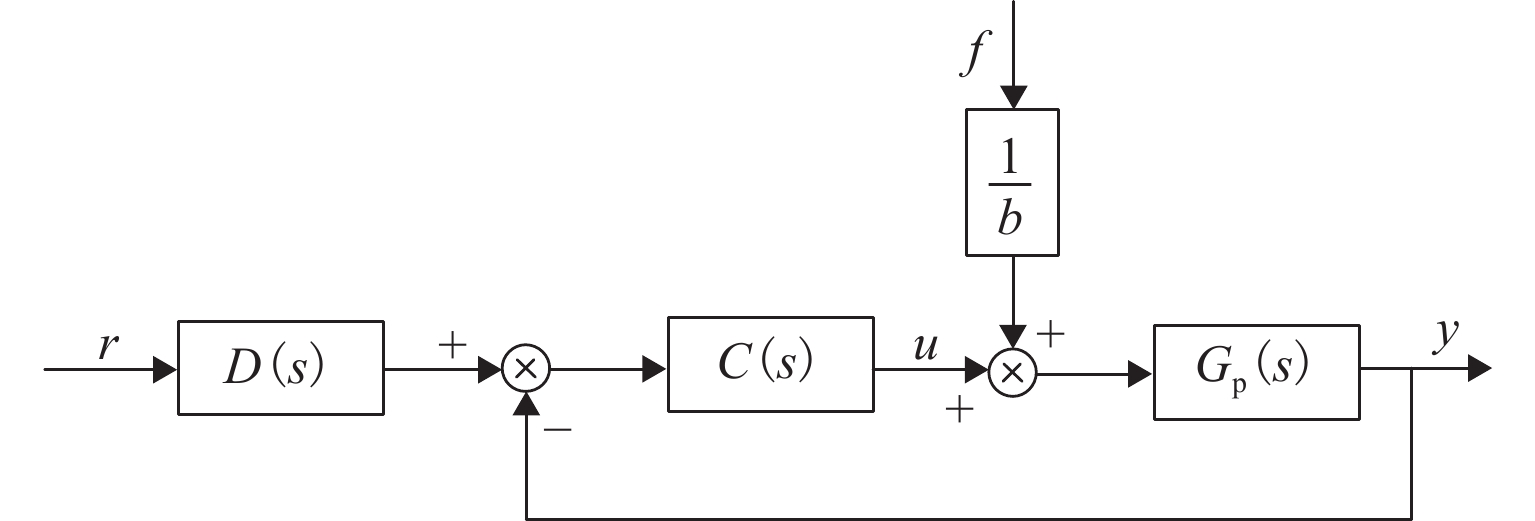
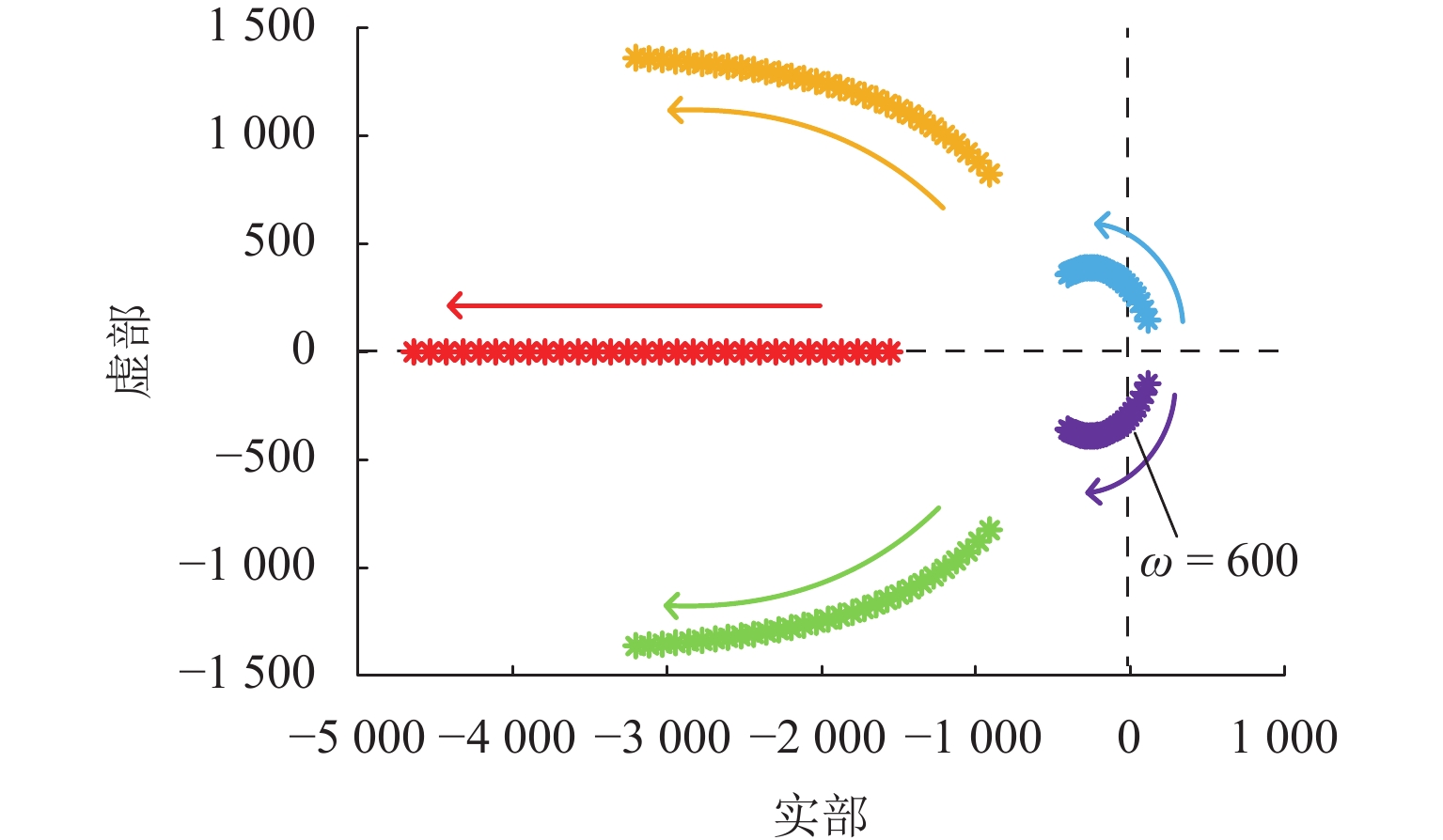
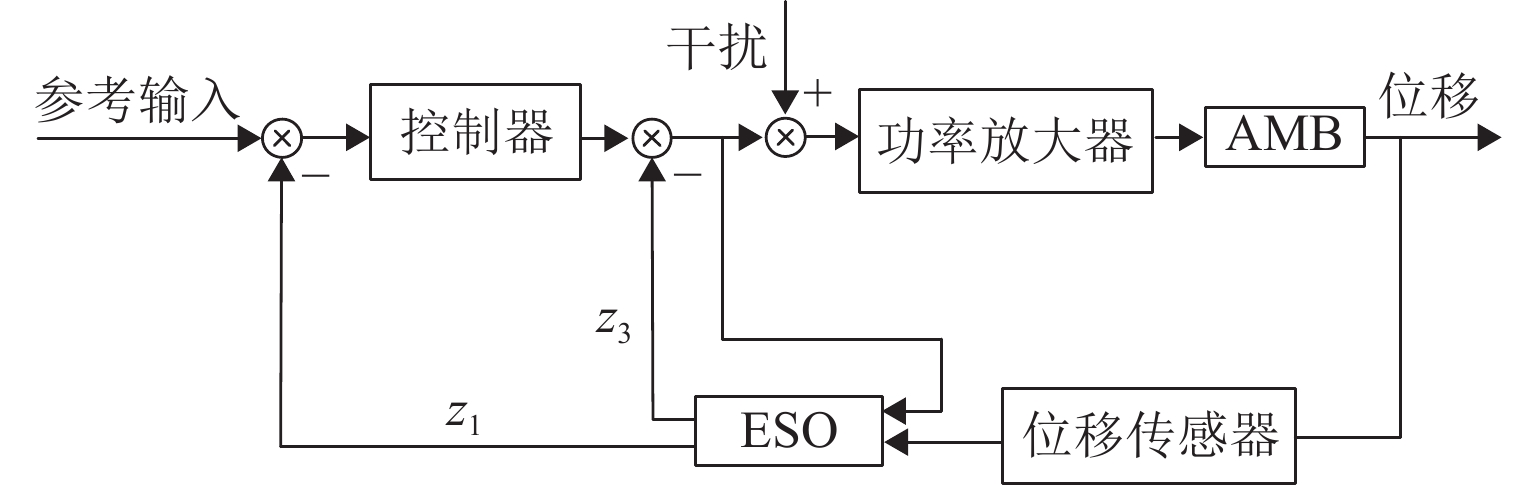
Anti-Disturbance Performance of Maglev Rotor Using Model Assisted Extended State Observer
-
摘要:
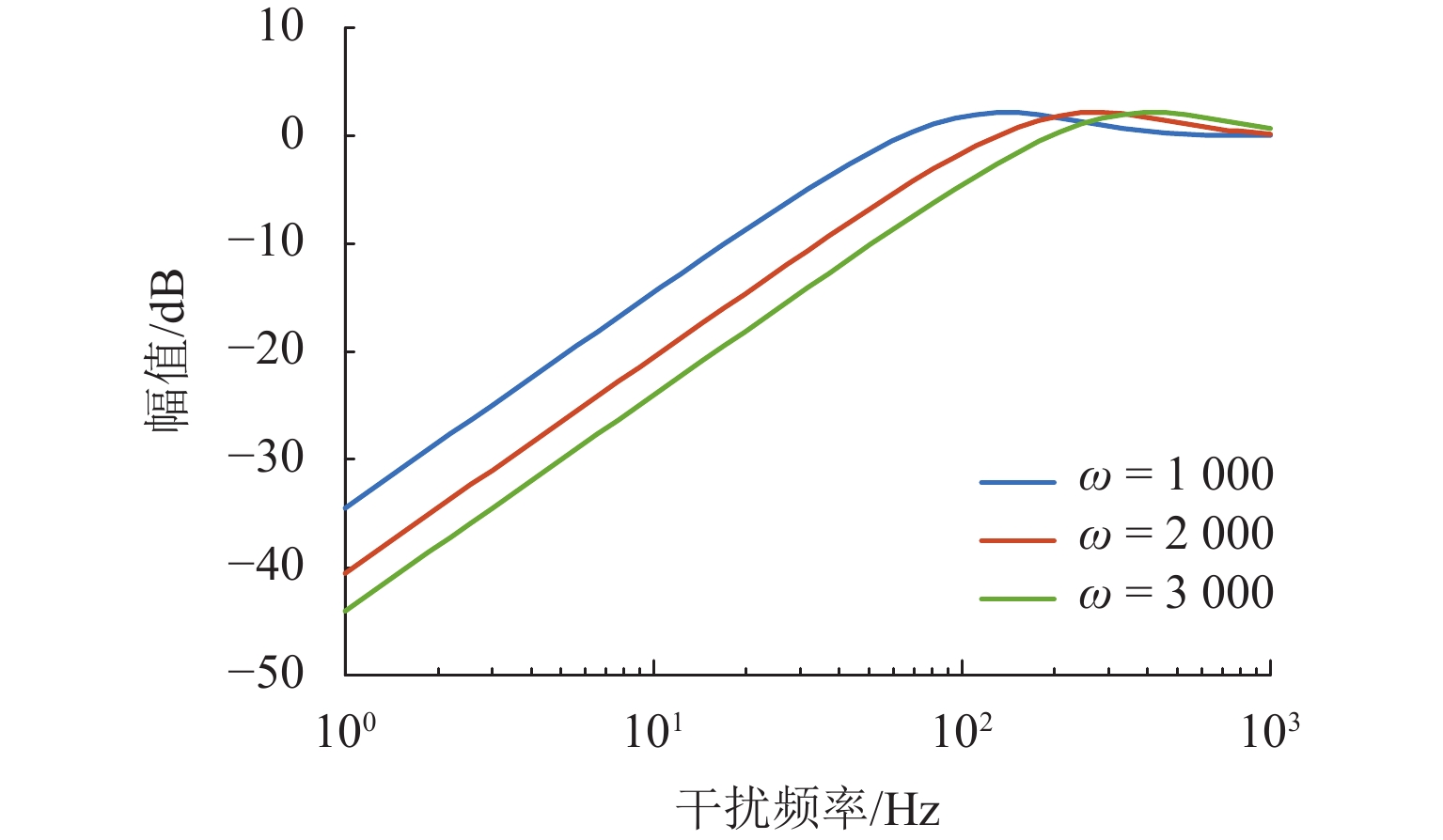
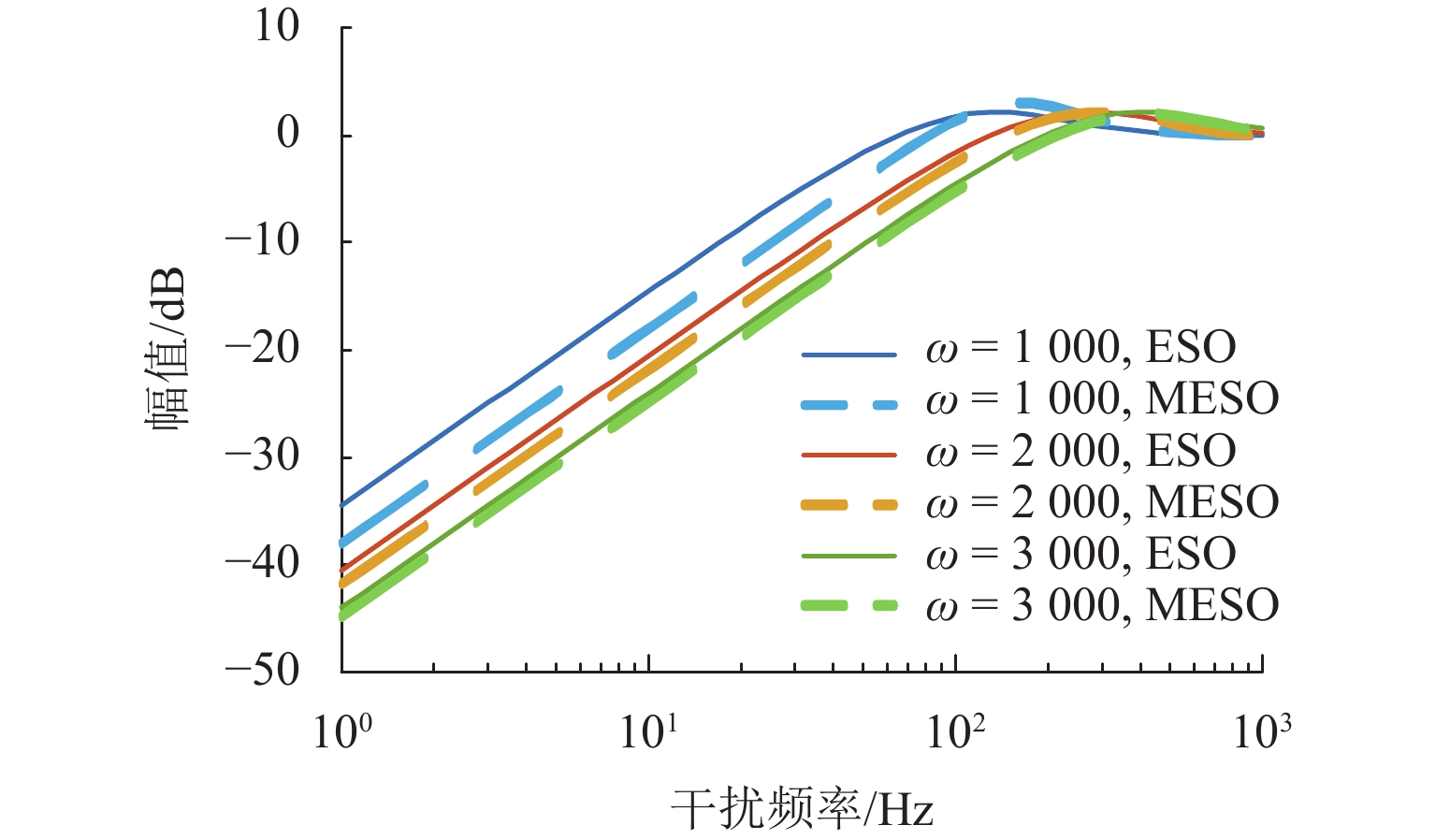
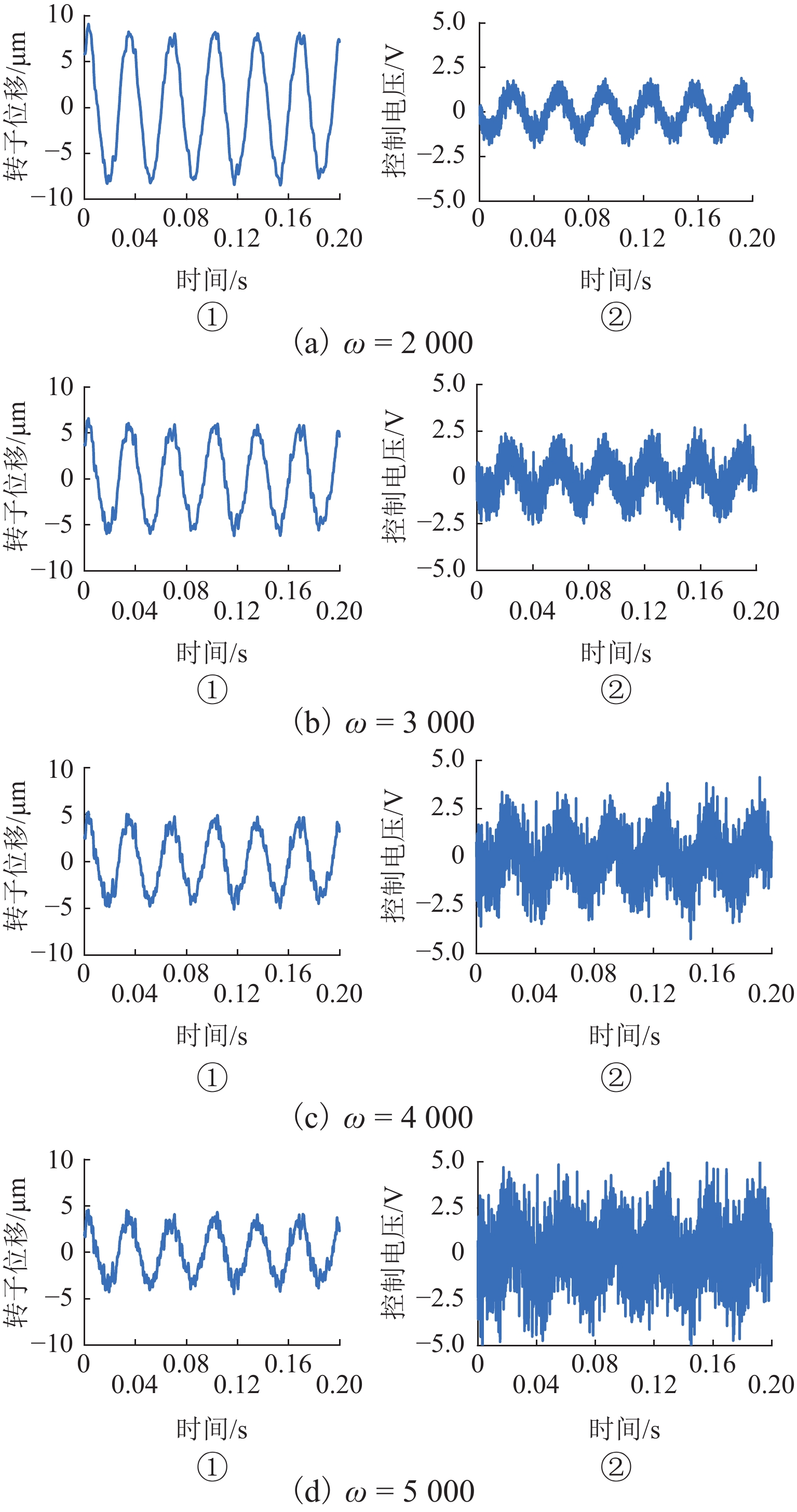
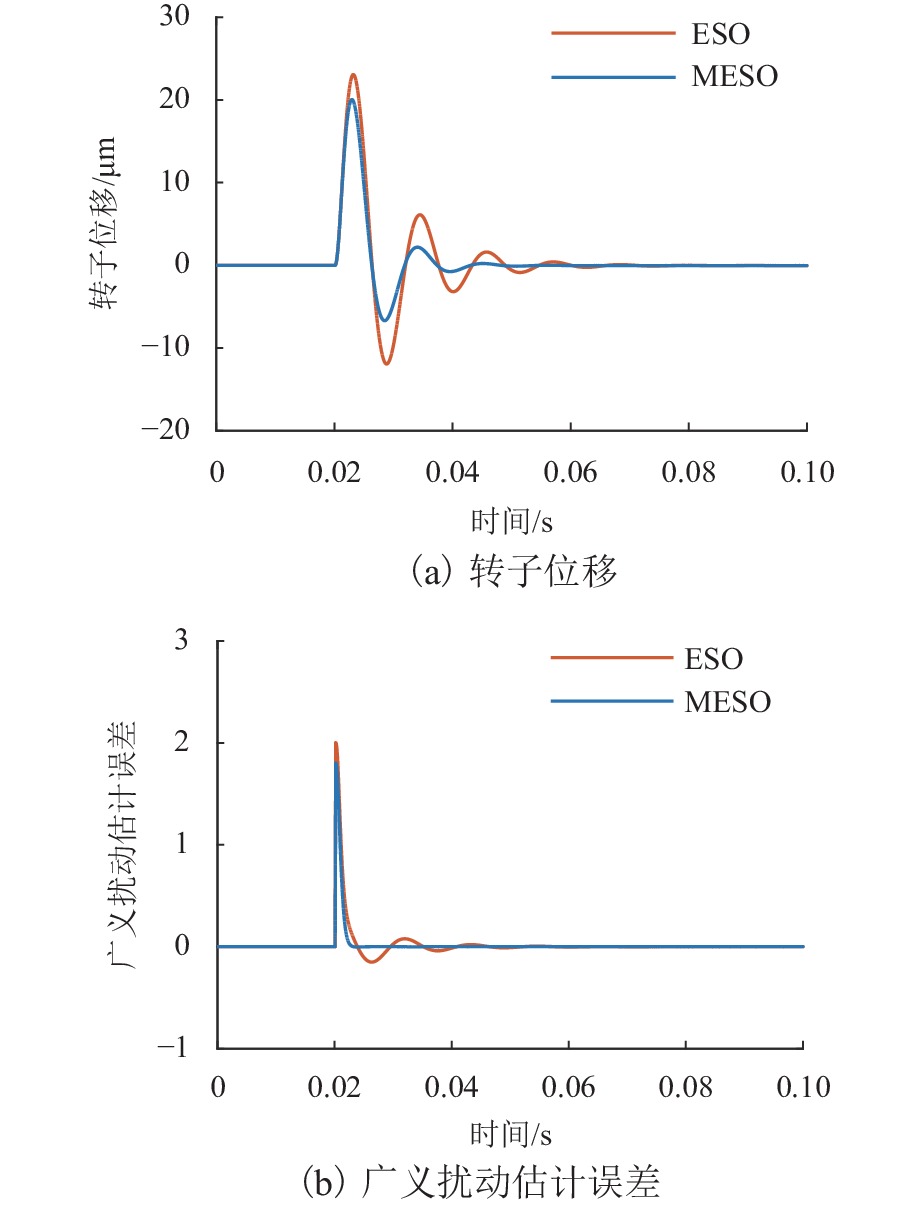
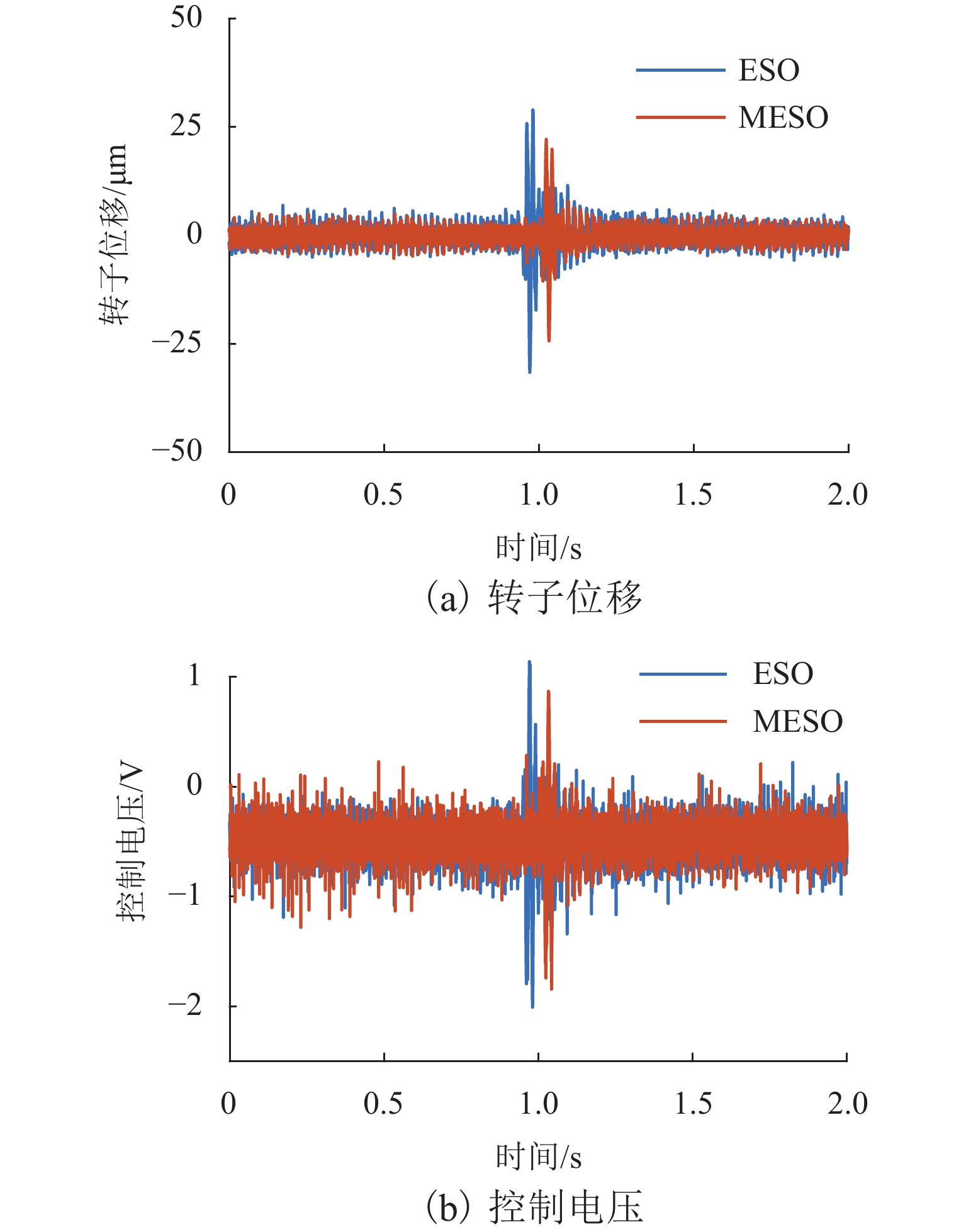
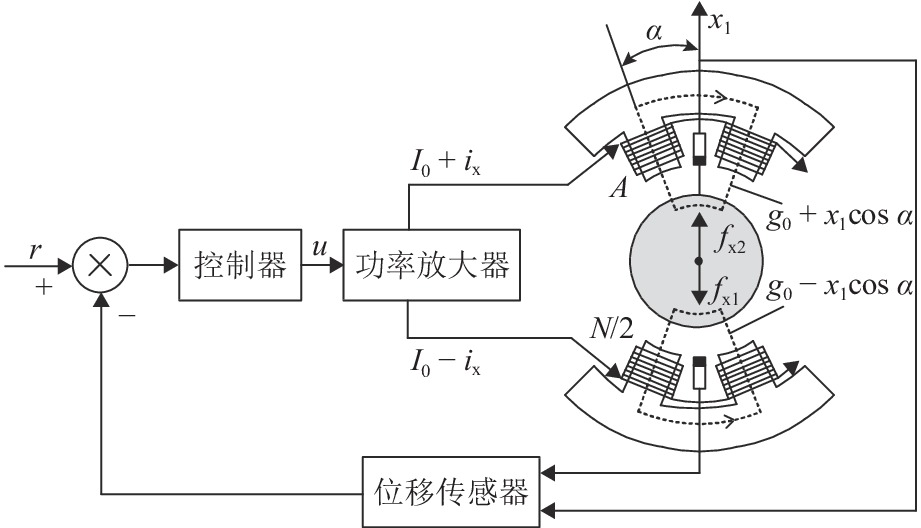
随着正弦干扰频率的提高,扩张状态观测器(extended state observer,ESO)的性能会下降,为提高磁悬浮转子系统中ESO的干扰抑制能力,首先,建立单自由度磁悬浮轴承转子系统数学模型;其次,设计ESO并分析其干扰抑制效果下降的原因;在此基础上,提出一种模型辅助扩张状态观测器(model assisted extended state observer, MESO)以改进带宽配置方式,提高干扰抑制效果;然后,在频域内分析基于MESO的自抗扰控制器的稳定性;最后,通过仿真与试验验证了所提出观测器的有效性. 研究结果表明:带宽的增加会放大系统噪声的影响,使系统的控制电压增加;随着干扰频率的提高,MESO对高频正弦干扰的抑制效果会下降,但仍可以降低转子的模态振幅;对50 Hz旋转频率下的转子分别施加频率为10 Hz、振幅为2 mm的基础简谐干扰与1
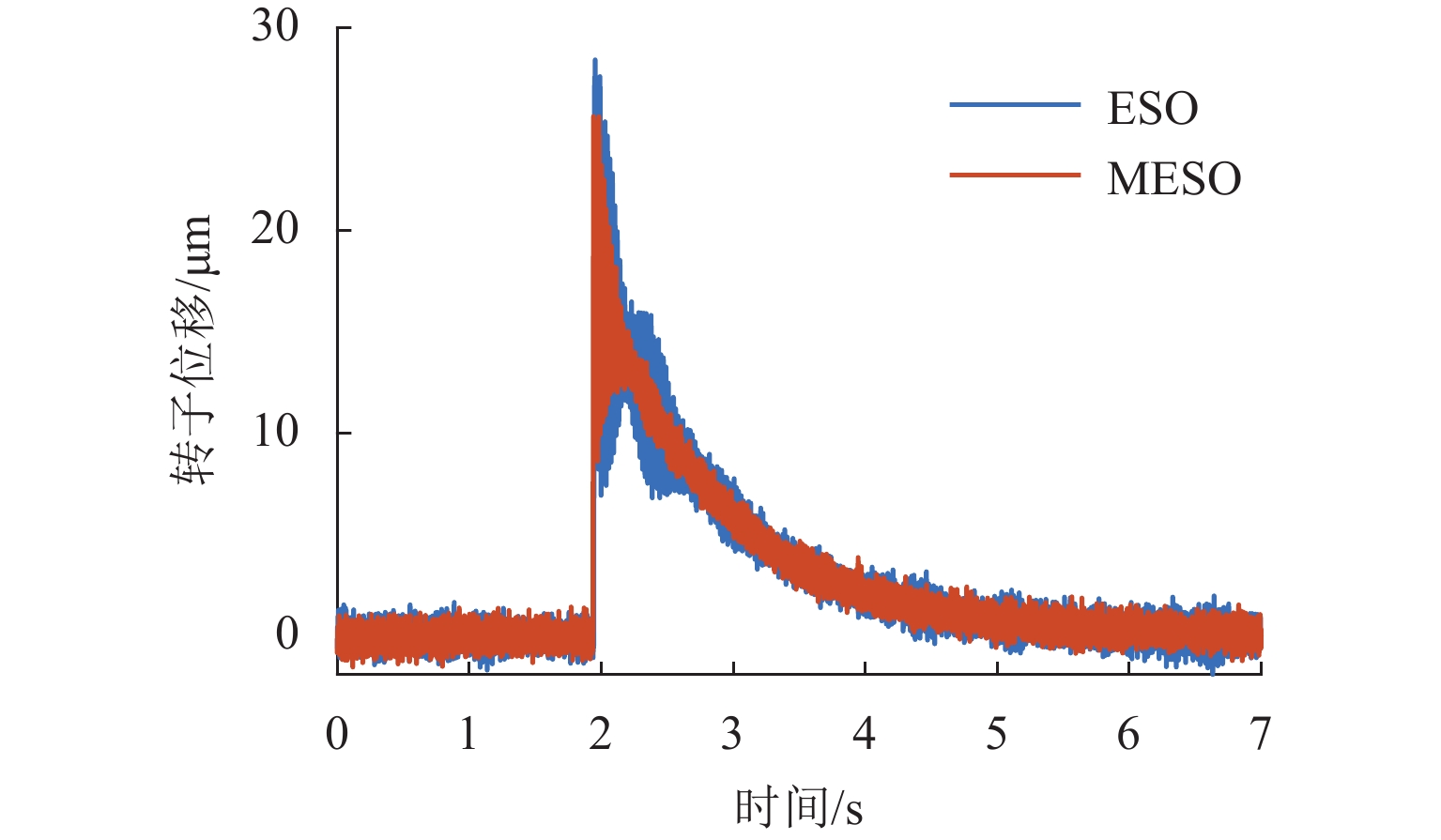
g 的基础冲击干扰, 相比ESO,MESO控制下的转子位移分别降低了16.3%与22.6%,控制电压降低了约14%.Abstract:With the increase in sinusoidal disturbance frequency, the performance of extended state observers (ESOs) will decrease. In order to improve the disturbance suppression ability of the ESO in the maglev rotor system, firstly, the mathematical model of a one-degree-of-freedom (1-DOF) maglev bearing rotor system was built. Secondly, ESO was designed, and the reasons for its reduced disturbance suppression effects were analyzed. On this basis, a model assisted ESO (MESO) was proposed to improve the bandwidth configuration and enhance the disturbance suppression effects. Then, the stability of the active disturbance rejection controller based on MESO was analyzed in the frequency domain. The effectiveness of the proposed observer was finally verified through simulation and experiments. The research results indicate that an increase in bandwidth amplifies the impact of system noises and increases the control voltage of the system. As the disturbance frequency increases, the suppression effect of MESO on high-frequency sinusoidal disturbance will decrease, but it can still reduce the modal amplitude of the rotor. After applying fundamental harmonic disturbance of 10 Hz−2 mm and fundamental impulse disturbance of 1
g to the rotor at a rotating frequency of 50 Hz respectively, the rotor displacement under MESO control is reduced by 16.3% and 22.6%, respectively compared with that under ESO control, and the control voltage is reduced by about 14%. -
表 1 AMB转子系统参数
Table 1. Parameters of AMB rotor system
符号 参数值 m/kg 3.55 A/m2 2 × 10−4 N/匝 150 g0/mm 0.2 保护轴承单边间隙 gmin/mm 0.125 I0/A 1.3 α/(°) 22.5 μ0/(N·A−2) 4π × 10−7 ka/(A·V−1) 0.26 ks/(V·m−1) 20000 转子转速 n/(r·min−1) 3000 kp 1.8 kd 0.002 ω 3000 表 2 转子位移二范数
Table 2. 2-Norm of rotor displacement
名称 二范数大小 相比 PID 控制器振幅降低比例/% ||ePID||2 7261.6 ||eESO||2 5684.6 21.7 ||eMESO||2 4608.7 36.5 -
[1] MASLEN E H, SCHWEITZER G. Magnetic bearings: theory, design, and application to rotating machinery[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2009. [2] 刘淑琴, 边忠国, 李瑞建, 等. 磁悬浮人工心脏泵及在体外循环系统(ECMO)上的实验研究[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报. [2022-12-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20220426.1933.010.html. [3] DU G H, XU W, ZHU J G, et al. Effects of design parameters on the multiphysics performance of high-speed permanent magnet machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(5): 3472-3483. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2922933 [4] 钟志贤,蔡忠侯,祁雁英. 单自由度磁悬浮系统无模型自适应控制的研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 549-557,581.ZHONG Zhixian, CAI Zhonghou, QI Yanying. Model-free adaptive control for single-degree-of-freedom magnetically levitated system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 549-557,581. [5] ZHANG S Y, WEI C B, LI J, et al. Robust H∞ controller based on multi-objective genetic algorithms for active magnetic bearing applied to cryogenic centrifugal compressor[C]//Proceedings of the 29th Chinese Control And Decision Conference. Chongqing: IEEE, 2017: 46-51. [6] XU Y P, SHEN Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Dynamic modeling of the active magnetic bearing system operating in base motion condition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 166003-166013. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3022996 [7] XU X B, FANG J C, LIU G, et al. Model development and harmonic current reduction in active magnetic bearing systems with rotor imbalance and sensor runout[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2015, 21(13): 2520-2535. doi: 10.1177/1077546313513624 [8] KATO J, TAKAGI K, INOUE T. On the stability analysis of active magnetic bearing with parametric uncertainty and position tracking control[C]// Proceedings of ASME 2016 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. Phoenix: [s.n.], 2017: 1-10 [9] HAN J Q. The extended state observer of a class of uncertain systems[J]. Control and Decision, 1995, 10(1): 85-88. [10] JIN C W, GUO K X, XU Y P, et al. Design of magnetic bearing control system based on active disturbance rejection theory[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2019, 141(1): 011009.1-011009.9. doi: 10.1115/1.4040837 [11] GUAN X D, ZHOU J, JIN C W, et al. Disturbance suppression in active magnetic bearings with adaptive control and extended state observer[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2020, 234(2): 272-284. [12] GUO B Z, ZHAO Z L. On the convergence of an extended state observer for nonlinear systems with uncertainty[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 2011, 60(6): 420-430. [13] ZHENG Q, GAOL L Q, GAO Z Q. On stability analysis of active disturbance rejection control for nonlinear time-varying plants with unknown dynamics[C]//2007 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Louisiana: IEEE, 2008: 3501-3506. [14] SUN B S, GAO Z Q. A DSP-based active disturbance rejection control design for a 1-kW H-bridge DC-DC power converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2005, 52(5): 1271-1277. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2005.855679 [15] GODBOLE A A, KOLHE J P, TALOLE S E. Performance analysis of generalized extended state observer in tackling sinusoidal disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 21(6): 2212-2223. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2231512 [16] GAO Z Q. Scaling and bandwidth-parameterization based controller tuning[C]//Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference. Ohio: IEEE, 2003: 4989-4996. [17] JIN H Y, SONG J C, ZENG S, et al. Linear active disturbance rejection control tuning approach guarantees stability margin[C]//2018 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV). Singapore: IEEE, 2018: 1132-1136 -




 下载:
下载: