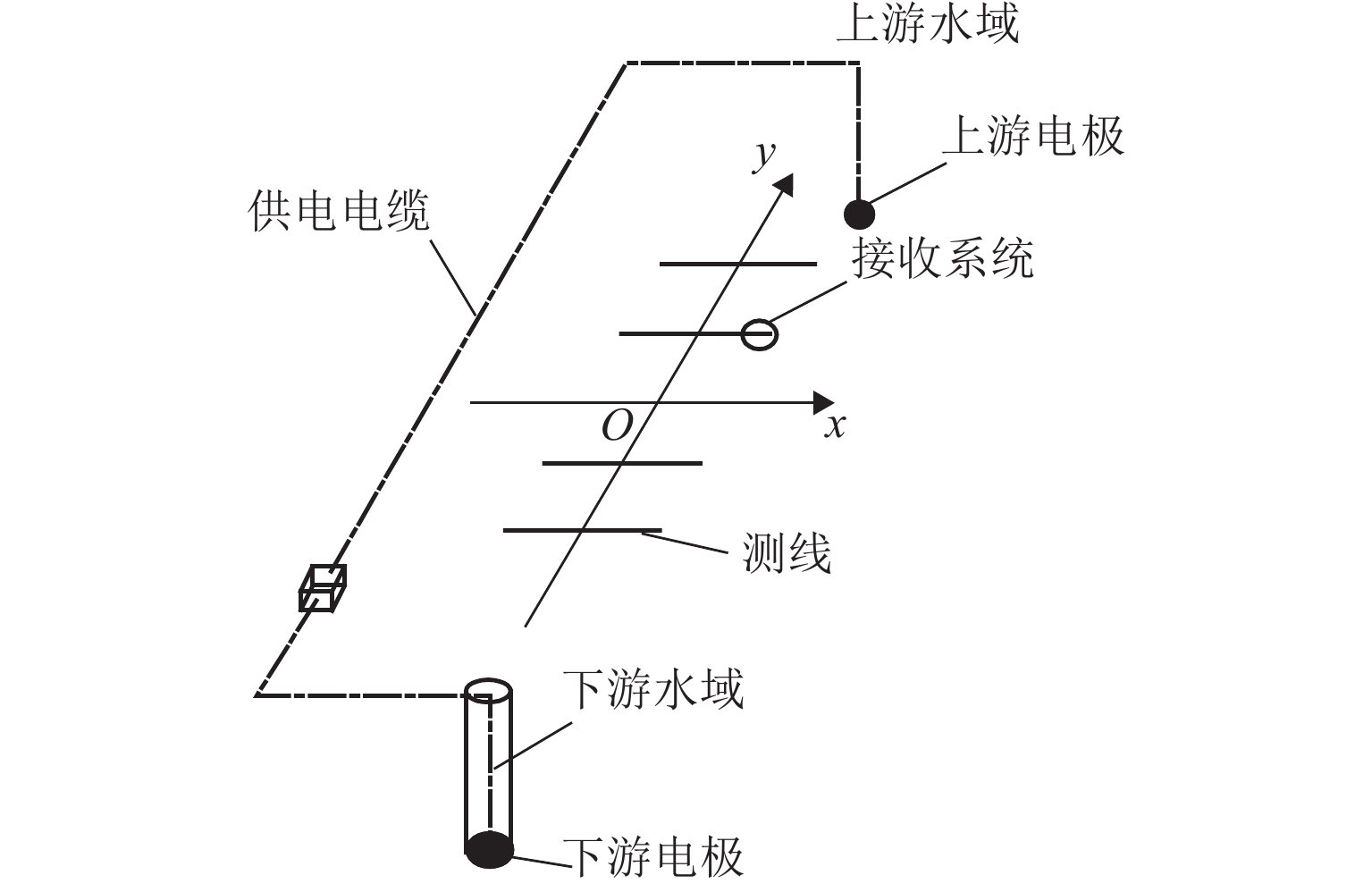
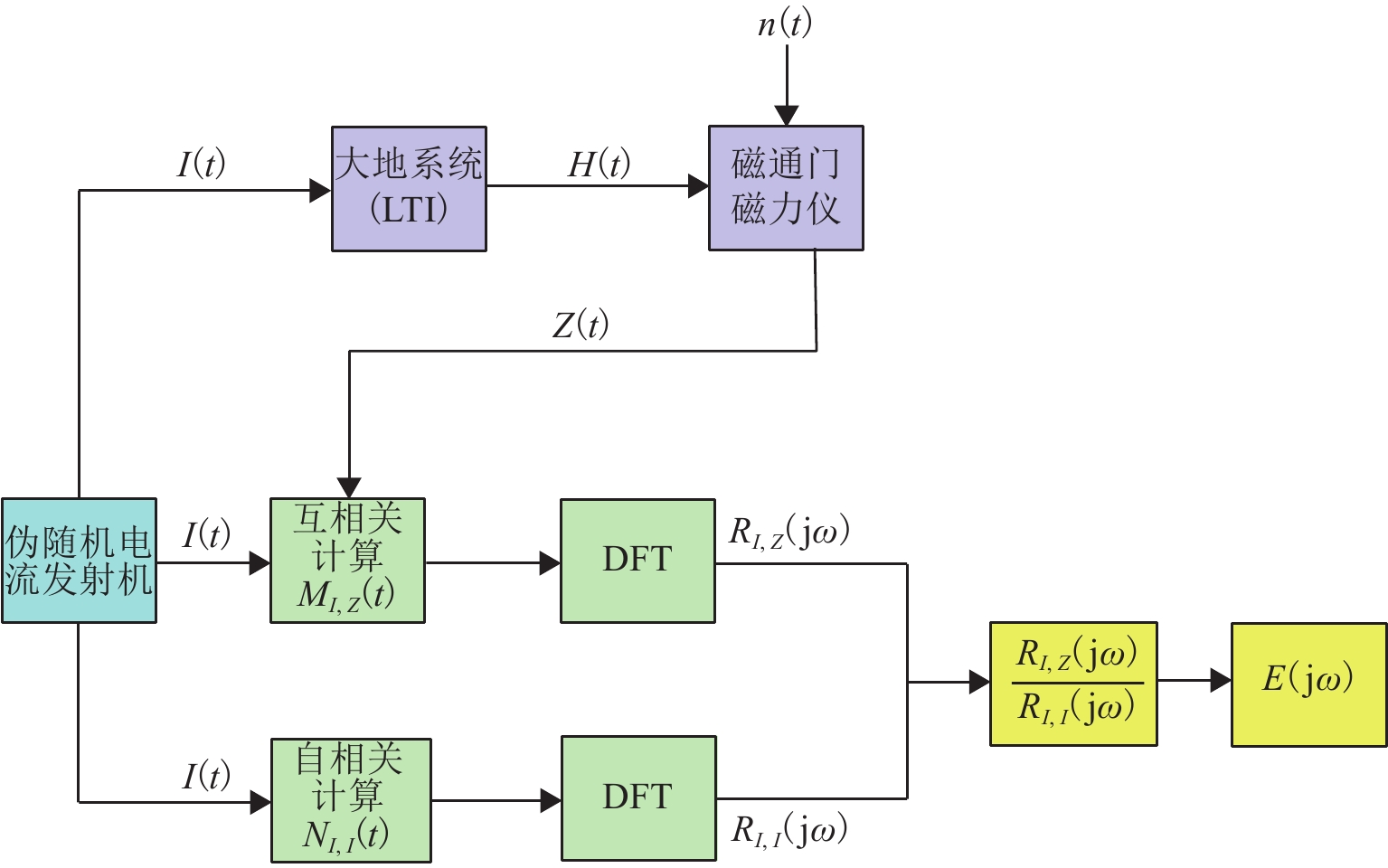
Experimental Study on Dam Foundation Leakage Detection by Magnetoelectric Method Based on M Sequence
-
摘要:
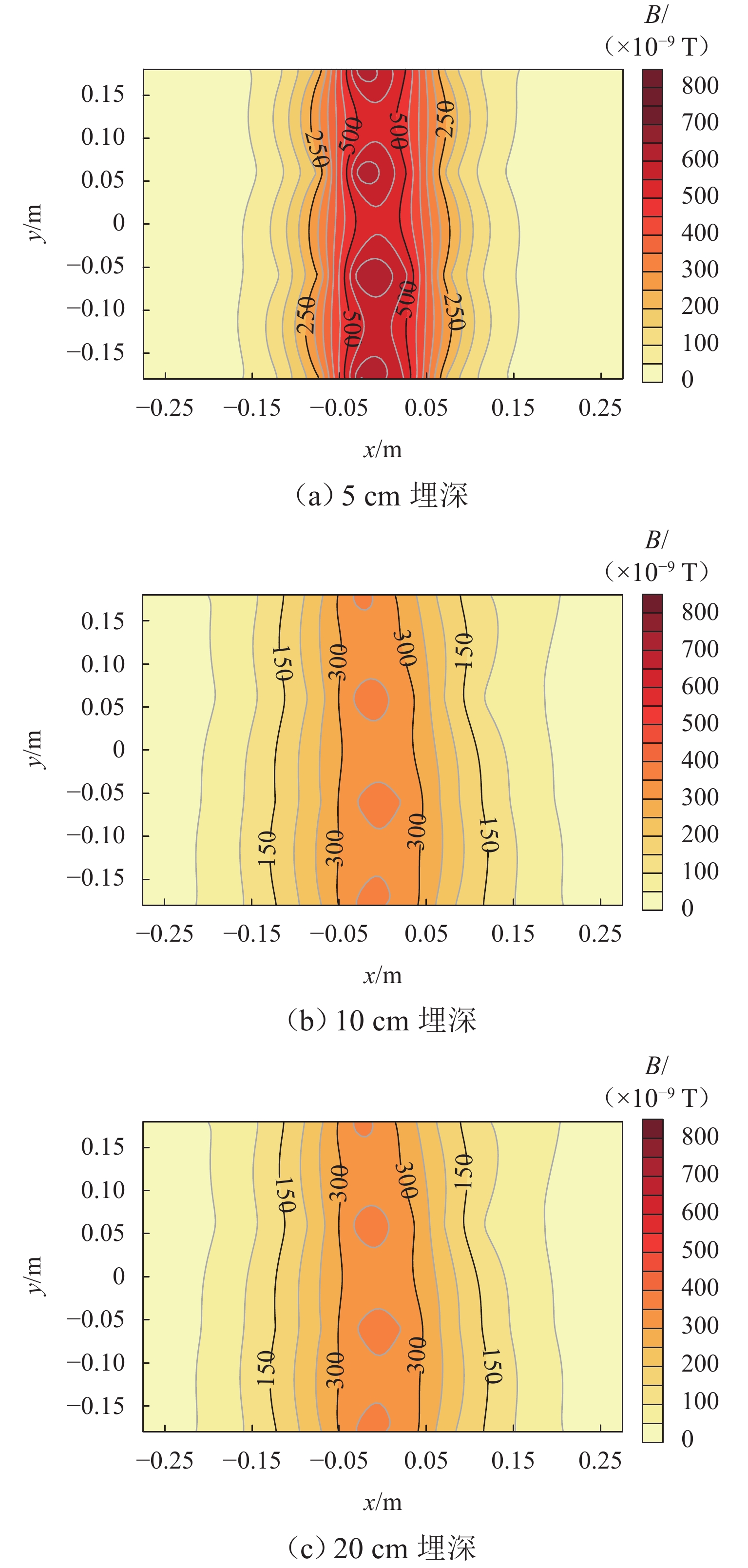
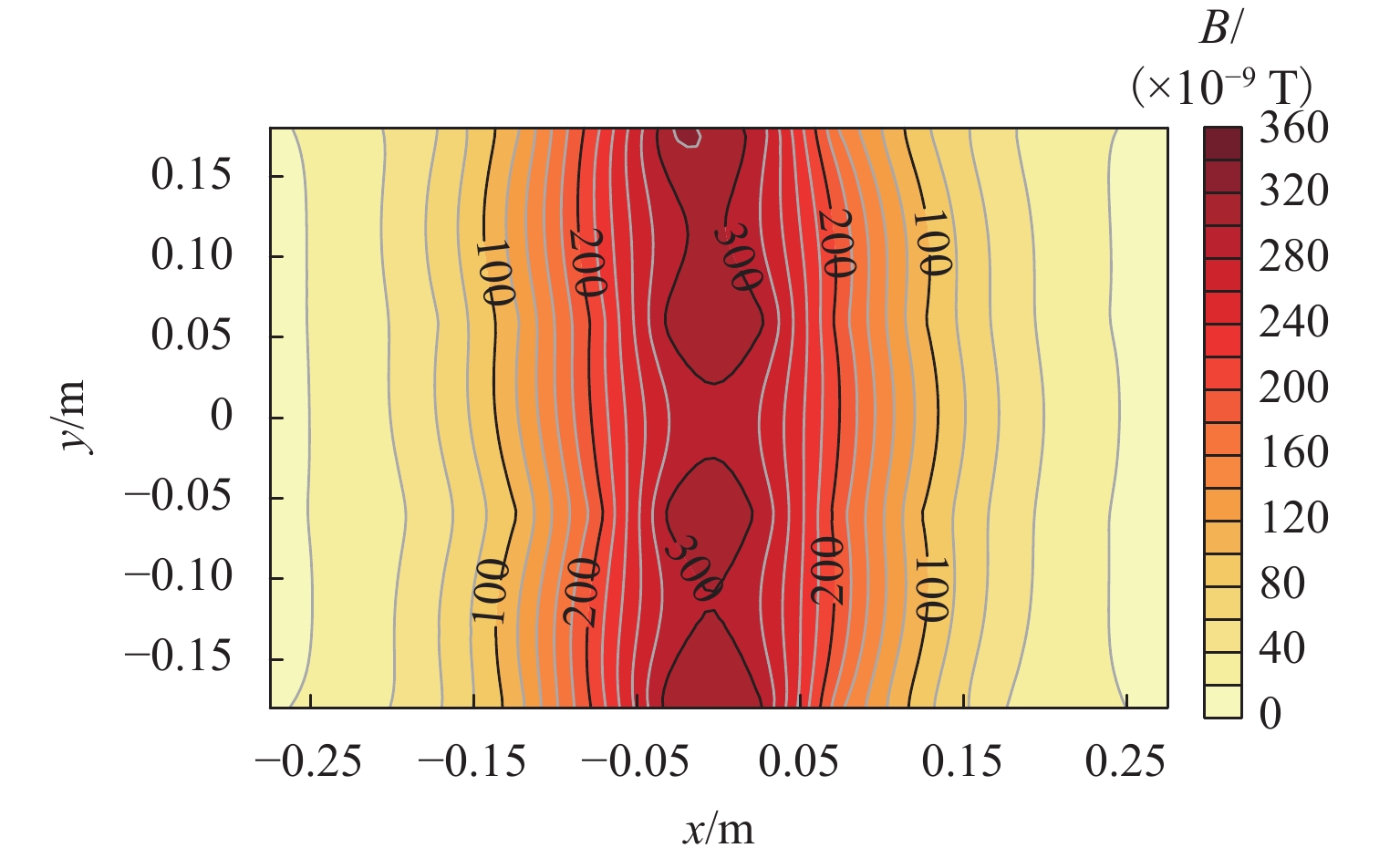
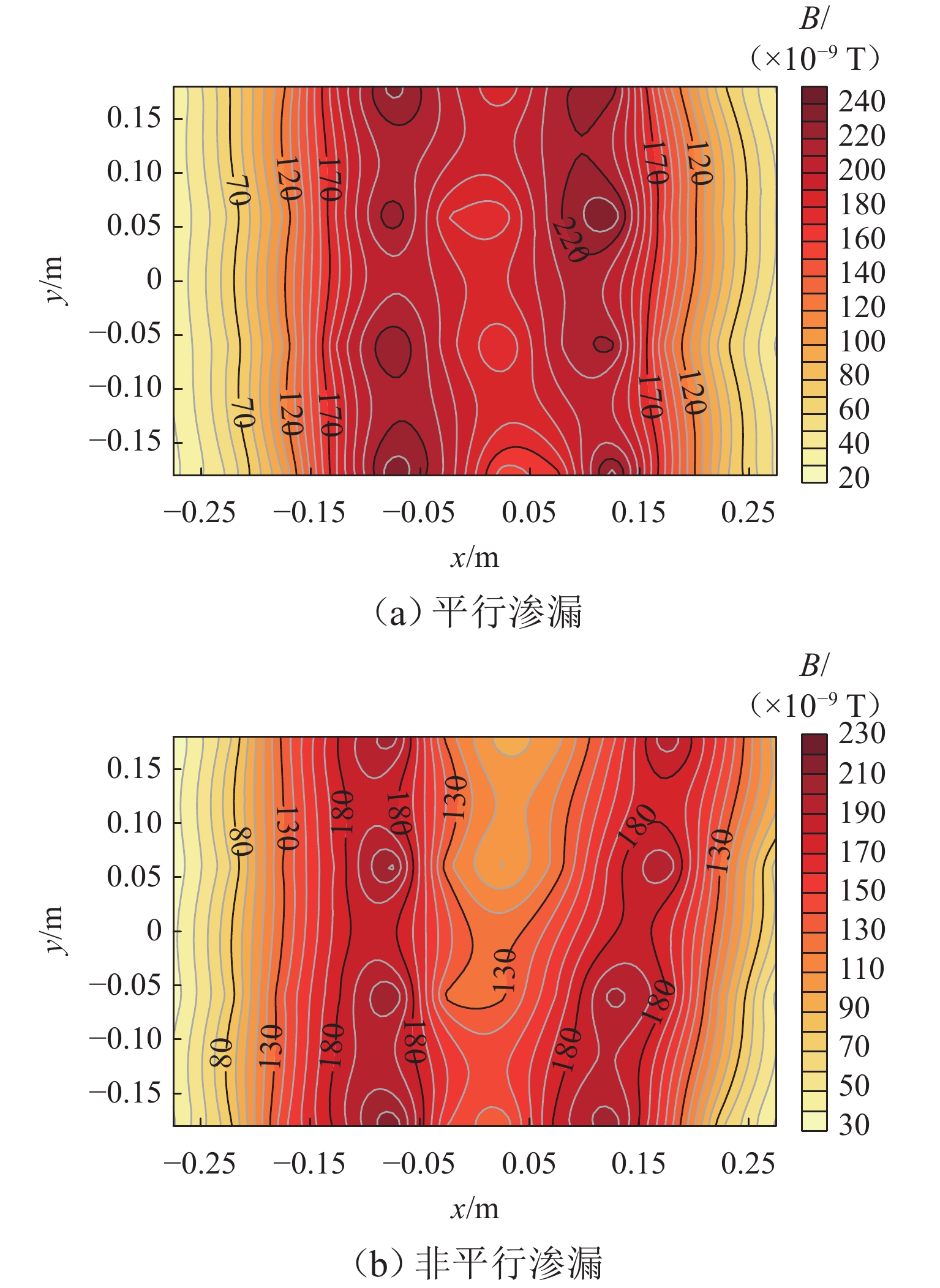
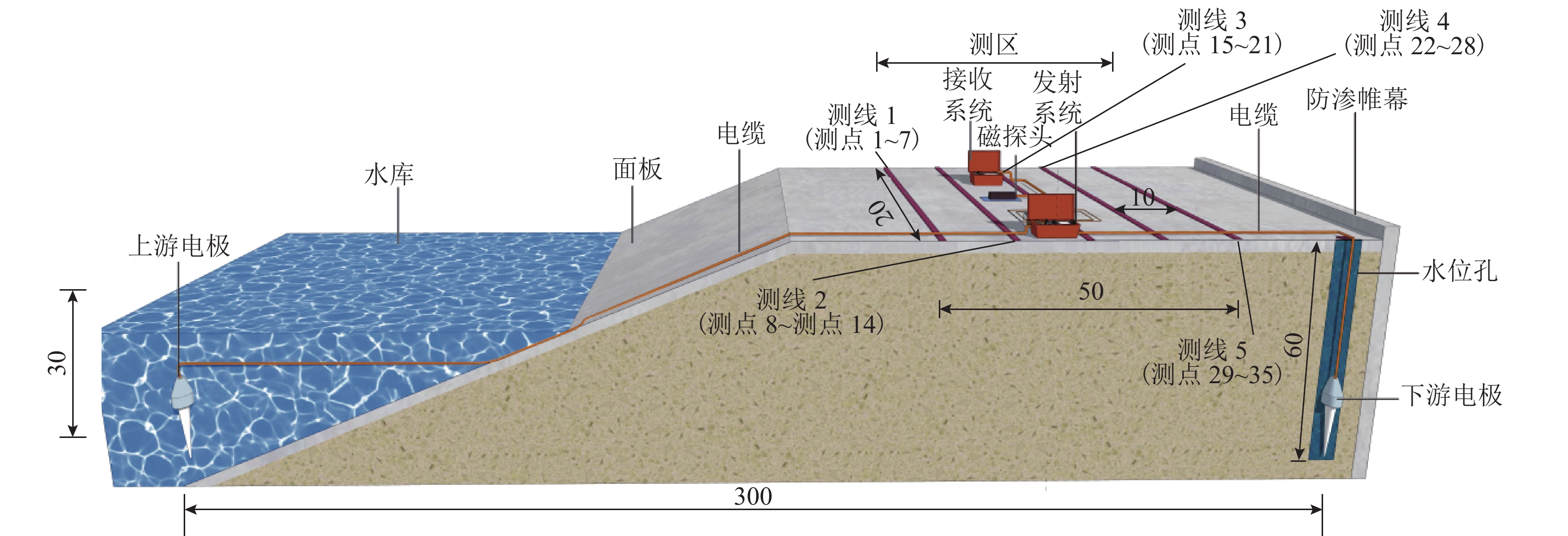
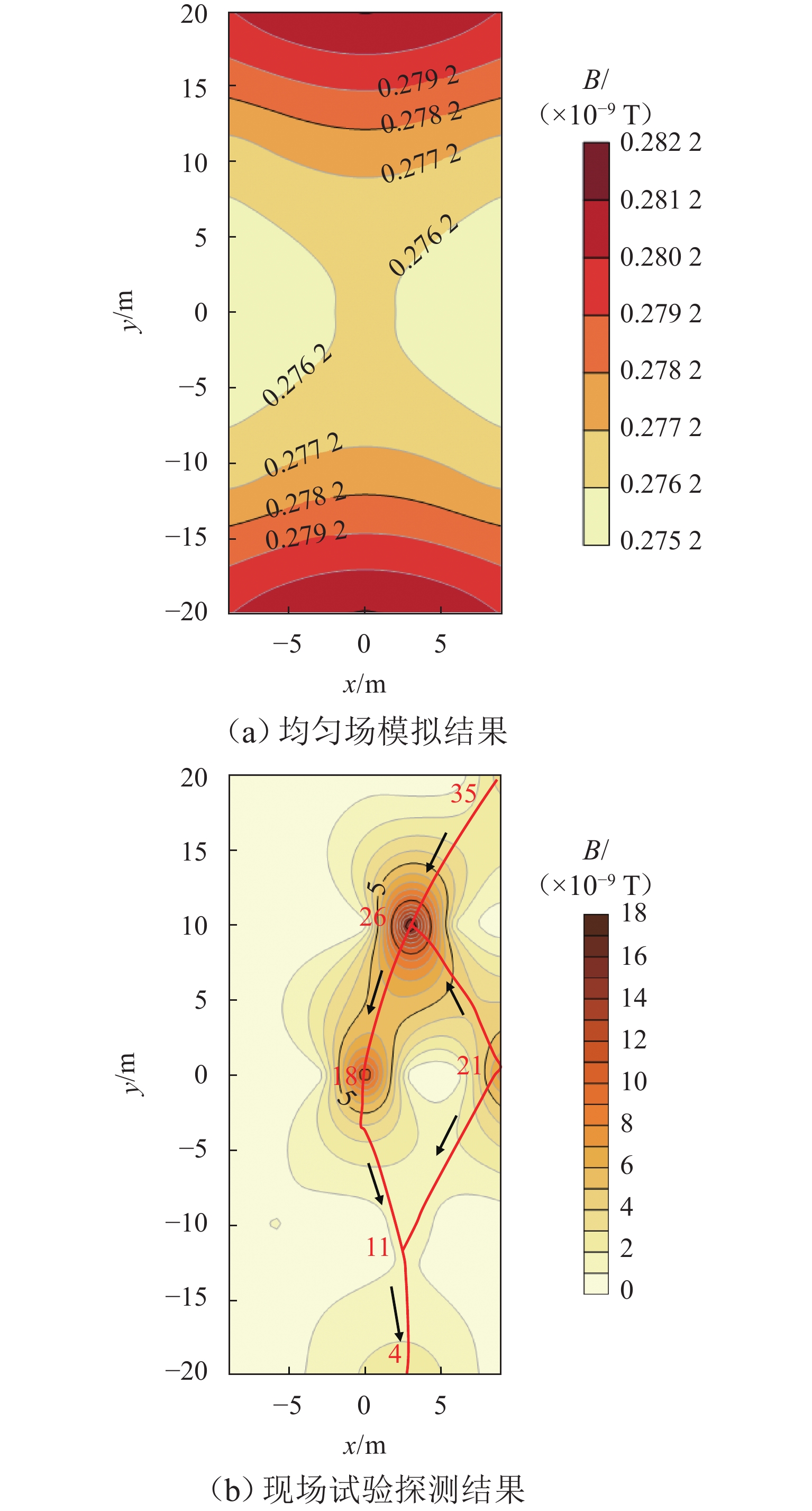
坝基渗漏问题是影响水库大坝整体安全的关键因素. 为有效、准确探测坝基渗漏,基于伪随机辨识原理,将M序列相关辨识的磁电法技术应用于堤坝渗漏探测. 首先,通过物理模型试验分析,获取不同渗漏深度下的磁感应强度分布、均方差及变异系数特征;然后,设计不同渗漏形态、高阻屏蔽层及渗漏通道数量条件,获取探测结果对倾斜通道、高阻屏蔽层以及多条渗漏通道的响应特征;最后,通过云南红石岩堰塞坝现场试验,分析该技术的可行性. 试验结果表明:在不同埋深条件下,磁感应强度最大值的变异系数均控制在2%以内;渗漏通道的倾斜引起磁感应强度沿渗漏方向缓慢降低,其磁场等值线图的脊线反映倾斜渗漏方向;高阻屏蔽层仅对磁感应强度产生影响,磁感应强度误差在10%~20%;多组渗漏通道会反映在磁场等值线图中异常场的多处集中分布;现场试验探测的渗流流向分别为NW300°、SW265°、W215°和NW305°.
Abstract:The dam foundation leakage problem has been a key factor affecting the overall safety of reservoir dams. To effectively and accurately detect dam foundation leakage, the magnetoelectric method based on M sequence correlation identification technology was applied to the dam leakage detection based on the pseudo-random identification principle. Firstly, the distribution of magnetic induction intensity, mean square error, and variation coefficient under various leakage depth conditions were characterized through the analysis of physical model experiments. Then, various leakage forms, high-resistance shielding layers, and leakage channel numbers were designed, so as to obtain the response characteristics of the detection results to the inclined channel, high-resistance shielding layer, and multiple leakage channels. Finally, the field test of Hongshiyan Dam in Yunnan Province was conducted to study the feasibility of this technology. The results show that under different burial depth conditions, the variation coefficients of maximum magnetic induction intensity vary within 2%. Along the inclined leakage channel, the magnetic induction intensity decreases slowly, and the ridge direction of the magnetic field contour map can be considered as the inclined leakage direction. The magnetic induction intensity is affected by the high-resistance shielding layer and has an error between 10% and 20%. The multiple leakage channels can be reflected by the concentrative distribution of abnormal zones in magnetic field contour maps. The leakage directions are observed in the field test, containing NW300°, SW265°, W215°, and NW305°, respectively.
-
Key words:
- leakage identification /
- M sequence /
- magnetoelectric method /
- dam foundation leakage /
- soil bin test
-
表 1 高精度磁电探测仪器性能指标
Table 1. Performance indexes of high-precision magnetoelectric detection instrument
项目 性能 发射功率/W 2000 发射电压/V 20 ~ 1200 发射电流/A 0.01~5.00 发射波形 M 序列 位宽/ms 100~ 2000 阶数/阶 4~12 频带宽度/Hz 0.01~50.00 同步方式 GPS 同步 工作温度/℃ −20~70 磁力仪精度/T 1 × 10−9 最大测深/m 1000 表 2 模型试验方案设置
Table 2. Scheme setting of model test
试验组 渗漏通道电阻率/
(Ω·m)通道埋深/cm 通道数量/个 渗漏通道
状态屏蔽层 2.5 Ω•m 土槽试验 2.5 5 1 平直 无 10 平直 20 平直 5 倾斜 高阻屏蔽层影响试验 2.5 10 1 平直 有 双渗漏土槽模型试验 2.5 10 2 平直,平行 无 平直,不平行 表 3 2.5 Ω•m模型试验均方差及变异系数
Table 3. Mean square errors and variation coefficients in 2.5 Ω•m model test
渗漏埋深/cm S/(×10−9 T) CV/% 5 2.78 0.41 10 3.16 0.94 20 3.32 1.93 表 4 渗漏磁感应强度最大值
Table 4. Maximum magnetic induction intensity of leakage
× 10−7 T 测线 测点 平行渗漏 非平行渗漏 1 5 2.38 2.19 9 2.36 2.07 2 17 2.30 2.11 21 2.23 2.04 3 29 2.28 2.13 33 2.39 1.98 4 41 2.35 2.06 45 2.26 1.99 表 5 磁感应强度极值大小及异常埋深
Table 5. Extreme values of magnetic induction intensity and abnormal burial depth
测点 B/(×10−9 T) 埋深/m 4 2.7 14.6 18 11.4 3.6 21 7.8 5.2 26 17.0 2.2 -
[1] 中华人民共和国水利部. 2021中国水利发展报告[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,2021. [2] 张聪,姚令侃,黄艺丹,等. 地震共振涌浪作用下冰碛堰塞坝的漫顶溃决[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(3): 564-571.ZHANG Cong, YAO Lingkan, HUANG Yidan, et al. Overtopping failure of moraine dams under action of earthquake-induced resonant water surges[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 564-571. [3] 赵海鑫,姚令侃,黄艺丹,等. 地震与滑坡碎屑流引发堰塞湖涌浪动水压力研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(3): 558-563.ZHAO Haixin, YAO Lingkan, HUANG Yidan, et al. Hydrodynamic pressures study of barrier lake under coaction of earthquake and clastic flow landslide[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 558-563. [4] 杨雄兵. 某水库坝基渗漏规律与模式研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2019. [5] 徐轶,谭政,位敏. 水库大坝渗漏常用探测技术及工程应用[J]. 中国水利,2021(4): 48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2021.04.025XU Yi, TAN Zheng, WEI Min. Typical leakage detection techniques and the application for reservoir dams[J]. China Water Resources, 2021(4): 48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2021.04.025 [6] 苏怀智,周仁练. 土石堤坝渗漏病险探测模式和方法研究进展[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2022,42(1): 1-10,39.SU Huaizhi, ZHOU Renlian. Research progress and prospect of earth-rockfill dam leakage detection modes and method[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2022, 42(1): 1-10,39. [7] 邹德兵,傅兴安,闵征辉. 磁电阻率法在水库渗漏探测中的应用[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2019,17(5): 148-152.ZOU Debing, FU Xing’an, MIN Zhenghui. Application of magnetometric resistivity method in reservoir leakage detection[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2019, 17(5): 148-152. [8] 徐磊,张建清,严俊,等. 磁电阻率法在平原水库渗漏探测中的试验研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,2021,36(5): 2222-2233. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0069XU Lei, ZHANG Jianqing, YAN Jun, et al. Experimental research of magnetic resistivity method in plain reservoir leakage detection[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(5): 2222-2233. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0069 [9] EDWARDS R N. The magnetometric resistivity method and its application to the mapping of a fault[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1974, 11(8): 1136-1156. doi: 10.1139/e74-108 [10] HOWLAND-ROSE A W, LINFORD G, PITCHER D H, et al. Some recent magnetic induced-polarization developments—part I: theory[J]. Geophysics, 1980, 45(1): 37-54. doi: 10.1190/1.1441038 [11] PAI D, EDWARDS R N. Programme MMR2DFD: finite difference modeling of MMR anomlales[J]. Reports in Applied Geophysics, 1983, 25(4): 1453-1456. [12] OPPLIGER G L. Three-dimensional terrain corrections for mise-á-la-masse and magnetometric resistivity surveys[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 1984, 15(3): 194-195. [13] NABIGHIAN M N, OPPLIGER G L, EDWARDS R N, et al. Cross-hole magnetometric resistivity (MMR)[J]. Geophysics, 1984, 49(8): 1313-1326. doi: 10.1190/1.1441758 [14] CUNNINGHAM A B. Some alternate vibrator signals[J]. Geophysics, 1979, 44(12): 1901-1921. doi: 10.1190/1.1440947 [15] 柴治媛. 可控震源伪随机扫描方法与地震响应的数值模拟[D]. 长春: 吉林大学,2007. [16] 张群英,方广有. 伪随机序列编码脉冲信号在探地雷达中的应用研究[J]. 电子与信息学报,2011,33(2): 424-428.ZHANG Qunying, FANG Guangyou. The study of pseudo random sequence’s application to GPR[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(2): 424-428. [17] 齐彦福,殷长春,王若,等. 多通道瞬变电磁m序列全时正演模拟与反演[J]. 地球物理学报,2015,58(7): 2566-2577. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150731QI Yanfu, YIN Changchun, WANG Ruo, et al. Multi-transient EM full-time forward modeling and inversion of m-sequences[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(7): 2566-2577. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150731 [18] 王显祥,底青云,王妙月,等. 基于m伪随机序列的电磁法抗噪能力分析[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(5): 1861-1874. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160529WANG Xianxiang, DI Qingyun, WANG Miaoyue, et al. A study on the noise immunity of electromagnetic methods based on m pseudo-random sequence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(5): 1861-1874. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160529 [19] 颜廷杰,王赛昕,马一行,等. 人文干扰对电法勘探的影响及应对措施[J]. 矿产勘查,2016,7(4): 634-639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2016.04.016YAN Tingjie, WANG Saixin, MA Yixing, et al. Influence of human interference on application of electrical prospecting and corresponding anti-interference measures[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2016, 7(4): 634-639. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2016.04.016 [20] 王洪波. KGR-1B抗干扰电法仪在石墨矿地区的运用[J]. 煤炭与化工,2018,41(4): 79-82.WANG Hongbo. Application of KGR-1B anti-jamming electro-detecting in graphite ore deposit[J]. Coal and Chemical Industry, 2018, 41(4): 79-82. [21] 李巧灵,雷晓东,李晨. 抗干扰编码电法在通州深部岩溶发育区地质构造探测中的应用[J]. 工程勘察,2018,46(2): 71-78.LI Qiaoling, LEI Xiaodong, LI Chen. Application of a coded electrical method with anti-interference ability to detect geological structures in Tongzhou karst areas[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2018, 46(2): 71-78. [22] 罗先中,李达为,彭芳苹,等. 抗干扰编码电法仪的实现及应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,2014,29(2): 944-951. doi: 10.6038/pg20140263LUO Xianzhong, LI Dawei, PENG Fangping, et al. Implementation and applications of an coded electrical instrument with anti-interference ability[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(2): 944-951. doi: 10.6038/pg20140263 -




 下载:
下载: