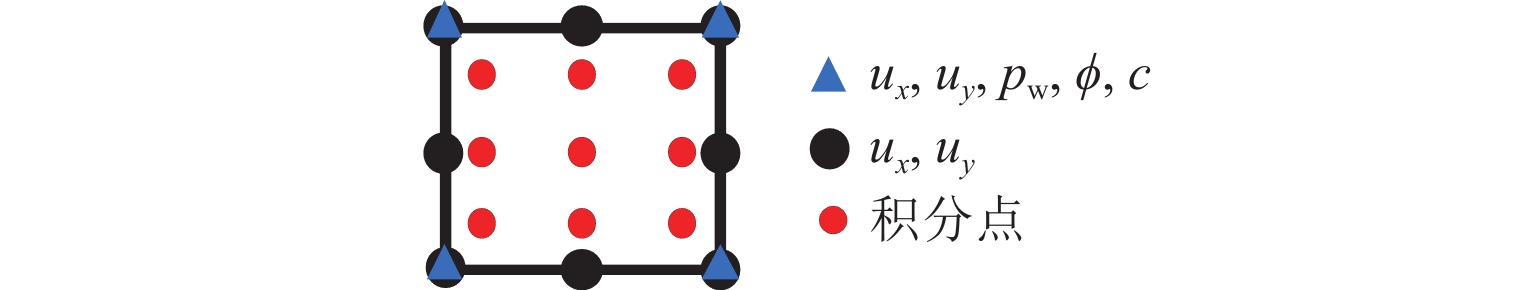
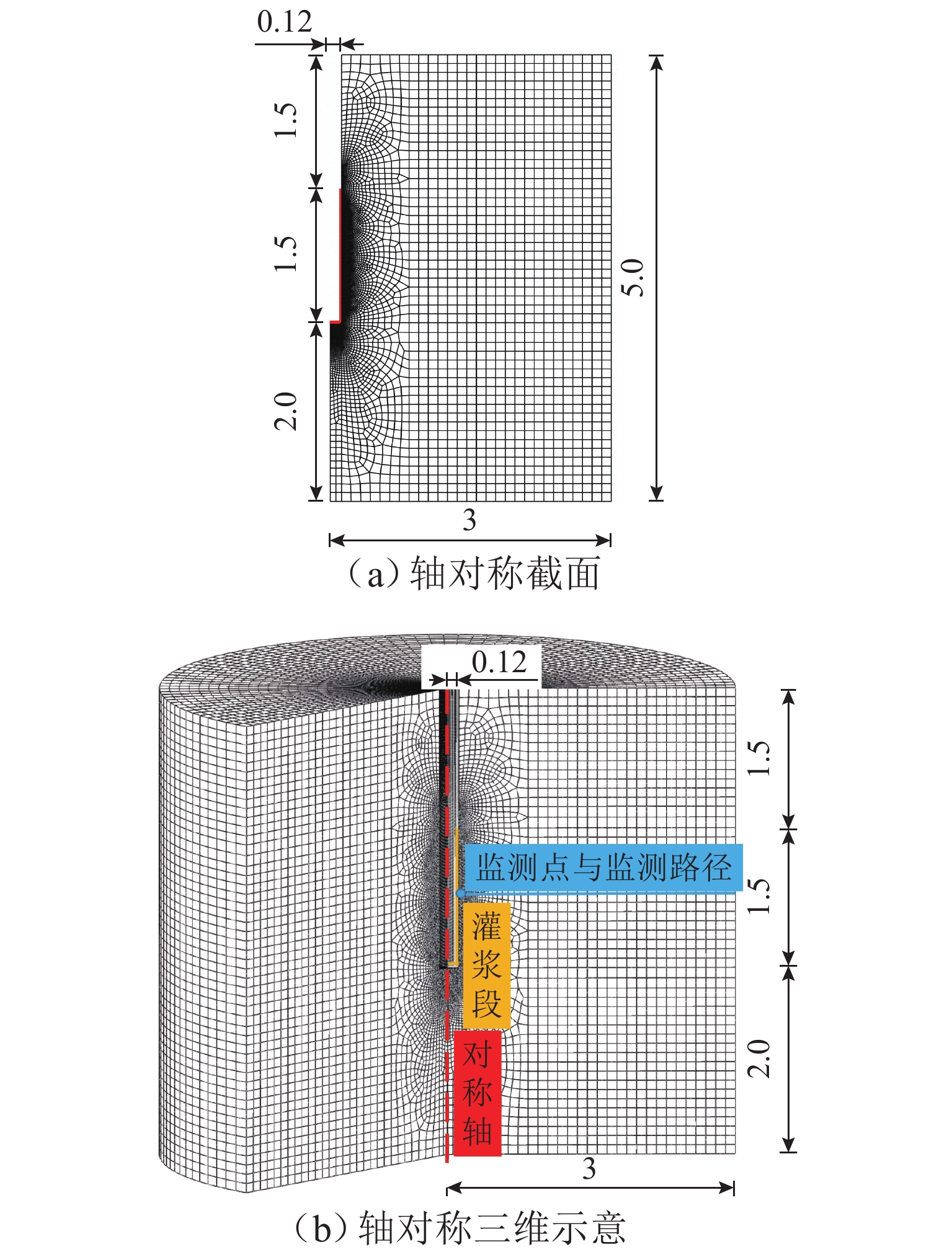
Numerical Analysis of Multiphysics Coupling of Grout Penetration
-
摘要:
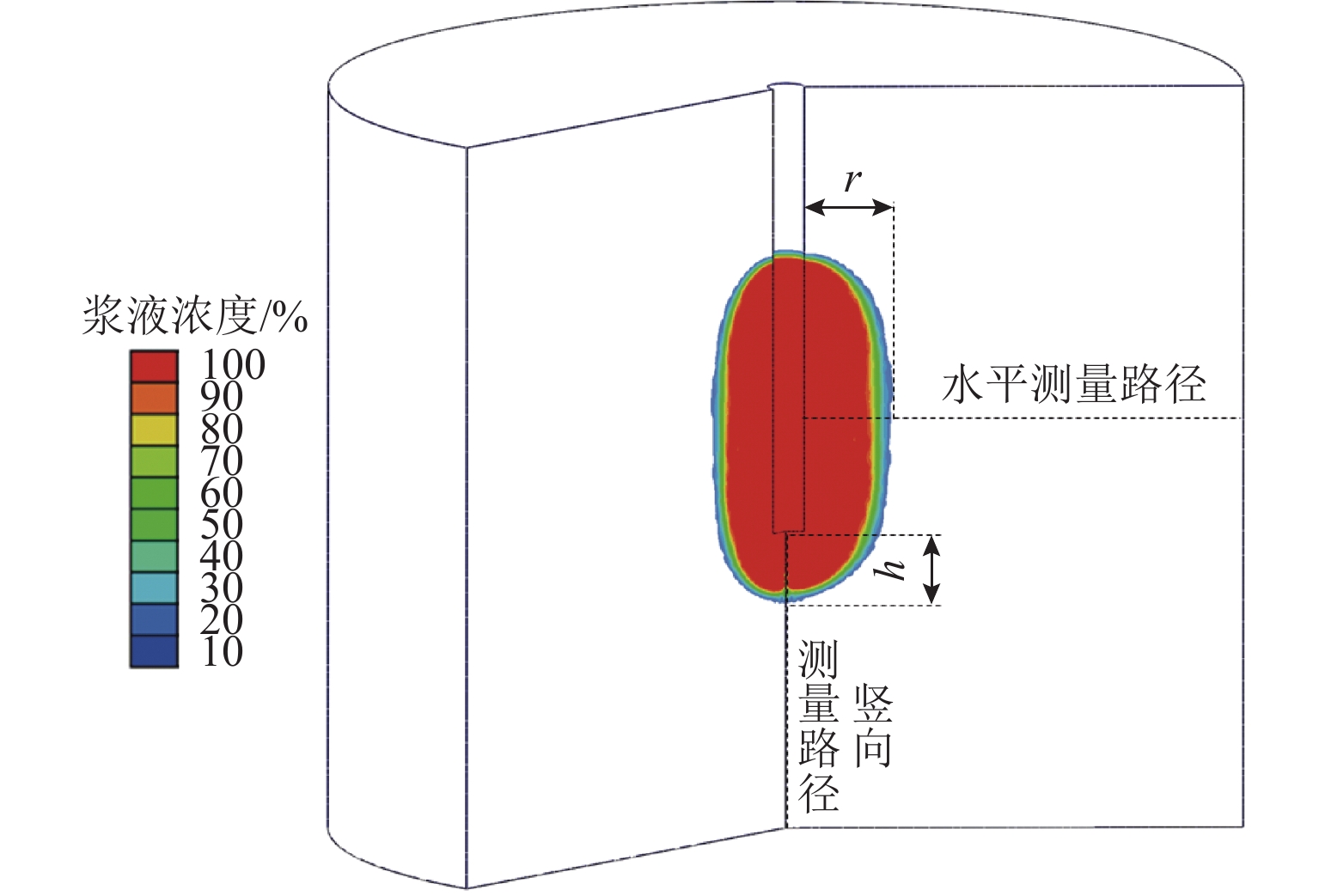
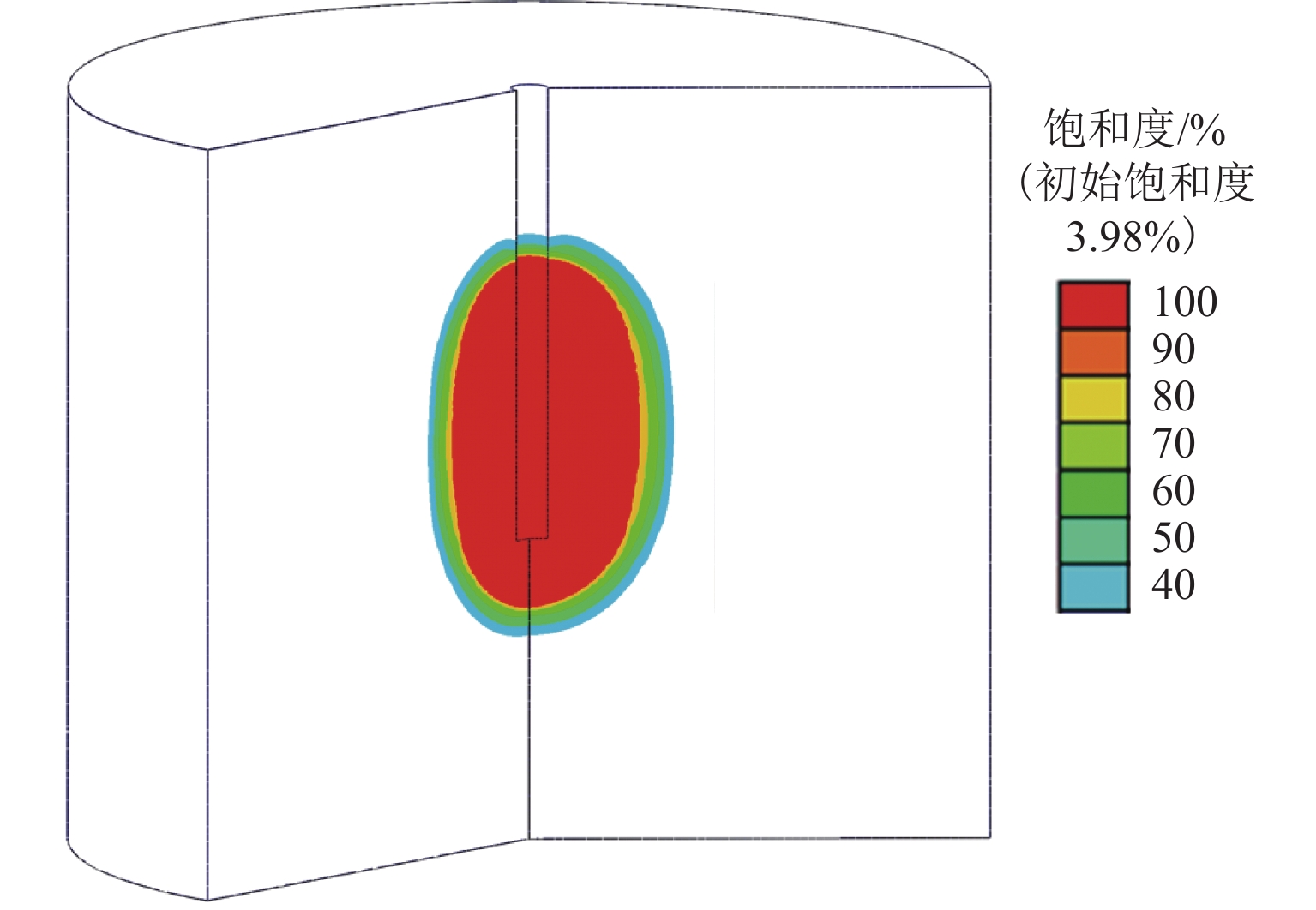
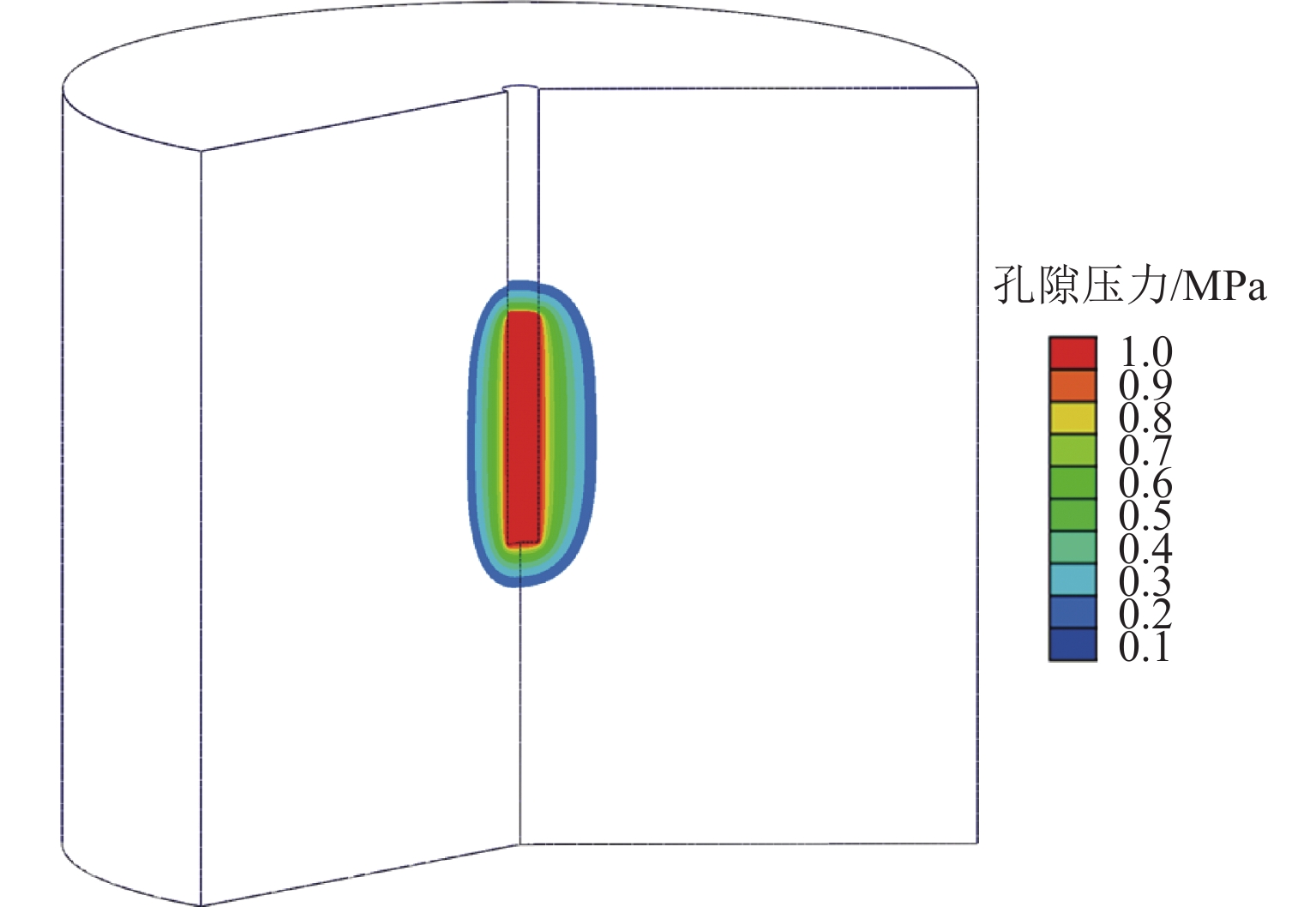
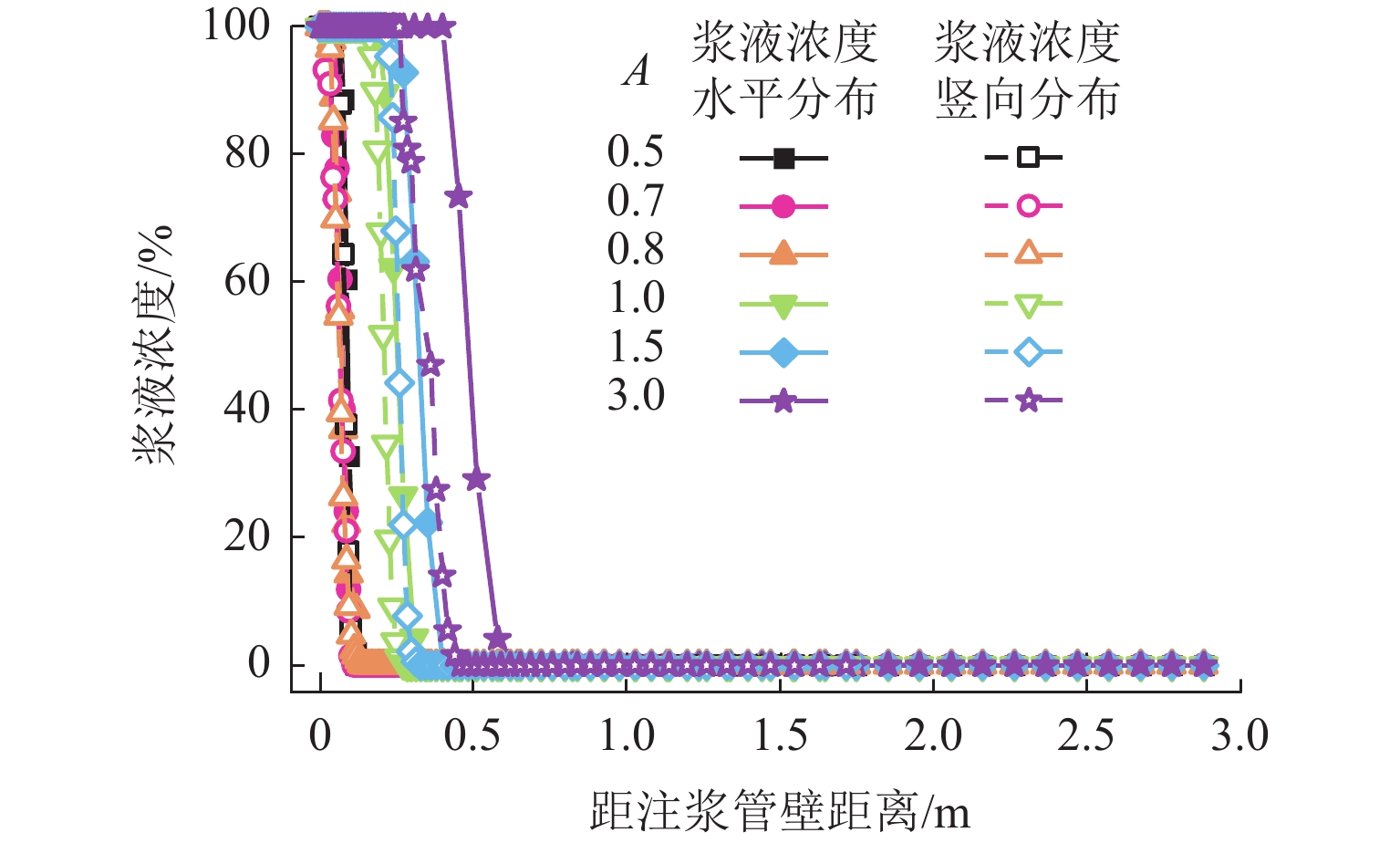
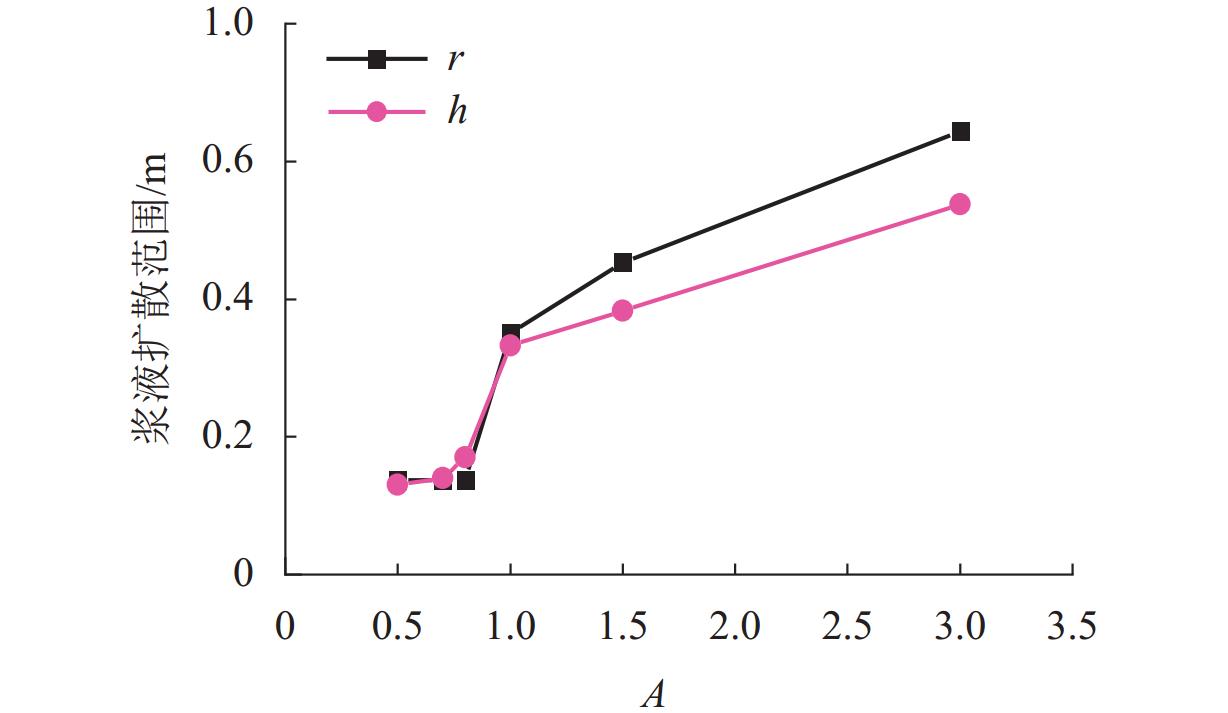
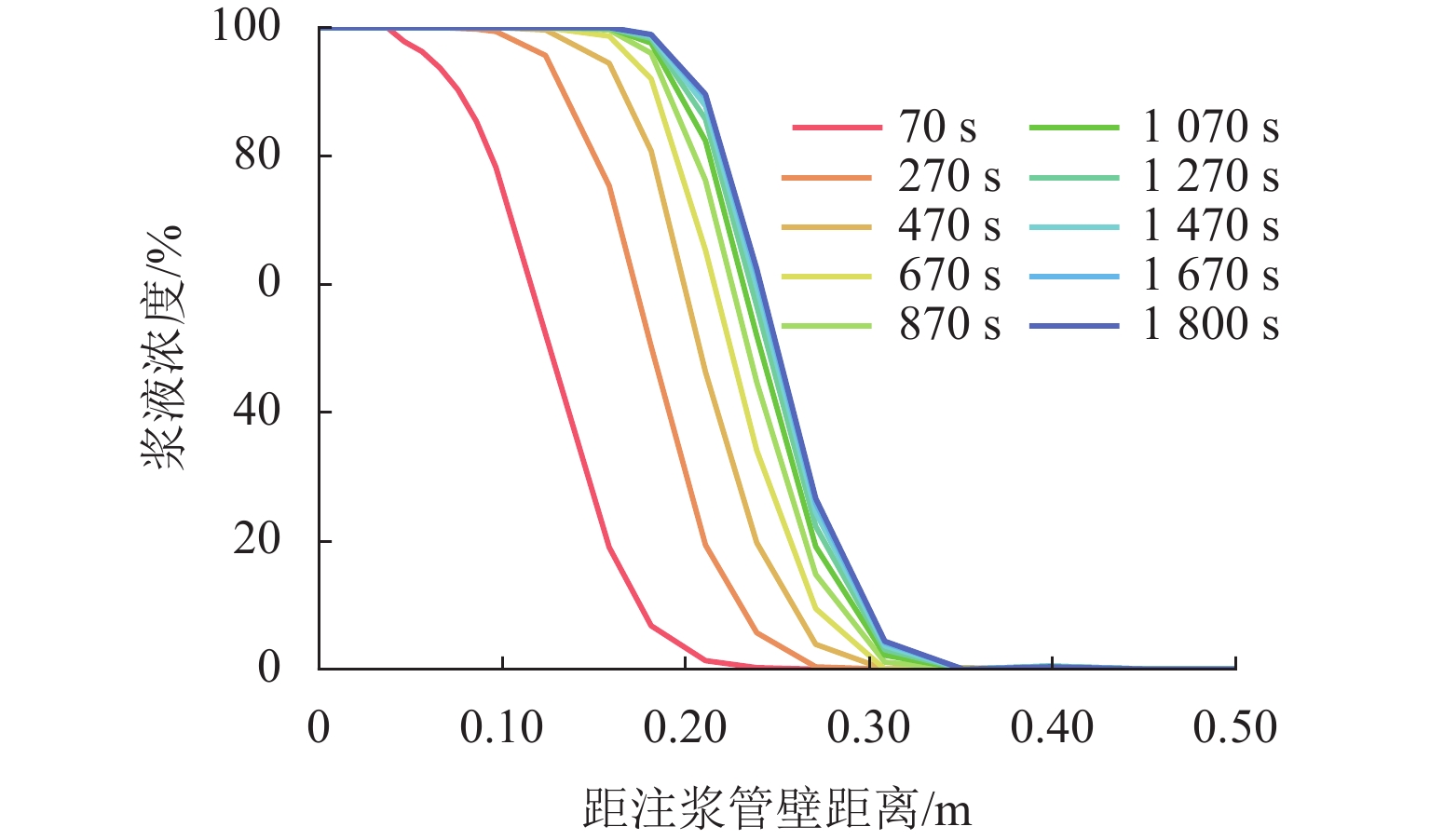
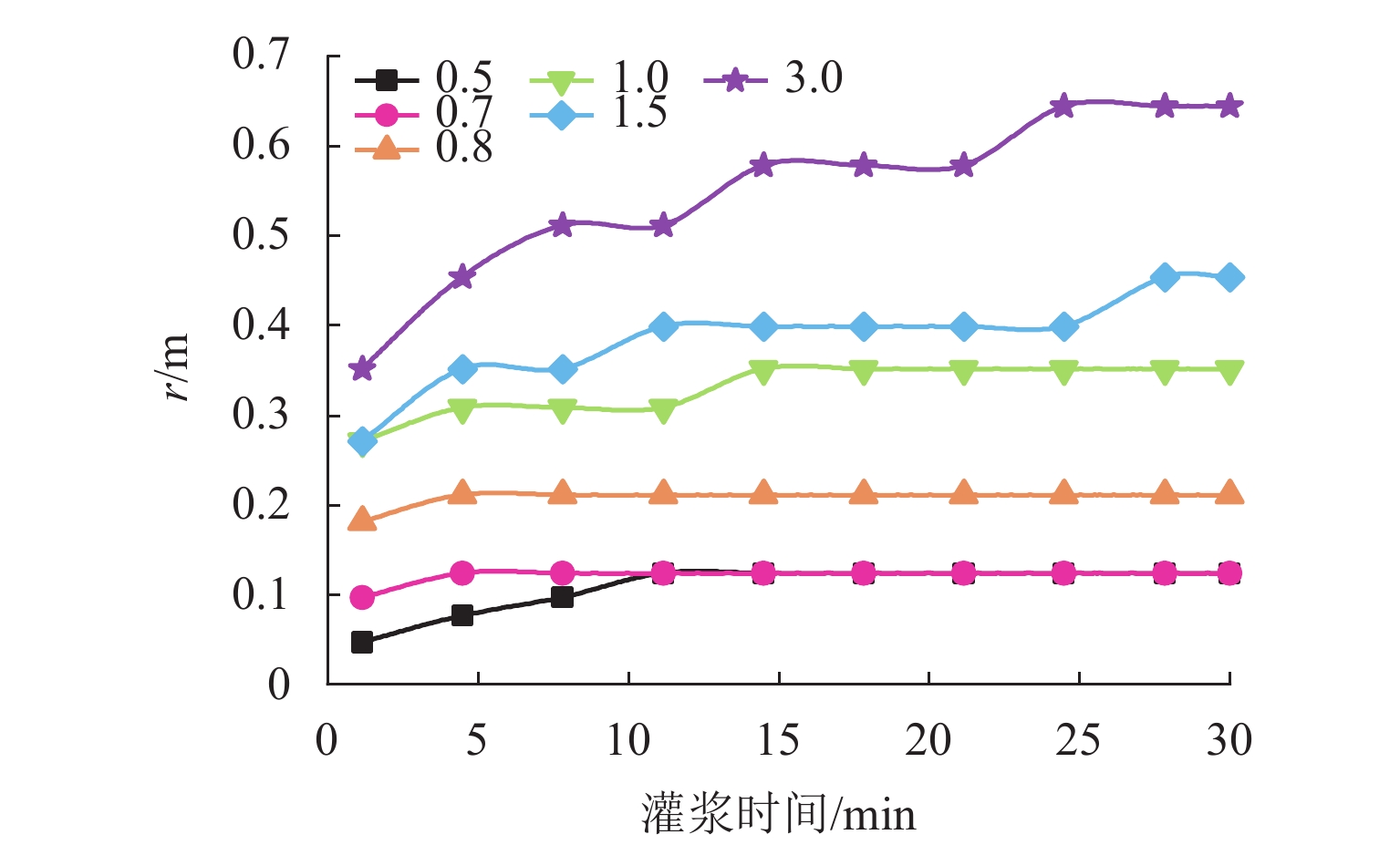
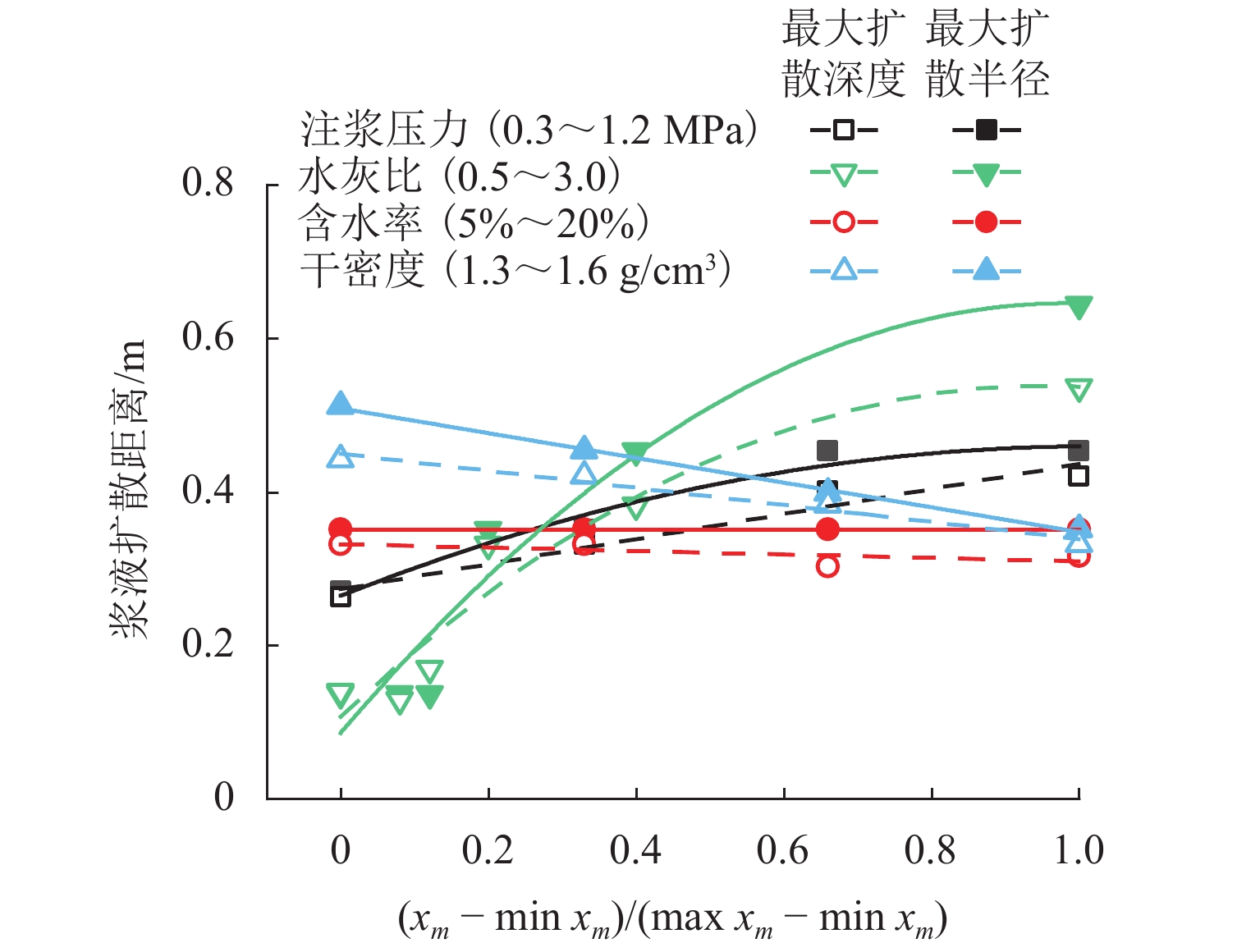
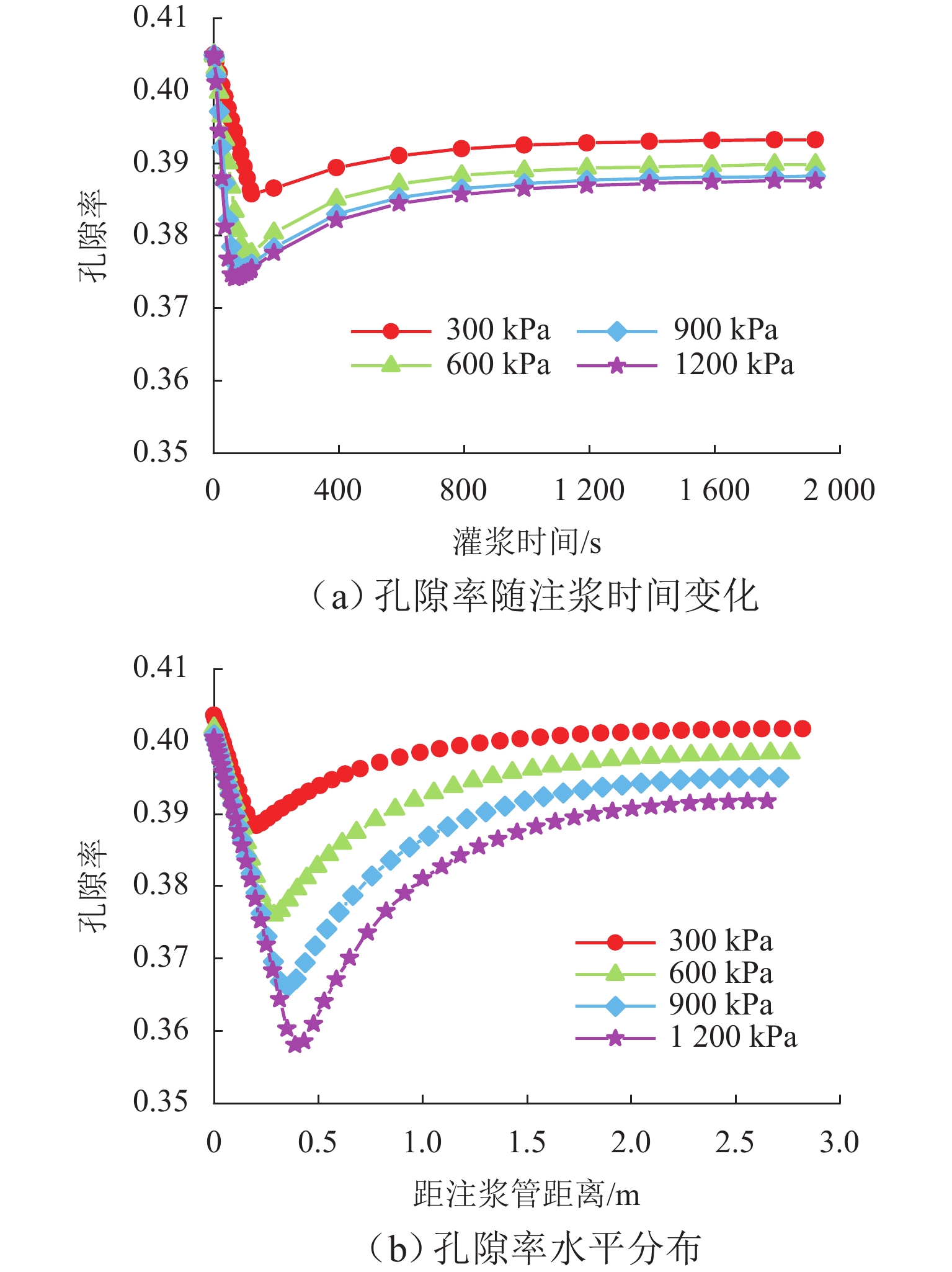
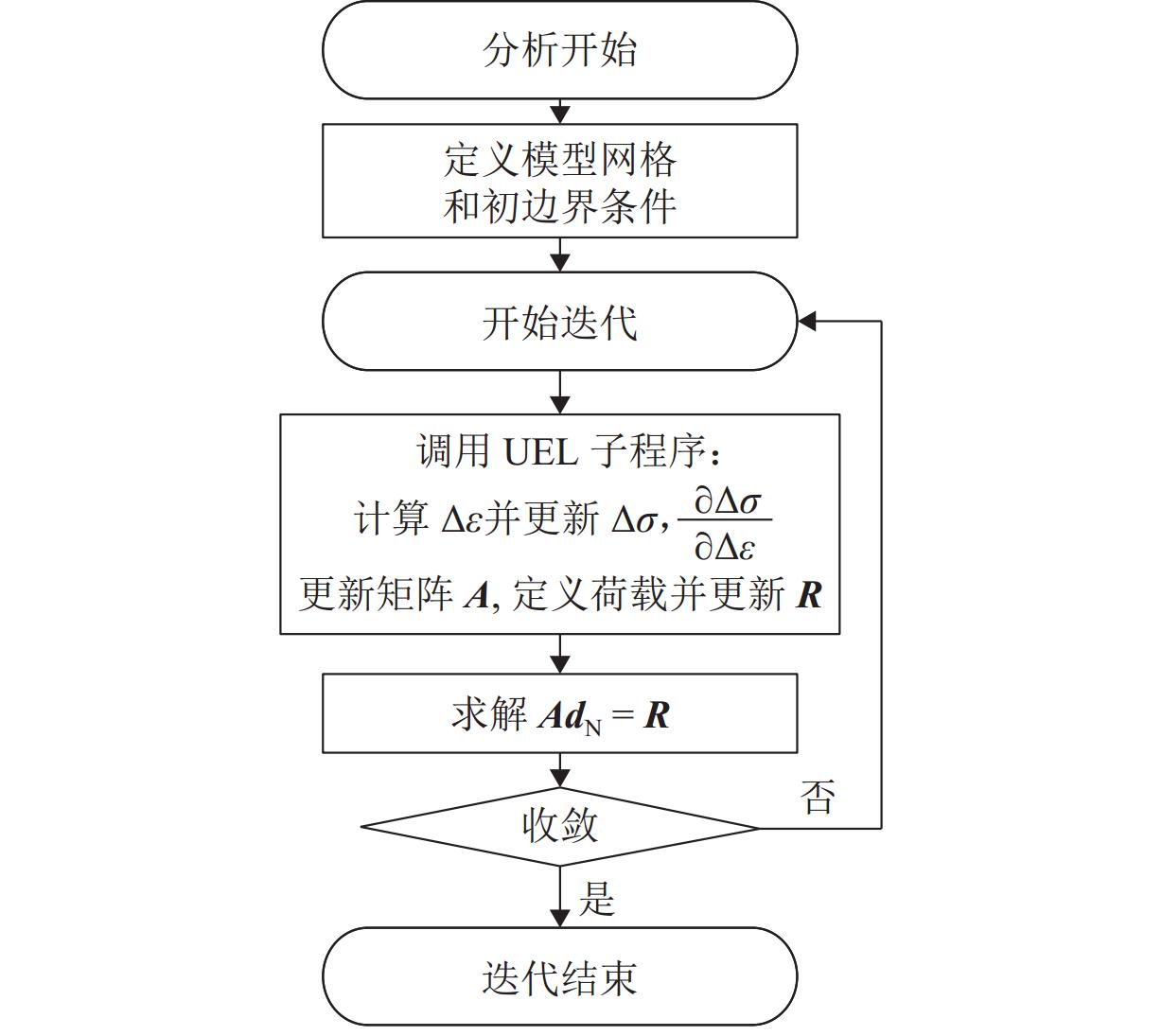
非饱和地层中的注浆渗透扩散是一个复杂的多物理场过程,为更加精确分析浆液在饱和与非饱和地层中的扩散特性,并估算注浆渗透扩散范围和注浆挤密区域,以混合理论为基础,建立一个非饱和多孔介质中的多物理场耦合模型. 通过ABAQUS二次开发,构建一种新型八节点五自由度四边形轴对称Serendipity单元,实现对注浆过程中土体变形、土体孔隙率、孔隙压力和浆液浓度分布的数值求解,以及对土体饱和度、渗透系数等状态变量的实时更新;结合一个三维轴对称注浆算例,分析浆液水灰比、注浆压力、土体初始干密度以及土体初始含水率对粉砂地层注浆效果的影响,并得到浆液水平和竖向扩散距离随不同因素变化的拟合曲线. 研究结果表明:浆液扩散范围受水灰比影响最显著,受注浆压力影响次之,受含水率和干密度影响最小;浆液扩散范围随水灰比增加而增长,水灰比大于1.0时增长显著;注浆管壁周围会形成挤密区域,浆液扩散区域内土体同时受到注浆压力的挤压和孔隙压力的支撑作用;随着远离注浆管壁,土体孔隙率在挤密区域内逐渐减小,在挤密区域外逐渐恢复,且挤密区域随注浆压力的增加而增大;研究成果可为土体注浆加固范围计算提供理论指导.
Abstract:Grout penetration in the unsaturated formation is a complex multiphysics process. In order to analyze more accurately the penetration characteristics of grout in saturated and unsaturated formations and estimate the range of grout penetration and grout compaction area, a multiphysics coupling model for unsaturated porous media was developed based on mixture theory. A novel five-degree-of-freedom eight-node quadrilateral axisymmetric Serendipity element was constructed through the secondary development of ABAQUS, so as to realize the numerical solution of soil deformation, soil porosity, pore pressure, and grout concentration distribution during grouting. The state variables, such as soil saturation and permeability coefficient, were updated in real time. The effects of grout water-cement ratio, grouting pressure, initial dry density, and water content of soil on the grouting in silty sand were analyzed with a three-dimensional axisymmetric grouting example, and the fitting curves of horizontal and vertical diffusion distance of grout with the above factors were obtained. The results show that the range of grout penetration is most significantly influenced by the water-cement ratio, followed by the grouting pressure, and it is least influenced by the water content and dry density of soil; the range of grout penetration increases with the increase in the water-cement ratio, especially when the water-cement ratio is greater than 1.0; a compacted area will be formed around the grouting pipe, where the soil is simultaneously subject to the grouting pressure and pore pressure; with the increase in the distance from the grouting pipe, the porosity of the soil gradually decreases in the compacted area and gradually recovers outside the compacted area, while the compacted area increases with the increase in the grouting pressure. The research results can provide theoretical guidance for calculating the grouting reinforcement in the soil.
-
Key words:
- grout penetration /
- multiphysics /
- finite element method /
- unsaturated soil
-
表 1 数值模拟主要试验变量
Table 1. Main test variables for numerical simulation
工况 注浆压力/MPa A 黏度时变[16]/
(MPa·s)初始干密
度/(g·cm−3)初始含水率/% 1 1.0 0.5 $ 407.41{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0005t}} $ 1.6 10 2 1.0 0.7 $ 43.864{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0088t}} $ 1.6 10 3 1.0 0.8 $ 28.183{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0114t}} $ 1.6 10 4 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 10 5 1.0 1.5 $ 10.867{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0017t}} $ 1.6 10 6 1.0 3.0 $ 6.8812{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0009t}} $ 1.6 10 7 0.3 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 10 8 0.6 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 10 9 0.9 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 10 10 1.2 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 10 11 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.5 10 12 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.4 10 13 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.3 10 14 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 5 15 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 15 16 1.0 1.0 $ 15.632{{\mathrm{e}}^{0.0021t}} $ 1.6 20 表 2 不同水灰比下的水泥浆液密度
Table 2. Density of grout with different water-cement ratios
A 0.5 0.7 0.8 1.0 1.5 3.0 水泥浆密度/
(g·cm−3)1.823 1.662 1.603 1.512 1.372 1.204 表 3 粉质砂土的水土特征[23]
Table 3. Soil and water characteristic of silty sand[23]
饱和度/% 100 94.9647 78.3324 28.0630 23.5915 20.0685 18.6214 17.3607 基质吸力/kPa 0 15.2868 19.6129 34.2297 53.6164 91.5849 156.0620 219.9930 表 4 各因素对浆液扩散距离影响的拟合曲线方程
Table 4. Fitting equations of grout penetration distance with various factors
因素 最大扩散半径 最大扩散深度 水灰比 $ \begin{array}{l} y_1 = {{ - }}0.16 + 0.55x_1 -\\\quad 0.09{x_1^2}\end{array} $ $ \;y_1 = {{ - }}0.09 + 0.44x_1 - 0.08{x_1^2} $ 注浆
压力$ \begin{array}{l} y_1 = 0.12 + 0.55x_1 -\\\quad 0.22{x_1^2}\end{array} $ $ y_1 = 0.16 + 0.38x_1 - 0.14{x_1^2} $ 干密度 $ y_1 = 1.21{{ - }}0.54x_1 $ $ y_1 = 0.93{{ - }}0.37x_1 $ 含水率 $ y_1 = 0.35{{ - 0}}{\text{.01}}x_1 $ $ y_1 = 0.34{{ - 0}}{\text{.15}}x_1 $ -
[1] 李天胜,何川,方砚兵,等. 基于围岩变形失效的隧道结构可靠度设计方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(3): 613-621. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.020LI Tiansheng, HE Chuan, FANG Yanbing, et al. Reliability-based design method of tunnel structures based on deformation failure of surrounding rock[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 613-621. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.020 [2] 潘钦锋,张丙强,黄志斌. 隧道下穿诱发既有管道-土体非协调变形解析研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(3): 637-645.PAN Qinfeng, ZHANG Bingqiang, HUANG Zhibin. Analytical study for uncoordinated deformation of existing pipeline and soil induced by tunnel undercrossing[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(3): 637-645. [3] 秦鹏飞,钟宏伟,刘坚,等. 考虑浆土应力耦合作用的劈裂注浆机理分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(3):584-591.QIN Pengfei, ZHONG Hongwei, LIU Jian, et al. Analysis of split grouting mechanism considering coupling effect of slurry and soil stress[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(3): 584-591. [4] 刘奇,陈卫忠,袁敬强,等. 基于渗流-侵蚀理论的岩溶充填介质注浆加固效果评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(3):572-580.LIU Qi, CHEN Weizhong, YUAN Jingqiang, et al. Evaluation of grouting reinforcement effect for karst filling medium based on seepage-erosion theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(3): 572-580. [5] 马明杰,杨新安,周建,等. 非达西渗流作用下饱和黏土压密注浆扩孔理论分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2022,54(3):32-40.MA Mingjie, YANG Xin’an, ZHOU Jian, et al. Theoretical analysis of cavity expansion for compaction grouting in saturated clay under non-Darcy seepage[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(3): 32-40. [6] YIN Z Y, YANG J, LAOUAFA F, et al. A framework for coupled hydro-mechanical continuous modelling of gap-graded granular soils subjected to suffusion[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2020, 27(1): 1-22. [7] YANG J, YIN Z Y, LAOUAFA F, et al. Analysis of suffusion in cohesionless soils with randomly distributed porosity and fines content[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 111: 157-171. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.03.011 [8] YANG J, YIN Z Y, LAOUAFA F, et al. Hydromechanical modeling of granular soils considering internal erosion[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2020, 57(2): 157-172. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2018-0653 [9] YANG J, YIN Z Y, LAOUAFA F, et al. Three-dimensional hydromechanical modeling of internal erosion in dike-on-foundation[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2020, 44(8): 1200-1218. doi: 10.1002/nag.3057 [10] RAATS P A C. Applications of the theory of mixtures in soil science[J]. Mathematical Modelling, 1987, 9(12): 849-856. doi: 10.1016/0270-0255(87)90003-0 [11] DE BOER R. Contemporary progress in porous media theory[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2000, 53(12): 323-370 doi: 10.1115/1.3097333 [12] UZUOKA R, BORJA R I. Dynamics of unsaturated poroelastic solids at finite strain[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2012, 36(13): 1535-1573. doi: 10.1002/nag.1061 [13] ZHOU Z L, ZANG H Z, WANG S Y, et al. Filtration behaviour of cement-based grout in porous media[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2018, 125(3):435-463. doi: 10.1007/s11242-018-1127-x [14] LIU X X, SHEN S L, XU Y S, et al. A diffusion model for backfill grout behind shield tunnel lining[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2021, 45(4): 457-477. doi: 10.1002/nag.3164 [15] REVIL A, CATHLES L. Permeability of shaly sands[J]. Water Resources Research, 1999, 35(3): 651-662. doi: 10.1029/98WR02700 [16] 雷进生. 碎石土地基注浆加固力学行为研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,2013. [17] LIANG Y, ZHANG J, LAI Z S, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of the grout pressure and its effects on lining segments during synchronous grouting in shield tunnelling[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2020, 24(1): 79-96. doi: 10.1080/19648189.2017.1364299 [18] SMITH M. ABAQUS/Standard: user’s manual[M]. Providence: [s.n.], 1997. [19] LADYZHENSKAYA O A. The mathematical theory of viscous incompressible flow[M]. New York:Gordon & Breach, 1969. [20] BREZZI F. On the existence, uniqueness and approximation of saddle-point problems arising from Lagrangian multipliers[J]. Revue Française D’automatique, Informatique, Recherche Opérationnelle Analyse Numérique, 1974, 8: 129-151. [21] 王勖成,邵敏. 有限单元法基本原理和数值方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社,1997. [22] YANG J. Numerical analyses of the multi-physics problem of sinkholes in the vicinity of a dike or a linear geo-structure[D]. Nantes: École centrale de Nantes, 2019. [23] 林鸿州,李广信,于玉贞,等. 基质吸力对非饱和土抗剪强度的影响[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(9):1931-1936. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.09.031LIN Hongzhou, LI Guangxin, YU Yuzhen, et al. Influence of matric suction on shear strength behavior of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(9): 1931-1936. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.09.031 [24] 李文. 路基沉陷劈裂注浆处治试验研究及力学参数计算[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学,2013. -




 下载:
下载: