Formation Mechanism of Metro Wheel Polygonal Based on Vehicle-Track Coupling
-
摘要:
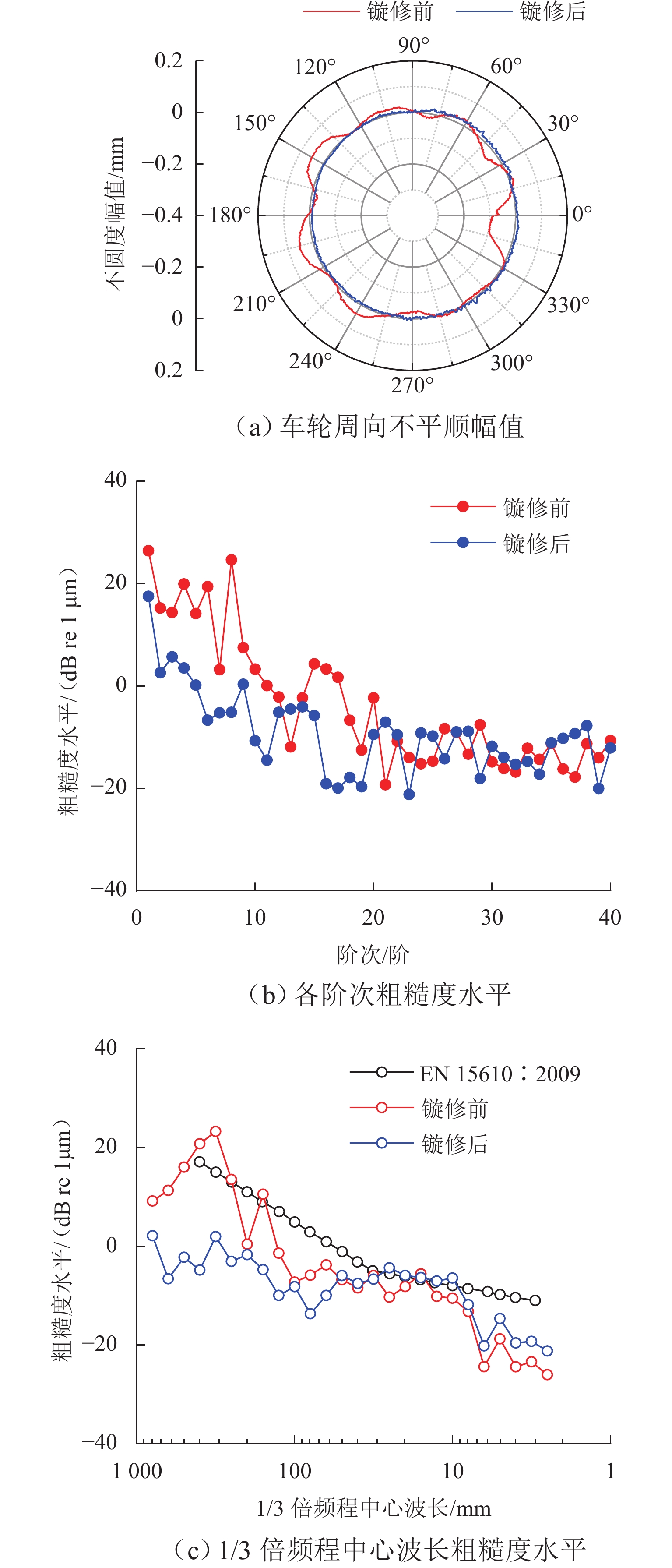
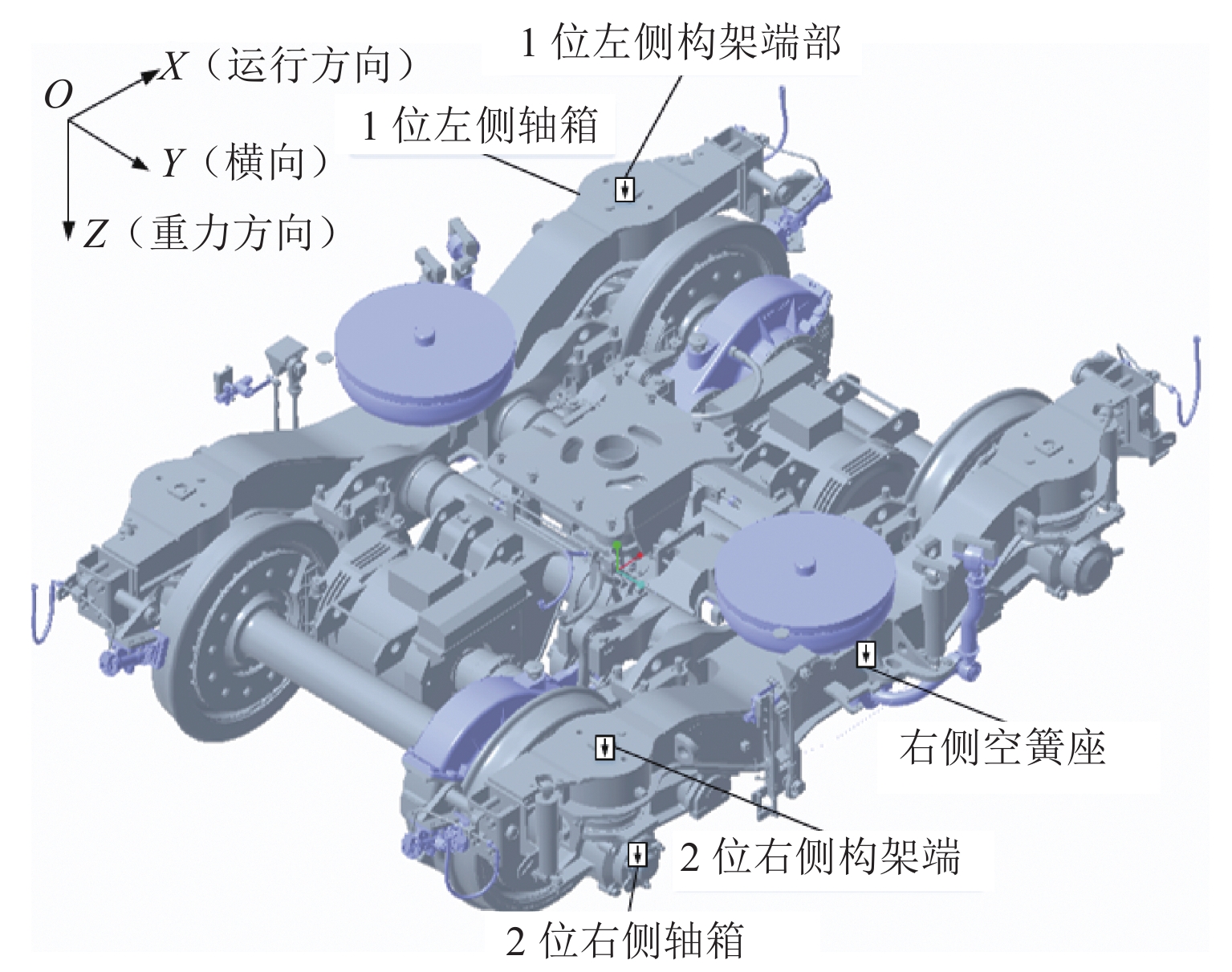
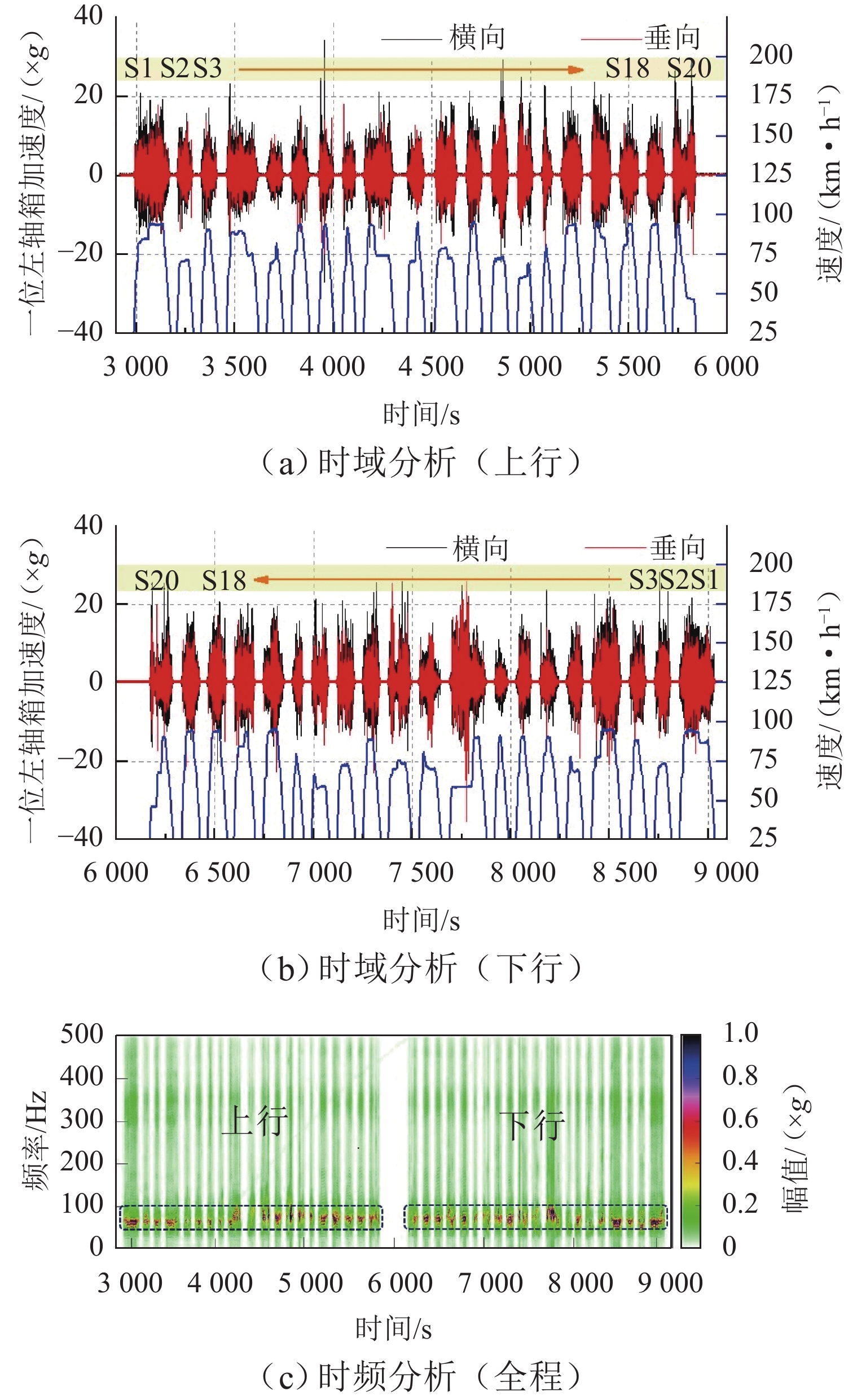
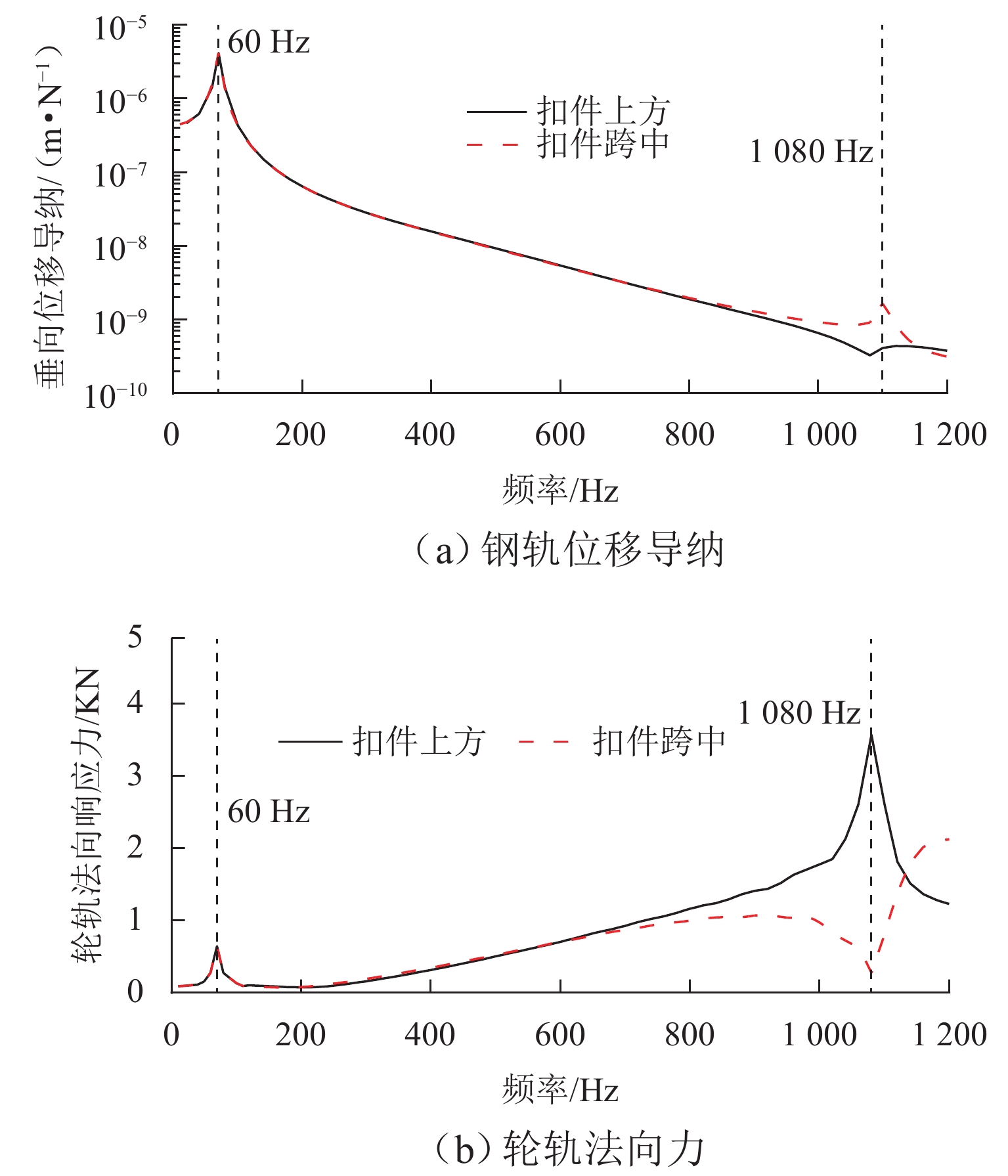
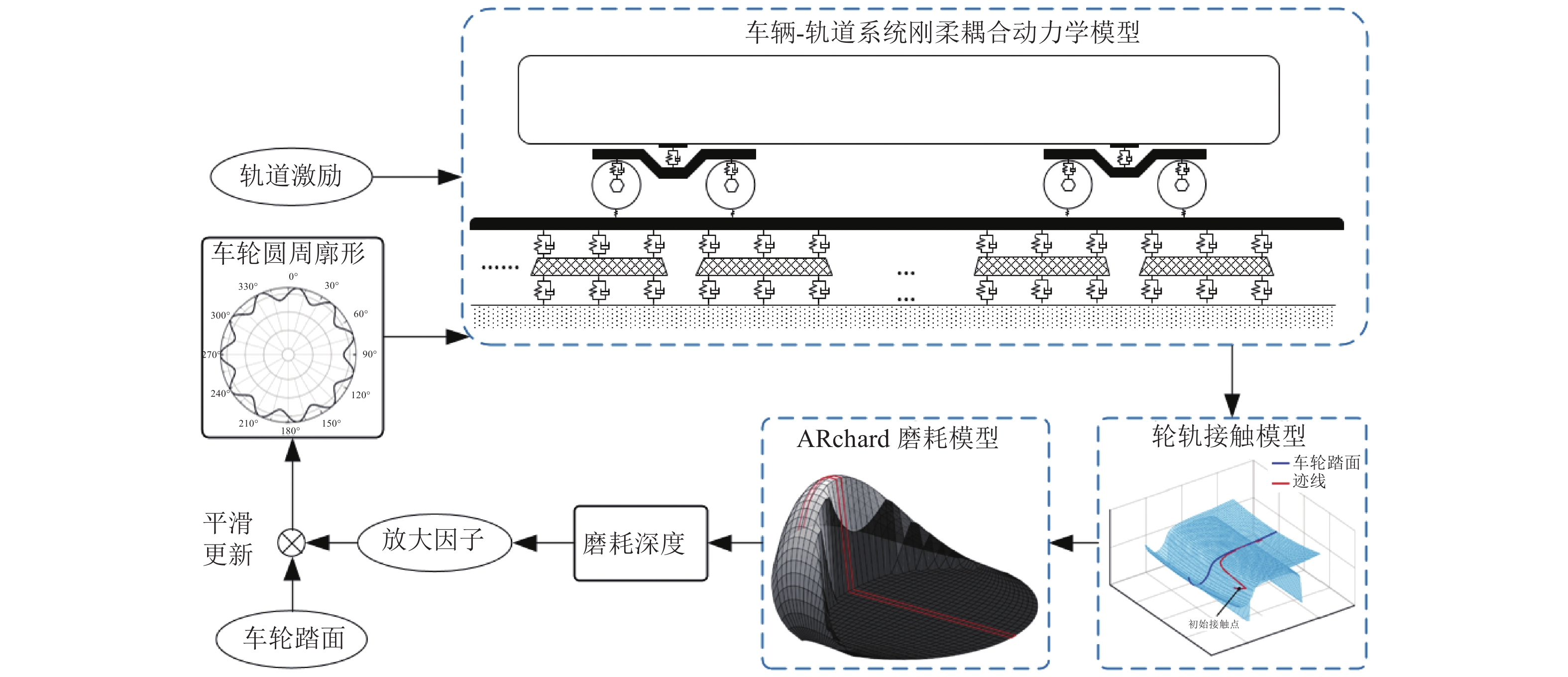
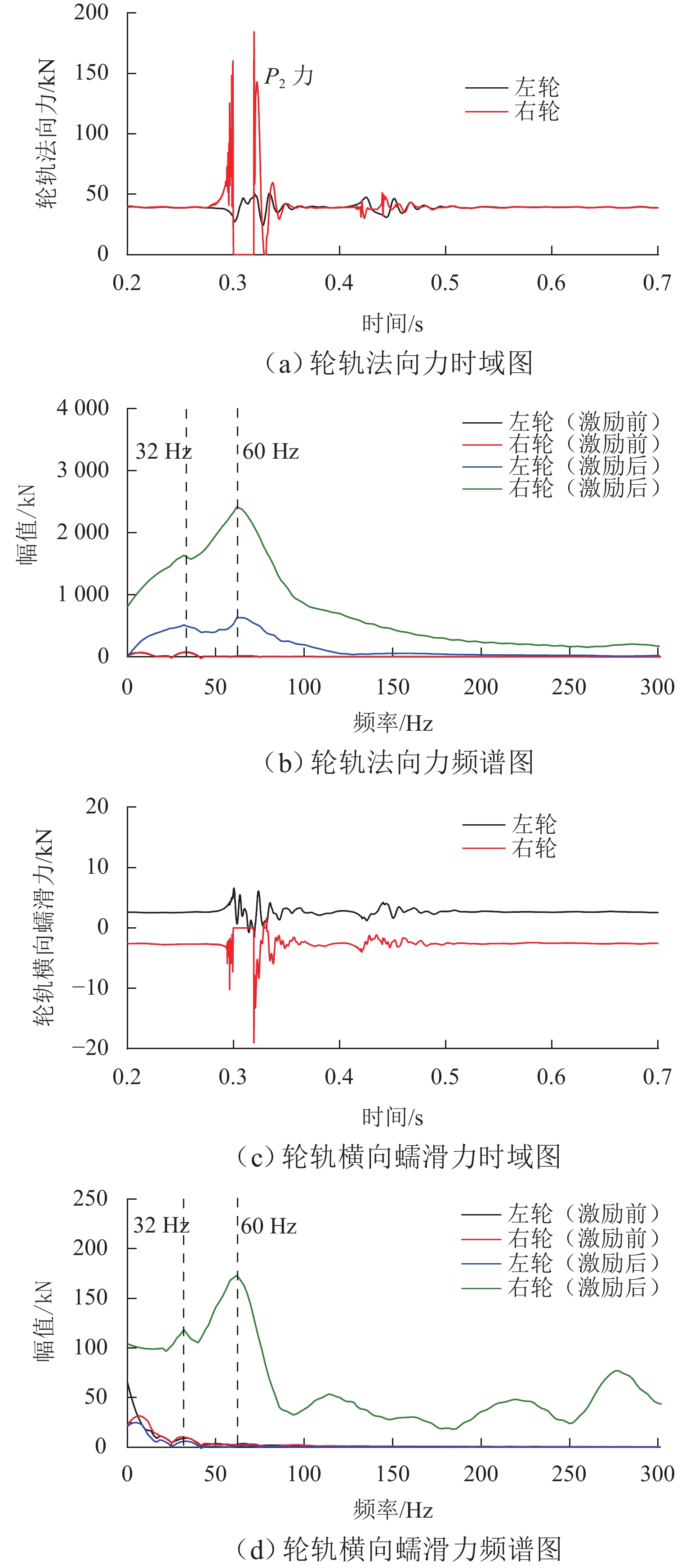
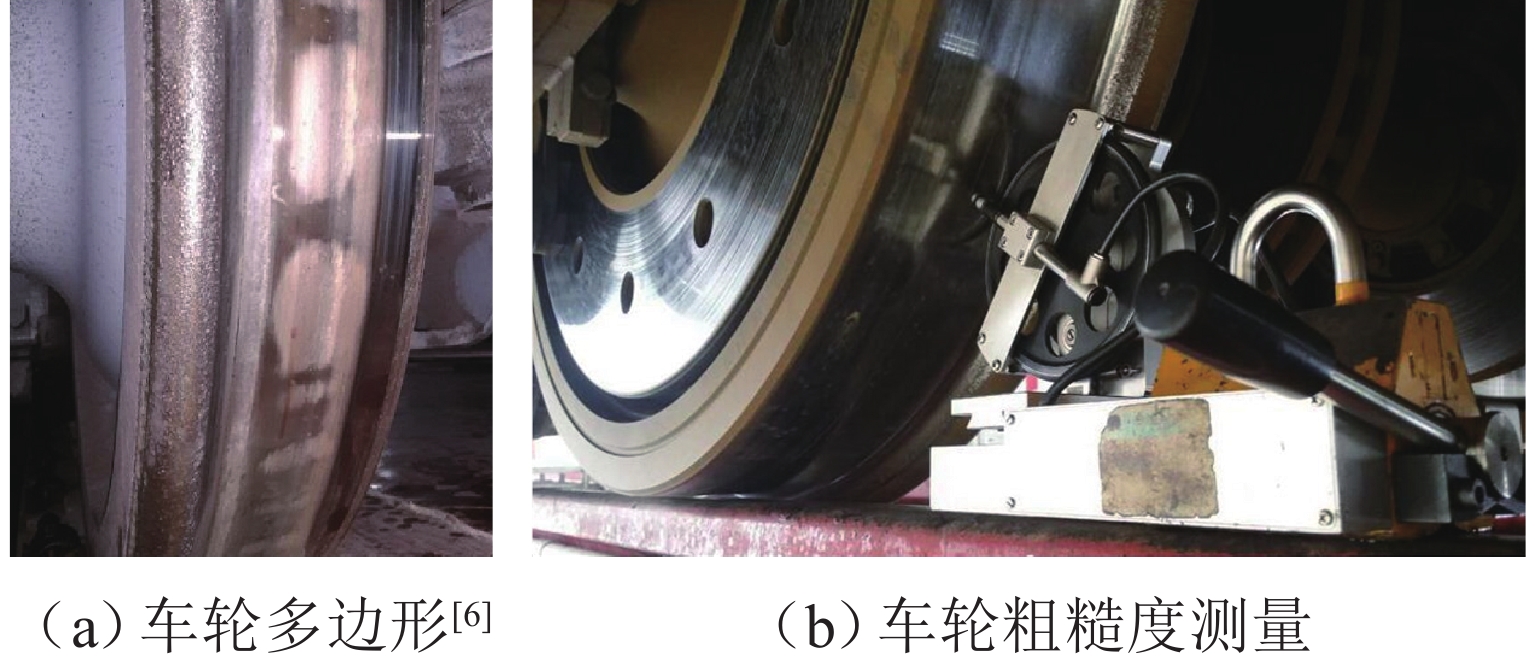
车轮多边形磨耗会恶化轨道车辆振动环境,导致结构部件的共振疲劳失效,严重威胁行车安全. 为研究地铁车辆车轮多边形磨耗的形成机理,开展线路动态跟踪试验研究,建立车轨垂向耦合有限元模型和动力学模型,并进行轮轨长期磨耗迭代仿真分析. 研究结果表明:实测车辆发生了明显的7~9阶的车轮多边形磨耗,导致车辆出现50~70 Hz的强迫振动,频率与轮轨系统耦合振动
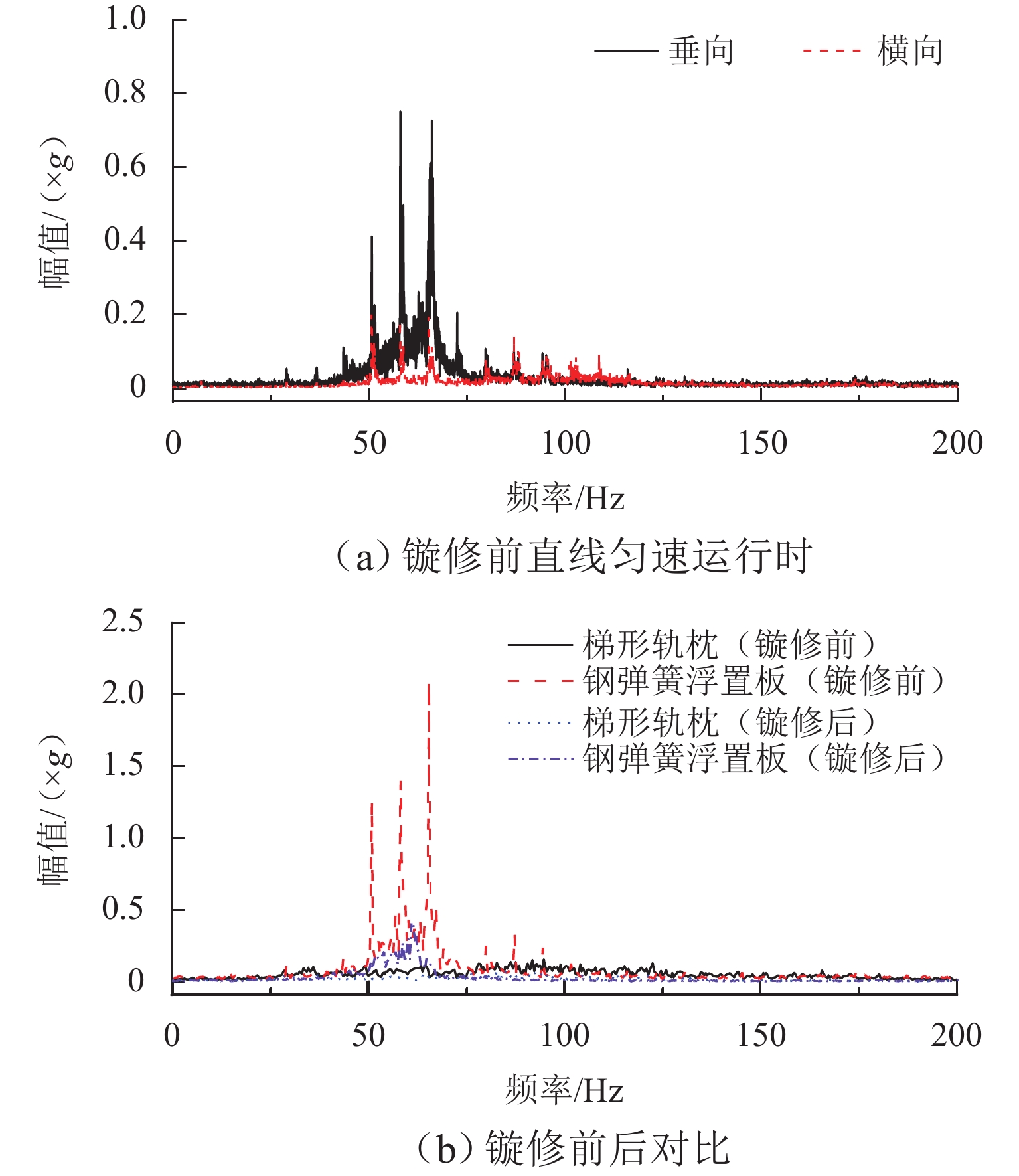
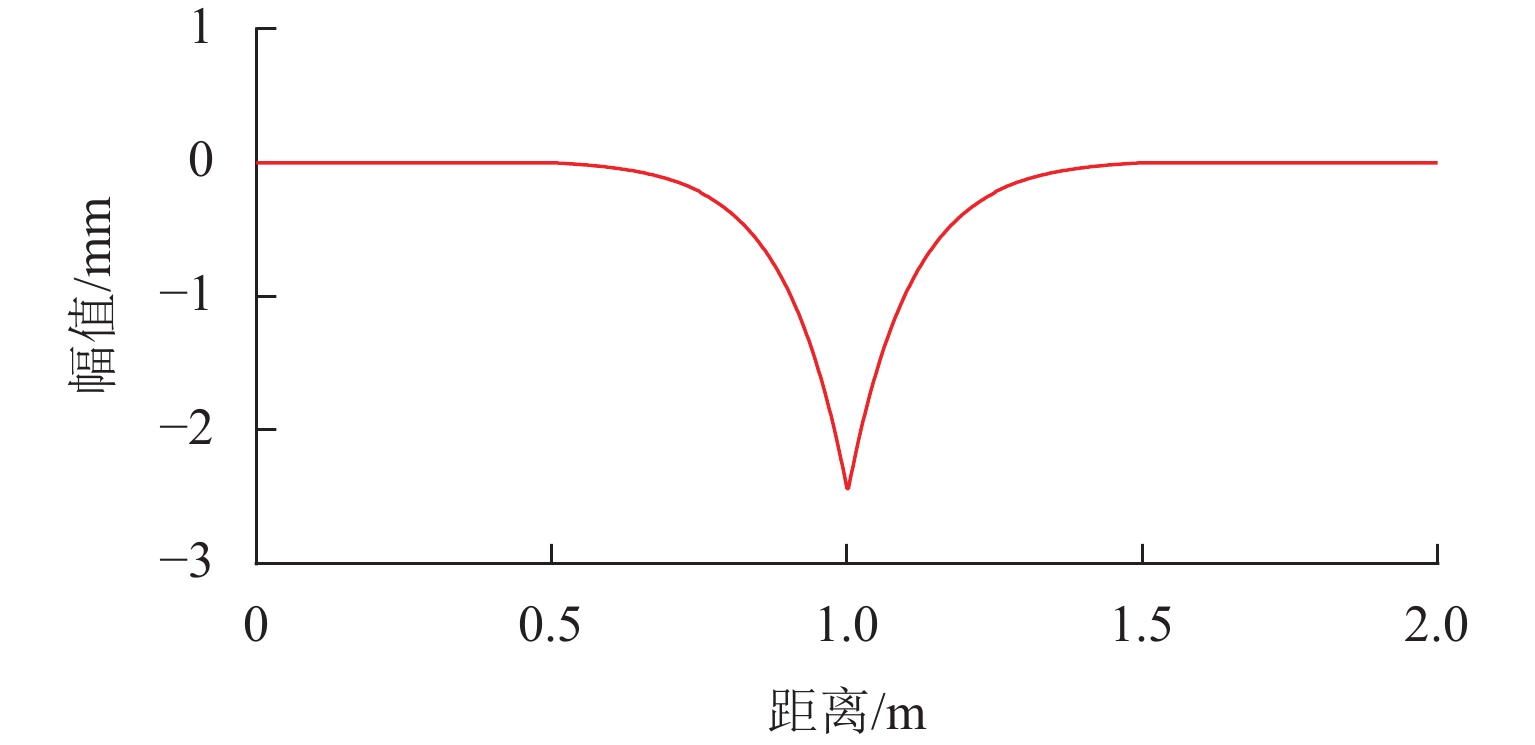
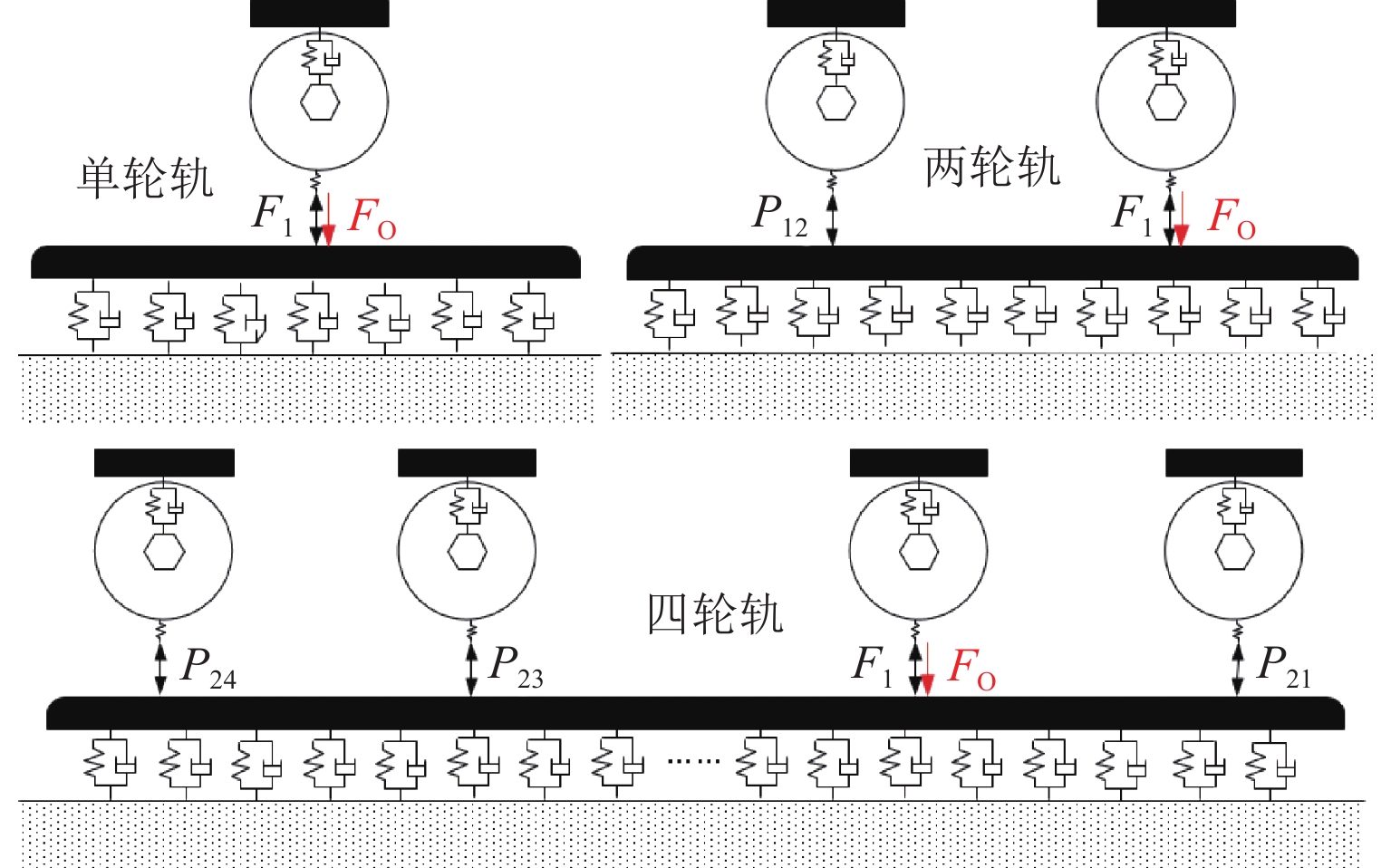
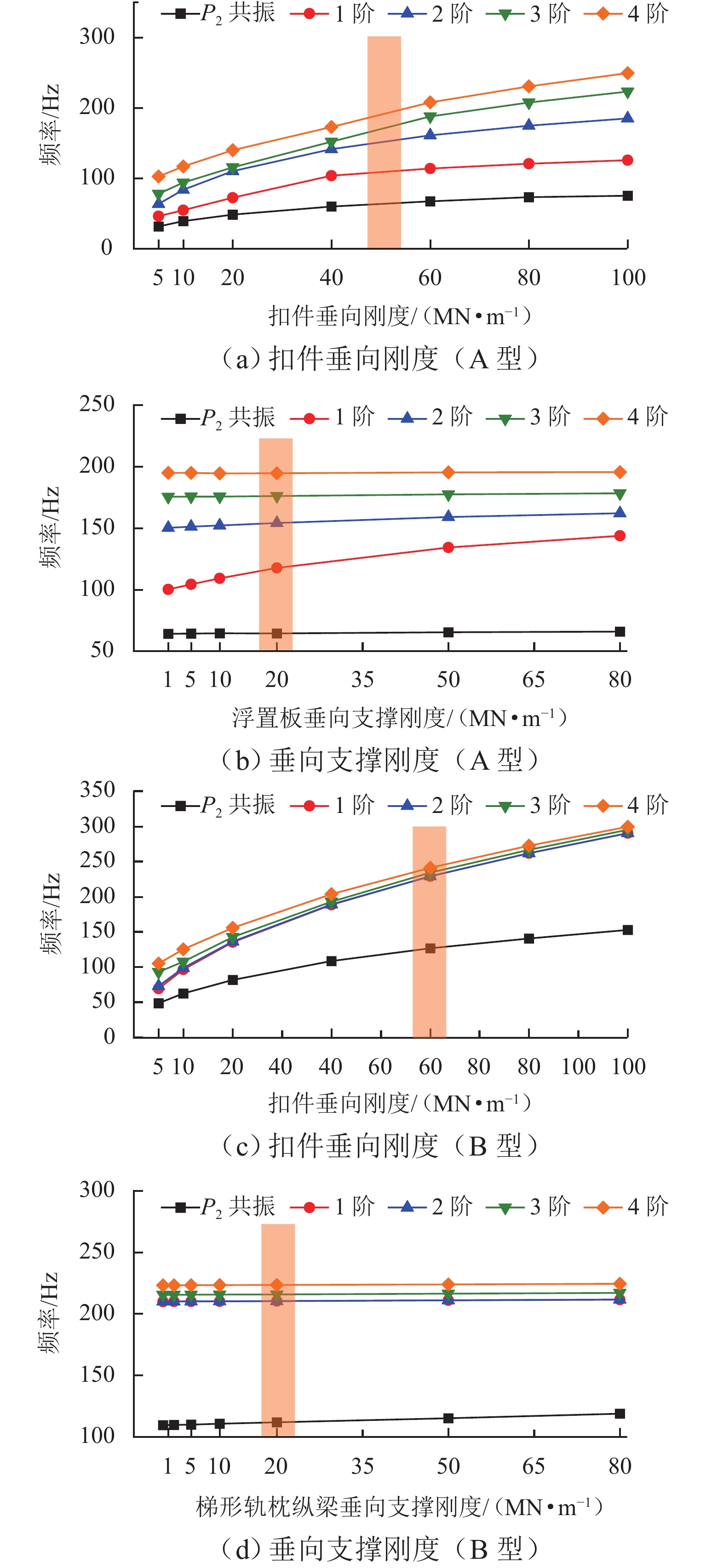
P 2力频率接近;通过车轮磨耗迭代仿真分析,确定了钢轨周期性接头焊缝不平顺引起的轮轨系统P 2力共振是导致车轮7~9阶多边形磨耗的根本原因;对钢弹簧浮置板道床和梯形轨枕道床而言,长期轮轨P 2力作用会分别引起8阶和15阶车轮多边形磨耗.Abstract:Wheel polygonal wear will deteriorate the vibration environment of rail vehicles, lead to resonance fatigue failure of structural components, and seriously threaten driving safety. To study the formation mechanism of wheel polygonal wear of metro vehicles, the dynamic line tracking test was carried out, and the vertical coupling finite element model and dynamics model of the track were established. In addition, the iterative simulation analysis of long-term wheel-track wear was carried out. The results show that the wheel polygonal wear of 7–9th order occurs in the measured vehicle, which leads to the forced vibration of 50–70 Hz, and the frequency is close to that of the
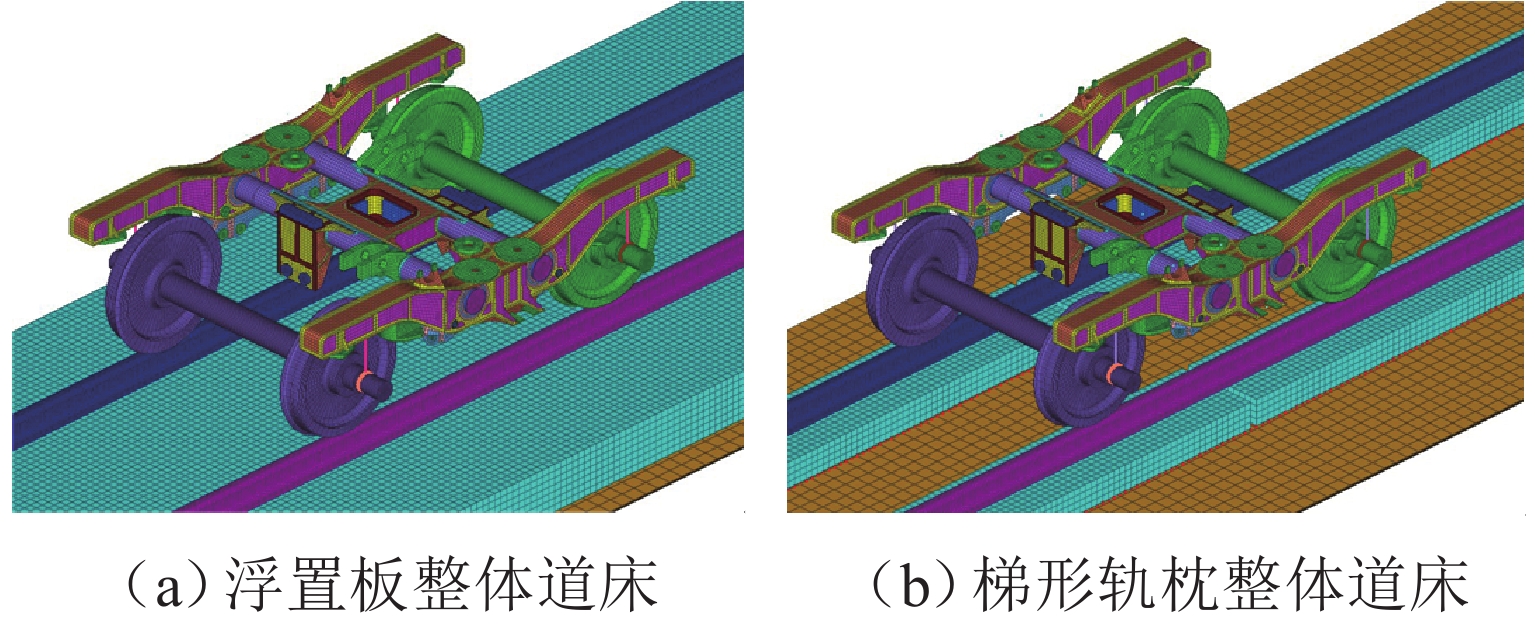
P 2 force during the coupling vibration of the wheel-track system. Through the iterative simulation analysis of wheel wear, it is determined thatP 2 force resonance of the wheel-rail system caused by periodic irregular rail joint weld is the root cause of the 7th–9th order wheel polygonal wear. Under the long-term action ofP 2 force, the floating slab track bed and the ladder sleeper track bed of steel spring will cause 8th and 15th order wheel polygonal wear, respectively.-
Key words:
- metro vehicle /
- wheel polygon /
- vehicle-track coupling /
- wear model /
- vehicle dynamics
-
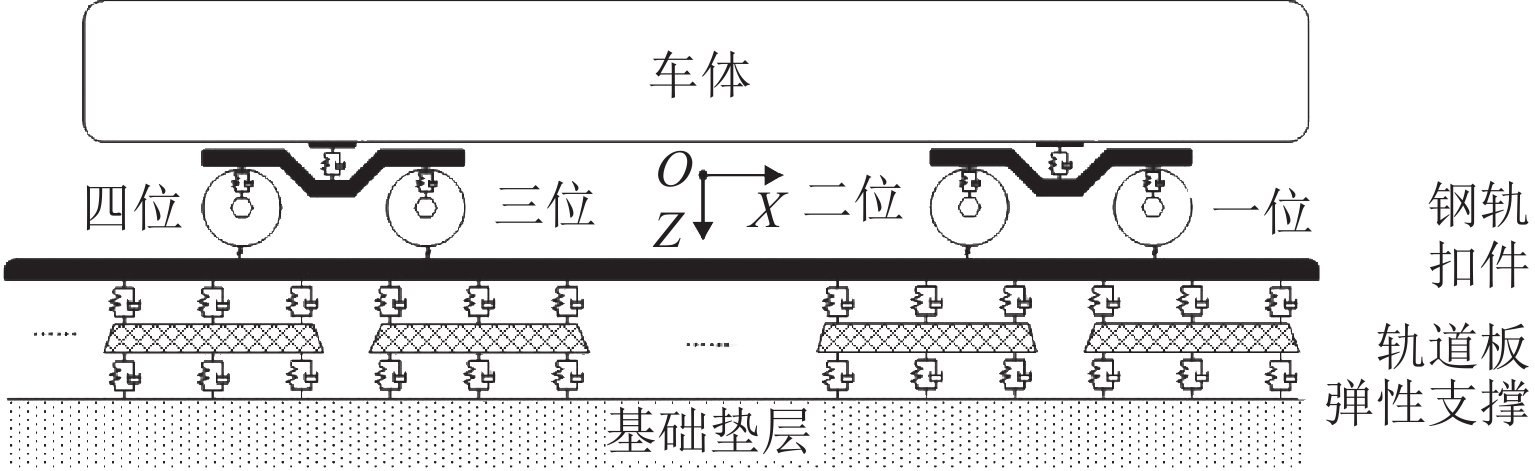
表 1 地铁车辆和轨道的主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of metro vehicles and tracks
参数 符号 数值 定距之半/m lc 7.85 轴距之半/m lw 1.25 车体质量/kg Mc 24937 构架质量/kg Mf 1830 轮对质量/kg Mw 1231 一系悬挂垂向刚度/(MN·m−1) Kps 1.5 一系悬挂垂向阻尼/(kN·s·m−1) Cps 2 浮置板道床扣件垂向刚度/(MN·m−1) Ka 50 浮置板支撑刚度/(kN·s·m−1) Ca 20 梯形轨枕扣件垂向刚度(MN·m−1) Kb 60 梯形轨枕纵梁支撑刚度/(kN·s·m−1) Cb 20 普通道床扣件垂向刚度/(MN·m−1) Kc 20 浮置板长度/m La 24 梯形轨枕纵梁长度/m Lb 6 -
[1] 刘维宁,马蒙,刘卫丰,等. 我国城市轨道交通环境振动影响的研究现况[J]. 中国科学:技术科学,2016,46(6): 547-559. doi: 10.1360/N092015-00334LIU Weining, MA Meng, LIU Weifeng, et al. Overview on current research of environmental vibration influence induced by urban mass transit in China[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Technologica, 2016, 46(6): 547-559. doi: 10.1360/N092015-00334 [2] 魏鹏勃. 城市轨道交通引起的环境振动预测与评估[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2009. [3] KANG X, CHEN G X, ZHU Q, et al. Study on wheel polygonal wear of metro trains caused by frictional self-excited oscillation[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2021, 64(6): 1108-1117. doi: 10.1080/10402004.2021.1970868 [4] ZHOU C, CHI M R, WEN Z F, et al. An investigation of abnormal vibration-induced coil spring failure in metro vehicles[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2020, 108: 104238.1-104238.13. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.104238 [5] JOHANSSON A, ANDERSSON C. Out-of-round railway wheels—a study of wheel polygonalization through simulation of three-dimensional wheel-rail interaction and wear[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2005, 43(8): 539-559. doi: 10.1080/00423110500184649 [6] TAO G Q, WEN Z F, LIANG X R, et al. An investigation into the mechanism of the out-of-round wheels of metro train and its mitigation measures[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2019, 57(1): 1-16. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2018.1445269 [7] SHI Y X, DAI H Y, WANG Q S, et al. Research on low-frequency swaying mechanism of metro vehicles based on wheel-rail relationship[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2020, 2020: 8878020.1-8878020.15. [8] CAI W B, CHI M R, WU X W, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of the polygonal wear of high-speed trains[J]. Wear, 2019, 440/441: 203079.1-203079.12. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2019.203079 [9] MA C Z, GAO L, CUI R X, et al. The initiation mechanism and distribution rule of wheel high-order polygonal wear on high-speed railway[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 119: 104937.1-104937.14. [10] YANG X X, TAO G Q, LI W, et al. On the formation mechanism of high-order polygonal wear of metro train wheels: experiment and simulation[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 127: 105512.1-105512.14. [11] QU S, ZHU B, ZENG J, et al. Experimental investigation for wheel polygonisation of high-speed trains[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2021, 59(10): 1573-1586. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2020.1772984 [12] 董雅宏,曹树谦. 车轮高阶多边形磨耗发生与演化特征分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(3): 665-676.DONG Yahong, CAO Shuqian. Analysis of occurrence and evolution characteristics of wheel high-order polygonal wear[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 665-676. [13] 胡晓依,任海星,成棣,等. 动车组车轮多边形磨耗形成与发展过程仿真研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2021,42(2): 107-115.HU Xiaoyi, REN Haixing, CHENG Di, et al. Numerical simulation on the formation and development of polygonal wear of EMU wheels[J]. China Railway Science, 2021, 42(2): 107-115. [14] The International Organization for Standardization. Railway applications—acoustics measurement of noise emitted by railbound vehicles: ISO 3095:2013[S]. [S.l.]: ISO Copyright Office, 2013. [15] 罗仁, 石怀龙. 铁道车辆系统动力学及应用[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2018. [16] ZHAI W M, WANG K Y, CAI C B. Fundamentals of vehicle−track coupled dynamics[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2009, 47(11): 1349-1376. doi: 10.1080/00423110802621561 [17] KORO K, ABE K, ISHIDA M, et al. Timoshenko beam finite element for vehicle—track vibration analysis and its application to jointed railway track[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2004, 218(2): 159-172. doi: 10.1243/0954409041319687 [18] 林国进. 轮对弹性及参数对轮轨接触关系影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2015. [19] WU T X, THOMPSON D J. Behaviour of the normal contact force under multiple wheel/rail interaction[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2002, 37(3): 157-174. doi: 10.1076/vesd.37.3.157.3533 [20] 关庆华,周业明,李伟,等. 车辆轨道系统的P2共振频率研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(8): 118-127. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.118GUAN Qinghua, ZHOU Yeming, LI Wei, et al. Study on the P2 resonance frequency of vehicle track system[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(8): 118-127. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.118 [21] 陈小平,王平,陈嵘. 弹性支承块式无砟轨道的减振机理[J]. 铁道学报,2007,29(5): 69-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2007.05.013CHEN Xiaoping, WANG Ping, CHEN Rong. Damping vibration mechanism of the elastic bearing block track[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2007, 29(5): 69-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.2007.05.013 [22] 赵晓男,陈光雄,康熙,等. 兰新客运专线动车组车轮多边形磨耗的机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(2): 364-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190027ZHAO Xiaonan, CHEN Guangxiong, KANG Xi, et al. Mechanism of polygonal wear on wheels of electric multiple units on lanzhou-Xinjiang passenger dedicated line[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(2): 364-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190027 [23] QI Y Y, DAI H Y, GAN F, et al. Optimization of rail profile design for high-speed lines based on Gaussian function correction method[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2023: 095440972311525.1-095440972311525.13. [24] 王鹏,陶功权,杨晓璇,等. 中国高速列车车轮多边形磨耗特征分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(6): 1357-1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210777WANG Peng, TAO Gongquan, YANG Xiaoxuan, et al. Analysis of polygonal wear characteristics of Chinese high-speed train wheels[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(6): 1357-1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210777 -




 下载:
下载: