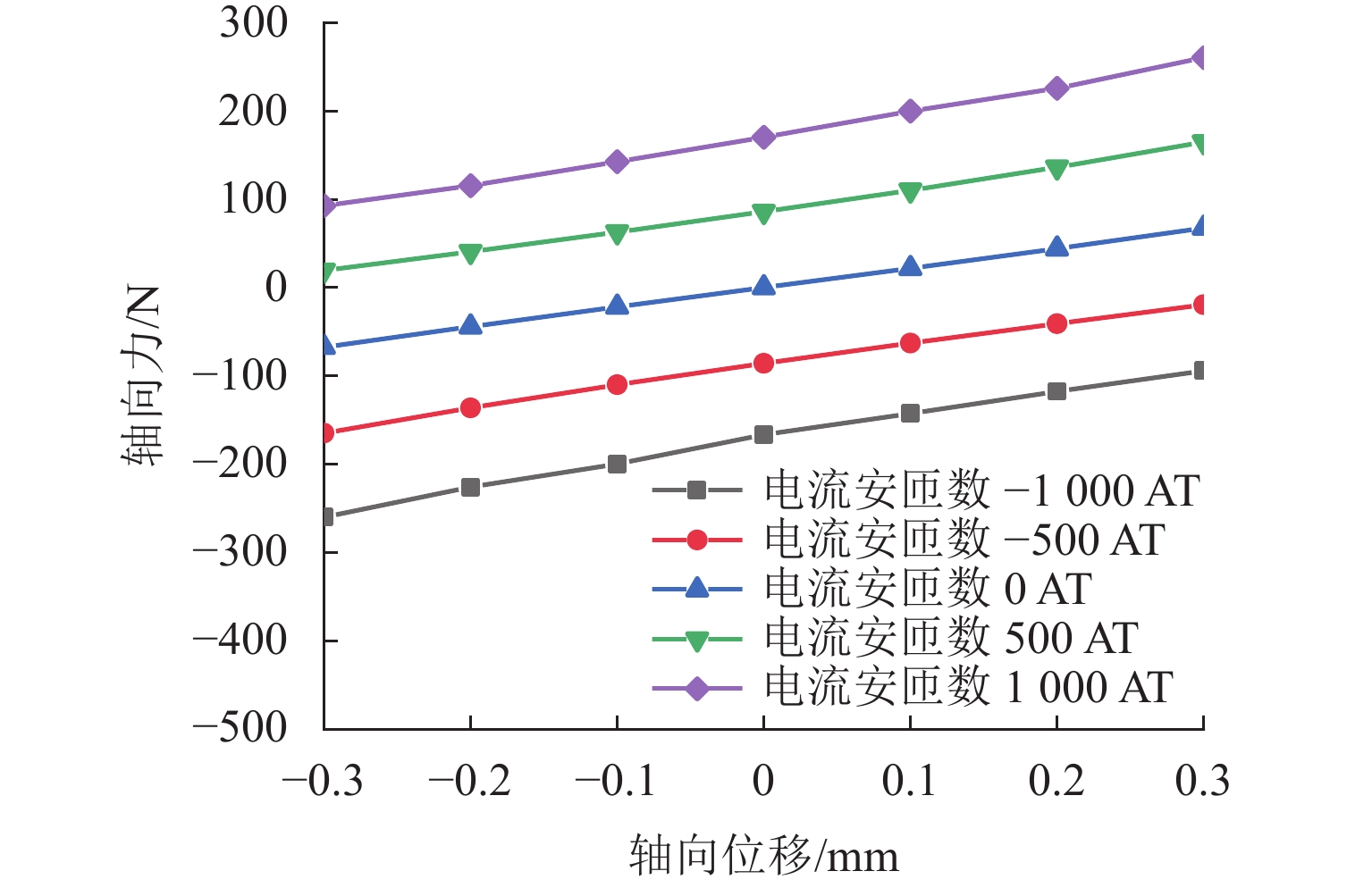
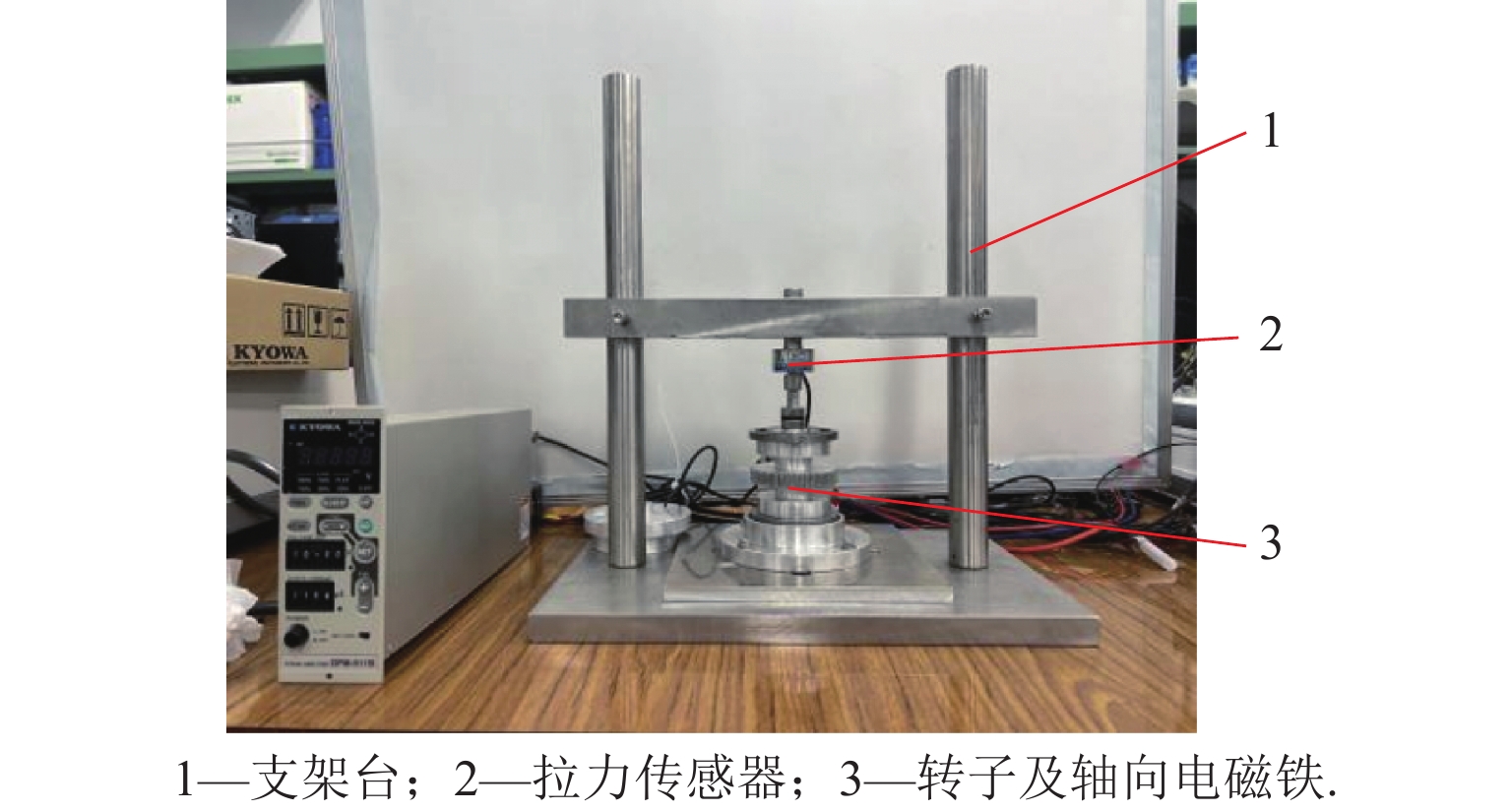
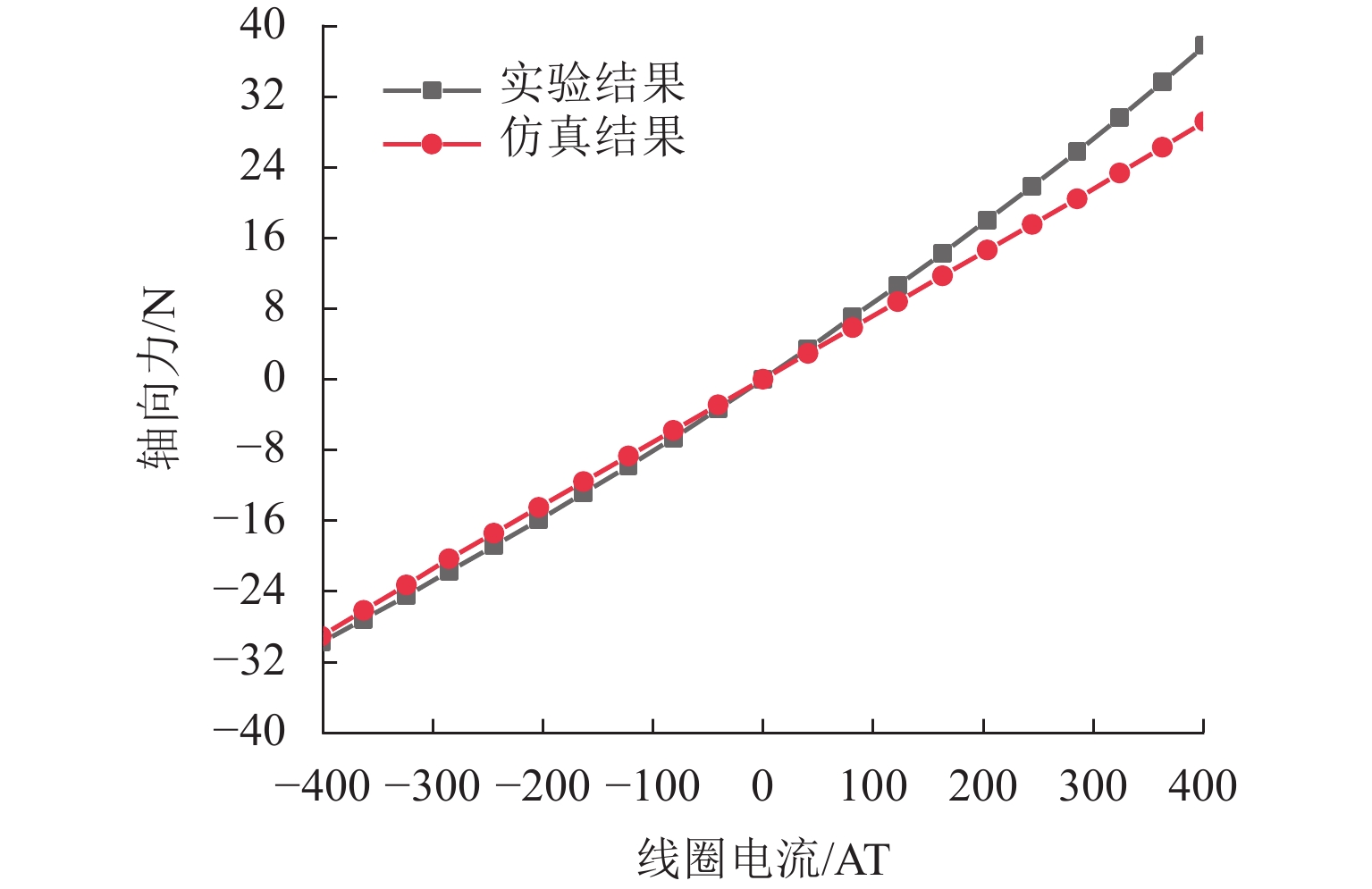
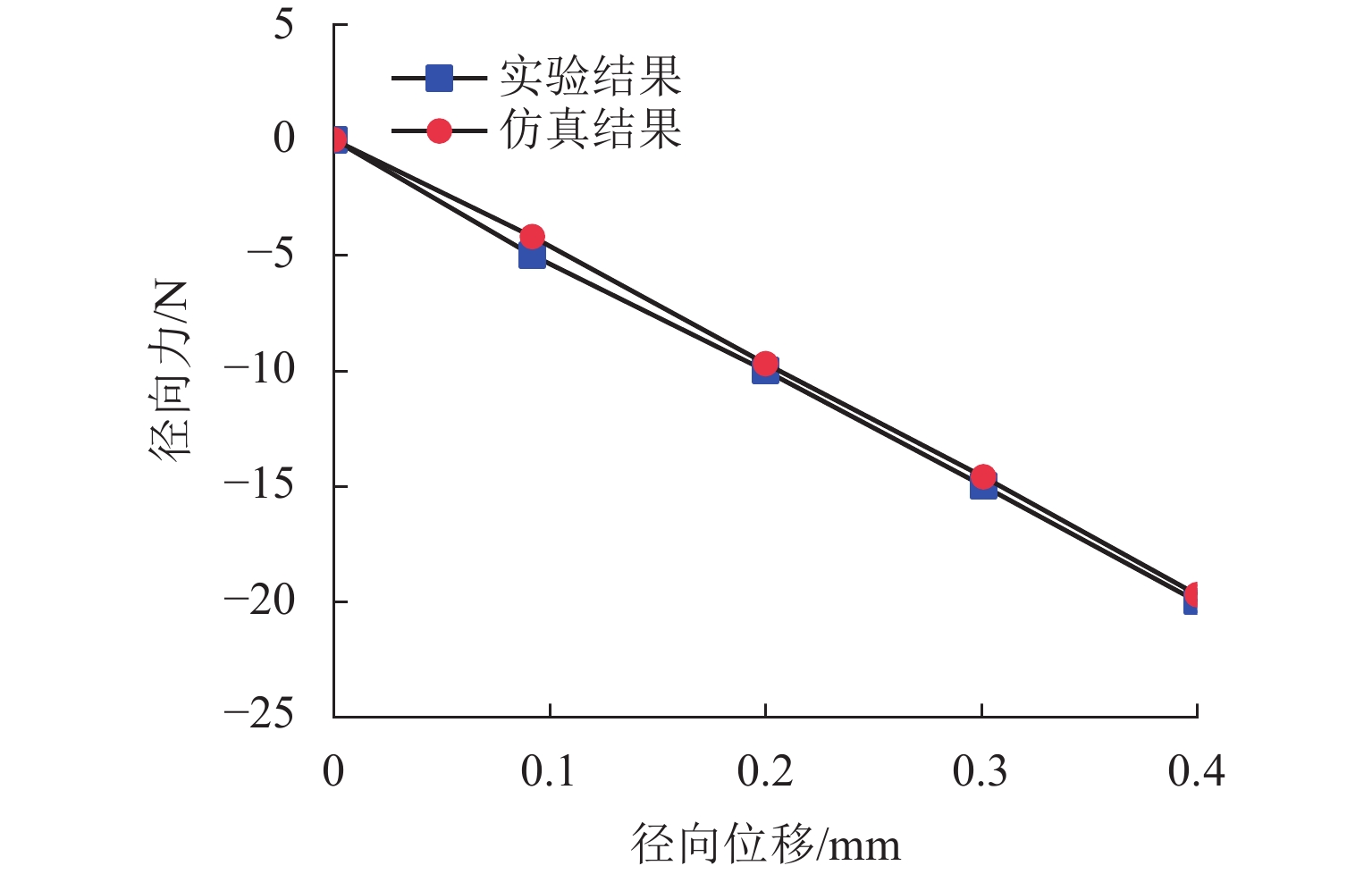
代替透析膜的持续离心分离新方法提高了依赖血液透析治疗的肾脏病患者生活质量,随之,人工肾脏泵的研究被很多学者关注. 但传统人工肾脏泵采用滚动轴承进行支撑,存在溶血高、血栓率高等问题,为此,本文利用磁悬浮轴承的非接触、无润滑、高转速等优点,研发了一种应用于人工肾脏泵的结构紧凑且节能的单自由度控制型磁悬浮轴承. 利用有限元分析软件进行仿真,探索径向被动控制部分和轴向主动控制部分的设计参数,并对总体进行仿真验证,进而对磁悬浮轴承进行结构性能评估. 结果表明:仿真与实验的径向位移刚度系数分别为47.432 N/mm和49.531 N/mm,轴向电流刚度系数分别为0.144 N/AT和0.135 N/AT,轴向位移刚度系数为223.071 N/mm,满足该磁悬浮轴承的五自由度稳定悬浮要求;所设计的磁悬浮轴承简化了系统结构,减小了控制难度以及降低了系统功耗.
Abstract:The new method of continuous centrifugal separation instead of dialysis membrane has improved the quality of life of patients with kidney disease who depend on hemodialysis treatment. As a result, the research on artificial kidney pumps has been paid much attention by many scholars, but the conventional artificial kidney pump is supported by rolling bearings, and it thus causes problems such as high hemolysis and high thrombosis rate. In order to solve these problems, this paper developed a compact and energy-saving single-degree-of-freedom controlled magnetic levitation bearing applied to an artificial kidney pump by using the advantages of non-contact, non-lubrication, and high rotation speed of magnetic levitation bearing. The finite element analysis software was used for simulation to explore the design parameters of the radial passive control part and the axial active control part, and the overall simulation was verified. Then the structural performance of the magnetic levitation bearing was evaluated. The results show that the simulated and experimental radial displacement stiffness coefficients are 47.432 N/mm and 49.531 N/mm; the axial current stiffness coefficients are 0.144 N/AT and 0.135 N/AT, and the axial displacement stiffness coefficient is 223.071 N/mm, which meet the requirements of five-degree-of-freedom stable suspension of this magnetic levitation bearing. The designed magnetic levitation bearing simplifies the system structure, reduces the control difficulty, and lowers the power consumption of the system.
-
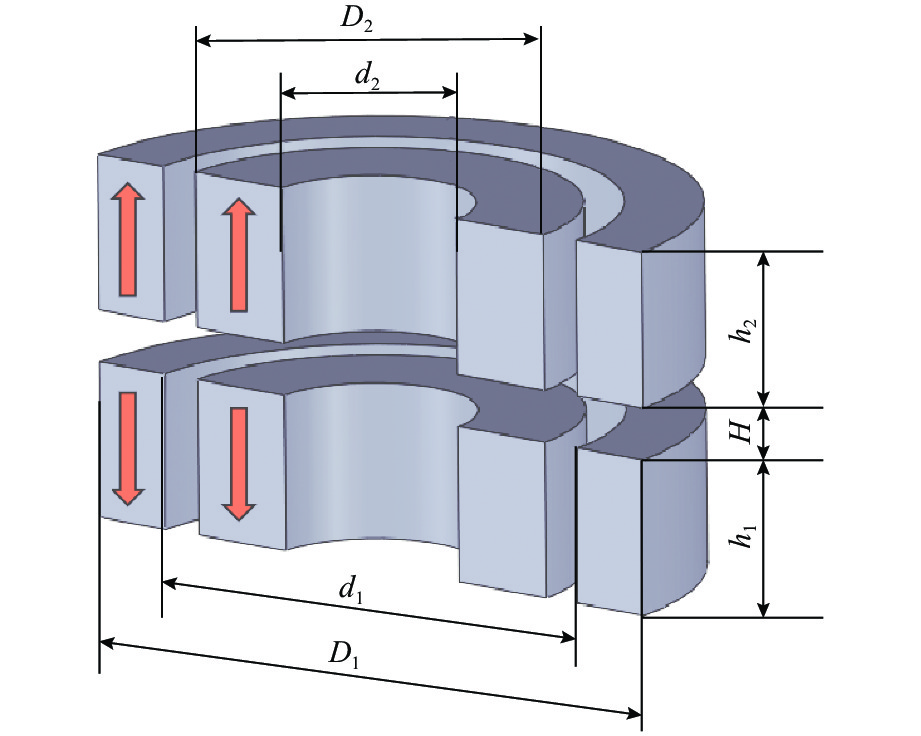
表 1 径向永磁铁参数
Table 1. Radial permanent magnet parameters
参数 数值 定子永磁铁外径 D1/mm 25 定子永磁铁内径 d1/mm 19 定子永磁铁高度 h1/mm 6 动子永磁铁外径 D2/mm 16 动子永磁铁内径 d2/mm 8 动子永磁铁高度 h2/mm 6 两永磁铁的轴向间隙 H/mm 2 永磁铁间距/mm 1.5 永磁铁材料 钕铁硼 N52 表 2 轴向主动控制结构参数
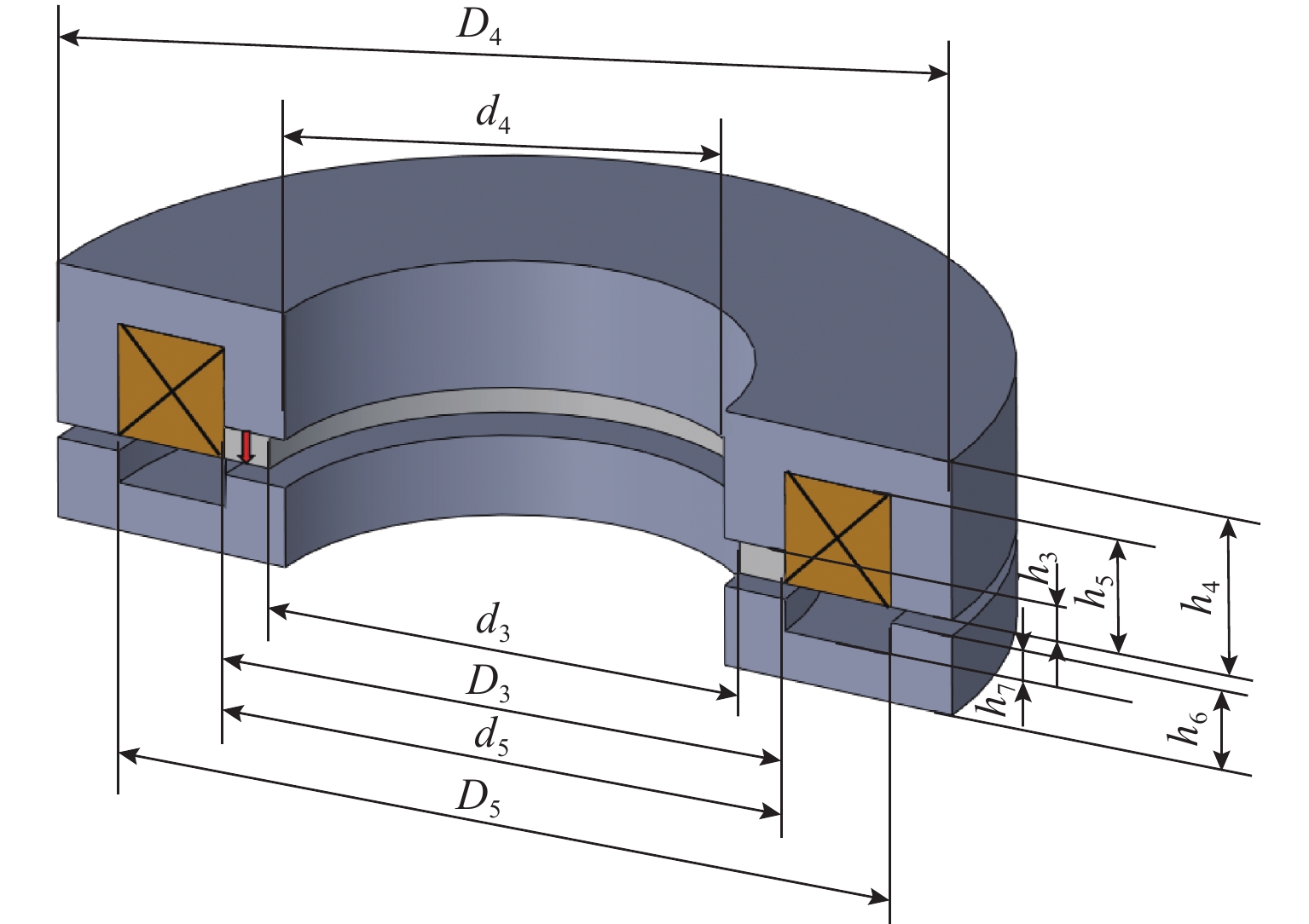
Table 2. Structural parameters of axial active control
参数 数值 永磁铁材料 钕铁硼 N33 永磁铁外径 D3 (内径 d3)/mm 37(31) 永磁铁的高度 h3/mm 2 法兰型背轭外径 D4 (内径 d4) /mm 59(29) 法兰型背轭总高度 h4/mm 10 法兰型背轭槽外径 D5 (内径 d5) /mm 51(37) 法兰型背轭槽深 h5/mm 7 磁轭总高 h6/mm 5 磁轭槽深 h7/mm 2 线圈线径/mm 0.493 线圈匝数 204 线圈截面积/mm2 49 线圈电感/mH 2.431 线圈电阻/Ω 3.252 -
[1] BIKBOV B, PURCELL C A, LEVEY A S, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990 —2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. The Lancet, 2020, 395(10225): 709-733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3 [2] MOLLAHOSSEINI A, ABDELRASOUL A, SHOKER A. A critical review of recent advances in hemodialysis membranes hemocompatibility and guidelines for future development[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 248: 122911.1-122911. 29. [3] ZHILO N M, LITINSKAIA E L, BAZAEV N A. Control system for glucose level regulation in peritoneal dialysis[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2091(1): 012019.1-012019.19. [4] ZHILO N M, BAZAEV N A. Control of wearable artificial kidney[C]//2019 Ⅲ International Conference on Control in Technical Systems (CTS). Petersburg: IEEE, 2020: 31-34. [5] PARSONS A D, SANSCRAINTE C, LEONE A, et al. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome and intracranial pressure fluctuations in neurosurgical patients undergoing renal replacement therapy: systematic review and pooled analysis[J]. World Neurosurgery, 2022,170: 2-6. [6] FLEMING G M. Renal replacement therapy review: past, present and future[J]. Organogenesis, 2011, 7(1): 2-12. doi: 10.4161/org.7.1.13997 [7] VAN GELDER M K, JONG J A W, FOLKERTSMA L, et al. Urea removal strategies for dialysate regeneration in a wearable artificial kidney[J]. Biomaterials, 2020, 234: 119735. 1-119735.18 [8] GURA V, RIVARA M B, BIEBER S, et al. A wearable artificial kidney for patients with end-stage renal disease[J]. JCI Insight, 2016, 1(8): e86397.1-e86397.15 [9] ARIYOSHI K, ISOYAMA T, HARA S, et al. Basic study of a centrifugal separator for the implantable centrifugal artificial kidney[J]. Transactions of Japanese Society for Medical and Biological Engineering, 2017, 55: 459-459. [10] MASUZAWA T. Magnetically suspended blood pump[J]. Journal of the Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 2017, 25(3): 325-331. doi: 10.14243/jsaem.25.325 [11] 胡余生,李立毅,郭伟林,等. 基于不等磁路面积设计方法的磁轴承刚度[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3):648-656.HU Yusheng, LI Liyi, GUO Weilin, et al. Support stiffness of magnetic bearing based on unequal magnetic circuit area design method[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 648-656. [12] 周扬,周瑾,张越,等. 基于RBF近似模型的磁悬浮轴承结构优化设计[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3):682-692.ZHOU Yang, ZHOU Jin, ZHANG Yue, et al. Optimum structural design of active magnetic bearing based on RBF approximation model[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 682-692. [13] 钟志贤,蔡忠侯,祁雁英. 单自由度磁悬浮系统无模型自适应控制的研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3):549-557,581.ZHONG Zhixian, CAI Zhonghou, QI Yanying. Model-free adaptive control for single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 549-557,581. [14] 贺艳晖,甘杨俊杰,周亮. 主动磁悬浮轴承在余热发电机的应用研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3):657-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210860HE Yanhui, GAN Yangjunjie, ZHOU Liang. Application of active magnetic bearing in waste heat generator[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 657-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210860 [15] ASAMA J, SHINSHI T, HOSHI H, et al. A new design for a compact centrifugal blood pump with a magnetically levitated rotor[J]. ASAIO Journal, 2004, 50(6): 550-556. doi: 10.1097/01.MAT.0000144364.62671.5A [16] 关勇,李红伟,刘淑琴. 轴流式磁悬浮人工心脏泵磁悬浮轴承系统设计[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版),2011,41(1):151-155.GUAN Yong, LI Hongwei, LIU Shuqin. System design of magnetic bearings in an axial-flow artificial blood pump[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2011, 41(1): 151-155. -




 下载:
下载: