Simulation of Dynamic Coupling of Metro-Earth-Grid for DC Interference in Rail Transit
-
摘要:
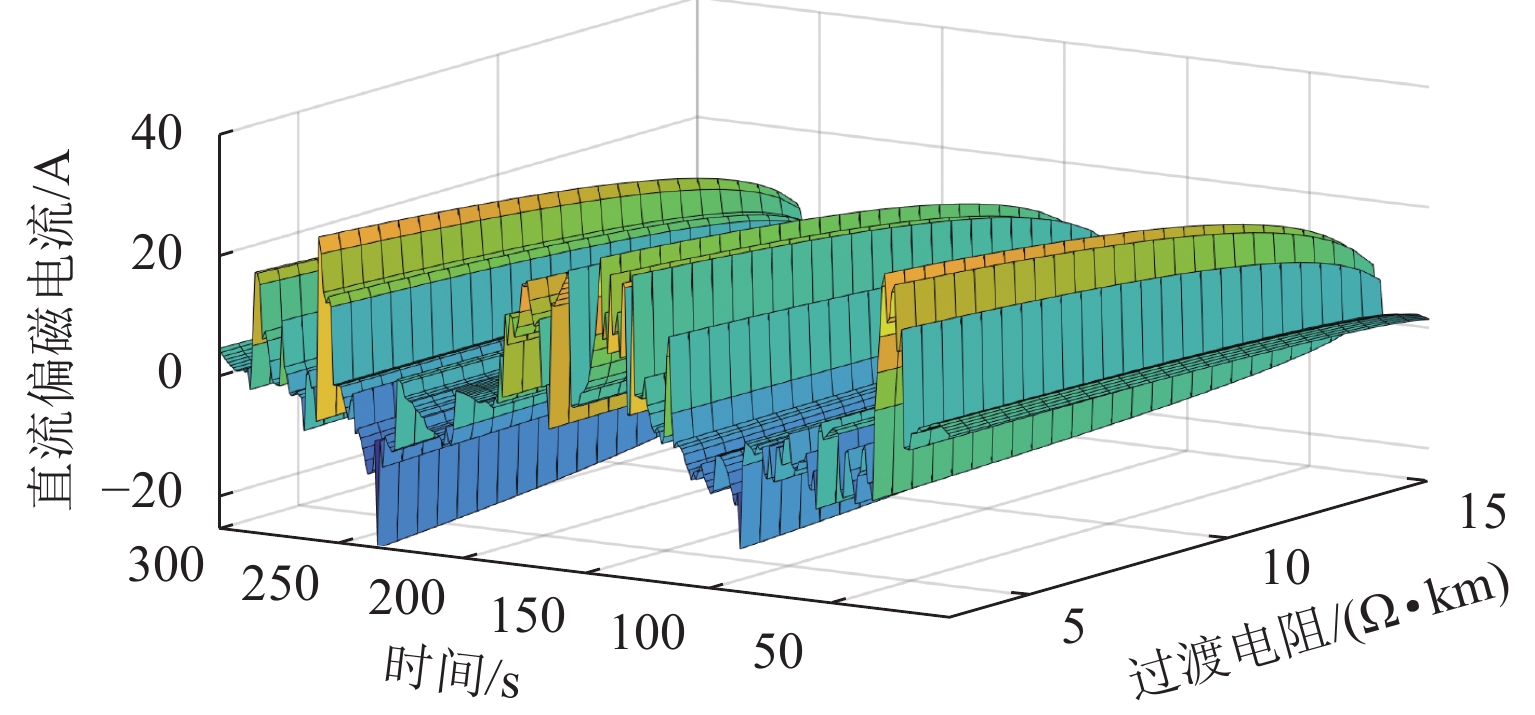
针对中性点接地变压器直流偏磁电流受轨道交通动态杂散电流泄漏和段场接地影响的问题,综合考虑多列车运行工况,建立杂散电流分布扩散的车-地-网耦合模型,并采用复镜像法计算大地电位;定义接地网的自电阻系数和互电阻系数,建立直流偏磁电流与大地电位的耦合关系,根据杂散电流侵入路径的拓扑结构,构建大地电位和直流偏磁电流的场路耦合模型;设计轨道交通杂散电流侵入电网的缩比模拟试验,并通过试验与模型计算进行验证. 研究结果表明:试验结果和模型计算之间的最大误差为8.41%;钢轨对地过渡电阻从3.00 Ω·km增大到15.00 Ω·km,直流偏磁电流的绝对平均值减小82.4%;在车辆段和正线之间采用阻断式连接装置比采用单向导通装置减小23.45%的直流偏磁电流.
Abstract:In response to the problem that direct current (DC) bias current of neutral grounded transformer is affected by dynamic stray current leakage and depot grounding of rail transit, a metro-earth-grid coupling model of stray current distribution and diffusion under multi-train operation was proposed, and the complex image method was used to calculate the earth potential. The self and mutual resistance coefficients of grounding grids were defined, and the coupling relationship between DC bias current and earth potential was proposed. The field-circuit coupling model of earth potential and DC bias current was built according to the topology of stray current intrusion path. A scaled-down simulation test of stray current intrusion into the grid for rail transit was designed, and tests and model calculation were conducted for verification. The results show that the maximum error between the experimental data and the model calculation data is 8.41%. The rail-to-earth transition resistance increases from 3.00 Ω·km to 15.00 Ω·km, and the absolute average of DC bias current decreases by 82.4%. Using a blocking connection device between the car depot and the main line can reduce DC bias current by 23.45% compared with using a unidirectional conduction device.
-
Key words:
- DC traction power supply system /
- stray current /
- DC magnetic bias
-
表 1 直流偏磁电流模拟试验主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of DC bias current simulation test
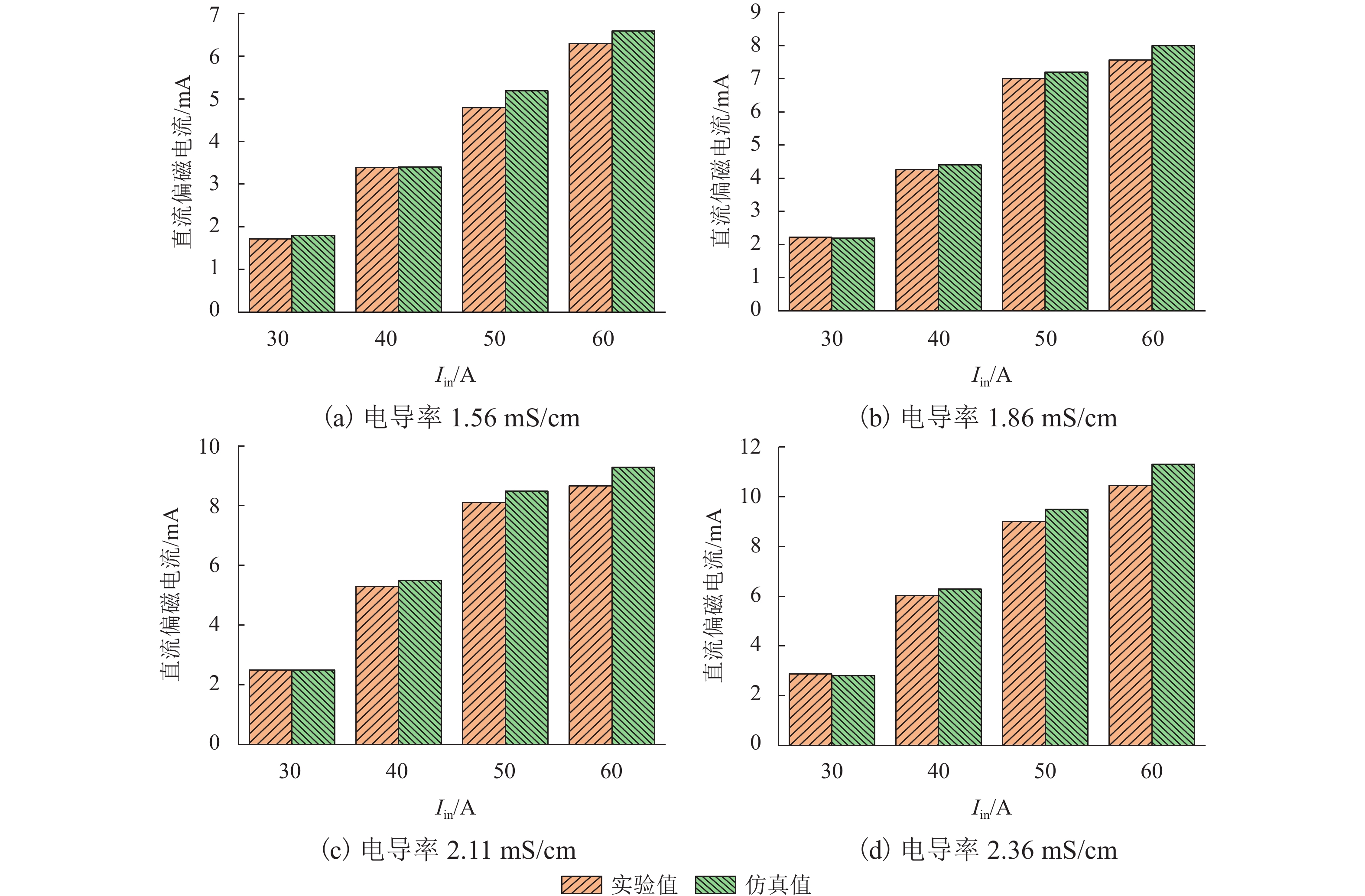
参数 数值 铜网深度/mm 10 石墨棒深度/mm 10 接地模块线路电阻/Ω 0.018 盐溶液电导率/(mS·cm−1) 1.56,1.86,2.11,2.36 石墨棒载流/A 30,40,50,60 表 2 变电所的位置坐标
Table 2. Location coordinates of substations
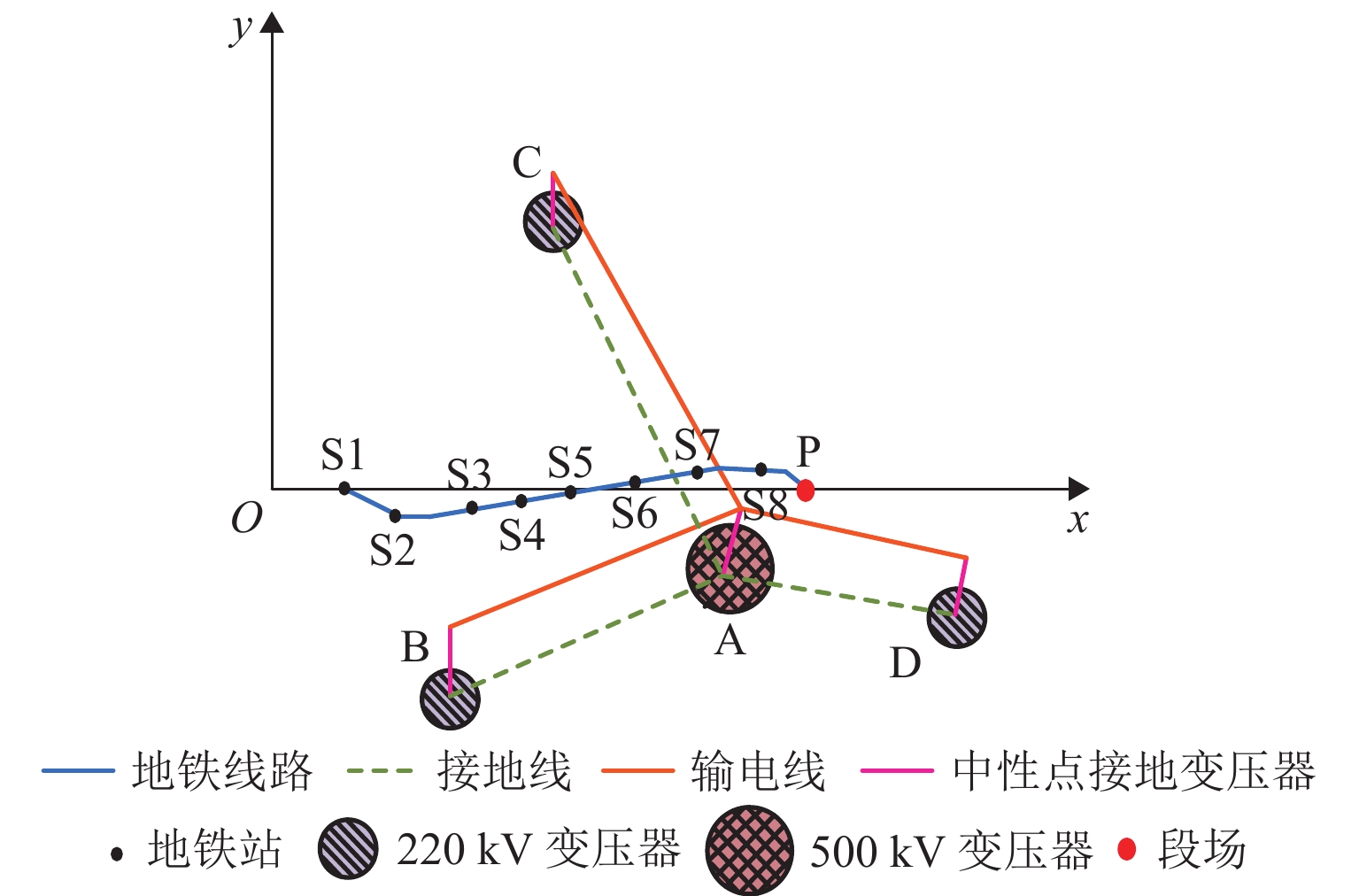
变电所 A B C D 坐标 (10,−2) (4,−5) (6,7) (15,−4) 表 3 模型的主要参数
Table 3. Main parameters of the model
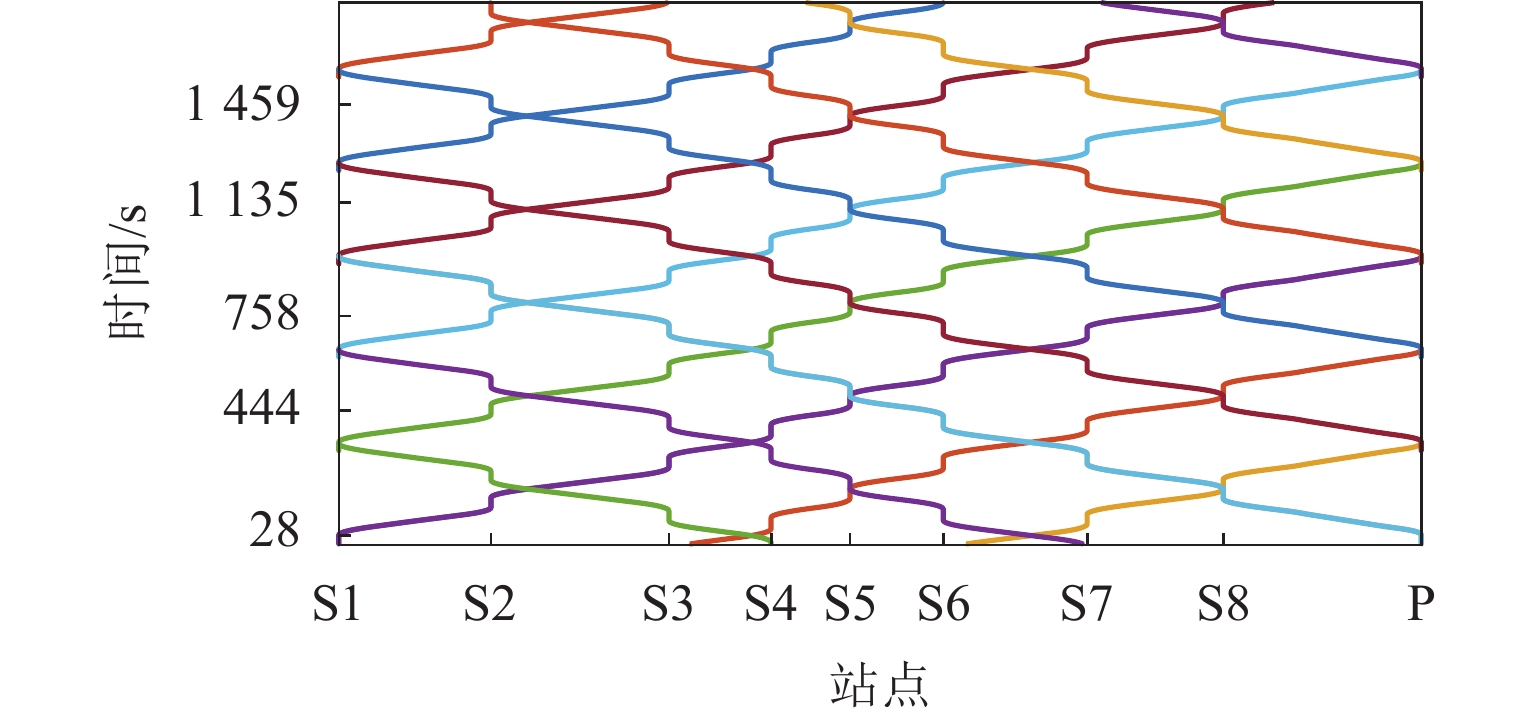
模型 参数 数值 直流地铁线路 一行钢轨电阻/(Ω·km−1) 0.018 SCCN 电阻/(Ω·km−1) 0.066 SCCN 埋地深度/m 0.6 钢轨对地过渡电阻/(Ω·km) 5.5 钢轨电位限制器接地电阻/Ω 0.04 发车间隔/s 300 停站时间/s 30 交流电网系统 接地网接地电阻/Ω 2 接地网埋地深度/m 0.8 避雷线/(Ω·km−1) 0.5 500 kV 变压器阻抗/Ω 1 220 kV 变压器阻抗/Ω 2 500 kV 变压器额定容量/(MV·A) 750 220 kV 变压器额定容量/(MV·A) 240 500 kV 变压器直流偏磁电流允许值/A 18.2 220 kV 变压器直流偏磁电流允许值/A 13.2 输电线路阻抗/(Ω·km−1) 0.01 土壤模型 混凝土/(Ω·m) 180 土壤/(Ω·m) 100 混凝土厚度/m 1 表 4 直流偏磁电流峰值的仿真值与计算值对比
Table 4. Comparison of simulation data and calculation data of peak DC bias current
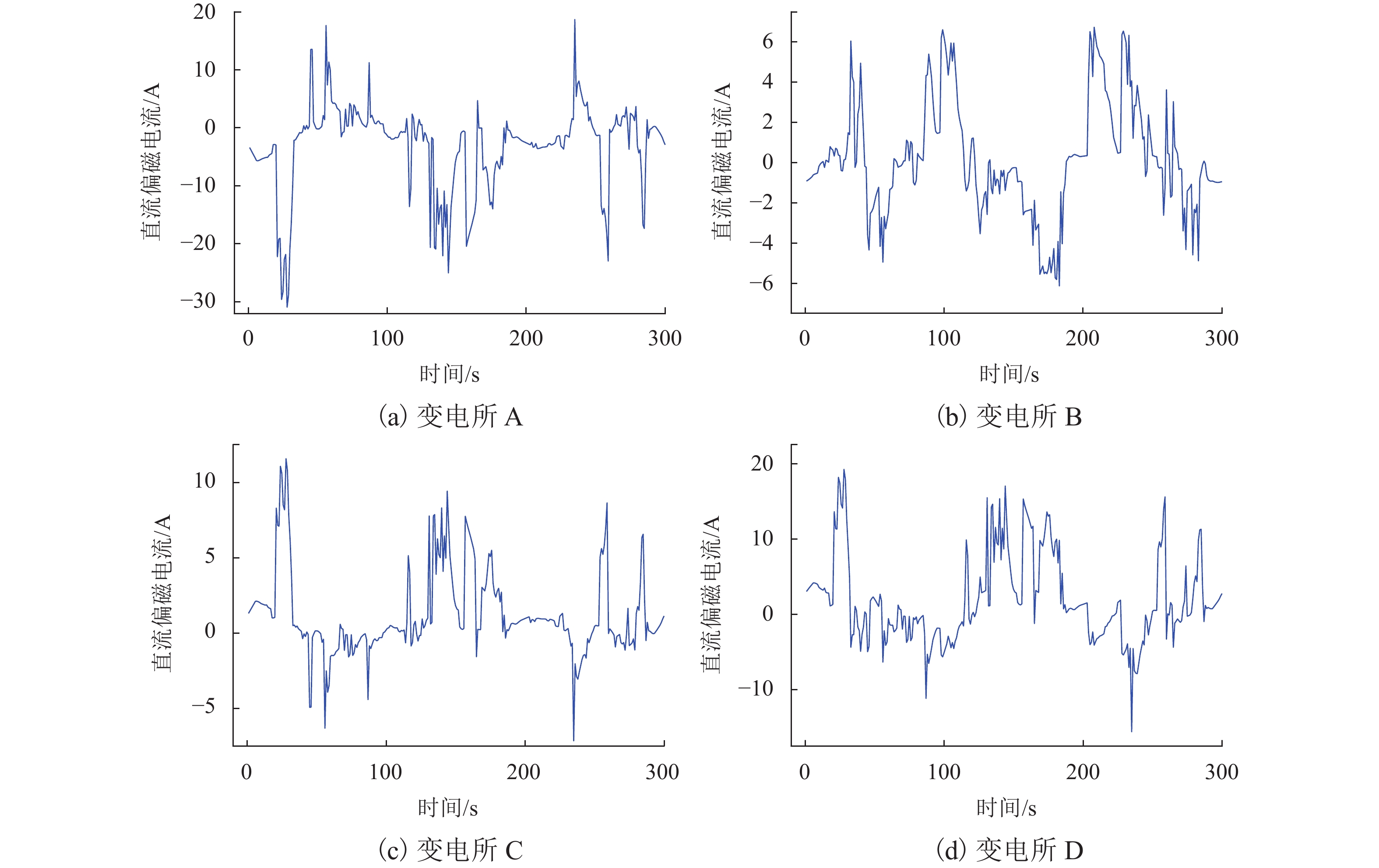
时间/s 变电所 计算数据/A 仿真数据/A 误差/% 28 A 30.94 31.30 1.16 B 0.14 0.15 7.14 C 11.57 10.94 5.45 D 19.23 18.37 4.47 144 A 25.04 23.95 4.35 B 1.39 1.27 8.63 C 9.42 8.84 6.16 D 17.02 16.22 4.70 158 A 19.36 20.44 5.58 B 2.44 2.21 9.43 C 7.34 7.16 2.45 D 14.47 15.25 5.39 235 A 18.67 17.69 5.25 B 4.07 3.81 6.39 C 7.15 7.26 1.54 D 15.60 15.27 2.12 259 A 22.99 22.63 1.57 B 1.23 1.12 8.94 C 8.64 8.03 7.06 D 15.59 16.56 5.86 表 5 不同发车间隔下直流偏磁电流的特征值
Table 5. Characteristic values of DC bias current at different departure intervals
A 发车间隔/s 变电所 绝对平均值 最大绝对值 120 A 9.30 33.84 B 3.69 7.42 C 3.50 12.65 D 7.78 21.78 180 A 7.16 27.64 B 2.24 7.33 C 2.68 10.47 D 5.85 19.99 240 A 5.81 26.28 B 2.28 7.83 C 2.07 9.87 D 3.48 16.07 300 A 5.16 30.94 B 2.02 6.05 C 1.91 11.57 D 4.31 19.23 表 6 不同治理方式下直流偏磁电流的特征值
Table 6. Characteristic values of DC bias current under different management modes
A 治理方式 变电所 绝对平均值 最大绝对值 隔直电容 A 0 0 B 5.67 31.09 C 7.07 42.52 D 8.86 50.19 限流电阻 A 4.82 18.31 B 1.58 3.19 C 1.35 6.49 D 4.03 11.28 表 7 BCD和UCD的直流偏磁电流特征值
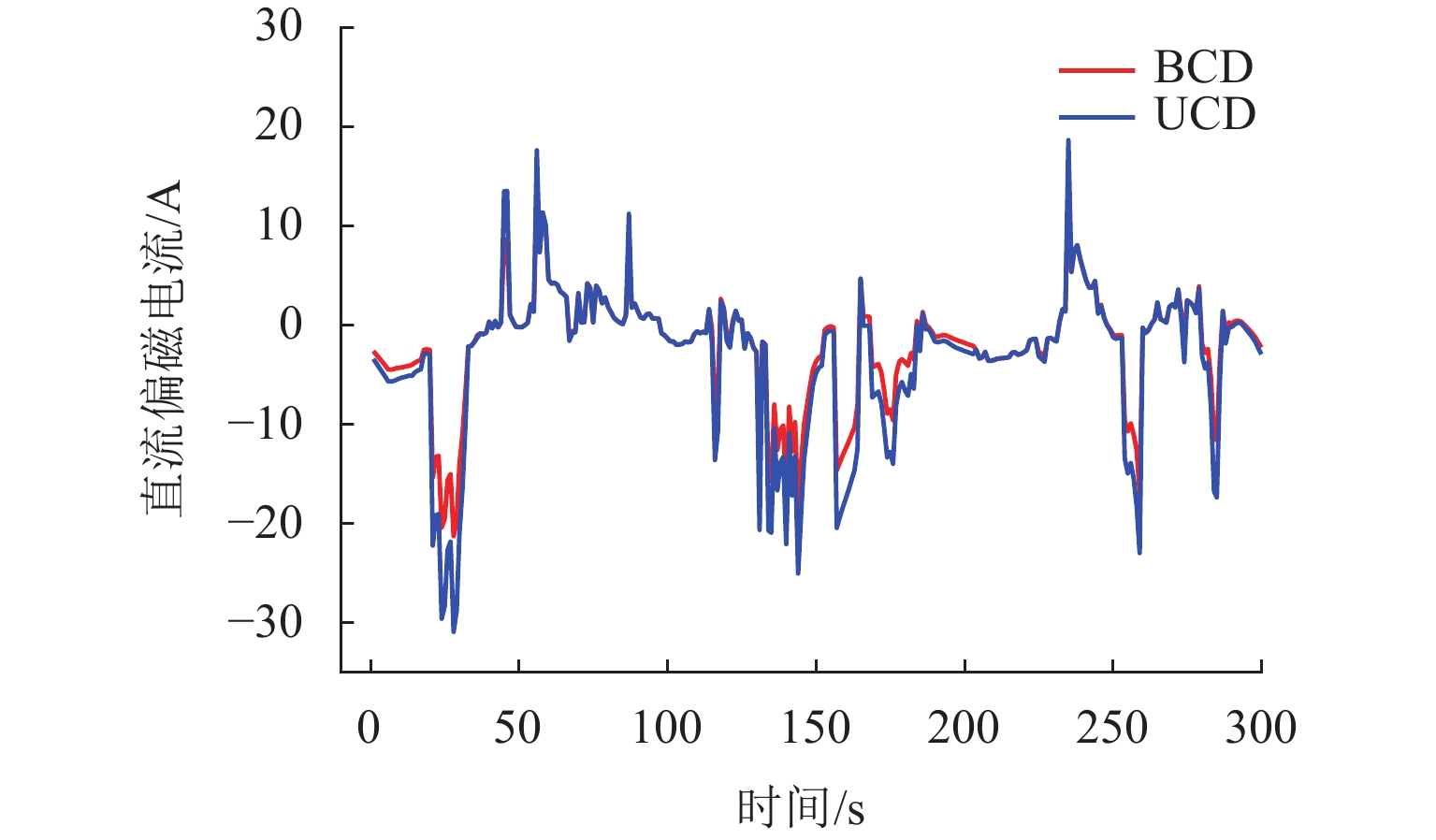
Table 7. Characteristic values of DC bias current in BCD and UCD
A CD 连接方式 变电所 绝对平均值 最大绝对值 BCD A 3.95 21.28 B 1.97 7.21 C 1.45 7.93 D 3.98 16.72 UCD A 5.16 30.94 B 2.02 6.74 C 1.91 11.57 D 4.31 19.23 -
[1] 施仲衡,丁树奎. 城市轨道交通绿色低碳发展策略[J]. 都市快轨交通,2022,35(1): 1-4,11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2020.01.001SHI Zhongheng, DING Shukui. Strategies for green and low-carbon development of urban rail transit[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2022, 35(1): 1-4,11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6073.2020.01.001 [2] 解绍锋,李卫兰,黄大锐,等. 市域铁路对埋地管道感性耦合干扰建模及仿真[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(6):1256-1266.XIE Shaofeng, LI Weilan, HUANG Darui, et al. Modelling and simulation of inductive coupled interference from suburban railways to buried pipelines[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(6):1256-1266. [3] 全江涛,谢志成,陈科基,等. 特/超高压直流输电系统单极运行下变压器中性点直流电流分布规律仿真分析[J]. 高电压技术,2015,41(3): 787-793.QUAN Jiangtao, XIE Zhicheng, CHEN Keji, et al. Mechanism analysis and simulation of DC current distribution along transformer neutral point under the condition of UHVDC/HVDC single-pole operation[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2015, 41(3): 787-793. [4] 张冰,刘连光,肖湘宁. 地磁感应电流对变压器振动、噪声的影响[J]. 高电压技术,2009,35(4): 900-904.ZHANG Bing, LIU Lianguang, XIAO Xiangning. Effects of geomagnetically induced current on the vibration and noise of transformers[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2009, 35(4): 900-904. [5] 李晓华,褚福源,时胜寒. 轨道交通对沿线220 kV变电站中性点电流及振动影响[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(增2): 423-429,437.LI Xiaohua, CHU Fuyuan, SHI Shenghan. Influence of rail transit on neutral current and vibration of 220 kV substation along the line[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(S2): 423-429,437. [6] 黄华,陈璐,吴天逸,等. 城市轨道交通动态运行对交流电网变压器偏磁直流的影响[J]. 电网技术,2022,46(11): 4524-4533.HUANG Hua, CHEN Lu , WU Tianyi, et al. Influence of dynamic operation of urban rail transit on DC magnetic bias of AC power grid transformer[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46(11): 4524-4533. [7] WANG A M, LIN S, HU Z H, et al. Evaluation model of DC current distribution in AC power systems caused by stray current of DC metro systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2021, 36(1): 114-123. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2020.2975367 [8] CHENG X X, NI Y R, YU K, et al. Analysis on harmonic characteristic of transformer DC bias caused by metro stray current[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2196(1): 012014.1-012014.10. [9] 倪砚茹,曾祥君,喻锟,等. 地铁杂散电流引起动态地电位分布建模及影响因素分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2023,43(23): 9059-9072.NI Yanru, ZENG Xiangjun, YU Kun, et al. Modeling and influencing factors analysis of dynamic potential distribution caused by metro stray current[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(23): 9059-9072. [10] 孙结中,刘力. 运用等值复数镜像法求解复合分层土壤结构的格林函数[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2003,23(9): 146-151. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2003.09.030SUN Jiezhong, LIU Li. Derivation of green’s function by equivalent complex image method in a horizontal and vertical combined-layer soil structure[J]. Proceeding of the CSEE, 2003, 23(9): 146-151. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2003.09.030 [11] 李中新,袁建生,张丽萍. 变电站接地网模拟计算[J]. 中国电机工程学报,1999,19(5): 76-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.1999.05.018LI Zhongxin, YUAN Jiansheng, ZHANG Liping. Numerical calculation of substation grounding systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 1999, 19(5): 76-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.1999.05.018 [12] 郭剑,邹军,何金良,等. 水平分层土壤中点电流源格林函数的递推算法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2004,24(7): 101-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2004.07.019GUO Jian, ZOU Jun, HE Jinliang, et al. Recursive method to obtain analytic expressions of Green’s functions in multi-layer soil by computer[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2004, 24(7): 101-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2004.07.019 [13] 史云涛,赵丽平,林圣,等. 城市电网中地铁杂散电流分布规律及影响因素分析[J]. 电网技术,2021,45(5): 1951-1957.SHI Yuntao, ZHAO Liping, LIN Sheng, et al. Analysis of distribution of metro stray current in urban power grid and its influencing factors[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(5): 1951-1957. [14] 刘炜,杨龙,李国玉,等. 计及回流系统设备行为过程的钢轨电位动态仿真[J]. 电工技术学报,2022,37(4): 1000-1009.LIU Wei, YANG Long, LI Guoyu, et al. Dynamic simulation of rail potential considering the equipment behavior process of recirculation system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(4): 1000-1009. [15] 国家能源局. 高压直流接地极技术导则:DL/T 437—2012[S]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2012. [16] Sahil Bhagat,杨晓峰,王淼,等. 城市轨道交通杂散电流治理的综述与评估[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(23): 4851-4863.SAHIL Bhagat, YANG Xiaofeng, WANG Miao, et al. Review and evaluation of stray current mitigation for urban rail transit[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(23): 4851-4863. [17] 何金良,曾嵘. 电力系统接地技术[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2007:359. [18] 刘炜,尹乙臣,潘卫国,等. 直流动态杂散电流在分层介质中的扩散模型[J]. 电工技术学报,2021,36(23): 4864-4873.LIU Wei, YIN Yichen, PAN Weiguo, et al. Diffusion model of DC dynamic stray current in layered soil[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(23): 4864-4873. [19] 许军,蓝磊,文习山,等. 三峡电站模型地网接地电阻小比例模型试验研究[J]. 电网技术,2003,27(1): 38-40.XU Jun, LAN Lei, WEN Xishan, et al. Small-scale model test for grounding resistance of grounding mesh model for Three Gorges hydroelectric power station[J]. Power System Technology, 2003, 27(1): 38-40. [20] 刘炜,刘童童,王辉,等. 运行图驱动的城轨供电系统负荷过程动态仿真[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(5): 967-975.LIU Wei, LIU Tongtong, WANG Hui, et al. Dynamic simulation of load process for urban rail power supply system driven by operation diagram[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(5): 967-975. -





 下载:
下载: