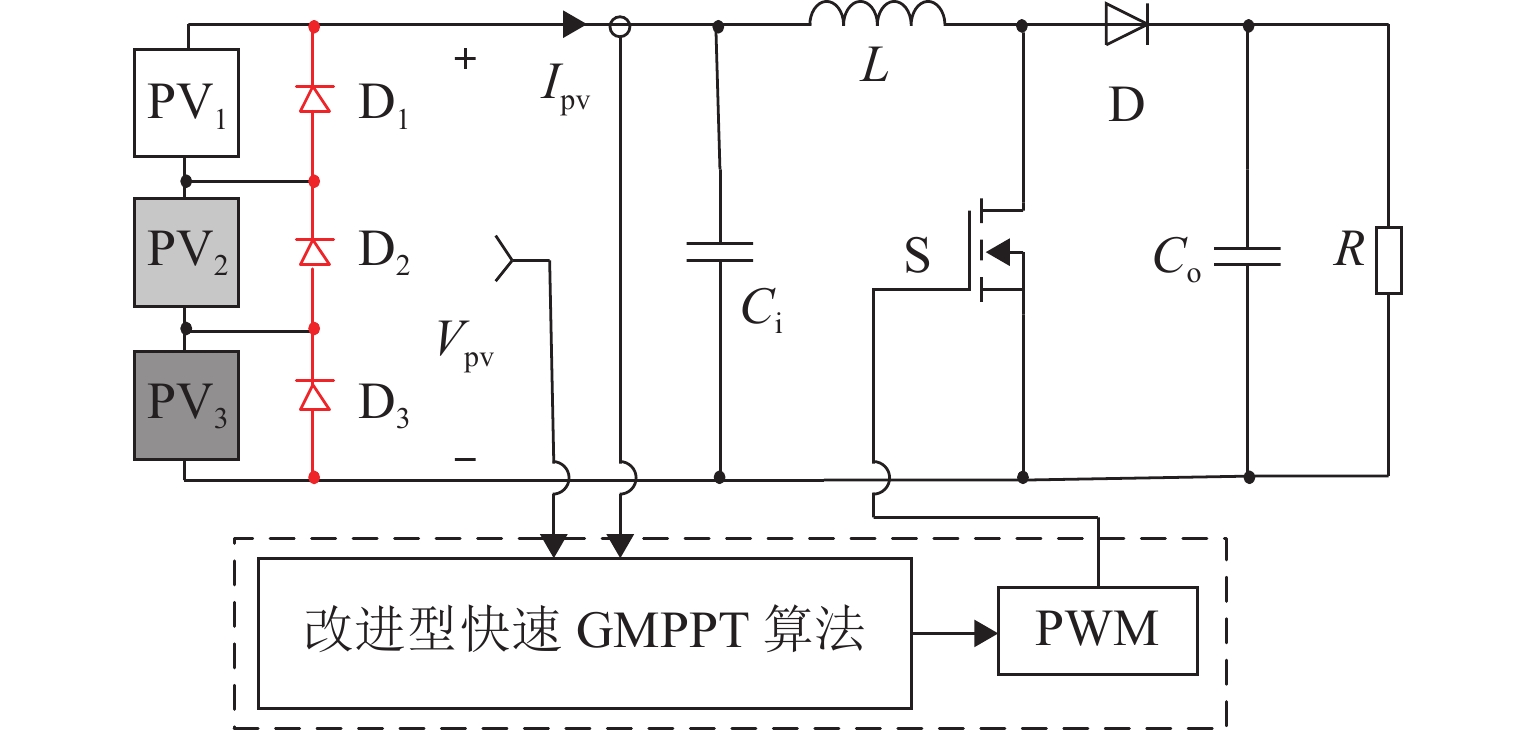
Improved and Fast Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm of Photovoltaic Power Generation System
-
摘要:
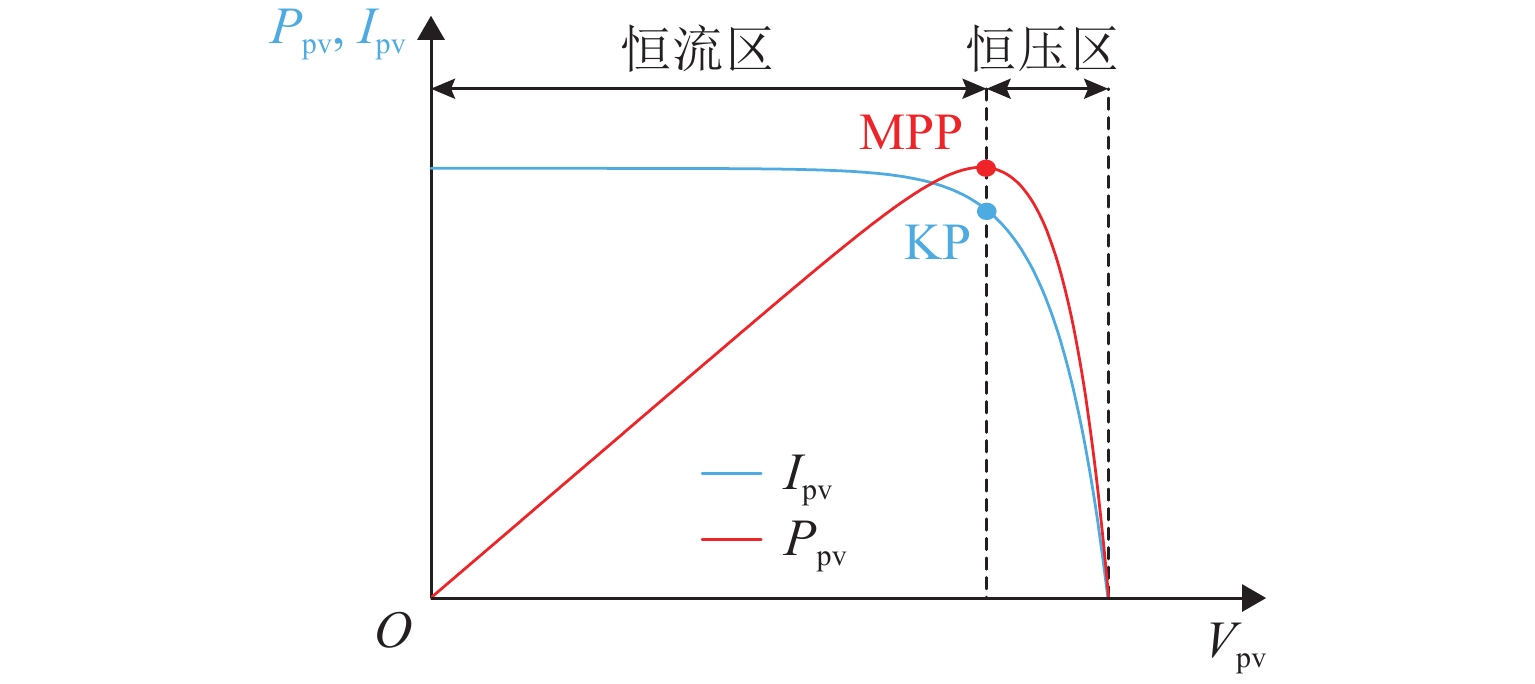
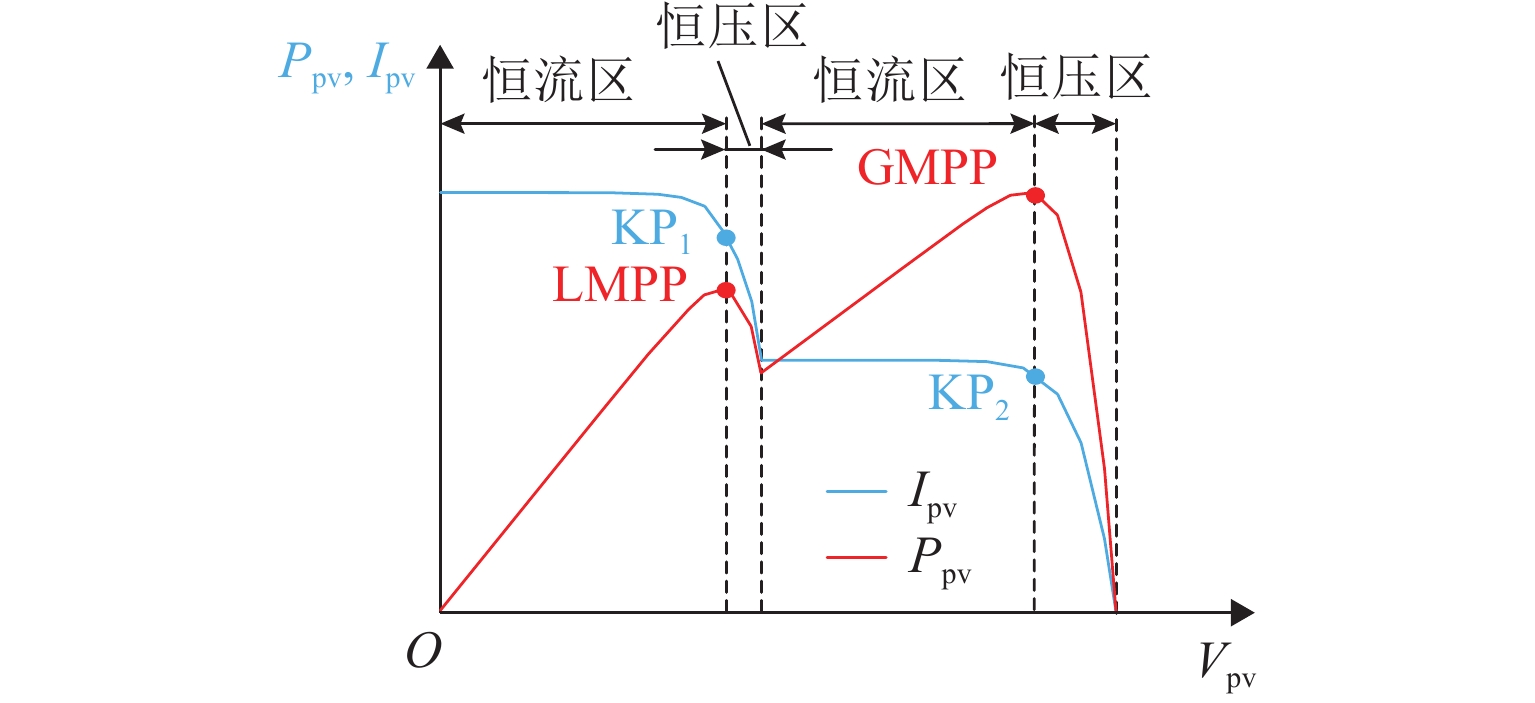
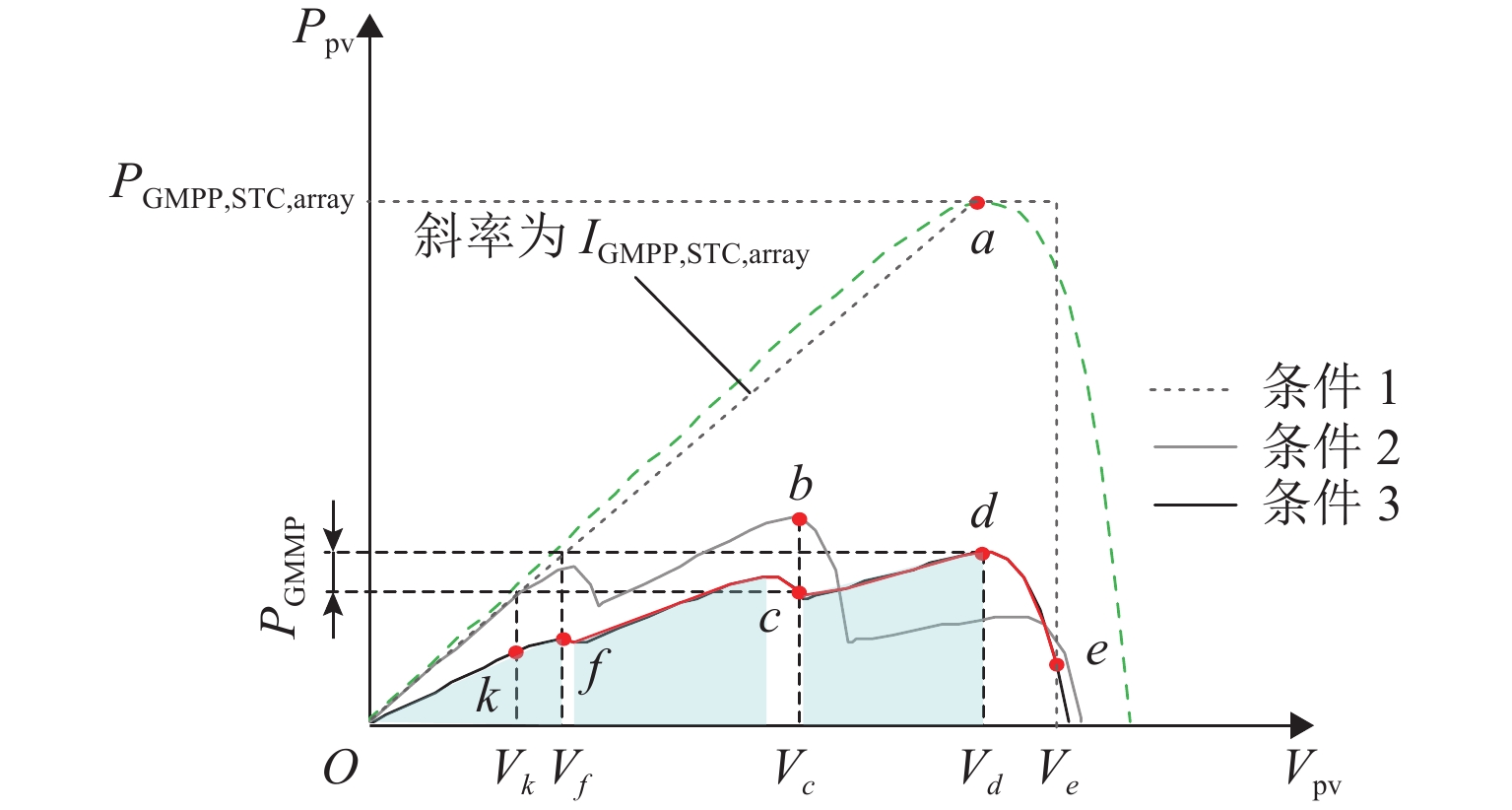
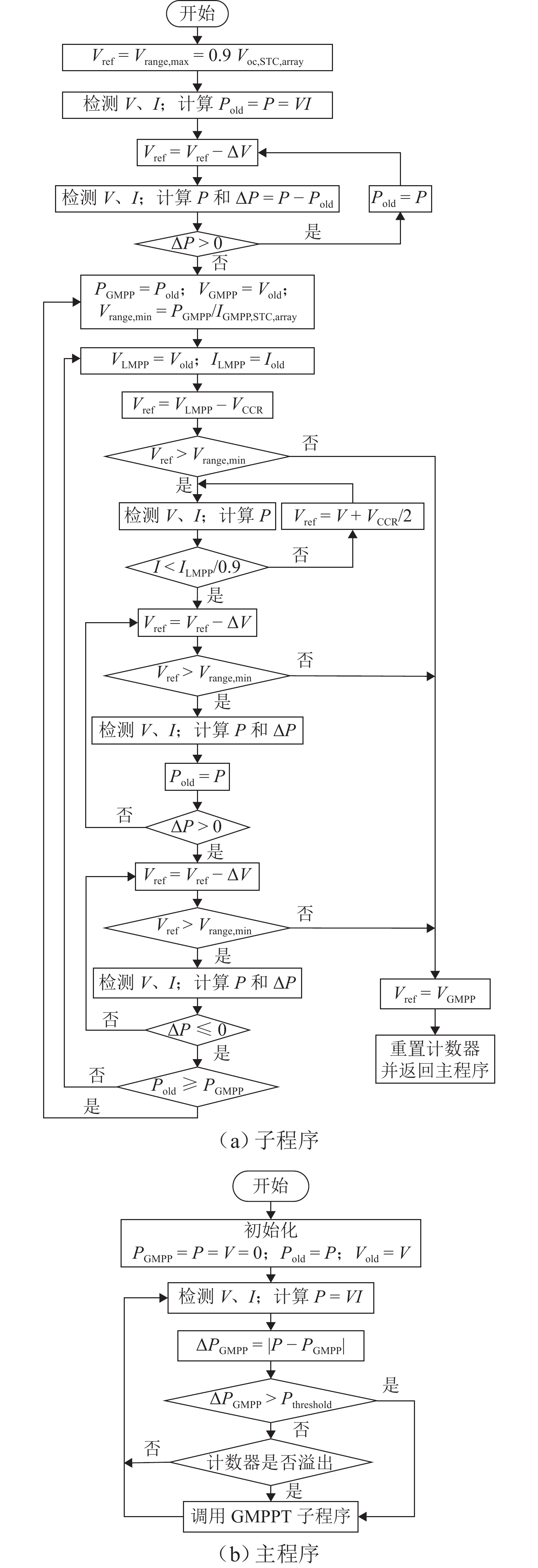
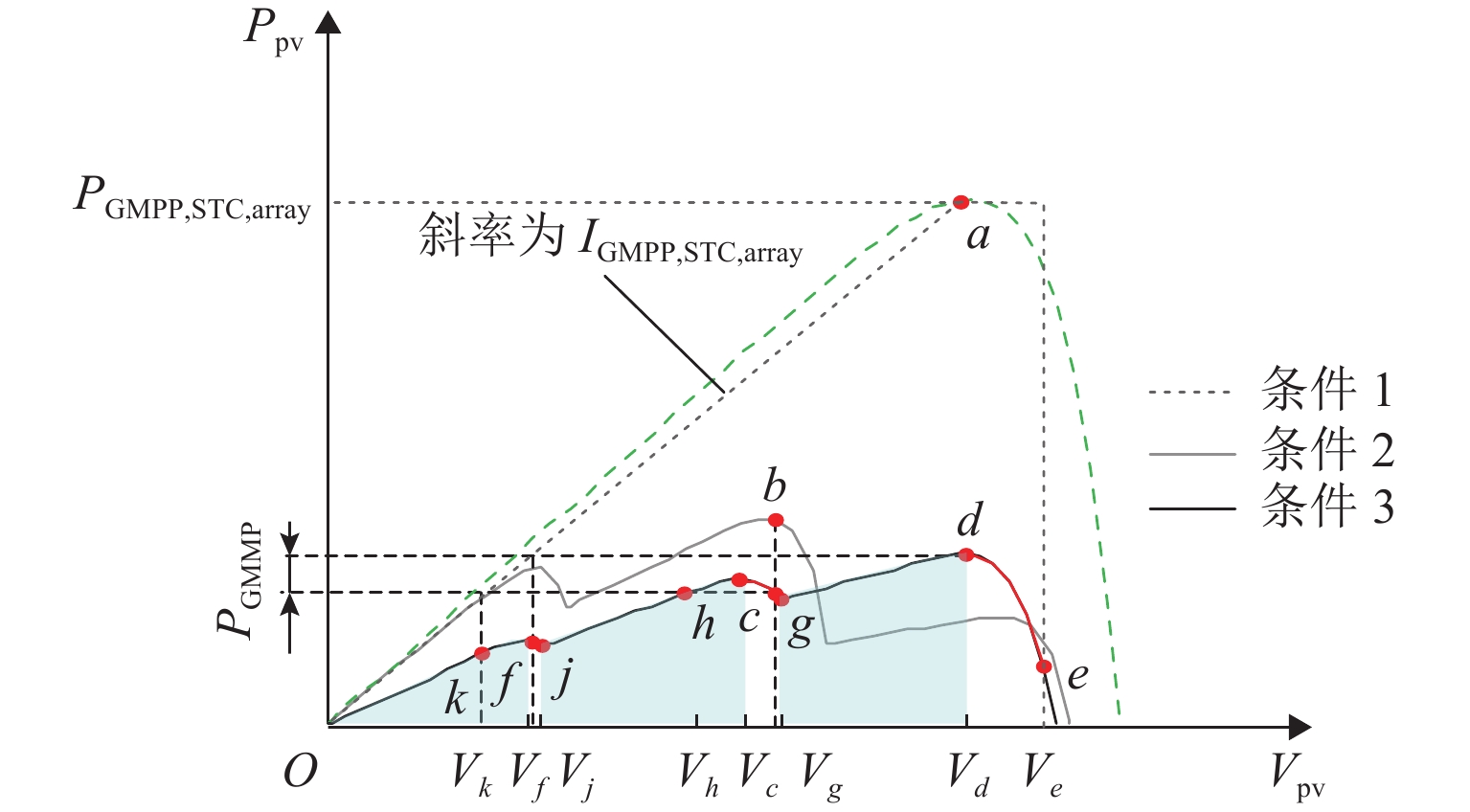
为提高局部阴影条件下光伏发电的能量利用率,提出一种改进型快速全局最大功率点跟踪(global maximum power point tracking, GMPPT)算法. 首先,研究局部阴影条件下光伏阵列的输出特性,并根据光伏阵列输出曲线中膝点与开路电压的关系,将其划分为恒流区和恒压区;其次,分析传统的最大功率梯形(maximum power trapezium,MPT)算法和以MPT算法为基础的改进型快速GMPPT算法的工作原理,改进型快速GMPPT算法利用电压的动态上、下限来限定搜索区间,并跳过调整时间较长的恒流区,以提高跟踪速度;最后,通过仿真与实验验证算法的有效性. 实验结果表明:改进型快速GMPPT算法的最短跟踪时间为4.0 s,扫描电压与能量损失分别为17.34 V和98.19 J;与传统全局扫描算法相比,跟踪时间缩短68.25%,扫描电压降低74.86%,能量损失减少58.19%;与MPT算法相比,跟踪时间缩短68.00%,扫描电压降低75.63%,能量损失减少62.31%.
Abstract:In order to improve the energy utilization of photovoltaic (PV) power generation under partial shading conditions (PSCs), an improved and fast global maximum power point tracking (GMPPT) algorithm was proposed. Firstly, the output characteristics of PV array under PSCs were researched, and the output curve of PV array was divided into constant current region (CCR) and constant voltage region (CVR) according to the relationship between knee point and open circuit voltage. Then, the operation principles of the traditional maximum power trapezium (MPT) algorithm and the improved and fast GMPPT algorithm were analyzed. The improved and fast GMPPT algorithm is based on the MPT algorithm, where the search interval is limited by dynamic upper and lower limits of voltage, and CCR with a long adjustment time was skipped to further improve the tracking speed. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm was verified by simulation and experiment. The experimental results reveal that the minimum tracking time of the improved and fast GMPPT algorithm is 4.0 s, and the scanning voltage and the energy loss of the proposed algorithm are 17.34 V and 98.19 J, respectively. Compared with the traditional global scanning algorithm and the MPT algorithm, the proposed algorithm decreases tracking time by 68.25% and 68.00%, lowers scanning voltage by 74.86% and 75.63%, and reduces energy loss by 58.19% and 62.31%, respectively.
-
表 1 光伏阵列的输出参数
Table 1. Output parameters of the PV array
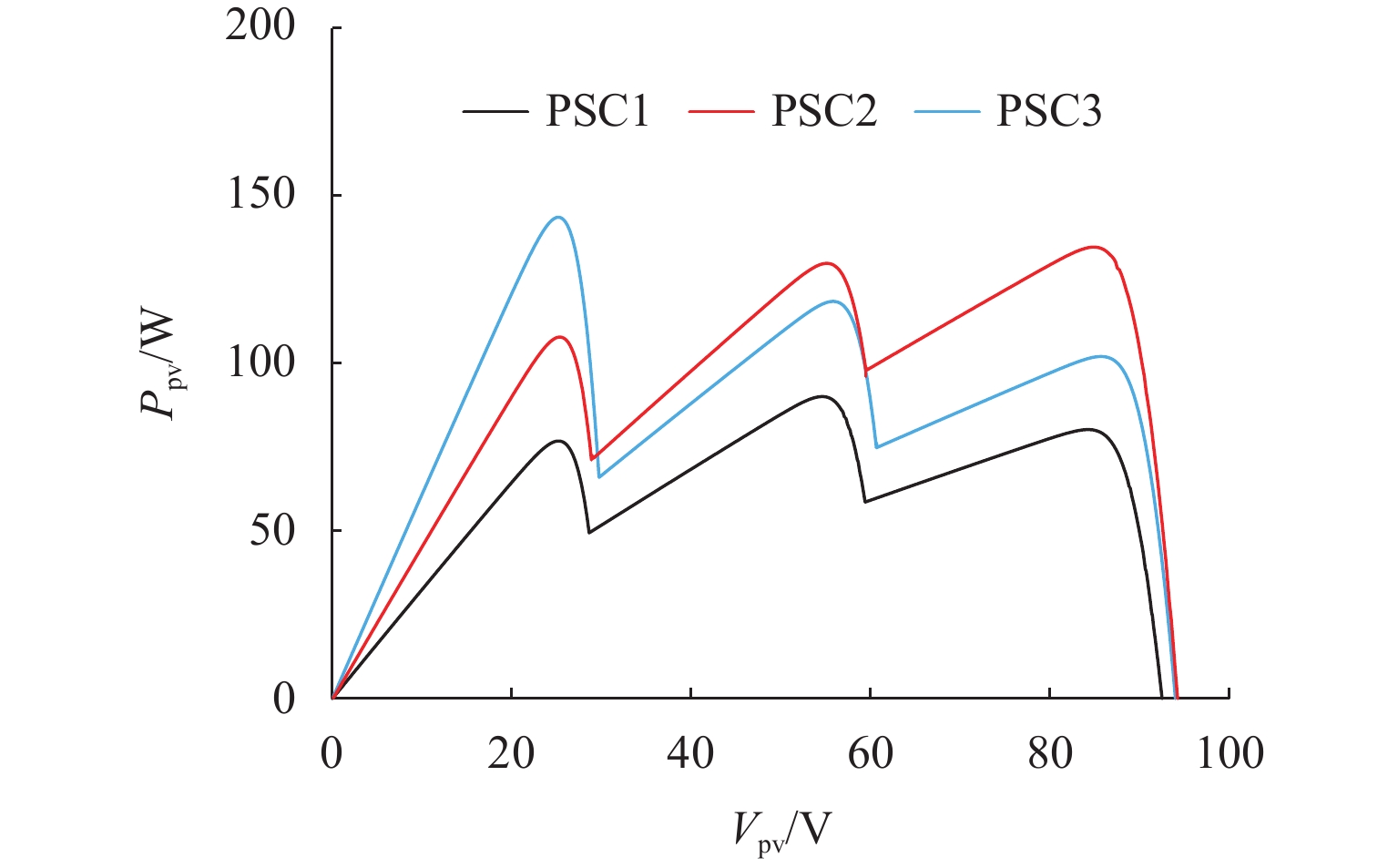
条件 光照强度/(W·m−2) 全局最大功率点 PV1 PV2 PV3 功率/W 电压/V 电流/A PSC1 120 210 400 90.13 54.60 1.65 PSC2 200 300 560 134.60 84.80 1.59 PSC3 150 270 750 143.60 25.20 5.70 表 2 阴影条件变化下3种算法的仿真跟踪性能比较
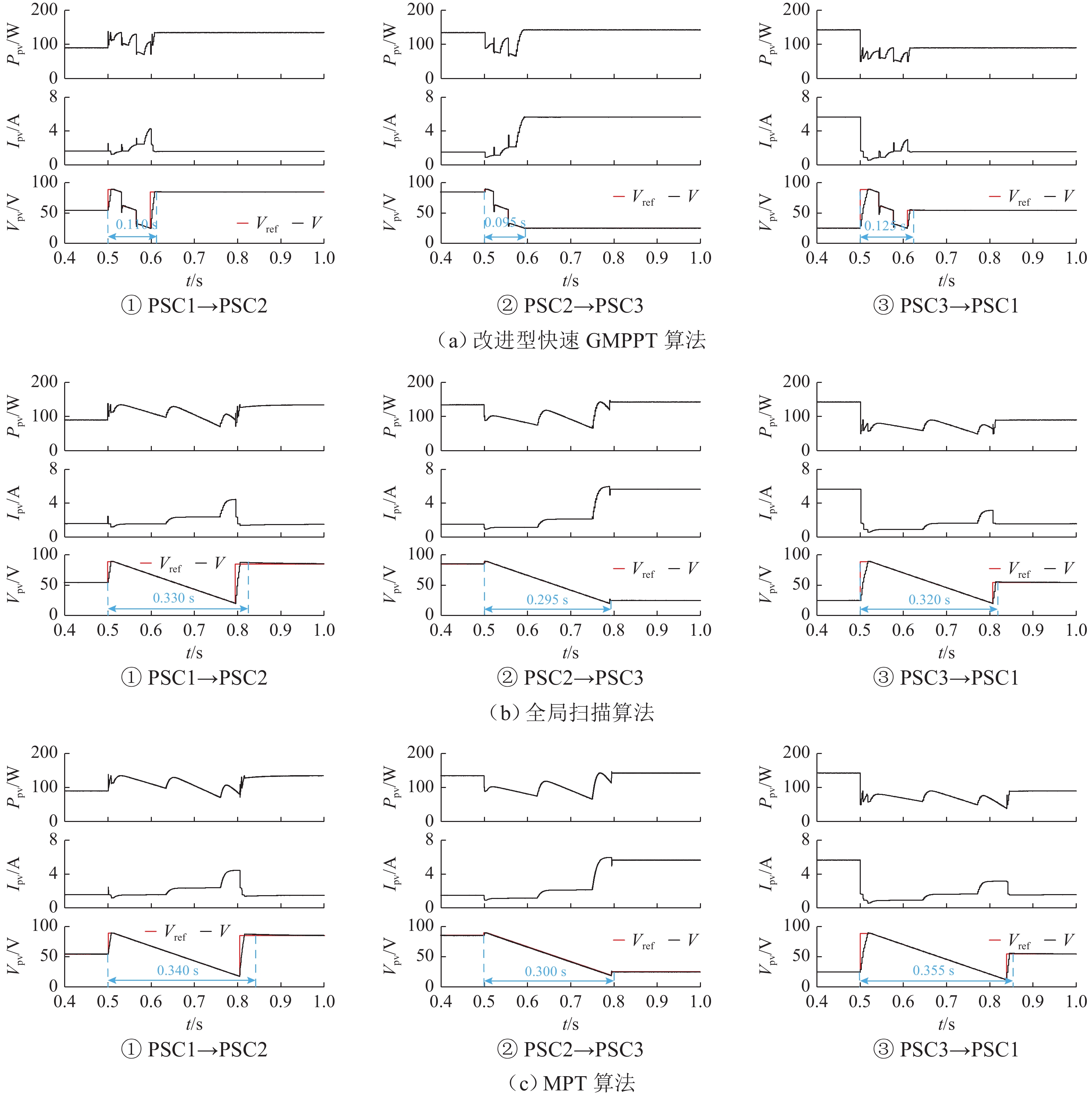
Table 2. Simulation tracking performance comparison of the three algorithms under shading variation
光照条件 扫描时间/s 总路径的扫描电压/V 能量损失/J 算法 1 算法 2 算法 3 算法 1 算法 2 算法 3 算法 1 算法 2 算法 3 PSC1→PSC2 0.110 0.330 0.340 17.34 69.09 71.14 2.94 7.81 8.25 PSC2→PSC3 0.095 0.295 0.300 17.57 69.09 69.96 4.76 13.66 13.69 PSC3→PSC1 0.125 0.320 0.355 17.34 69.09 76.99 2.63 6.13 7.41 表 3 阴影变化下3种算法的实验跟踪性能比较
Table 3. Experiment tracking performance comparison of the three algorithms under shading variation
光照条件 扫描时间/s 总路径的扫描电压/V 能量损失/J 算法 1 算法 2 算法 3 算法 1 算法 2 算法 3 算法 1 算法 2 算法 3 PSC1→PSC2 4.0 12.6 12.5 17.34 69.09 71.14 98.19 234.86 260.49 PSC2→PSC3 4.2 12.3 12.4 17.57 69.09 69.96 158.23 467.10 467.35 PSC3→PSC1 4.5 12.6 13.8 17.34 69.09 76.99 72.00 266.25 311.85 -
[1] GHANBARI T. Hot spot detection and prevention using a simple method in photovoltaic panels[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2017, 11(4): 883-890. [2] 杨永恒,周克亮. 光伏电池建模及MPPT控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2011,26(增1): 229-234.YANG Yongheng, ZHOU Keliang. Photovoltaic cell modeling and MPPT control strategies[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011, 26(S1): 229-234. [3] AHMED J, SALAM Z. An enhanced adaptive P&O MPPT for fast and efficient tracking under varying environmental conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2018, 9(3): 1487-1496. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2018.2791968 [4] 韩国鹏,薛聪聪,王伟,等. 应对移动阴影的车载光伏步进扫描快速功率追踪[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(2): 354-362.HAN Guopeng, XUE Congcong, WANG Wei, et al. Fast power tracking step-scanning method of vehicle-mounted photovoltaic system with moving shadows[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(2): 354-362. [5] 陈维荣,傅王璇,韩莹,等. 计及需求侧的风-光-氢多能互补微电网优化配置[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(3): 640-649.CHEN Weirong, FU Wangxuan, HAN Ying, et al. Optimal configuration of wind-solar-hydrogen multi-energy complementary microgrid with demand side[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 640-649. [6] VELASCO-QUESADA G, GUINJOAN-GISPERT F, PIQUE-LOPEZ R, et al. Electrical PV array reconfiguration strategy for energy extraction improvement in grid-connected PV systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(11): 4319-4331. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2024664 [7] NGUYEN D, LEHMAN B. An adaptive solar photovoltaic array using model-based reconfiguration algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2008, 55(7): 2644-2654. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.924169 [8] BISWAS J, KAMATH A M, GOPI A K, et al. Design, architecture, and real-time distributed coordination DMPPT algorithm for PV systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2018, 6(3): 1418-1433. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2017.2756698 [9] ISHAQUE K, SALAM Z. A deterministic particle swarm optimization maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic system under partial shading condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 60(8): 3195-3206. [10] 陈维荣,王伟颖,郑义斌,等. 局部阴影光伏发电系统中基于改进PSO的MPPT控制[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2018,53(6): 1095-1101,1129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.06.001CHEN Weirong, WANG Weiying, ZHENG Yibin, et al. MPPT control of partial shadow photovoltaic generation system based on improved PSO algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(6): 1095-1101,1129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2018.06.001 [11] NGUYEN T L, LOW K S. A global maximum power point tracking scheme employing DIRECT search algorithm for photovoltaic systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(10): 3456-3467. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2039450 [12] MALATHY S, RAMAPRABHA R. Maximum power point tracking algorithm of SPVA under inhomogeneous irradiation conditions: a modified Fibonacci search based approach[C]//2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems (PEDS). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 487-492. [13] MURTAZA A, CHIABERGE M, SPERTINO F, et al. A maximum power point tracking technique based on bypass diode mechanism for PV arrays under partial shading[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2014, 73: 13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.01.018 [14] 王云平,李颖,阮新波. 基于局部阴影下光伏阵列电流特性的最大功率点跟踪算法[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(14): 201-210,218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2016.14.023WANG Yunping, LI Ying, RUAN Xinbo. Maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic array under partial shading based on current property[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(14): 201-210,218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2016.14.023 [15] FURTADO A M S, BRADASCHIA F, CAVALCANTI M C, et al. A reduced voltage range global maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(4): 3252-3262. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2750623 [16] AQUIB M, JAIN S, AGARWAL V. A time-based global maximum power point tracking technique for PV system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(1): 393-402. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2915774 [17] AQUIB M, JAIN S. A global maximum power point tracking technique based on current source region detection of I-V curve[C]//2018 IEEMA Engineer Infinite Conference (eTechNxT). New Delhi: IEEE, 2018: 1-5. [18] 王云平. 局部阴影条件下光伏阵列结构、MPPT方法及阻抗匹配变换器研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学,2018. [19] WANG Y P, LI Y, RUAN X B. High-accuracy and fast-speed MPPT methods for PV string under partially shaded conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(1): 235-245. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2465897 [20] 丁金磊,程晓舫,翟载腾,等. 太阳电池填充因子随日照强度变化的理论分析与计算[J]. 中国工程科学,2007,9(6): 82-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2007.06.015DING Jinlei, CHENG Xiaofang, ZHAI Zaiteng, et al. Theoretical analysis and calculation for filling factor of solar cell varying along with illumination intensity[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2007, 9(6): 82-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2007.06.015 -




 下载:
下载: