Frictional Self-Excited Vibration of a Metro Pantograph-Catenary System
-
摘要:
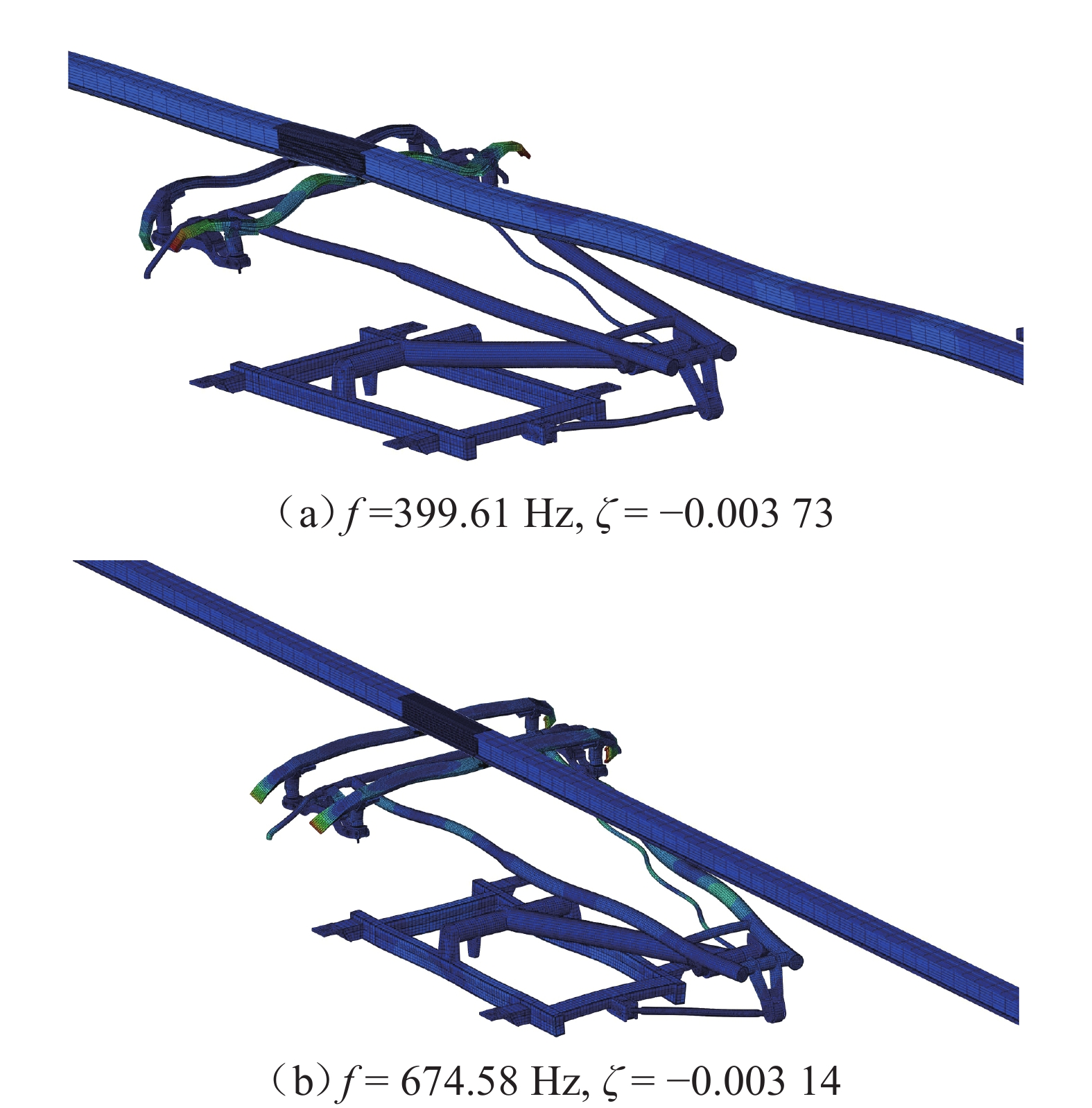
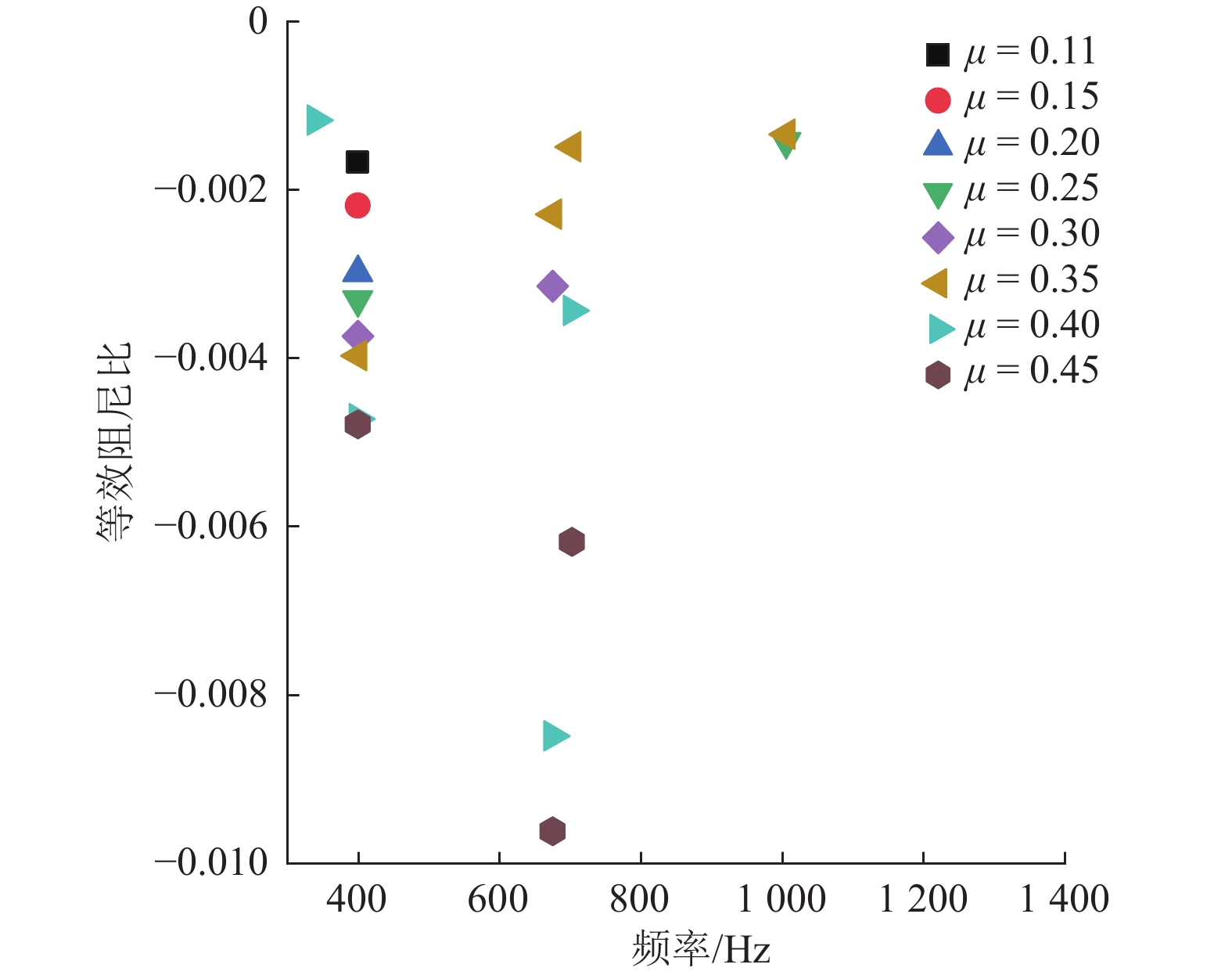
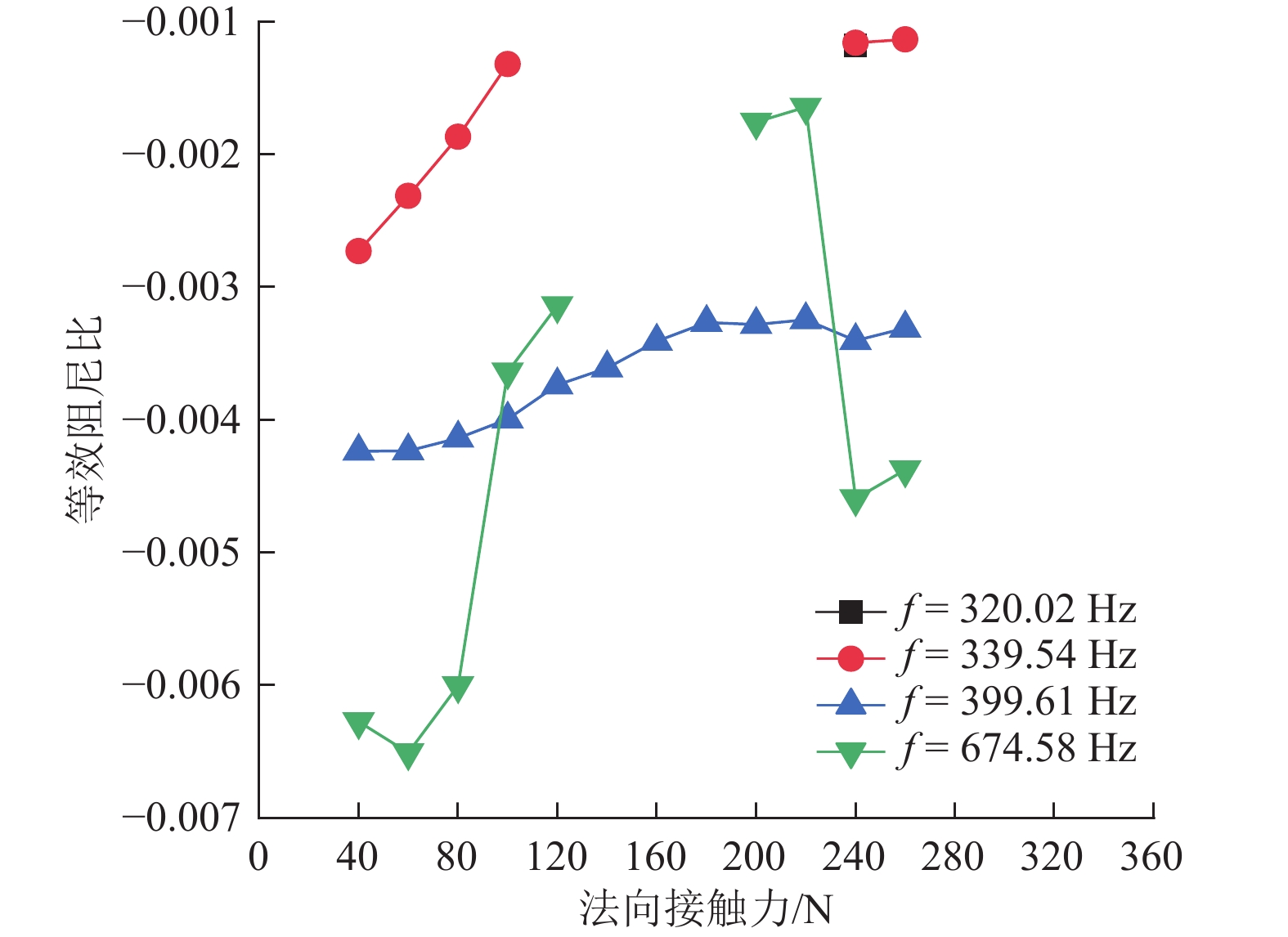
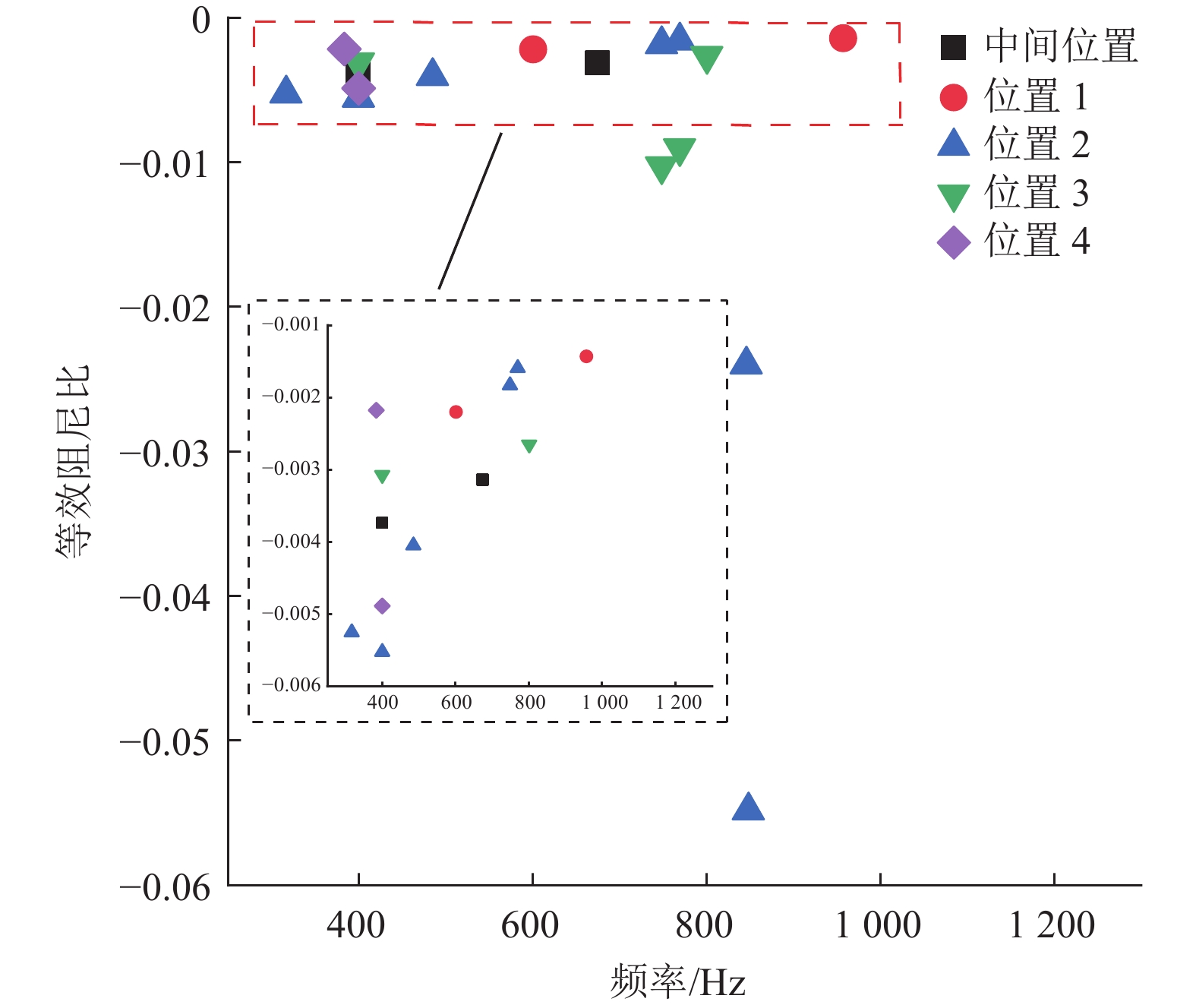
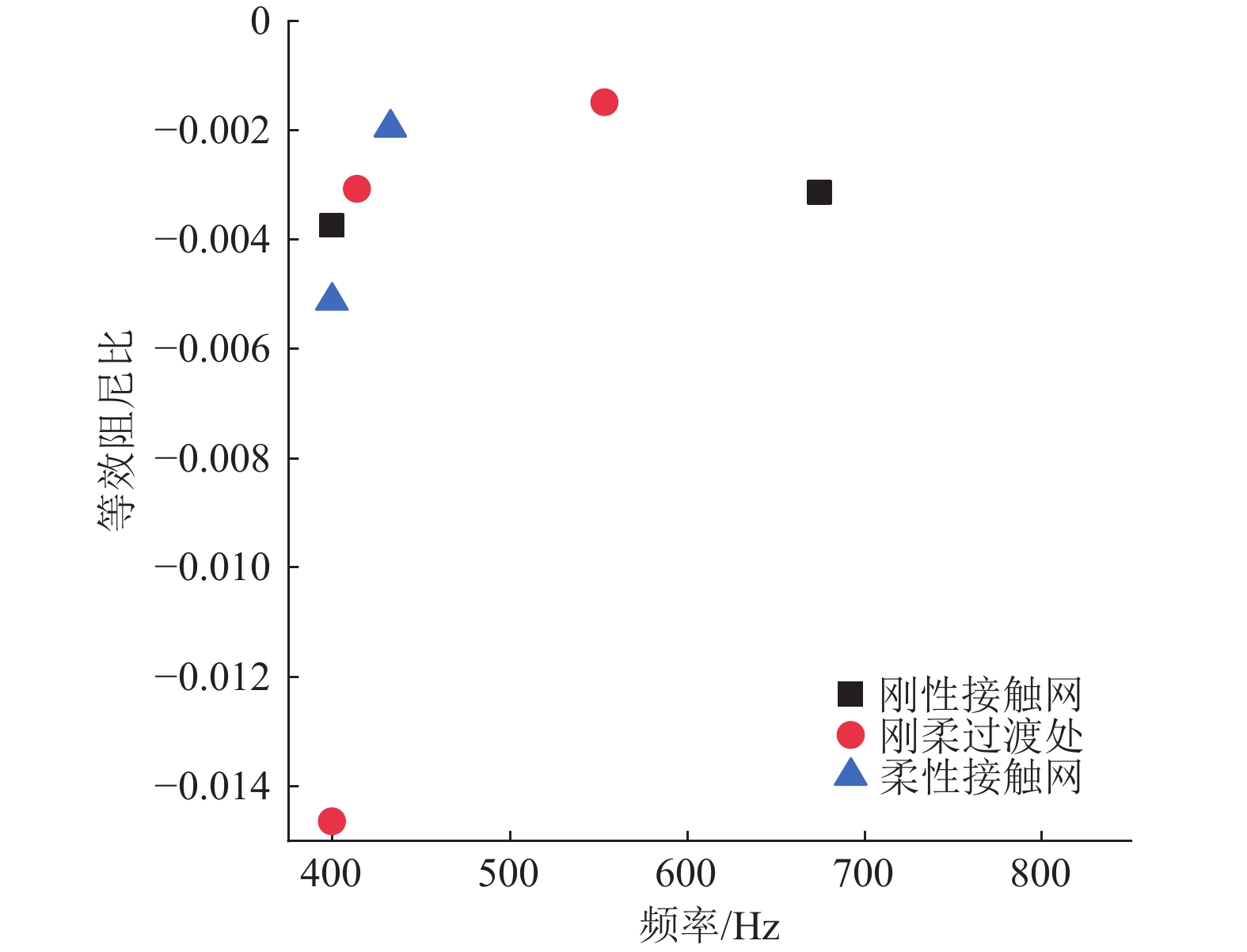
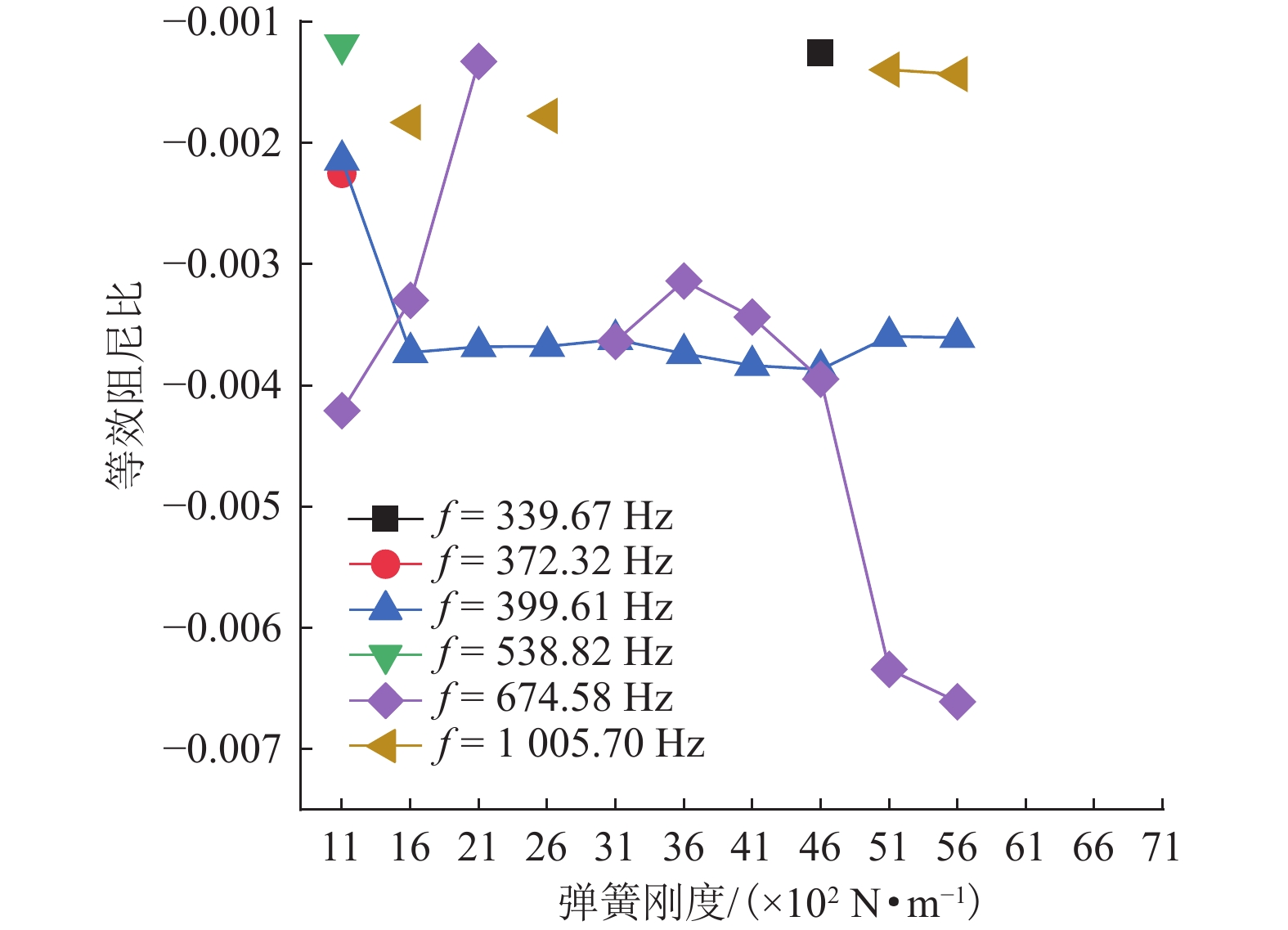
为研究弓网系统摩擦自激振动对碳滑板与接触线之间接触损耗的影响,基于摩擦自激振动理论,建立地铁刚柔过渡段处受电弓-接触网系统有限元模型,并利用复特征值分析方法研究不同弓网参数对该系统摩擦自激振动的影响. 分析结果显示:弓网系统由摩擦自激振动引起接触线波磨产生的主频为399.61 Hz;当摩擦系数大于或等于0.11时,受电弓-接触网系统出现不稳定振动,且摩擦系数越大,该系统出现不稳定振动的趋势越强;法向接触力、碳滑板与接触线的接触位置以及弓头弹簧刚度对弓网系统摩擦自激振动的产生有很大影响;摩擦系数低于0.11并且选择合适的法向接触力或调整弓头弹簧刚度可以抑制甚至消除弓网系统的摩擦自激振动,进而减少弓/网间摩擦引起的接触损耗.
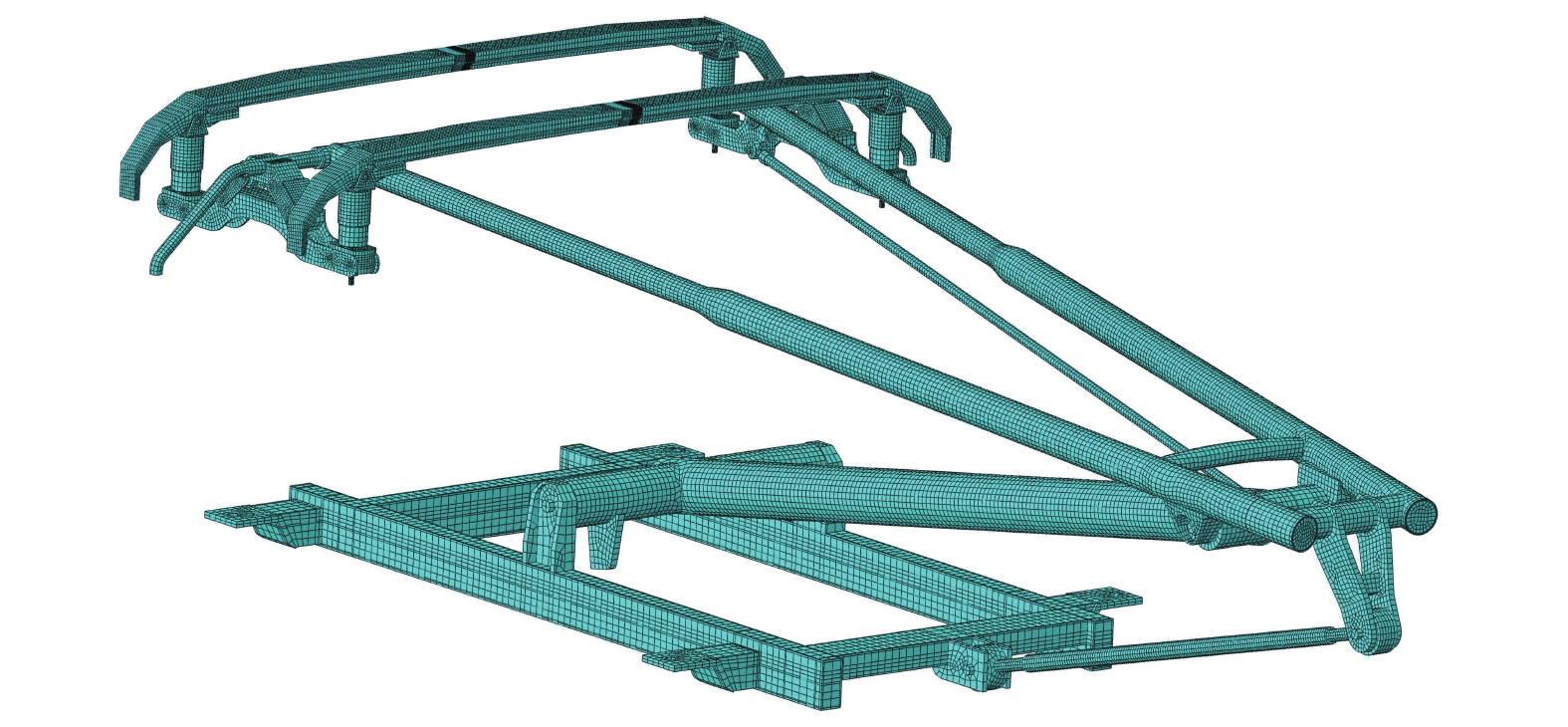
Abstract:In order to study the influence of frictional self-excited vibration of a pantograph-catenary system on the contact loss between the carbon strip and contact wire, a finite element model of the pantograph-catenary system at the rigid and flexible transition section of a metro was established based on the theory of frictional self-excited vibration. The complex eigenvalue analysis method was used to study the influence of different pantograph-catenary parameters on the frictional self-excited vibration of the system. The analysis results show that the main frequency of contact line corrugation caused by frictional self-excited vibration of the pantograph-catenary system is 399.61 Hz. When the friction coefficient is greater than or equal to 0.11, the pantograph-catenary system has unstable vibration, and with the increase in the friction coefficient, the unstable vibration tends to be stronger. The normal contact force, the contact position between the carbon strip and the contact wire, and the stiffness of the pantograph bow spring have great influences on the occurrence of the frictional self-excited vibration of the pantograph-catenary system. When the friction coefficient is less than 0.11, selecting the appropriate normal contact force or adjusting the stiffness of the pantograph bow spring can restrain or even eliminate the frictional self-excited vibration of the pantograph-catenary system and then reduce the contact loss caused by the friction between the pantograph and catenary.
-
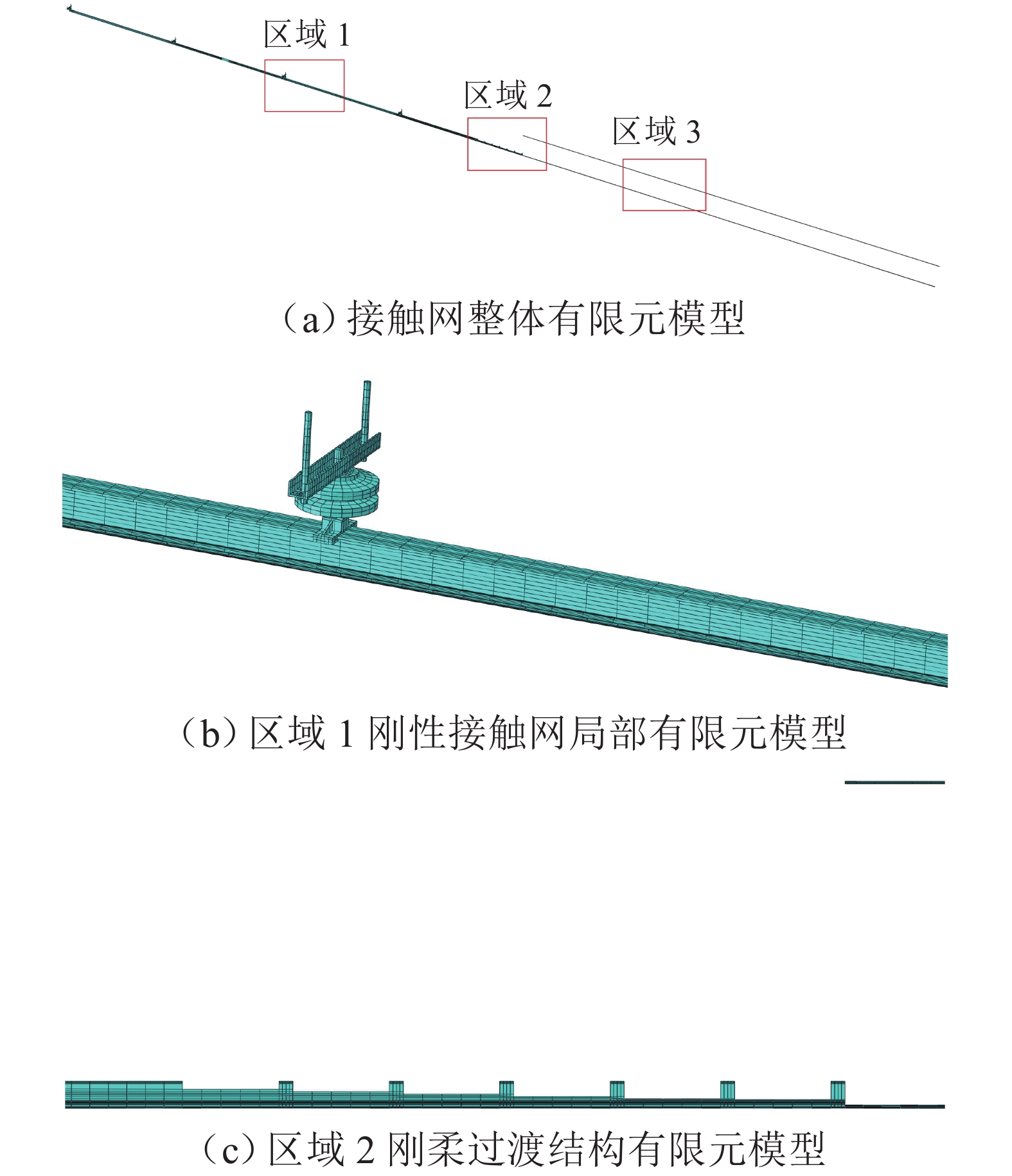
表 1 刚性接触网模型参数
Table 1. Rigid catenary model parameters
部件 材料 密度/
(× 103 kg•m−3)弹性模量/
GPa泊松比 汇流排 6101B 2.71 69 0.33 接触线 CTHA120 8.92 130 0.30 定位线夹 铝合金 2.70 70 0.34 绝缘子 陶瓷 3.80 340 0.22 表 2 柔性接触网模型参数
Table 2. Flexible catenary model parameters
部件 材料 密度/
(× 103 kg•m−3)弹性模量/
GPa泊松比 承力索 JT150 9.20 105 0.30 接触线 CTHA120 8.92 130 0.30 表 3 受电弓各部件材料
Table 3. Material properties of pantograph components
部件 材料 密度/
( × 103 kg•m–3)弹性模量/
GPa泊松比 平衡杆 碳纤维 1.9 231 0.23 碳滑板 铜、碳 2.4 12.6 0.43 下臂杆 铝合金 2.8 72 0.33 弓头支架 钛合金 4.5 117 0.34 其他部件 Q235 7.8 210 0.30 表 4 弓网系统计算参数变化范围
Table 4. Variation range of calculation parameters of pantograph-catenary system
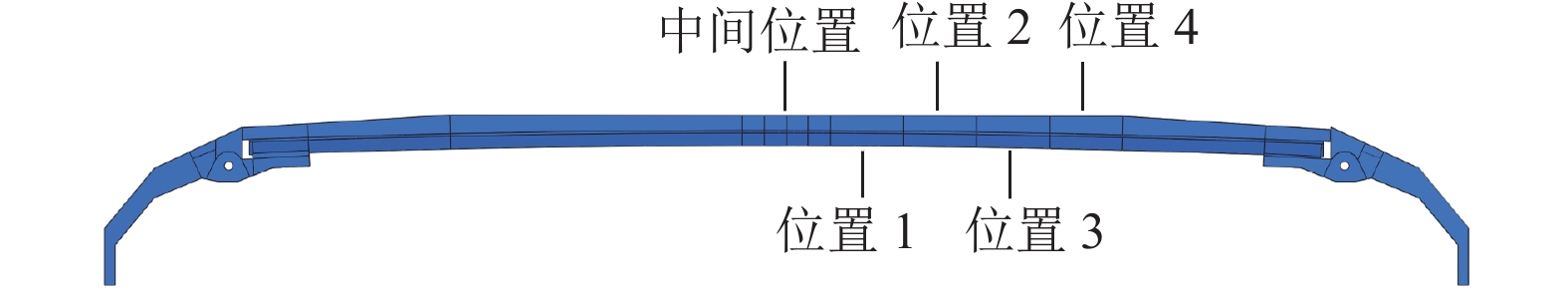
参数 数值 摩擦系数 0.11~0.45 法向接触力/N 40~260 碳滑板接触位置 中间位置,位置 1~4 接触网类型 刚性接触网、刚柔过渡处、柔性接触网 弓头弹簧刚度/
(N•m−1)1100 ~5600 -
[1] 关金发,田志军,吴积钦. 基于弓网动力仿真的160 km/h刚柔过渡系统方案研究[J]. 铁道学报,2018,40(9): 48-56.GUAN Jinfa, TIAN Zhijun, WU Jiqin. Research of 160 km/h transition structure proposal between overhead conductor railand contact line based on dynamic simulation[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2018, 40(9): 48-56. [2] 王建红. 重庆轨道六号线支线二期工程接触网刚柔过渡[J]. 现代制造技术与装备,2022,58(9): 127-129.WANG Jianhong. Rigid flexible transition of OCS of Chongqing rail line 6 branch line phase Ⅱ project[J]. Modern Manufacturing Technology and Equipment, 2022, 58(9): 127-129. [3] 杨清太. 既有线铁路接触网刚柔过渡问题探析[J]. 工程建设与设计,2021(13): 74-76.YANG Qingtai. A study on rigid and flexible catenary transition for existing rail-line[J]. Construction & Design for Engineering, 2021(13): 74-76. [4] 梅桂明. 刚性接触网-受电弓载流磨损性能的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(6): 1305-1310.MEI Guiming. Experimental study on wear performance of rigid catenary-pantograph system with direct current[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(6): 1305-1310. [5] 周宁,支兴帅,张静,等. 电气化铁路弓网系统摩擦磨损性能研究进展[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(5):990-1005.ZHOU Ning, ZHI Xingshuai, ZHANG Jing, et al. Friction and wear performance of pantograph-catenary system in electrified railways: State of the art[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5):990-1005. [6] 范杰,刘达毅,董丙杰,等. 地铁刚性弓网系统接触线磨损特性试验研究[J]. 润滑与密封,2022,47(6): 45-51.FAN Jie, LIU Dayi, DONG Bingjie, et al. Experimental study on the wear characteristics of contact wire of metro rigid pantograph-catenary systems[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2022, 47(6): 45-51. [7] YANG H J, LI C, LIU Y H, et al. Study on the delamination wear and its influence on the conductivity of the carbon contact strip in pantograph-catenary system under high-speed current-carrying condition[J]. Wear, 2021, 477:203823.1-203823.14. [8] MANDAI T, HARADA S, SHIMIZU M, et al. Improvement of rigid conductor lines[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2003, 44(2): 78-81. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.44.78 [9] WU T X, BRENNAN M J. Dynamic stiffness of a railway overhead wire system and its effect on pantograph-catenary system dynamics[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1999, 219(3): 483-502. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.1998.1869 [10] CHEN L, LIU Z G, ZHANG J, et al. Influence of key parameters on high speed overhead conductor rail and pantograph system[C]//The IAVSD International Symposium on Dynamics of Vehicles on Roads and Tracks. Cham: Springer, 2020: 201-211. [11] SHIMIZU M, HARADA S, OYA A, et al. Improving performance of type T overhead rigid conductor lines[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2006, 47(1): 52-58. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.47.52 [12] 钱世勇,陈珍宝,陈明国,等. 地铁弓网动态试验研究及分析[J]. 科协论坛(下半月),2012(5): 26-27.QIAN Shiyong, CHEN Zhenbao, CHEN Mingguo, et al. Research and analysis on dynamic test of metro pantograph and catenary[J]. Science & Technology Association Forum, 2012(5): 26-27. [13] 谭冬华. 架空刚性接触悬挂弓网磨耗异常的解决办法[J]. 都市快轨交通,2007,20(2): 88-91.TAN Donghua. Causes and solutions for the abnormal pantograph-catenary attrition of rigid catenary[J]. Urban Rapid Rail Transit, 2007, 20(2): 88-91. [14] 裴志禹. AC25 kV刚性接触网过渡段结构优化研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2018. [15] QIAN W J, CHEN G X, ZHANG W H, et al. Friction-induced, self-excited vibration of a pantograph-catenary system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2013, 135(5): 051021.1- 051021. 8 [16] WU B W, SHANG Z Y, PAN J B, et al. Analysis on the formation cause for the high-order wheel polygonization of the high-speed trains based on the finite element method[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2023, 61(1): 1-18. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2022.2035777 [17] CUI X L, CHENG Z, YANG Z C, et al. Study on the phenomenon of rail corrugation on high-speed rail based on the friction-induced vibration and feedback vibration[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2022, 60(2): 413-432. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2020.1817507 [18] 康熙,陈光雄,吕金洲,等. 缩尺轮轨模型中钢轨波磨的相似性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(6): 1320-1327.KANG Xi, CHEN Guangxiong, LÜ Jinzhou, et al. Similarity of small-scale wheelset-track model for investigation of rail corrugation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1320-1327. [19] 陈光雄. 钢轨波磨预测模型验证工况的研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(5): 1017-1023,1054.CHEN Guangxiong. Study on validation conditions of rail corrugation prediction models[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(5): 1017-1023,1054. [20] 田珂. 地铁受电弓—刚性接触网建模及仿真研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2018. [21] 朱志增. 基于有限元分析的刚性悬挂弓网接触压力仿真研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2014. [22] 杨艺,周宁,李瑞平,等. 基于有限元法的弓网过渡段处动态性能仿真分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2016,35(18): 71-75,116.YANG Yi, ZHOU Ning, LI Ruiping, et al. Dynamic performance analysis of different sections of overhead catenary based on finite element model[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(18): 71-75,116. [23] YUAN Y. An eigenvalue analysis approach to break squeal problem[C]//Proceedings of the 29th ISATA conference on automotive braking systems. Florence: ISATA, 1996: 3-6. [24] 黄之元. 两种地铁刚性接触网摩擦副异常磨耗的试验研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2020. -




 下载:
下载: