Edge-Aware Semi-Supervised Built-up Area Extraction Using Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Images
-
摘要:
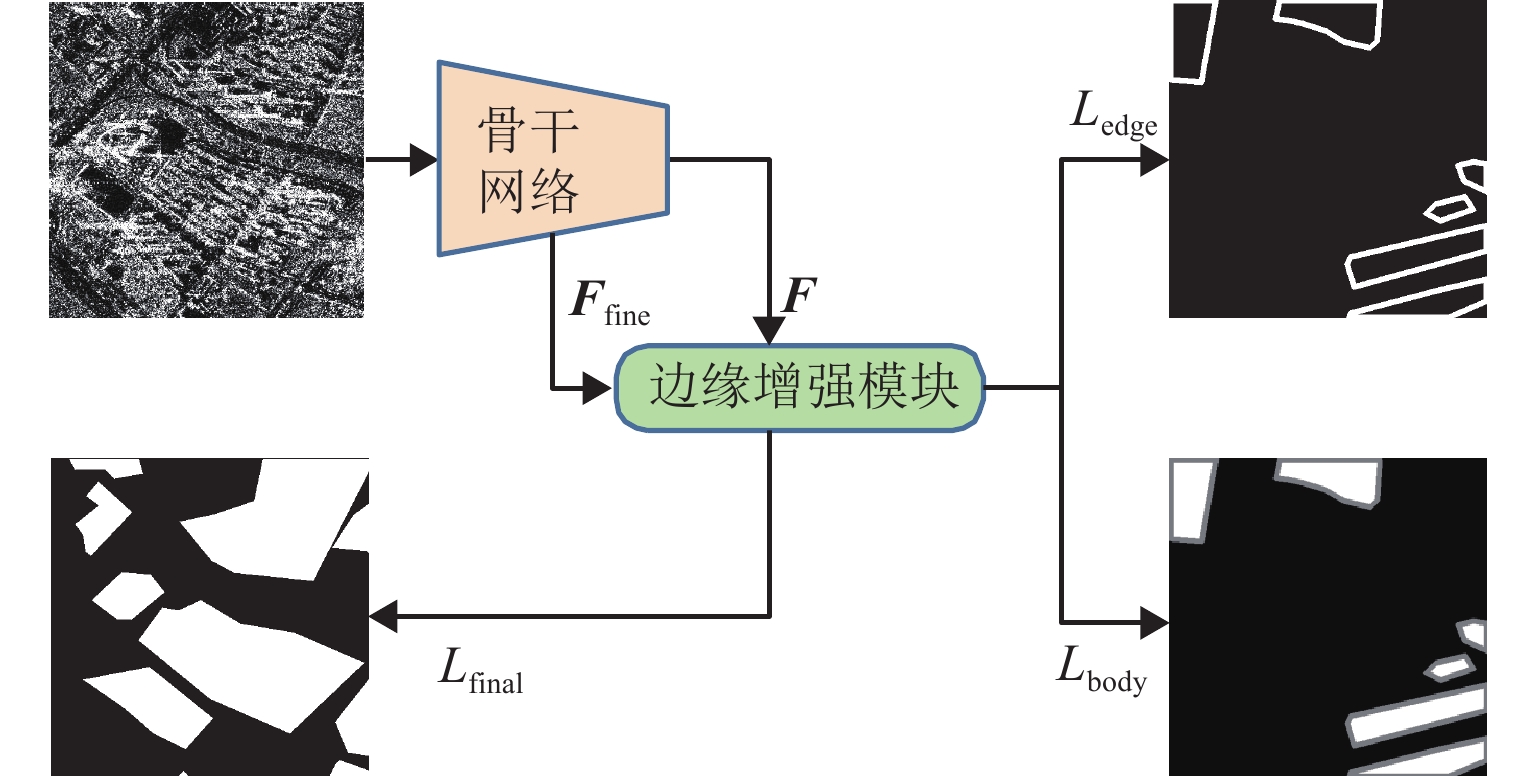
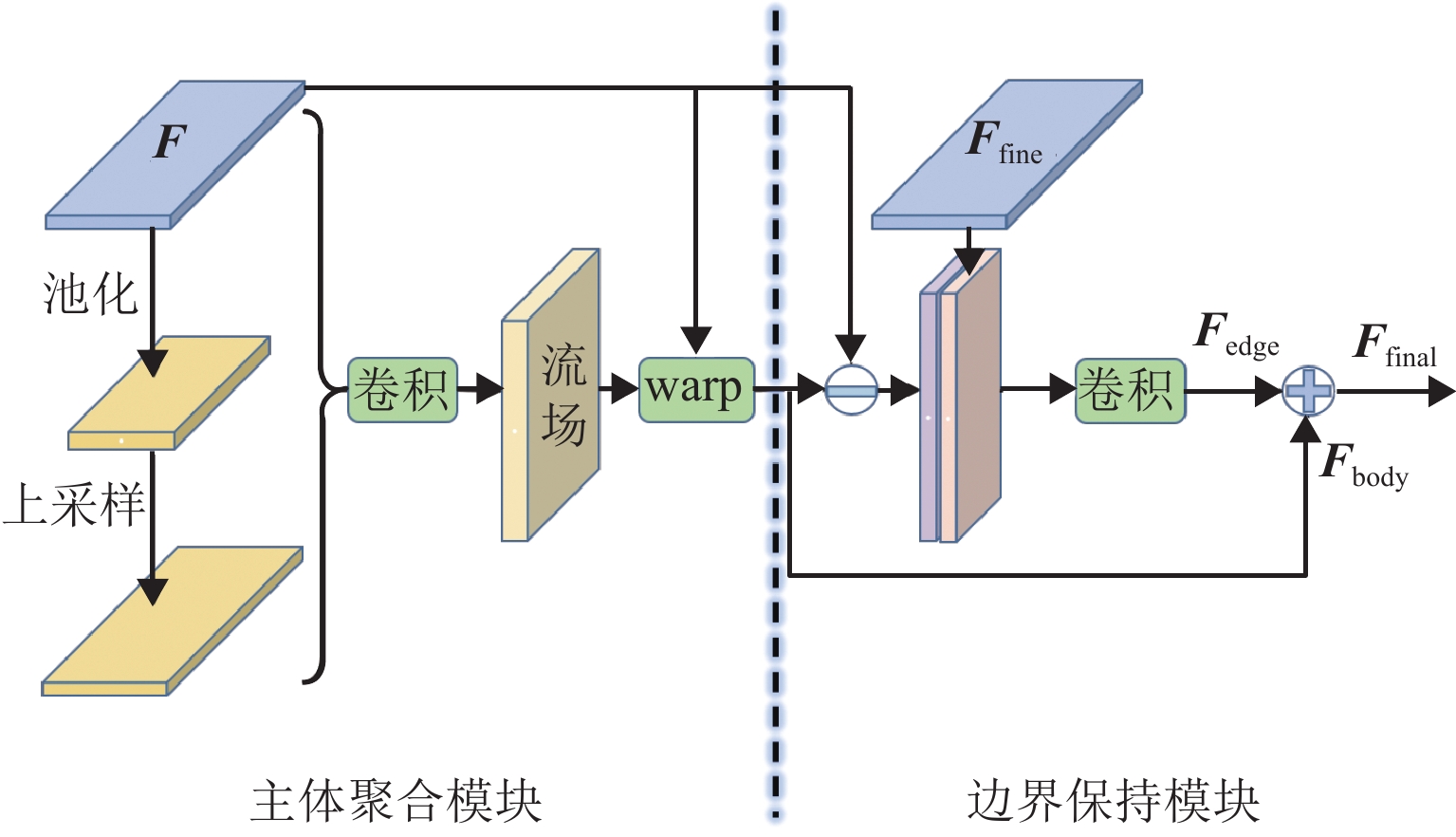
针对合成孔径雷达(synthetic aperture radar,SAR)图像中建筑区域难以辨识与标注的问题,提出一种结合改进的伪标签技术和边缘增强策略的半监督建筑区提取新方法. 首先,引入同一位置、不同时相的SAR图像作为自然数据增强手段,并通过多个不同时相图像的预测结果投票确定伪标签;其次,设计一种边缘增强辅助模块,通过特征图变形以修正建筑区主体特征,辅以跳跃连接改进边缘特征,并针对主体和边缘特征进行分离式监督;此外,构建一个包含2种传感器和2个城市区域的多时相SAR图像建筑区提取数据集,含
1000 幅带标注图像和800组无标注时序图像,并基于该数据集进行实验验证. 实验表明,在所构建测试集上,基线方法使用全量数据训练后交并比(intersection over union, IoU)为63.43%,而所提方法在使用10%和全量数据时IoU分别为63.46%和68.24%,仅利用10%的标注数据即可达到基线方法使用全量标注数据训练的精度.Abstract:To address the challenges of identifying and annotating built-up areas in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, a novel semi-supervised method for extracting built-up areas that combined improved pseudo-labeling techniques with an edge enhancement strategy was proposed. Initially, SAR images from the same location but at different time were introduced as a natural data augmentation method, and the pseudo-labels were determined by voting based on the prediction results of multi-temporal images. Subsequently, an edge-enhancement auxiliary module was designed, which corrected the body features of the built-up areas through feature map warping and improved edge features with skip connections. Separate supervision for the body and edge features was performed. Moreover, a dataset for extracting built-up areas in multi-temporal SAR images, which included two types of sensors and two urban areas, was constructed. This dataset contains 1,000 annotated images and 800 groups of unlabeled temporal images. Experimental validations based on this dataset have demonstrated that on the constructed test set, the baseline method trained with full data achieves an intersection over union (IoU) of 63.43%, while the proposed method reaches an IoU of 63.46% and 68.24% when using 10% and full data, respectively. Remarkably, using only 10% of the annotated data, the proposed method can achieve the precision that the baseline method has obtained with full annotated data.
-
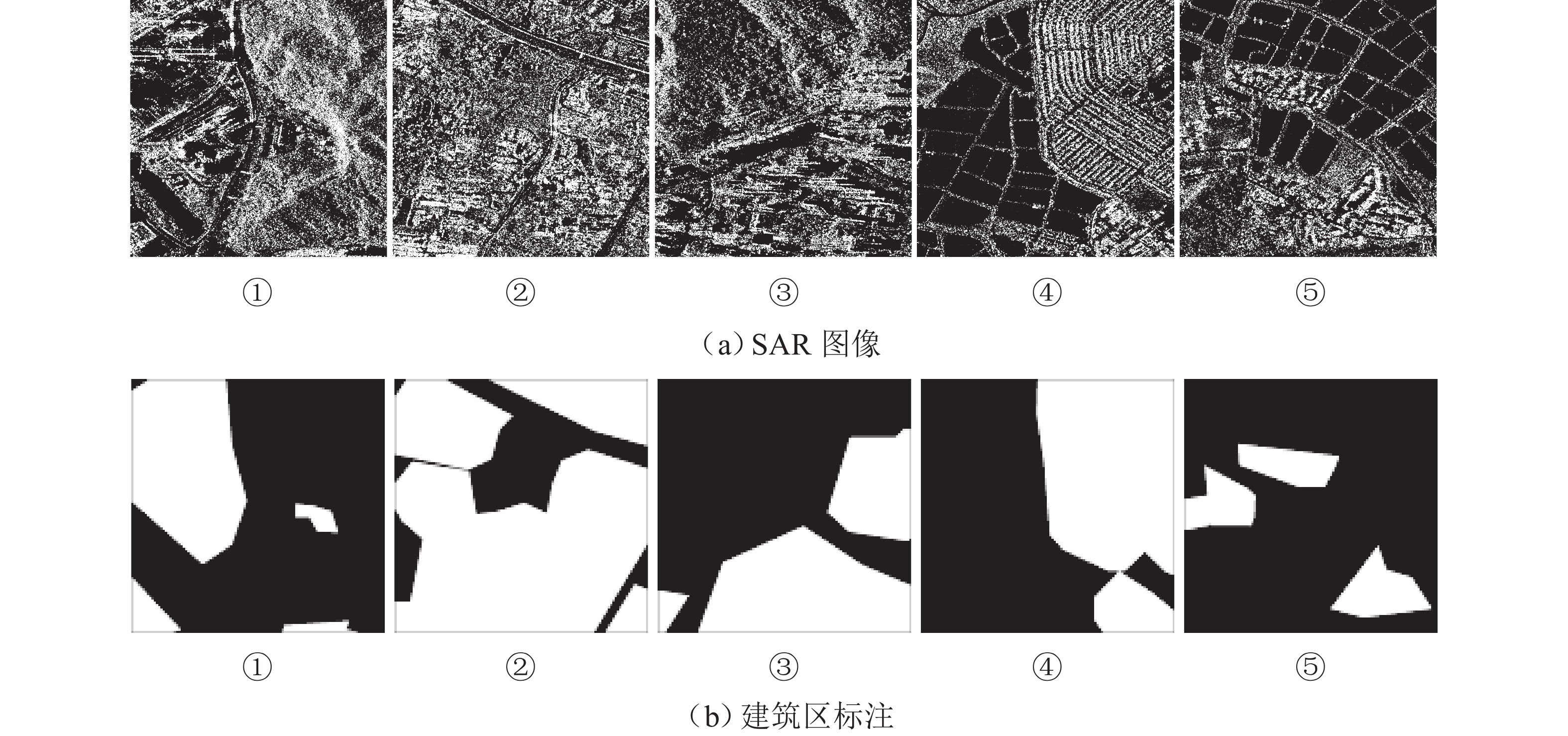
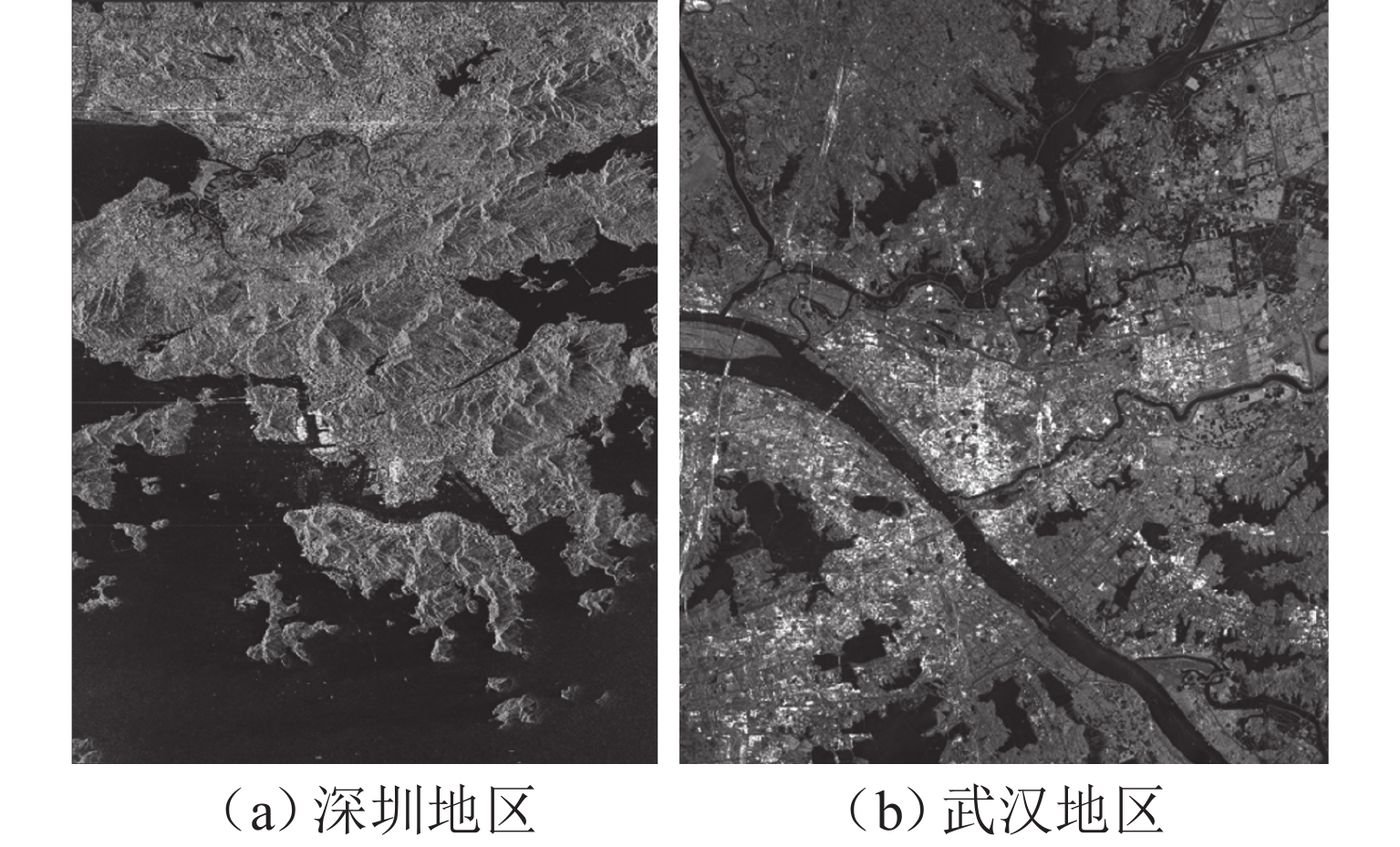
表 1 MTSBED数据集介绍
Table 1. Introduction of MTSBED dataset
参数 深圳地区 武汉地区 传感器 TerraSAR-X COSMO-SkyMed 成像模式 条带 条带 入射角/(°) 35~39 20~25 分辨率/m 3 3 拍摄时间 2008 年 10 月—
2009 年 3 月2011 年 5 月—
2020 年 11 月时间分辨率/d 11~22 4~36 景数/张 9 13 注:这里的时间分辨率为MTSBED所包含数据的时间分辨率,不是SAR卫星重访的时间分辨率. 表 2 不同方法在MTSBED上的IoU性能比较
Table 2. Comparison of IoU performance of different methods on MTSBED
% 表 3 边缘增强模块消融实验(IoU指标)
Table 3. Ablation experiment of edge enhancement module (IoU)
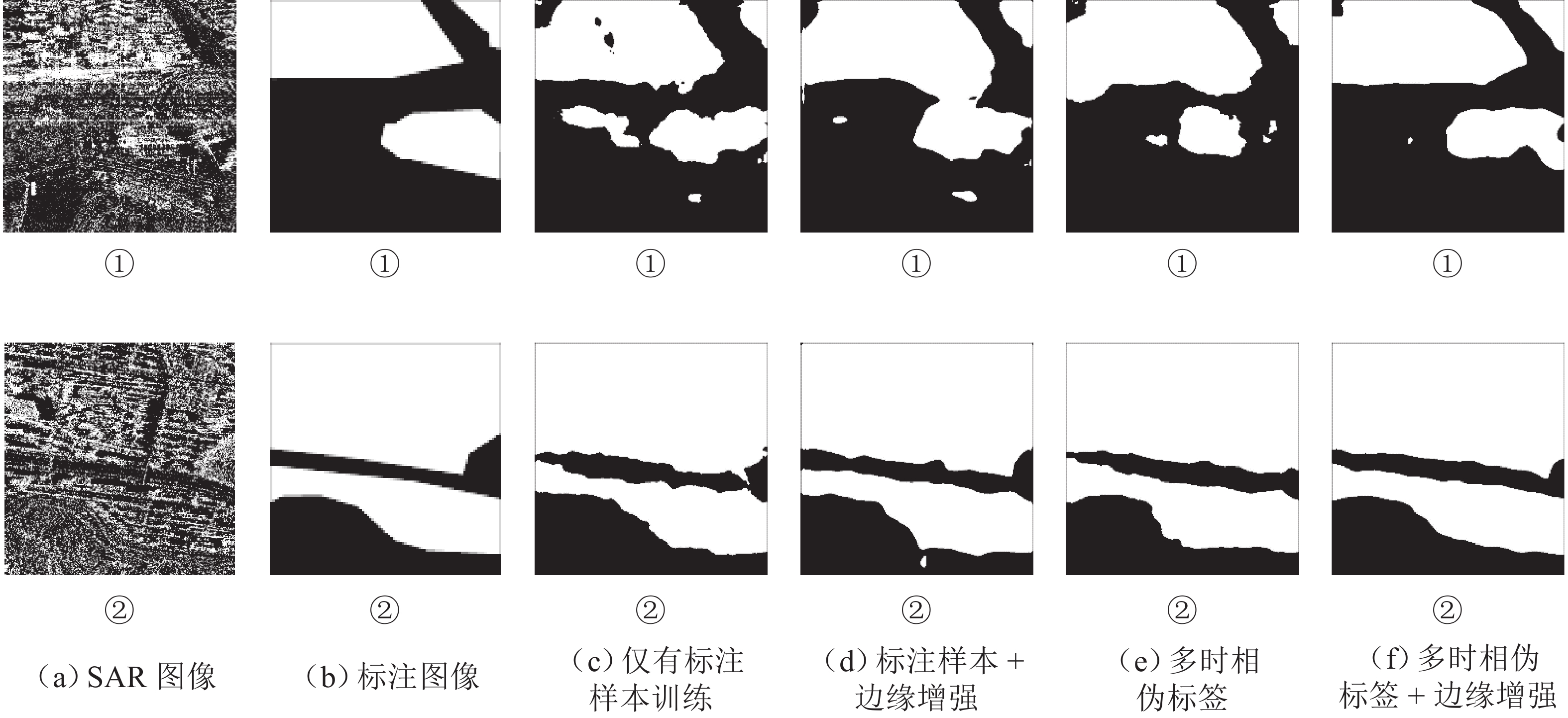
% 有标注样本
比例/%仅标注
样本标注样本 +
边缘增强多时相
伪标签多时相伪标签 +
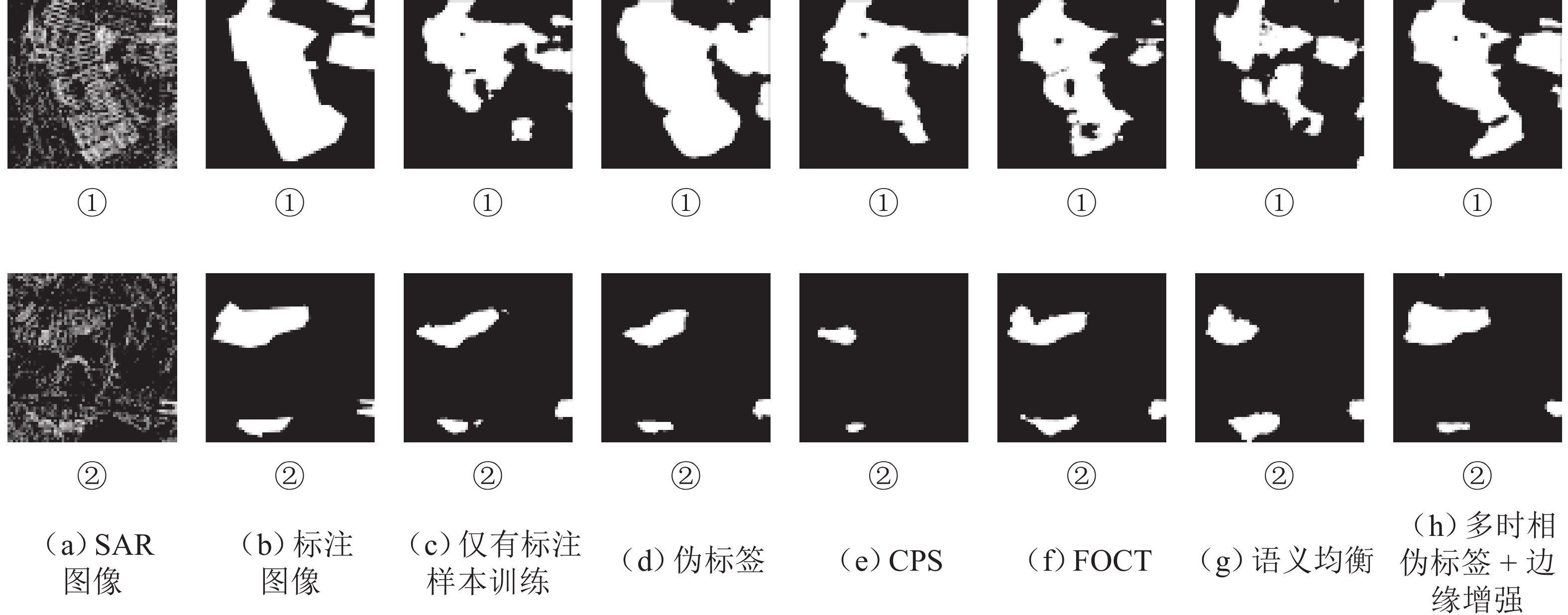
边缘增强10 57.68 59.56 63.43 63.46 20 58.16 61.02 63.82 64.69 50 61.50 62.82 65.13 66.17 100 63.43 67.54 67.01 68.24 表 4 不同预测概率阈值对结果的影响(IoU指标)
Table 4. Effect of different prediction probability thresholds on results (IoU)
% 项目 0.85 0.90 0.95 0.99 伪标签 63.15 64.02 64.68 63.94 多时相伪标签 64.58 65.13 64.84 63.71 -
[1] LEE J S, POTTIER E. Polarimetric radar imaging: from basics to applications[M]. Florida: CRC Press,2017. [2] WU W J, GUO H D, LI X W. Urban area SAR image man-made target extraction based on the product model and the time–frequency analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(3): 943-952. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2371064 [3] IANNELLI G C, GAMBA P. Urban extent extraction combining sentinel data in the optical and microwave range[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(7): 2209-2216. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2920678 [4] CHEN Q H, XIAO Y, GAO W L, et al. Building density change monitoring using dual-polarimetric sentinel-1 SAR data[C]//2021 SAR in Big Data Era (BIGSARDATA). Nanjing: IEEE,2021:1-4. [5] CHEN S W, WANG X S, XIAO S P. Urban damage level mapping based on co-polarization coherence pattern using multitemporal polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(8): 2657-2667. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2818939 [6] YANG X L, SONG Z X, KING I, et al. A survey on deep semi-supervised learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(9): 8934-8954. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2022.3220219 [7] 吴樊,张红,王超,等. SARBuD 1.0:面向深度学习的GF-3精细模式SAR建筑数据集[J]. 遥感学报,2022,26(4): 620-631. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20220296WU Fan, ZHANG Hong, WANG Chao, et al. SARBuD 1.0: a SAR building dataset based on GF-3 FSⅡ imageries for built-up area extraction with deep learning method[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2022, 26(4): 620-631. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20220296 [8] LIU X Y, HUANG Y L, WANG C W, et al. Semi-supervised SAR ATR via conditional generative adversarial network with multi-discriminator[C]//2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Brussels:IEEE,2021:2361-2364. [9] ZHENG C, JIANG X, LIU X Z. Semi-supervised SAR ATR via multi-discriminator generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(17): 7525-7533. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2915379 [10] SUN Q G, LI X F, LI L L, et al. Semi-supervised complex-valued GAN for polarimetric SAR image classification[C]//2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Yokohama:IEEE,2019: 3245-3248. [11] LIAO L Y, DU L, GUO Y C. Semi-supervised SAR target detection based on an improved faster R-CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 14(1): 143.1-143.22. [12] WANG C C, GU H, SU W M. SAR image classification using contrastive learning and pseudo-labels with limited data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4012505.1-4012505.5. [13] KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: a tutorial[C]// Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery Ⅲ. Orlando: SPIE, 1996: 228-242. [14] RIZVE M N, DUARTE K, RAWAT Y S, et al. In defense of pseudo-labeling: an uncertainty-aware pseudo-label selection framework for semi-supervised learning[EB/OL]. (2021-01-15)[2022-08-10]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.06329. [15] LI Y Y, XING R T, JIAO L C, et al. Semi-supervised PolSAR image classification based on self-training and superpixels[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(16): 1933-1951. doi: 10.3390/rs11161933 [16] ZHAO F, TIAN M, XIE W, et al. A new parallel dual-channel fully convolutional network via semi-supervised FCM for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4493-4505. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3014966 [17] 邓云凯,禹卫东,张衡,等. 未来星载SAR技术发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报,2020,9(1): 1-33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008DENG Yunkai, YU Weidong, ZHANG Heng, et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 1-33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008 [18] TANG L Y, ZHAN Y B, CHEN Z, et al. Contrastive boundary learning for point cloud segmentation [C]//2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans: IEEE, 2022: 8479-8489. [19] 梁烽,张瑞祥,柴英特,等. 一种结合上下文与边缘注意力的SAR图像海陆分割深度网络方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2023,48(8): 1286-1295.LIANG Feng, ZHANG Ruixiang, CHAI Yingte, et al. A sea-land segmentation method for SAR images using context-aware and edge attention based CNNs[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(8): 1286-1295. [20] JUNG H, CHOI H S, KANG M. Boundary enhancement semantic segmentation for building extraction from remote sensed image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5215512.1-5215512.12. [21] LI X T, LI X, ZHANG L, et al. Improving semantic segmentation via decoupled body and edge supervision [C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2020: 435-452. [22] 陈帅霖,杨文,李恒超,等. 顾及边缘的多时相SAR图像半监督建筑区提取[EB/OL]. [2023-03-02]. https://github.com/slchenchn/MTSBED. [23] PITZ W, MILLER D. The TerraSAR-X satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 615-622. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037432 [24] COVELLO F, BATTAZZA F, COLETTA A, et al. COSMO-SkyMed an existing opportunity for observing the earth[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2010, 49(3): 171-180. [25] ARAZO E, ORTEGO D, ALBERT P, et al. Pseudo-labeling and confirmation bias in deep semi-supervised learning[C]//2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Glasgow: IEEE, 2020: 1-8. [26] TOMPSON J, GOROSHIN R, JAIN A, et al. Efficient object localization using convolutional networks[C]// 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston: IEEE, 2015: 648-656. [27] DOSOVITSKIY A, FISCHER P, ILG E, et al. FlowNet: learning optical flow with convolutional networks[C]// 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago: IEEE, 2015: 2758-2766. [28] ZHU Y, SAPRA K, REDA F A, et al. Improving semantic segmentation via video propagation and label relaxation[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach: IEEE, 2019: 8848-8857. [29] WANG J D, SUN K, CHENG T H, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(10): 3349-3364. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2983686 [30] CHEN X K, YUAN Y H, ZENG G, et al. Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with cross pseudo supervision[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville: IEEE, 2021: 2613-2622. [31] LI Q Y, SHI Y L, ZHU X X. Semi-supervised building footprint generation with feature and output consistency training[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5623217. 1-5623217. 17. [32] LEE E, JEONG S, KIM J, et al. Semantic equalization learning for semi-supervised SAR building segmentation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4511505.1-4511505.5. [33] YUN S, HAN D, CHUN S, et al. CutMix: regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 6022-6031. [34] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice: IEEE, 2017: 2999-3007. -




 下载:
下载: