Simplified Calculation Method for Dynamic Characteristics of Pulse Wind Tunnel Balance Foundation
-
摘要:
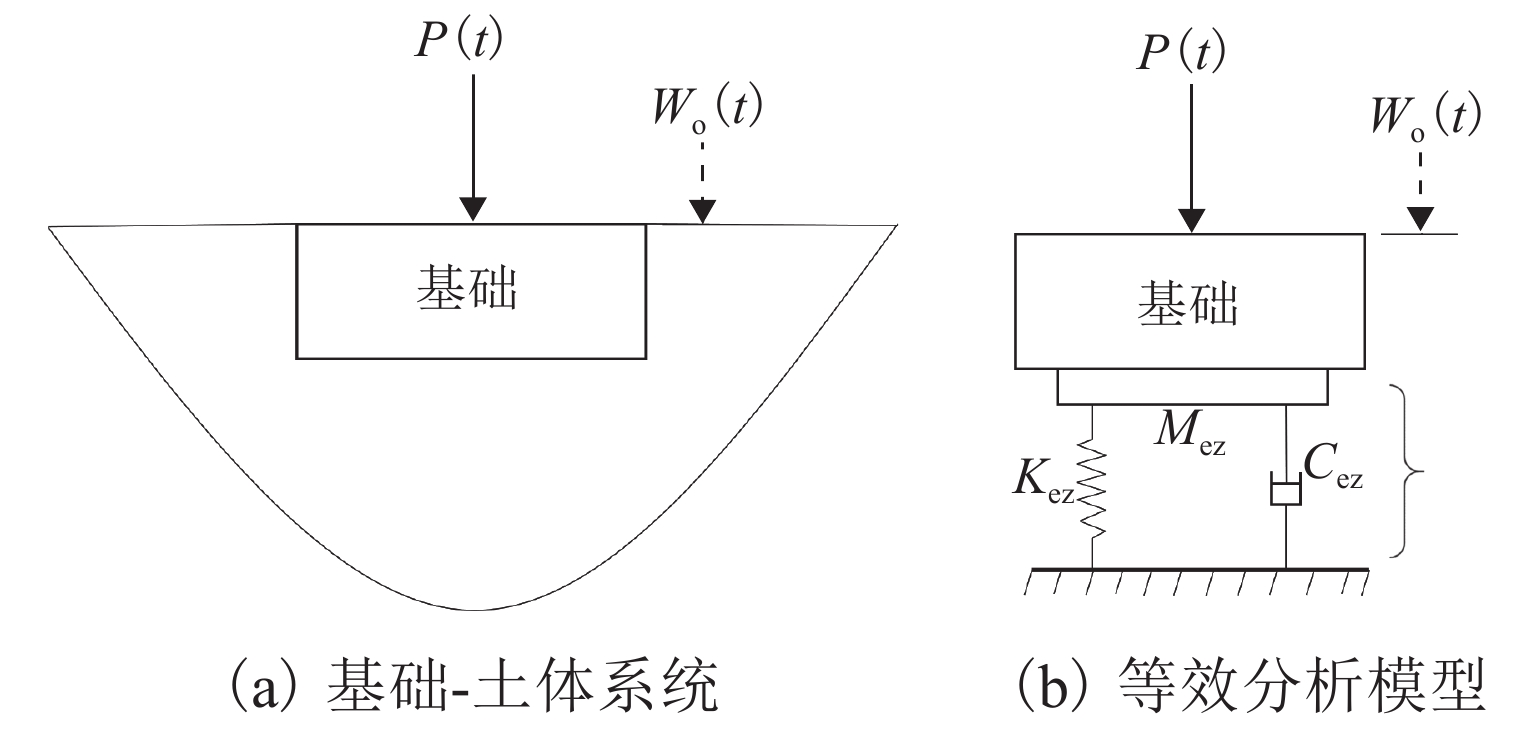
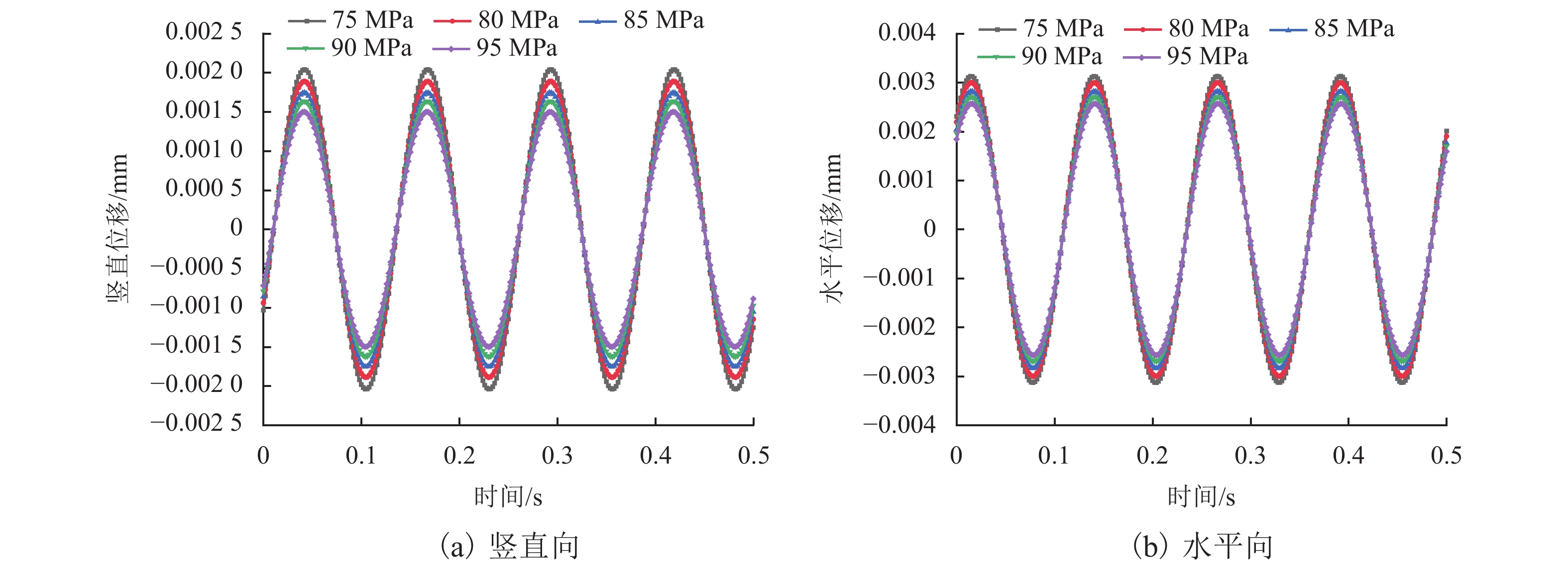
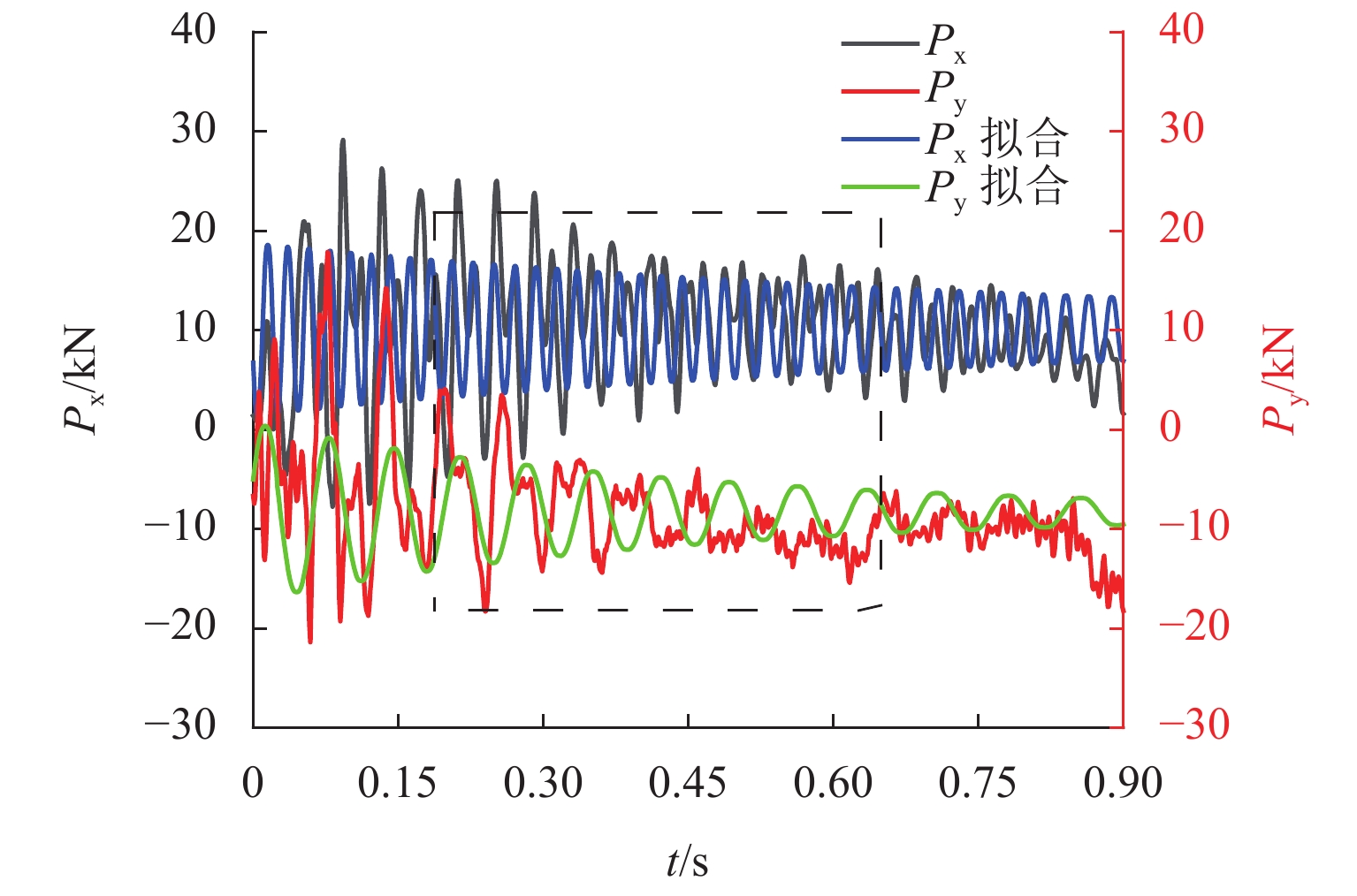
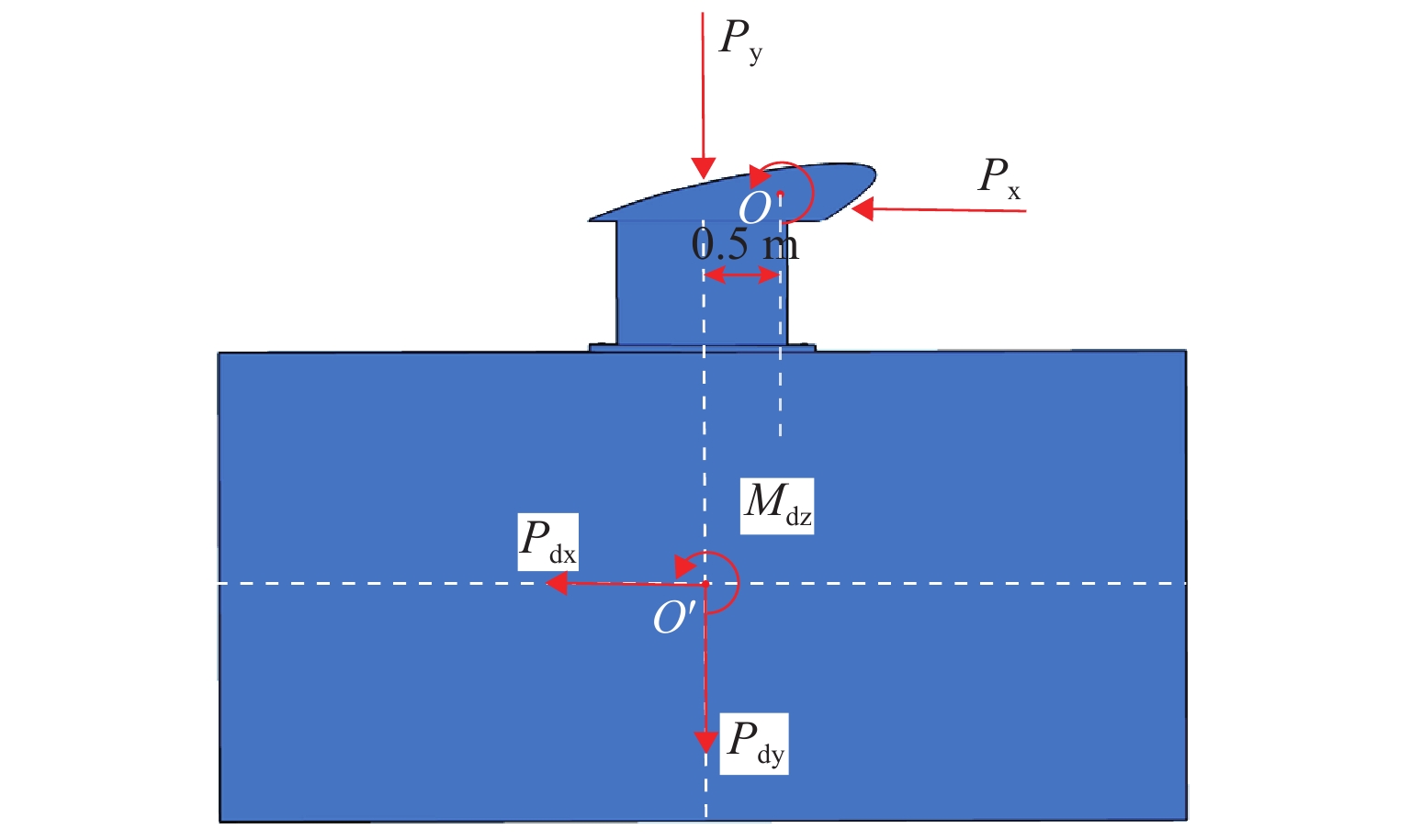
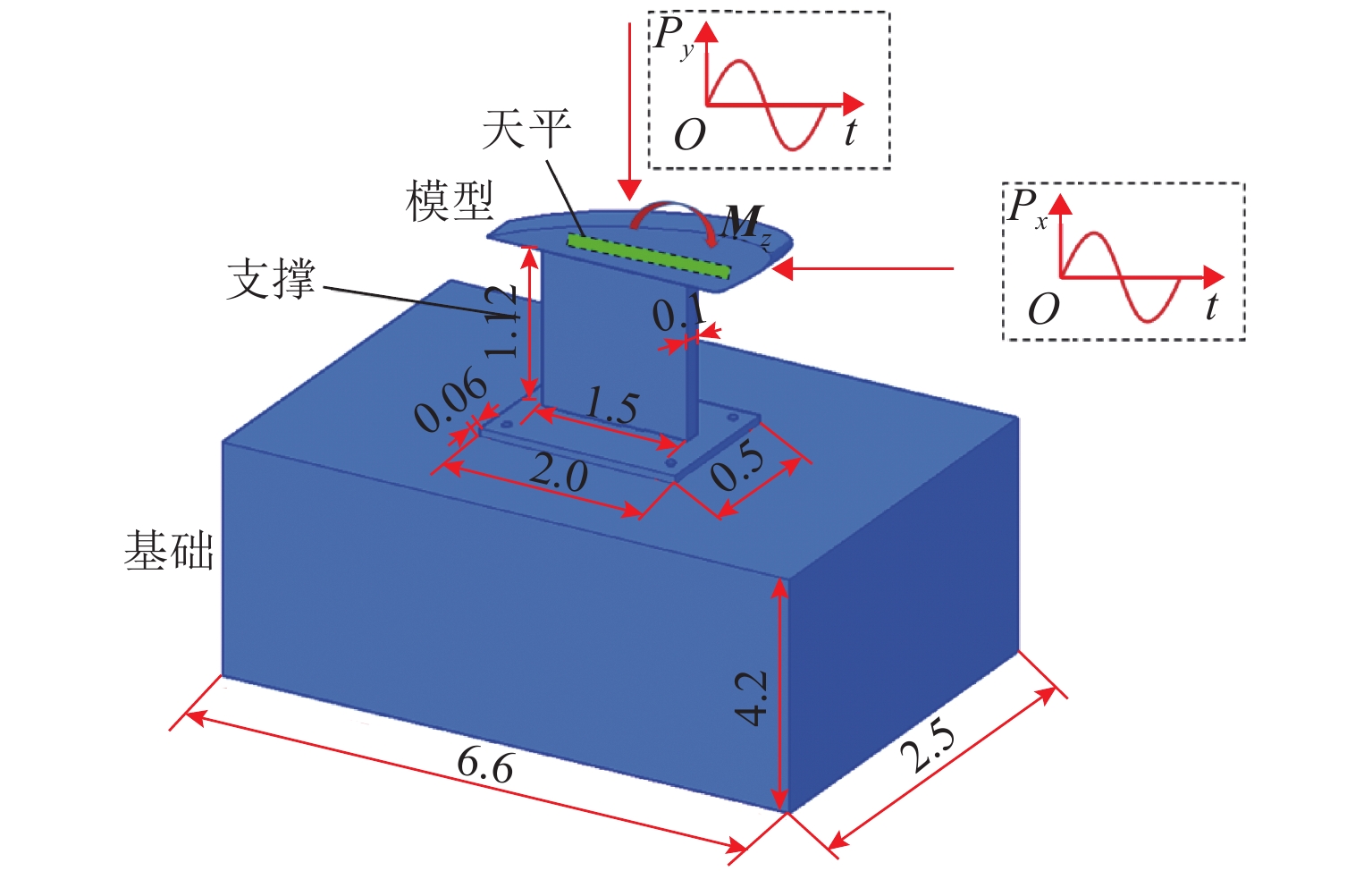
为了研究脉冲风洞天平基础在脉冲气动荷载作用下的动力响应特征,以某脉冲风洞为例,选择某典型气动荷载作用形式,建立了脉冲风洞天平基础在气动荷载作用下竖直方向、水平方向位移以及回转角度等动力特征的简化计算方法,并采用数值模拟的方法验证其可靠性. 研究结果表明:天平基础在典型气动荷载作用下,竖直向最大振幅0.00175 mm,频率7.94 Hz,水平向最大振幅0.00283 mm,频率7.94 Hz,回转角度最大振幅0.00034°,频率7.94 Hz,典型气动荷载对天平基础振动影响较小,也未产生共振现象;基础振动最大振幅随气动荷载增大而增大,基础振动频率随气动荷载频率增大而增大;在气动荷载不变的条件下,基础振动的最大振幅与频率随尺寸的变大而变小,基础振动的最大振幅也随地基土性质的增强而减小,但地基土性质的变化对基础振动频率无影响.
Abstract:In order to study the dynamic response characteristics of the pulse wind tunnel balance foundation under the action of pulse aerodynamic loads, a pulse wind tunnel was taken as an example, and a typical aerodynamic load action type was selected. As a result, a simplified calculation method for dynamic characteristics of the pulse wind tunnel balance foundation such as displacement of the vertical direction, displacement of the horizontal direction, and rotation angle was established, and its reliability was verified by numerical simulation. The results show that under the action of a typical aerodynamic load, the balance foundation has a maximum vertical vibration amplitude of 0.001 75 mm and a frequency of 7.94 Hz; a maximum horizontal vibration amplitude of 0.002 83 mm and a frequency of 7.94 Hz; a maximum amplitude of the rotation angle of 0.000 34° and a frequency of 7.94 Hz. The typical aerodynamic load has little effect on the vibration of the balance foundation, and no resonance phenomenon occurs. Meanwhile, the maximum amplitude of foundation vibration increases with the increase in aerodynamic load, and the frequency of foundation vibration increases with the increase in aerodynamic load frequency; under the condition of constant aerodynamic load, the maximum amplitude and frequency of foundation vibration gradually decrease with the increase in size; the maximum amplitude of the foundation vibration decreases with the increase in foundation soil properties, but the change of foundation soil properties has no effect on the foundation vibration frequency.
-
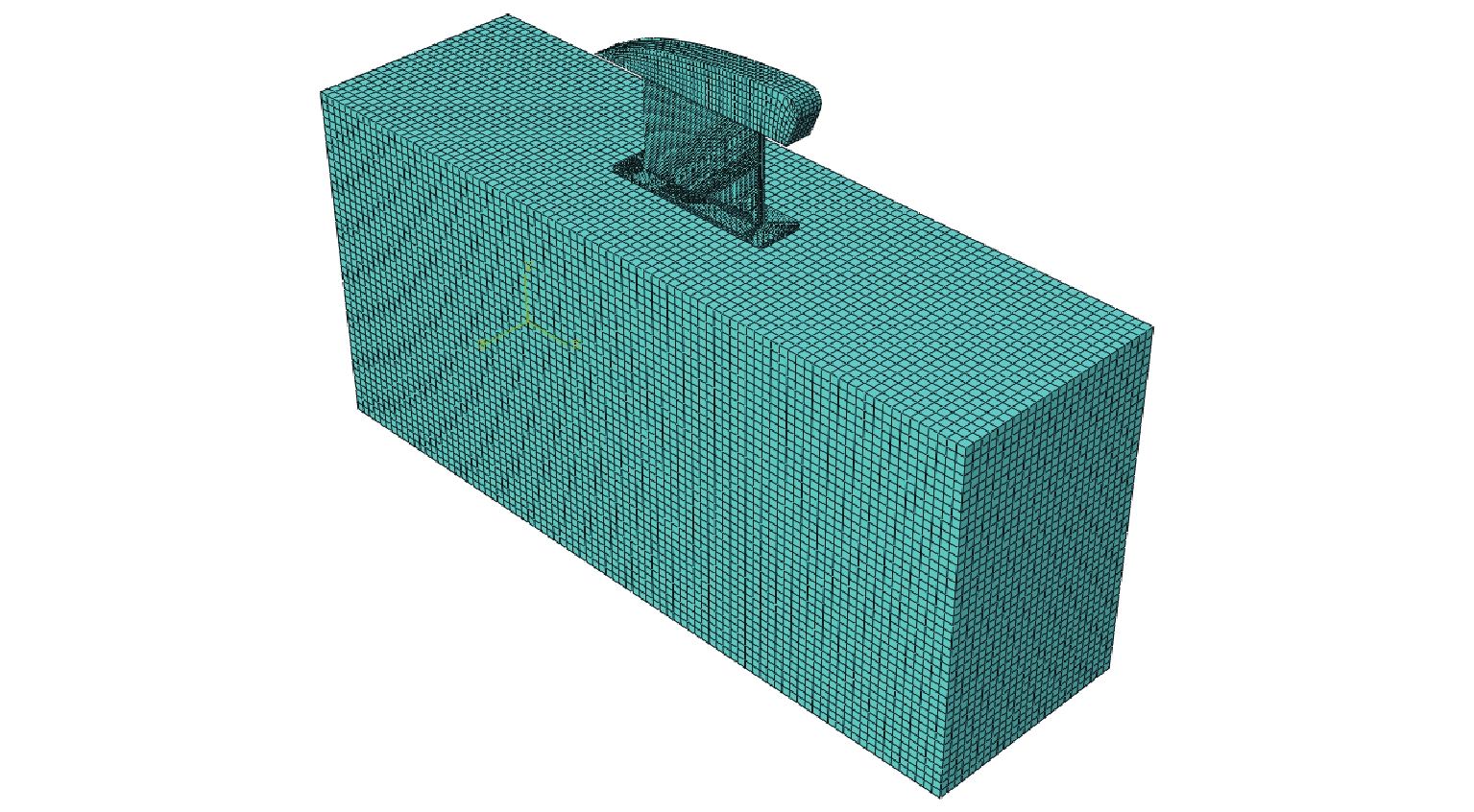
表 1 网格无关性检验方案及计算结果
Table 1. Test scheme and calculation results of mesh independence
方案 节点
数/个单元
数/个竖直向最大振幅/μm 水平向最大振幅/μm 回转角度最大振幅/(°) 1 12749 17392 1.71 2.78 3.1×10−4 2 18308 24878 1.75 2.83 3.4×10−4 3 32637 44583 1.77 2.86 3.6×10−4 4 59842 78949 1.78 2.87 3.6×10−4 表 2 材料计算参数
Table 2. Parameters of materials
名称 重度/
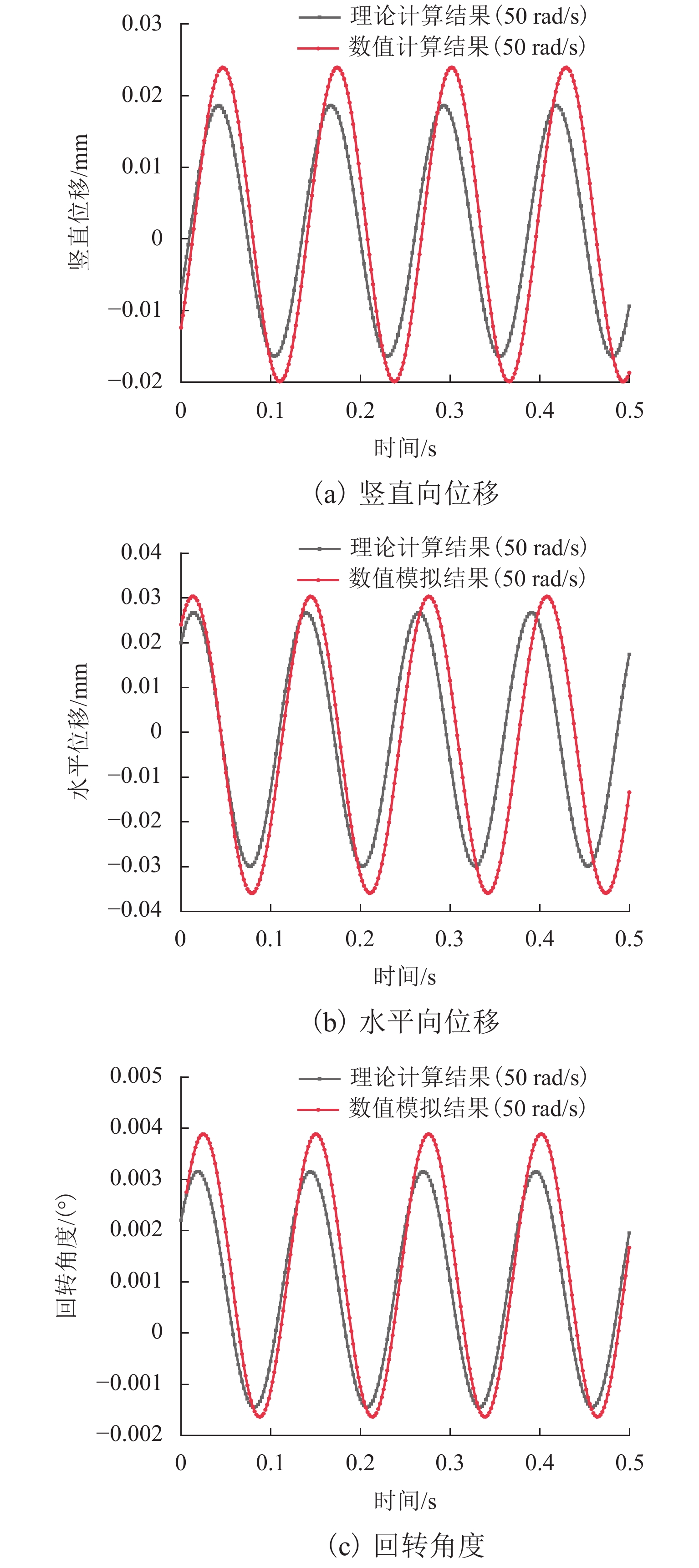
(kN·m−3)弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 剪胀角/(°) 偏心率 fb0/fc0 K 黏性系数 支撑 78 210 0.2 地基 19 30 0.25 38 0.1 1.16 0.67 0.005 基础 25 30 0.25 38 0.1 1.16 0.67 0.005 表 3 理论计算结果与数值模拟结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of theoretically calculated results and numerically simulated results
方法 频率/Hz 最大振幅/μm 竖直向 水平向 回转角 竖直向 水平向 回转角 理论计算 8.06 1.75 7.94 0.00283 7.94 3.4×10−4 数值模拟 7.81 2.19 7.75 0.00331 7.94 4.1×10−4 表 4 不同基础尺寸计算结果
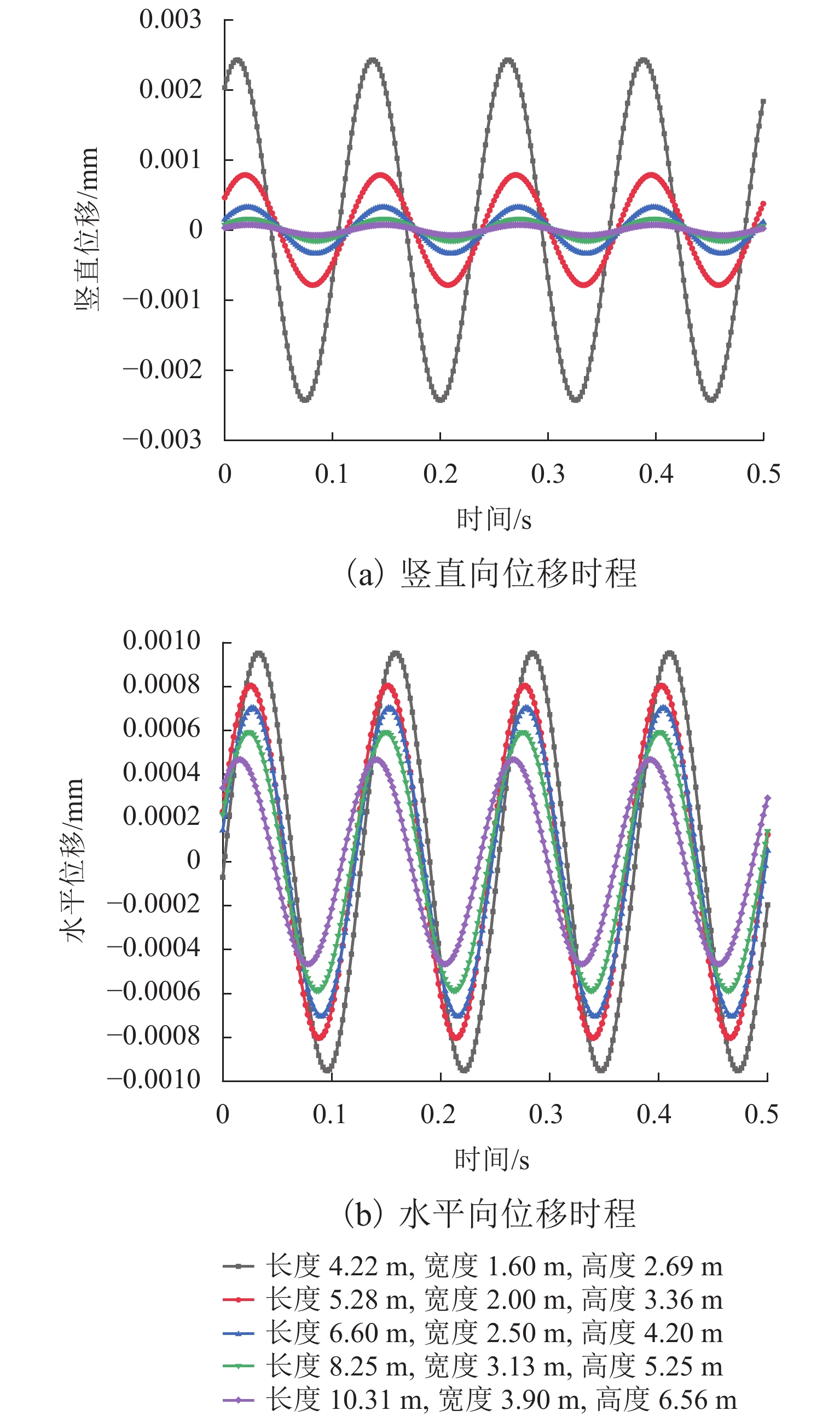
Table 4. Calculation results of foundation with different sizes
基础尺寸 最大振幅/μm 频率/Hz 竖直振动 水平振动 竖直振动 水平振动 0.64S 2.24 6.45 9.52442 7.48 0.80S 0.787 5.35 8.03606 6.21 S 0.331 4.49 7.03641 5.22 1.25S 0.155 4.02 5.89714 4.66 1.56S 0.075 3.59 4.66436 4.17 -
[1] 乐嘉陵. 吸气式高超声速技术研究进展[J]. 推进技术,2010,31(6): 641-649.LE Jialing. Progress in air-breathing hypersonic technology[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2010, 31(6): 641-649. [2] GAZETAS G. Analysis of machine foundation vibrations: state of the art[J]. International Journal of Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 1983, 2(1): 2-42. doi: 10.1016/0261-7277(83)90025-6 [3] MIZUNO H. Effects of structurefh soil-structure interaction during various excitations[C]//Proc., 7th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. Istanbul: [s.n.], 1980: 149-156. [4] NII Y. Experimental half-space dynamic stiffness[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1987, 113(11): 1359-1373. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1987)113:11(1359) [5] SARRAZIN M A, ROESSET J M, WHITMAN R V. Dynamic soil-structure interaction[J]. Journal of the Structural Division, 1972, 98(7): 1525-1544. doi: 10.1061/JSDEAG.0003278 [6] VELETSOS A S, TANG Y. Vertical vibration of ring foundations[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 1987, 15(1): 1-21. [7] MITA A, LUCO J E. Impedance functions and input motions for embedded square foundations[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1989, 115(4): 491-503. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1989)115:4(491) [8] AVILÉS J, PÉREZ-ROCHA L E. A simplified procedure for torsional impedance functions of embedded foundations in a soil layer[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 1996, 19(2): 97-115. doi: 10.1016/0266-352X(95)00038-C [9] MAUGERI M, MUSUMECI G, NOVITÀ D, et al. Shaking table test of failure of a shallow foundation subjected to an eccentric load[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2000, 20(5/6/7/8): 435-444. [10] GAJAN S, KUTTER B L, PHALEN J D, et al. Centrifuge modeling of load-deformation behavior of rocking shallow foundations[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2005, 25(7/8/9/10): 773-783. [11] BHATTACHARYA S, ADHIKARI S. Experimental validation of soil-structure interaction of offshore wind turbines[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 31(5/6): 805-816. [12] 钱鸿缙. 动力机器基础设计[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1980: 23-66. [13] 严人觉. 动力基础半空间理论概论[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1981. [14] GAZETAS G. Formulas and charts for impedances of surface and embedded foundations[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1991, 117(9): 1363-1381. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1991)117:9(1363) [15] ÇELEBI E, FıRAT S, ÇANKAYA İ. The effectiveness of wave barriers on the dynamic stiffness coefficients of foundations using boundary element method[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2006, 180(2): 683-699. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2006.01.008 [16] CELEBI E, FIRAT S, CANKAYA L. Dynamic impedance functions for rectangular rigid foundations[J]. Teknik Dergi/Technical Journal of Turkish Chamber of Civil Engineers, 2006, 17(2): 3827-3849. [17] 蒋东旗,谢定义. 动力机器基础设计的数值方法研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2002,35(1): 74-78.JIANG Dongqi, XIE Dingyi. Numerical simulation method for foundation design of dynamic machine[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(1): 74-78. [18] 王幼青,张克绪,朱腾明. 动力机器基础与地基体系分析[J]. 哈尔滨建筑大学学报,1999(3): 43-47.WANG Youqing, ZHANG Kexu, ZHU Tengming. Dynamic machine soil-foundation system analysis[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 1999(3): 43-47. [19] 刘志久,尚守平,徐建. 埋置基础扭转振动的实用化计算与试验的对比[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(12): 3618-3622.LIU Zhijiu, SHANG Shouping, XU Jian. Comparison of practical calculation for torsional vibration of embedded foundations and experiments[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(12): 3618-3622. [20] 燕彬,黄义,王成林. 任意刚性基础竖向动阻抗的简化计算[J]. 世界地震工程,2005,21(1): 91-96.YAN Bin, HUANG Yi, WANG Chenglin. Simplified method for dynamic vertical impedances of rigid foundations with arbitrary shapes[J]. World Information on Earthquake Engineering, 2005, 21(1): 91-96. [21] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 动力机器基础设计标准: GB 50040—2020[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2020. [22] CHEN S S, SHI J Y. A response-based simplified model for vertical vibrations of embedded foundations[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 31(5/6): 773-784. [23] 刘庆宽,何书勇,贾娅娅,等. 防雪栅与路基间距对路基积雪分布影响规律的数值模拟研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2021,40(6): 227-234,264.LIU Qingkuan, HE Shuyong, JIA Yaya, et al. Numerical simulation on the influence of the distance between snow fence and subgrade on the snow distribution on subgrade[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(6): 227-234,264. [24] 王毅刚,朱朗贤,王玉鹏,等. 高速列车转向架区域气动噪声源的特征识别[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(2): 261-271,286.WANG Yigang, ZHU Langxian, WANG Yupeng, et al. Characteristic identification of aerodynamic noise sources in high-speed train bogie area[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(2): 261-271,286. [25] 于梦阁,李美香,刘加利,等. 考虑风速纵、横分量的列车气动载荷变化特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(1): 29-35.YU Mengge, LI Meixiang, LIU Jiali, et al. Study on unsteady aerodynamic loads of high-speed trains exposed to stochastic wind for ant wind angle[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(1): 29-35. [26] 第一机械工业部设计研究总院. 动力机器基础设计手册[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1983. [27] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑结构荷载规范: GB 50009—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. [28] 柯世堂,葛耀君,赵林,等. 大型冷却塔结构的等效静力风荷载[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2011,39(8): 1132-1137.KE Shitang, GE Yaojun, ZHAO Lin, et al. Equivalent static wind load of large cooling tower[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2011, 39(8): 1132-1137. -




 下载:
下载: