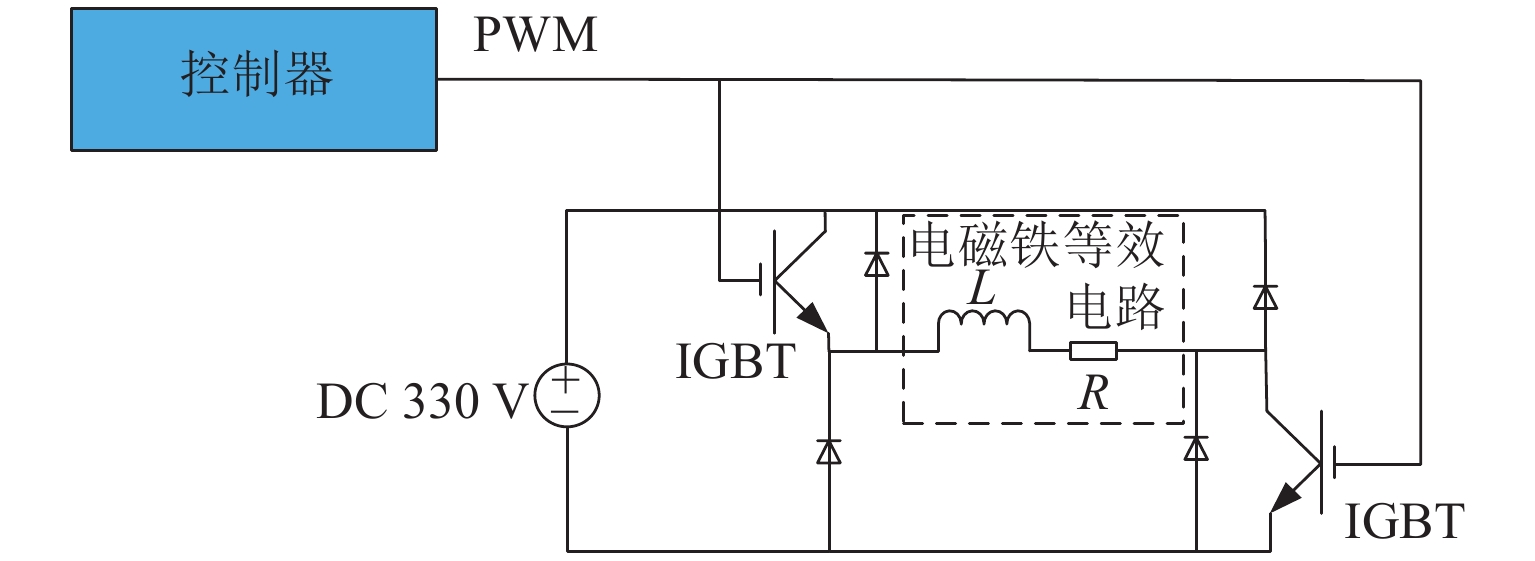
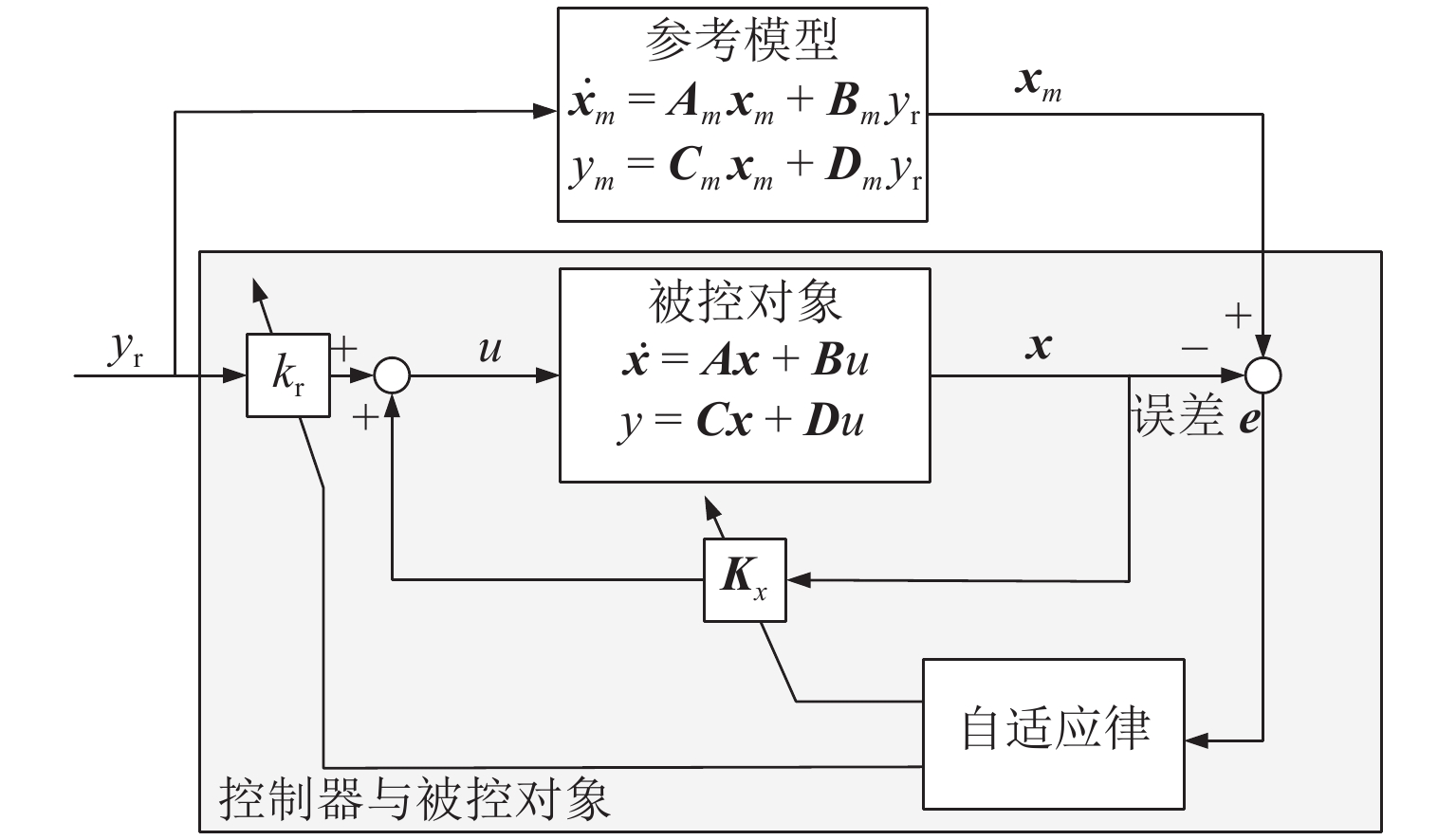
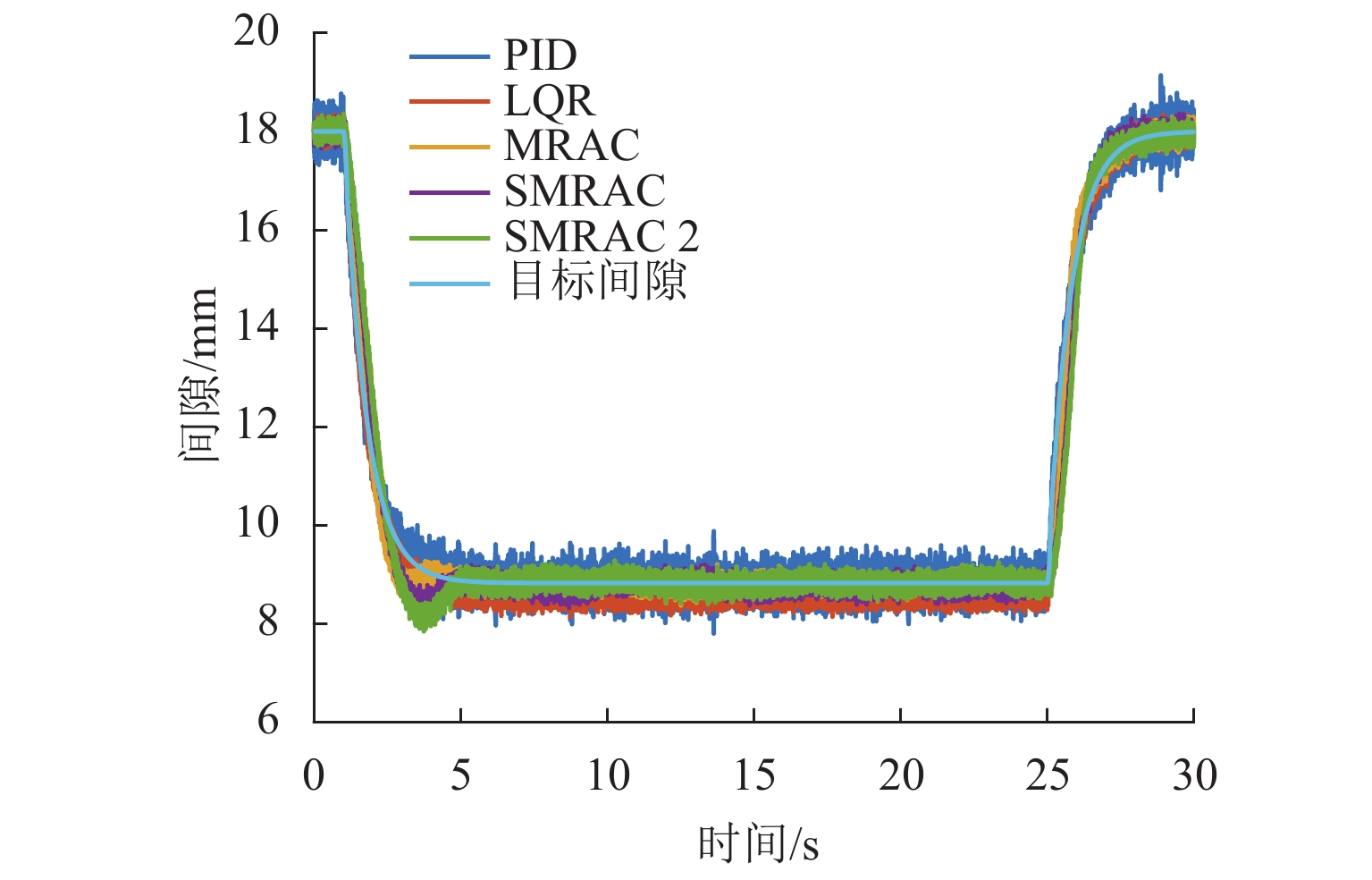
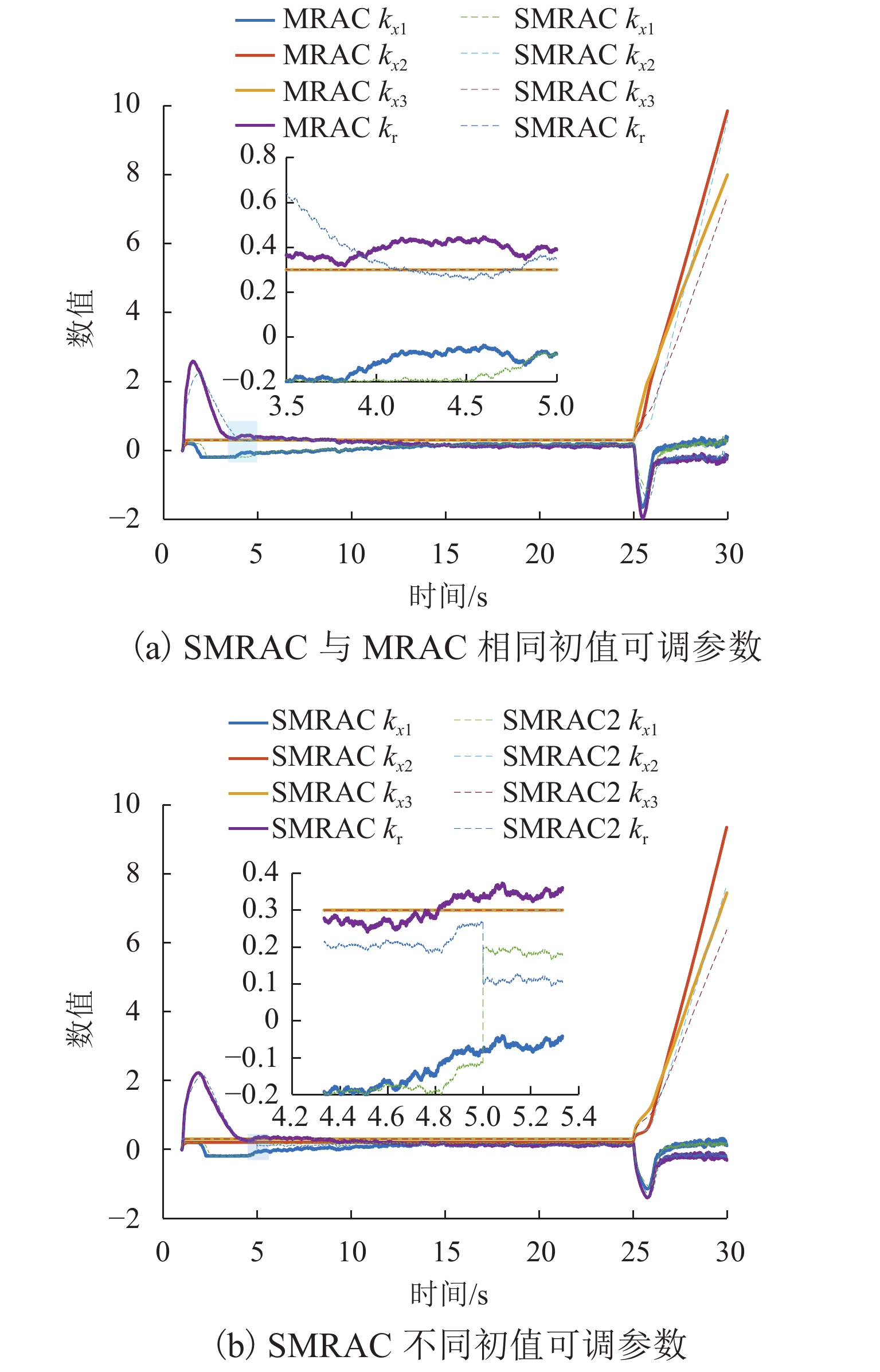
Self-Learning Model Reference Adaptive Levitation Control Strategy
-
摘要:
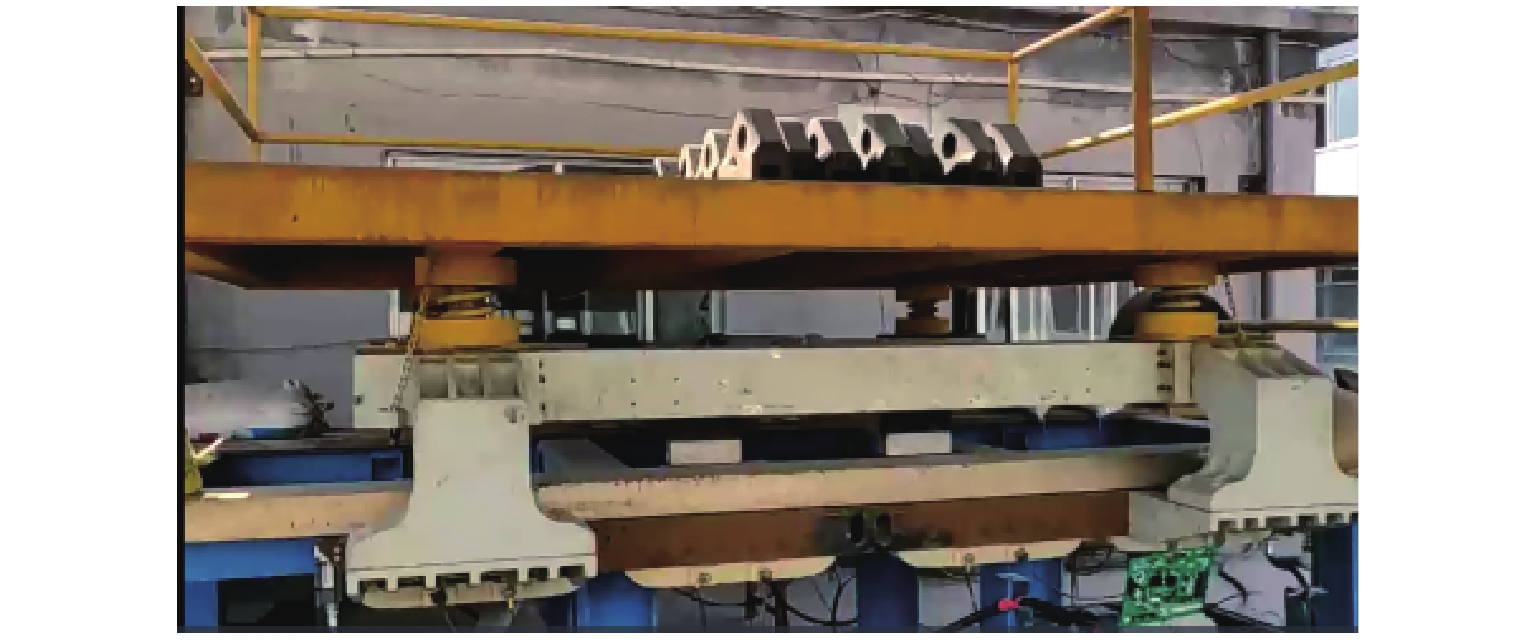
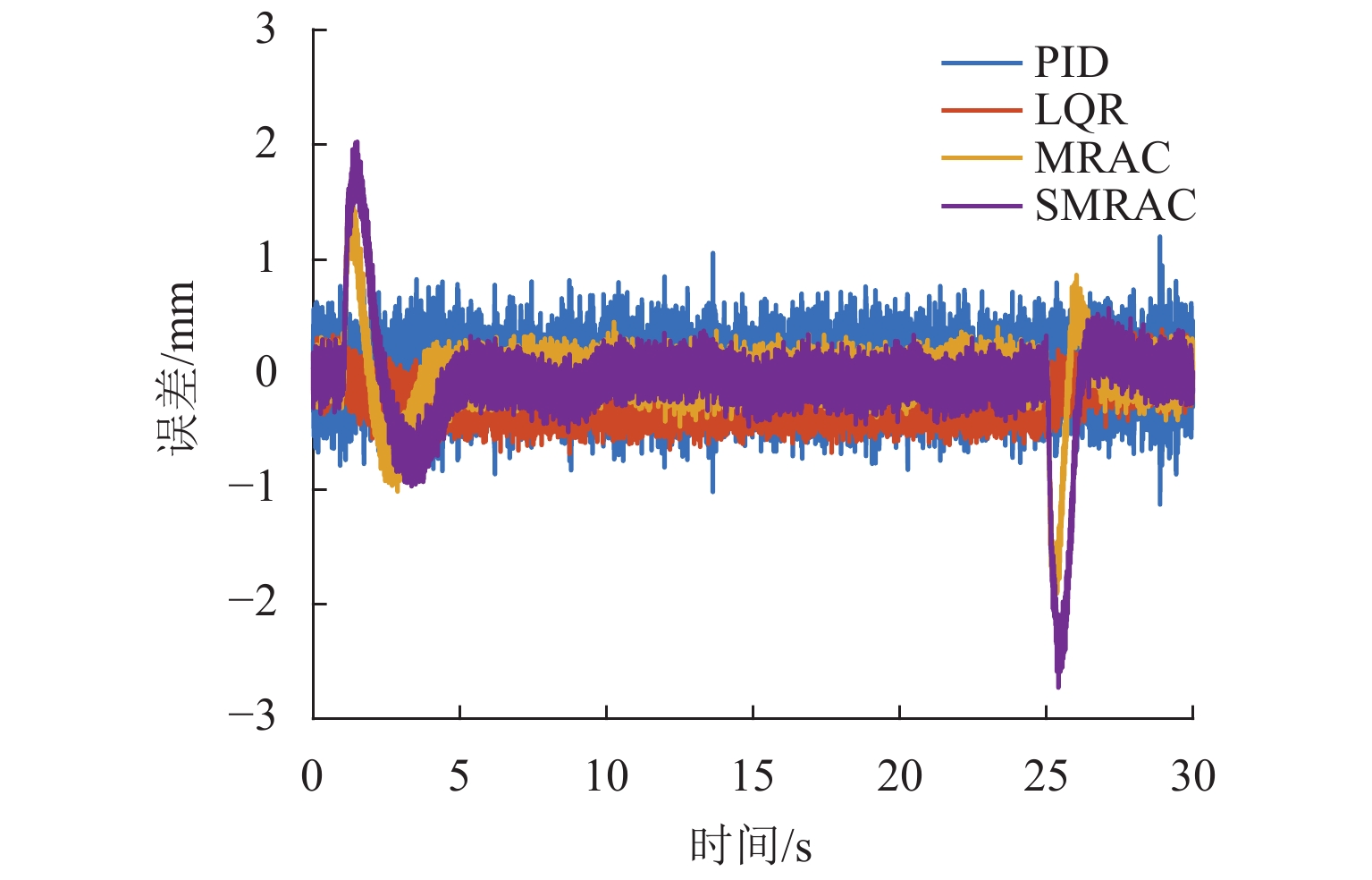
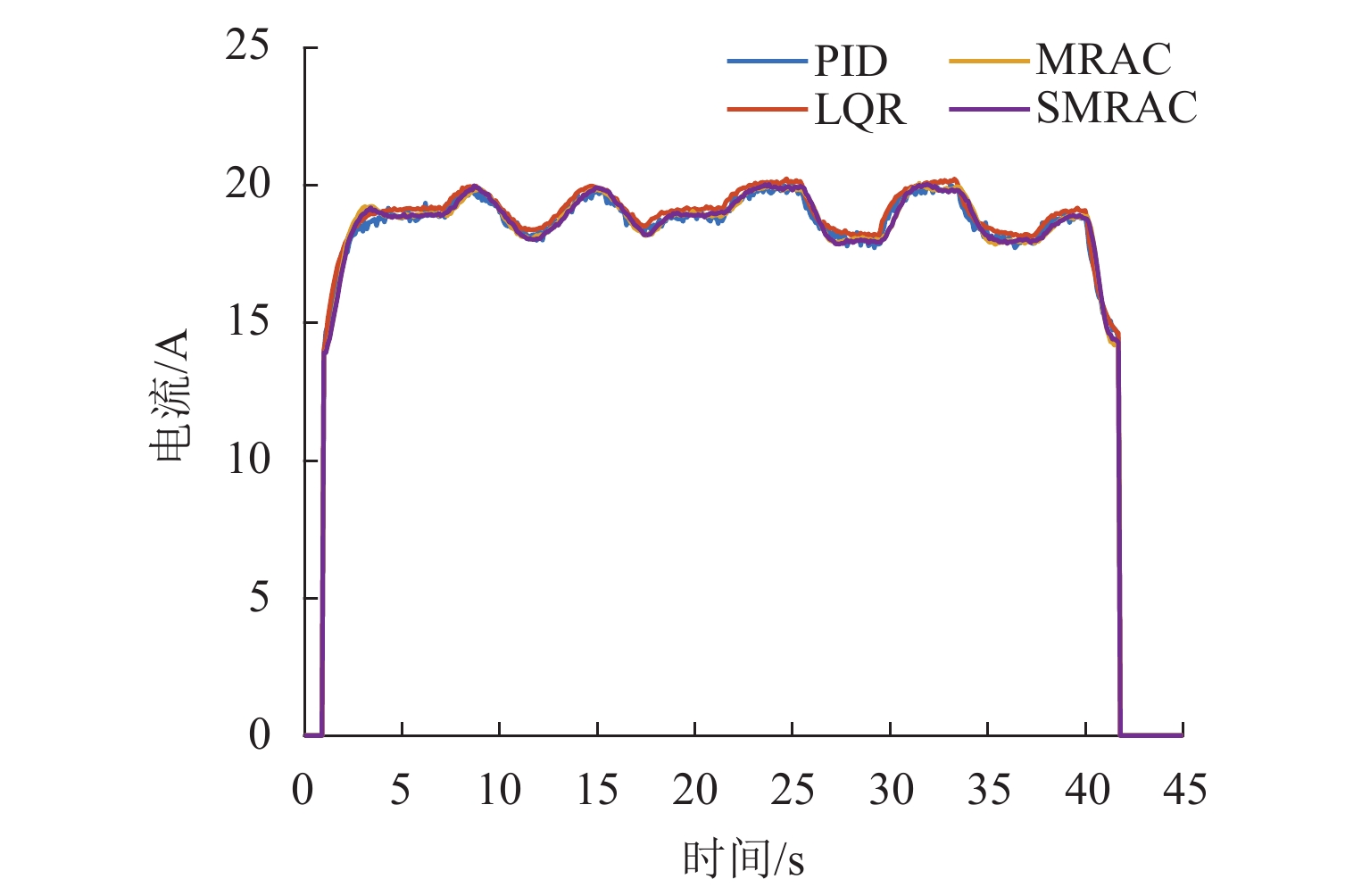
针对电磁悬浮列车悬浮控制器因轨道不平顺所引发的未知非线性力和传递函数不确定问题,提出一种基于模型参考自适应的自学习控制方案,控制算法中可调参数根据系统状态、误差和时间调整,使悬浮间隙稳定在恒定数值;学习率根据目标间隙误差大小动态调节,避免可调参数调节过慢,同时保证在稳定悬浮时间隙波动更小;通过李雅普诺夫稳定性判据证明了模型参考自适应控制系统的稳定性;通过MATLAB/Simulink对所提出的控制方案进行仿真. 研究结果表明:自学习模型参考自适应控制算法间隙的均方根误差为0.12,设定合适的可调参数初始值并对其限幅能够提升控制器的鲁棒性;在单悬浮架测试时,控制器获取到加速度信号,所提出算法的上升时间和调节时间分别为1.21 s和2.04 s,该方法学习率可动态调节,提升了控制器的适应能力.
Abstract:A self-learning model reference adaptive control strategy was proposed to solve the problems of unknown nonlinear force and uncertain transfer function of levitation controllers, which were caused by track irregularity in electromagnetic levitation trains. The tunable parameters in the control algorithm were adjusted according to the system state, error, and time, so as to make the gap stabilize at a constant value. In order to avoid slow adjustment of tunable parameters, the learning rate was dynamically adjusted according to the error of target gaps, so as to guarantee that the gap fluctuation was smaller during stable levitation. The stability of the model reference adaptive control system was confirmed by a Lyapunov framework, and the proposed control strategy was simulated by MATLAB/Simulink. The results show that the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of the gap of the self-learning model reference adaptive control algorithm is 0.12, and setting appropriate initial values of tunable parameters and limiting their amplitude can improve the robustness of the controller. When the algorithm is tested on a single levitation frame, the acceleration signal is obtained by the controller. The rising and adjustment time of the proposed algorithm is 1.21 s and 2.04 s, respectively. It proves that the learning rate of the method can be adjusted dynamically, which improves the adaptive ability of the controller.
-
Key words:
- maglev trains /
- levitation control /
- model reference adaptive /
- Lyapunov functions
-
表 1 悬浮架参数
Table 1. Parameters of levitation frame
参 数 数 值 等效质量/kg 510 电磁铁等效内阻/Ω 0.98 电磁铁等效电感/mH 36 电磁铁匝数 N 640 正对横截面积/m2 0.078 4 真空磁导率/(H·m−1) 4π × 10−7 表 2 仿真中不同参考信号算法误差的对比
Table 2. Comparison of reference signal errors of different algorithms in simulation
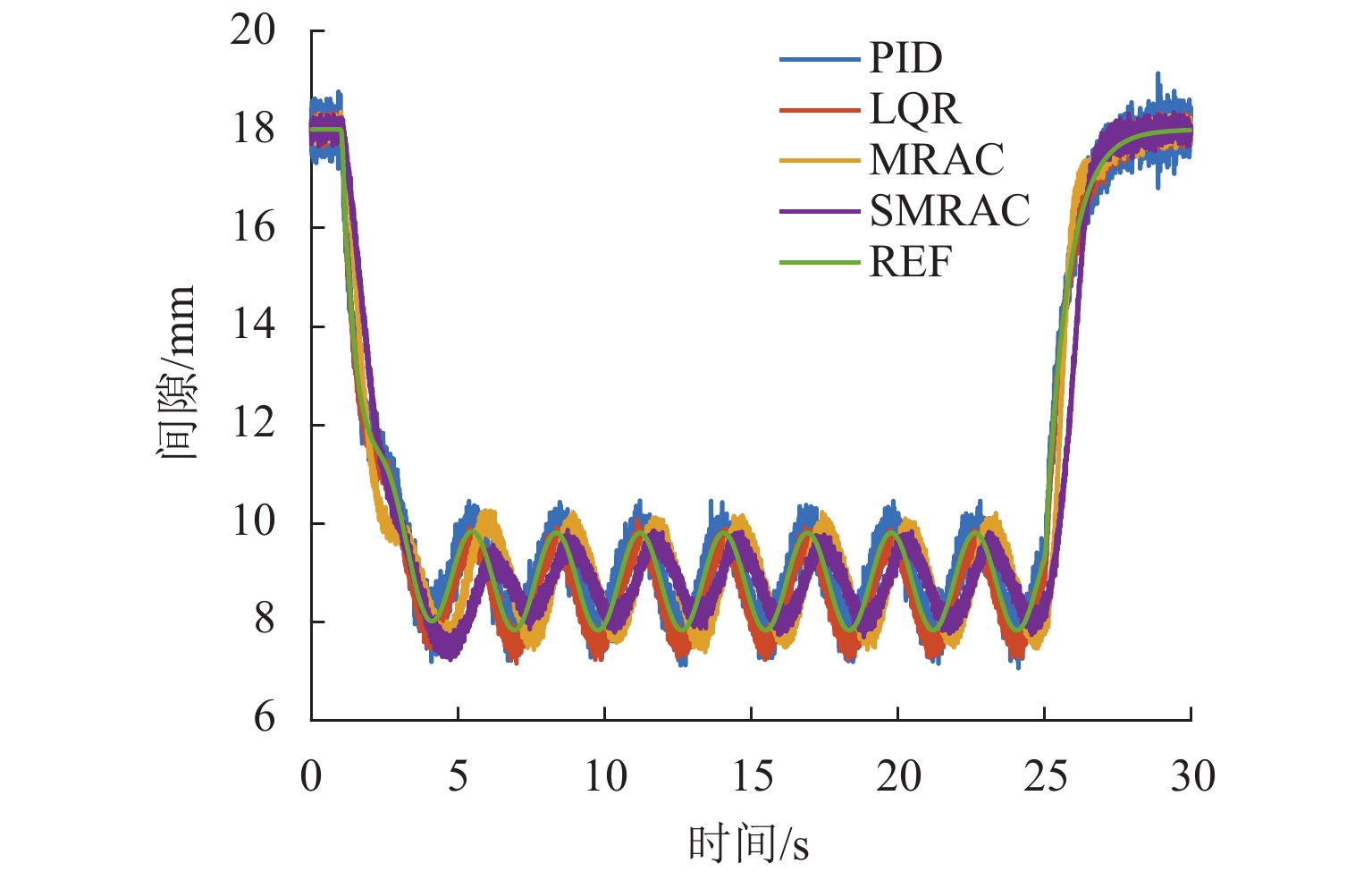
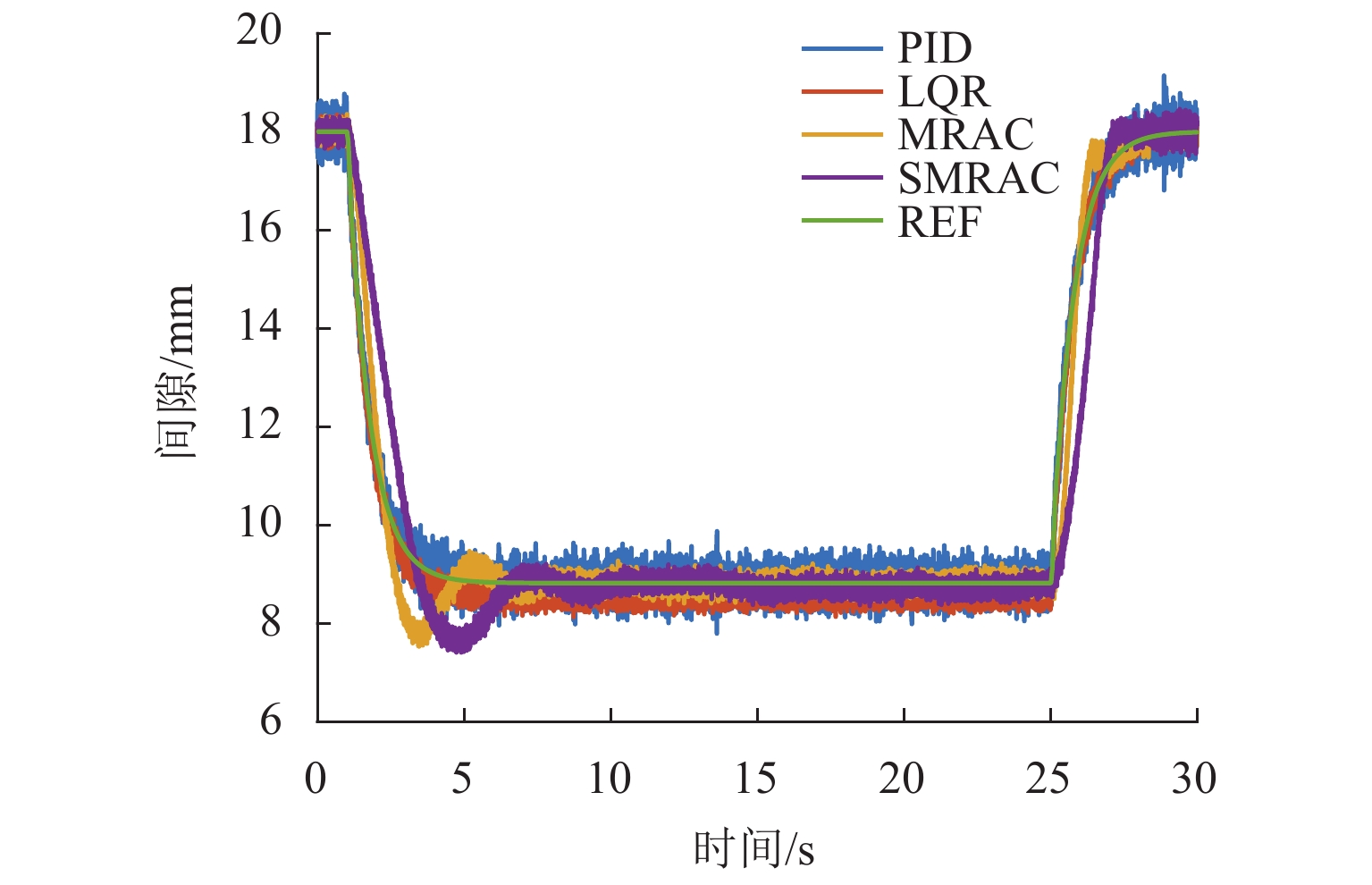
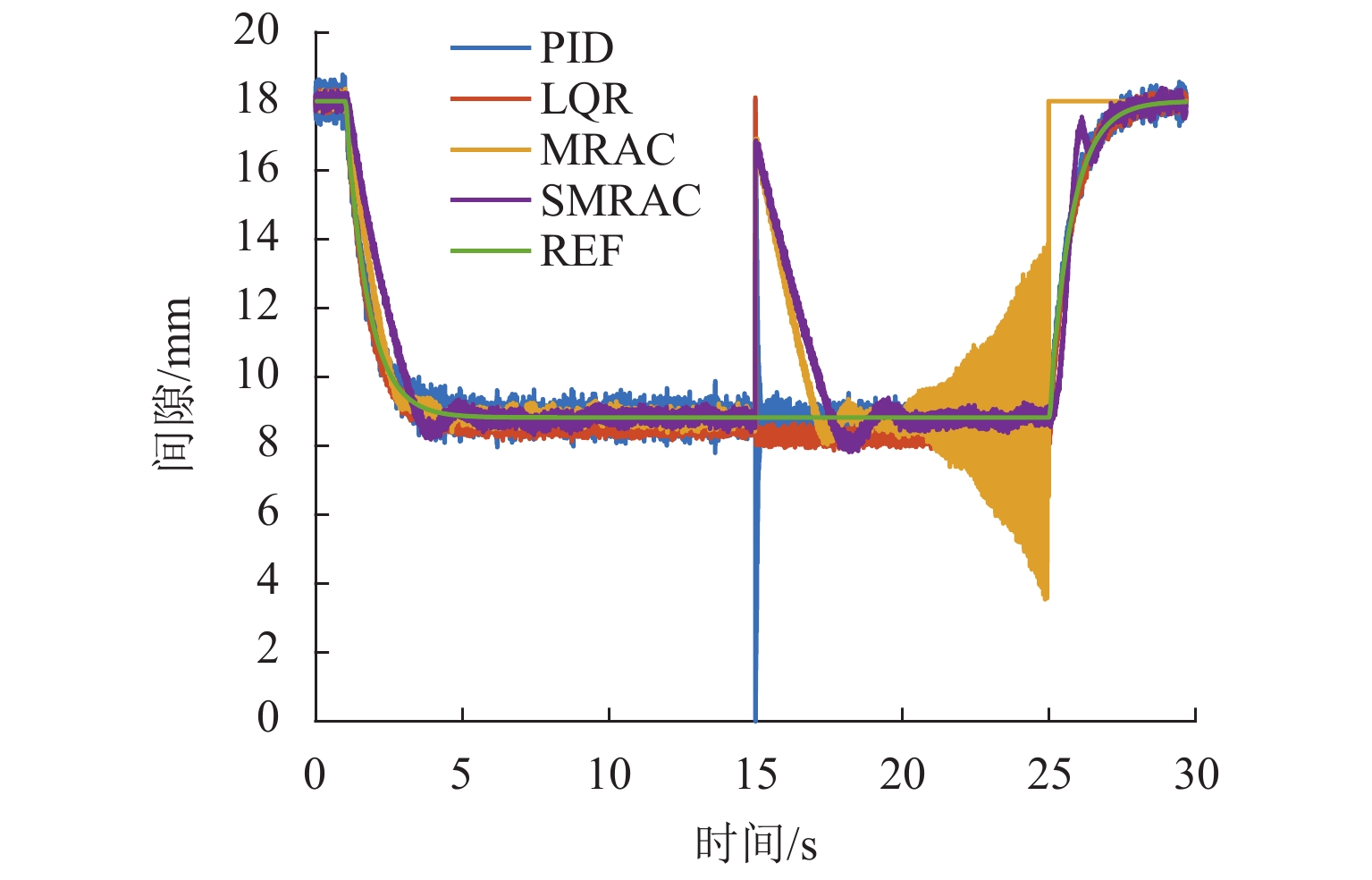
参考信号
控制器正常悬浮 方波信号 正弦信号 EITAE EIAE ERMSE EITAE EI AE ERMSE EITAE EIAE ERMSE PID 38.67 3.82 0.24 38.68 3.82 0.24 38.68 3.82 0.24 LQR 51.20 5.10 0.28 51.44 5.12 0.28 51.43 5.11 0.28 MRAC 16.72 1.69 0.11 34.34 3.3 0.22 164.78 16.44 0.92 SMRAC 19.51 1.97 0.12 43.23 4.28 0.27 128.23 13.37 0.76 表 3 仿真中不同算法上升时间和调节时间对比
Table 3. Comparison of rising time and adjustment time of different algorithms in simulation
s 控制算法 上升时间 调节时间 PID 1.57 2.03 LQR 1.40 1.71 MRAC 1.57 2.03 SMRAC 1.02 1.41 表 4 悬浮架质量变为 3 倍后不同算法的误差对比
Table 4. Comparison of different algorithms after mass increase by three times
控制算法 PID LQR MRAC SMRAC EITAE 35.10 51.07 26.55 57.22 EIAE 3.54 5.09 2.70 7.23 ERMSE 0.22 0.28 0.17 0.45 表 5 质量增加3倍后不同算法的上升时间和调节时间
Table 5. Rising time and adjustment time of different algorithms after mass increase by three times
s 控制算法 上升时间 调节时间 PID 1.84 2.02 LQR 1.57 2.02 MRAC 1.37 1.74 SMRAC 1.57 1.78 表 6 实测中不同算法的性能对比
Table 6. Comparison of performance indexes in experiment
控制算法 EITAE EIAE ERMSE PID 57.57 3.38 0.16 LQR 83.72 4.82 0.19 MRAC 79.78 4.13 0.22 SMRAC 77.15 4.15 0.21 表 7 实测中不同算法的上升时间和调节时间
Table 7. Rising time and adjustment time of different algorithms in experiment
s 控制算法 上升时间 调节时间 PID 2.20 2.80 LQR 1.41 1.70 MRAC 1.47 2.06 SMRAC 1.21 2.04 -
[1] 马卫华,罗世辉,张敏,等. 中低速磁浮车辆研究综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 199-216.MA Weihua, LUO Shihui, ZHANG Min, et al. Research review on medium and low speed maglev vehicle[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 199-216. [2] SCHMID P, EBERHARD P. Offset-free nonlinear model predictive control by the example of maglev vehicles[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2021, 54(6): 83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.528 [3] SHI Y, MA W H, LI M A, et al. Research on dynamics of a new high-speed maglev vehicle[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2022, 60(3): 721-742. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2020.1838568 [4] NI F, MU S Y, KANG J S, et al. Robust controller design for maglev suspension systems based on improved suspension force model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2021, 7(3): 1765-1779. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2021.3058137 [5] WAHYUDIE A, SUSILO T B, ALI NANDAR C S, et al. Simple robust PID tuning for magnetic levitation systems using model-free control and H-infinity control strategies[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2021, 19(12): 3956-3966. doi: 10.1007/s12555-020-0253-8 [6] LI B W, LI X L, LONG Z Q. Design of model reference adaptive controller for active guidance system of high speed maglev train[C]//2020 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Hefei: IEEE, 2020: 945-950. [7] 张锟,崔鹏,李杰. 磁悬浮系统的加速度计反馈控制算法[J]. 控制理论与应用,2009,26(9): 988-992.ZHANG Kun, CUI Peng, LI Jie. Accelerometer feedback control algorithm for maglev system[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2009, 26(9): 988-992. [8] WEI W, XUE W C, LI D H. On disturbance rejection in magnetic levitation[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 82: 24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2018.09.018 [9] LI B W, LI X L, WANG Z Q, et al. Design of ADRC for guidance system of high speed maglev train[C]//2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). Shanghai: IEEE, 2021: 1471-1476. [10] 靖永志,冯伟,王森,等. 基于自适应非奇异终端滑模的悬浮控制策略[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 566-573.JING Yongzhi, FENG Wei, WANG Sen, et al. Levitation control strategy based on adaptive non-singular terminal sliding mode[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 566-573. [11] SUN Y G, XU J Q, ZHANG W Y, et al. Neural network-based adaptive control for EMS type maglev vehicle systems with time-varying mass[C]//International Conference on Neural Computing for Advanced Applications. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 381-394. [12] 陈萍,史天成,于明月,等. 中低速磁浮列车滑模自抗扰悬浮控制算法[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2023,20(2): 682-693.CHEN Ping, SHI Tiancheng, YU Mingyue, et al. Sliding mode active disturbance rejection levitation control algorithm of the medium-and low-speed maglev vehicles[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2023, 20(2): 682-693. [13] LI S Q, ZHANG K L, LIU G Q, et al. EMS maglev vehicles model reference adaptive control[C]//2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Hangzhou: IEEE, 2015: 2989-2993. [14] WANG H M, GE X L, LIU Y C. Second-order sliding-mode MRAS observer-based sensorless vector control of linear induction motor drives for medium-low speed maglev applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(12): 9938-9952. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2818664 [15] 曾国保. 中低速磁浮交通的适应性及工程化发展方向[J]. 铁道工程学报,2016,33(10): 111-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.10.023ZENG Guobao. The adaptability and the improvement in engineering of the lower-medium speed maglev transit system[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2016, 33(10): 111-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.10.023 [16] 曹广忠. 磁悬浮系统控制算法及实现[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013. [17] ZHANG M, LUO S H, GAO C, et al. Research on the mechanism of a newly developed levitation frame with mid-set air spring[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(12): 1797-1816. doi: 10.1080/00423114.2018.1435892 [18] 刘清辉, 单磊, 马卫华, 等. 考虑剩磁作用的中低速磁浮电磁力分析[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, [2022-9-25]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C45S0n9fL2suRadTyEVl2pW9UrhTDCdPD65IXe8xbsrGOD399GtDO21yEnpsZPB2dzXbpP36DTmjFAOzm3-A2U4V&uniplatform=NZKPT. [19] XU J Q, SUN Y G, GAO D G, et al. Dynamic modeling and adaptive sliding mode control for a maglev train system based on a magnetic flux observer[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 31571-31579. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2836348 [20] JIBRIL M. Comparisons of fuzzy MRAS and PID controllers for EMS maglev train[J]. Information and Knowledge Management, 2020, 10(4): 34-40. [21] 孙凤, 邢大壮, 周冉, 等. 考虑能耗的电磁主动悬架 LQR 控制[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报. [2023-4-3]. https://kns.cnki.net/ kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20230329.1507.006.html. -





 下载:
下载: