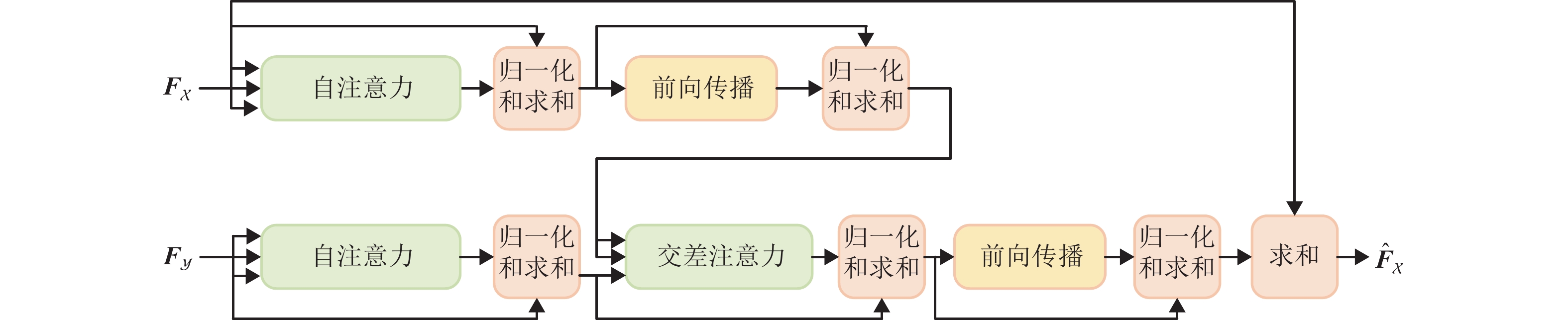
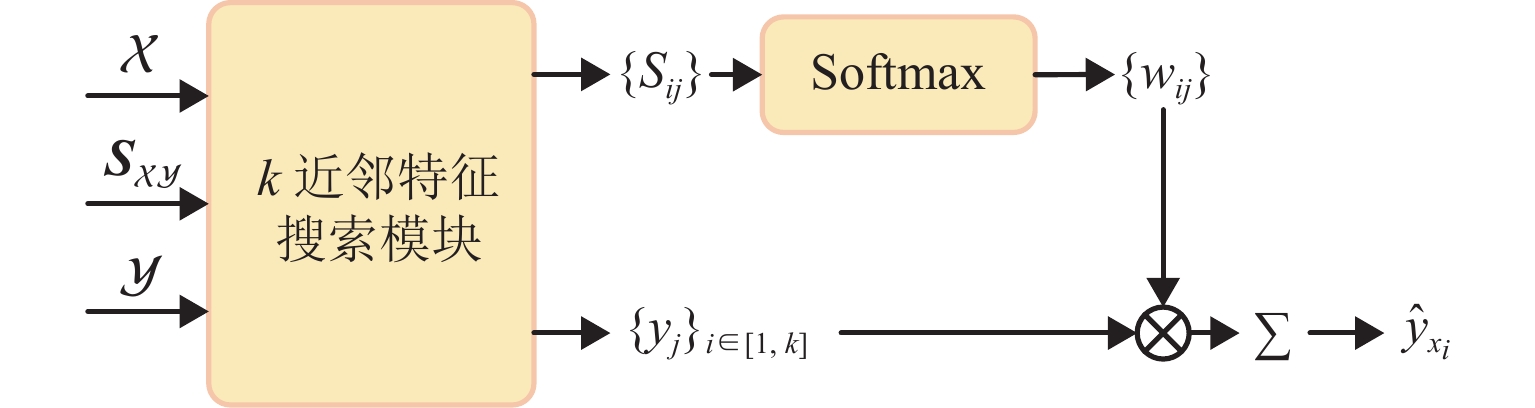
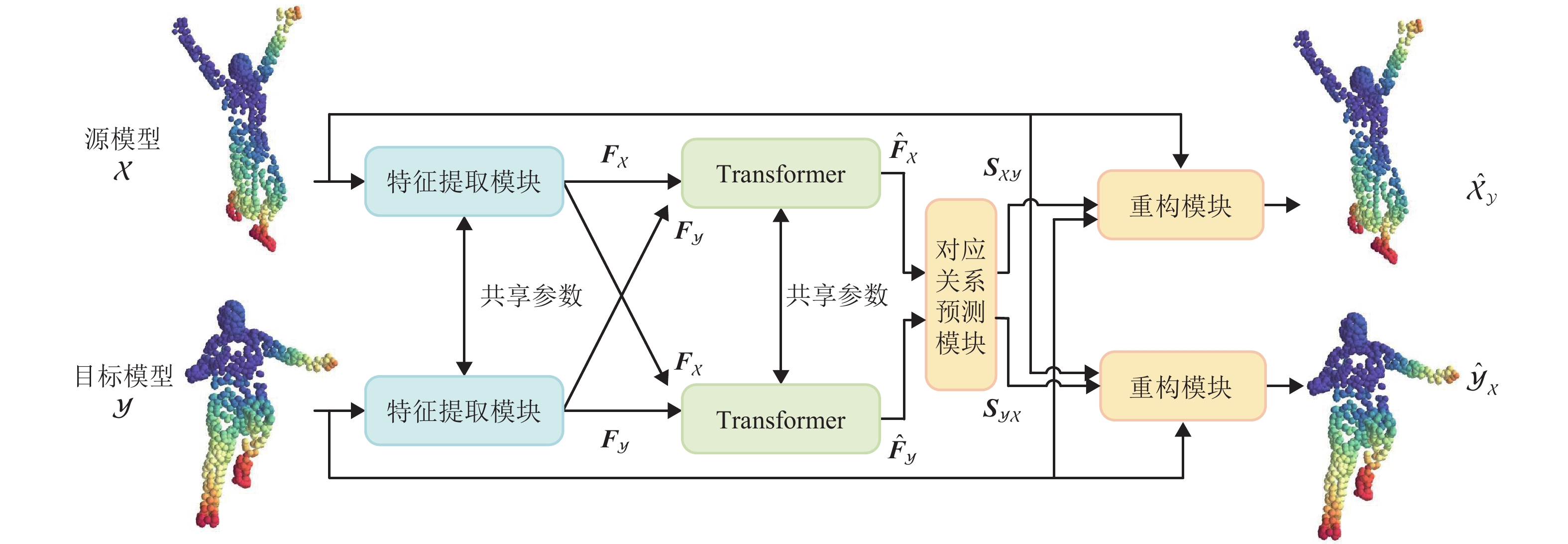
Correspondence Calculation of Three-Dimensional Point Cloud Model Based on Attention Mechanism
-
摘要:
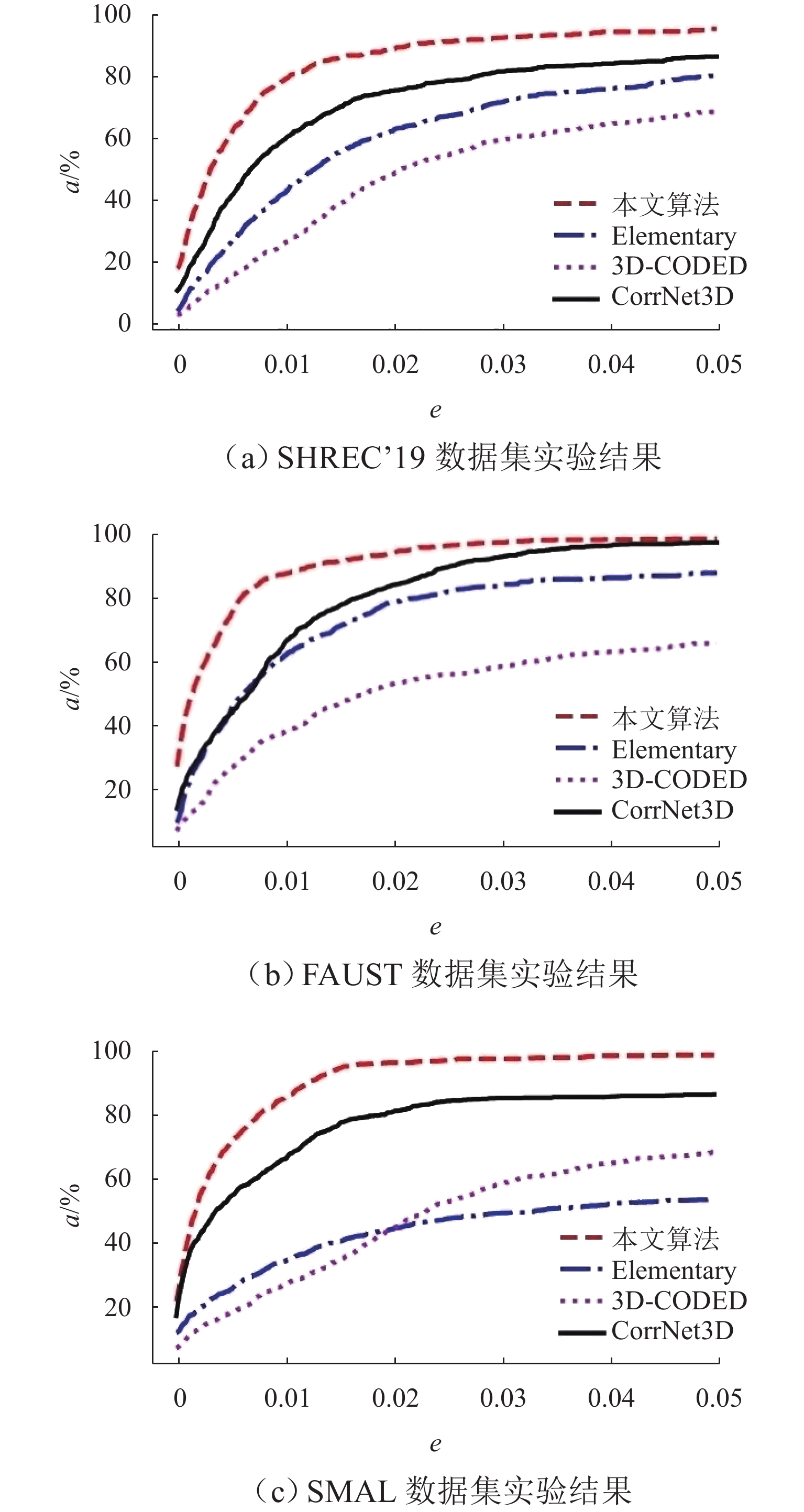
针对现有深度学习方法计算非刚性点云模型间稠密对应关系时精度不高,且算法泛化能力较差的问题,提出一种基于特征序列注意力机制的无监督三维点云模型对应关系计算新方法. 首先,使用特征提取模块提取输入点云模型对的特征;然后,通过Transformer模块捕获自注意力和交叉注意力,学习共同上下文信息,并由对应关系预测模块生成软映射矩阵;最后,重构模块根据得到的软映射矩阵重构点云模型,并利用无监督损失函数完成训练. 在FAUST、SHREC’19和SMAL数据集上的实验结果表明,本算法的平均对应误差分别为5.1、5.8和5.4,均低于3D-CODED、Elementary Structures和CorrNet3D经典算法;本算法所计算的非刚性三维点云模型间对应关系准确率更高,且具有更强的泛化能力.
Abstract:The existing deep learning methods have low precision and poor generalization ability in calculating dense correspondence between non-rigid point cloud models. To address these issues, a novel method for calculating unsupervised three-dimensional (3D) point cloud model correspondence based on a feature sequence attention mechanism was proposed. Firstly, the feature extraction module was used to extract the features of the input point cloud model pair. Secondly, the transformer module learned context information by capturing self-attention and cross-attention and generated a soft mapping matrix through the correspondence prediction module. Finally, the reconstruction module reconstructed the point cloud model based on the obtained soft mapping matrix and used the unsupervised loss function to complete training. The experimental results on FAUST, SHREC’19, and SMAL datasets show that the average correspondence errors of this algorithm are 5.1, 5.8, and 5.4, respectively, which are lower than those of the classical algorithms including 3D-CODED, Elementary Structures, and CorrNet3D. The correspondence between non-rigid 3D point cloud models calculated by the proposed algorithm has higher accuracy and stronger generalization ability.
-
Key words:
- computer vision /
- correspondence /
- unsupervised /
- point cloud reconstruction /
- attention mechanism
-
表 1 FAUST数据集上各方法的实验结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of experimental results of methods onFAUST dataset
示例 源模型 Groud-truth 3D-CODED Elementary Structures CorrNet3D 本文算法 1 
2 
表 2 SHREC’19数据集上各方法的实验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental results of methods on SHREC’19 dataset
示例 源模型 Groud-truth 3D-CODED Elementary Structures CorrNet3D 本文算法 3 
4 
表 3 SMAL数据集上各方法的实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental results of methods on SMAL dataset
示例 源模型 Groud-truth 3D-CODED Elementary Structures CorrNet3D 本文算法 5 
6 
7 
表 4 不同方法平均对应误差
Table 4. Average correspondence errors of different methods
数据集 3D-
CODEDElementary
StructuresCorrNet
3D本文
算法FAUST 7.2 6.6 5.3 5.1 SHREC’19 8.1 7.6 6.9 5.8 SMAL 6.8 6.4 5.7 5.4 表 5 Transformer模块消融实验误差
Table 5. Errors of ablation experiment on Transformer module
数据集 无 Transformer 模块 有 Transformer 模块 FAUST 5.6 5.1 SHREC’19 6.1 5.8 SMAL 7.6 5.4 表 6 对应关系预测模块消融实验误差
Table 6. Errors of ablation experiment on correspondence prediction module
数据集 无对应关系
预测模块有对应关系
预测模块FAUST 6.1 5.1 SHREC’19 7.3 5.8 SMAL 8.0 5.4 -
[1] 朱军,陈逸东,张昀昊,等. 网络环境下全景图和点云数据快速融合可视化方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(1): 18-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200360ZHU Jun, CHEN Yidong, ZHANG Yunhao, et al. Visualization method for fast fusion of panorama and point cloud data in network environment[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(1): 18-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20200360 [2] ZHANG Z F, WANG Z W, LIN Z, et al. Image super-resolution by neural texture transfer[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach: IEEE,2019: 7982-7991. [3] BOGO F, ROMERO J, LOPER M, et al. FAUST: dataset and evaluation for 3D mesh registration[C]//2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus:IEEE,2014: 3794-3801. [4] WOLTER D, LATECKI L J. Shape matching for robot mapping[C]//Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Berlin: Springer, 2004: 693-702. [5] BRONSTEIN A M, BRONSTEIN M M, KIMMEL R. Generalized multidimensional scaling: a framework for isometry-invariant partial surface matching[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(5): 1168-1172. [6] HUANG Q X, ADAMS B, WICKE M, et al. Non-rigid registration under isometric deformations[C]// Proceedings of the Symposium on Geometry Processing. Copenhagen: ACM, 2008: 1449-1457. [7] TEVS A, BERNER A, WAND M, et al. Intrinsic shape matching by planned landmark sampling[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2011, 30(2): 543-552. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2011.01879.x [8] OVSJANIKOV M, BEN-CHEN M, SOLOMON J, et al. Functional maps: a flexible representation of maps between shapes[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 31(4): 30.1-30.11. [9] LITANY O, REMEZ T, RODOLÀ E, et al. Deep functional maps: structured prediction for dense shape correspondence[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice:IEEE,2017: 5660-5668. [10] DONATI N, SHARMA A, OVSJANIKOV M. Deep geometric functional maps: robust feature learning for shape correspondence[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle: IEEE, 2020: 8589-8598. [11] GINZBURG D, RAVIV D. Cyclic functional mapping: self-supervised correspondence between non-isometric deformable shapes[C]//The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow: ACM, 2020: 36-52. [12] ROUFOSSE J M, SHARMA A, OVSJANIKOV M. Unsupervised deep learning for structured shape matching[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul:IEEE,2019: 1617-1627. [13] 杨军,王博. 非刚性部分模型与完整模型的对应关系计算[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2021,46(3): 434-441.YANG Jun, WANG Bo. Non-rigid shape correspondence between partial shape and full shape[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(3): 434-441. [14] WU Y, YANG J. Multi-part shape matching by simultaneous partial functional correspondence[J]. The Visual Computer, 2023, 39(1): 393-412. doi: 10.1007/s00371-021-02337-6 [15] MARIN R, RAKOTOSAONA M J, MELZI S, et al. Correspondence learning via linearly-invariant embedding[C]//The 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2020). Vancouver: MIT Press, 2020: 1341-1350. [16] WU Y, YANG J, ZHAO J L. Partial 3D shape functional correspondence via fully spectral eigenvalue alignment and upsampling refinement[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2020, 92: 99-113. [17] 杨军,闫寒. 校准三维模型基矩阵的函数映射的对应关系计算[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2018,43(10): 1518-1525.YANG Jun, YAN Han. An algorithm for calculating shape correspondences using functional maps by calibrating base matrix of 3D shapes[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(10): 1518-1525. [18] GROUEIX T, FISHER M, KIM V G, et al. 3D-CODED: 3D correspondences by deep deformation[C]// Computer Vision—ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference. Munich: ACM, 2018: 235-251. [19] DEPRELLE T, GROUEIX T, FISHER M, et al. Learning elementary structures for 3D shape generation and matching[C]//Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver: MIT Press, 2019: 7433-7443. [20] ZENG Y M, QIAN Y, ZHU Z Y, et al. CorrNet3D: unsupervised end-to-end learning of dense correspondence for 3D point clouds[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville: IEEE, 2021: 6048-6057. [21] WANG Y, SOLOMON J. Deep closest point: learning representations for point cloud registration[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 3522-3531. [22] WANG Y, SUN Y B, LIU Z W, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 38(5): 146.1-146.12. [23] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: ACM, 2017: 6000-6010. [24] LOPER M, MAHMOOD N, ROMERO J, et al. SMPL: a skinned multi-person linear model[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(6):248.1-248.16. [25] MELZI S, MARIN R, RODOLÀ E, et al. Matching humans with different connectivity[C]//Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval. Genoa: Springer, 2019: 121-128. [26] ZUFFI S, KANAZAWA A, JACOBS D W, et al. 3D menagerie: modeling the 3D shape and pose of animals[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 5524-5532. [27] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 -




 下载:
下载: