Cascading Failure Analysis of Transmission Tower–Line System Under Strong Wind
-
摘要:
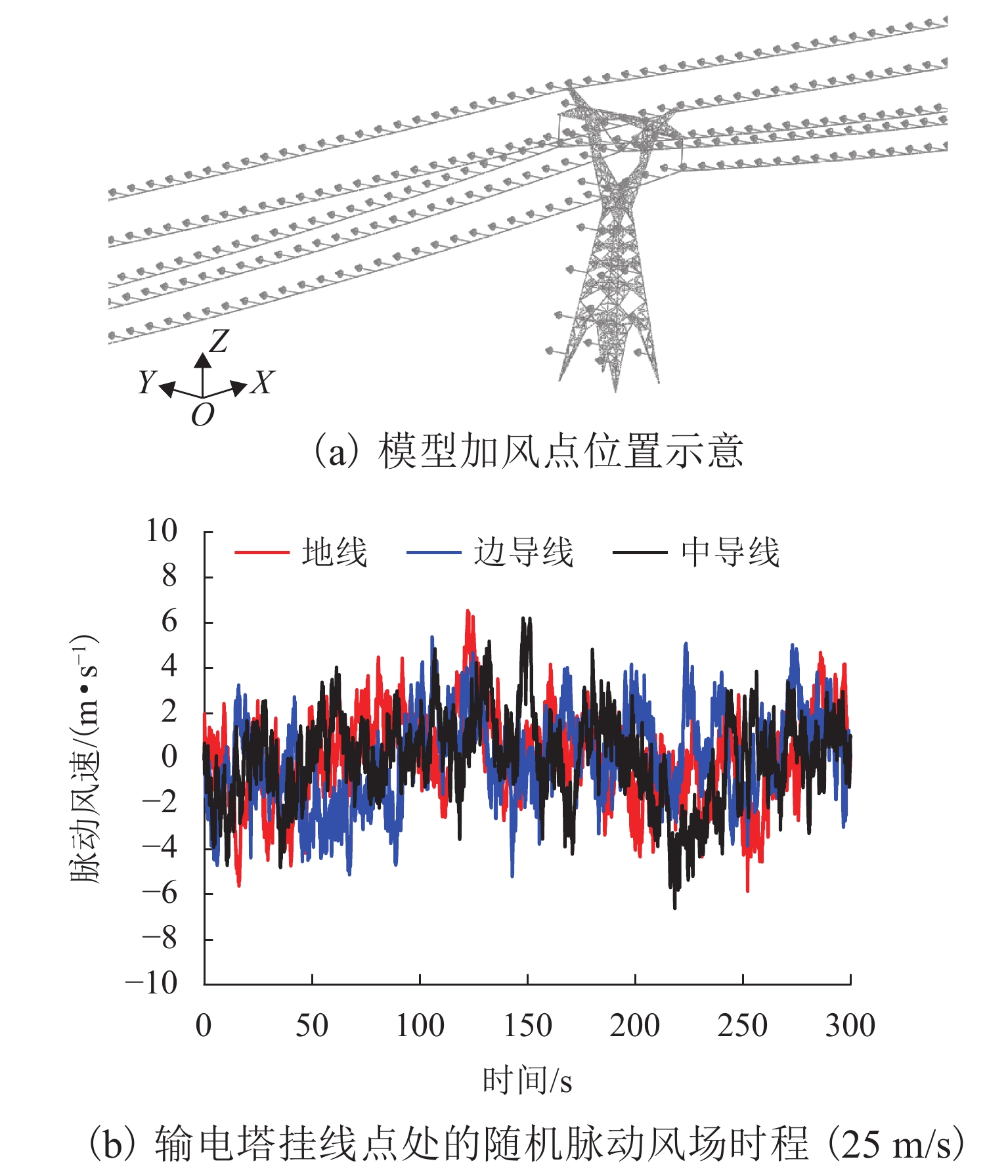
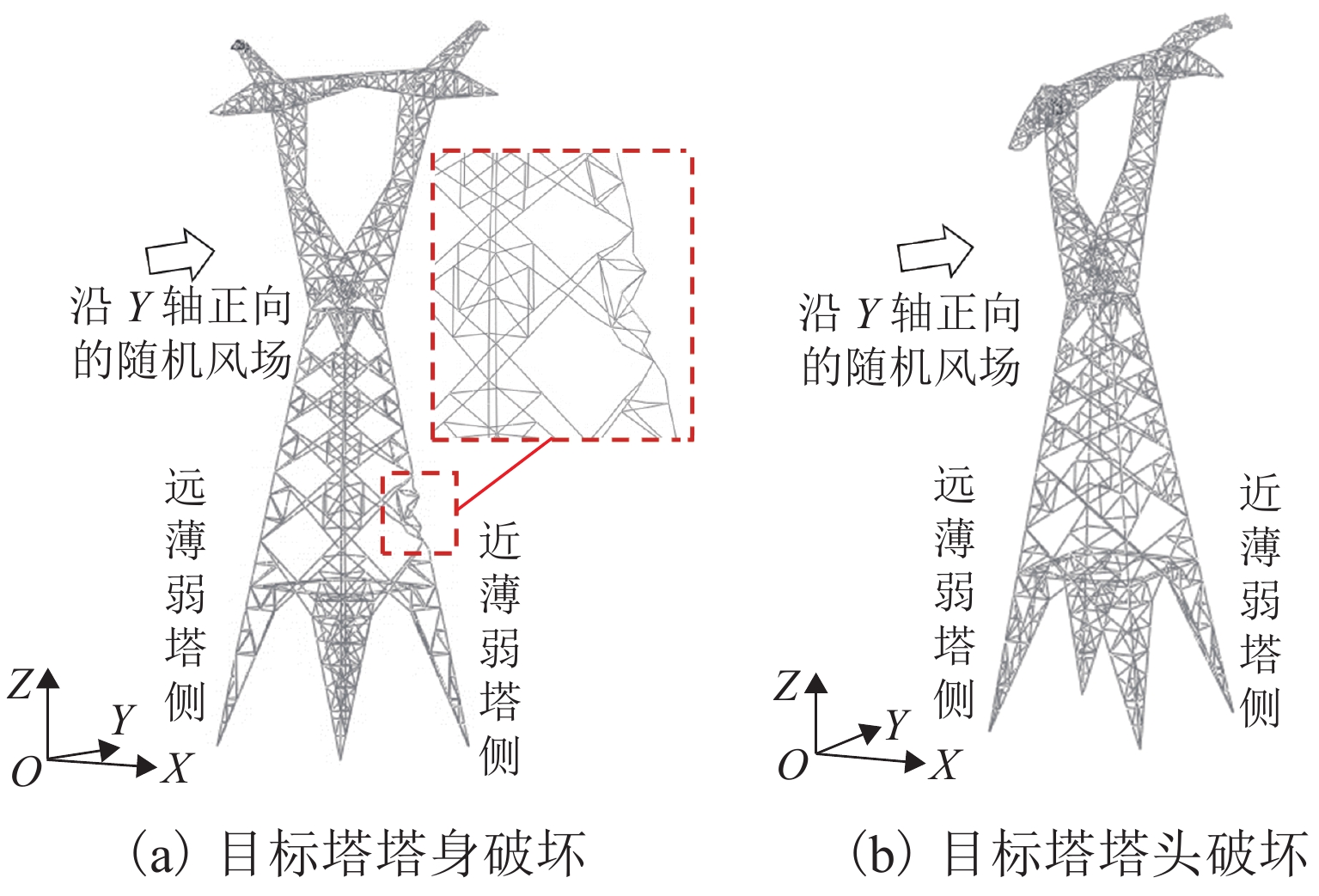
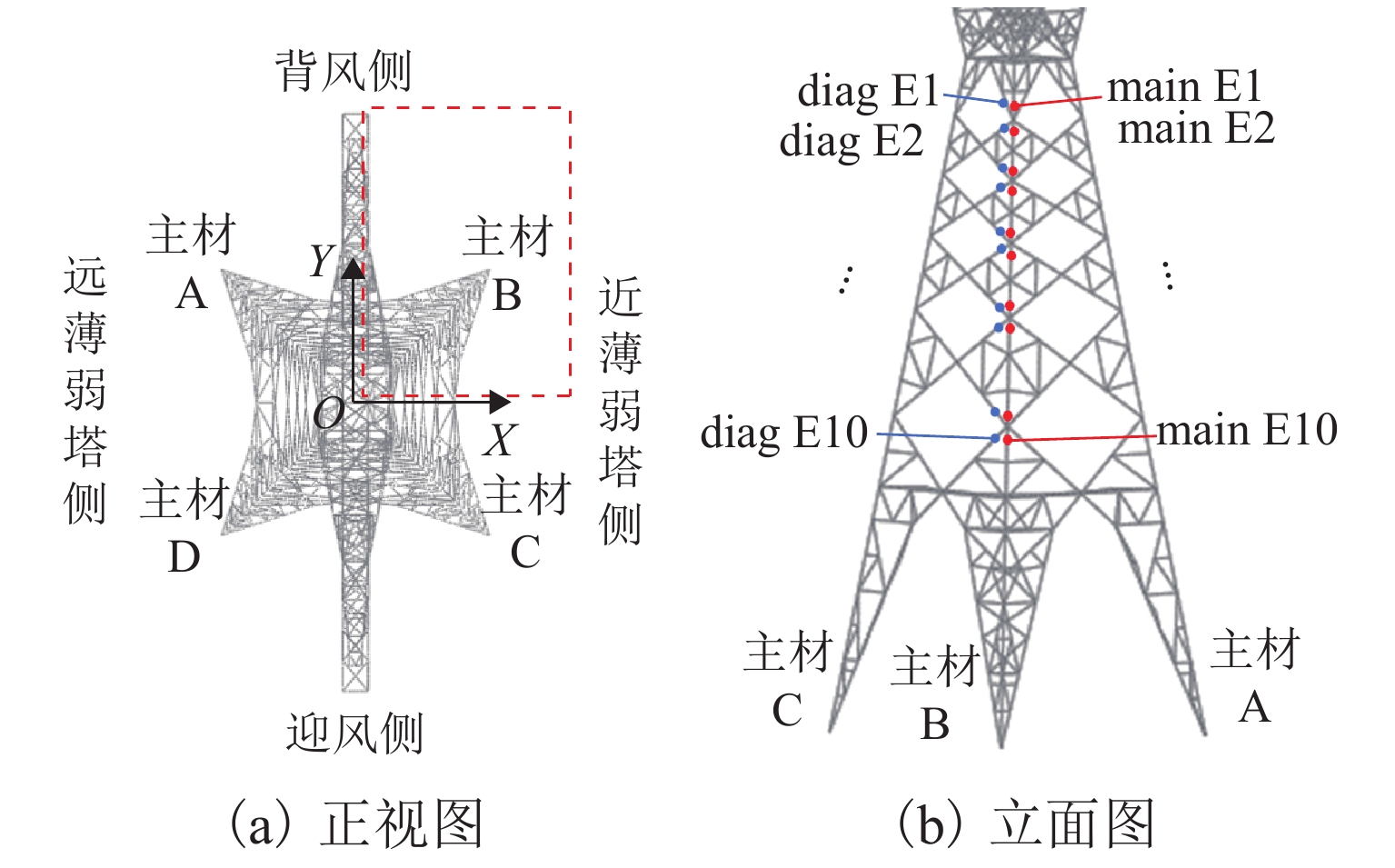
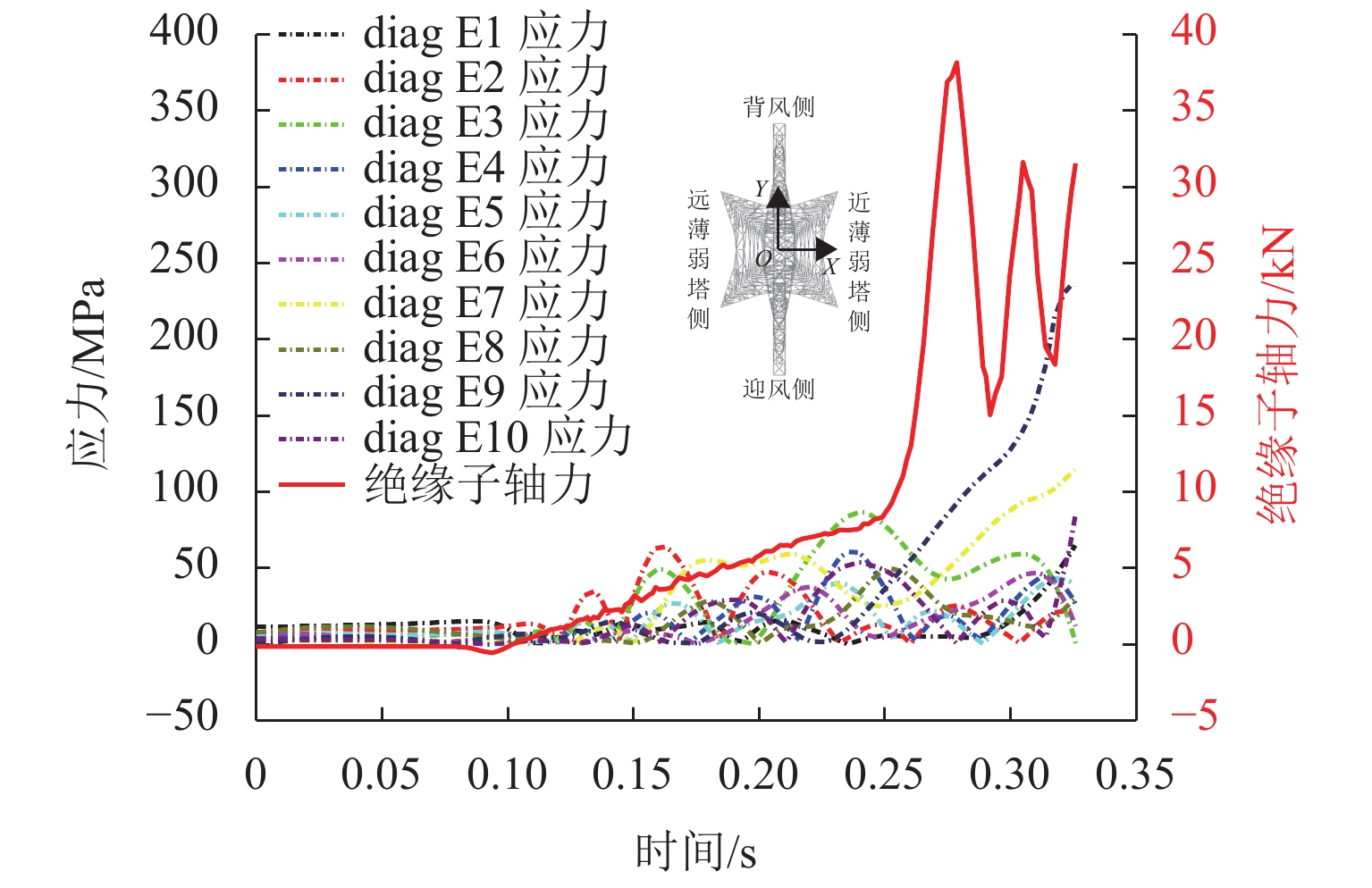
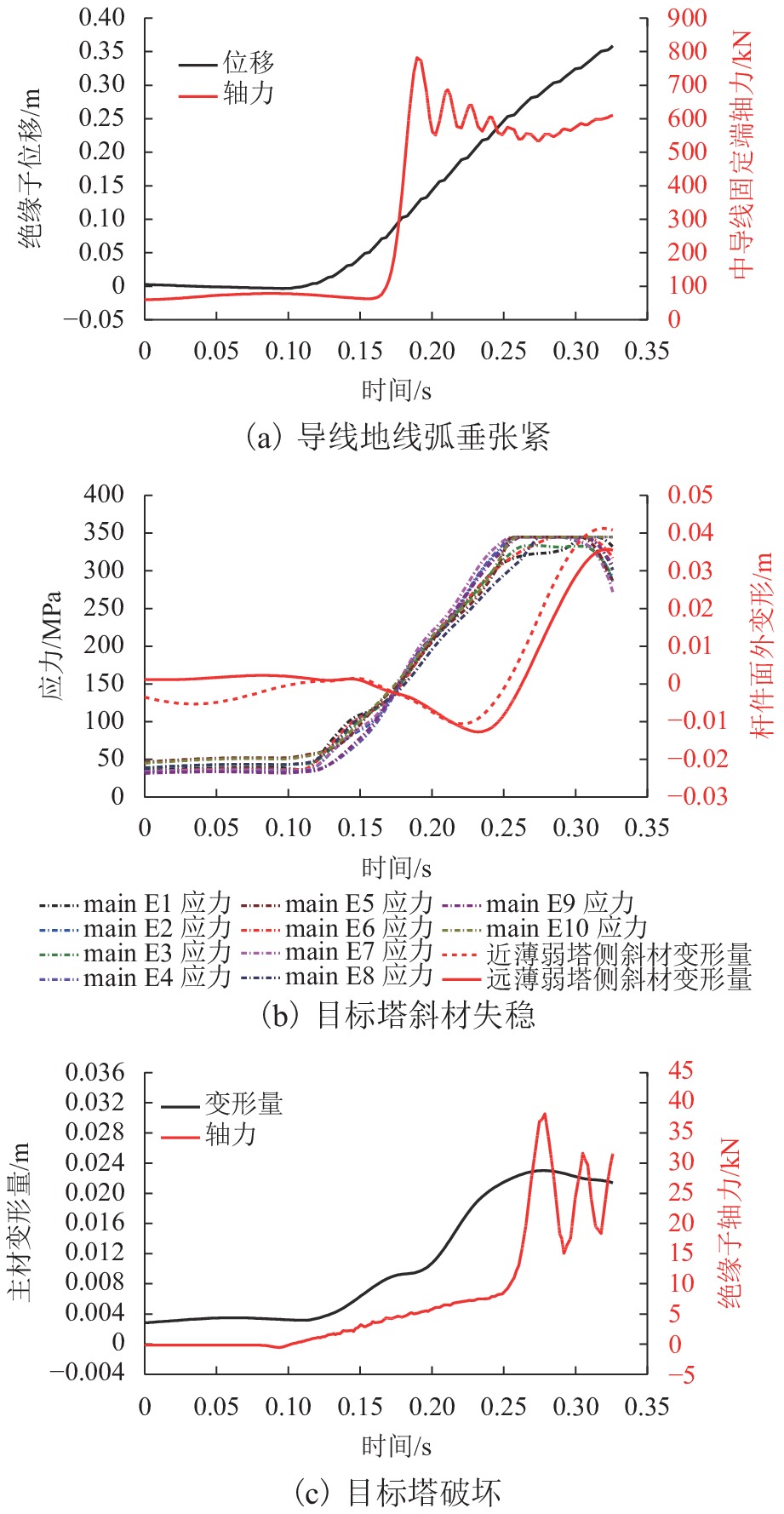
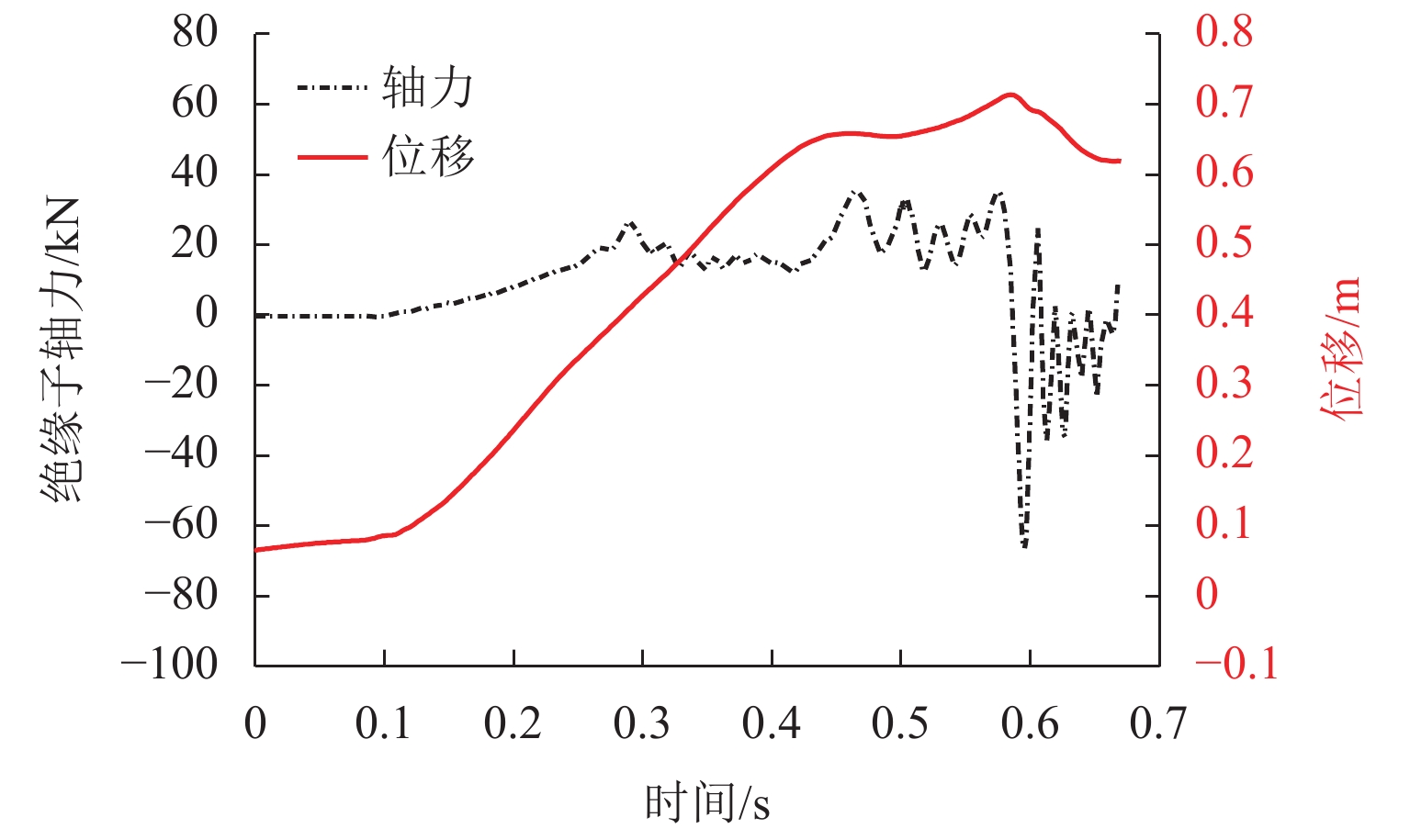
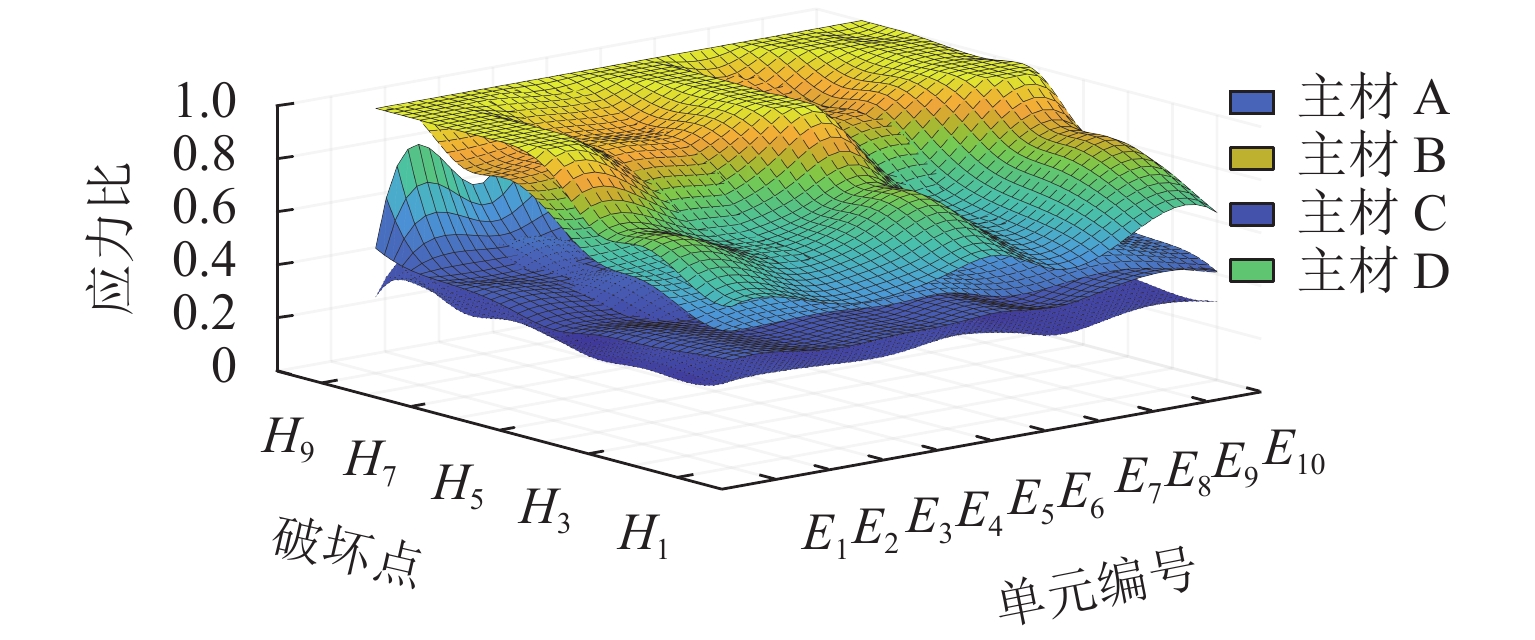
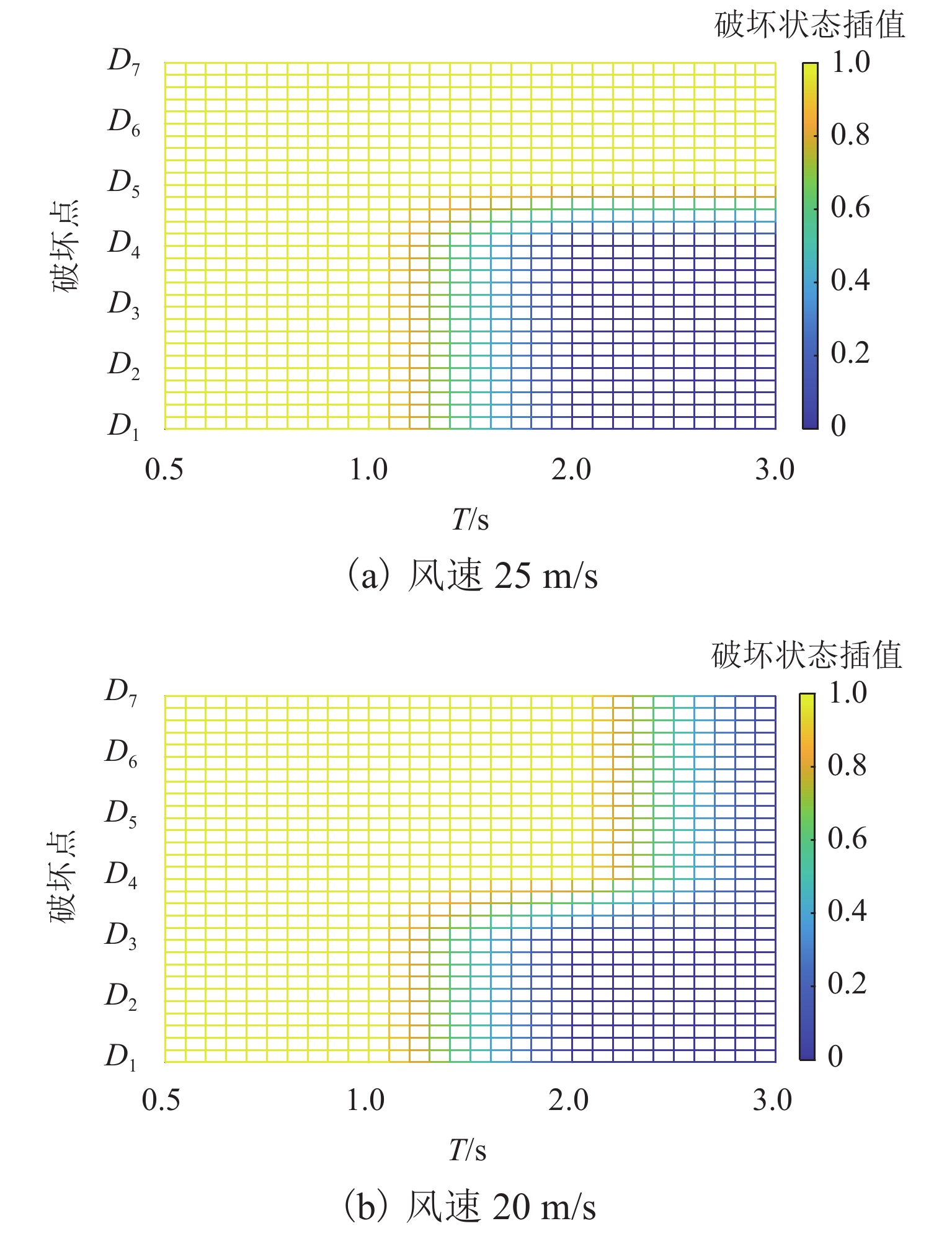
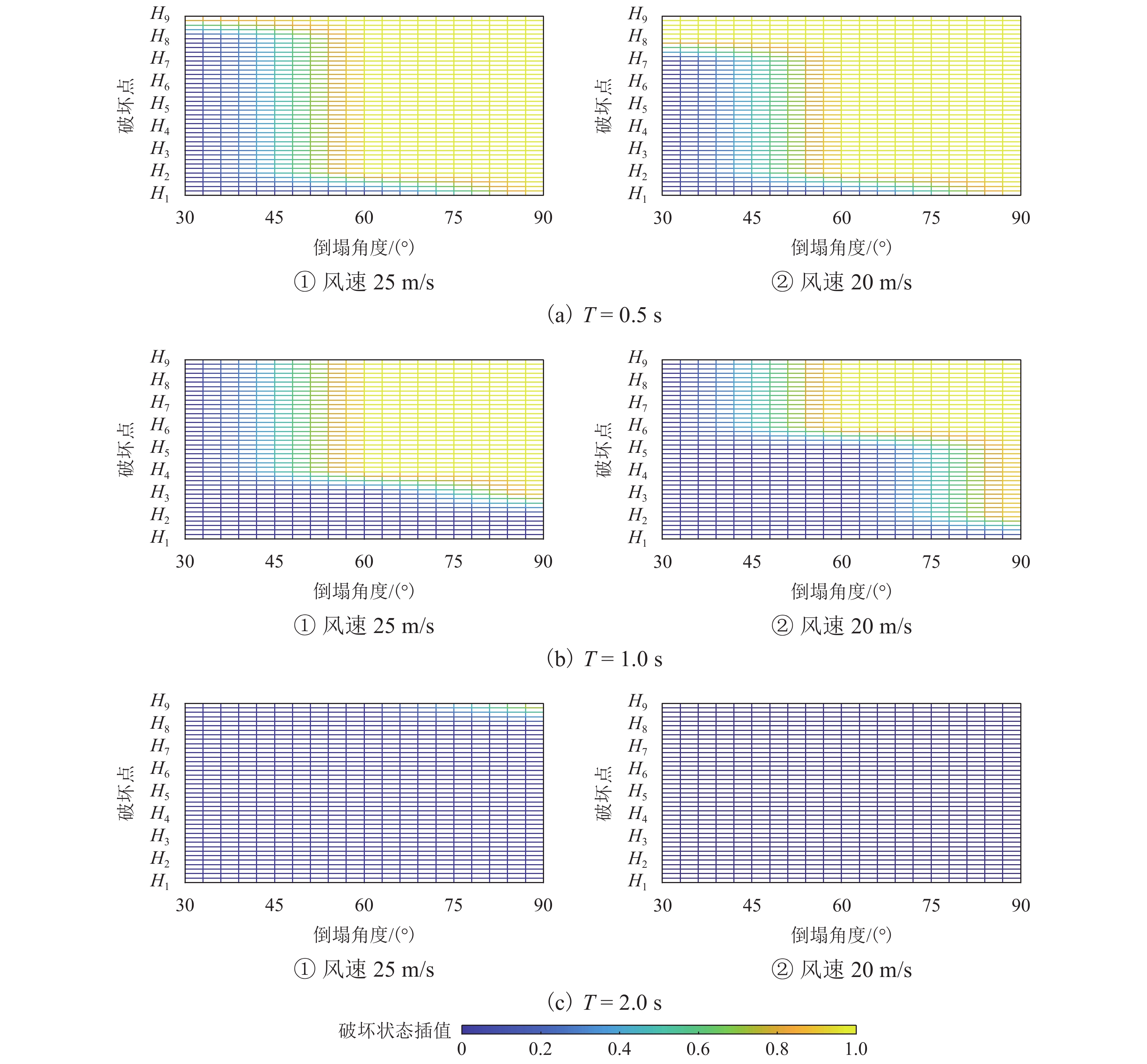
为分析强风作用下输电塔线体系连续性倒塌的过程,将已发生破坏的输电塔作为薄弱塔,采用等效位移的方式考虑薄弱塔倒塌对挂线点空间位置的影响,计算相邻输电塔(目标塔)在薄弱塔多组倒塌特征变量组合工况下的响应和破坏特征,确定对目标塔具有最大影响的薄弱塔倒塌特征变量. 结果表明:在发生连续性倒塌时,目标塔的破坏包括近薄弱塔侧的塔身破坏和塔头破坏2种形式;目标塔近薄弱塔侧背风面主材应力比最高,斜材应力比一直较低;塔身下部斜材失稳与主材应力的持续增大是目标塔整体倒塌的最直接原因;薄弱塔的倒塌过程持续时间是目标塔是否破坏的主要控制变量.
Abstract:In order to analyze the cascading failure of the transmission tower–line system under strong wind, this paper took the collapsed transmission tower as the weak tower and used equivalent displacement to consider the influence of weak tower collapse on the spatial location of suspension points. The responses and failure characteristics of the adjacent transmission tower (target tower) under multiple combined groups of the weak tower collapse parameters were calculated, and the weak tower collapse parameters with the greatest influence on the target tower were determined. The results show that when cascading failure happens, the failure of the target tower includes two types, the failure of the tower body near the weak tower and the failure of the tower head. The main bracing on the leeward side of the weak tower has the highest stress ratio. The stress ratios of diagonal bracings are always low. The most direct causes of the overall collapse of the target tower are the instability of diagonal bracings at the lower part of the target tower and the continuous increase in stress of the main bracing. The duration of the weak tower collapse is the main control variable for the failure of the target tower.
-
Key words:
- transmission lines /
- distributed wind /
- cascading failure /
- numerical simulation /
- parameter analysis
-
表 1 输电塔材料
Table 1. Material of transmission tower
输电塔 屈服强度/MPa 屈服应变/% 本构模型 Q235 235 0.15 理想弹塑性 Q345 345 0.15 理想弹塑性 表 2 输电线材料
Table 2. Material of transmission line
输电线 综合截面/mm2 弹性模量/MPa 线密度/(kg•km−1) 地线 118.9 123 631.00 导线 338.9 69 1085.50 表 3 薄弱塔倒塌触地工况
Table 3. Weak tower collapse and ground contact condition
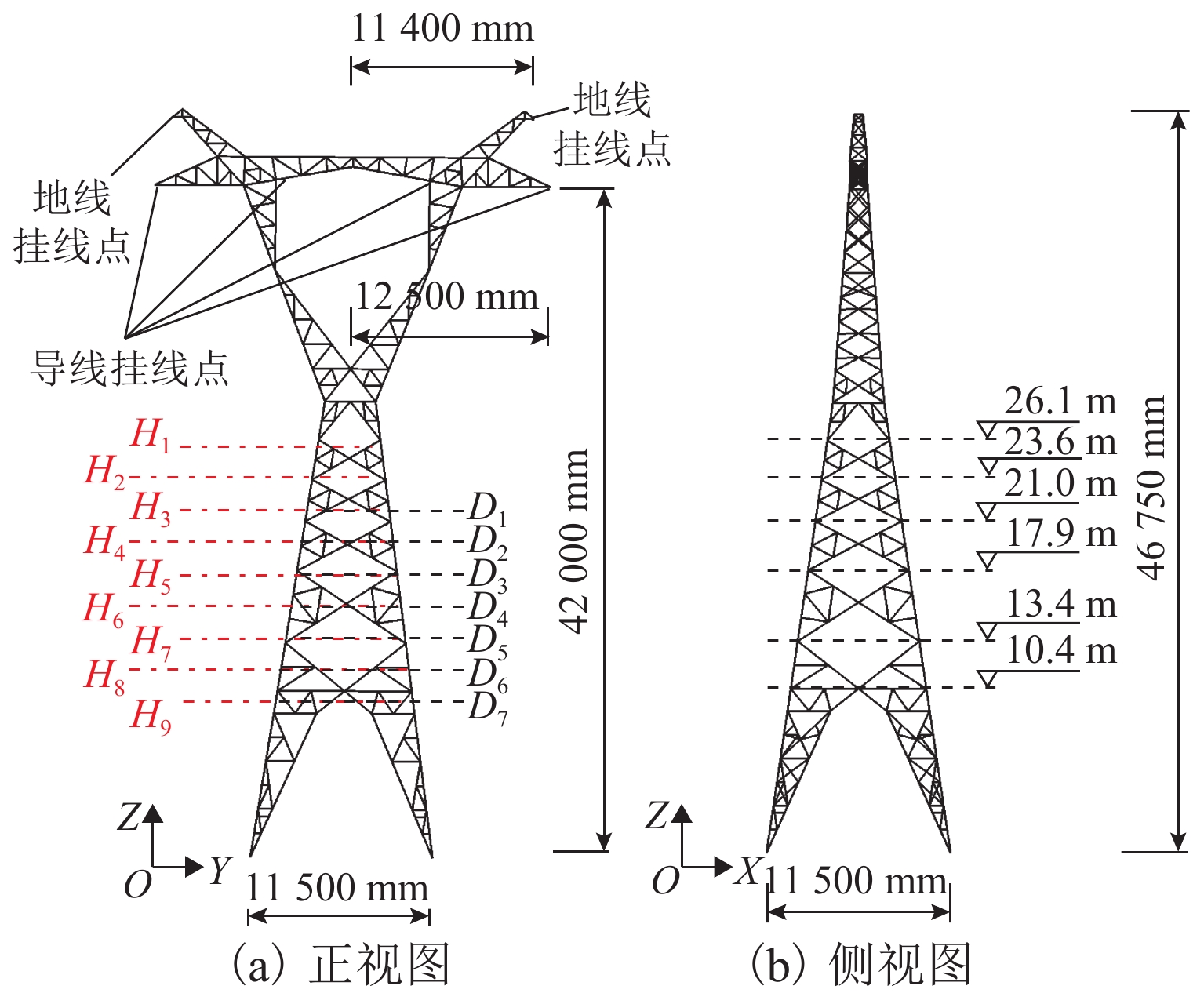
破坏点 h/m θ/(°) T/s y/m z/m D1 22.0 156.4 0.5,1.0,
2.0,3.09.59 −42.00 D2 20.0 140.3 16.61 −42.00 D3 18.0 130.0 21.45 −42.00 D4 16.0 122.2 25.38 −42.00 D5 14.0 115.9 28.77 −42.00 D6 12.0 110.7 31.81 −42.00 D7 10.0 106.1 34.58 −42.00 -
[1] 陈波,宋欣欣,吴镜泊. 输电塔线体系力学模型研究进展[J]. 工程力学,2021,38(5): 1-21. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.08.ST07CHEN Bo, SONG Xinxin, WU Jingbo. Advances in mechanical models of transmission tower-line systems[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(5): 1-21. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2020.08.ST07 [2] 汪之松,刘兴龙,武彦君,等. 考虑SSI效应的输电塔-线体系风振响应简化分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(2): 319-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170715WANG Zhisong, LIU Xinglong, WU Yanjun, et al. Simplified analysis of wind-induced response of transmission tower-line system considering SSI effect[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(2): 319-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170715 [3] CAI Y Z, XIE Q, XUE S T, et al. Fragility modelling framework for transmission line towers under winds[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 191: 686-697. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.04.096 [4] 杨雄骏,黄金山,张建国,等. 基于插值与降维方法的输电塔线体系随机脉动风场有效模拟[J]. 振动与冲击,2021,40(9): 77-83. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.09.011YANG Xiongjun, HUANG Jinshan, ZHANG Jianguo, et al. Effective simulation of stochastic fluctuating wind field of transmission tower-line system based on interpolation and dimension reduction method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(9): 77-83. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.09.011 [5] 杨风利,陈兵,许志勇,等. 500 kV长江大跨越输电塔风振系数研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2022,42(7): 2542-2556.YANG Fengli, CHEN Bing, XU Zhiyong, et al. Study on wind-induced vibration coefficients of the transmission tower in 500 kV long span line crossing the Yangtze River[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(7): 2542-2556. [6] 沈国辉,李保珩,郭勇,等. 输电塔扭转响应和扭转等效风荷载的计算方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2022,56(3): 579-589. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2022.03.017SHEN Guohui, LI Baoheng, GUO Yong, et al. Calculation methods of torsion response and torsion equivalent static wind loading of transmission tower[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(3): 579-589. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2022.03.017 [7] ZHANG Z Q, WANG D H, WANG T, et al. Aeroelastic wind tunnel testing on the wind-induced dynamic reaction response of transmission line[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 34(1): 04020105.1-04020105.11. [8] TAPIA-HERNÁNDEZ E, IBARRA-GONZÁLEZ S, DE-LEÓN-ESCOBEDO D. Collapse mechanisms of power towers under wind loading[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 13(6): 766-782. doi: 10.1080/15732479.2016.1190765 [9] ASGARIAN B, DADRAS ESLAMLOU S, ZAGHI A E, et al. Progressive collapse analysis of power transmission towers[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 123: 31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.04.021 [10] 姚瑶,王凌旭,张有佳. 高压输电塔主材的角钢并联加固轴压承载力[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(3): 561-569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190370YAO Yao, WANG Lingxu, ZHANG Youjia. Axial bearing capacity of angle parallel reinforcement for high voltage transmission towers[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(3): 561-569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20190370 [11] 刘慕广,黄琳玲,谢壮宁. 雷暴风和良态风下输电塔气弹模型风洞试验[J]. 高电压技术,2022,48(2): 594-602.LIU Muguang, HUANG Linling, XIE Zhuangning. Wind tunnel testing of aeroelastic transmission tower under thunderstorm wind and boundary layer wind[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48(2): 594-602. [12] 赵爽,晏致涛,李正良,等. 1000 kV苏通大跨越输电塔线体系气弹模型的风洞试验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2018,38(17): 5257-5265,5323.ZHAO Shuang, YAN Zhitao, LI Zhengliang, et al. Investigation on wind tunnel tests of an aeroelastic model of 1000 kV Sutong long span transmission tower-line system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(17): 5257-5265,5323. [13] ZHANG J, XIE Q. Failure analysis of transmission tower subjected to strong wind load[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2019, 160: 271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2019.05.041 [14] TIAN L, MA R S, PAN H Y, et al. Progressive collapse analysis of long-span transmission tower-line system under multi-component seismic excitations[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2017, 20(12): 1920-1932. doi: 10.1177/1369433217700426 [15] ALMINHANA F, ALBERMANI F, MASON M. Cascading collapse of transmission lines[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers− Engineering and Computational Mechanics, 2018, 171(3): 115-132. doi: 10.1680/jencm.18.00010 [16] 阎启,李杰. 基于演化相位谱的脉动风速模拟[J]. 振动与冲击,2011,30(9): 163-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.09.035YAN Qi, LI Jie. Evolutionary-phase-spectrum based simulation of fluctuating wind speed[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(9): 163-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.09.035 -




 下载:
下载: