Comprehensive Comparison of Inversion Performance of Urban Traffic Congestion Source Parameters
-
摘要:
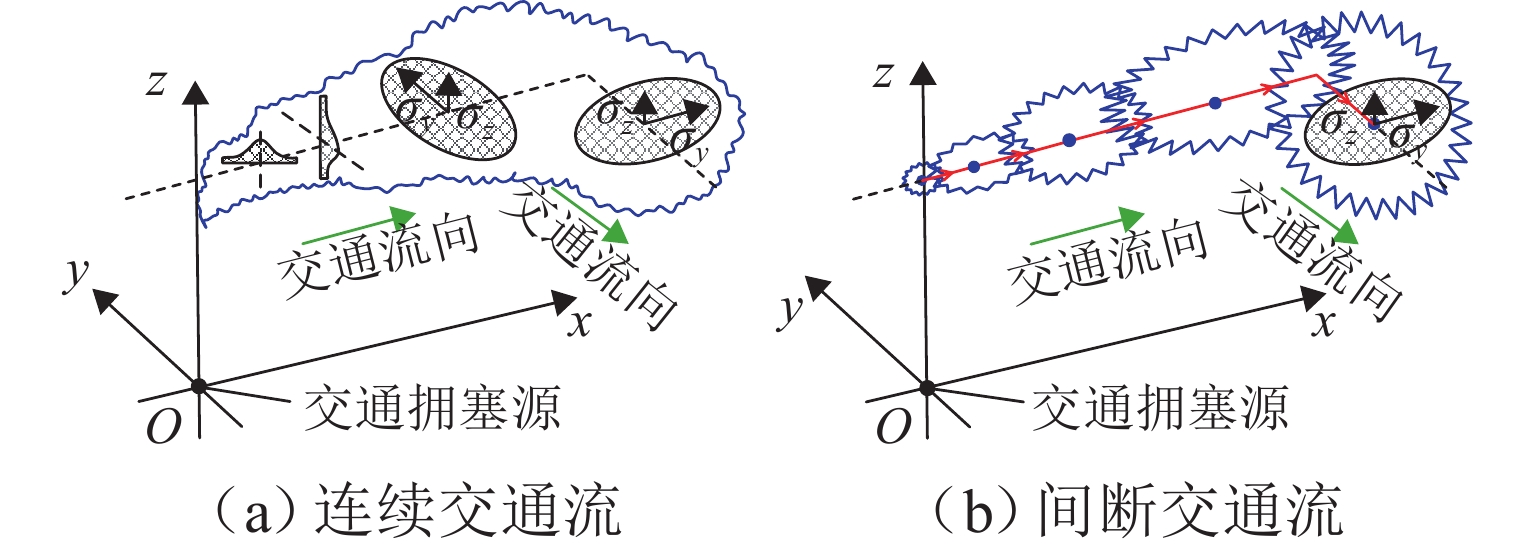
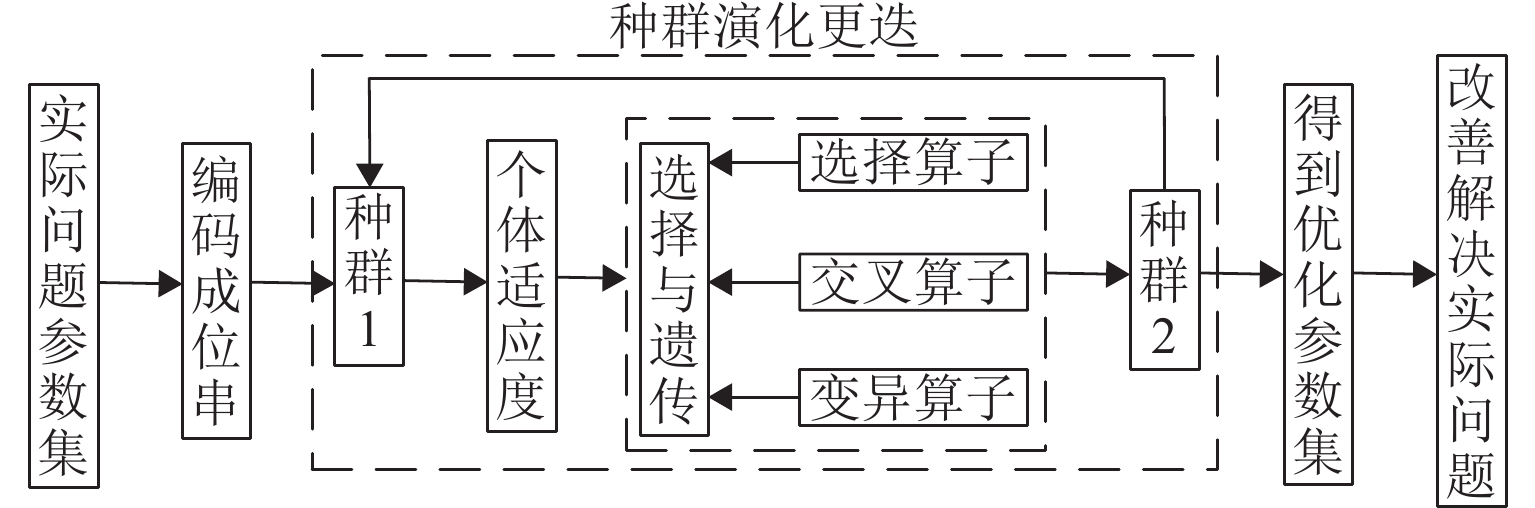
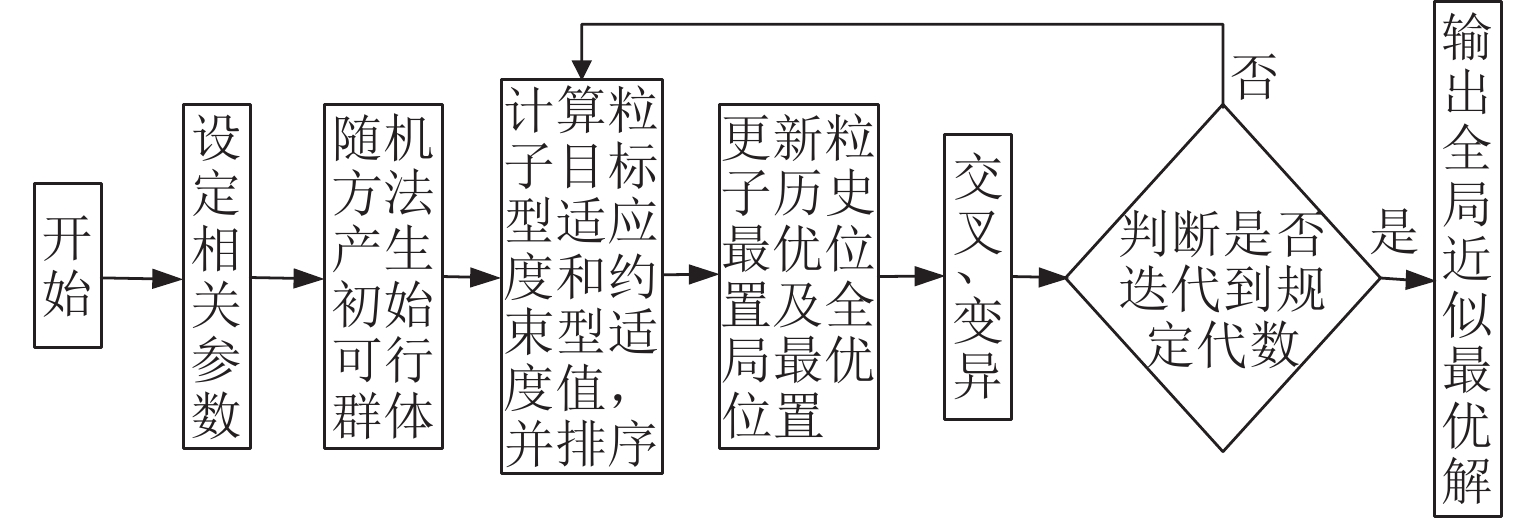
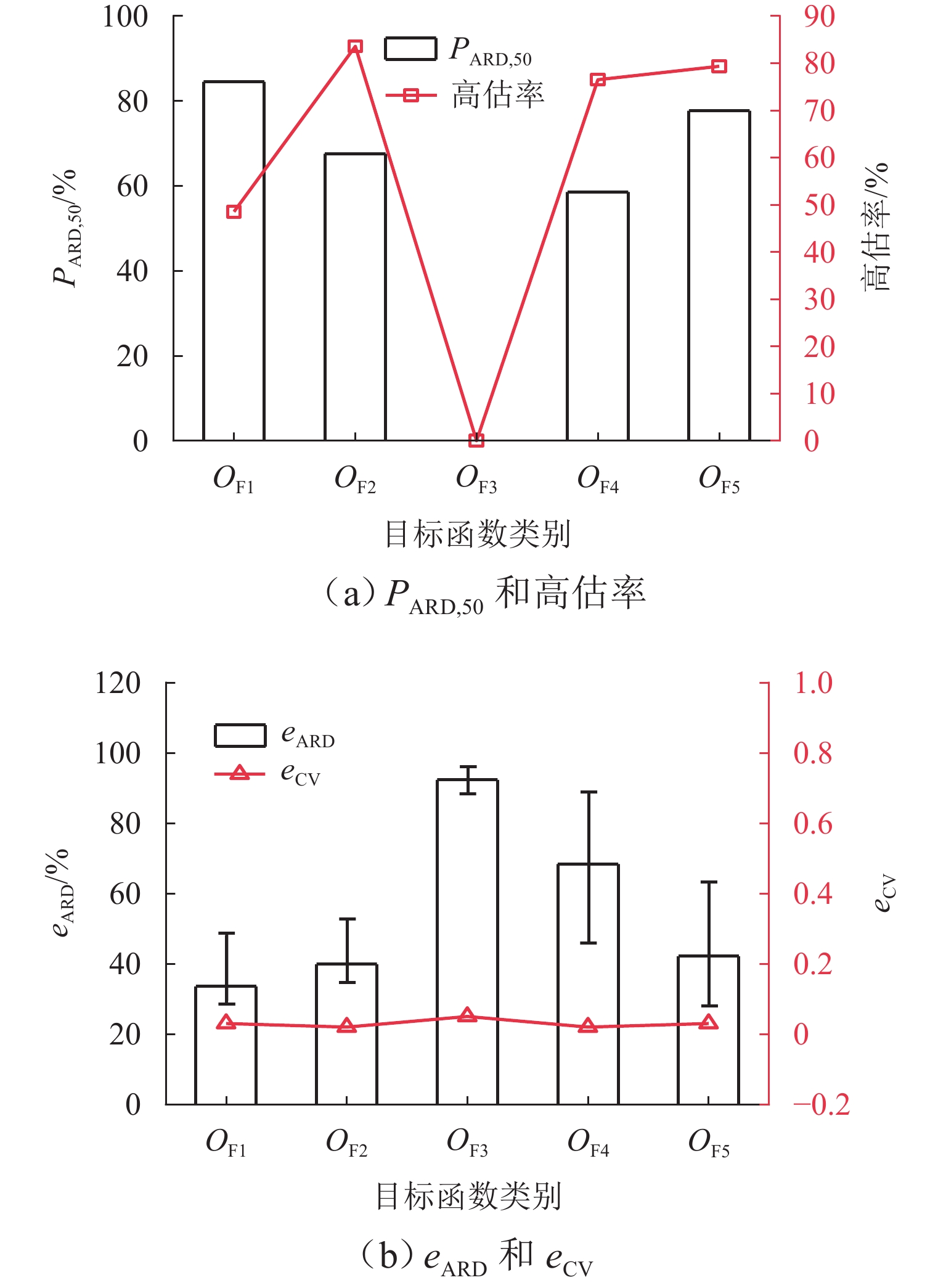
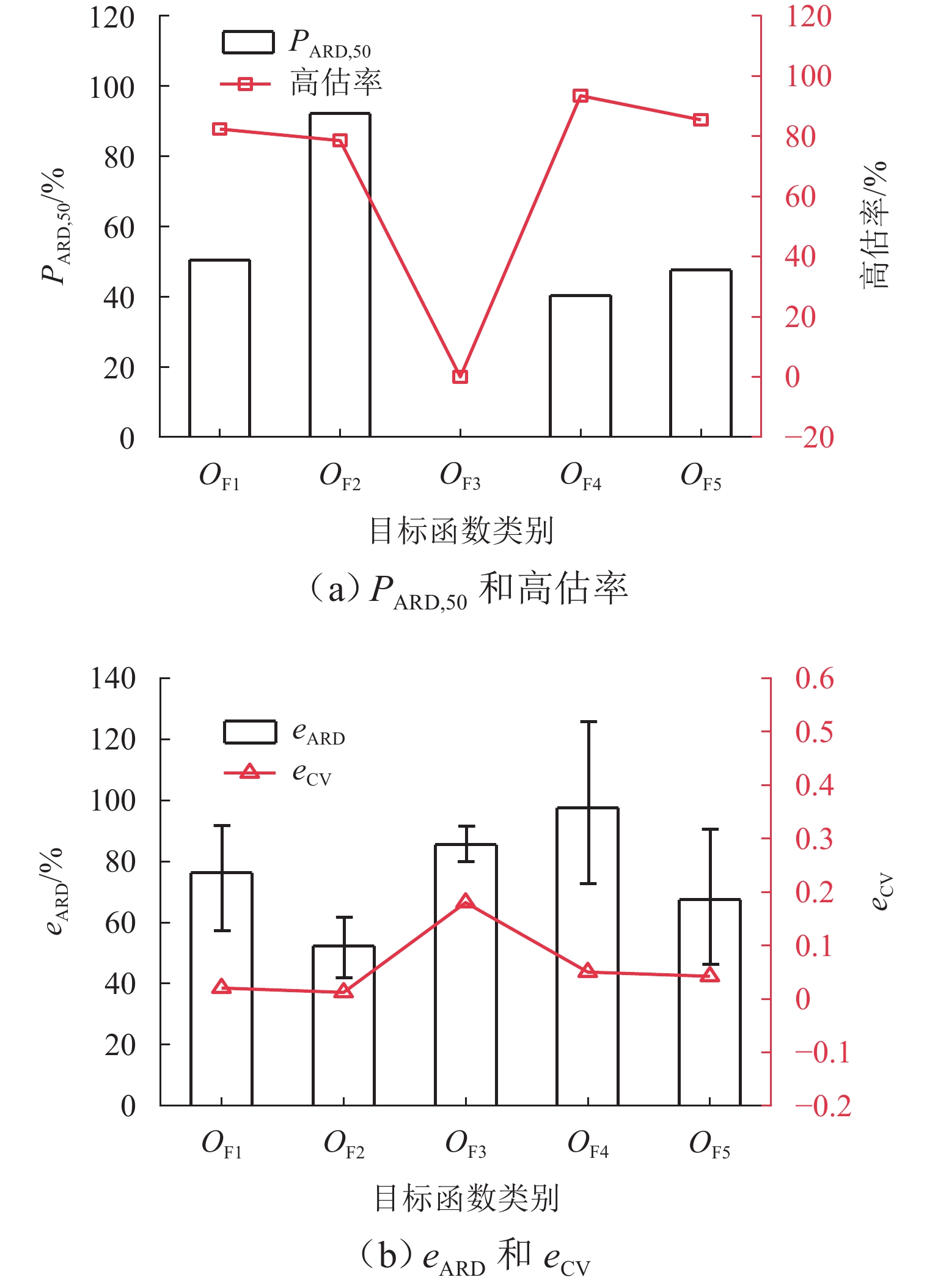
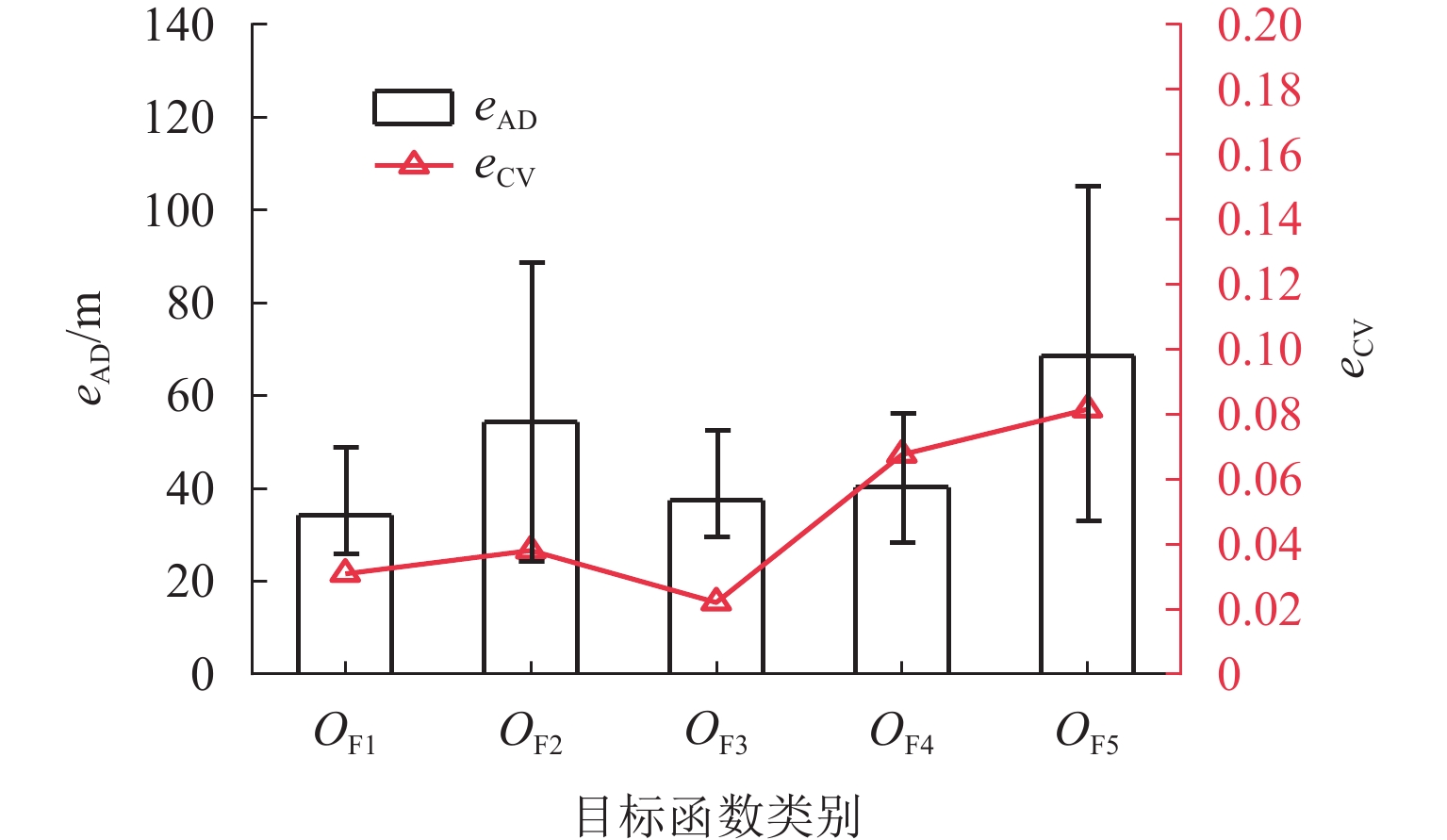
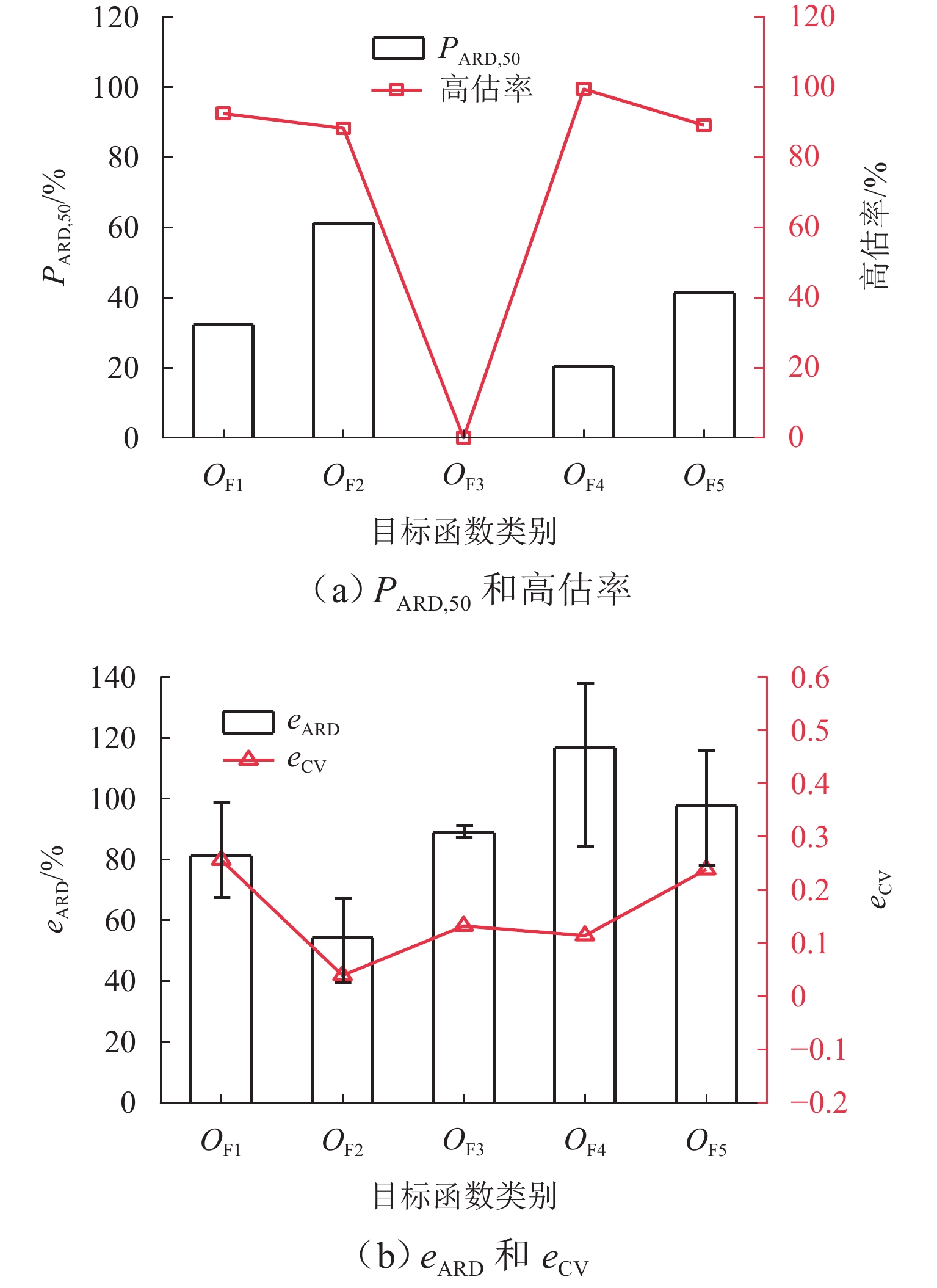
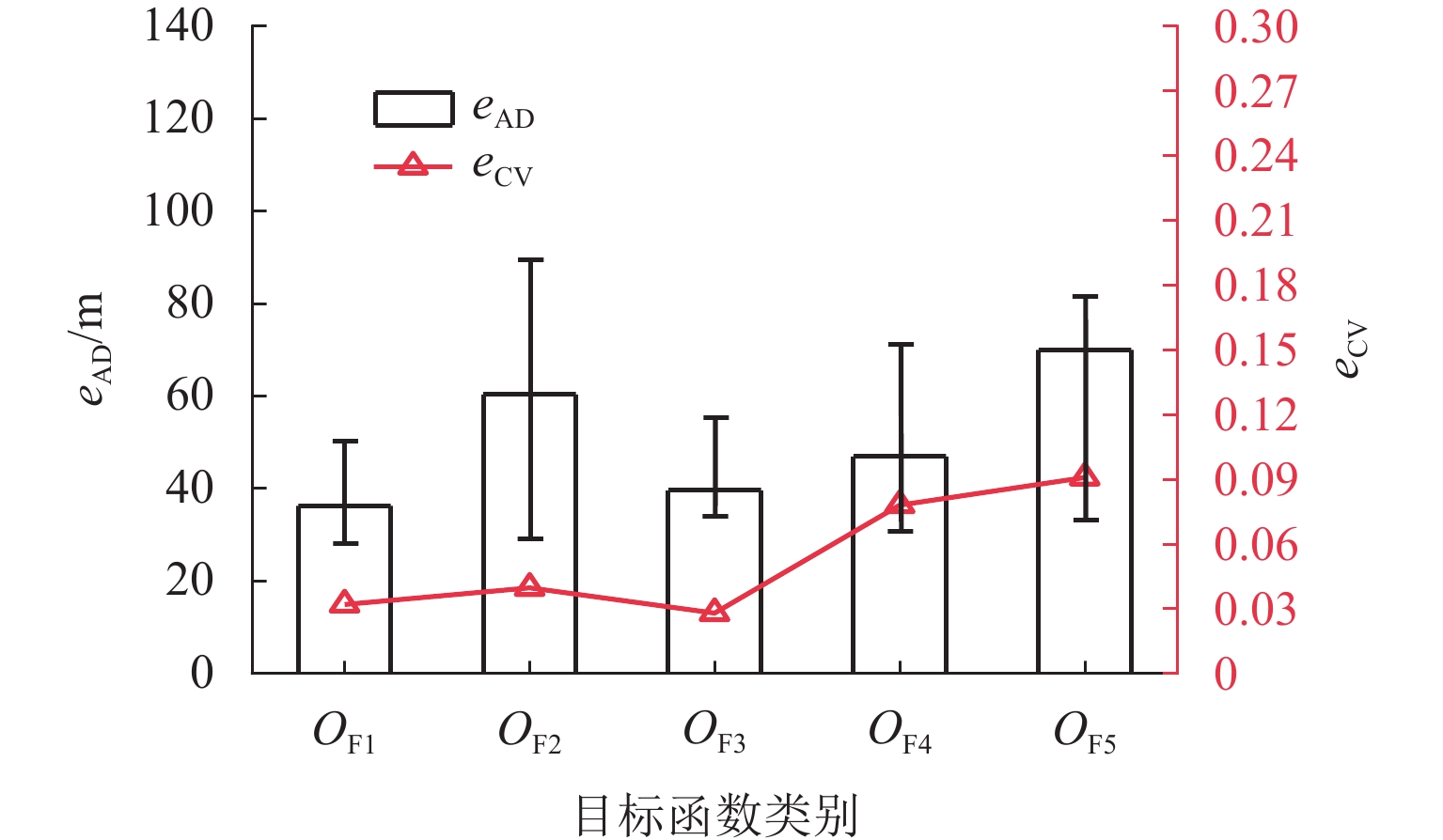
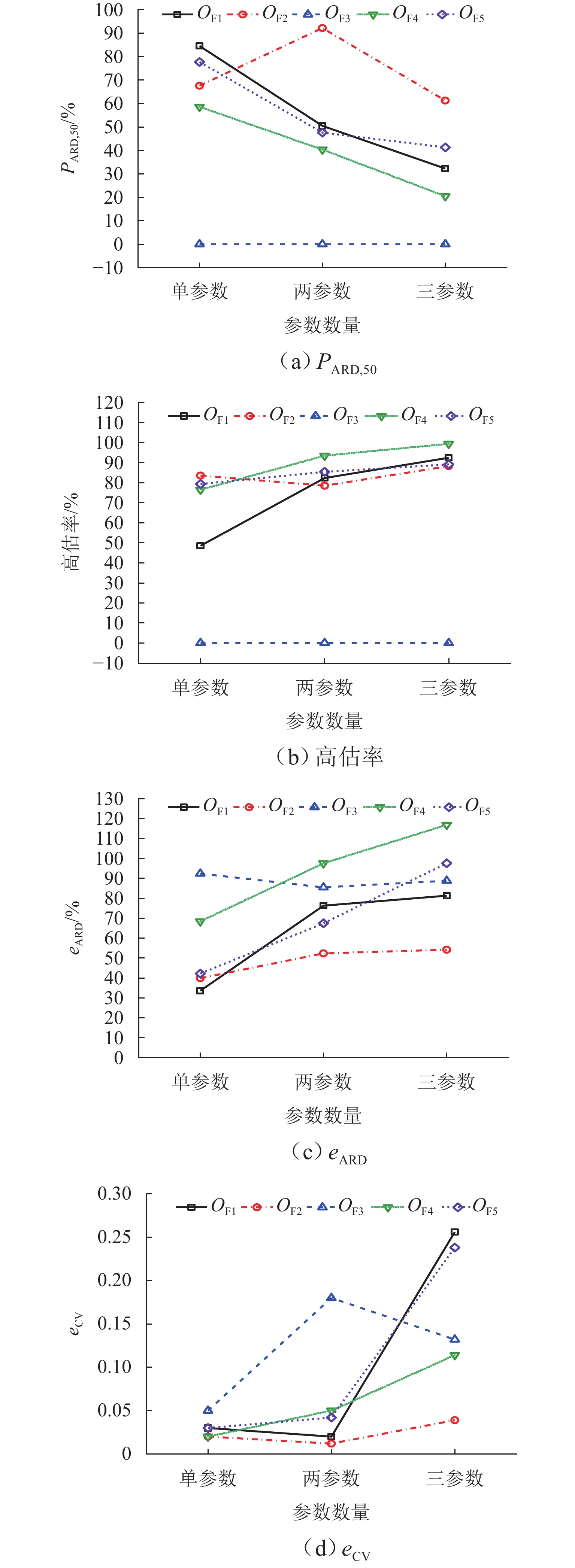
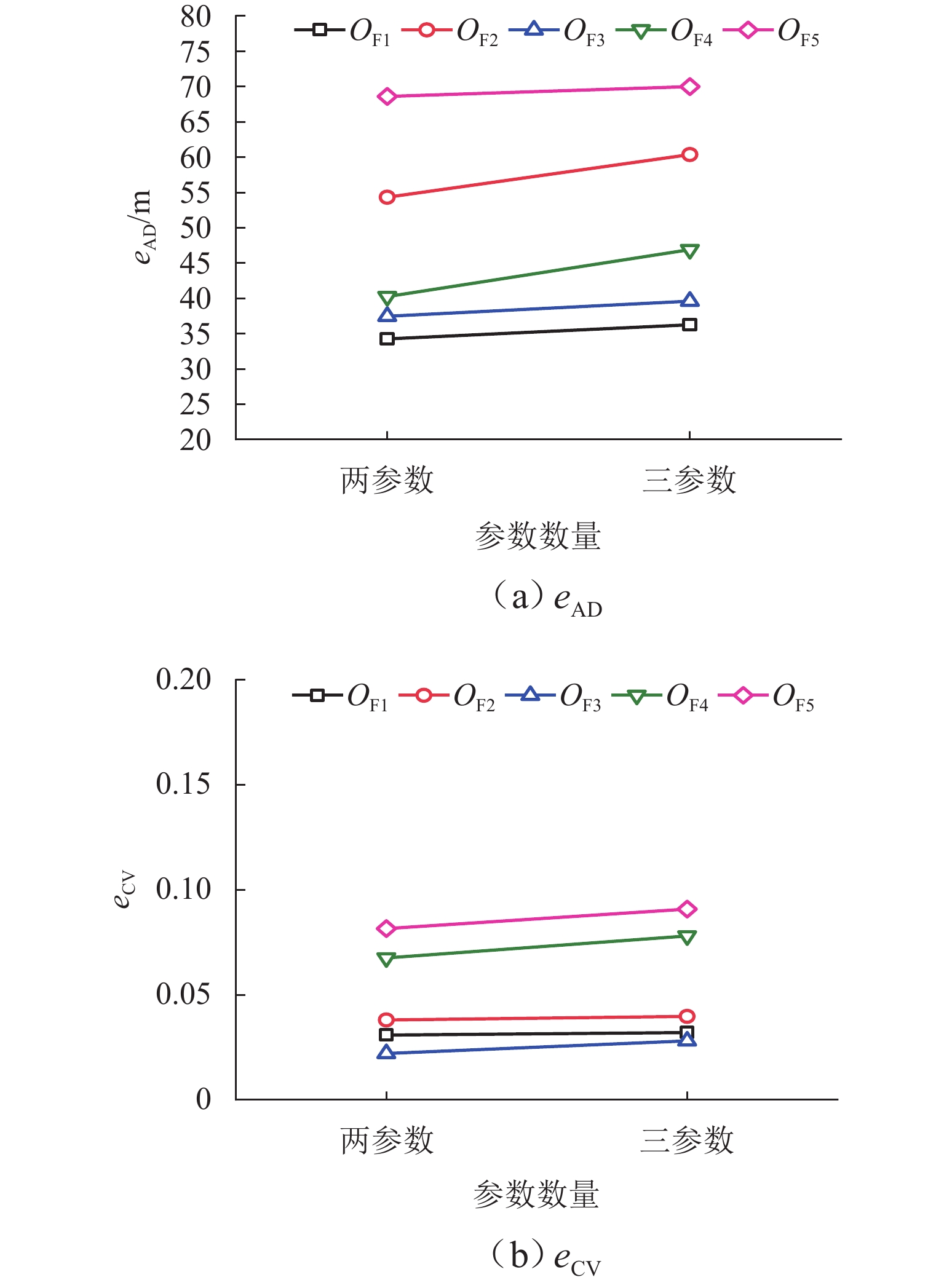
为准确掌握城市交通拥塞源内在的主要参数及扩散传播规律,以实现交通拥塞源科学管控. 首先,引入用于大气污染物扩散的高斯烟羽模型并进行改进,将城市交通拥塞源划分为连续交通流和一系列间断性交通流,实现高斯烟羽模型结构解析;其次,利用Griewank、Schaffer和Rastrigin 3种测试函数对“单点源”参数反演算法进行测试,最终选用人群搜索算法;最后,通过交通拥塞源观测数据,从3个维度评估5种典型目标函数在不同参数数量(单、两、三)下的性能差异. 研究结果表明:在单参数情形下,基于单位面积交通密度偏差平方和目标函数稳定性较好;反演源强相对偏差绝对值置信区间为38.38% ± 9.94%,小于50.00%实验次数占全部实验次数的84.52%,各目标函数稳定性均较好;在两参数反演源强情形下,基于对数变换单位面积交通密度均方根误差目标函数准确性最高,反演源强相对偏差绝对值置信区间为51.42% ± 9.84%,小于50.00%实验次数占全部实验次数的92.16%,在反演位置方面,基于单位面积交通密度偏差平方和目标函数准确性最好(反演位置偏差的绝对值为37.22 m ± 10.64 m),基于相关系数的目标函数稳定性最强(变异系数为0.022);三参数情形下,准确性反演结果和两参数较一致,除对数变换目标函数外各目标函数源强稳定性均较差,但位置稳定性均较好.
Abstract:In order to accurately grasp the main parameters and diffusion and propagation laws inherent in urban traffic congestion sources and realize scientific control of traffic congestion sources, the Gaussian plume model for air pollutant dispersion was introduced and improved. The urban traffic congestion sources were divided into continuous traffic flow and a series of intermittent traffic flow, so as to realize the structural analysis of the Gaussian plume model. Then, three test functions, namely Griewank, Schaffer, and Rastrigin were used to test the “single point source” parameter inversion algorithm, and the seeker optimization algorithm was selected. Finally, the performance of the five typical objective functions with different numbers of parameters (one, two, and three) was evaluated in three dimensions based on the observed traffic congestion source data. The results show that in the one-parameter case, the stability of the objective function based on the sum of squared deviations of traffic density per unit area is better, and the confidence interval of the absolute value of the relative deviation of the inverse source strength is 38.38% ± 9.94%; the number of experiments less than 50.00% accounts for 84.52% of all experiments, and the stability of each objective function is better. In the two-parameter case of source strength inversion, the accuracy of the objective function based on the root-mean-square error of traffic density per unit area in the form of logarithmic transformation is the highest, and the confidence interval of the absolute value of the relative deviation of source strength inversion is 51.42% ± 9.84%; the number of experiments less than 50.00% accounts for 92.16% of all experiments. In terms of inversion location, the accuracy of the objective function based on the sum of squared deviations of traffic density per unit area is the best (absolute value of position deviation inversion is 37.22 m ± 10.64 m), and the stability of the objective function based on correlation coefficient is the strongest (coefficient of variation is 0.022). In the three-parameter case, the accuracy inversion results are more consistent with those in the two-parameter case, and the source strength stability of each objective function is poor except for the objective function in the form of logarithmic transformation, but the position stability is better.
-
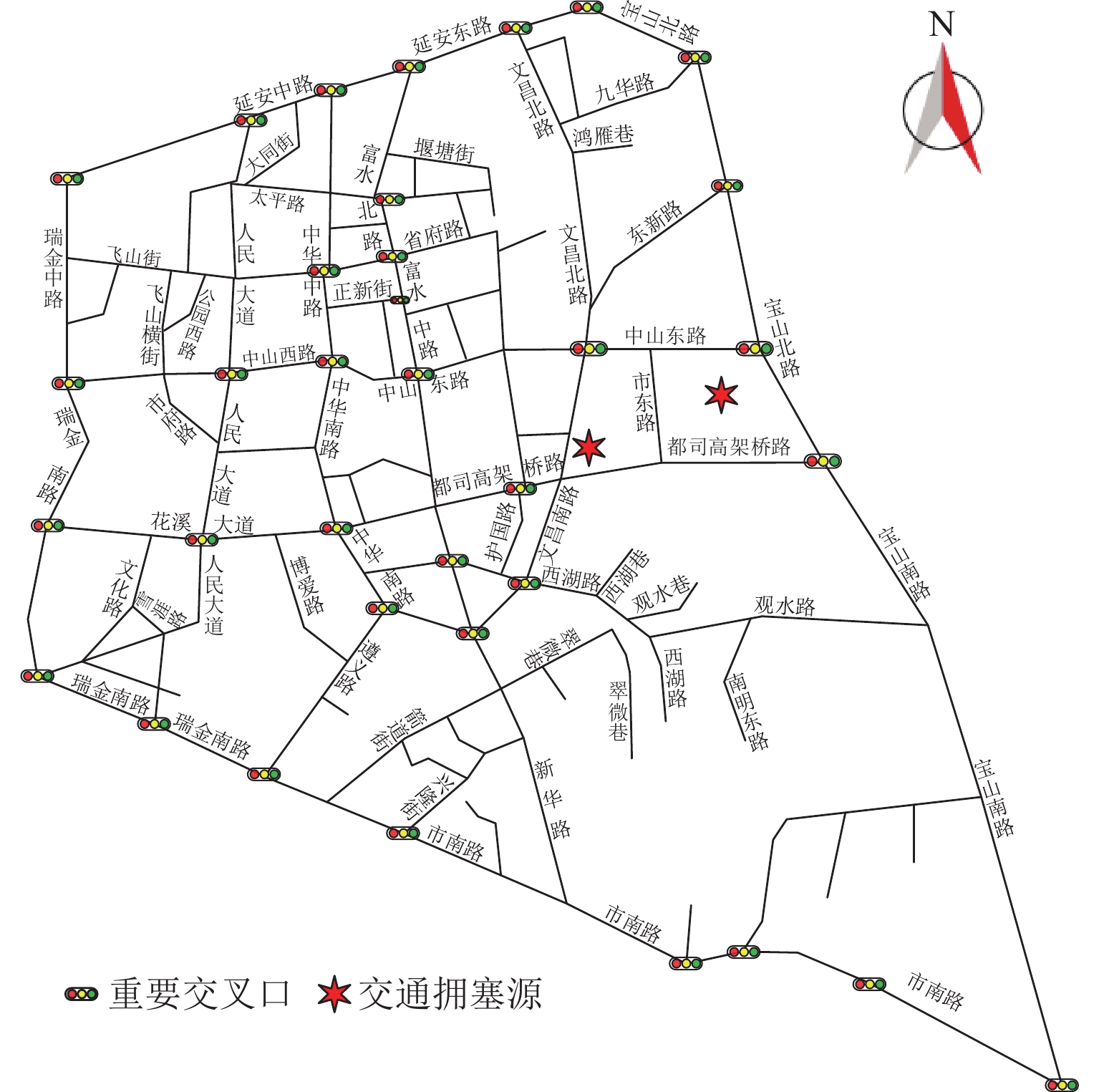
表 1 交通拥塞源基本参数取值
Table 1. Basic parameter values of traffic congestion source
交通拥塞源编号 所在位置紧邻标志性建筑 道路名称 道路等级 车道数 区域平均行车速度/
(km·h−1)进口道断面平均速度/
(km·h−1)出口道断面平均速度/
(km·h−1)饱和度 1 贵州省人民
医院中山东路(北侧) 主干路 双向 6 车道 29.87 15.34 47.92 0.819 都司高架桥路(南侧) 主干路 双向 6 车道 29.43 13.85 45.58 0.895 市东路(西侧) 支路 双向 2 车道 20.28 8.73 24.32 0.889 宝山南路(东侧) 城市快速路 双向 8 车道 + 潮汐车道 40.85 22.94 58.14 0.831 2 亨特城市
广场中山东路(北侧) 主干路 双向 6 车道 29.87 14.79 48.35 0.819 都司高架桥路(南侧) 主干路 双向 6 车道 29.43 13.19 46.39 0.895 文昌南路(西侧) 次干路 单向 4 车道 27.86 11.37 43.21 0.908 市东路(东侧) 支路 双向 2 车道 20.28 8.73 24.32 0.889 表 2 各测试函数优化结果
Table 2. Optimization results for each test function
评价指标 GA PSO SOA Griewank Schaffer Rastrigin Griewank Schaffer Rastrigin Griewank Schaffer Rastrigin 平均最优值 1.25 × 10−2 7.52 × 10−1 1.85 × 10−4 1.32 × 10−1 2.67 × 10−4 1.59 × 10−1 8.53 × 10−3 3.89 × 10−6 6.12 × 10−6 标准差 1.19 × 10−2 2.31 3.57 × 10−4 6.74 × 10−2 3.12 × 10−4 3.79 × 10−1 3.43 × 10−3 4.21 × 10−6 6.21 × 10−6 最大值 5.34 × 10−2 8.97 2.34 × 10−3 3.26 × 10−1 1.74 × 10−3 1.21 2.45 × 10−2 2.16 × 10−5 4.46 × 10−5 最小值 9.26 × 10−4 7.69 × 10−7 0.89 × 10−7 1.06 × 10−2 7.08 × 10−7 3.85 × 10−6 1.86 × 10−3 4.32 × 10−8 7.96 × 10−8 -
[1] ZHANG S, YAO Y, HU J, et al. Deep autoencoder neural networks for short-term traffic congestion prediction of transportation networks[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(10): 2229.1-2229.19. doi: 10.3390/s19102229 [2] PI M Y, YEON H, SON H, et al. Visual cause analytics for traffic congestion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2019, 27(3): 2186-2201. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2019.2940580 [3] CHEN H R, ZHOU R Y, CHEN H, et al. A resilience-oriented evaluation and identification of critical thresholds for traffic congestion diffusion[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2022, 600(8): 127592.1-127592.15. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2022.127592 [4] ZHU S X, DING R Y, ZHANG M H, et al. Spatio-temporal point processes with attention for traffic congestion event modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 7298-7309. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3068139 [5] CHEN Y T, MAO J N, ZHANG Z, et al. A quasi-contagion process modeling and characteristic analysis for real-world urban traffic network congestion patterns[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2022, 603(10): 127729.1-127729.17. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2022.127729 [6] 陈美林,郑治豪,郭宝,等. 基于因果关联的交通拥堵传播分析[J]. 中南大学学报 (自然科学版),2020,51(12): 3575-3583. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.12.031CHEN Meilin, ZHENG Zhihao, GUO Bao, et al. Traffic congestion spreading analysis based on causal nexus[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(12): 3575-3583. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.12.031 [7] 石敏,蔡少委,易清明. 基于空洞-稠密网络的交通拥堵预测模型[J]. 上海交通大学学报,2021,55(2): 124-130. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2020.99.009SHI Min, CAI Shaowei, YI Qingming, et al. A traffic congestion prediction model based on dilated-dense network[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2021, 55(2): 124-130. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2020.99.009 [8] 曾筠程,邵敏华,孙立军,等. 基于有向图卷积神经网络的交通预测与拥堵管控[J]. 中国公路学报,2021,34(12): 239-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.12.018ZENG Yuncheng, SHAO Minhua, SUN Lijun, et al. Traffic prediction and congestion control based on directed graph convolution neural network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(12): 239-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2021.12.018 [9] 周辉宇,李瑞敏,黄安强,等. 基于时空关联规则挖掘的城市交通拥堵传导预测[J]. 系统工程理论与实践,2022,42(8): 2210-2223. doi: 10.12011/SETP2020-2752ZHOU Huiyu, LI Ruimin, HUANG Anqiang, et al. Forecasting urban traffic congestion conduction based on spatiotemporal association rule mining[J]. Systems Engineering - Theory & Practice, 2022, 42(8): 2210-2223. doi: 10.12011/SETP2020-2752 [10] 梁军,彭嘉恒. 考虑路网拓扑时变的交通拥堵自适应预测方法研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2022,35(9): 157-170. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2022.09.012LIANG Jun, PEN Jiaheng. Research on an adaptive traffic congestion prediction method considering a time-varying network topology[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(9): 157-170. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2022.09.012 [11] 马庆禄,牛圣平,曾皓威,等. 网联环境下混合交通流偶发拥堵演化机理研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2022,22(5): 97-106. doi: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2022.05.010MA Qinglu, NIU Shengping, ZENG Haowei, et al. Mechanism of non-recurring congestion evolution under mixed traffic flow with connected and autonomous vehicles[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(5): 97-106. doi: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2022.05.010 [12] 孙超,尹浩为,张玮,等. 基于有限理性的交通网络可靠性均衡模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(1): 83-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210679SUN Chao, YIN Haowei, ZHANG Wei, et al. Traffic equilibrium model of reliable network based on bounded rationality[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(1): 83-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210679 [13] 王丽,刘小明,任福田,等. 烟羽模型在交通影响分析中的应用[J]. 公路交通科技,2001,18(6): 82-85.WANG Li, LIU Xiaoming, REN Futian, et al. The application of cloud model in traffic impact analysis[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2001, 18(6): 82-85. [14] 胡立伟,杨锦青,何越人,等. 城市交通拥塞辐射模型及其对路网服务能力损伤研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2019,32(3): 145-154. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.03.0016HU Liwei, YANG Jinqing, HE Yueren, et al. Urban traffic congestion radiation model and damage caused to service capacity of road network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(3): 145-154. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.03.0016 [15] 刘立群,韩俊英,代永强,等. 果蝇优化算法优化性能对比研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展,2015,25(8): 94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2015.08.020LIU Liqun, HAN Junying, DAI Yongqiang, et al. Comparative study on optimization performance of fruit fly optimization algorithm[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2015, 25(8): 94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2015.08.020 -




 下载:
下载: