Modeling and Simulation of Inductive Coupling Interference from Suburban Railways to Buried Pipelines
-
摘要:
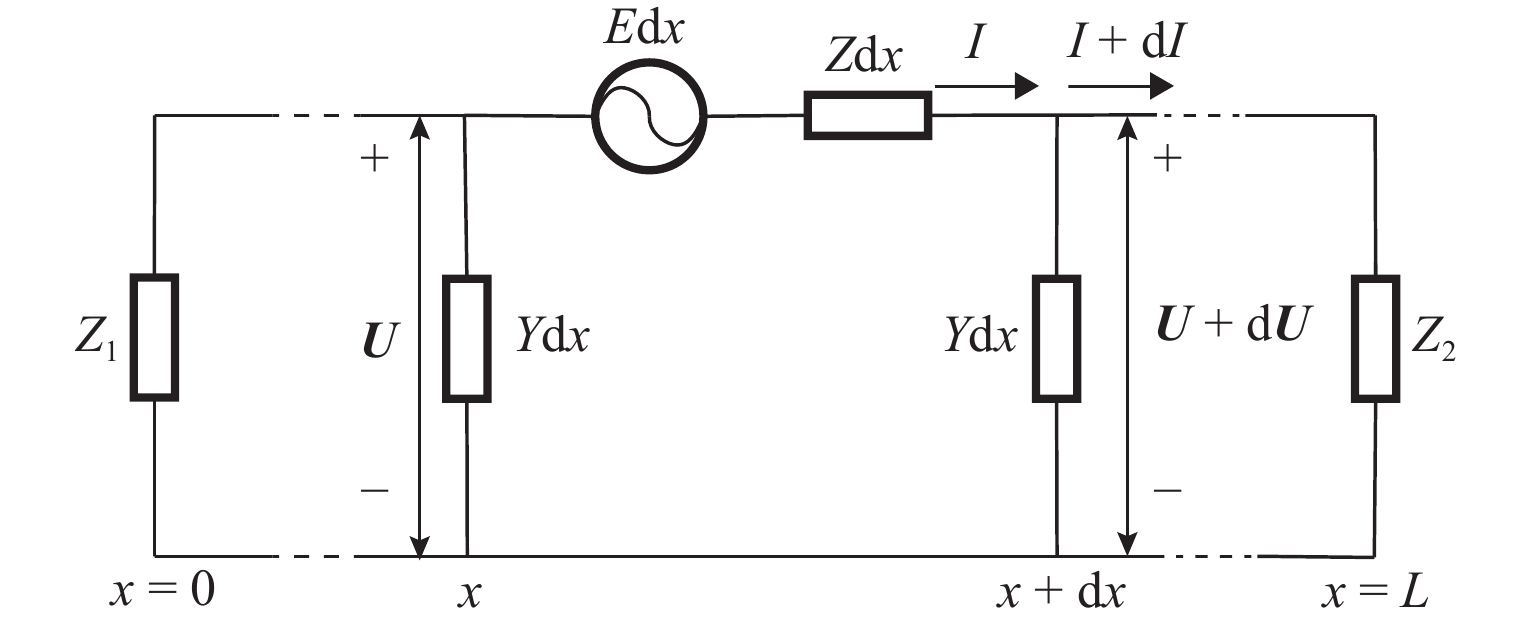
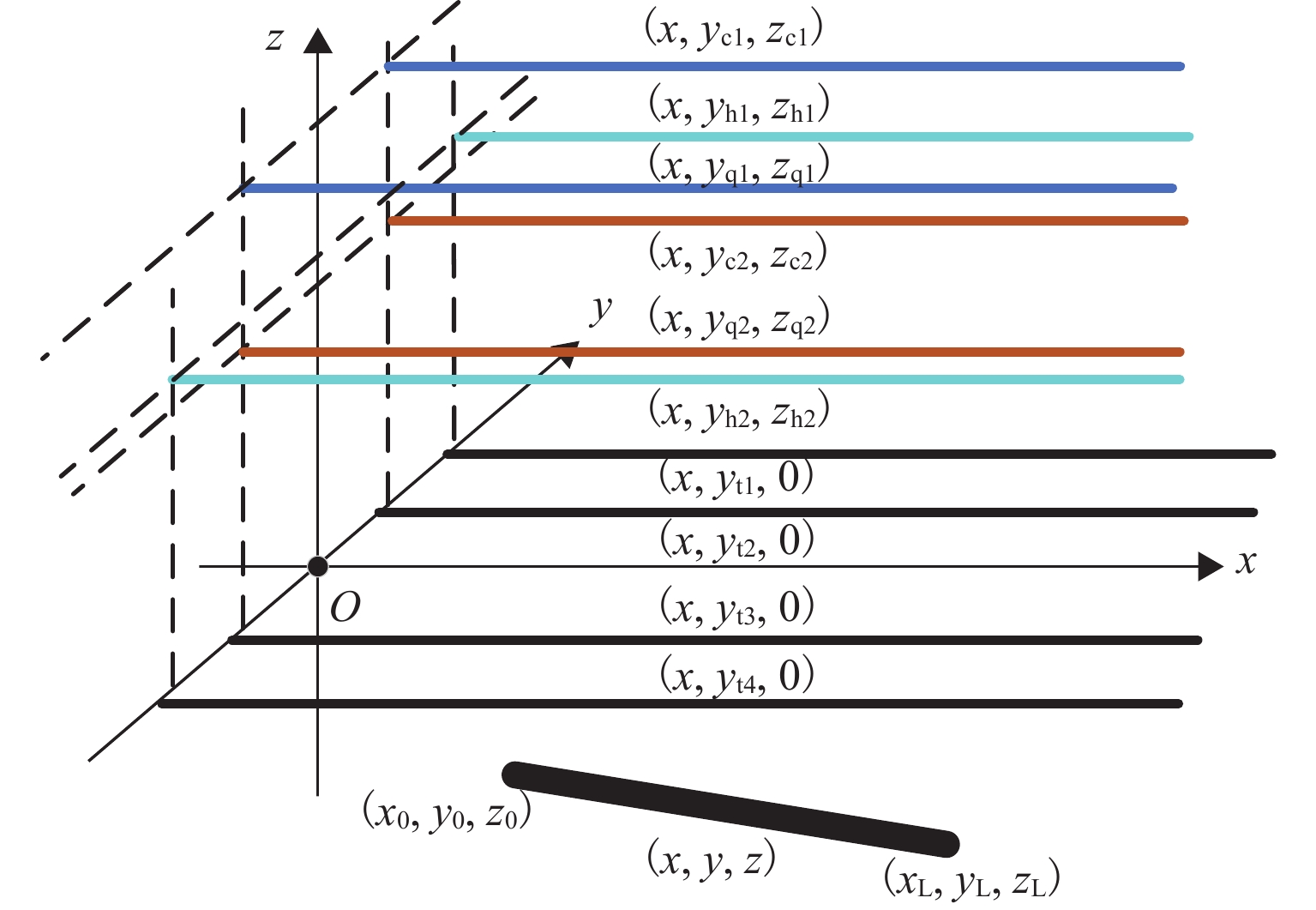
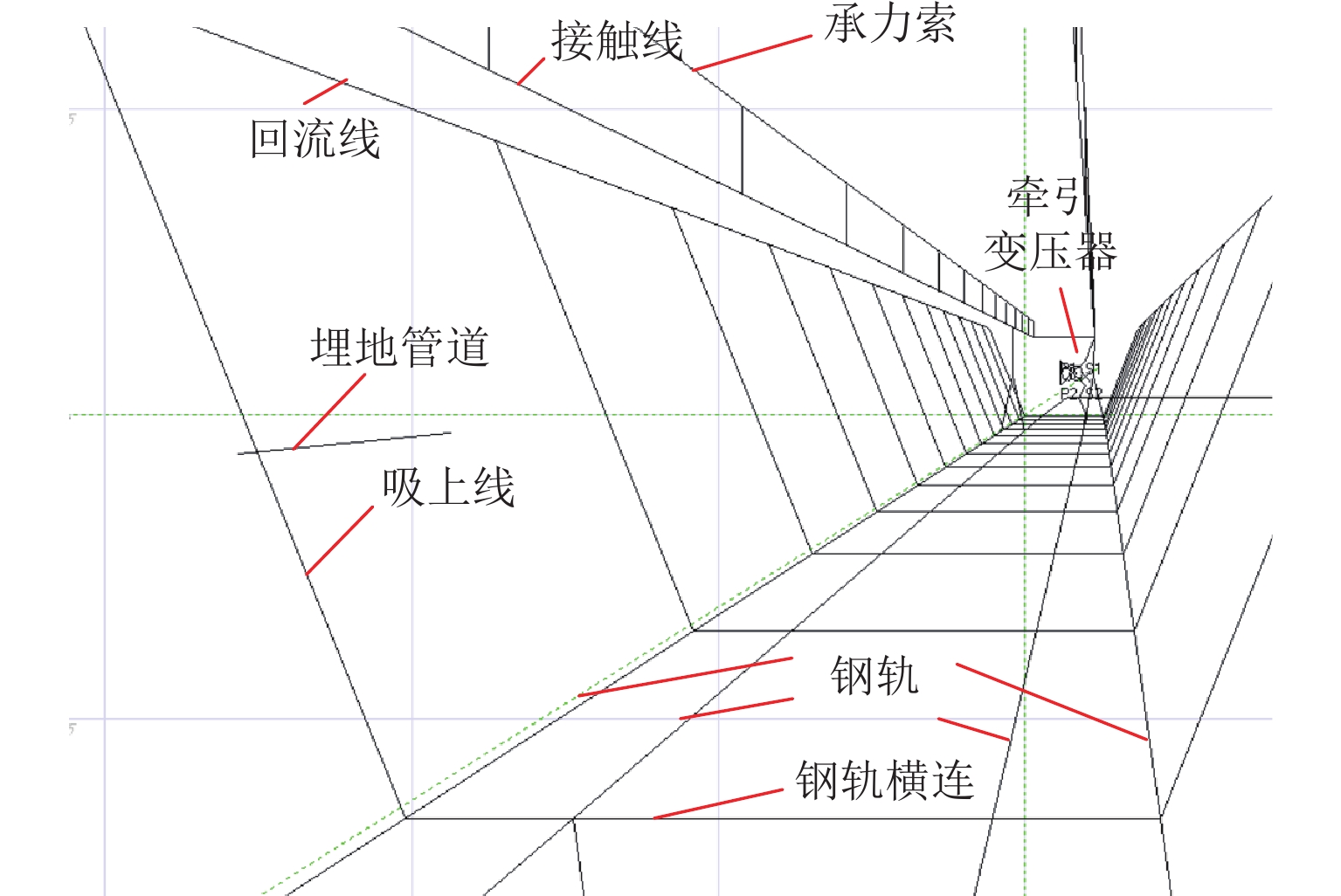
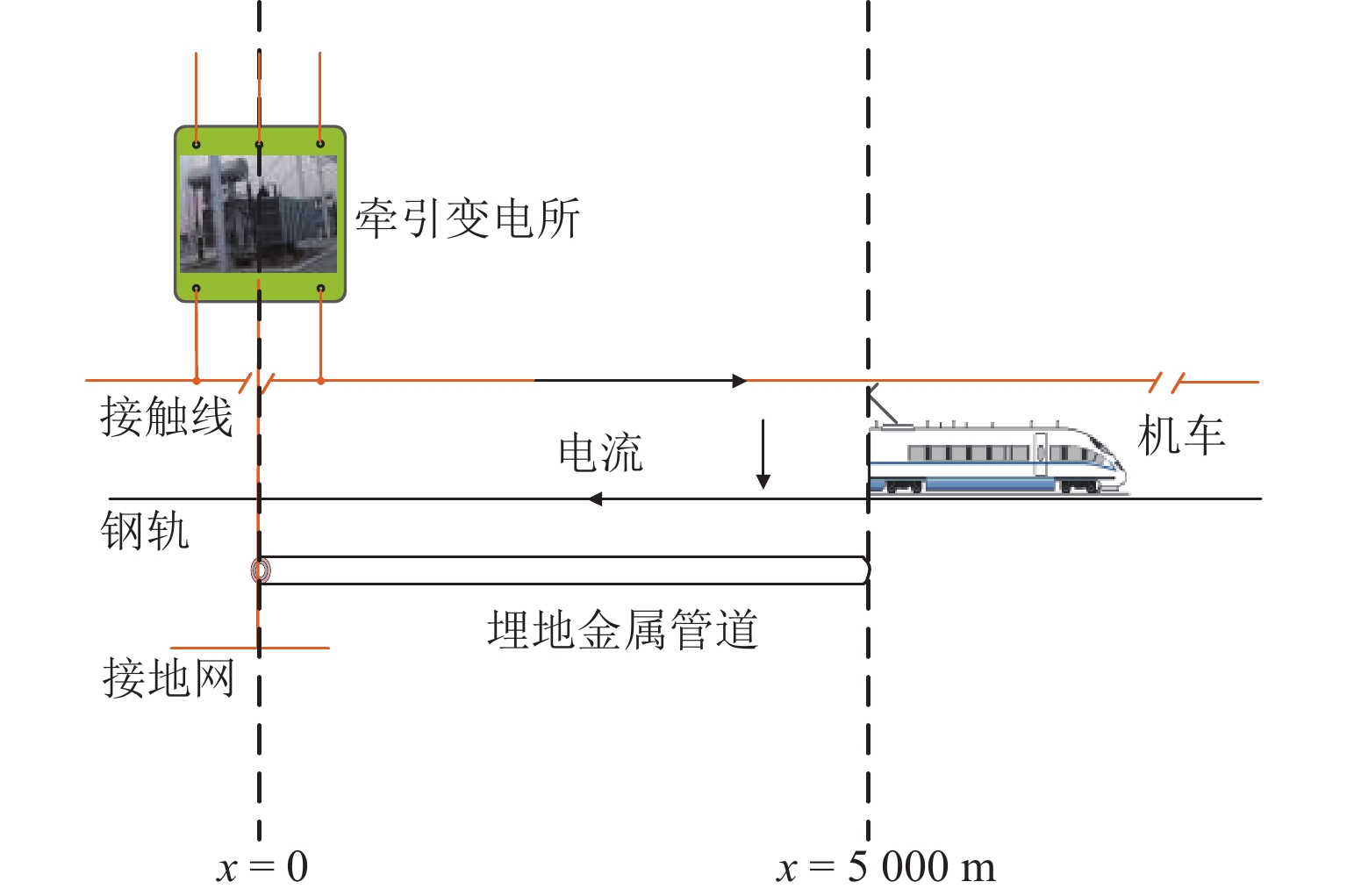
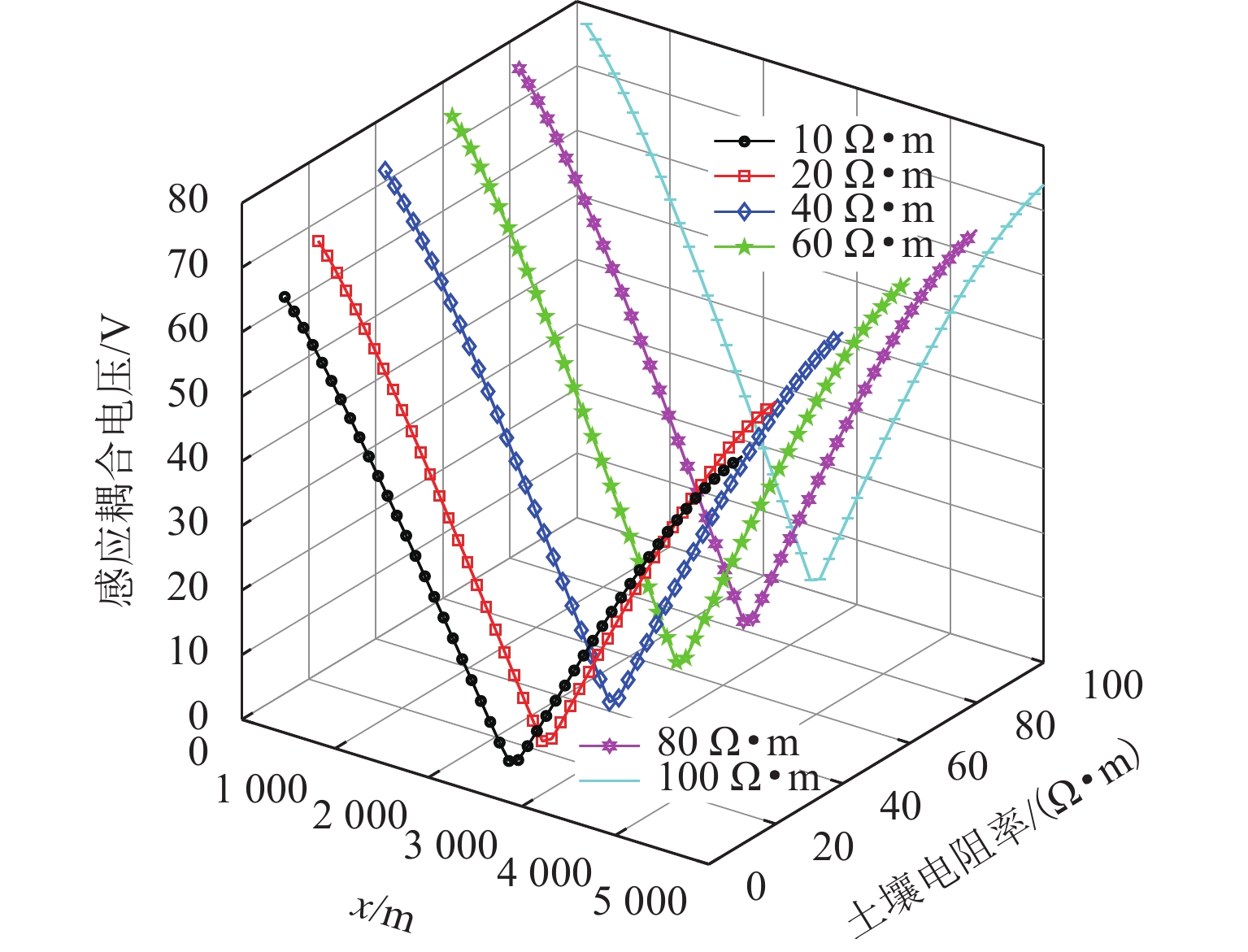
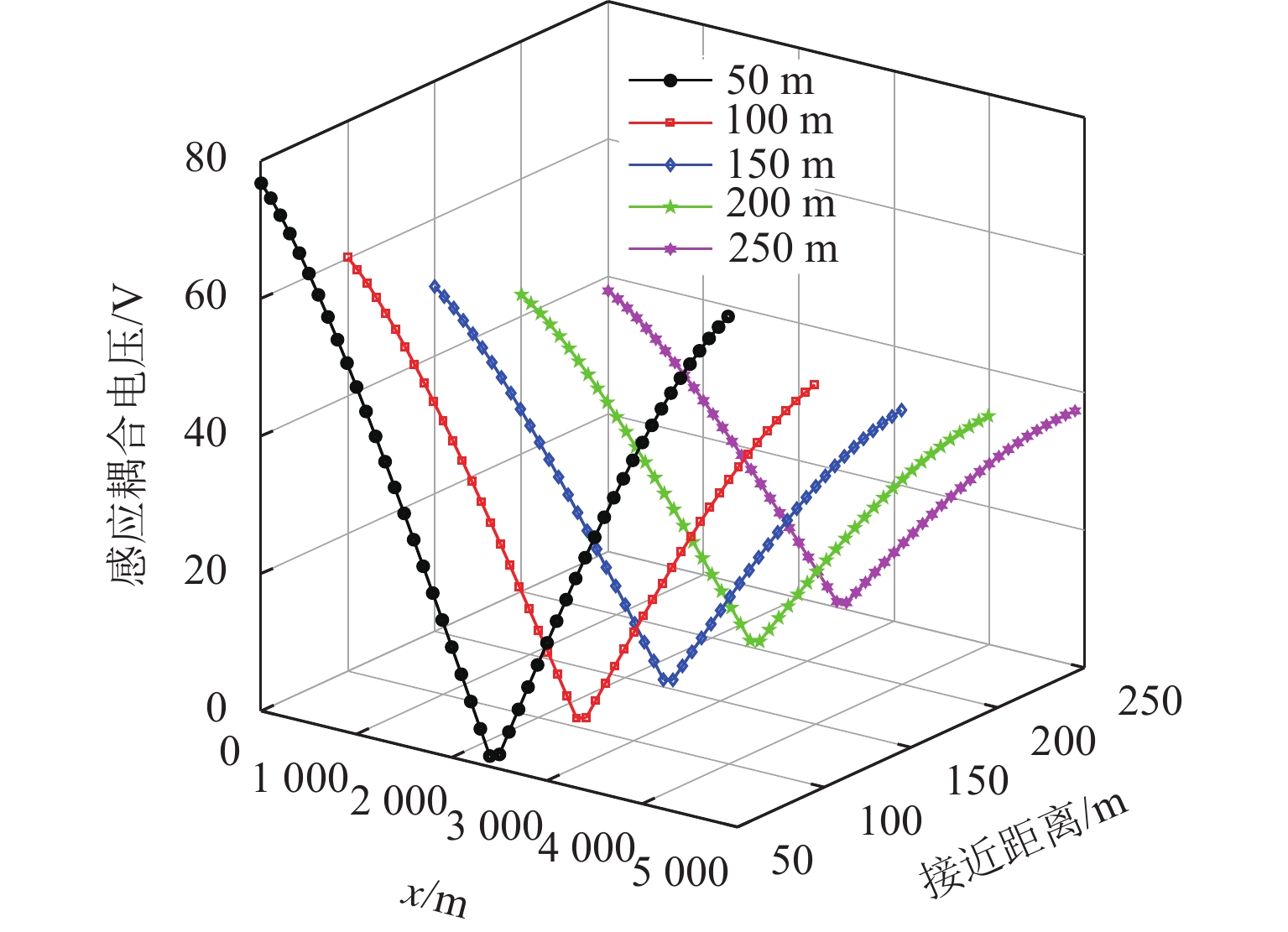
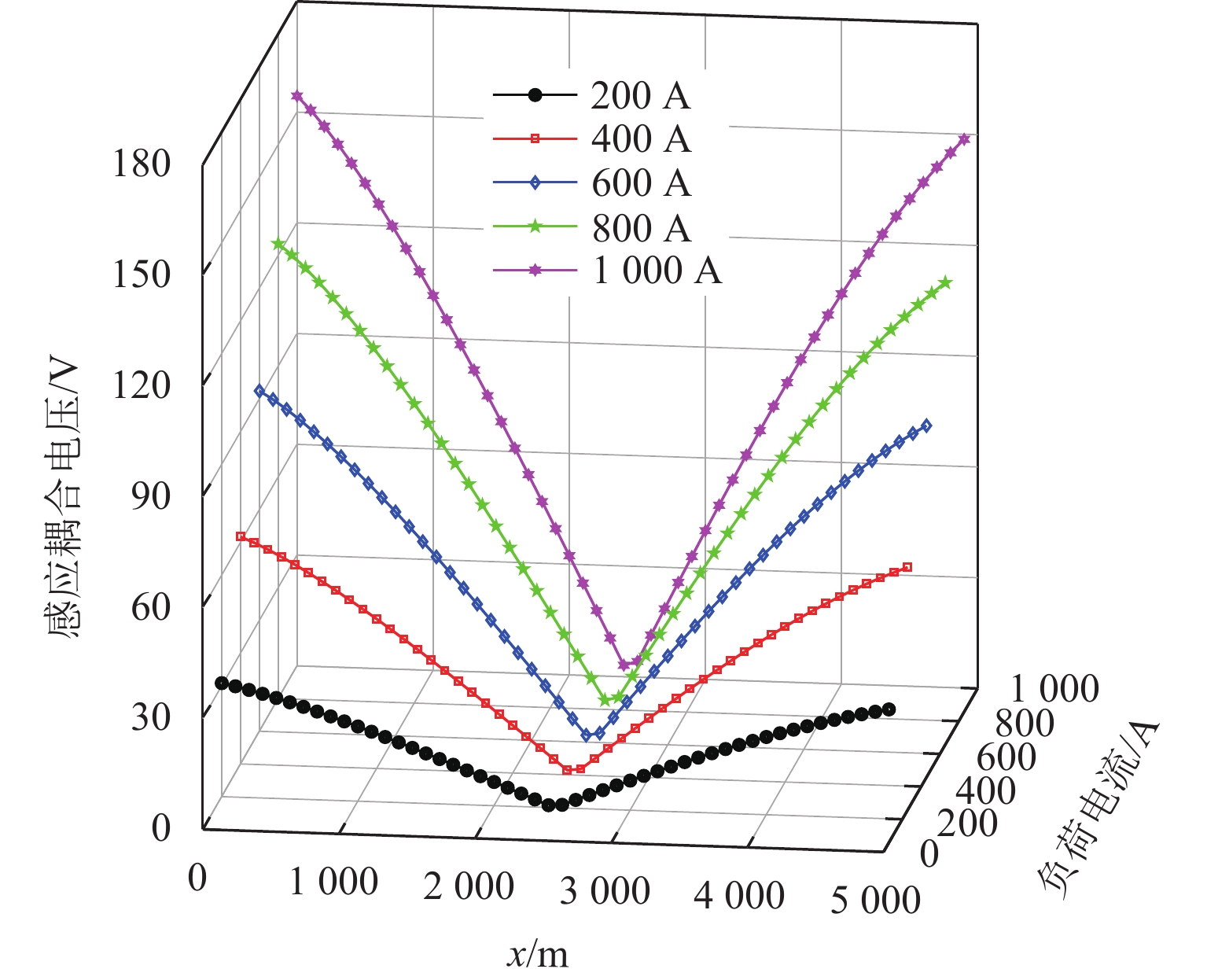
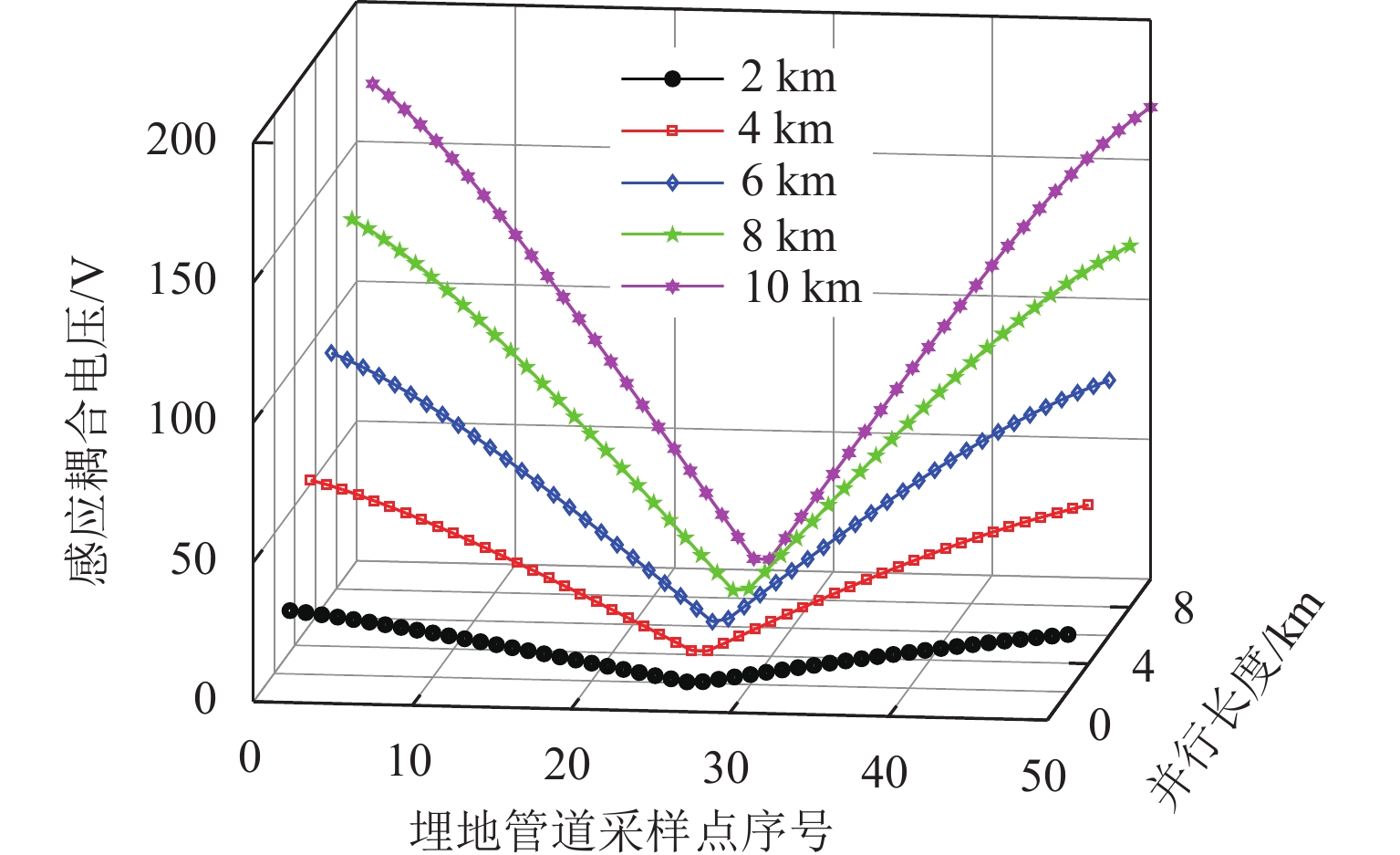
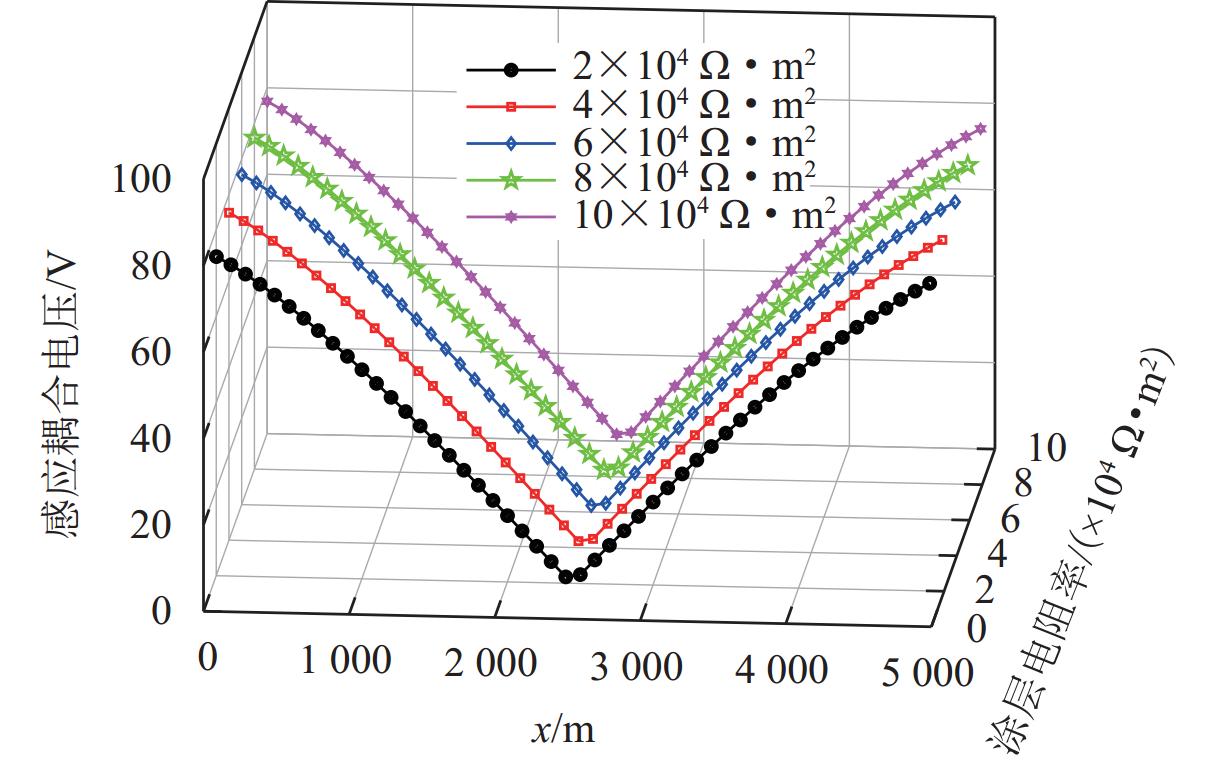
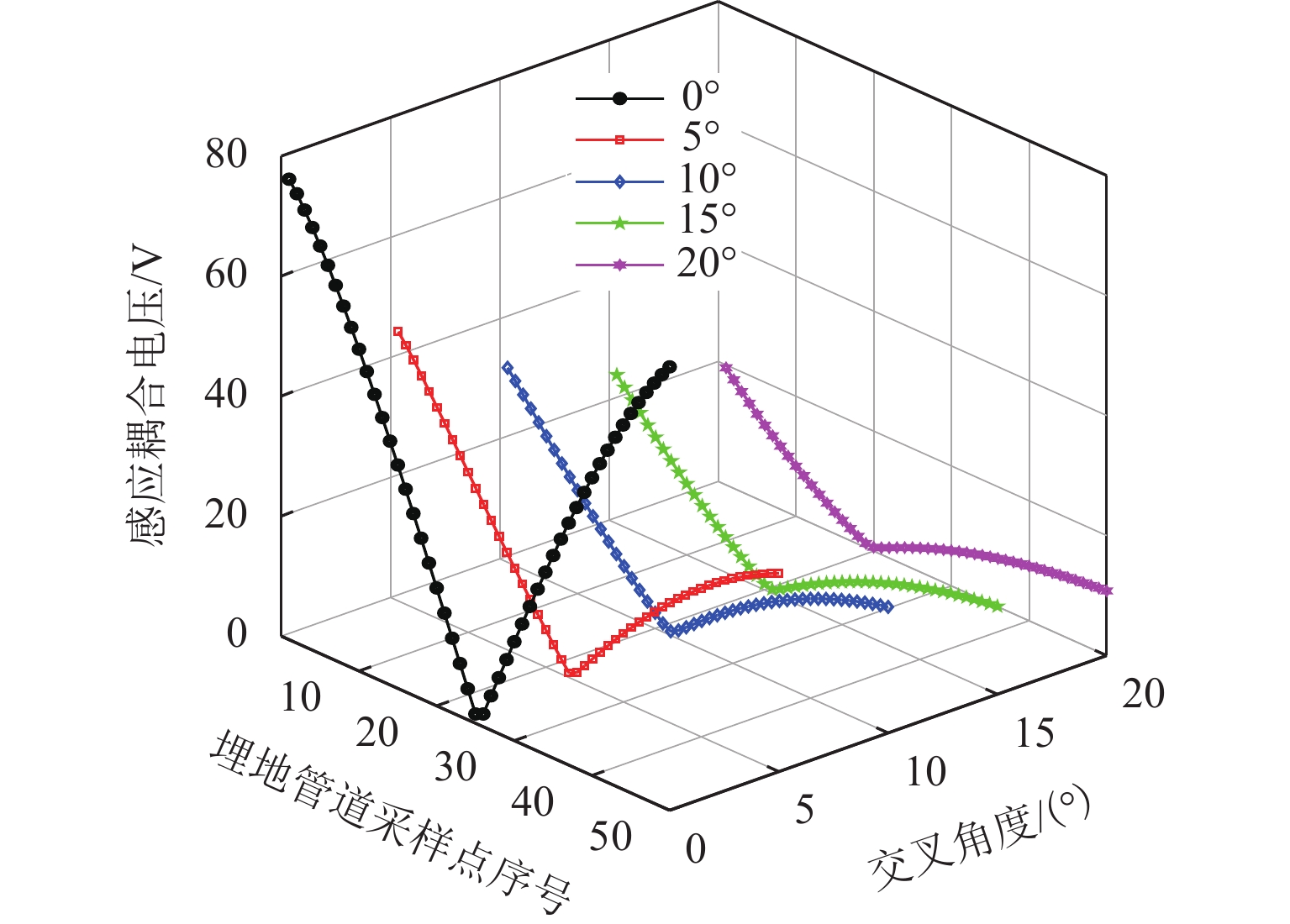
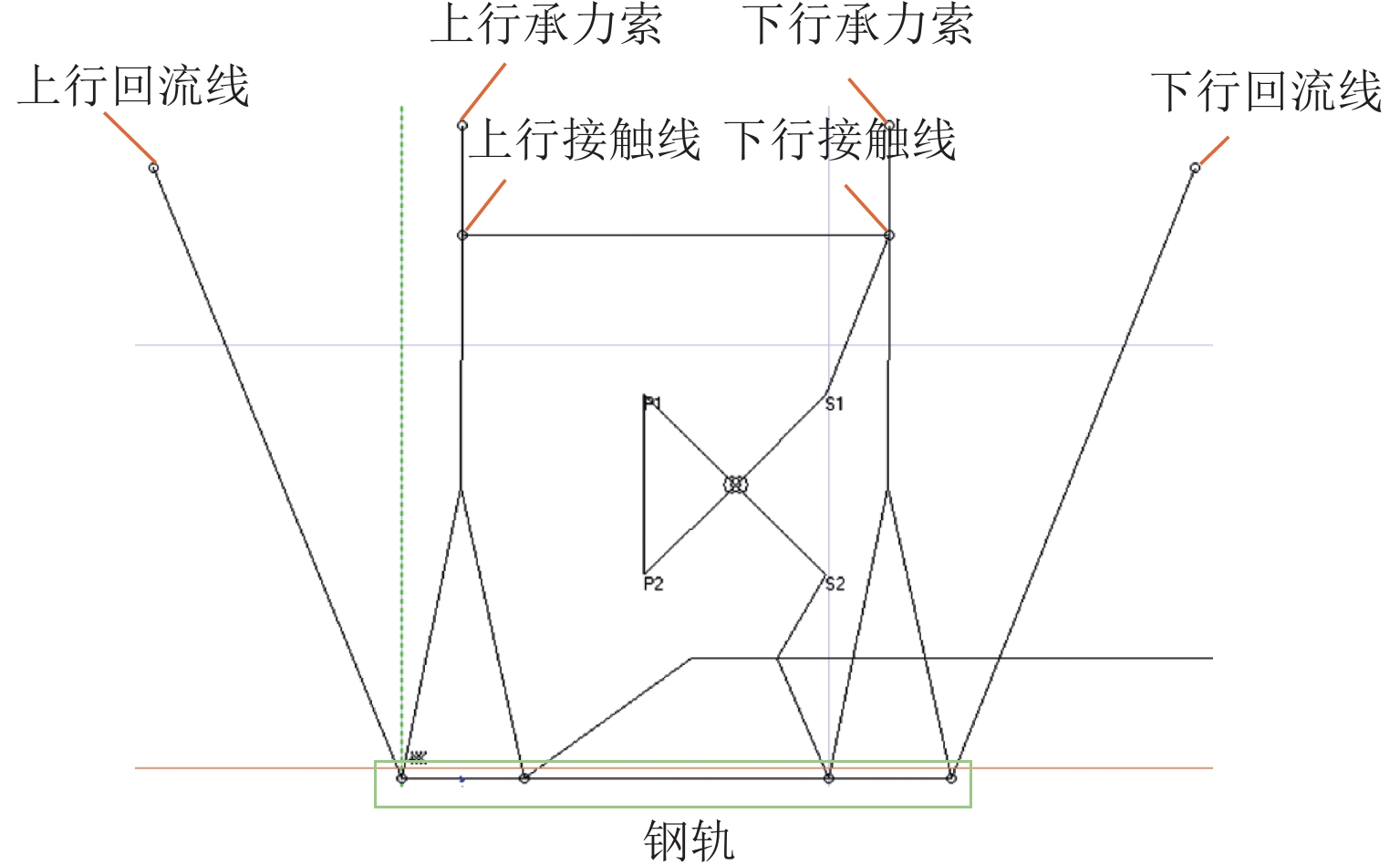
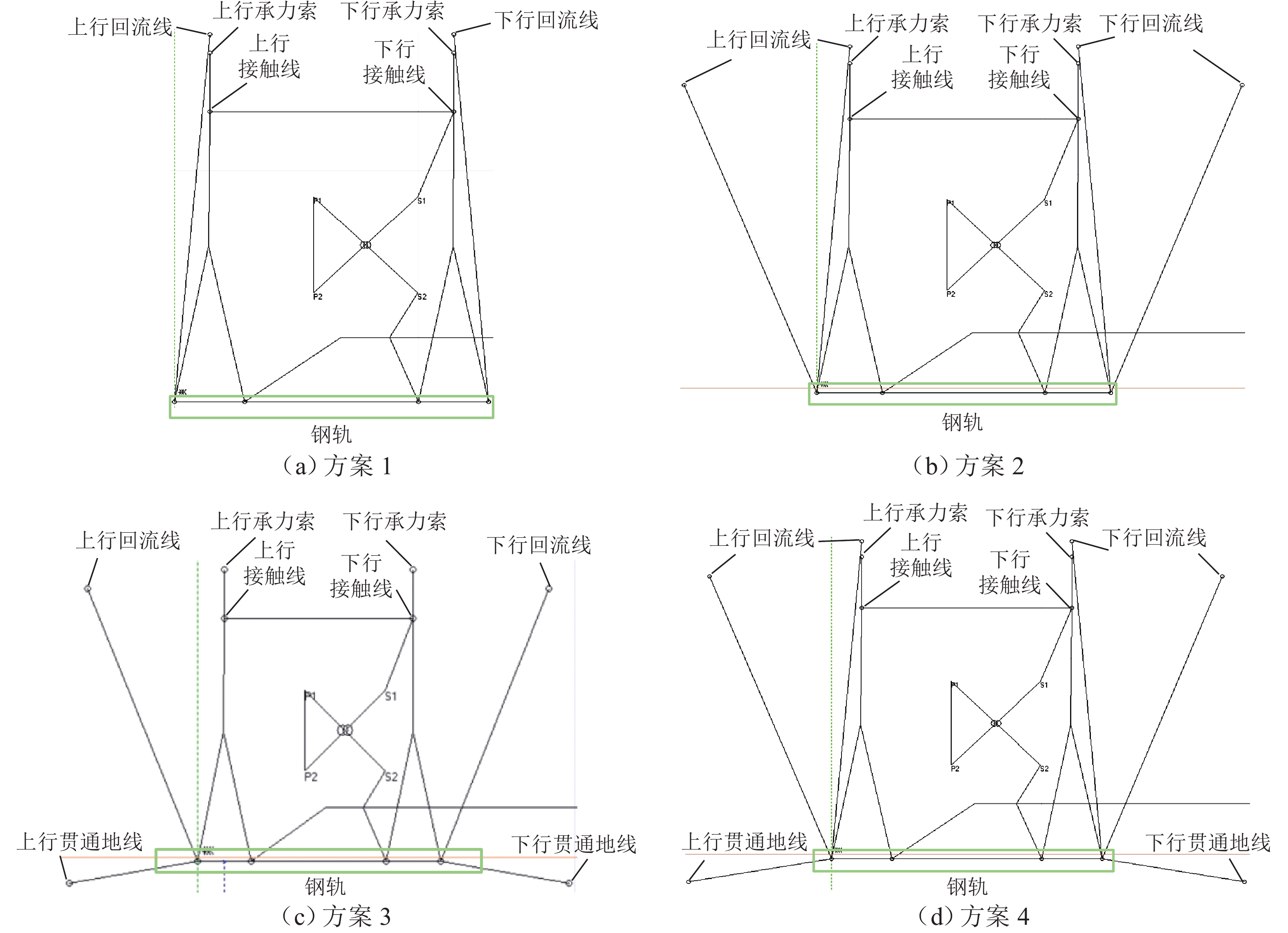
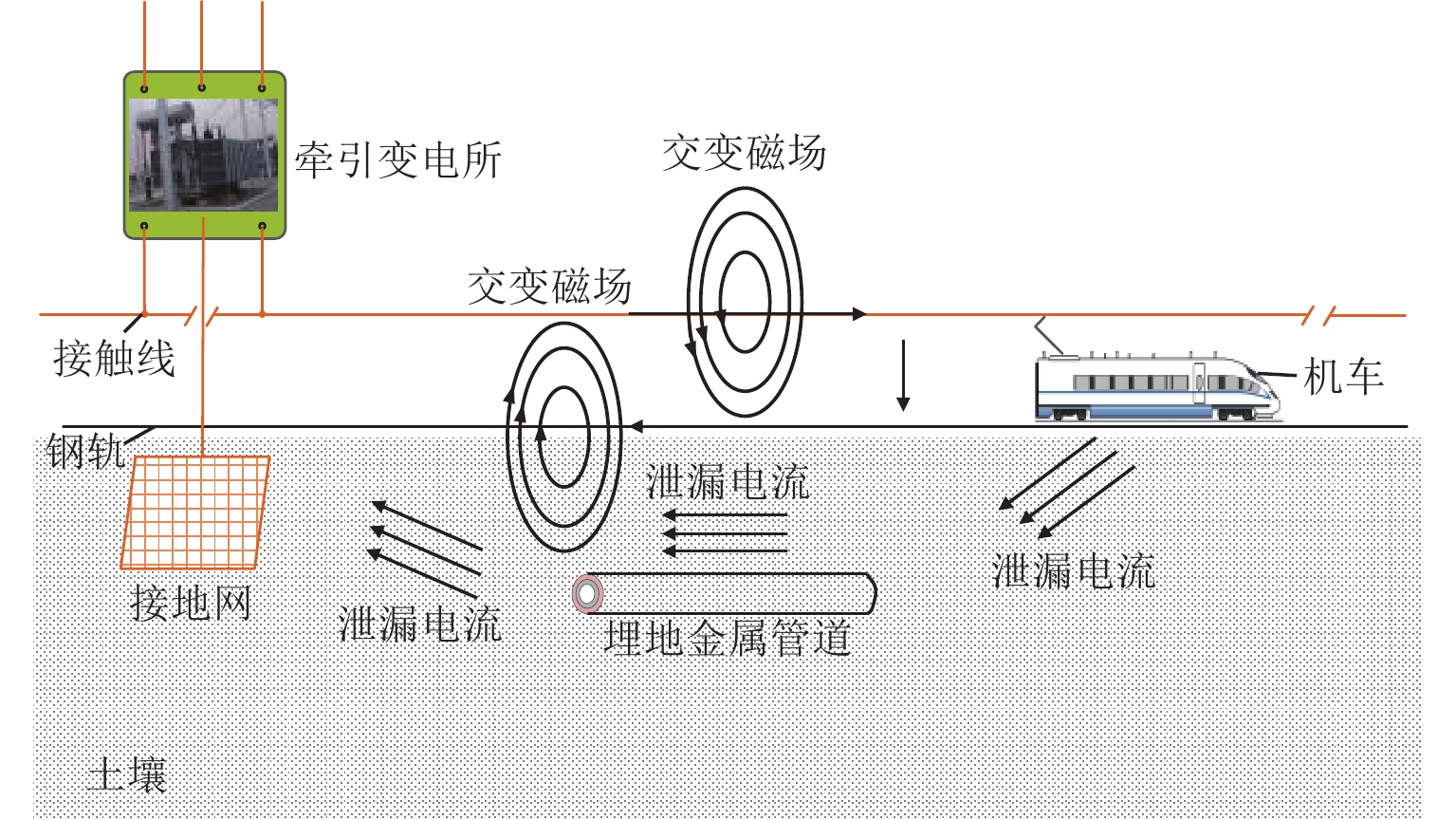
随着市域铁路和油气管道的快速发展,铁路与埋地管道平行或交叉铺设的情况已不可避免. 为分析市域铁路牵引供电系统对油气管道安全运行的影响,首先,建立铁路交流牵引供电系统与邻近埋地管道的数学模型,并利用CDEGS软件进行仿真验证;然后,采用等效距离方法将斜接近和平行接近2种情况进行统一,探究牵引供电系统对邻近埋地管道的影响机理,分析土壤电阻率、导线与埋地管道间接近距离、机车负荷电流、铁路与埋地管道间并行长度、管道涂层电阻率、动车组电流谐波次数等因素对管道沿线感应耦合电压分布的影响;最后,结合贯通地线的设置,提出4种抑制感应耦合电压的方案进行对比分析. 研究结果表明:当市域铁路牵引供电系统与埋地管道的最大间距与最小间距比值小于4.5时,采用等效距离方法的偏差在5%以内;管道上的感应耦合电压极大值随着土壤电阻率的增加而增大;接近距离由50 m增大到250 m时,感应耦合电压降幅为50.6%;机车负荷电流在200~
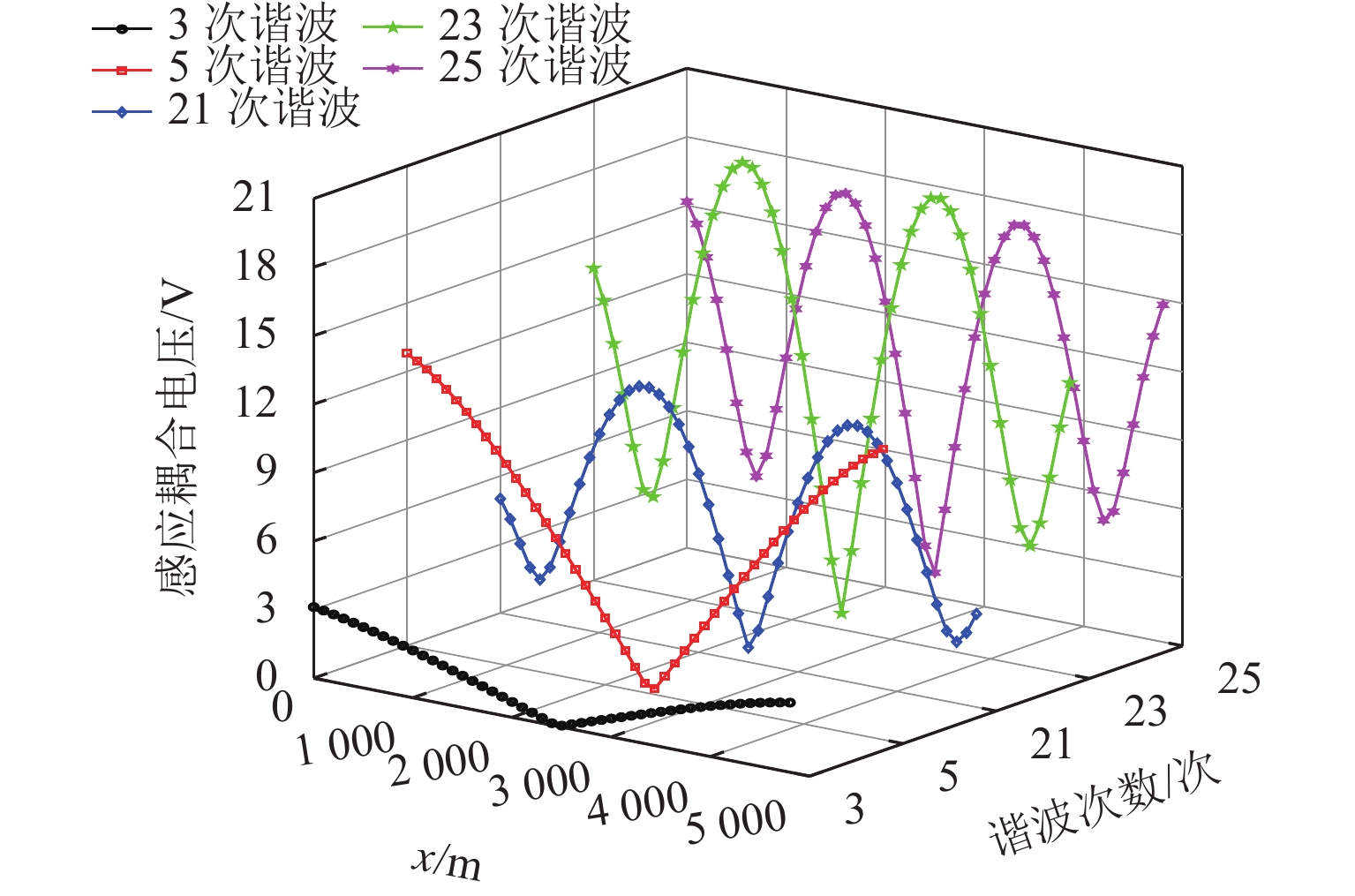
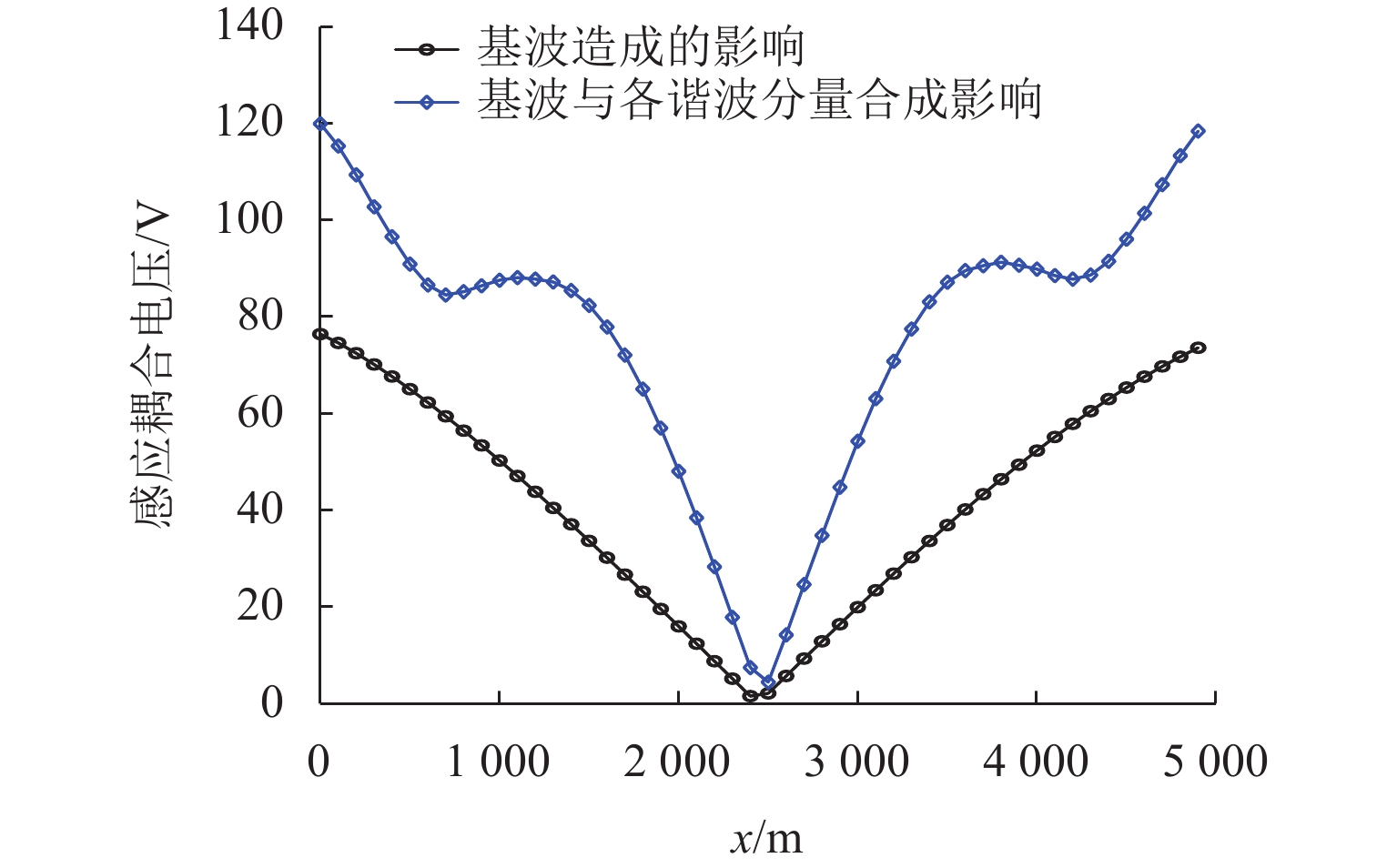
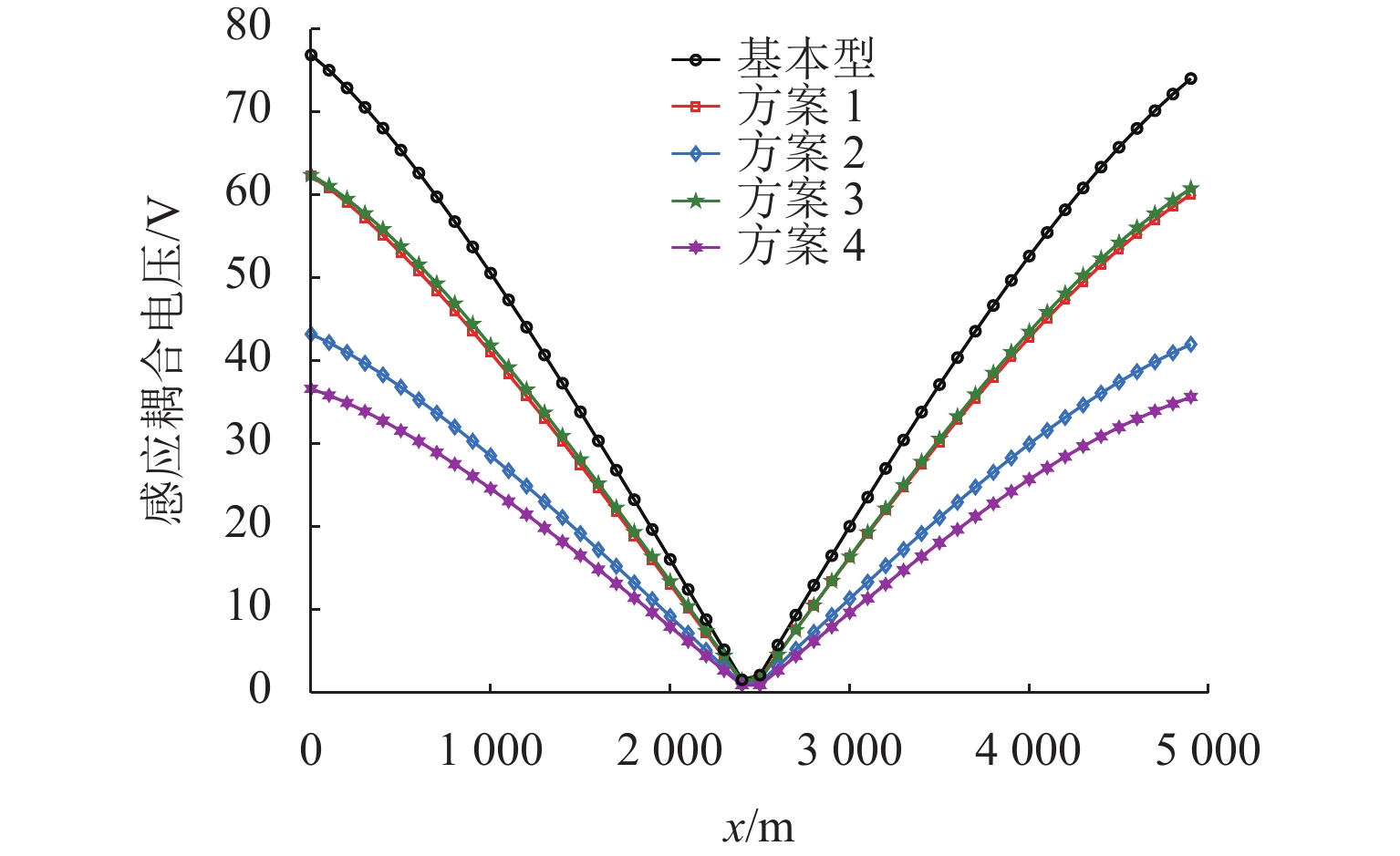
1000 A变化时,感应耦合电压增幅较大;并行长度在2~10 km变化时,感应耦合电压从22.6 V增加到170.7 V;谐波含有率和谐波次数对感应耦合电压的影响不可忽视;在贯通地线基础上增设一根回流线的方案对抑制感应耦合电压的效果最佳.Abstract:With the rapid development of suburban railways and oil and gas pipelines, parallel laying or cross-laying is inevitable for suburban railways and buried pipelines. In order to assess the impact of the traction power supply system of suburban railways on the safe operation of oil and gas pipelines, firstly, the mathematical model of the alternating current (AC) traction power supply system of the suburban railways and the adjacent buried pipelines was established, and the simulation based on CDEGS software was conducted. Next, the two cases of the oblique approach and parallel approach were unified by the equivalent distance method. The influence mechanism of the traction power supply system of the suburban railways on the adjacent buried pipeline was investigated, and the influence of factors including soil resistivity, distance between the conductor and the buried pipeline, locomotive load current, parallel length of railway and buried pipeline, pipeline coating resistivity, and number of current harmonics of electric multiple units on the inductive coupling voltage distribution along the pipeline was investigated. Finally, combined with the setting of a through ground line, four schemes to suppress the inductive coupling voltage were put forward for comparative analysis. The results show that the error of the equivalent distance method is within 5% when the ratio of the maximum distance to the minimum distance between the traction power supply system of the suburban railway and the buried pipeline is less than 4.5. The maximum value of the inductive coupling voltage of the pipeline increases with increasing soil resistivity. The decrease in the inductive coupling voltage is 50.6% when the distance between the suburban railway and the buried pipeline varies from 50 m to 250 m. The increase in the inductive coupling voltage rises significantly when the locomotive load current varies from 200 A to 1 000 A. The inductive coupling voltage increases from 22.6 V to 170.7 V when the parallel length varies from 2 km to 10 km. The harmonic content and the number of harmonics have a significant influence on the inductive coupling voltage. The best inductive coupling voltage suppression effect is achieved by adding a return line on the basis of the through ground line.
-
Key words:
- suburban railway /
- buried pipelines /
- inductive coupling voltage /
- oblique approach /
- harmonics
-
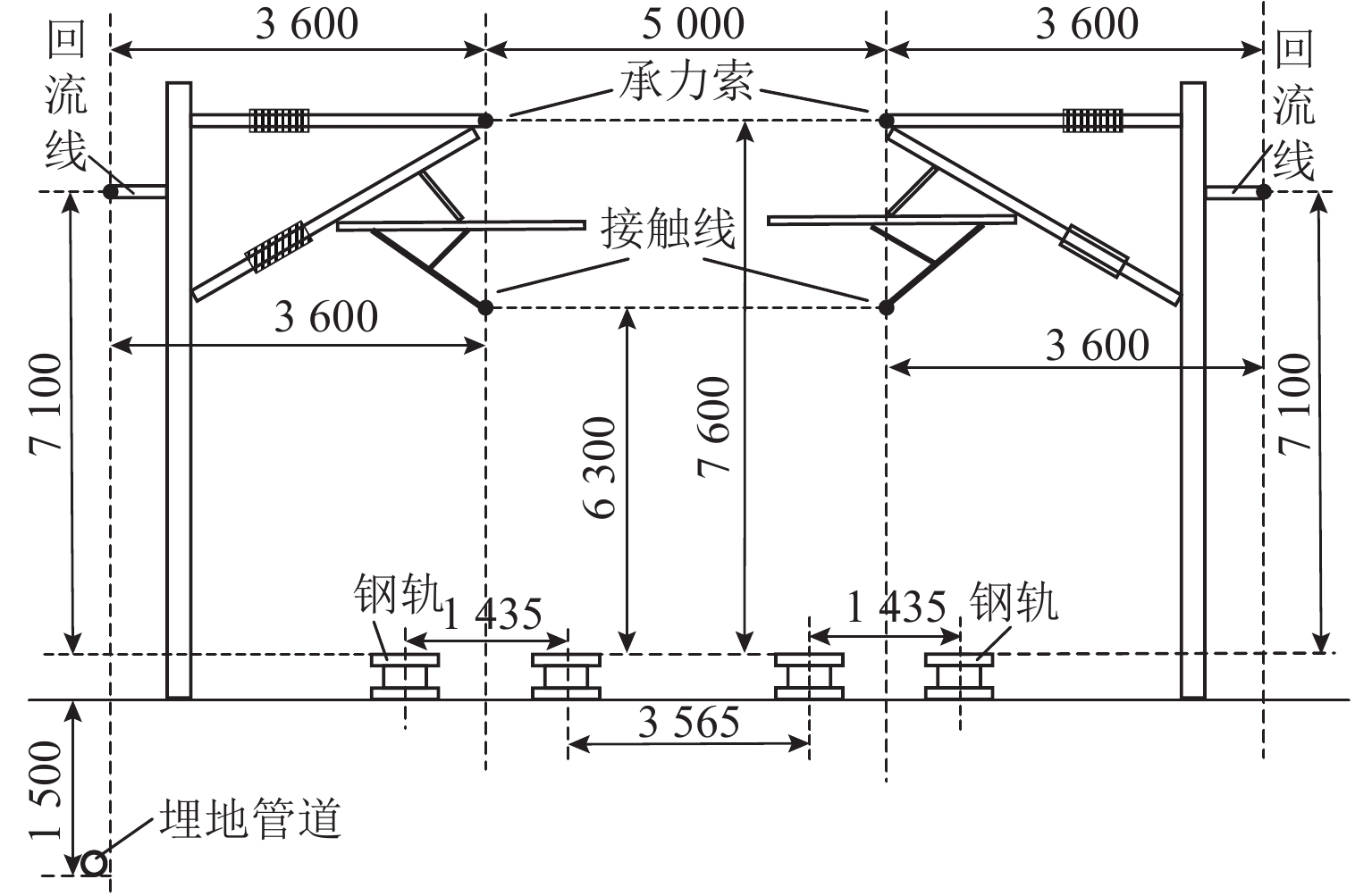
表 1 直供加回流供电方式牵引网导线规格参数
Table 1. Specifications of traction network conductors for direct power supply with return wire
导线类型 导线规格 计算半
径/mm电阻/
(Ω·km−1)等效半
径/mm接触线 CTA-120 6.45 0.148 5.03 承力索 JTMH-95 5.90 0.303 5.30 回流线 LBGLJ-185 7.85 0.146 6.11 表 2 钢轨规格参数
Table 2. Specifications of rail
参数 规格/(kg·m−1) 截面面积/cm2 计算半径/mm 电阻/(Ω·km−1) 等效半径/mm 取值 60 77.08 109.10 0.135 12.79 表 3 埋地管道参数
Table 3. Parameters of buried pipeline
参数 规格 管道金属相对磁导率 300 管道金属电阻率/(× 10−7 Ω·m) 1.7 管道涂层相对介电常数 5 管道涂层电阻率/(× 105 Ω·m2) 1.0 管道半径/m 0.3 管道涂层厚度/m 0.003 管道埋深/m 1.5 表 4 负荷电流变化时埋地管道感应耦合电压最大值
Table 4. Maximum values of inductive coupling voltage of buried pipeline during load current variations
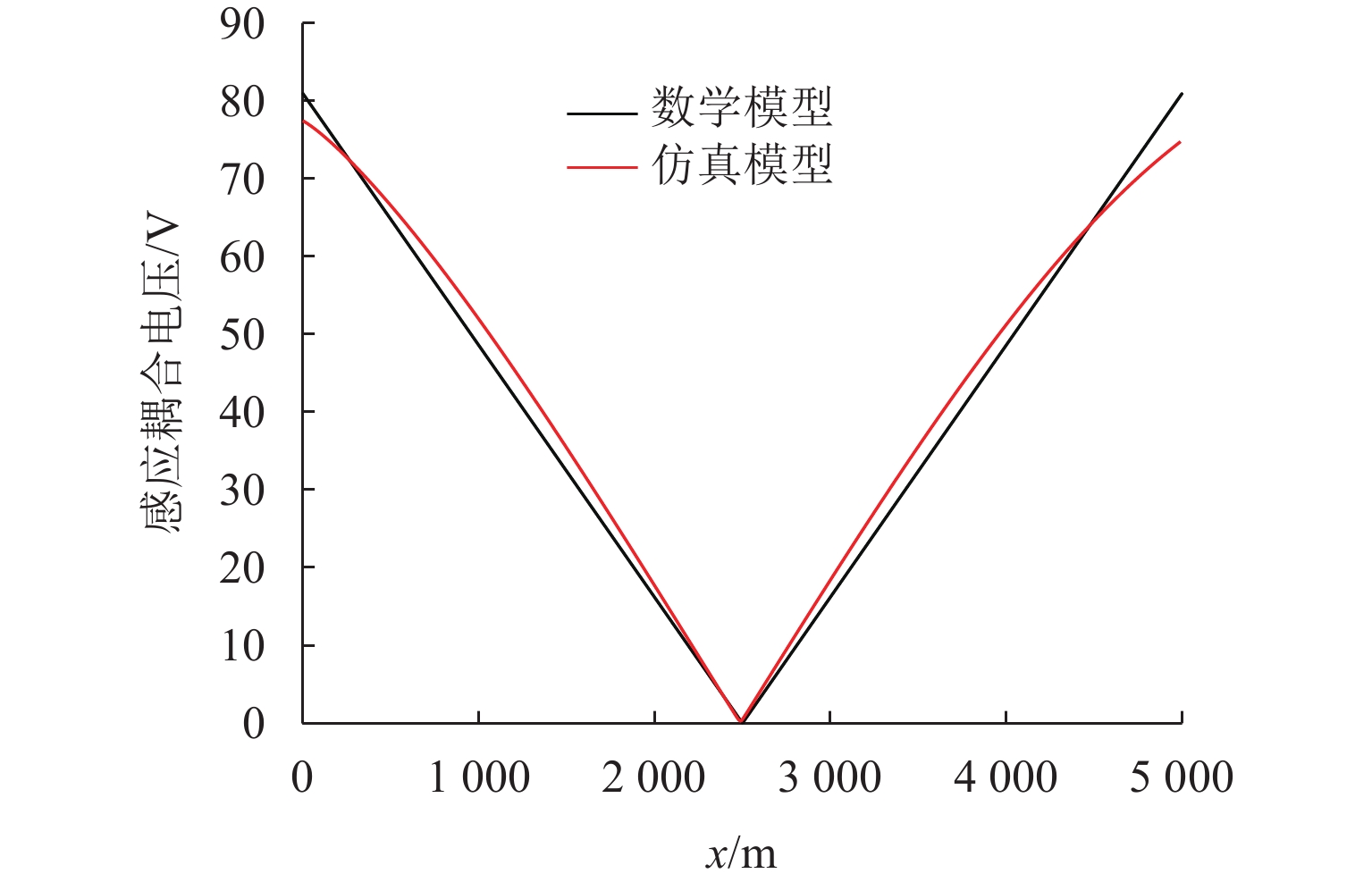
负荷电流幅值/A 数学模型/V 仿真模型/V 偏差/% 200 32.5 30.7 5.5 400 64.9 61.5 5.2 600 97.1 92.2 5.0 800 129.5 123.2 4.9 1000 162.2 154.4 4.8 表 5 间距比值变化时埋地管道感应耦合电压最大值
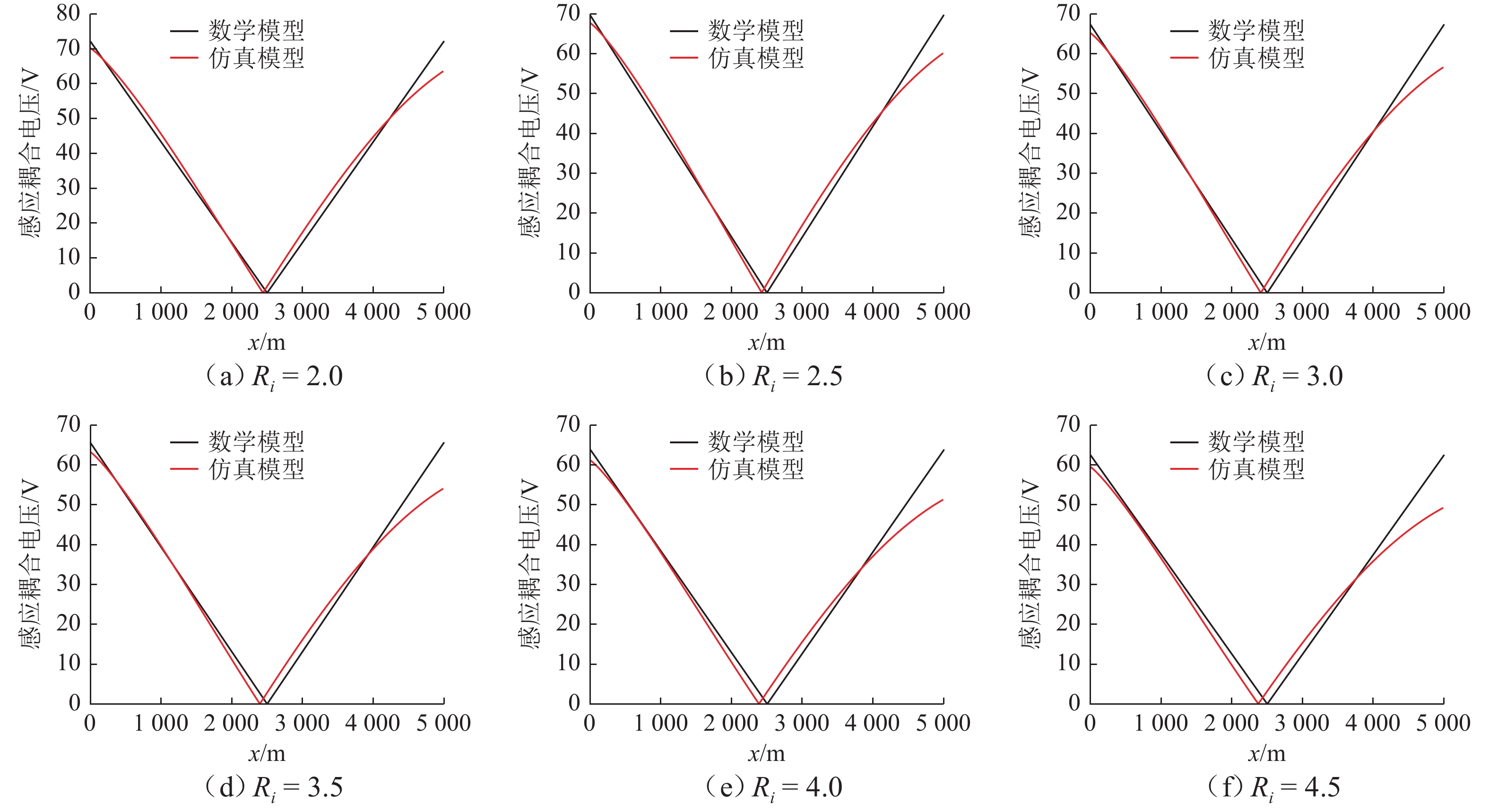
Table 5. Maximum values of inductive coupling voltage of buried pipeline with varying distance ratios
Ri 数学模型/V 仿真模型/V 偏差/% 1.5 75.9 73.5 3.2 2.0 72.2 70.2 2.8 2.5 69.7 67.8 2.7 3.0 67.3 65.2 3.1 3.5 65.6 63.2 3.7 4.0 63.8 61.1 4.2 4.5 62.4 59.4 4.8 表 6 某动车组谐波参数
Table 6. Harmonic parameters of electric multiple unit
主要谐波次数/次 含有率/% 3 1.38 5 2.84 21 3.00 23 4.07 25 2.40 -
[1] 曹建猷. 电气化铁道供电系统[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社,1983. [2] 李群湛,贺建闽. 牵引供电系统分析[M]. 3版. 成都:西南交通大学出版社,2012. [3] 国家发展改革委,交通运输部,国家铁路局,等. 关于推动都市圈市域(郊)铁路加快发展的意见[Z]. 2020. [4] 万红霞,李婷婷,宋东东,等. 杂散电流对埋地管道的腐蚀及排流方式的研究进展[J]. 表面技术,2021,50(4): 125-134.WAN Hongxia, LI Tingting, SONG Dongdong, et al. Research progress of stray current on corrosion and drainage method of buried pipeline[J]. Surface Technology, 2021, 50(4): 125-134. [5] 梁毅,杜艳霞. 交流干扰和阴极保护协同作用下的腐蚀评判标准与机理研究进展[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报,2020,40(3): 215-222. doi: 10.11902/1005.4537.2019.053LIANG Yi, DU Yanxia. Research progress on evaluation criteria and mechanism of corrosion under cathodic protection and AC interference[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2020, 40(3): 215-222. doi: 10.11902/1005.4537.2019.053 [6] 朱久国. 交流电气化铁路对埋地油气管道电磁干扰特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学,2018. [7] 胡士信,路民旭,杜艳霞,等. 管道交流腐蚀的新观点[J]. 腐蚀与防护,2010,31(6): 419-424. [8] 吴荫顺,曹备. 阴极保护和阳极保护:原理、技术及工程应用[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社,2007: 223. [9] WAKELIN R G, SHELDON C. Investigation and mitigation of AC corrosion on a 300 mm diameter natural gas pipeline[C]//The 59th NACE Annual Conference. New Orleans: Corrosion, 2004: 04205.1-04205.9. [10] FLOYD R. Testing and mitigation of AC corrosion on 8 line: a field study[C]//The 59th NACE Annual Conference. New Orleans: Corrosion, 2004: 04210.1-04210.9. [11] LINHARDT P, BALL G. AC corrosion: results from laboratory investigations and from a failure analysis[C]//The 61th NACE Annual Conference. Houston: Corrosion, 2006: 06160.1-06160.9. [12] 任增珺. 日东管道杂散电流干扰检测与防护[J]. 油气储运,2015,34(1): 111-114. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2015.01.024REN Zengjun. Detection and protection of stray current interference of Rizhao–Dongming oil pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2015, 34(1): 111-114. doi: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2015.01.024 [13] CARSON J R. Wave propagation in overhead wires with ground return[J]. Bell System Technical Journal, 1926, 5(4): 539-554 doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1926.tb00122.x [14] 高攸纲,沈远茂,石丹. 交流电气化铁道对周围电气及电子系统的阻性耦合影响[J]. 邮电设计技术,2007(3): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3043.2007.03.013GAO Youzang, SHEN Yuanmao, SHI Dan. Resistive coupling effects of AC electric railway to surrounding electric and electronic system[J]. Designing Techniques of Posts and Telecommunications, 2007(3): 57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3043.2007.03.013 [15] 蒋俊. 交流线路正常运行时对平行敷设油气管道的电磁影响[J]. 电网技术,2008,32(2): 78-80,92.JIANG Jun. Electromagnetic influence of normally operating AC power transmission line on gas/oil pipeline parallel to transmission line[J]. Power System Technology, 2008, 32(2): 78-80,92. [16] 汪可. 电气化铁路对油气管道的影响及防护措施[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学,2013. [17] YONG J, XIA B, YONG H, et al. Harmonic voltage induction on pipelines: measurement results and methods of assessment[C]//IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2018: 2170-2179. [18] 陈民武,朱久国,解绍锋,等. 牵引供电系统对埋地管道阻性耦合交流干扰建模及仿真[J]. 中国铁道科学,2018,39(2): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2018.02.10CHEN Minwu, ZHU Jiuguo, XIE Shaofeng, et al. Modeling and simulation of resistive coupling AC interference of traction power supply system to buried pipeline[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(2): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4632.2018.02.10 [19] 盛望群. 基于CDEGS的交流电气化铁路对沿线油气管道电磁干扰影响研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2020,17(8): 2101-2108.SHENG Wangqun. Study on influence of AC electrified railway on electromagnetic interference of oil and gas pipelines along the line based on CDEGS[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(8): 2101-2108. [20] CHARALAMBOUS C A, DEMETRIOU A, LAZARI A L, et al. Effects of electromagnetic interference on underground pipelines caused by the operation of high voltage AC traction systems: the impact of harmonics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2018, 33(6): 2664-2672. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2018.2803080 [21] 齐磊,崔翔,郭剑,等. 特高压交流输电线路正常运行时对输油输气管道的感性耦合计算模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2010,30(21): 121-126.QI Lei, CUI Xiang, GUO Jian, et al. Inductive coupling modelling of normally operating UHV AC transmission line to adjacent oil/gas pipeline[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30(21): 121-126. [22] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 接地系统的土壤电阻率、接地阻抗和地面电位测量导则 第1部分:常规测量:GB/T 17949.1—2000[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社,2000. [23] 解绍锋,孙镜堤,骆冰祥,等. 高速铁路对邻近普速铁路电力电缆的干扰机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(1): 206-213.XIE Shaofeng, SUN Jingdi, LUO Bingxiang, et al. Mechanism of high-speed railway interference on power cables of adjacent normal-speed railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(1): 206-213. [24] 周胜军,谈萌. 基于监测数据的高铁动车组谐波特性分析[J]. 电力科学与技术学报,2018,33(3): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9140.2018.03.020ZHOU Shengjun, TAN Meng. Harmonic characteristics analysis of electric multiple units in high-speed railway based on the monitoring data[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2018, 33(3): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9140.2018.03.020 [25] 周秀荣. 电气化铁路对通信线路的干扰影响及防护措施[J]. 中国铁路,2007(6): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-683X.2007.06.017 -




 下载:
下载: