Collaborative Computing Method for Highly Available Operation of Digital Twin Manufacturing Equipment
-
摘要:
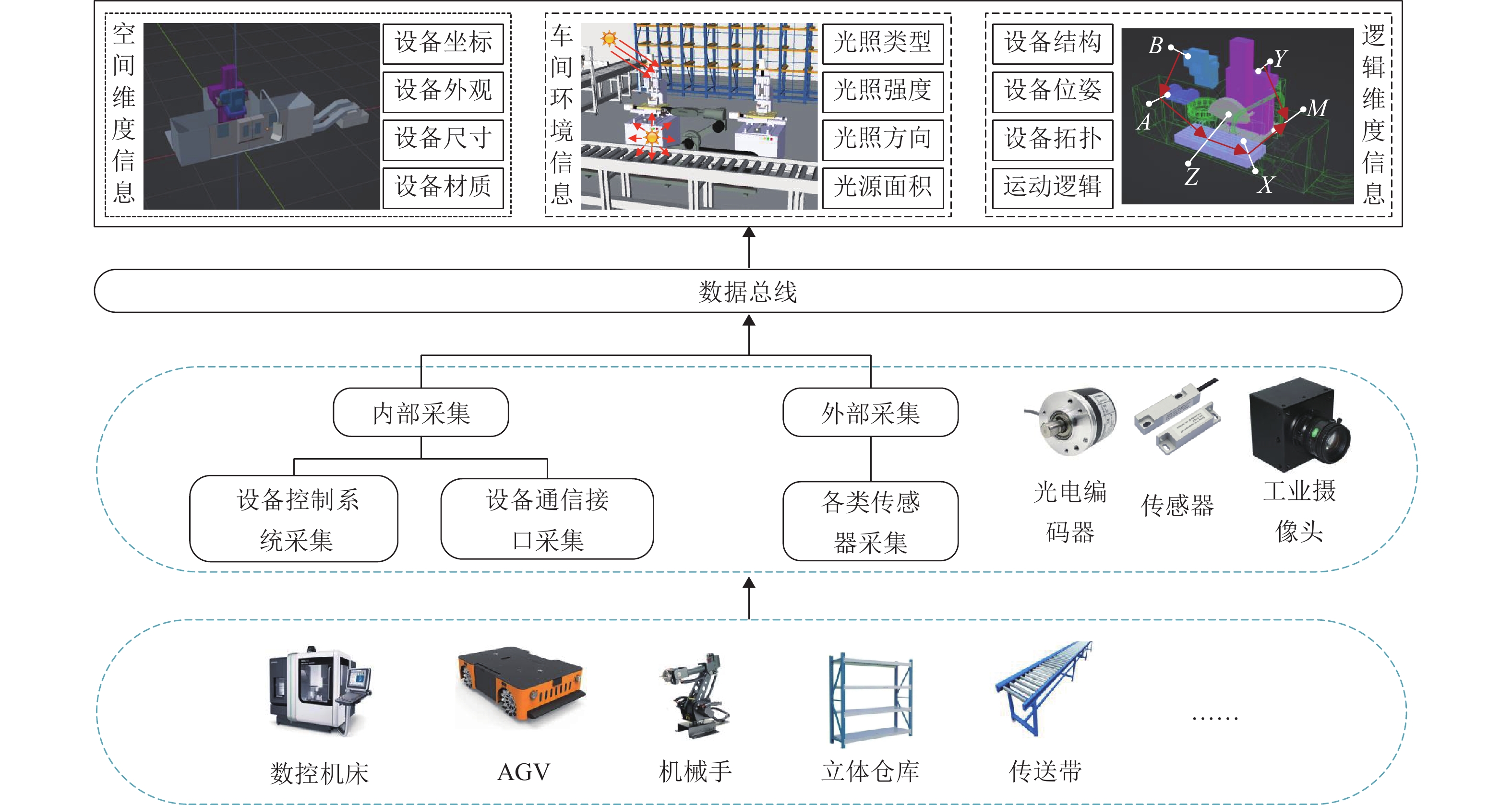
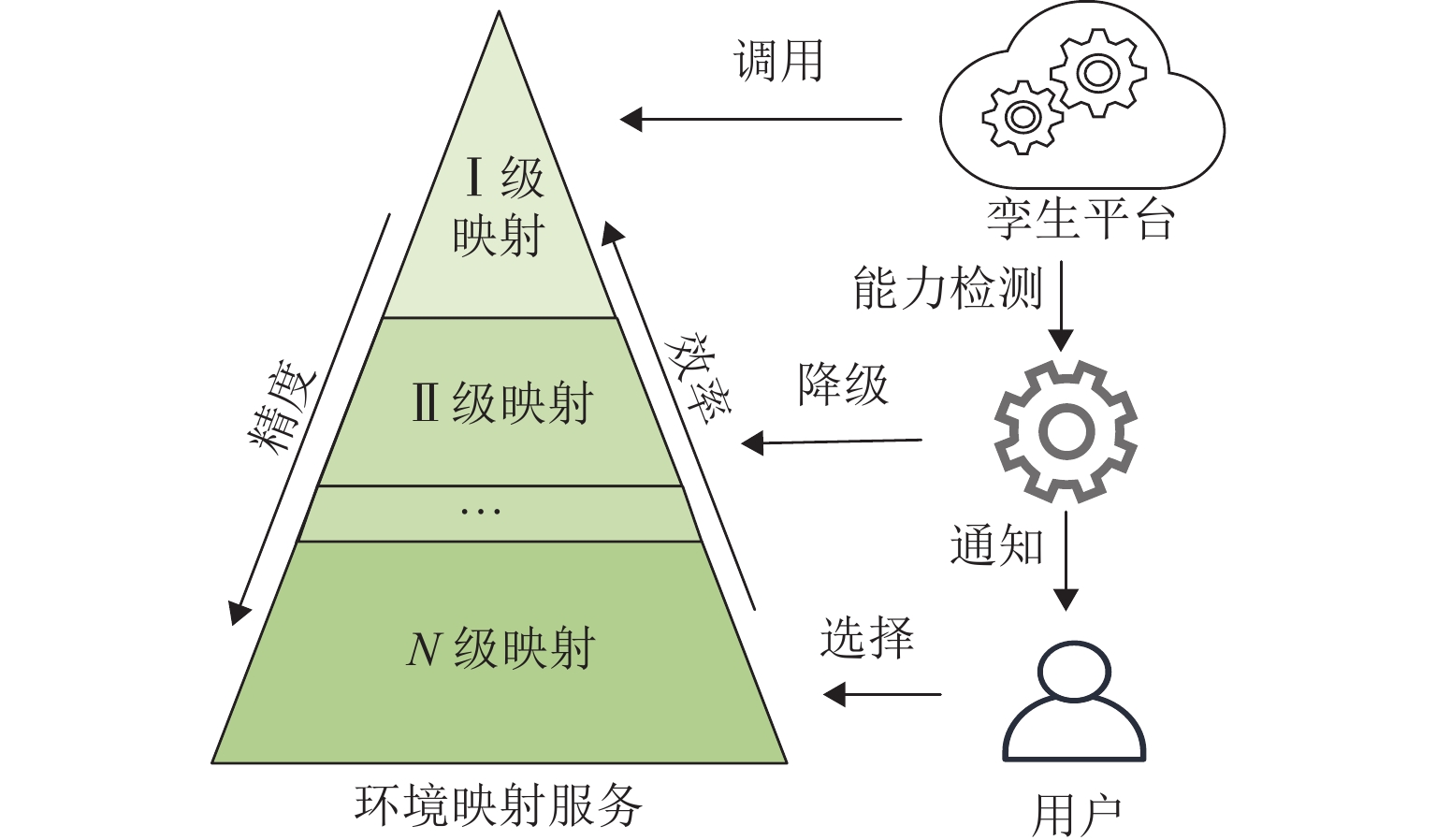
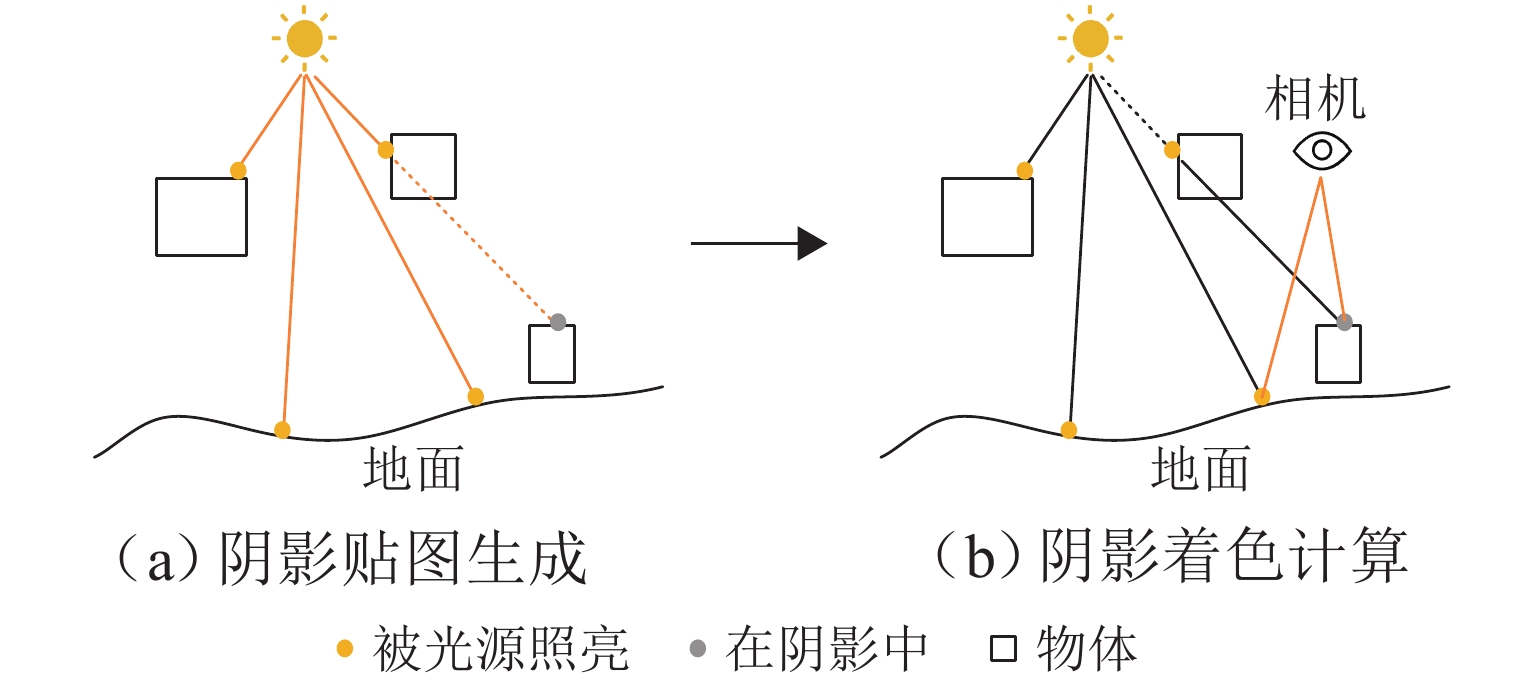
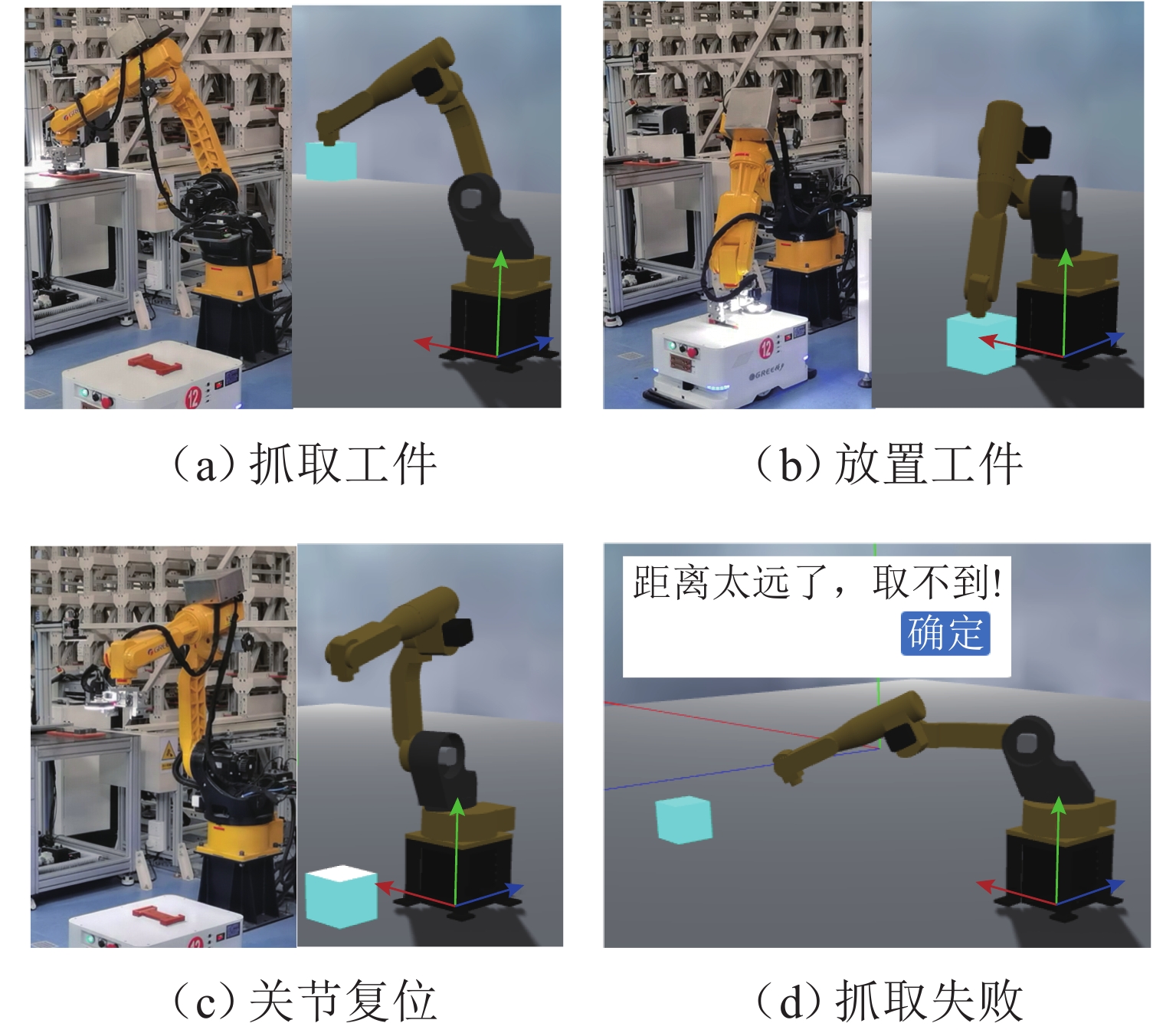
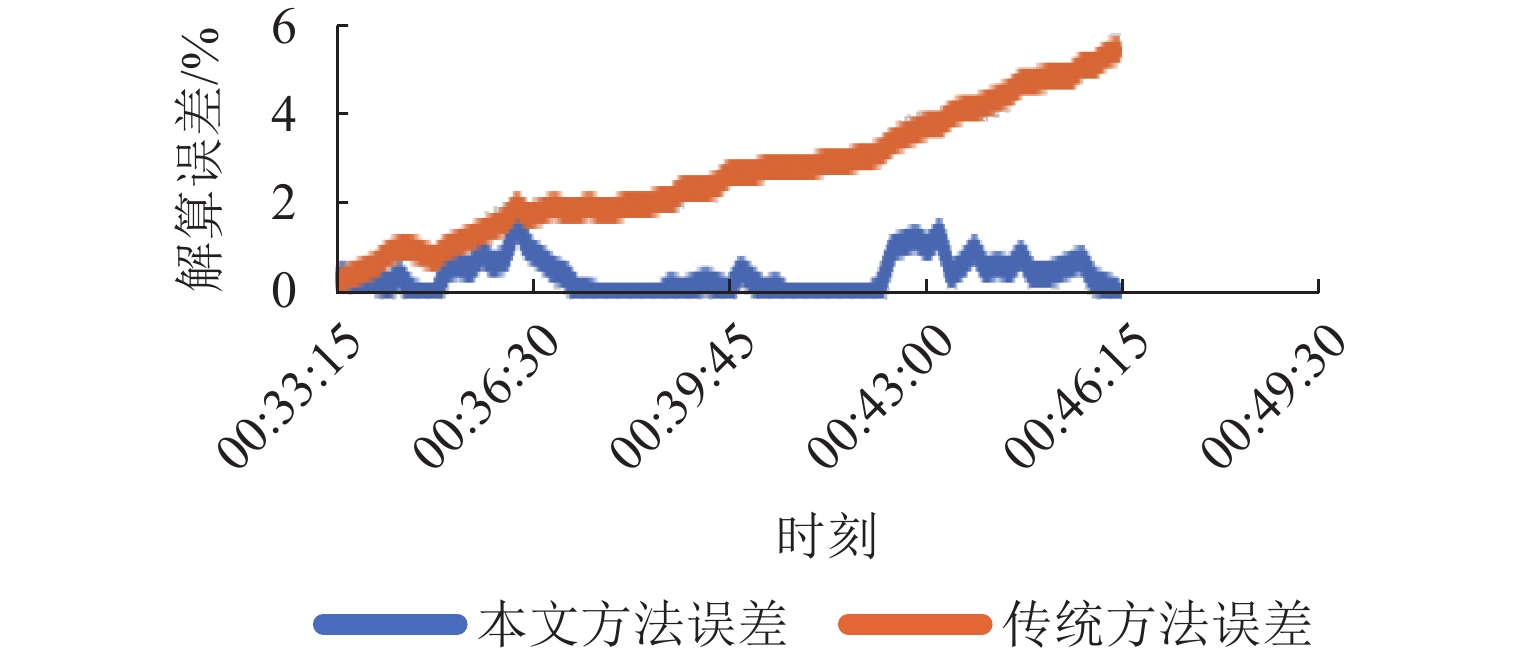
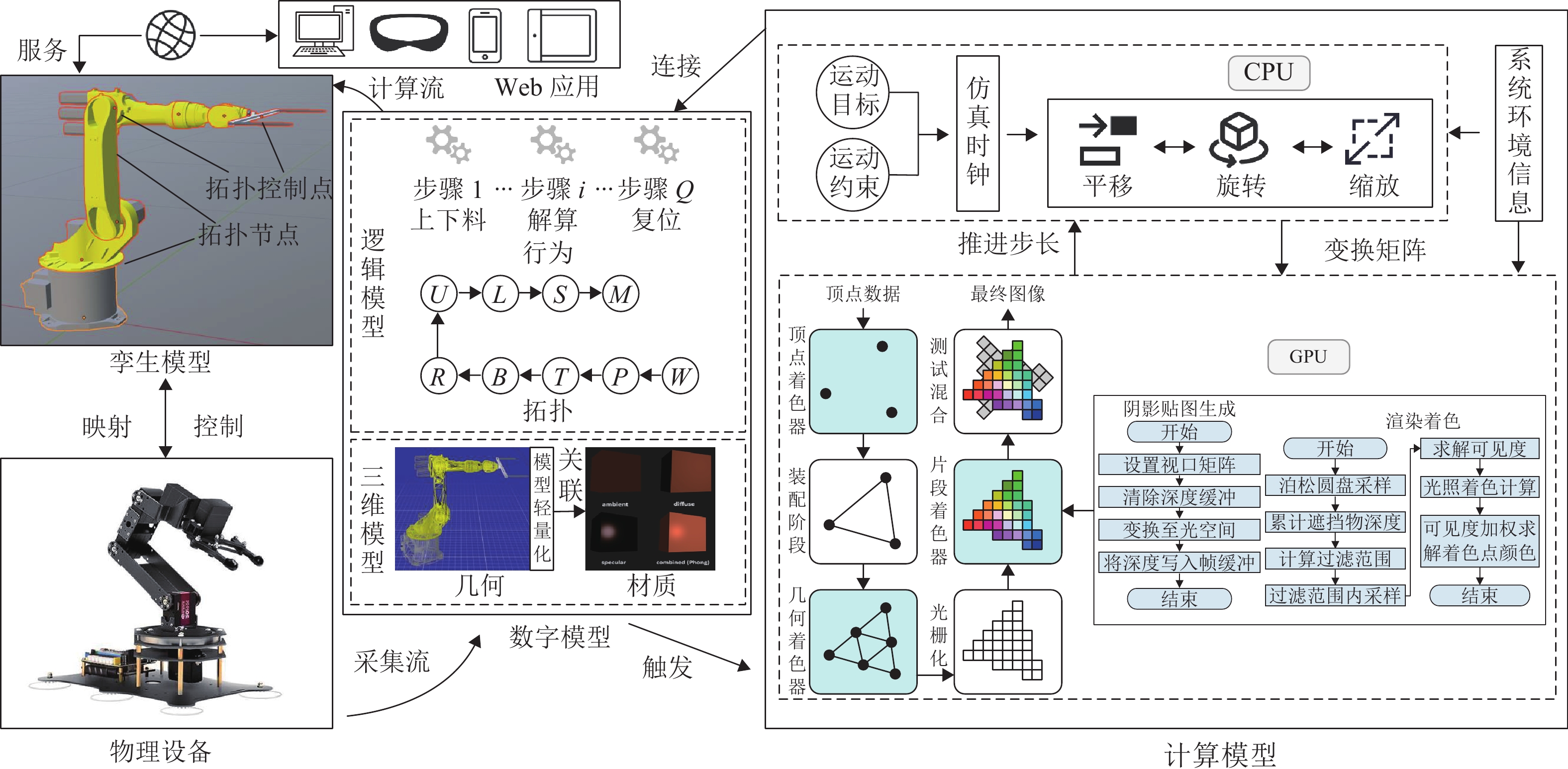
在数字孪生技术中,复杂模型和生产逻辑的运行会消耗大量资源,且硬件能力与用户需求存在差异,进而导致模拟精度和实时性难以得到保证,降低系统可用性. 为此,提出一种可视化与逻辑运算协同处理的数字孪生制造装备实时同步计算框架. 首先,根据车间多维度信息构建设备数字模型,考虑硬件能力和用户个性化计算需求,提出可配置、自适应的系统环境映射方法以修正模拟保真度,确保孪生装备的实时准确运行,并以光照环境映射为例说明其流程;然后,提出基于仿真的六自由度机械手运动逻辑解算算法,将渲染帧时作为仿真时钟推进步长,保证模型运动准确以及可视化与解算同步,并将算法泛化,以应用到其他多体设备中;最后,基于Web设计并开发数字孪生车间建模仿真云平台,以六自由度机械手与某转向架构架加工车间为应用对象对所提方法进行验证. 结果表明:随着映射保真度自适应下降,模拟响应速度提升45%,同时GPU和CPU的资源利用率有效降低;证明本文所提方法可实现资源合理配置与系统高效计算,并减少误差累计,是一种高可用的实时协同计算方法.
Abstract:In digital twin technology, the operation of complex models and production logic consumes a large number of resources. Meanwhile, differences in hardware capabilities and user requirements make it difficult to ensure simulation accuracy and real-time performance, reducing system availability. To address this issue, a real-time synchronous computing framework for digital twin manufacturing equipment that collaboratively processed visualization and logic computation was proposed. Firstly, a digital model of the equipment was constructed based on multidimensional workshop information. According to hardware capabilities and users’ personalized computational needs, a configurable and adaptive system environment mapping method was introduced to adjust simulation fidelity, ensuring the real-time and correct operation of the twin equipment. The process was illustrated by using lighting environment mapping as an example. Secondly, a simulation-based motion logic solving algorithm for a six-degree-of-freedom (6-DOF) manipulator was presented, which used the rendering frame time as the simulation clock advancement step to ensure accurate model motion and synchronization between visualization and computation. The algorithm was generalized for application to other multi-body equipment. Finally, a Web-based digital twin workshop modeling and simulation cloud platform was designed and developed. A 6-DOF manipulator and a specific bogie frame processing workshop were used as application cases, and the proposed method was validated. The results show that with the adaptive reduction of mapping fidelity, simulation response speed is increased by 45%, while GPU and CPU resource utilization is effectively reduced. It proves that the method can achieve reasonable resource allocation and efficient system computation while reducing error accumulation, making it a highly available real-time collaborative computing method.
-
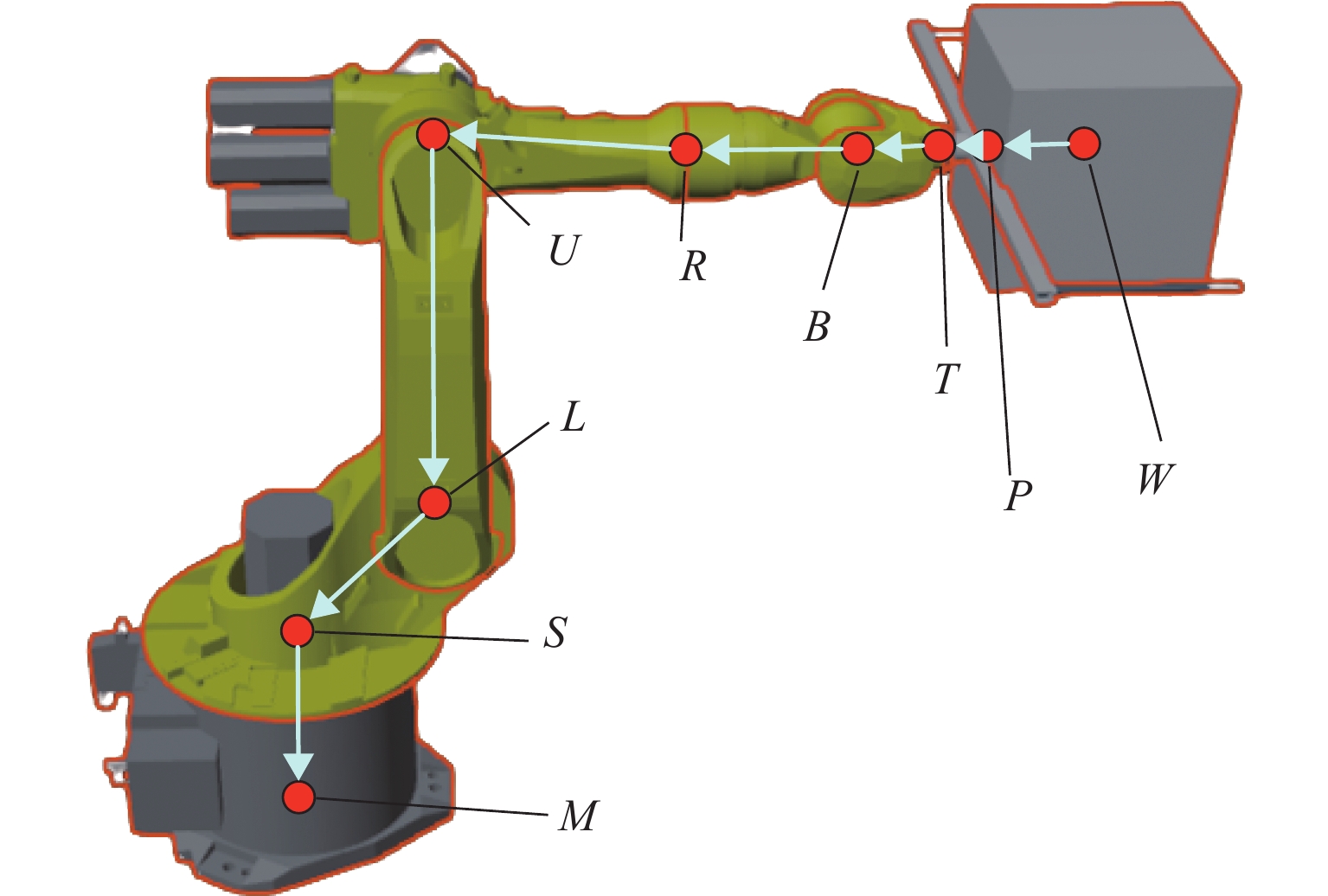
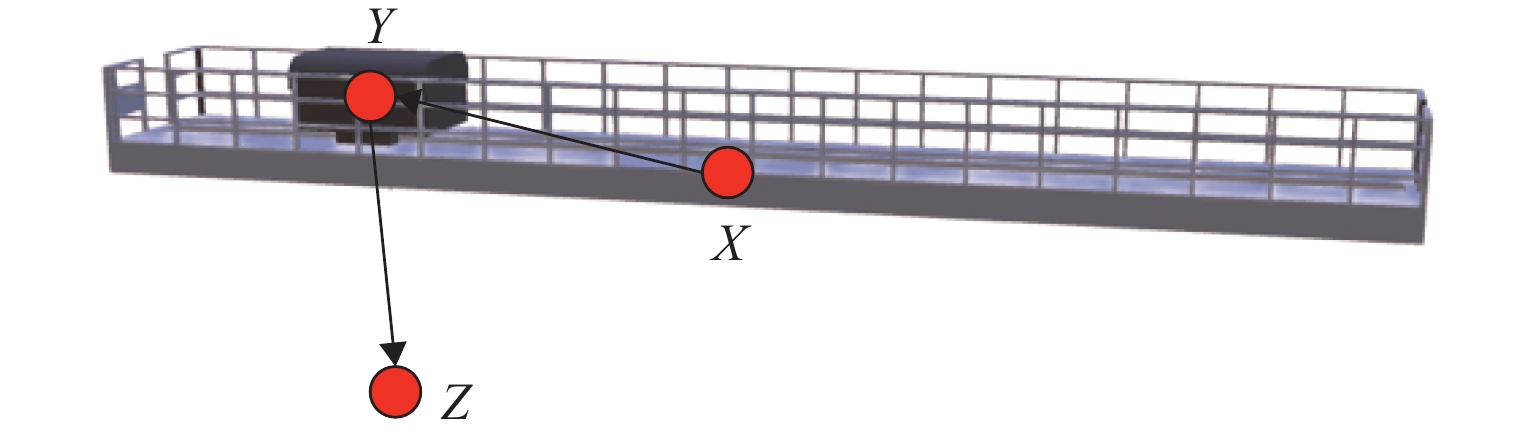
表 1 六自由度机械手拓扑节点定义
Table 1. Topological node definition of 6-DOF manipulator
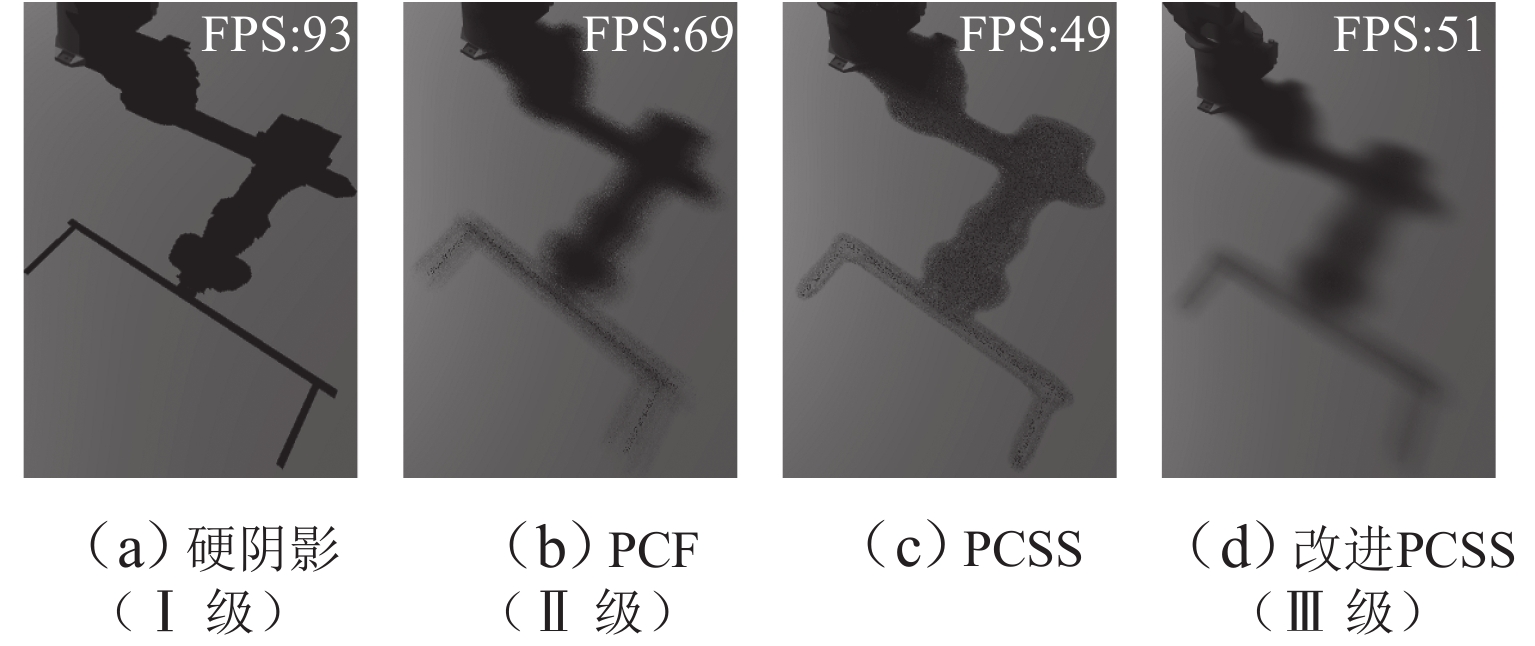
拓扑节点名称 运动类型 旋转轴(局部坐标) M 静止 S 旋转 y L 旋转 z U 旋转 z R 旋转 x B 旋转 z T 旋转 x P 跟随 W 跟随 表 2 映射服务等级与系统运行效率对比表
Table 2. Comparison of mapping service level and system operation efficiency
等级 帧率/
(帧•s−1)步长/
msCPU 利用率/% GPU 利用率/% 方法 1 方法 2 方法 1 方法 2 Ⅰ级 93 10.75 62.8 28.3 2.3 26.9 Ⅱ级 69 14.49 67.0 29.5 2.7 38.7 Ⅲ级 51 19.60 91.3 31.5 3.8 55.2 -
[1] 陶飞,刘蔚然,刘检华,等. 数字孪生及其应用探索[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2018,24(1): 1-18.TAO Fei, LIU Weiran, LIU Jianhua, et al. Digital twin and its potential application exploration[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 24(1): 1-18. [2] 周济. 智能制造—“中国制造2025” 的主攻方向[J]. 中国机械工程,2015,26(17): 2273-2284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2015.17.001ZHOU Ji. Intelligent manufacturing-main direction of “made in China 2025”[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 26(17): 2273-2284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2015.17.001 [3] 江海凡,丁国富,张剑. 数字孪生车间演化机理及运行机制[J]. 中国机械工程,2020,31(7): 824-832,841. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.07.008JIANG Haifan, DING Guofu, ZHANG Jian. Evolution and operation mechanism of digital twin shopfloors[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(7): 824-832,841. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.07.008 [4] JONES D, SNIDER C, NASSEHI A, et al. Characterising the digital twin: a systematic literature review[J]. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2020, 29: 36-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.02.002 [5] LIU M N, FANG S L, DONG H Y, et al. Review of digital twin about concepts, technologies, and industrial applications[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 58: 346-361. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2020.06.017 [6] TAO F, ZHANG H, LIU A, et al. Digital twin in industry: state-of-the-art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(4): 2405-2415. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2873186 [7] 陶飞,张贺,戚庆林,等. 数字孪生模型构建理论及应用[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2021,27(1): 1-15.TAO Fei, ZHANG He, QI Qinglin, et al. Theory of digital twin modeling and its application[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 27(1): 1-15. [8] QI Q L, TAO F. Digital twin and big data towards smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 degree comparison[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 3585-3593. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2793265 [9] JIANG H F, QIN S F, FU J L, et al. How to model and implement connections between physical and virtual models for digital twin application[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 58: 36-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2020.05.012 [10] KONG T X, HU T L, ZHOU T T, et al. Data construction method for the applications of workshop digital twin system[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 58: 323-328. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2020.02.003 [11] 李浩,王昊琪,刘根,等. 工业数字孪生系统的概念、系统结构与运行模式[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2021,27(12): 3373-3390.LI Hao, WANG Haoqi, LIU Gen, et al. Concept, system structure and operating mode of industrial digital twin system[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 27(12): 3373-3390. [12] SCHROEDER G, STEINMETZ C, PEREIRA C E, et al. Visualising the digital twin using web services and augmented reality[C]//2016 IEEE 14th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN). Poitiers: IEEE, 2016: 522-527. [13] 施佳宏,刘晓军,刘庭煜,等. 面向生产线仿真的数字孪生逻辑模型构建方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统,2022,28(2): 442-454.SHI Jiahong, LIU Xiaojun, LIU Tingyu, et al. Method of digital twin logic model oriented to production line simulation[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 28(2): 442-454. [14] HU L W, NGUYEN N T, TAO W J, et al. Modeling of cloud-based digital twins for smart manufacturing with MT connect[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2018, 26: 1193-1203. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.155 [15] 李莎莎,舒亮,杨艳芳,等. 逻辑与模型数据并行计算的数字孪生车间系统快速架构方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2021,57(17): 76-85. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.17.076LI Shasha, SHU Liang, YANG Yanfang, et al. Digital twin workshop system rapid construction method based on parallel computing of logic and model data[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(17): 76-85. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.17.076 [16] LIU C, JIANG P Y, JIANG W L. Web-based digital twin modeling and remote control of cyber-physical production systems[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2020, 64: 101956.1-101956.16. [17] ZHENG P, SIVABALAN A S. A generic tri-model-based approach for product-level digital twin development in a smart manufacturing environment[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2020, 64: 101958.1-101958.12. [18] BRODTKORB A R, HAGEN T R, SÆTRA M L. Graphics processing unit (GPU) programming strategies and trends in GPU computing[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2013, 73(1): 4-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2012.04.003 [19] GARLAND M, HECKBERT P S. Simplifying surfaces with color and texture using quadric error metrics[C]//Visualization. North Carolina: IEEE, 1998: 263-269. [20] Google. Draco 3D data compression[EB/OL]. (2014-01-14)[2023-01-08]. https://github.com/google/draco. [21] ZHANG L, ZHOU L F, HORN B K P. Building a right digital twin with model engineering[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 59: 151-164. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.02.009 [22] 卢荣胜,吴昂,张腾达,等. 自动光学(视觉)检测技术及其在缺陷检测中的应用综述[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(8): 23-58. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0815002LU Rongsheng, WU Ang, ZHANG Tengda, et al. Review on automated optical (visual) inspection and its applications in defect detection[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(8): 23-58. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0815002 [23] REEVES W T, SALESIN D H, COOK R L. Rendering antialiased shadows with depth maps[J]. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1987, 21(4): 283-291. doi: 10.1145/37402.37435 [24] FERNANDO R. Percentage-closer soft shadows[C]//Association for Computing Machinery. New York:ACM, 2005: 1-38. [25] YANG B G, DONG Z, FENG J Q, et al. Variance soft shadow mapping[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2010, 29(7): 2127-2134. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2010.01800.x [26] 丁国富,邹益胜,张卫华,等. 基于虚拟原型的机械多体系统建模可视化[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2006,18(6): 793-799. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.06.007DING Guofu, ZOU Yisheng, ZHANG Weihua, et al. Visualized modeling of multi-body mechanical system based on virtual prototyping[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2006, 18(6): 793-799. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9775.2006.06.007 [27] BYRNE J, HEAVEY C, BYRNE P J. A review of Web-based simulation and supporting tools[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2010, 18(3): 253-276. doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2009.09.013 -




 下载:
下载: