Optimization of Joint Navigation Scheduling of Cascade Hubs in Inland River Basin from Perspective of Carbon Emission Reduction
-
摘要:
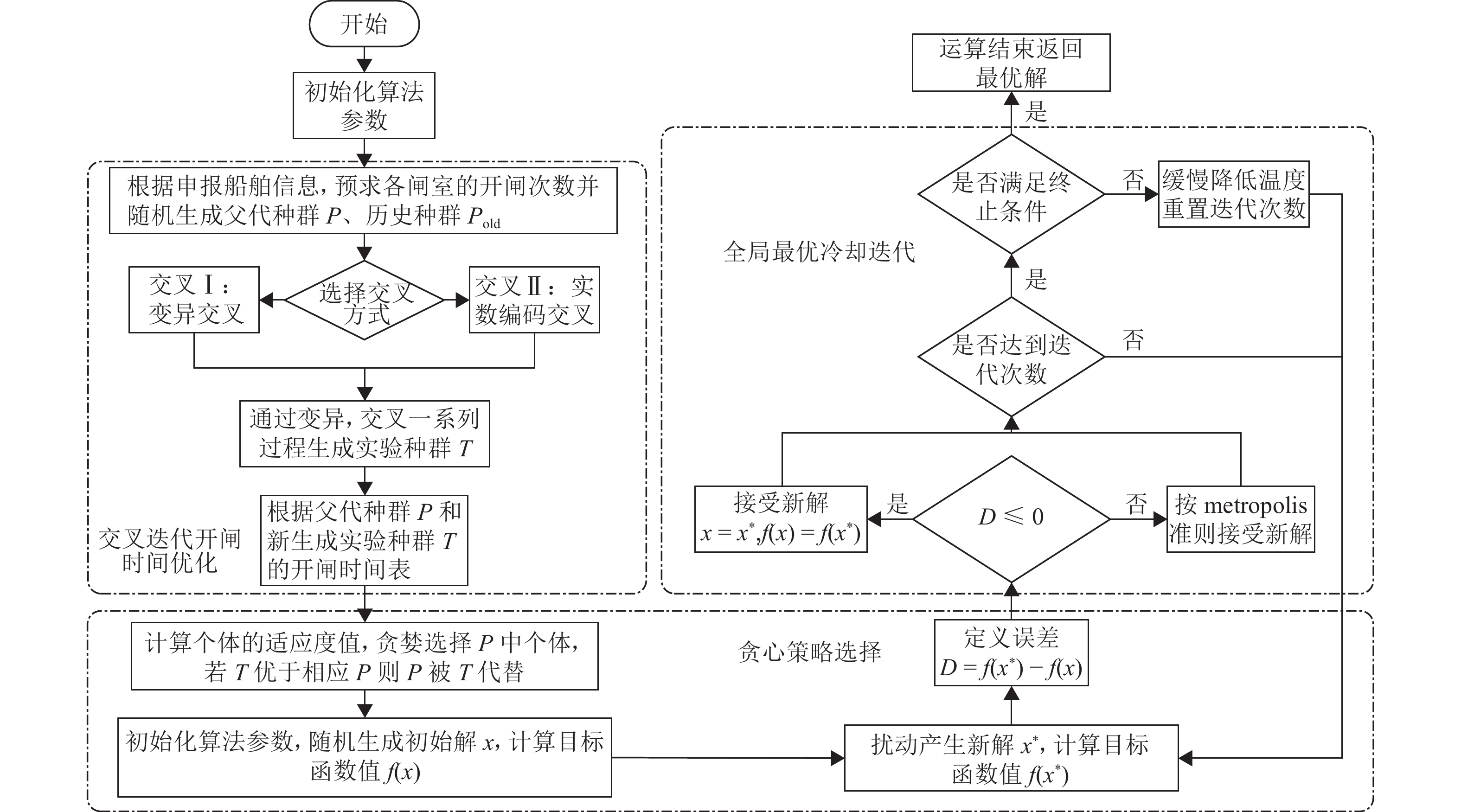
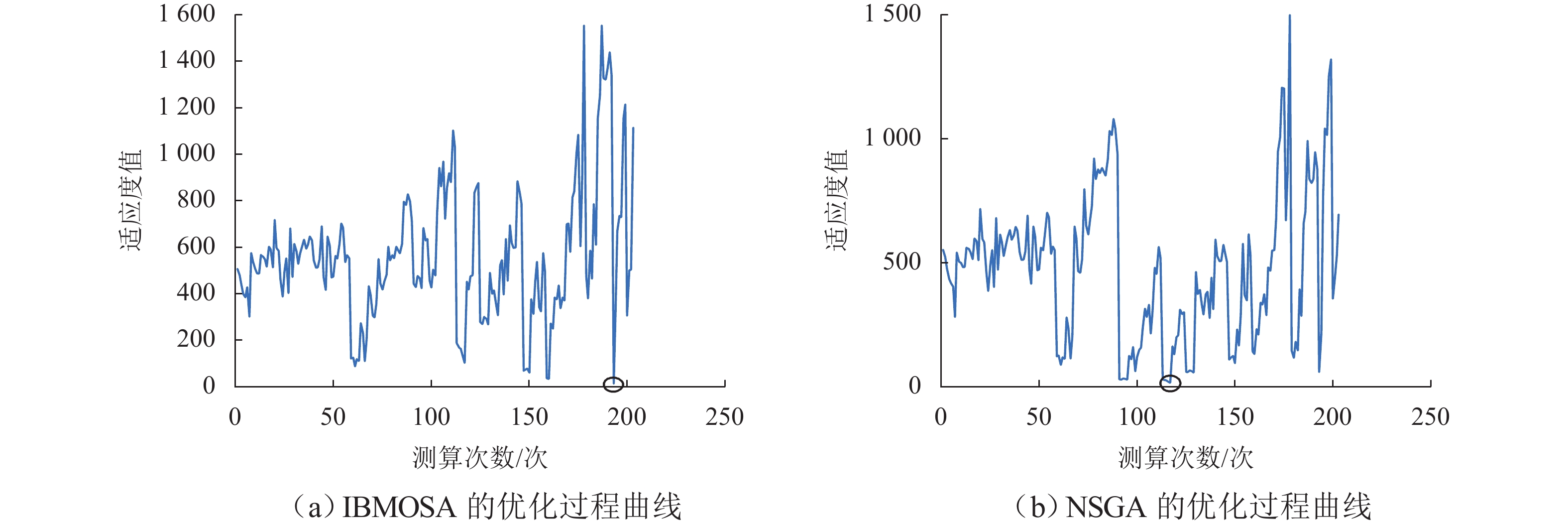
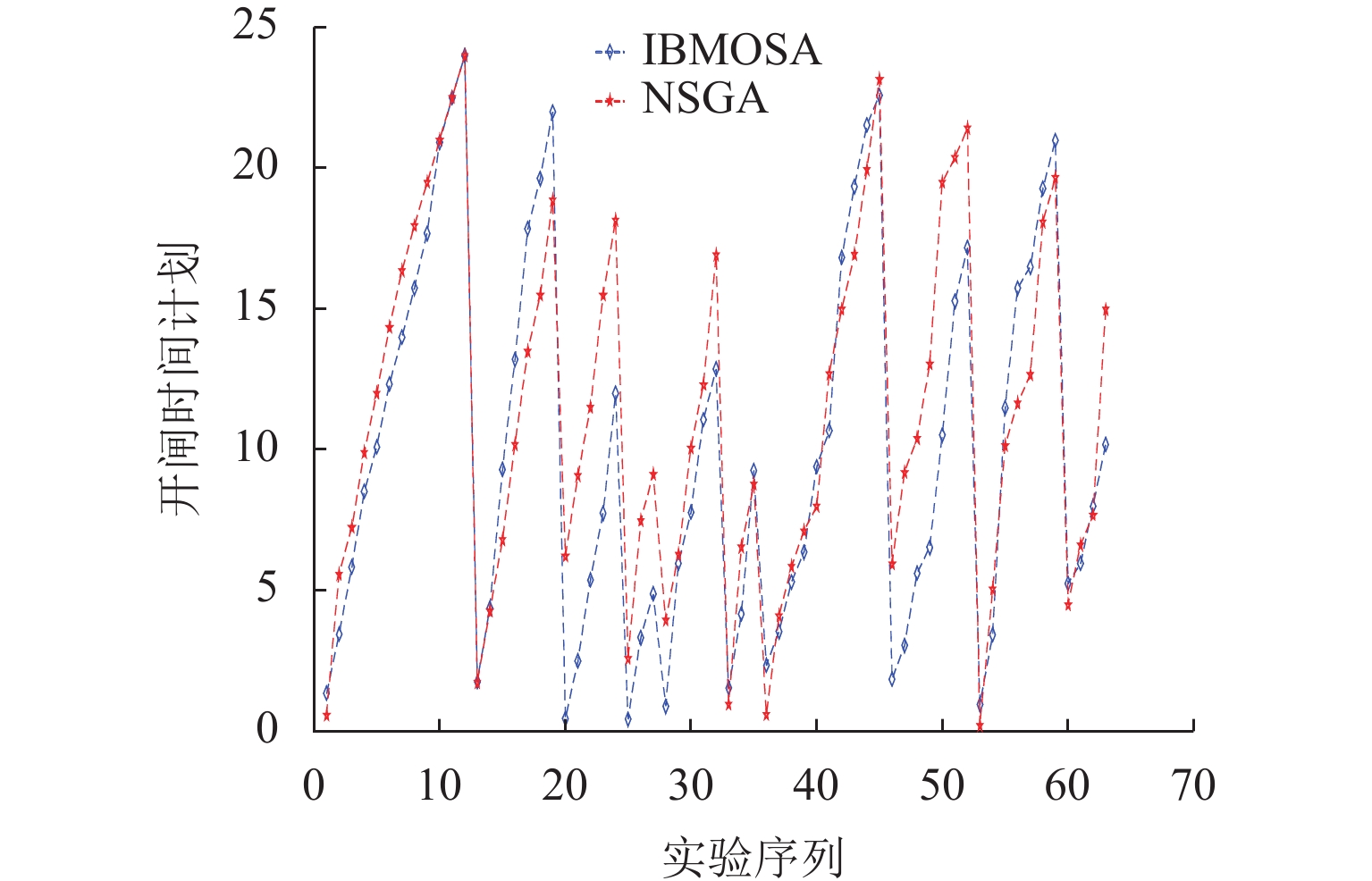
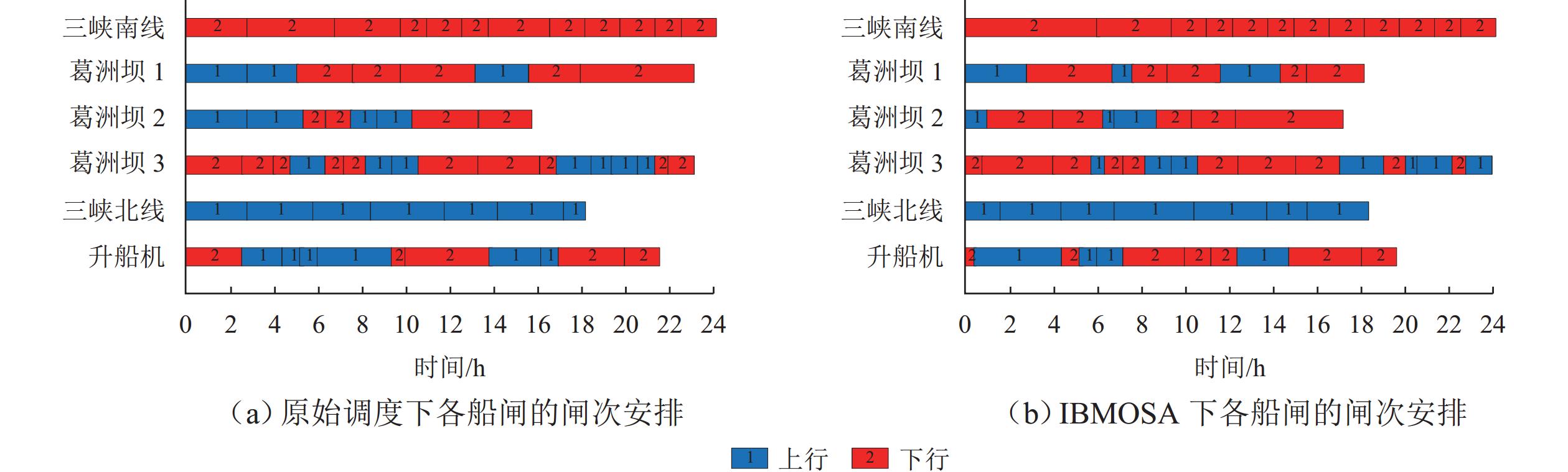
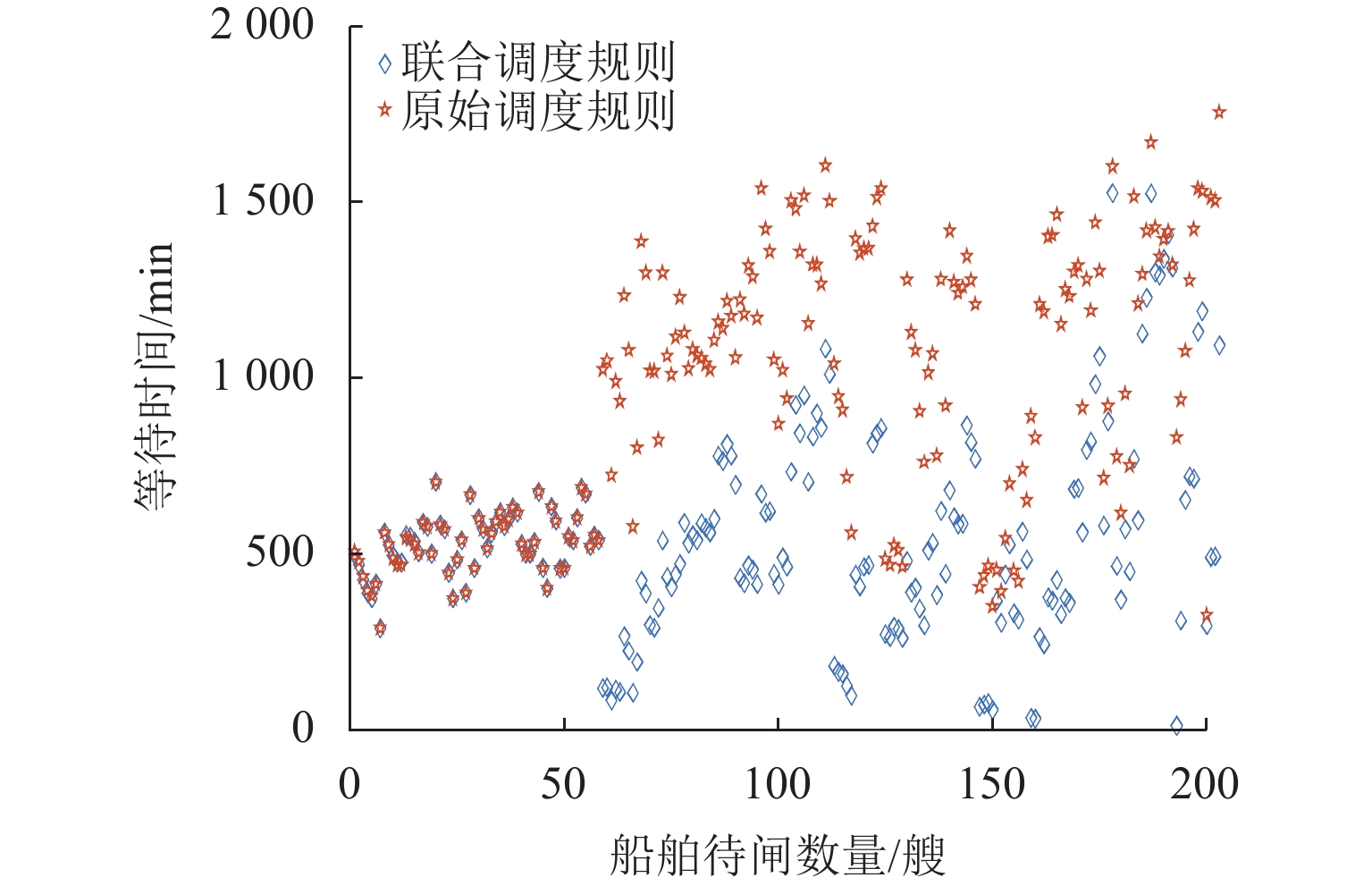
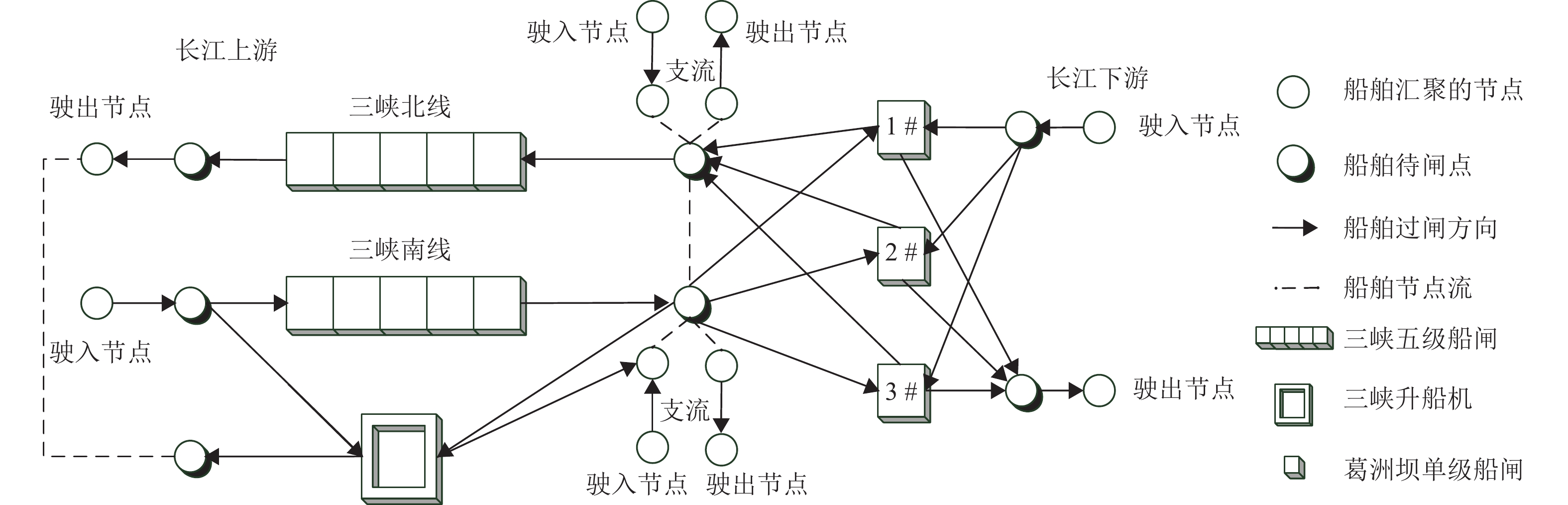
为解决梯级枢纽联合通航调度中船闸运行规则不统一、船舶调度不同步等问题,以船舶综合通航效率、待闸成本和碳排放为决策目标,构建考虑船舶优先级的多维非线性规划(MDNP)模型;随后,拟用改进的回溯多目标模拟退火算法(IBMOSA)对MDNP进行求解,提出梯级枢纽联合调度的优化方案;最后,以“三峡-葛洲坝”梯级枢纽为例,验证MDNP模型与IBMOSA的有效性与可靠性. 结果表明:MDNP模型能够有效兼顾船舶通航效率和公平性,且IBMOSA具有较好的收敛性和全局性;通过编制协同排闸计划,对各船闸闸次安排进行合理布局,可规避梯级船闸的倒闸现象,减少船舶整体过坝时间;与原始调度方案相比,联合调度方案对3个决策目标的优化效率均接近40%,梯级枢纽通航拥堵缓解率约为16%,有效化解了梯级枢纽间的通航矛盾,提升了三峡水域的整体通航效益.
Abstract:In view of non-uniform operation rules of ship locks and non-synchronous ship scheduling in the joint navigation scheduling of cascade hubs, a multi-dimensional nonlinear programming (MDNP) model considering ship priority was constructed with the comprehensive navigation efficiency of ships, the cost of waiting for lock opening, and the carbon emission as the decision-making objectives. Then, the improved backtracking multi-objective simulated annealing algorithm (IBMOSA) was used to solve the MDNP, and the optimization scheme for joint scheduling of cascade hubs was proposed. Finally, the effectiveness and reliability of the MDNP model and IBMOSA were verified by taking the “Three Gorges-Gezhouba” Cascade Hub as an example. The results show that the MDNP model can effectively take into account the navigation efficiency of ships and fairness, and IBMOSA has good convergence and global property. At the same time, through the coordinated drainage sluice plan formulation, the opening of each lock is reasonably arranged, which avoids the phenomenon of switching operation of cascade locks and reduces the overall dam crossing time of ships. Compared with that of the original scheduling scheme, the optimization efficiency of the three decision-making objectives of the joint scheduling scheme is nearly 40%, and the traffic congestion relief rate of cascade hubs is about 16%, which effectively solves the navigation contradiction among cascade hubs and improves the overall navigation efficiency of the Three Gorges water area.
-
Key words:
- traffic management /
- joint scheduling /
- cascade hub /
- simulated annealing
-
表 1 变量说明
Table 1. Variable specification
变量类型 符号 说明 模型
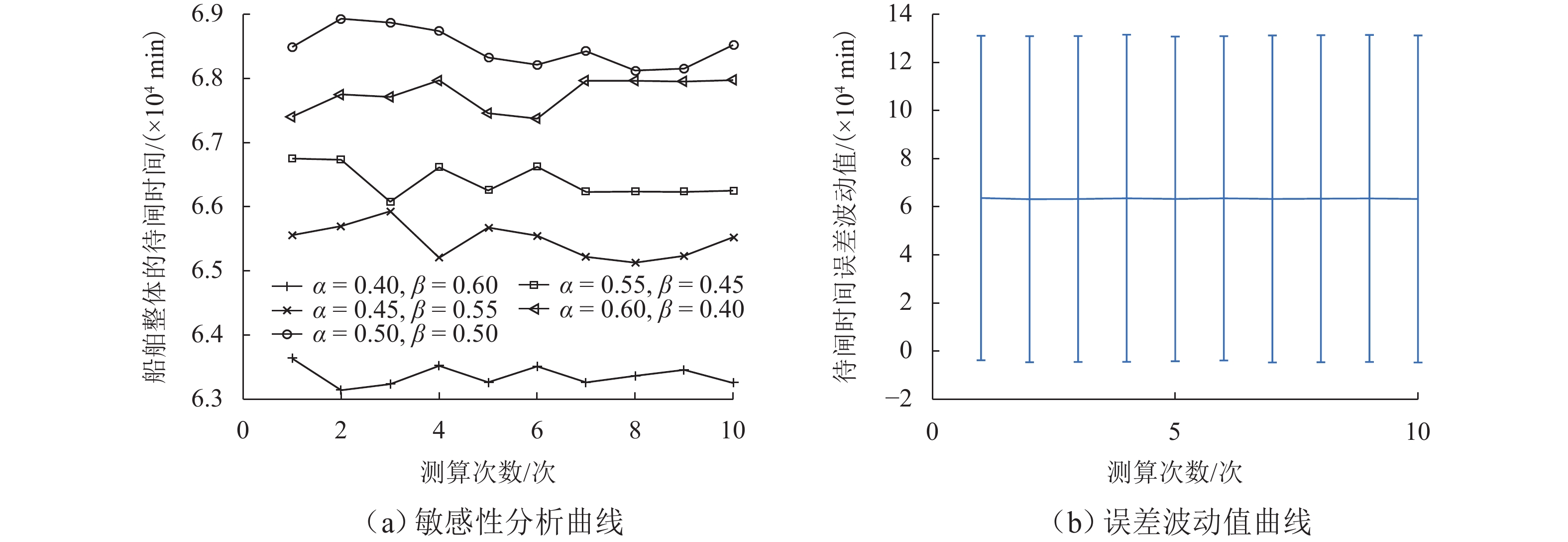
参数$U_{{\mathrm{weight}}}$ 静态权重与动态权重的相关系数 $\alpha $ 静态权重在综合权重中的比例系数 ${L_k}$ 船舶$k$的长度,${\text{m}}$ ${P_1}$ 燃油单位价格,元/L ${C_1}$ 船舶单位时间供电燃油消耗,L/min ${A_i}$ 闸室$i$的闸室面积,m2 ${X_k}$ 船舶$k$的横坐标 ${F_i}$ 由于倒闸(葛洲坝和升船机)或换向(三峡南线和北线)引起闸室$i$的附加运行时间,${\text{s}}$ ${a_k}$ 船舶$k$的船舶面积,m2 ${Q_i}$ 船闸$i$在1个调度期内的开闸总次数 ${\omega _i}$ 葛洲坝船闸$i$的开闸次数在 3 个葛洲坝船闸总开闸次数中的分配比例 ${\gamma _{m}}$ 船舶信息m的权重系数 ${K_1}$ 葛洲坝运行状态相关的参数 ${X_i}$ 闸室$i$的长度,${\text{m}}$ ${n_i}$ 闸室$i$的开闸次数,次 ${T_{i jk}}$ 船舶$k$在闸室$i$第$j$闸次的到闸时刻 $\beta $ 动态权重在综合权重中的比例系数 ${W_k}$ 船舶$k$的宽度,${\text{m}}$ ${P_2}$ 人工成本,元/min $ \mathrm{\mathit{E}_{CO}}_{_2} $ 船舶${{\mathrm{CO}}}_2$排放系数,kg/L ${B_i}$ 升船机的闸室面积,m2 ${Y_k}$ 船舶$k$的纵坐标 ${E_i}$ 闸室$i$运行一次的时间,${\text{s}}$ $N$ 申请过闸的船舶总数,艘 $ {P_{i jk}} $ 船舶$k$通过闸室i 第$j$次升降时的重量,${\text{t}}$ ${M_i}$ 闸室i计划期内通过的船舶面积和,m2 $\theta $ 影响船舶信息优先级的量化值 ${K_2}$ 葛洲坝运行状态相关的参数 ${Y_i}$ 闸室$i$的宽度,${\text{m}}$ 决策
变量${{{W}}_{\mathrm{S}}}$ 静态权重值 ${S_{i jk}}$ 船舶$k$是否通过船闸(或升船机)的0-1 决策变量, ${S_{i jk}} = 1$表示船舶$k$通过闸
室$i$第$j$闸次,反之${S_{i jk}} = 0 $${d_{i j}}$ 闸室$i$第$j$闸次的运行方向,1 为上行,0 为下行 ${t_{i jk}}$ 船舶$k$在闸室$i$第$j$闸次的过闸时刻 ${W_{\mathrm{D}}}$ 动态权重值 $W$ 综合优先级权重 表 2 通航拥堵优化效率
Table 2. Optimization efficiency of navigation congestion
目标函数值 联合调度方案 原始调度方案 优化效率 总目标值 76035.4 193925.0 0.392086631 ${F_1}$平均值 74452.1 189937.3 0.391982512 ${F_2}$平均值 1583.3 3987.7 0.397045916 ${F_3}$平均值 527.8 1329.2 0.397080951 综合通航
效率值158830.0 189940.0 0.166417290 -
[1] 交通运输部. 交通运输部关于印发《内河航运发展纲要》的通知[EB/OL]. (2020-05-29)[2023-04-17]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-06/04/content_5517185.htm. [2] 赵旭,尹熙琛,高攀. 主导权异质性视角下的过坝方式货运量分担率研究[J]. 运筹与管理,2020,29(8): 192-201.ZHAO Xu, YIN Xichen, GAO Pan. Research on the share of freight volume of via-dam method under the perspective of dominance heterogeneity[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2020, 29(8): 192-201. [3] 长江三峡通航管理局. 2022年三峡枢纽航运通过量近1.6亿吨[EB/OL]. (2023-01-01)[2023-04-17]. https://cjhy.mot.gov.cn/xw/slxw/202301/t20230104_287113.shtml. [4] 长江三峡通航管理局. 宜昌“充电站”为绿色长江赋能 [EB/OL]. (2023-01-07)[2023-04-17]. https://news.hubeidaily.net/mobile/1040558. [5] JI B, YUAN X H, YUAN Y B, et al. An adaptive large neighborhood search for solving generalized lock scheduling problem: comparative study with exact methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(8): 3344-3356. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2926405 [6] 张红颖,周子林,李彪. 基于多Agent的通航运力资源协同调度[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(1): 214-221.ZHANG Hongying, ZHOU Zilin, LI Biao. Collaborative schedule of general aviation resource based on multi-agent[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(1): 214-221. [7] 马亮,胡宸瀚,金福才,等. 铁水运输调度双层多目标约束优化模型研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(2): 357-366,397MA Liang, HU Chenhan, JIN Fucai, et al. Research on double-layer multi-objective constrained optimization model for hot metal transportation scheduling[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 357-366,397 [8] 高攀,刘顺,赵旭,等. 绿色通航视域下过坝船舶预约调度双目标优化研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2022,22(5): 293-299,336.GAO Pan, LIU Shun, ZHAO Xu, et al. Bi-objective optimization of ship dam-passing appointment scheduling considering green navigation[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(5): 293-299,336. [9] GOLAK J A P, DEFRYN C, GRIGORIEV A. Optimizing fuel consumption on inland waterway networks: local search heuristic for lock scheduling[J]. Omega, 2022, 109: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2021.102580 [10] JI B, ZHANG D Z, YU S S, et al. Optimally solving the generalized serial-lock scheduling problem from a graph-theory-based multi-commodity network perspective[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2021, 288(1): 47-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2020.05.035 [11] JI B, ZHANG D Z, YU S S, et al. An exact approach to the generalized serial-lock scheduling problem from a flexible job-shop scheduling perspective[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2021, 127: 1-17. [12] JI B, ZHANG D Z, YU S S, et al. Mathematical programming models for scheduling multiple cascaded waterway locks[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 156: 1-13. [13] 章建玲,王澎涛,袁晓辉,等. 基于进化算法和气象信息的三峡-葛洲坝通航调度研究[J]. 水电能源科学,2017,35(2): 91-94.ZHANG Jianling, WANG Pengtao, YUAN Xiaohui, et al. Co-navigation scheduling of Three Gorges-gezhouba Dam based on evolutionary algorithm and meteorological information[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2017, 35(2): 91-94. [14] 鲁彦汝. 基于随机Petri网的三峡-葛洲坝通航系统联合调度研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学,2017. [15] 甘家华,毛新华,赵京. 考虑动态交通流的停车场车辆最优疏散模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 123-130.GAN Jiahua, MAO Xinhua, ZHAO Jing. Optimal evacuation model of parking vehicles in dynamic traffic flows[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 123-130. -




 下载:
下载: