Electric Truck Route Planning Considering Multiple Charging Pile Queues and Time Windows
-
摘要:
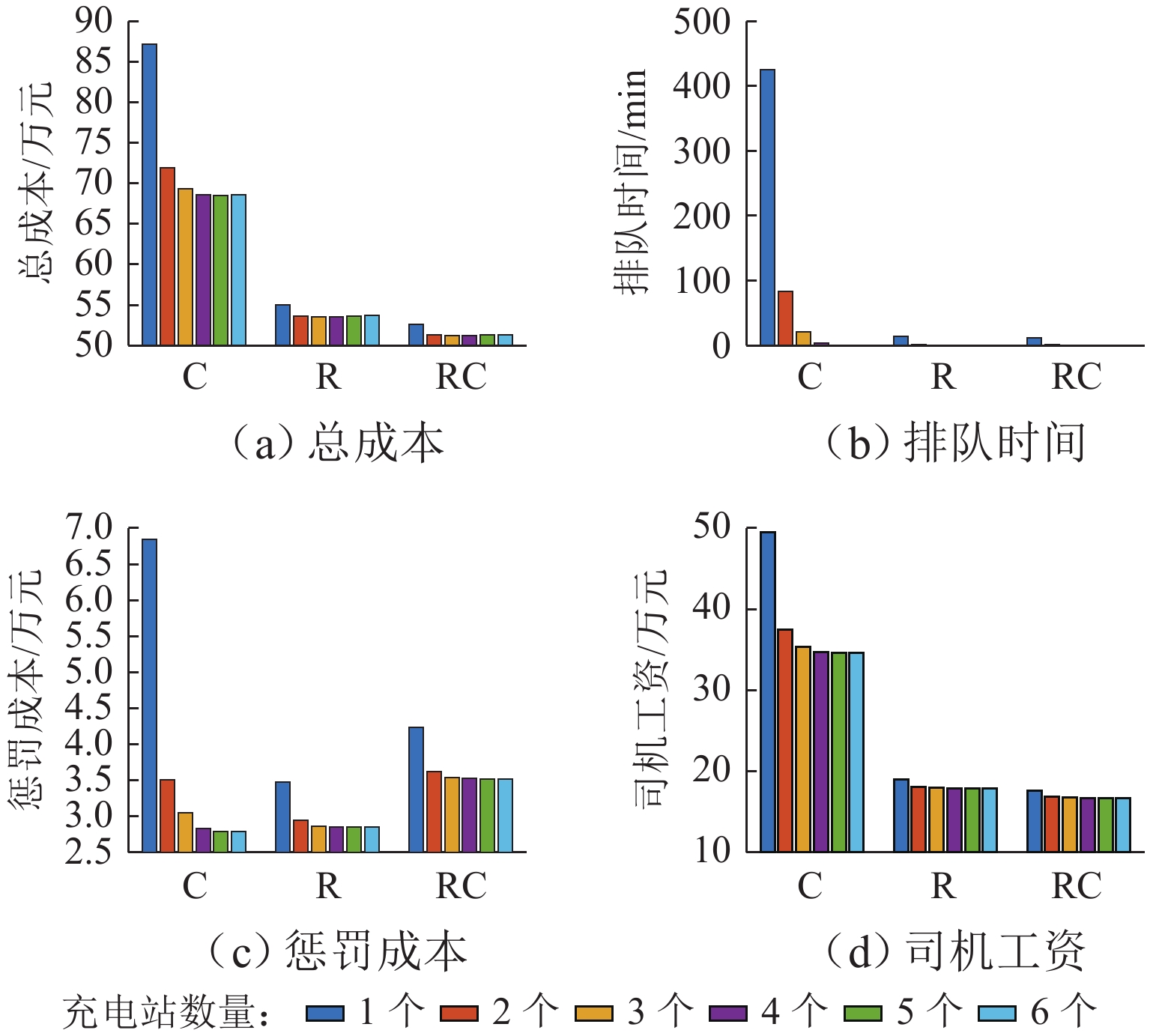
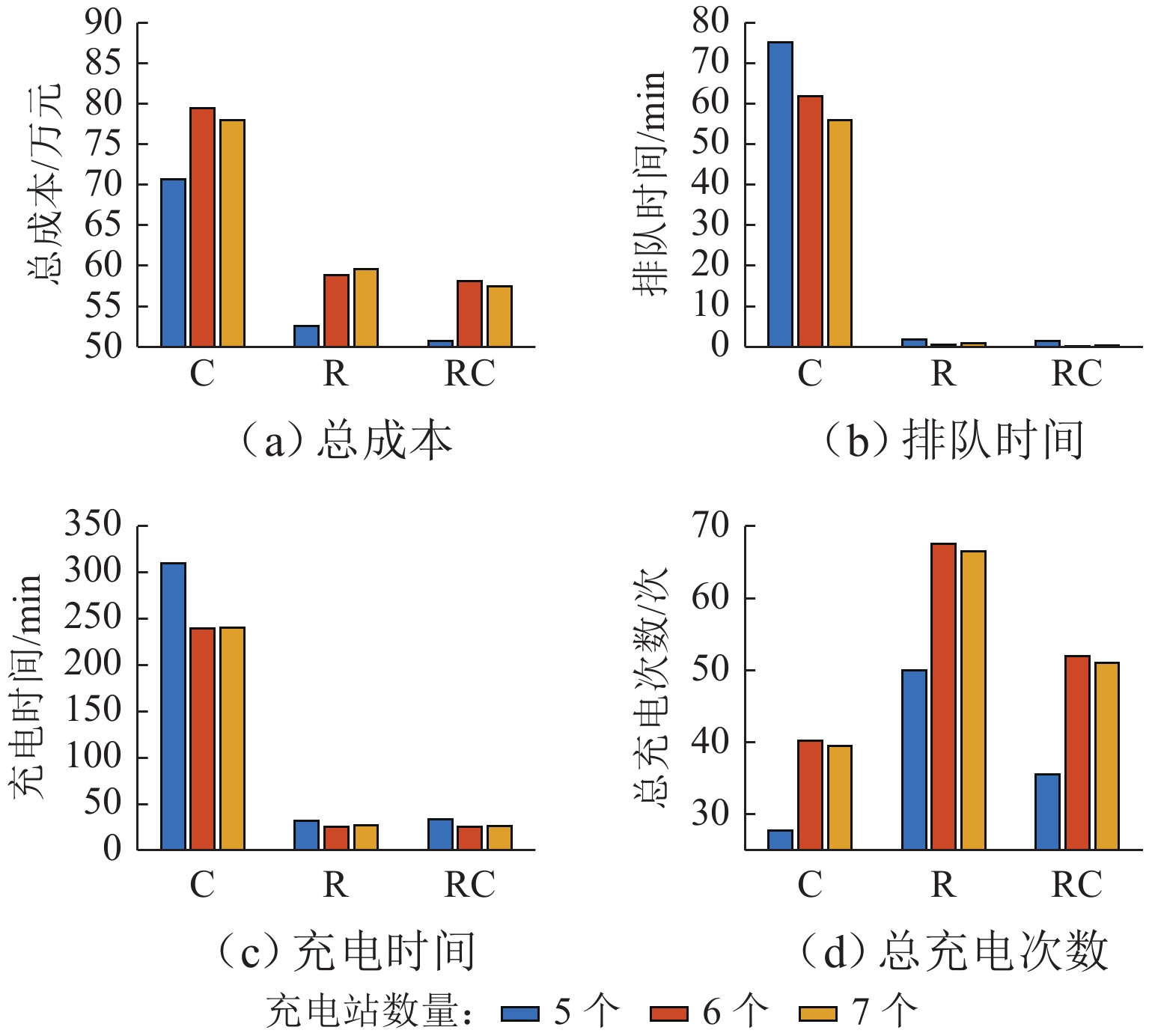
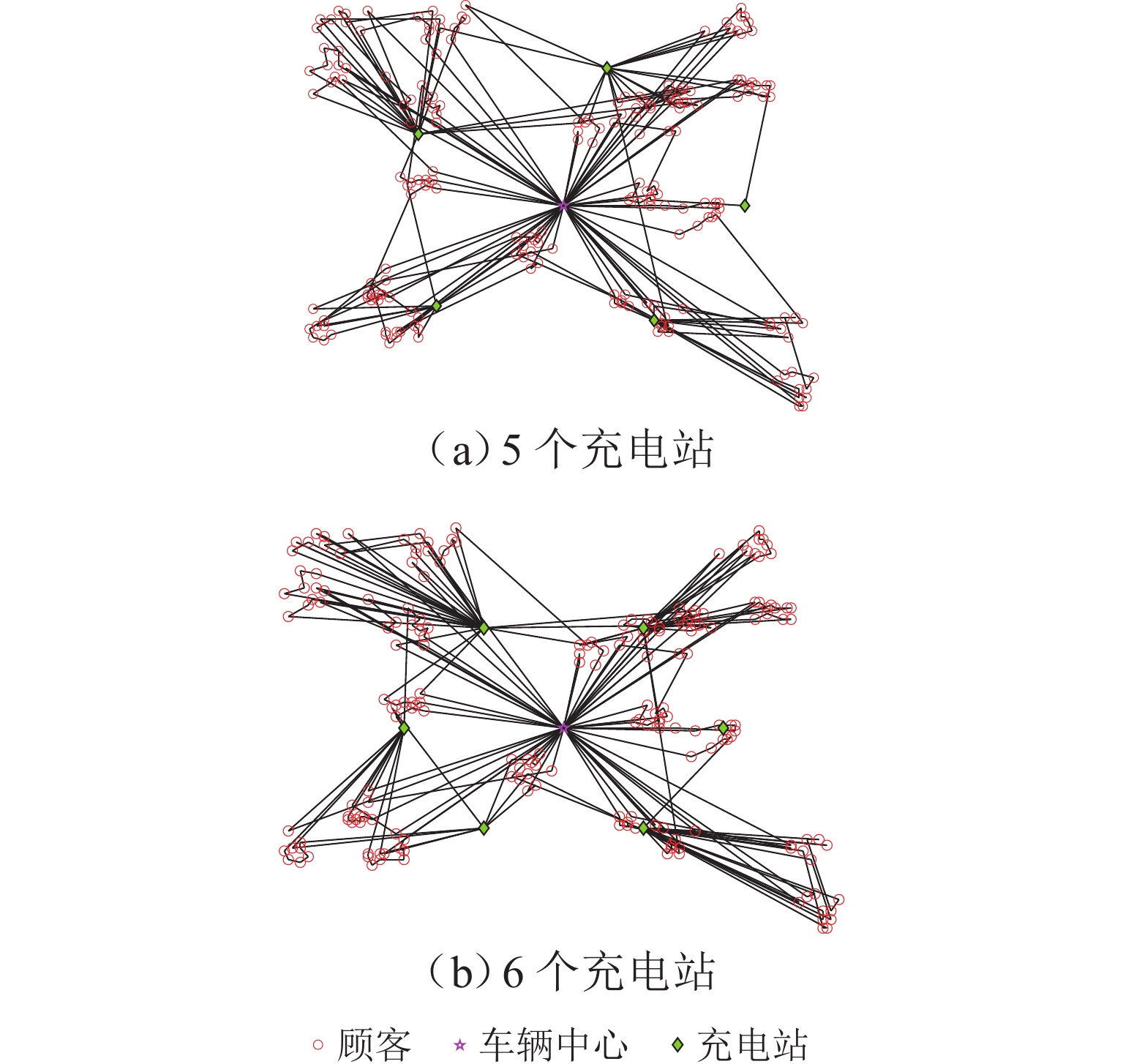
在带时间窗的电动货车路径规划问题(EVRPTW)中,电动货车(EV)在前往充电站充电时可能需要排队. 为研究不同充电站配置方案对车辆路径和系统性能的影响,首先构建排队模型,刻画充电站中的排队现象;在EVRPTW基础上,综合考虑电量和流量约束,建立路径优化模型,并将充电站排队模型嵌入其中;优化目标包括最小化车辆耗电成本、司机工资、时间窗惩罚成本、充电桩总成本;为求解该模型,提出一种结合节约里程(C-W)和改进大邻域搜索(LNS)的混合启发式算法,其中,充电站的系统性能指标采用递归算法获得. 18组实验结果表明:同步增加充电桩数量可将车辆单次充电的平均排队时间控制在1~5 min,并有效减少2.6%~21.0%的总成本;增加充电站数量可缩短排队时间,但会增加整体路径总成本;当客户时间窗较短或服务时间较长时,充电桩数量变化对时间窗满足的影响更为显著.
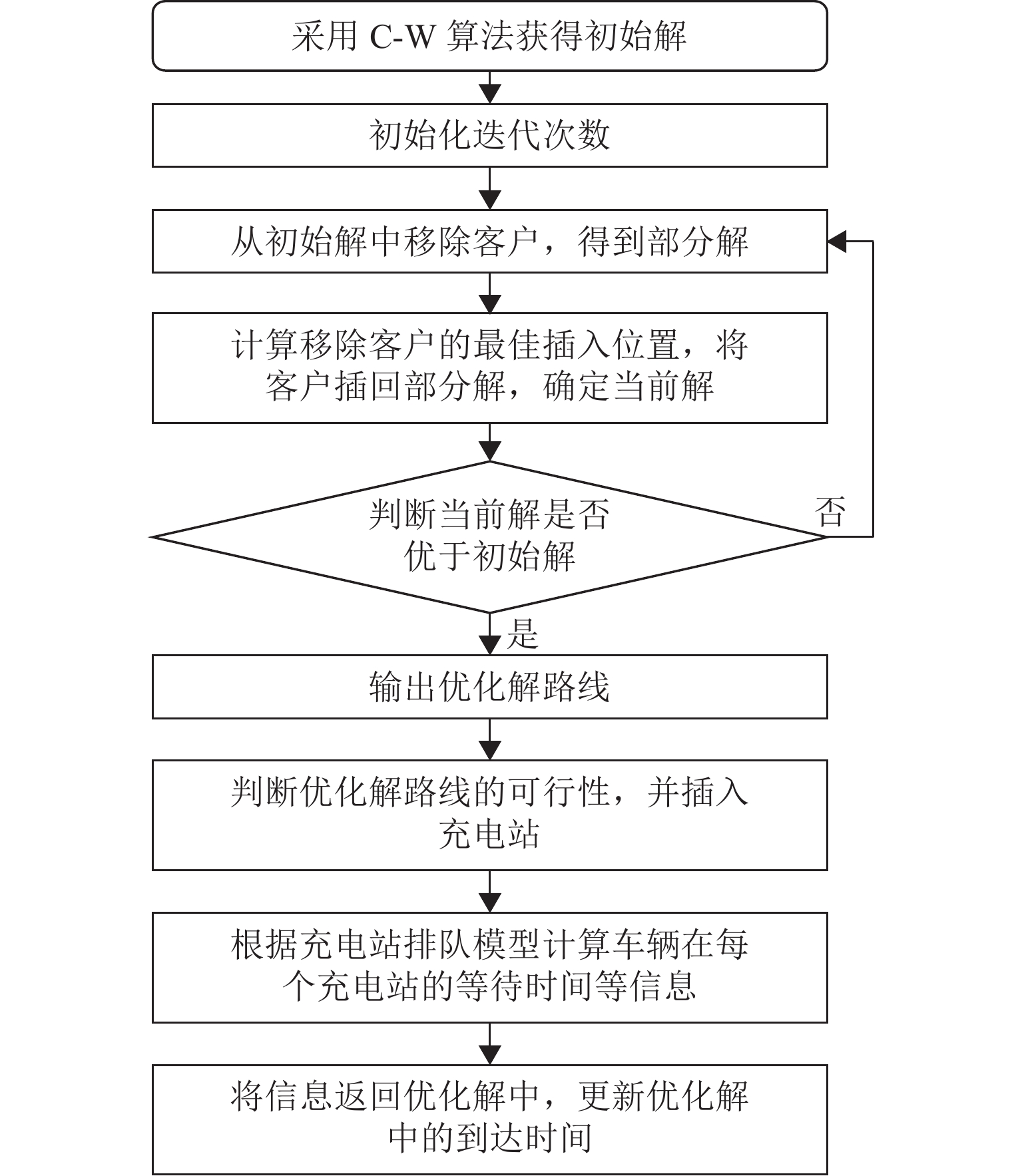
Abstract:In the electric truck route planning problem with time windows, electric trucks may need to queue up when they go to charging stations for charging. To study the impact of different charging station configuration schemes on vehicle route planning and system performance, the queuing model was first built to describe the queuing phenomenon at charging stations. Then, a route optimization model was established by considering the power and flow constraints based on the electric truck route planning problem with time windows, with the queuing model of charging stations embedded into the optimization model. The optimization goals included minimizing vehicle power consumption costs, driver’s wages, penalty costs of time windows, and total costs of all charging piles. To solve the model, a hybrid heuristic algorithm combining mileage saving (C-W) and improved large neighborhood search (LNS) was designed, and the system performance metrics of charging stations were obtained by a recursive algorithm. 18 sets of experimental results show that increasing the number of charging piles simultaneously can control the average queuing time of a vehicle for charging within 1–5 minutes and effectively reduce the total cost by 2.6%–21.0%; increasing the number of charging stations can reduce the queuing time but increase the total cost of the entire route; when the customer time window is short, or the service time is long, the change in the number of charging piles has a more significant impact on the satisfaction of the time window.
-
Key words:
- logistics /
- electric truck /
- charging station /
- hybrid heuristic algorithm /
- recursive algorithm
-
表 1 符号说明
Table 1. Symbol descriptions
符号 说明 符号 说明 ${d_{i,j}}$ 顶点$i$到顶点$j$的行驶距离 ${c_{\mathrm{s}}}$ 所有充电站安装充电桩的总费用 ${t_{i,j}}$ 顶点$i$到顶点$j$的行驶时间 ${x_{i,j}}$ 当顶点$i$与顶点$j$在有向图中的路径被访问时为1,否则为0 ${q_i}$ 客户点$i$的需求 $y_i^{\mathrm{a}}$ 到达顶点$i$时剩余电量 ${s_i}$ 客户点$i$的服务时间 $y_i^{\text{d}}$ 离开顶点$i$时剩余电量 ${e_i}$ 客户点$i$的最早服务时间 ${v_i}$ 到达顶点$i$时的迟到时长 ${l_i}$ 客户点$i$的最晚服务时间 ${a_i}$ 到达顶点$i\;(i \in {V_{0,n + 1}})$的时间 $G_0$ 车辆装载容量 ${f_i}$ 在返回仓库之前,以顶点$i$为最后访问节点的路线所花费的总时间 $Q$ 车辆电池容量 ${u_i}$ 抵达顶点$i$时的剩余货物容量 $g$ 电池充电速率 ${w_{i,k}}$ 顶点$i\;(i \in F)$进行第$k$次所服务车辆需要的等待时间 $h$ 电池单位距离消耗速率 ${{\textit{z}}_{i,k}}$ 顶点$i\;(i \in F)$进行第$k$次所服务车辆需要的充电时间 ${c_{\mathrm{e}}}$ 每单位距离消耗的电量成本 ${a_{i,k}}$ 顶点$i\;(i \in F)$第$k$次服务的车辆到达时间 ${c_{\mathrm{p}}}$ 每单位时间惩罚成本 $y_i^{\mathrm{a}}({a_{i,k}})$ 当车辆到达顶点$i$时间为${a_{i,k}}$时的剩余电量 ${c_{\mathrm{f}}}$ 每个顶点的运行成本,包括维护、购置成本以及在客户点工作的成本 ${w_{i,k}}( {a_{i,k}} )$ 当车辆到达顶点$i$时间为${a_{i,k}}$时的等待时间 ${c_{\mathrm{d}}}$ 每单位时间司机工资 -
[1] 袁庆达,杜文,周再玲. 带软时间窗的混合车队车辆路线问题的模型和算法研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2001,36(4): 401-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2001.04.015YUAN Qingda, DU Wen, ZHOU Zailing. Model and algorithms for mixed fleet vehicle routing problem with soft time windows[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2001, 36(4): 401-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2001.04.015 [2] SCHNEIDER M, STENGER A, GOEKE D. The electric vehicle-routing problem with time windows and recharging stations[J]. Transportation Science, 2014, 48(4): 500-520. doi: 10.1287/trsc.2013.0490 [3] DESAULNIERS G, ERRICO F, IRNICH S, et al. Exact algorithms for electric vehicle-routing problems with time windows[J]. Operations Research, 2016, 64(6): 1388-1405. doi: 10.1287/opre.2016.1535 [4] GOEKE D. Granular tabu search for the pickup and delivery problem with time windows and electric vehicles[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 278(3): 821-836. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.05.010 [5] PELLETIER S, JABALI O, LAPORTE G. The electric vehicle routing problem with energy consumption uncertainty[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2019, 126: 225-255. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2019.06.006 [6] CORTÉS-MURCIA D L, PRODHON C, MURAT AFSAR H. The electric vehicle routing problem with time windows, partial recharges and satellite customers[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2019, 130: 184-206. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2019.08.015 [7] DOPPSTADT C, KOBERSTEIN A, VIGO D. The hybrid electric vehicle–traveling salesman problem with time windows[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 284(2): 675-692. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.12.031 [8] KESKIN M, ÇATAY B, LAPORTE G. A simulation-based heuristic for the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows and stochastic waiting times at recharging stations[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2021, 125: 105060.1-105060.15. [9] YANG S Y, NING L J, TONG L C, et al. Optimizing electric vehicle routing problems with mixed backhauls and recharging strategies in multi-dimensional representation network[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 176: 114804.1-114804.48. [10] YAO C Q, CHEN S B, YANG Z Y. Joint routing and charging problem of multiple electric vehicles: a fast optimization algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 8184-8193. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3076601 [11] KESKIN M, ÇATAY B. Partial recharge strategies for the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 65: 111-127. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2016.01.013 [12] 葛显龙,竹自强. 带软时间窗的电动车辆路径优化问题[J]. 工业工程与管理,2019,24(4): 96-104,112.GE Xianlong, ZHU Ziqiang. The electric vehicles routing problem with soft time window[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2019, 24(4): 96-104,112. [13] XIAO Y Y, KONAK A. The heterogeneous green vehicle routing and scheduling problem with time-varying traffic congestion[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2016, 88: 146-166. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2016.01.011 [14] XU Z T, ELOMRI A, POKHAREL S, et al. A model for capacitated green vehicle routing problem with the time-varying vehicle speed and soft time windows[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 137: 106011.1-106011.14. [15] ZULVIA F E, KUO R J, NUGROHO D Y. A many-objective gradient evolution algorithm for solving a green vehicle routing problem with time windows and time dependency for perishable products[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 242: 118428.1-118428.14. [16] MONTOYA A, GUÉRET C, MENDOZA J E, et al. The electric vehicle routing problem with nonlinear charging function[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2017, 103: 87-110. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2017.02.004 [17] ZUO X R, XIAO Y Y, YOU M, et al. A new formulation of the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows considering concave nonlinear charging function[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 236: 117687.1-117687.18. [18] FROGER A, MENDOZA J E, JABALI O, et al. Improved formulations and algorithmic components for the electric vehicle routing problem with nonlinear charging functions[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2019, 104: 256-294. [19] POONTHALIR G, NADARAJAN R. Green vehicle routing problem with queues[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 138: 112823.1-112823.18. [20] KESKIN M, LAPORTE G, ÇATAY B. Electric vehicle routing problem with time-dependent waiting times at recharging stations[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2019, 107: 77-94. [21] SHAW P. Using constraint programming and local search methods to solve vehicle routing problems[M]// GOEBEL R, WAHLSTER W, ZHOU Z H. Lecture notes in computer science. Berlin:Springer, 1998:417-431. [22] 刘小兰,郝志峰,汪国强,等. 有时间窗的车辆路径问题的近似算法研究[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2004,10(7): 825-831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5911.2004.07.019LIU Xiaolan, HAO Zhifeng, WANG Guoqiang, et al. Improved large neighborhood search algorithm for vehicle routing problem with time windows[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2004, 10(7): 825-831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5911.2004.07.019 [23] SINTEF Digital. Transportation optimization portal [DB/OL]. (2008-02-27)[2023-02-19]. https://www.sintef.no/projectweb/top/vrptw. [24] KESKIN M, ÇATAY B. A matheuristic method for the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows and fast chargers[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2018, 100: 172-188. [25] EMEÇ U, ÇATAY B, BOZKAYA B. An adaptive large neighborhood search for an E-grocery delivery routing problem[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2016, 69: 109-125. -




 下载:
下载: