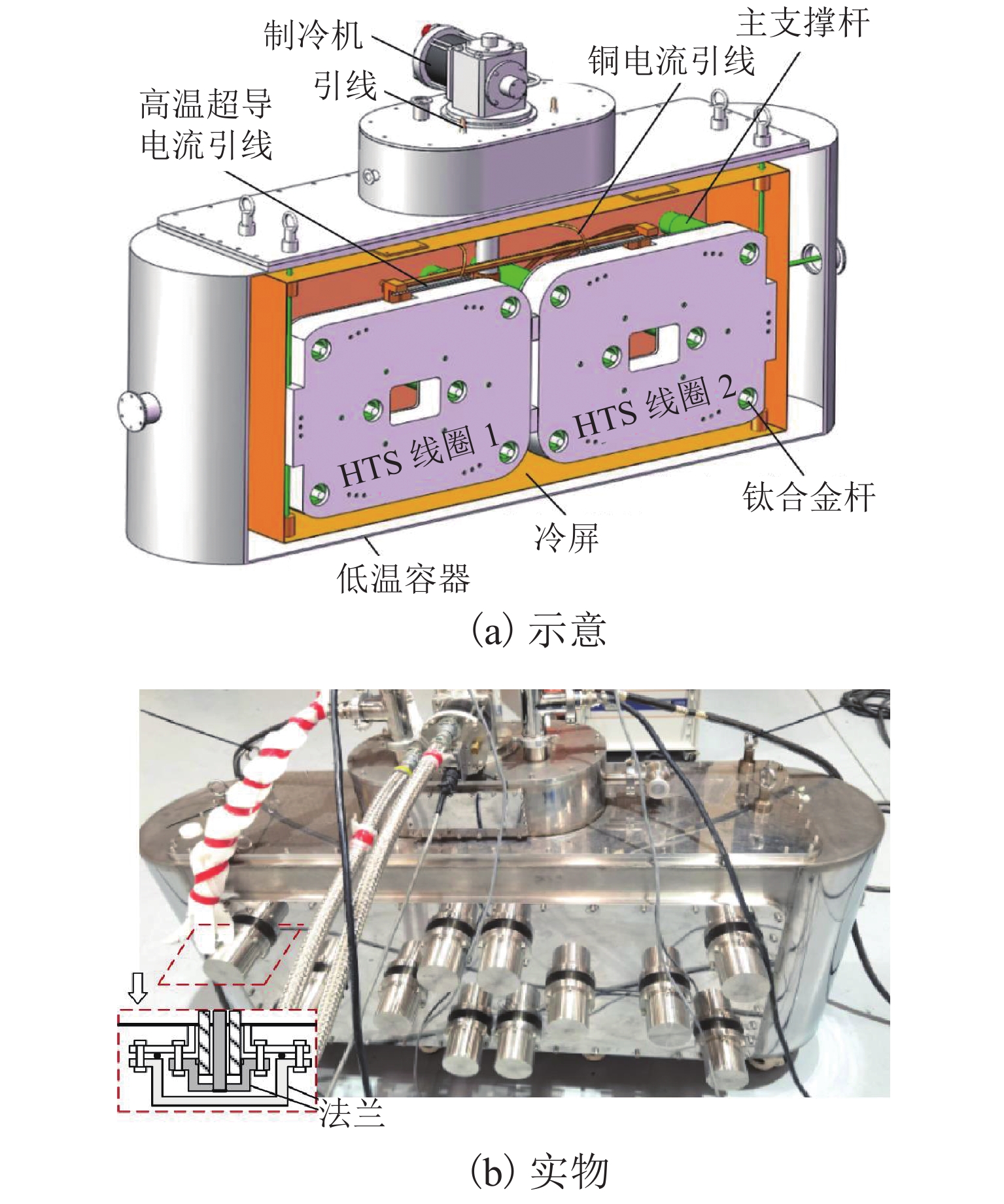
Review on Electrodynamic Suspension Trains and on-Board Superconducting Magnets
-
摘要:
电动悬浮列车具有速度高、悬浮间隙大、安全系数高等优点,在超高速磁悬浮列车领域具有十分光明的应用前景. 车载超导磁体是超导电动悬浮列车的核心组成部分之一,其服役可靠性是列车安全运行的重要基础. 本文系统地阐述国内外电动悬浮列车的发展历史及现状,针对国内外电动悬浮系统中车载超导磁体的结构和技术方案进行对比和总结. 高温超导磁体技术已经成为超导电动悬浮领域的重要发展方向,在列车行驶过程中车载超导磁体系统的热稳定性和振动稳定性是影响其可靠服役的重要因素. 高温超导磁体闭环运行技术、轻量小型化低温系统结构设计、高强度低漏热支撑结构设计等将是未来超导电动悬浮系统中车载超导磁体需要重点研究和解决的关键技术难题.
Abstract:The electrodynamic suspension (EDS) train has the advantages of high speed, large suspension gap, and high safety factor. It has a bright application prospect in the field of ultra-high-speed maglev trains. The on-board superconducting magnet is one of the core components of the superconducting EDS train, and its reliability in service is the basis for the safe operation of the train. In this paper, the development history and status of EDS trains in China and abroad were summarized, and the structure and technical solutions of on-board superconducting magnets in global EDS systems were compared and summarized. The high-temperature superconducting (HTS) magnet technology has become an important development direction in the field of superconducting EDS. The thermal and vibration stability of the on-board superconducting magnet system during the running of the train is an important factor affecting its reliable service. The closed-loop operation technology of HTS magnets, the structural design of lightweight and miniaturized cryogenic systems, and that of high-strength and low heat leakage support devices will be the key technical problems that need to be studied and solved for the on-board superconducting magnets in superconducting EDS systems in the future.
-
悬浮
类型悬浮原理 悬浮高
度/mm最高试验速
度/(km·h−1)最高应用速
度/(km·h−1)悬浮、导
向控制车载
磁体路轨
铺设车辆重量
(单节车厢)研究
进展EMS 车载磁体与铁磁轨道之间的相互吸引产生悬浮力 8~10 550
(德国 TR09)430
(上海磁浮
线 TR08)需要闭环控制,有静态悬浮 电磁铁 硅钢片 重,56.5 t
(德国 TR09)商业
运营EDS 车载磁体与“8”字线圈、导电板之间相对运动产生悬浮力 80~150
(超导电动
悬浮),
20~30
(永磁电动
悬浮)603
(JR 东
海 L0)505
(日本山梨
试验线 L0)自稳定,无需控制,无静态悬浮 超导磁
体,永磁体“8”字线圈,金属导电板 轻,25 t
(JR 东
海 L0)准商
业运营SPL 非理想第二类超导体的抗磁特性产生
悬浮力10~30 300
(西南交通
大学模型车)自稳定,无需控制,有静态悬浮 超导块材 永磁导轨 轻,12 t
(西南交通
大学工程
化样车)试验
阶段参数 取值 悬浮方式 电动悬浮 编组 5 / 7 / 12 车辆尺寸(单节车厢)/m 长 25,宽 2.9,高 3.08 重量/(t·车厢−1) 25 设计最高速度/(km·h−1) 603 运行速度/(km·h−1) 505 表 3 日本历代车载超导磁体主要技术参数对比[51, 59]
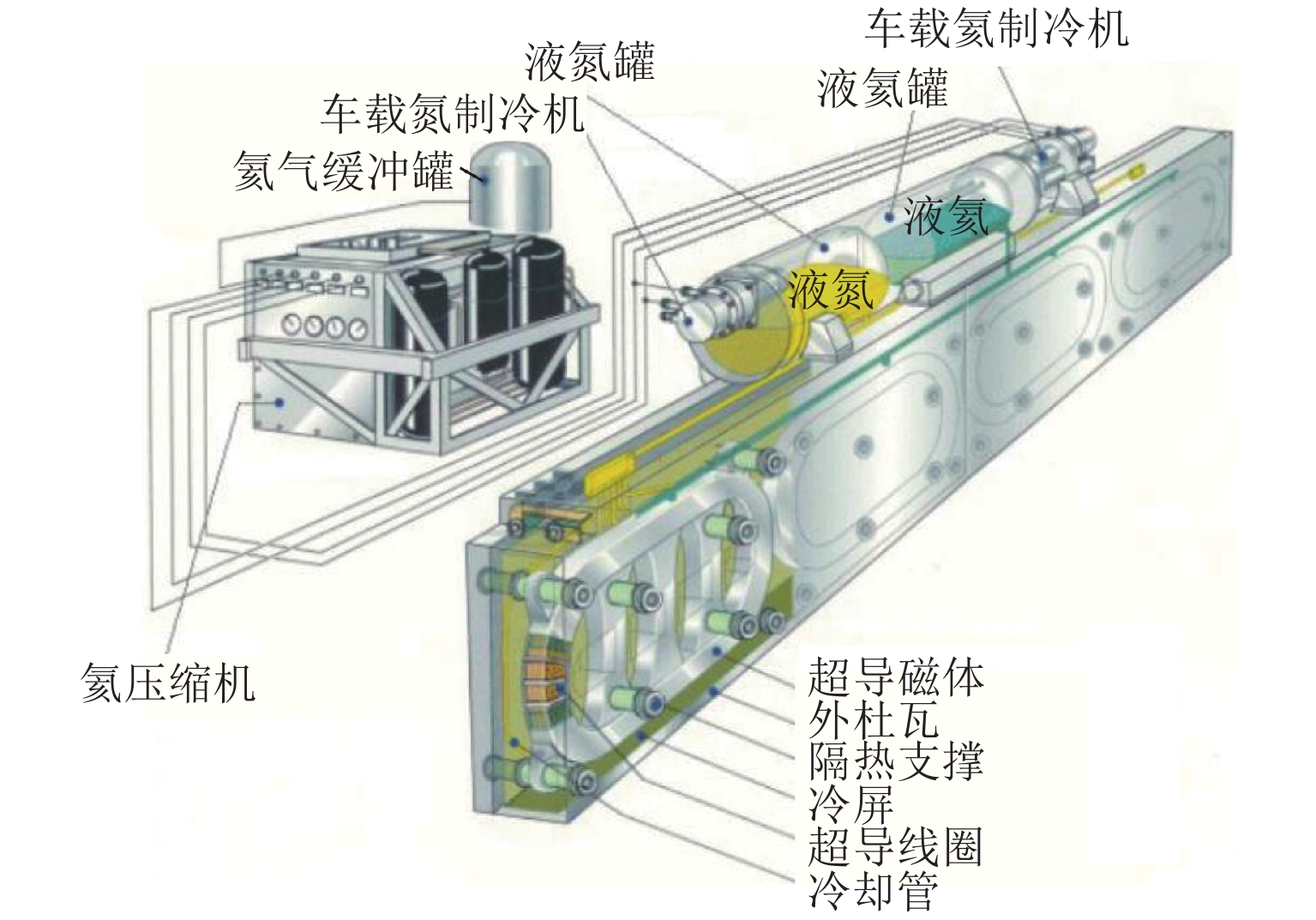
Table 3. Comparison of main technical parameters of on-board superconducting magnets developed in Japan[51, 59]
磁体
类型线圈尺寸/
mm额定电
流/A匝数/匝 导线材料 匝间
绝缘运行
方式电流衰减
率/(%·d−1)线圈工作
温度/K冷却方式 研究进展 LTS 长 1070,
宽 500500 1400 NbTi 闭环 < 0.1 4.2 液氦浸泡冷却,GM-JT 制冷机辅助 装车运行 一代
HTS长 1070,
宽 500536 1400 Bi-2223 闭环 0.4~0.7 < 20.0 GM 双极制冷机,
传导冷却单个磁体装车运行 二代
HTS长 1070,
宽 500250 2800 ReBCO 绝缘 开环 约 13.0 30.0~40.0 GM 制冷机,
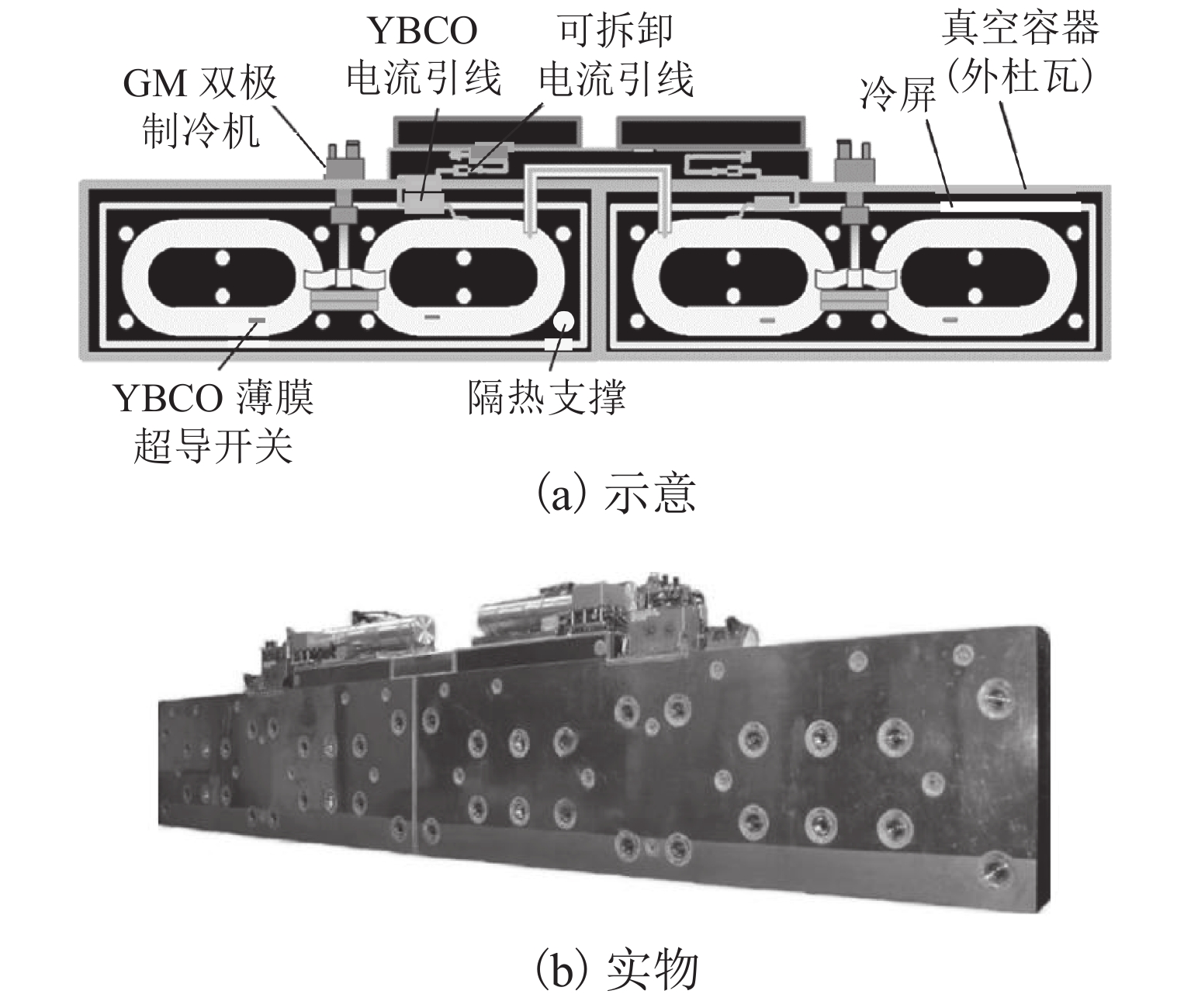
传导冷却降温、励磁、振动、涡流,地面试验 磁体类型 线圈尺
寸/mm磁动势/
kA运行电
流/A匝数/匝 导线
材料匝间
绝缘运行
方式线圈工作温度/K 冷却方式 研究进展 2020 年全尺寸推进车载磁体 长 520,
宽 420300 126.0 2610 ReBCO 无绝缘 开环 < 20.0 GM 双极制冷机,传导冷却 降温、励磁、推进,地面实验 2021 年1/2 尺寸车载磁体 长 600,
宽300150 85.4 1760 ReBCO 金属
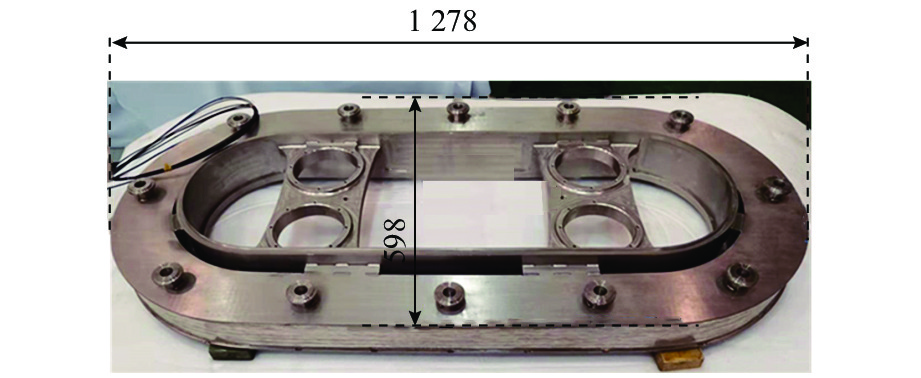
绝缘闭环 30.0~40.0 氦气提前冷却,固氮保温 降温、励磁,地面实验 表 5 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院车载LTS磁体主要技术参数[68-69]
Table 5. Main technical parameters of on-board LTS magnet developed by Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, CAS[68-69]
项目 参数 磁体尺寸/mm 长 1278,宽 598,高 78 导线材料 NbTi 额定电流/A 274 匝数/匝 2 738 线圈工作温度/K 4.6 研究进展 试验阶段 表 6 中国上海交通大学车载HTS磁体主要技术参数[71-74, 76-77]
Table 6. Main technical parameters of on-board HTS magnet developed by SJTU, China [71-74, 76-77]
团队
名称磁体尺
寸/m磁动
势/kA导线材料 匝数/匝 匝间绝缘 运行
方式电流衰减
率/( %·d−1)线圈工作
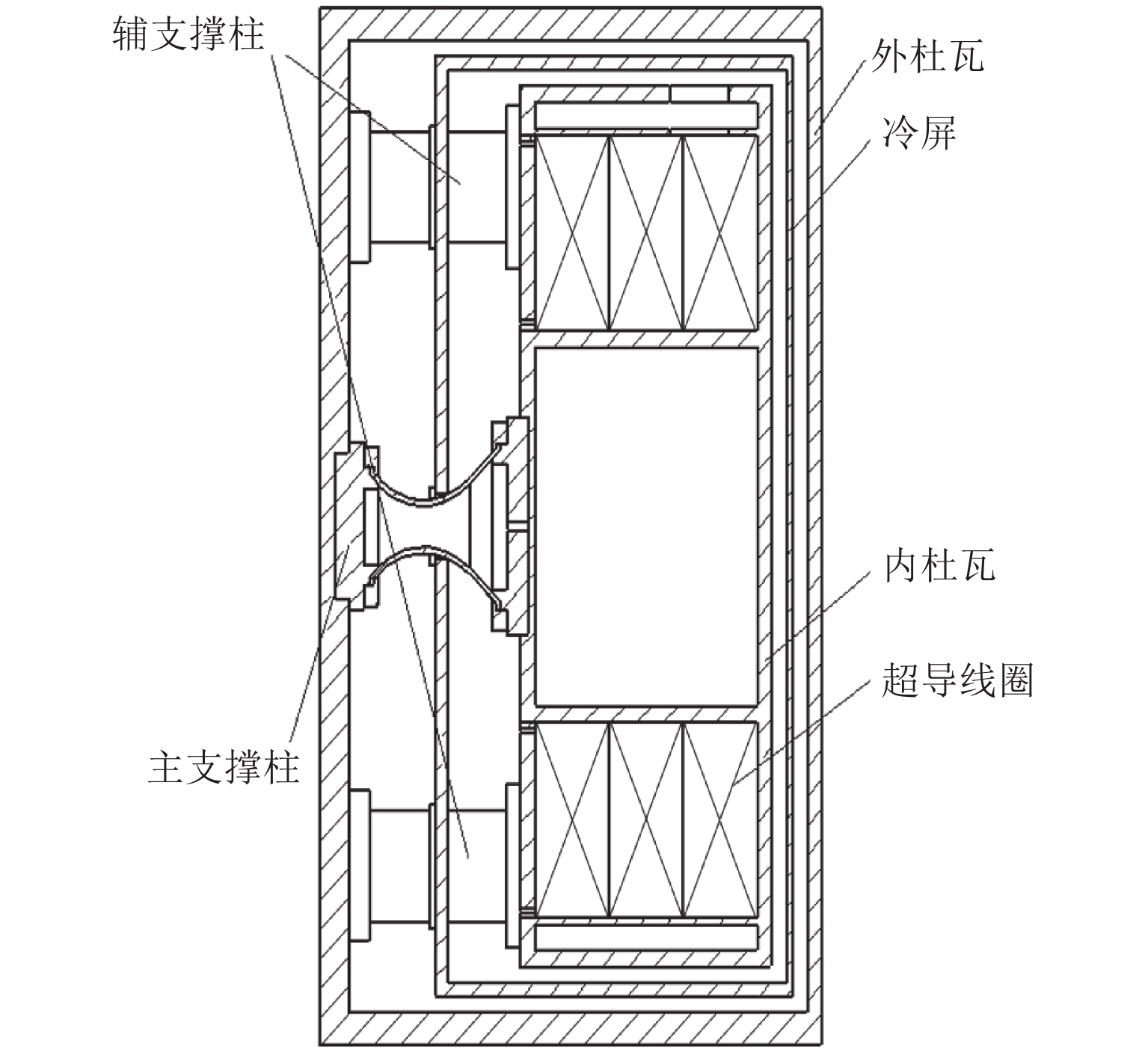
温度/K冷却方式 研究进展 黄振团队 长 0.83,
宽 0.24,
高 0.93360 ReBCO 2400 无绝缘 闭环 2.0 30.0~40.0 可插拔制冷机冷却,固氮辅助冷却 降温、励磁、振动,
地面试验吴蔚团队 长 1.6,
宽 0.3,
高 0.8360 ReBCO 1800 无绝缘 闭环 < 1.1 < 35.6 可插拔制冷机冷却,
固氮辅助冷却已研制5台磁体,
并投入试验运行 -
[1] 魏庆朝, 孔永健, 时瑾. 磁浮铁路系统与技术 [M]. 2版. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2010. [2] LEE H W, KIM K C, LEE J. Review of maglev train technologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2006, 42(7): 1917-1925. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2006.875842 [3] 熊嘉阳,邓自刚. 高速磁悬浮轨道交通研究进展[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 177-198. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.01.008XIONG Jiayang, DENG Zigang. Research progress of high-speed maglev rail transit[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 177-198. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.01.008 [4] DENG Z G, ZHANG W H, WANG L, et al. A high-speed running test platform for high-temperature superconducting maglev[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2022, 32(4): 3600905.1-3600905.5. [5] 朱雪黎. 世界首台高温超导高速磁浮工程化样车在川启用 [N/OL]. 四川日报, 2021-01-14 [2022-09-05]. https://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/12771/2021/1 /14/5cd0cf013e9f4cb0bce30fb0f58f5230.shtml. [6] Central Japan Railway Company. About the vehicle[EB/OL]. [2022-09-05]. https://scmaglev.jr-central-global.com/abou t/design. [7] MEINS J, MILLER L, MAYER W J. The high speed maglev transport system TRANSRAPID[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1988, 24(2): 808-811. doi: 10.1109/20.11347 [8] NAKAMURA S. Development of high speed surface transport system (IISST)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1979, 15(6): 1428-1433. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.1979.1060437 [9] 吴祥明,常文森,刘万明. 上海高速磁浮列车及磁浮技术发展刍议[J]. 综合运输,2005,27(1): 28-31. [10] 宫崎聡夫,张芳. 磁悬浮列车的液压制动装置[J]. 国外机车车辆工艺,2017(4): 20-23. [11] 付敬懿. 长沙中低速磁浮快线开通试运营[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2016,19(6): 116. [12] 刘珜. S1线等三条地铁新线周六开通 [N/OL]. 北京青年报, 2017-12-28 [2022-09-05]. https://www.so hu.com/a/213177044_255783. [13] 黎棠. 凤凰磁浮观光快线正式开通运营 [N/OL]. 潇湘晨报, 2022-07-30 [2022-10-27]. https://baijiah ao.baidu.com/s?id=1739780194246544640&wfr=spider&for=pc. [14] 张娟. 超导电动悬浮磁力特性及超导磁浮车辆动力学仿真分析 [D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020. [15] 王麟. 轨道交通的前世今生 [M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2018. [16] 马光同,杨文姣,王志涛,等. 超导磁浮交通研究进展[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(7): 68-74,82.MA Guangtong, YANG Wenjiao, WANG Zhitao, et al. Research development of superconducting maglev transportation[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(7): 68-74,82. [17] 邓自刚,刘宗鑫,李海涛,等. 磁悬浮列车发展现状与展望[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2022,57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001DENG Zigang, LIU Zongxin, LI Haitao, et al. Development status and prospect of maglev train[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(3): 455-474,530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220001 [18] 邓自刚,李海涛. 高温超导磁悬浮车研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展,2017,36(5): 329-334,351. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2017.05.02DENG Zigang, LI Haitao. Recent development of high-temperature superconducting maglev[J]. Materials China, 2017, 36(5): 329-334,351. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2017.05.02 [19] 王家素,王素玉. 高温超导磁悬浮列车研究综述[J]. 电气工程学报,2015,10(11): 1-10. doi: 10.11985/2015.11.001WANG Jiasu, WANG Suyu. High temperature superconducting maglev train[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2015, 10(11): 1-10. doi: 10.11985/2015.11.001 [20] 马卫华,罗世辉,张敏,等. 中低速磁浮车辆研究综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(1): 199-216. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.01.009MA Weihua, LUO Shihui, ZHANG Min, et al. Research review on medium and low speed maglev vehicle[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 199-216. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.01.009 [21] 李家志,索红莉,王毅,等. 超导材料在磁悬浮列车上的应用进展(上)[J]. 铁道技术监督,2020,48(3): 38-44.LI Jiazhi, SUO Hongli, WANG Yi, et al. Progress in the application of superconducting materials on maglev trains (part 1 of 2)[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2020, 48(3): 38-44. [22] OHSAKI H. Review and update on maglev[R]. Karlsruhe: European Cryogenics Days, 2017. [23] EASTHAM A R, HAYES W F. Maglev systems development status[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 1988, 3(1): 21-30. doi: 10.1109/62.843 [24] SAIJO T, KOIKE S, TADAKUMA S. Characteristics of linear synchronous motor drive cycloconverter for maglev vehicle ML-500 at Miyazaki test track[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 1981, IA-17(5): 533-543. doi: 10.1109/TIA.1981.4503994 [25] KYOTANI Y. Recent progress by JNR on maglev[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1988, 24(2): 804-807. doi: 10.1109/20.11346 [26] 商福昆. 宫崎实验线新磁浮实验车MLU—002N[J]. 铁道机车车辆,1995,15(1): 58-60. [27] ONO M, KOGA S, OHTSUKI H. Japan’s superconducting maglev train[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2002, 5(1): 9-15. [28] SAWADA K. Outlook of the superconducting maglev[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2009, 97(11): 1881-1885. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030246 [29] 蓝建中. 日本超导磁浮列车时速创纪录[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2015,18(5): 134. [30] POWELL J R, DANBY G R. High speed transport by magnetically suspended trains[J]. Mechanical Engineering, 1966, 89(4): 66. [31] THORNTON R D. Efficient and affordable maglev opportunities in the United States[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2009, 97(11): 1901-1921. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030251 [32] THOME R, RADOVINSKY A, MONTGOMERY B. EDS levitation and guidance using sheet guideways [C]//Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Magnetically Levitated Systems and Linear Drives. Rio de Janeiro: [s.n.], 2000: 236-241. [33] 张瑞华,刘育红,徐善纲. 美国Magplane磁悬浮列车方案介绍[J]. 变流技术与电力牵引,2005(5): 40-43.ZHANG Ruihua, LIU Yuhong, XU Shangang. American Magplane schemes[J]. Converter Technology & Electric Traction, 2005(5): 40-43. [34] Courtesy Hyperloop Transportation Technologies. New full-scale hyperloop passenger capsule revealed [EB/OL]. (2018-10-03) [2022-09-05]. https://edition.cnn.com/travel/article/hyperloop-capsule/index.html. [35] 武瑛严,陆光,徐善纲. Inductrack磁浮技术及其在磁浮列车系统中的应用[J]. 电气应用,2006,25(1): 1-3. [36] ANDREW J H. Mile stone: the first human passenger test [EB/OL]. (2020-11-19) [2022-09-05]. https://virginhyperloop.com/pegasus. [37] 谭斌. 高温超导电动悬浮轨道结构研究[J]. 铁道建筑技术,2021(6): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2021.06.006TAN Bin. Study on the structure of high-temperature superconducting electrodynamic suspension track[J]. Railway Construction Technology, 2021(6): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2021.06.006 [38] 杨文俊. 高速飞车山西省实验室揭牌暨大同(阳高)试验线工程开工奠基仪式在大同举行 [N/OL]. 山西日报, 2021-05-25 [2022-09-05]. http://www.shanxi.gov.cn/yw/zwhd/202105/t20210525_920032.shtml. [39] 磁电总体部. 国内首次全尺寸超导航行试验成功 [EB/OL]. 2023-01-14 [2023-02-20]. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_ dPNZyZqVDNCsqUcOhZC2Q. [40] NISHIJIMA S, ECKROAD S, MARIAN A, et al. Superconductivity and the environment: a roadmap[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2013, 26(11): 113001.1-113001.35. [41] FUJIMOTO S, TANEYA S, KURIHARA T, et al. Development of a 4K GM/JT refrigerator for maglev vehicle [C]//Proceedings of 16th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference/International Cryogenic Materials Conference. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1997: 331-334. [42] KONDO Y, TERAI M, NISHIKAWA Y, et al. Development of a GM-type pulse tube refrigerator cooling system for superconducting maglev vehicles [M]//ROSS R G. Cryocoolers 13. Boston: Springer, 2005: 681-687. [43] 中尾裕行, 高橋政彦, 真田芳直, 等. 浮上式鉄道用超電導磁石の4K/80K両用GM冷凍システムの開発[J]. 低温工学, 1999, 34(2): 65-72. doi: 10.2221/jcsj.34.65NAKAO H, TAKAHASHI M, SANADA Y, et al. Development of a 4K/80K multiple operating type of GM refrigeration system for the superconducting magnet in maglev use cooling characteristics of the nitrogen self-circulated cooling-type radiation shield plate [J]. TEION KOGAKU (Journal of Cryogenics and Superconductivity Society of Japan), 1999, 34(2): 65-72. doi: 10.2221/jcsj.34.65 [44] 服部敏雄, 青山博, 福士慶滋. 超電導磁石の荷重支持構造, 荷重支持体並びに磁気浮上列車: 平 4-162405[P]. 1992-06-05. [45] 王秋良. 高磁场超导磁体科学 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. [46] KUSADA S, IGARASHI M, KUWANO K, et al. Persistent current HTS magnet cooled by cryocooler (2)−magnet configuration and persistent current operation test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2005, 15(2): 2285-2288. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.849632 [47] TOSAKA T, TASAKI K, MARUKAWA K, et al. Persistent current HTS magnet cooled by cryocooler (4)−persistent current switch characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2005, 15(2): 2293-2296. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.849634 [48] TASAKI K, TOSAKA T, MARUKAWA K, et al. Persistent current HTS magnet cooled by cryocooler (3)−HTS magnet characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2005, 15(2): 2289-2292. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.849633 [49] IGARASHI M, NAKAO H, TERAI M, et al. Persistent current HTS magnet cooled by cryocooler (1)−project overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2005, 15(2): 1469-1472. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2005.849130 [50] TERAI M, IGARASHI M, KUSADA S, et al. The R&D project of HTS magnets for the superconducting maglev[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2006, 16(2): 1124-1129. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2006.871342 [51] KUWANO K, IGARASHI M, KUSADA S, et al. The running tests of the superconducting maglev using the HTS magnet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2007, 17(2): 2125-2128. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2007.899003 [52] OGATA M, MIYAZAKI Y, HASEGAWA H, et al. Basic study of HTS magnet using 2G wires for maglev train[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2010, 470(20): 1782-1786. doi: 10.1016/j.physc.2010.05.206 [53] OGATA M, MIZUNO K, ARAI Y, et al. Study on applicability of rare earth high-temperature superconducting wires to superconducting magnet for maglev system[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2010, 51(3): 151-155. [54] OGATA M, MIZUNO K, ARAI Y, et al. Trial manufacture of small HTS magnet using 2G tapes for maglev train application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2011, 21(3): 1556-1559. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2010.2091487 [55] TAKEMATSU T, HU R, TAKAO T, et al. Degradation of the performance of a YBCO-coated conductor double pancake coil due to epoxy impregnation[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2010, 470(17/18): 674-677. [56] IWAI S, MIYAZAKI H, TOSAKA T, et al. Development of large-scale racetrack coil wound with REBCO-coated conductors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2014, 24(3): 4600705.1-4600705.5. [57] MIZUNO K, OGATA M, HASEGAWA H. Manufacturing of REBCO coils strongly bonded to cooling members with epoxy resin aimed at its application to maglev[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2014, 506: 138-142. doi: 10.1016/j.physc.2014.06.009 [58] MIZUNO K, OGATA M, HASEGAWA H. Manufacturing of a REBCO racetrack coil using thermoplastic resin aiming at maglev application[J]. Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications, 2015, 518: 101-105. doi: 10.1016/j.physc.2015.06.016 [59] MIZUNO K, SUGINO M, TANAKA M, et al. Experimental production of a real-scale REBCO magnet aimed at its application to maglev[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2017, 27(4): 3600205.1-3600205.5. [60] MIZUNO K, SUGINO M, OGATA M. Experimental production and evaluation of racetrack coils for REBCO on-board magnet[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2016, 57(3): 234-239. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.57.3_234 [61] MIZUNO K, SUGINO M, TANAKA M, et al. Development of a real-scale REBCO coil for the demonstration of a magnetomotive force of 700 kA[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2017, 58(4): 318-323. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.58.4_318 [62] MIZUNO K, TANAKA M, OGATA M. Evaluation of eddy current heating in a REBCO magnet due to the magnetic field of ground coils for the maglev[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2020, 33(7): 074009.1-074009.6. [63] MIZUNO K, TANAKA M, OGATA M, et al. Mechanical vibration test of a REBCO coil designed for application to the maglev[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2018, 28(4): 3601107.1-3601107.6. [64] PARK C B, LEE C Y, YOON S, et al. Development of a small-scale superconducting LSM using Gd-Ba-Cu-O high-temperature superconducting wire[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2016, 31(4): 1250-1256. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2016.2577058 [65] MUN J, LEE C, KIM K, et al. Operating thermal characteristics of REBCO magnet for maglev train using detachable cooling system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2019, 29(5): 3603305.1-3603305.5. [66] LEE C Y, LEE J H, LIM J, et al. Design and evaluation of prototype high-Tc superconducting linear synchronous motor for high-speed transportation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2020, 30(4): 3602205.1-3602205.5. [67] MUN J, LEE C, LEE C, et al. Thermal and electromagnetic performance evaluation of REBCO magnet with solid nitrogen thermal battery for maglev train[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2021, 31(5): 3601405.1-3601405.5. [68] ZHENG J X, ZOU C L, LIU X F, et al. Development of high current density, compactness NbTi superconducting coil for the maglev system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2023, 33(1): 4900205.1-4900205.10. [69] 中国科学技术大学. 中科院合肥物质研究院“高载流跑道型低温超导磁体研制”项目通过航天科工集团验收 [EB/OL]. (2022-05-25) [2022-09-05]. http://qybx.ustc.edu.cn/2022/0525/c20985a 556003/page.htm [70] 宋云涛, 郑金星, 刘旭峰, 等. 一种用于超导磁悬浮列车的高温超导磁体装置及使用方法: 202011185421[P]. 2021-07-20. [71] DONG F L, HUANG Z, HAO L N, et al. An on-board 2G HTS magnets system with cooling-power-free and persistent-current operation for ultrahigh speed superconducting maglevs[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 11844.1-11844.12. [72] DONG F L, HUANG Z, XU X Y, et al. Improvement of magnetic and cryogenic energy preservation performances in a feeding-power-free superconducting magnet system for maglevs[J]. Energy, 2020, 190: 116403.1-116403.11. [73] WU W, YU X, ZHANG C, et al. Development of on-board HTS magnets for EDS-type maglev trains[R]. Tampa: Applied Superconductivity Conference, 2020. [74] 吴蔚, 李凯, 邵南, 等. 电动磁浮车载高温超导磁体全断电运行特性 [C]//第十届全国磁悬浮技术与振动控制学术会议论文集. 沈阳: [出版地不详], 2022: 101. [75] SHAO Q, LI K, SHAO N, et al. Multiphysics field topology optimization design of main support structure of high-temperature superconducting magnets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2022, 32(6): 4902005.1-4902005.5. [76] DONG F L, HUANG Z, LI X F, et al. R&D of no-insulation HTS magnets using 2G wires in a prototype for maglev applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2019, 29(5): 4601905.1-4601905.5. [77] LU L, WU W, YU X, et al. High-temperature superconducting non-insulation closed-loop coils for electro-dynamic suspension system[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(16): 1980.1-1980.14. [78] MA G T, GONG T Y, WANG R C, et al. Design, fabrication and testing of a coated conductor magnet for electrodynamic suspension[J]. Superconductor Science and Technology, 2022, 35(2): 025013.1-025013.13. [79] 蒋久福,盛荣进,聂兴超,等. 铝制传导冷却低温容器的结构设计与强度分析[J]. 低温与超导,2021,49(9): 32-37.JIANG Jiufu, SHENG Rongjin, NIE Xingchao, et al. Structural design and strength analysis of aluminum cryostat with conduction cooling[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2021, 49(9): 32-37. [80] 盛荣进,蒋久福,聂兴超,等. 制冷机可插拔式固氮低温容器的热性能研究[J]. 低温工程,2021(4): 40-46,58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6516.2021.04.008SHENG Rongjin, JIANG Jiufu, NIE Xingchao, et al. Study on thermal characteristics of solid nitrogen cryogenic system with detachable cryocooler[J]. Cryogenics, 2021(4): 40-46,58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6516.2021.04.008 [81] HE J L, ROTE D M, COFFEY H T. Applications of the dynamic circuit theory to maglev suspension systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1993, 29(6): 4153-4164. doi: 10.1109/20.280868 [82] HE J L, ROTE D M. Double-row loop-coil configuration for EDS maglev suspension, guidance, and electromagnetic guideway directional switching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1993, 29(6): 2956-2958. doi: 10.1109/20.280905 [83] DAVEY K, MORRIS T, SHAAF J, et al. Calculation of motion induced eddy current forces in null flux coils[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1995, 31(6): 4214-4216. doi: 10.1109/20.489930 [84] MURAI T. Characteristics of LSM combined propulsion, levitation and guidance[J]. Electrical Engineering in Japan, 1995, 115(4): 134-145. doi: 10.1002/eej.4391150412 [85] MURAI T, FUJIMOTO T, FUJIWARA S. Test run of combined propulsion, levitation and guidance system at Miyazaki test track[J]. Electrical Engineering in Japan, 1996, 117(2): 68-79. doi: 10.1002/eej.4391170207 [86] 万尚军,钱金根,倪光正,等. 电动悬浮型磁悬浮列车悬浮与导向技术剖析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2000,20(9): 23-25,31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2000.09.006WAN Shangjun, QIAN Jingen, NI Guangzheng, et al. Study of the levitation and guidance technology for electrodynamic suspension maglev vehicle[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2000, 20(9): 23-25,31. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2000.09.006 [87] CAI Y, MA G T, WANG Y Y, et al. Semianalytical calculation of superconducting electrodynamic suspension train using figure-eight-shaped ground coil[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2020, 30(5): 3602509.1-3602509.9. [88] GONG T Y, MA G T, WANG R C, et al. 3-D FEM modeling of the superconducting EDS train with cross-connected figure-eight-shaped suspension coils[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2021, 31(3): 3600213.1-3600213.13. [89] SU Z H, LUO J, MA G T, et al. Fast and precise calculation of mutual inductance for electrodynamic suspension: methodology and validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(6): 6046-6057. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3088362 [90] SU Z H, MA G T, LUO J. Analytical modeling of the closed-loop operation and quench behavior for superconducting electrodynamic suspension train[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2022, 8(1): 1026-1039. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2021.3119290 [91] FUJIMOTO T, AIBA M, SUZUKI H, et al. Characteristics of electromagnetic force of ground coil for levitation and guidance at the yamanashi maglev test line[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2000, 41(2): 63-67. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.41.63 [92] CAI Y, ROTE D M, MULCAHY T M, et al. Dynamic stability of repulsive-force maglev suspension systems [R]. Illinois: Argonne National Laboratory, 1996. [93] CHO H, BAE D K, SUNG H K, et al. Experimental study on the electrodynamic suspension system with HTSC and PM Halbach array magnets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2008, 18(2): 808-811. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2008.921290 [94] MA G T, WANG Y Y, LUO J, et al. An analytical-experiment coupling method to characterize the electrodynamic suspension system at various speeds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(7): 7170-7180. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3097600 [95] OHMORI J, NAKAO H, YAMASHITA T, et al. Heat load tests of superconducting magnets vibrated electromagnetically for the Maglev train[J]. Cryogenics, 1997, 37(8): 403-407. doi: 10.1016/S0011-2275(97)00033-7 [96] TANAKA M, AIBA M, SUZUKI M. Electromagnetic vibration test for durability verification of ground coil[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2007, 48(2): 110-114. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.48.110 [97] JIZO Y, AKAGI H, YAMAGUCHI T, et al. Heat load characteristics and new design using one-coil model superconducting magnets[J]. Cryogenics, 1997, 37(7): 371-379. doi: 10.1016/S0011-2275(97)00034-9 [98] SUZUKI E. Heating phenomena in the superconducting magnet of a maglev vehicle caused by electromagnetic vibration[J]. Cryogenics, 1997, 37(7): 363-370. doi: 10.1016/S0011-2275(97)00029-5 [99] 龚天勇,马光同,罗俊,等. 行波磁场中高温超导电动悬浮磁体的热性能研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2023,43(1): 415-425. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.220245GONG Tianyong, MA Guangtong, LUO Jun, et al. Study on the thermal performance of high-temperature superconducting electrodynamic suspension magnet subjected to travelling magnetic fields[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(1): 415-425. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.220245 [100] OHASHI S. Effect of the damper coils on the rotational motion of the superconducting magnetically levitated bogie[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2000, 36(5): 3680-3682. doi: 10.1109/20.908939 [101] OHASHI S. Effect of the active damper coils of the superconducting magnetically levitated bogie in case of acceleration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2008, 44(11): 4163-4166. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2008.2002788 [102] OHASHI S, OHSAKI H, MASADA E. Effect of the active damper coil system on the lateral displacement of the magnetically levitated bogie[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1999, 35(5): 4001-4003. doi: 10.1109/20.800735 [103] OHASHI S, UESHIMA T. Control method of the semi-active damper coil system in the superconducting magnetically levitated bogie against vertical and pitching oscillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2012, 48(11): 4542-4545. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2012.2202378 [104] 胡道宇,冯馨月,张志华. 超导电动悬浮系统阻尼特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2021,41(13): 4679-4688.HU Daoyu, FENG Xinyue, ZHANG Zhihua. Study on the damping characteristics of superconducting electrodynamic suspension system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(13): 4679-4688. [105] OGATA M, OKINO T, IKEDA K, et al. Vibration characteristics of superconducting magnets for the yamanashi maglev test line vehicles[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2000, 41(2): 79-82. doi: 10.2219/rtriqr.41.79 [106] 村井敏昭,岩松勝,吉岡博. 超電導磁気浮上方式における8字型コイル諸元の最適化[J]. 電気学会論文誌D (産業応用部門誌),2003,123(1): 9-14. [107] HUANG Z, DONG F L, XU X Y, et al. Evaluation of the structural dynamics of a 2G HTS magnet system considering electromagnetic and thermal stress[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2021, 31(5): 4901005.1-4901005.5. [108] 王琦,刘振兴,何杰,等. 超导开关及其控制方式研究进展[J]. 低温与超导,2022,50(1): 1-6,26.WANG Qi, LIU Zhenxing, HE Jie, et al. Research review on superconducting switch and control mode[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2022, 50(1): 1-6,26. [109] 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央、国务院印发《交通强国建设纲要》[EB/OL]. (2019-09-19) [2022-05-29]. https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2019/content_5437132.htm. -





 下载:
下载: