LQR Control Strategy for Electromagnetic Active Suspension Considering Energy Consumption
-
摘要:
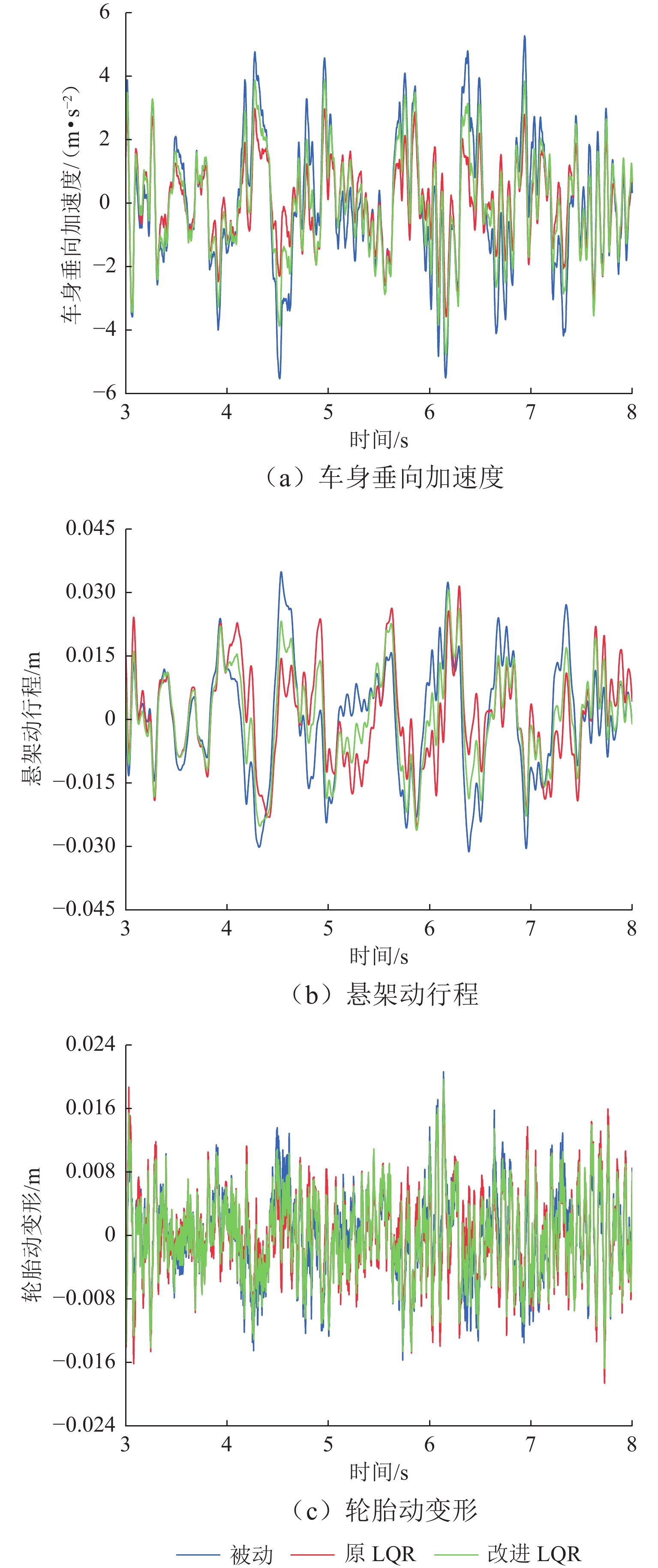
为改善车辆电磁主动悬架功率过大的问题,提出一种考虑能耗的改进线性二次型调节器(linear quadratic regulator,LQR)控制策略. 首先,介绍电磁主动悬架的结构,由等效磁路法得出直线电机的推力模型,再建立电磁主动悬架的动力学模型;其次,在传统的LQR加权系数优化模型基础上提出增加有关能耗的约束条件,设计了一种改进LQR控制策略;最后,使用MATLAB/Simulink进行仿真,通过主动力大小进行控制器正确性的验证,并对比分析随机路面下的能耗与动力学效果. 结果表明:改进LQR控制策略的主动力大小符合优化时约束的概率最低为99.89%;改进LQR控制策略与原LQR控制策略相比,功率均方根降低80.29%,悬架动行程均方根没有明显差别,轮胎动变形均方根优于原LQR控制策略约5%,车身垂向加速度降幅最低仍能达到原LQR控制策略的50%.
Abstract:In order to reduce the excessive power consumption of vehicle electromagnetic active suspension, a modified linear quadratic regulator (LQR) control strategy considering energy consumption was raised. Firstly, the structure of electromagnetic active suspension was introduced. The thrust model of the linear motor was established by the equivalent magnetic circuit method, and the dynamic model of electromagnetic active suspension was built. Secondly, based on the optimization model of weighting coefficients in the original LQR control strategy, a constraint condition considering energy consumption was put forward, and a modified LQR control strategy was designed. Finally, MATLAB/Simulink was adopted for simulations, and the correctness of the controller was verified by active force values. Energy consumption and dynamic performance in random road were compared. The results show that the active force value of the modified LQR control strategy meets the optimization constraint condition with a probability of 99.89%. Compared with the original LQR control strategy, the modified LQR control strategy reduces the root-mean-square (RMS) of power by 80.29%. In addition, there is no significant difference in the RMS of suspension working space, and the RMS of dynamic tyre deformation is 5% lower than that of the original LQR control strategy. The reduction of body vertical acceleration can still reach more than 50% of the original LQR control strategy.
-
Key words:
- linear motor /
- vehicle suspensions /
- LQR control /
- optimization /
- random road
-
表 1 1/4悬架参数
Table 1. Parameters of quarter suspension
参数 数值 mb/kg 459 mw/kg 50 ks/(N·m−1) 57000 cs/(N·s·m−1) 1800 kt/(N·m−1) 230000 kf/(N·A−1) 40 r/Ω 25.3 表 2 性能指标均方根
Table 2. RMS of performance indexes
策略 车身垂向加
速度/(m·s−2)悬架动行
程/mm轮胎动变
形/mm被动 2.2197 14.7514 5.8153 原 LQR
控制策略1.3202 12.0841 5.6834 改进 LQR
控制策略1.7254 12.1087 5.3656 表 3 性能指标均方根降幅
Table 3. Reduction of RMS of performance indexes
% 策略 车身垂向
加速度悬架动
行程轮胎动
变形原 LQR控制策略 40.52 18.08 2.27 改进 LQR控制策略 22.27 17.91 7.73 -
[1] WEI W, ZHANG X Y, SUN F. An electromagnetic actuator for vibration control and energy recycle[J]. The Proceedings of JSME Annual Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (Robomec), 2018(2018): 2P1-E13. [2] 杨超,李以农,郑玲,等. 基于多目标粒子群算法的电磁主动悬架作动器优化[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(19): 154-166. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.19.154YANG Chao, LI Yinong, ZHENG Ling, et al. Optimum of electromagnetic active suspension actuator using multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(19): 154-166. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.19.154 [3] MIN X, LI Y M, TONG S C. Adaptive fuzzy output feedback inverse optimal control for vehicle active suspension systems[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 403: 257-267. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.096 [4] 孙凤,李华辰,单光坤,等. 磁力馈能悬架的设计与实验研究[J]. 机械科学与技术,2023,42(3): 402-407. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200579SUN Feng, LI Huachen, SHAN Guangkun, et al. Design and experimental study of magnetic energy-harvesting suspension[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 402-407. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200579 [5] GU C, YIN J, LUO J, et al. Performance-oriented controls of a novel rocker-pushrod electromagnetic active vehicle suspension[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 109: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.019 [6] LIU J, LI X J, ZHANG X L, et al. Modeling and simulation of energy-regenerative active suspension based on BP neural network PID control[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019: 4609754.1-4609754.8. [7] KOU F R, JING Q Q, CHEN C, et al. Endocrine composite skyhook-groundhook control of electromagnetic linear hybrid active suspension[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2020, 2020: 3402168.1-3402168.17. [8] SATYANARAYANA V S V, RAO N M, SATEESH B. Parameters optimisation of vehicle suspension system for better ride comfort[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Performance, 2018, 4(2): 186-199. doi: 10.1504/IJVP.2018.090956 [9] DING R K, WANG R C, MENG X P, et al. Energy consumption sensitivity analysis and energy-reduction control of hybrid electromagnetic active suspension[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 134: 106301.1-106301.20. [10] SHAHID Y, WEI M X. Comparative analysis of different model-based controllers using active vehicle suspension system[J]. Algorithms, 2019, 13(1): 13010010.1-13010010.15. [11] MANNA S, MAZUMDAR R. Comparative performance analysis of LQR and MPC for active suspension system[C]//2020 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA). Greater Noida: IEEE, 2020: 352-356. [12] MONTAZERI-GH M, KAVIANIPOUR O. Investigation of the active electromagnetic suspension system considering hybrid control strategy[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2014, 228(10): 1658-1669. doi: 10.1177/0954406213511430 [13] ATAEI M, ASADI E, GOODARZI A, et al. Multi-objective optimization of a hybrid electromagnetic suspension system for ride comfort, road holding and regenerated power[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2017, 23(5): 782-793. doi: 10.1177/1077546315585219 [14] YAMIN A H M, DARUS I Z M, NOR N S M, et al. Intelligent cuckoo search algorithm of PID and skyhook controller for semi-active suspension system using magneto-rheological damper[J]. Malaysian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, 2021, 17(4): 402-415. doi: 10.11113/mjfas.v17n4.2067 [15] 史文库,张曙光,陈志勇,等. 磁流变半主动座椅悬架建模及振动特性分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(2): 253-260.SHI Wenku, ZHANG Shuguang, CHEN Zhiyong, et al. Modeling and vibration analysis of semi-active seat suspension with magnetorheological damper[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 253-260. [16] 韦伟. 电磁主动悬架设计与控制策略研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2020. [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 机械振动道路路面谱测量数据报告: GB/T 7031—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. [18] 陈杰平,陈无畏,祝辉,等. 基于Matlab/Simulink的随机路面建模与不平度仿真[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(3): 11-15.CHEN Jieping, CHEN Wuwei, ZHU Hui, et al. Modeling and simulation on stochastic road surface irregularity based on Matlab/simulink[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(3): 11-15. [19] 孟杰,张凯,焦洪宇. 基于遗传算法优化的汽车主动悬架LQG控制器的设计[J]. 机械科学与技术,2013,32(6): 914-918. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.2013.06.030MENG Jie, ZHANG Kai, JIAO Hongyu. Optimal control design of the vehicle active suspension based on the genetic algorithm[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2013, 32(6): 914-918. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.2013.06.030 [20] 庄表中, 王行新. 随机振动概论[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1982. -





 下载:
下载: