Heat-Mass Transfer Test and Coupling Model of Sulfate Saline Soil
-
摘要:
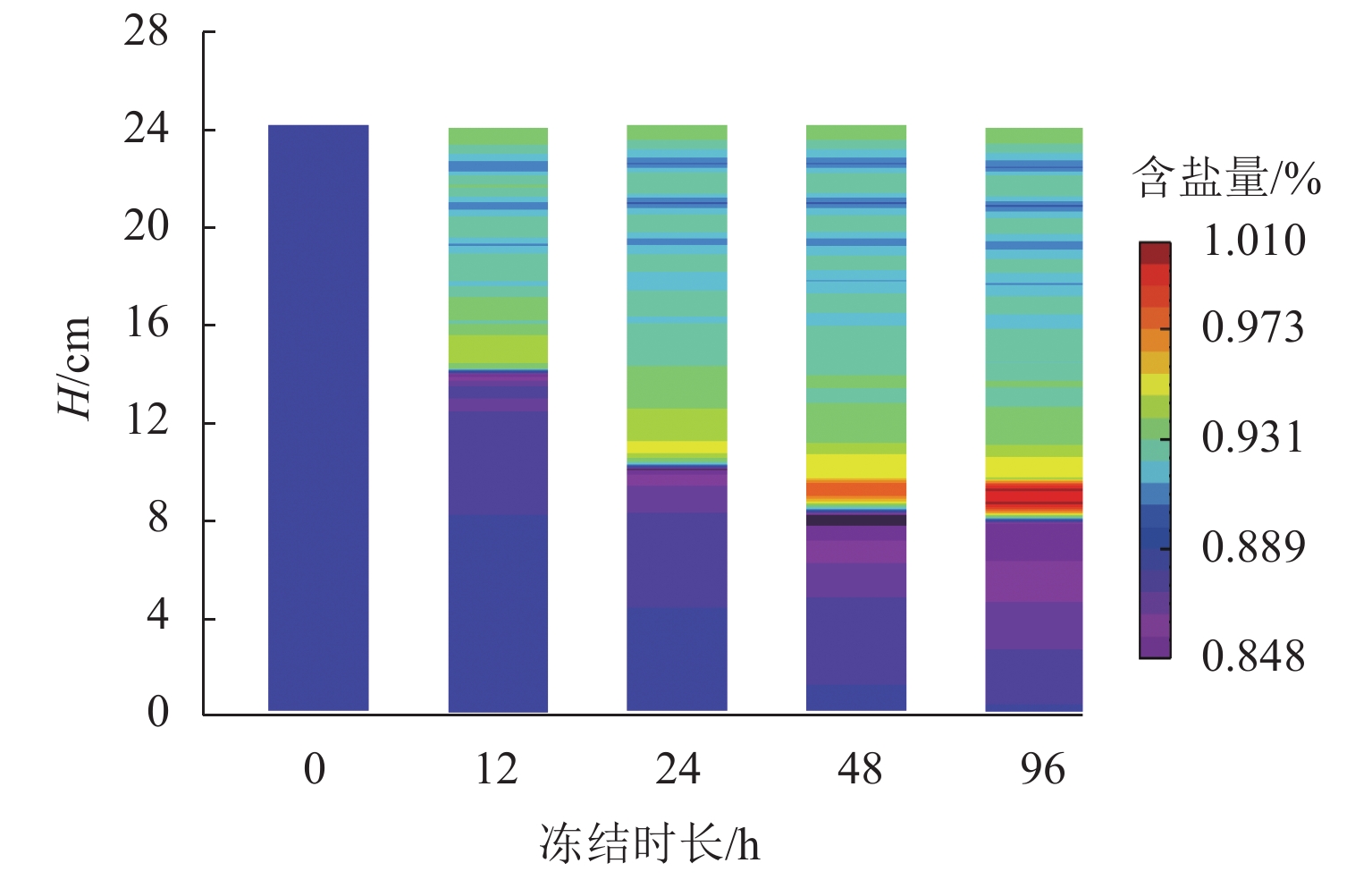
为研究西部寒旱区盐渍土传热传质行为,首先,在无压补给条件下进行非饱和硫酸盐渍土的单向冻结试验;其次,考虑结晶潜热、结晶阻抗及结晶消耗等因素,建立非饱和硫酸盐渍土水-热-盐三场耦合模型;最后,采用COMSOL Multi-physics对耦合模型进行数值模拟,将模拟结果与试验数据进行对比分析. 研究结果表明:盐渍土内温度随冻结时长呈三阶段发展,逐步形成上冷下暖的温度梯度;在温度梯度和基质吸力双重驱动下,水、盐向冻结锋位置迁移,冻结锋位置水、盐含量出现峰值,峰值含水率、含盐量相较初始值分别增加2.16%和0.28%;冻结锋沿冻结温度线移动,形成冻结锋面;土柱最大冻结深度约为15.5 cm.
Abstract:In order to study the heat and mass transfer behavior of saline soil in western cold-arid regions, firstly unsaturated sulfate saline soil experienced unidirectional freezing tests with no pressure recharge. In addition, while the latent heat of crystallization, crystallization impedance and crystallization consumption are considered, a three-field coupling model of water-heat-salt for unsaturated sulfate saline soil is established. Finally, COMSOL Multi-physics is used to simulate the coupling model, the simulation results of which are then compared with the experimental data for analysis. The results show that the internal temperature of saline soils develops in three stages with the freezing time, gradually forming a temperature gradient of cold at the top and warm at the bottom. Driven by both temperature gradient and matrix suction, water and salt migrate to the freezing front position, and the water and salt contents reach peaks at the freezing front position, and compared with the initial values, the peak water content and salt content increase by 2.16% and 0.28%, respectively. The freezing front moves along the frozen temperature line, and forms a freezing front. The maximum freezing depth of soil column is about 15.5 cm.
-
表 1 脱盐后土壤物理力学指标
Table 1. Physical and mechanical indexes of soil samples after desalination
参数 Gs ρmax/(g·cm−3) ωopt/% wL/% wP/% Cu Cc 取值 2.70 1.78 13.7 25.35 12.62 5.29 0.59 表 2 模型参数
Table 2. Model parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 a0 2 Li/(kJ·kg−1) 334.6 m 0.15 Lc/(kJ·kg−1) 210 l 0.5 Cw/(J·(kg·℃) −1) 4180 ɵr 0.002 Ci/(J·(kg·℃) −1) 2090 ɵs 0.397 Cc/(J·(kg·℃) −1) 1090 ks/(m·s−1) 10−6 Cs/(J·(kg·℃) −1) 850 B 0.61 λw/(W·(m·K) −1) 0.58 ρw/(kg·m−3) 1000 λi/(W·(m·K) −1) 2.22 ρi/(kg·m−3) 918 λc/(W·(m·K) −1) 0.14 ρc/(kg·m−3) 1460 λs/(W·(m·K) −1) 1.50 ρs/(kg·m−3) 2700 D0/(m2·h−1) 1.098 × 10−5 ρd/(kg·m−3) 1600 a 0.00261 Mw/(g·mol−1) 180 b 10 Mc/(g·mol−1) 322 α/mm 7.021 -
[1] ZHANG J, LAI Y M, ZHAO Y H, et al. Study on the mechanism of crystallization deformation of sulfate saline soil during the unidirectional freezing process[J]. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 2021, 32(1): 102-118. doi: 10.1002/ppp.2080 [2] WEISBROD N, NIEMET M R, ROCKHOLD M L, et al. Migration of saline solutions in variably saturated porous media[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2004, 72(1/2/3/4): 109-133. [3] 肖泽岸,朱霖泽,侯振荣,等. 盐渍土二次相变温度变化规律[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(8): 64-71. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.08.008XIAO Zean, ZHU Linze, HOU Zhenrong, et al. Temporal variation in eutectic temperature of pore solution in saline soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(8): 64-71. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.08.008 [4] 路建国,万旭升,刘力,等. 降温过程硫酸钠盐渍土水-热-盐相互作用过程[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2022,54(2): 126-134. doi: 10.11918/202102029LU Jianguo, WAN Xusheng, LIU Li, et al. Water-heat-salt interaction of sodium sulfate saline soil during a cooling process[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(2): 126-134. doi: 10.11918/202102029 [5] 张树明,蒋关鲁,杜登峰,等. 新型桩板结构路基在季节冻土区的适用性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(3): 541-549.ZHANG Shuming, JIANG Guanlu, DU Dengfeng, et al. Applicability of novel pile-plank embankment in seasonally frozen regions[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 541-549. [6] 张文,罗艳珍,刘昕,等. 青海盐湖区路基结构层级配及其阻盐效果[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(6): 1264-1271,1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190056ZHANG Wen, LUO Yanzhen, LIU Xin, et al. Gradation of subgrade soil and its salt-resistance effect in salt lake area in Qinghai[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1264-1271,1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190056 [7] XIE Y L, YU Q H, YOU Y H, et al. The changing process and trend of ground temperature around tower foundations of Qinghai−Tibet power transmission line[J]. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 2019, 11(1): 13-20. [8] 罗金明,许林书,邓伟,等. 盐渍土的热力构型对水盐运移的影响研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2008,22(9): 118-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2008.09.023LUO Jinming, XU Linshu, DENG Wei, et al. The influence of thermal dynamic structure of saline soil on water and salinity transportation[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2008, 22(9): 118-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2008.09.023 [9] 周凤玺,周立增,王立业,等. 温度梯度作用下非饱和盐渍土水盐迁移及变形特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(10): 2115-2130.ZHOU Fengxi, ZHOU Lizeng, WANG Liye, et al. Study on water and salt migration and deformation properties of unsaturated saline soil under temperature gradient[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(10): 2115-2130. [10] XU J, LAN W, REN C, et al. Modeling of coupled transfer of water, heat and solute in saline loess considering sodium sulfate crystallization[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2021, 189: 103335.1-103335.13. [11] ZHANG J, LAI Y M, LI J F, et al. Study on the influence of hydro-thermal-salt-mechanical interaction in saturated frozen sulfate saline soil based on crystallization kinetics[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 146: 118868.1-118868.14. [12] RICHARDS L A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums[J]. Physics, 1931, 1(5): 318-333. doi: 10.1063/1.1745010 [13] HANSSON K, ŠIMUNEK J, MIZOGUCHI M, et al. Water flow and heat transport in frozen soil[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2004, 3(2): 693-704. [14] YOUNES A. On modelling the multidimensional coupled fluid flow and heat or mass transport in porous media[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 46(2): 367-379. doi: 10.1016/S0017-9310(02)00264-8 [15] 田亚护,刘建坤,钱征宇,等. 多年冻土区含保温夹层路基温度场的数值模拟[J]. 中国铁道科学,2002(2): 59-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2002.02.009TIAN Yahu, LIU Jiankun, QIAN Zhengyu, et al. Numerical simulation for temperature field of roadlbed on permafrost with insulation[J]. China Railway Science, 2002(2): 59-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4632.2002.02.009 [16] XU J, LAN W, LI Y F, et al. Heat, water and solute transfer in saline loess under uniaxial freezing condition[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2020, 118: 103319.1-103319.20. [17] WANG D Y, LIU J K, LI X. Numerical simulation of coupled water and salt transfer in soil and a case study of the expansion of subgrade composed by saline soil[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 143: 315-322. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.040 [18] 马敏,邴慧,李国玉. 硫酸钠盐渍土未冻水含量的实验研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2016,38(4): 963-969. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2016.0110MA Min, BING Hui, LI Guoyu. Experimental research on unfrozen water content of sodium sulphate saline soil[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2016, 38(4): 963-969. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2016.0110 [19] 张莎莎,叶素纤,张林,等. 粗粒盐渍土路基水热盐力耦合方程修正及试验验证[J]. 公路交通科技,2020,37(3): 31-40.ZHANG Shasha, YE Suqian, ZHANG Lin, et al. Correction of hydrothermal salt force coupled equations for coarse-grained sulphate saline soil roadbed and its experimental verification[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2020, 37(3): 31-40. [20] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路土工试验规程: JTG 3430—2020[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2020. [21] 白青波,李旭,田亚护,等. 冻土水热耦合方程及数值模拟研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(增2): 131-136. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2015S2026BAI Qingbo, LI Xu, TIAN Yahu, et al. Equations and numerical simulation for coupled water and heat transfer in frozen soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(S2): 131-136. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2015S2026 [22] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892-898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x [23] 牛玺荣. 硫酸盐渍土地区路基水、热、盐、力四场耦合机理及数值模拟研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2006. [24] 徐学祖, 王家澄, 张立新. 冻土物理学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. -





 下载:
下载: