Protection Scheme of New Continuous Cable Power Supply System
-
摘要:
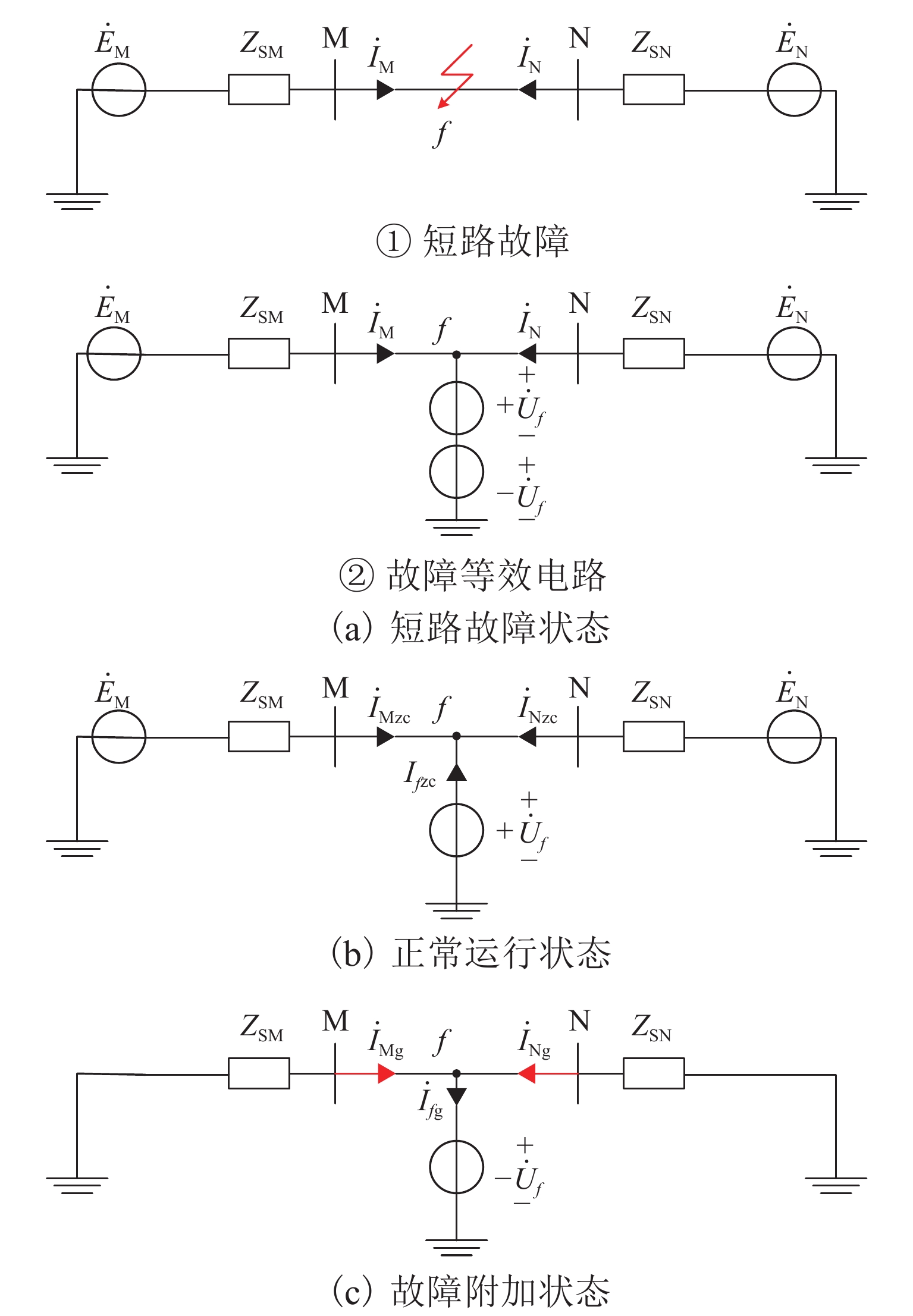
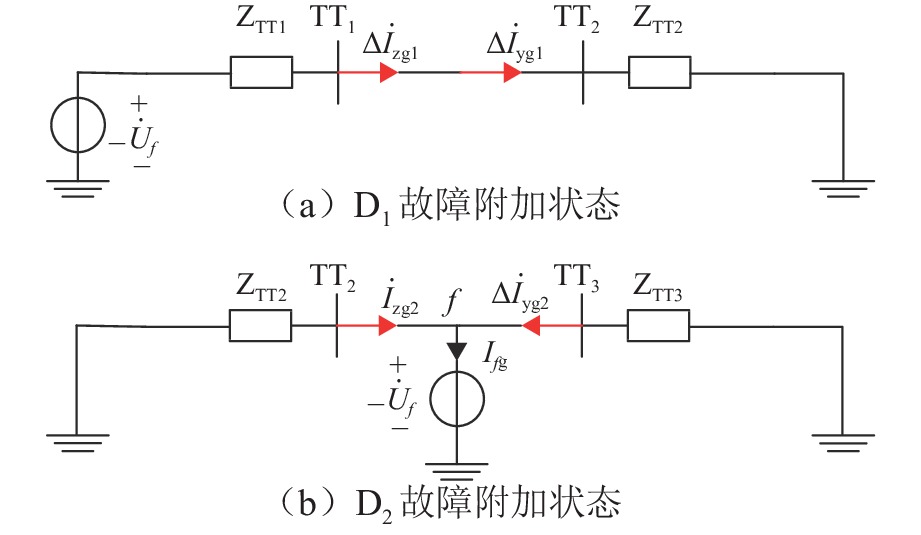
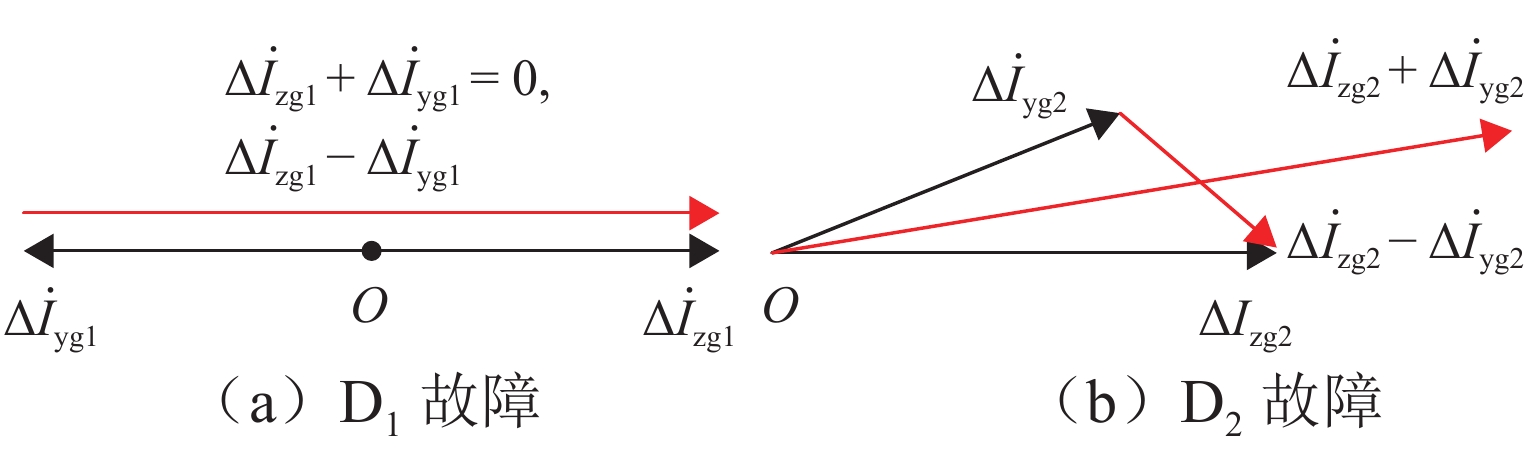
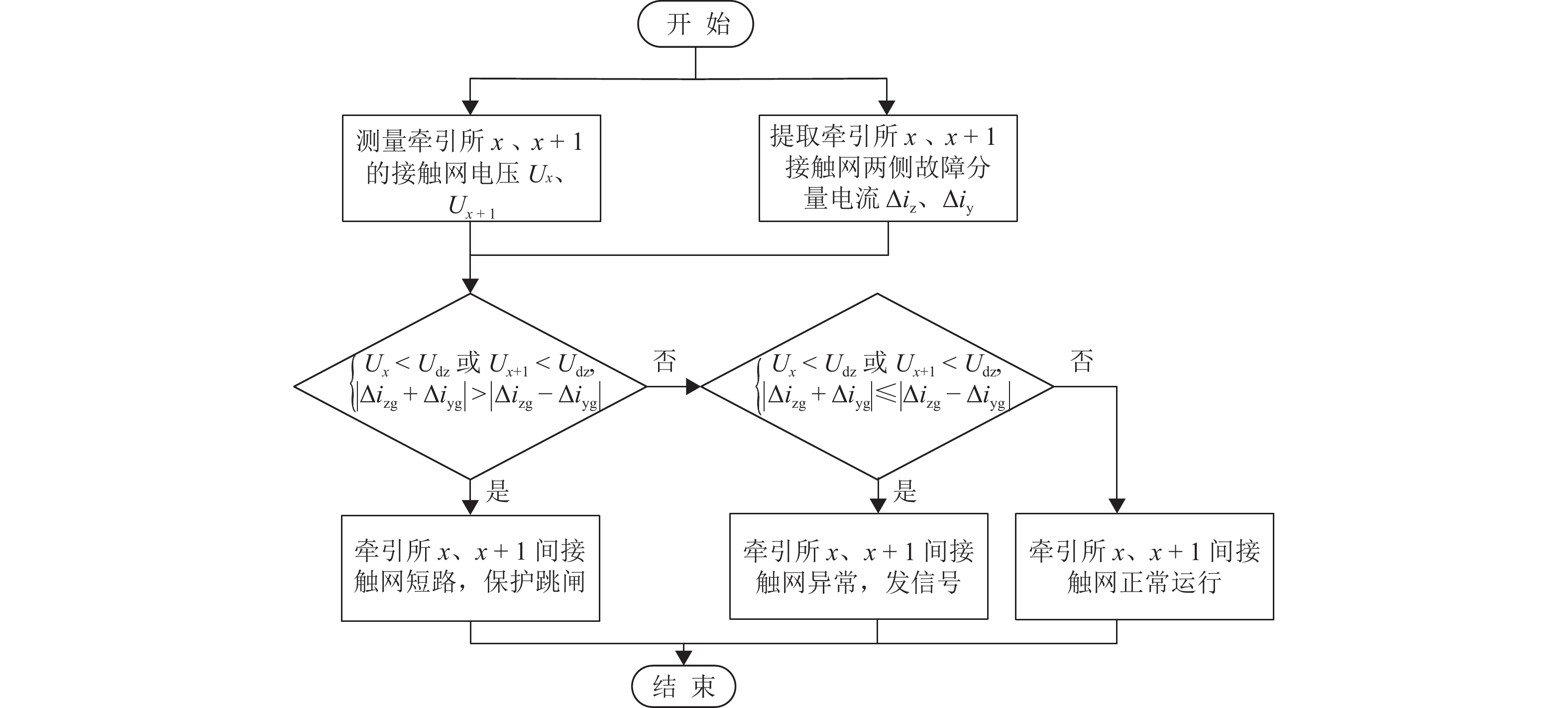
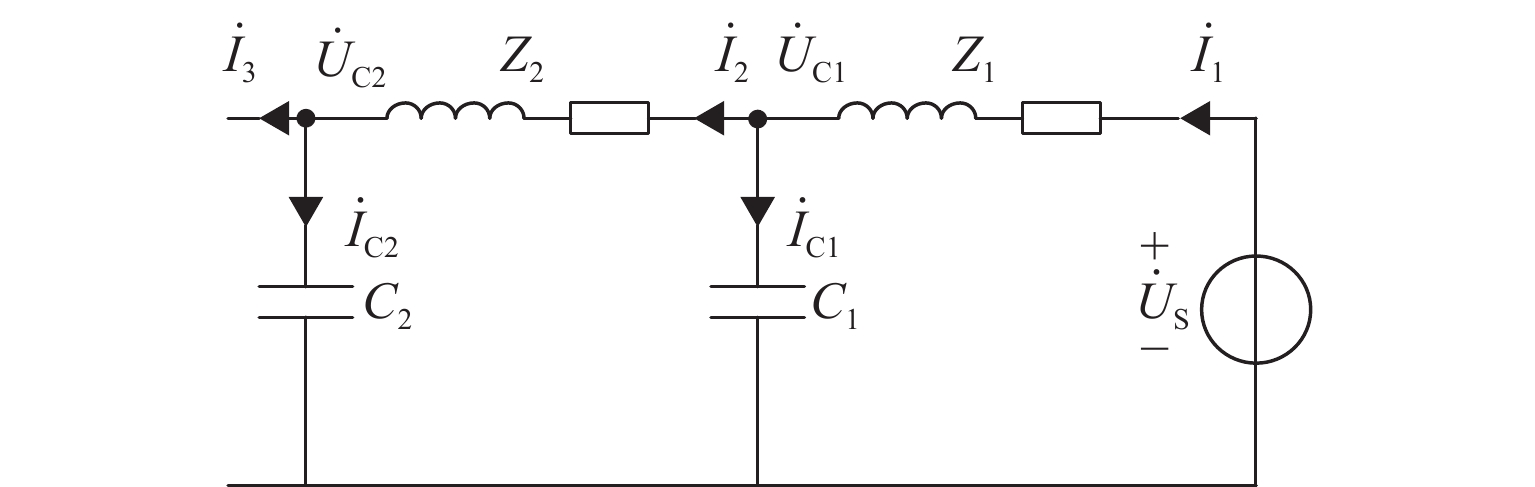
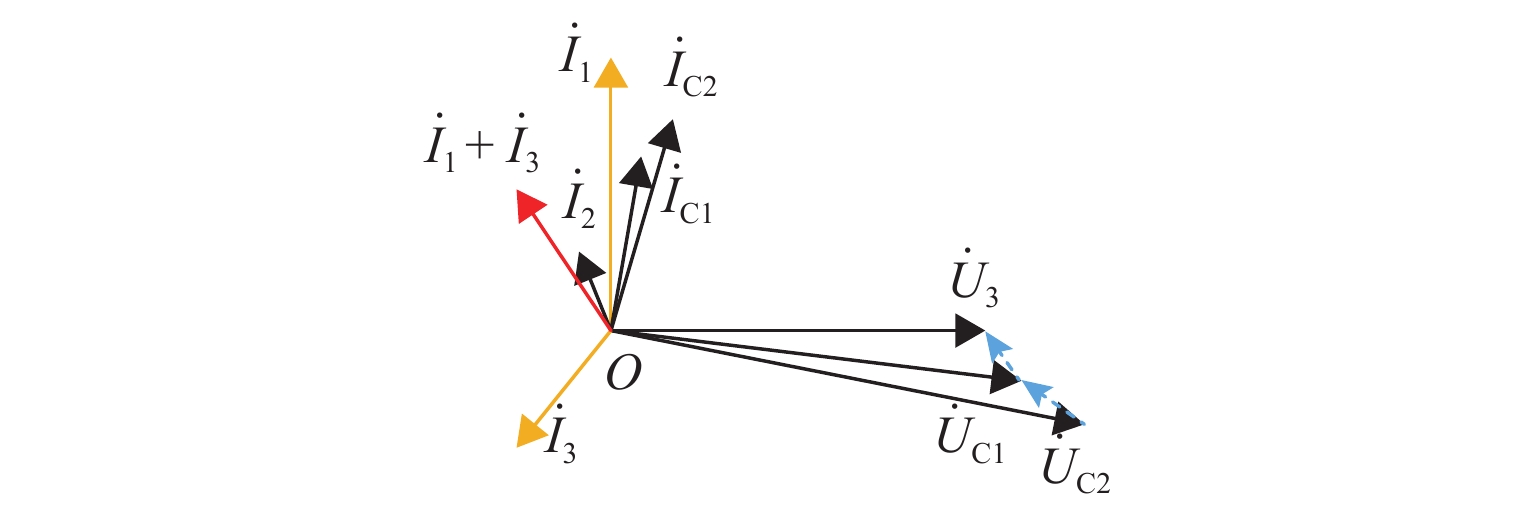
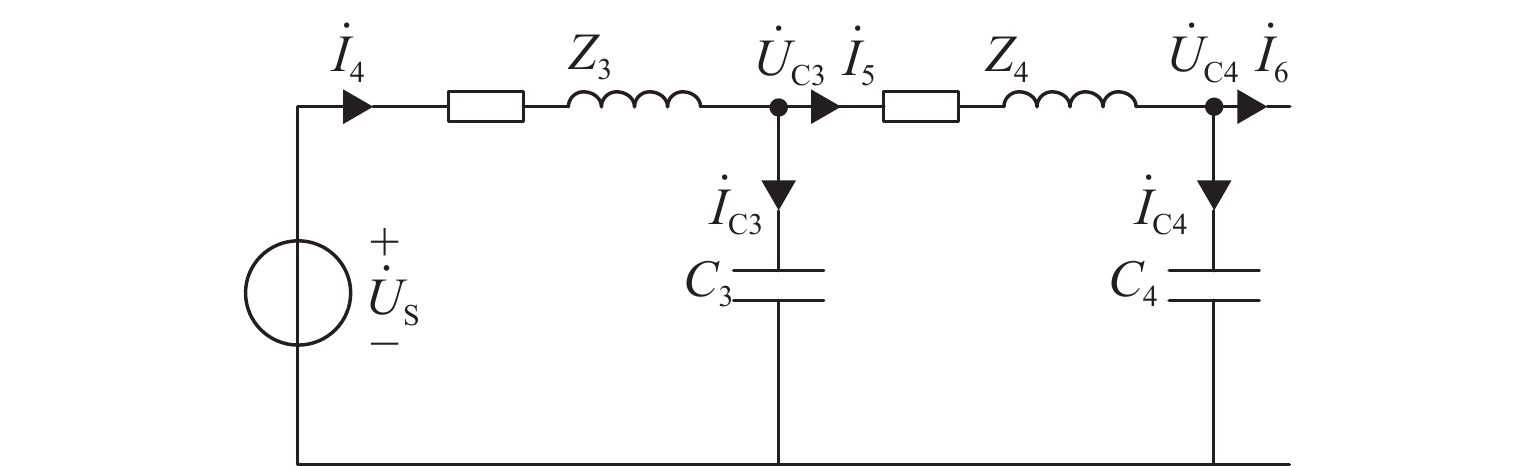
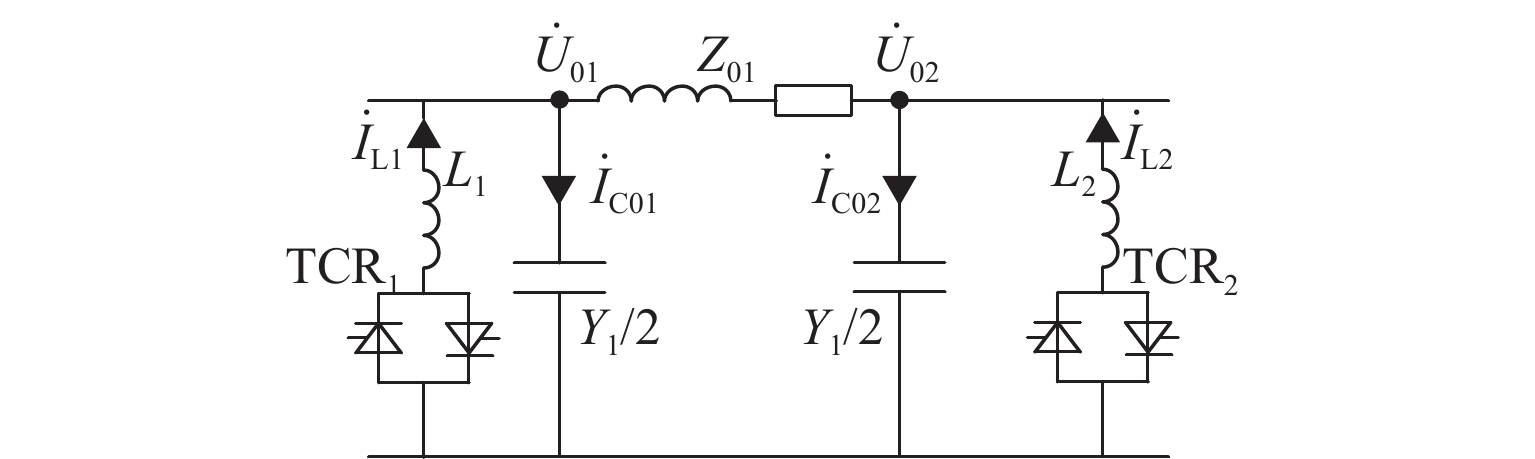
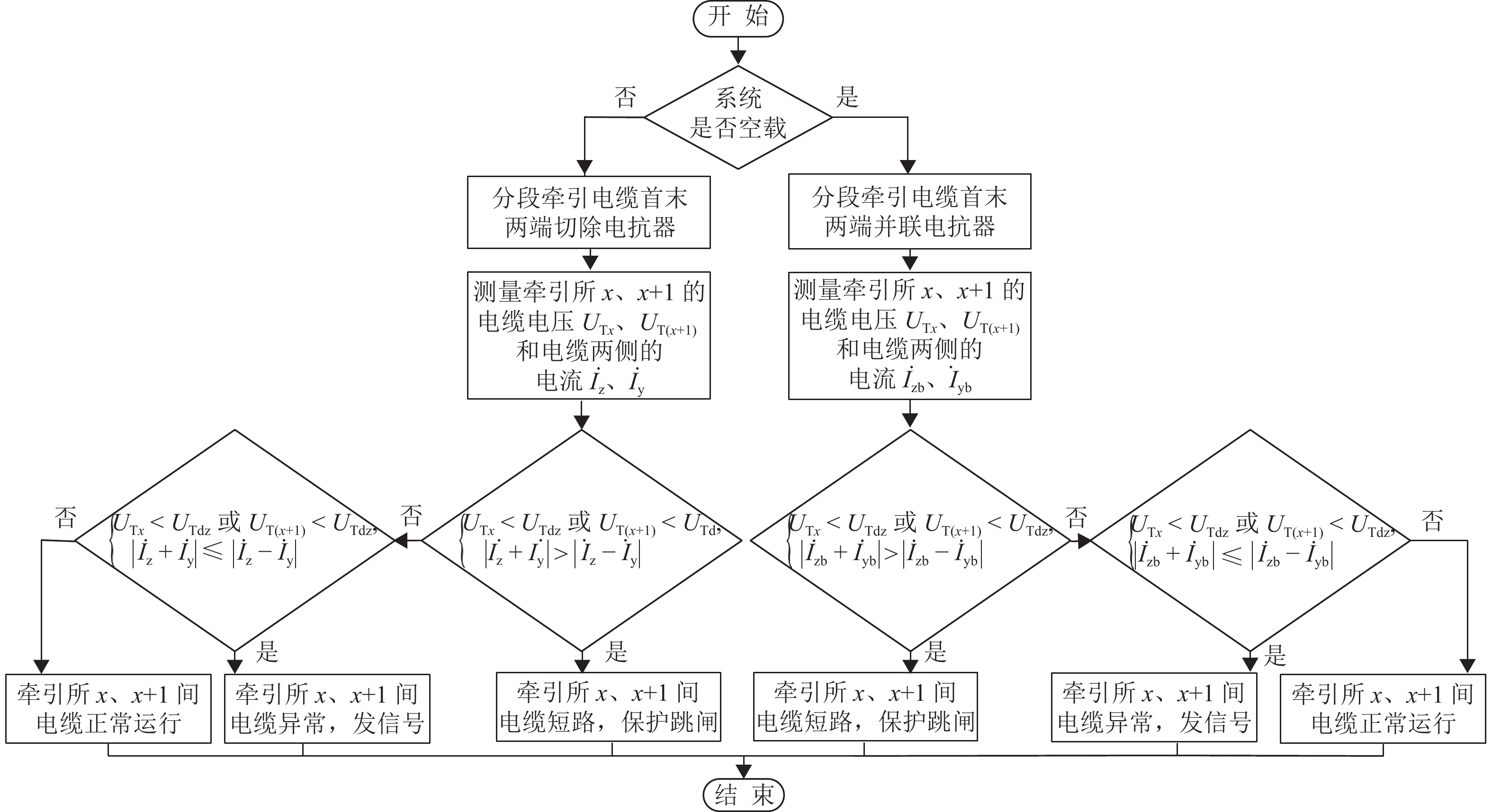
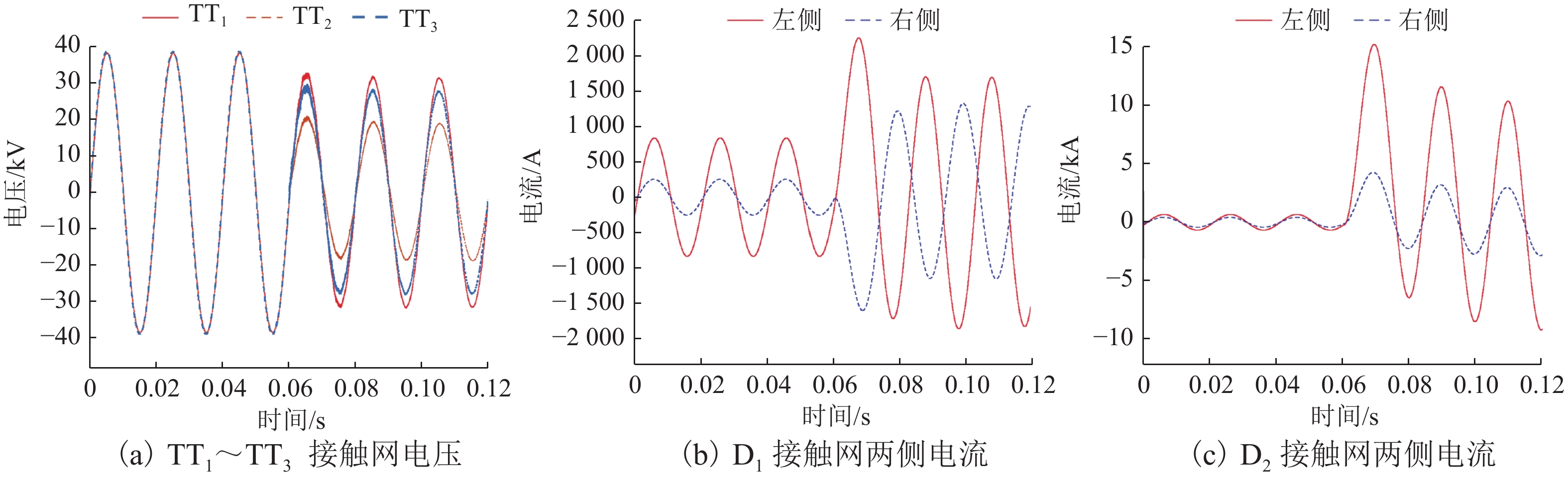
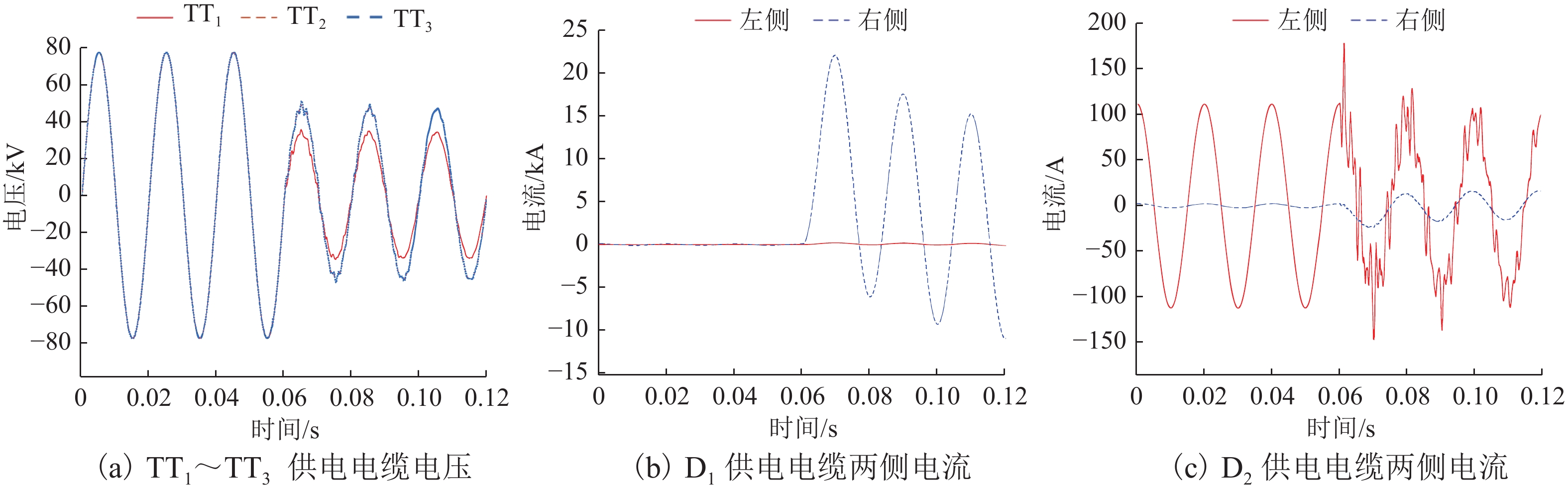
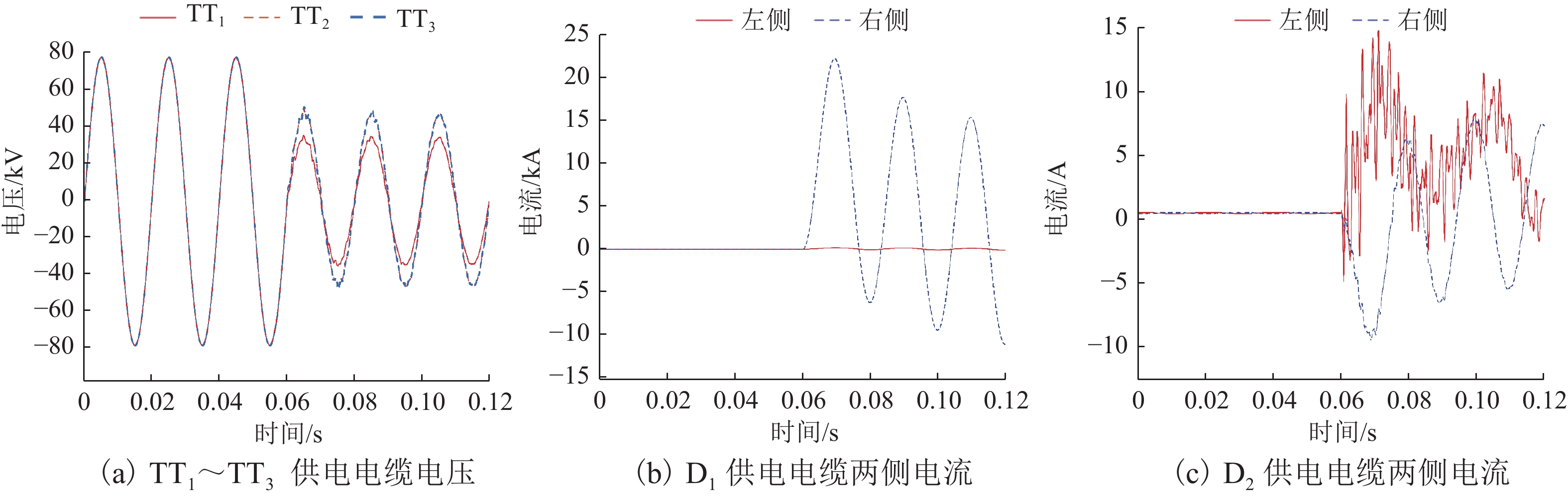
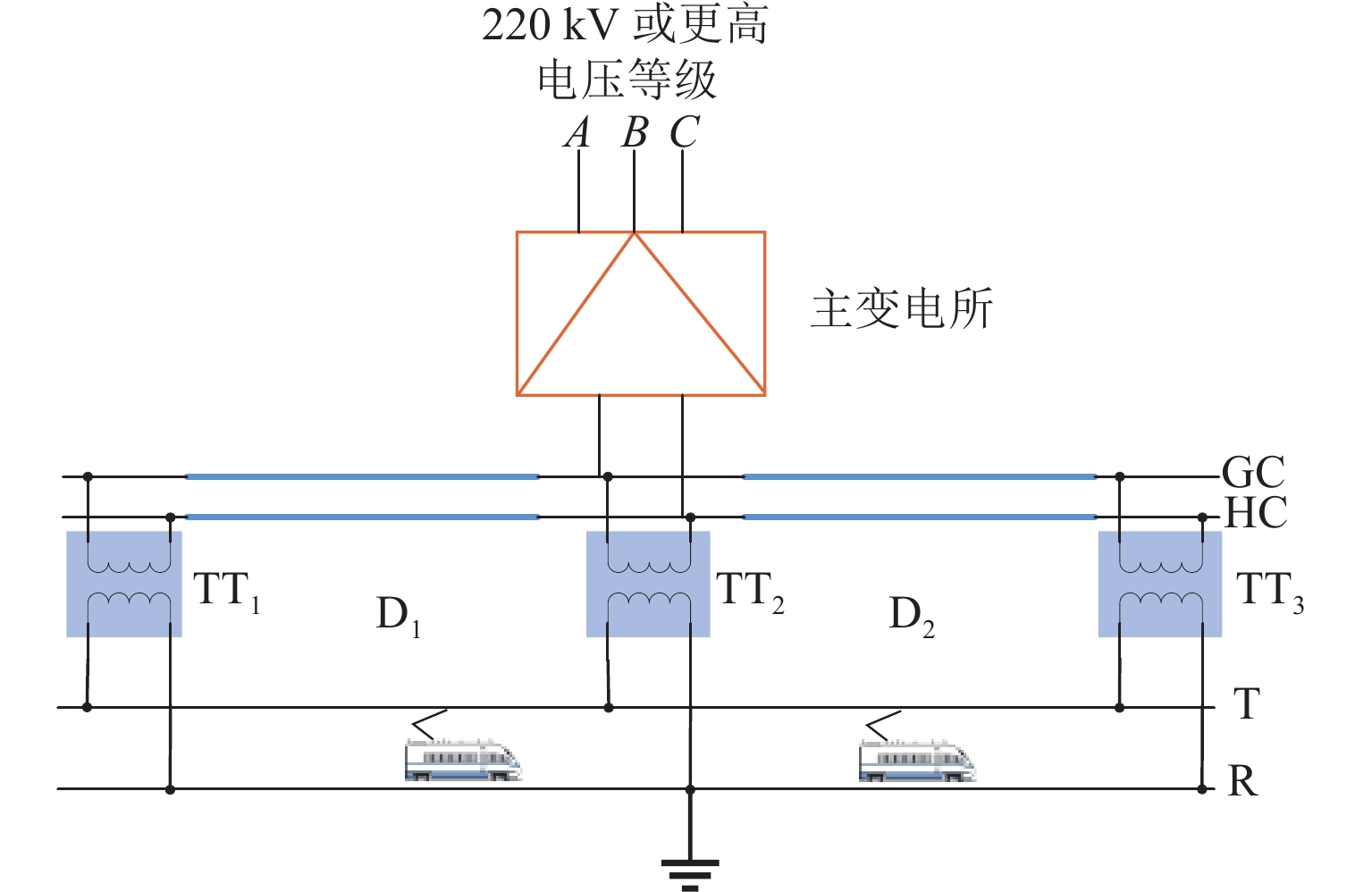
为解决新型电缆贯通供电系统的接触网和牵引电缆使用现有分段保护方案会误动作的问题,研究负荷电流对接触网电流纵差保护的作用机理,提出接触网采用故障分量电流纵差保护方案;并利用相量法分析空载情况下电容电流对牵引电缆现有保护方案的影响,通过在每个分段回路牵引电缆的首、末两端空载时并联电抗器,及负载时切除电抗器,实现电流纵差的保护. 研究结果表明:接触网中的负荷电流由两侧牵引变压器一起供给是引起接触网电流纵差保护误动作的原因,而提出的采用故障分量电流构成的接触网短路保护不受双边供电下正常负荷电流的影响;空载情况下,电容电流会使牵引电缆末端电流较首端电流的幅值和相角发生变化,导致保护误动作,提出的牵引电缆首末两端并联电抗器的方法可以解决这个问题.
-
关键词:
- 新型电缆贯通供电系统 /
- 分段保护 /
- 电流纵差保护 /
- 故障分量电流 /
- 电容电流
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of misoperation of catenary and traction cables in a new continuous cable power supply system using the existing sectional protection scheme, firstly, the mechanism of load current on current longitudinal differential protection of the catenary was studied, and a fault component current longitudinal differential protection scheme of the catenary was proposed. Then the phasor method was used to analyze the influence of capacitance current on the existing protection scheme of traction cables under no load condition. The protection of longitudinal current difference was realized by shunting reactors at both ends of the traction cable in each sectional loop under no load and cutting off the reactor under load. The results show that the load current in the catenary supplied by the traction transformers on both sides is the cause of the misoperation of the current longitudinal differential protection of the catenary. However, the proposed short-circuit protection of the catenary composed of fault component current is not affected by the normal load current under the bilateral power supply. Under no load condition, the capacitance current will change the amplitude and phase angle of the end current of the traction cable compared with the first end current, resulting in the misoperation of the protection. The proposed method of shunting reactors at both ends of traction cables can solve this problem.
-
表 1 工况1数据
Table 1. Data under working condition 1
方法 U1/kV U2/kV U3/kV D1 差动电流/A D1 制动电流/A D2 差动电流/A D2 制动电流/A 现有方法 17.198 17.247 17.385 491.264 0 496.225 0 本文方法 17.198 17.247 17.385 0 0 0 0 表 2 工况2数据
Table 2. Data under working condition 2
方法 U1/kV U2/kV U3/kV D1 差动电流/A D1 制动电流/A D2 差动电流/A D2 制动电流/A 现有方法 22.402 13.588 19.798 582.223 0 8951.995 0 本文方法采样 1 26.719 26.291 26.813 84.654 332.961 3480.336 828.158 本文方法采样 2 25.524 23.080 24.869 115.695 1049.229 11058.398 2368.965 本文方法采样 3 25.103 21.813 24.144 11.336 1161.157 13402.426 2740.661 本文方法采样 4 24.627 20.622 23.409 120.269 382.164 7222.369 1448.219 本文方法采样 5 23.018 15.829 20.827 144.321 682.623 2614.296 442.224 本文方法采样 6 22.402 13.588 19.798 36.965 1012.364 6693.269 1117.495 表 3 空载电容电流
Table 3. Capacitance current without load
A D1 左侧 D1 右侧 D2 左侧 D2 右侧 33.522i 33.429i 40.123i 40.284i 表 4 各种工况下回路D1、D2供电电缆数据
Table 4. Data of power supply cables in D1 and D2 loops under various working conditions
工况 UT1/kV UT2 /kV UT3/kV D1 差动电流/A D1 制动电流/A D2 差动电流/A D2 制动电流/A 负载正常运行 54.784 55.042 55.019 66.124 284.125 83.256 155.546 负载 D1 供电电缆接地 24.124 32.890 32.821 9154.159 9049.589 77.553 94.227 负载 D1 电缆相间短路 0.653 24.842 24.677 12614.594 12186.234 35.556 85.269 现有方法空载非短路运行 35.326 35.228 35.368 63.334 0 79.956 0 现有方法空载 D1 供电电缆接地 24.390 32.984 33.055 9191.226 0 154.953 0 现有方法空载 D1 电缆相间短路 0.686 24.886 24.817 12650.221 0 133.895 0 本文方法空载非短路运行 35.001 35.001 35.001 0.080 221.665 0.110 311.000 本文方法空载 D1 供电电缆接地 24.147 32.765 32.652 9203.228 9038.965 0.211 199.356 本文方法空载 D1 电缆相间短路 0.667 24.837 24.681 12633.968 12178.846 0.051 568.596 -
[1] MA F J, LUO A, XU X Y, et al. A simplified power conditioner based on half-bridge converter for high-speed railway system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 60(2): 728-738. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2206358 [2] CHEN M W, LI Q Z, ROBERTS C, et al. Modelling and performance analysis of advanced combined co-phase traction power supply system in electrified railway[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2016, 10(4): 906-916. [3] 李群湛. 城市轨道交通交流牵引供电系统及其关键技术[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(2): 199-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.001LI Qunzhan. Industrial frequency single-phase AC traction power supply system and its key technologies for urban rail transit[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(2): 199-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.02.001 [4] 李群湛,易东,贺建闽. 交流电气化铁路牵引电缆供电分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2013,48(1): 81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.01.013LI Qunzhan, YI Dong, HE Jianmin, el al. Power supply capacity of traction cable for AC electrified railway[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(1): 81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2013.01.013 [5] 周婷,解绍锋. 电气化铁路新型电缆供电方案[J]. 电力自动化设备,2018,38(7): 189-195,206. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.07.026ZHOU Ting, XIE Shaofeng. New-type cable traction power supply scheme of electric railroad[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38(7): 189-195,206. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.07.026 [6] 张丽艳,梁世文,李鑫,等. 新型电缆贯通供电系统载流机制[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(3): 650-658.ZHANG Liyan, LIANG Shiwen, LI Xin, et al. Current-carrying mechanism of new continuous cable traction power supply system[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021, 56(3): 650-658. [7] 张丽艳,梁世文,李鑫,等. 新型电缆贯通供电系统运行特性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(16): 5229-5239.ZHANG Liyan, LIANG Shiwen, LI Xin, et al. Operation characteristic analysis on new continuous cable power supply system[J]. Processdings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(16): 5229-5239. [8] 郭鑫鑫,李群湛,解绍锋,等. 电气化铁路高压电缆牵引网电气特性研究[J]. 电力自动化设备,2015,35(12): 132-137. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2015.12.020GUO Xinxin, LI Qunzhan, XIE Shaofeng, et al. Electrical characteristic of cable traction network for electrified railway[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2015, 35(12): 132-137. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2015.12.020 [9] ZHANG L Y, LIANG S W, LI X. Research on the harmonic in new continuous cable traction power supply system and its transmission characteristic[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2020, 14(14): 2710-2719. [10] ZHANG L Y, LIANG S W, JIA Y, et al. Modelling on novel cable traction power supply system and power distribution analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2022, 37(2): 745-754. [11] 范芳芳. 电气化铁路新型电缆牵引供电方式继电保护方案研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. [12] 郭鑫鑫. 电气化铁路电缆牵引网研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. [13] 高厚磊,江世芳,贺家李. 输电线路新型电流差动保护的研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,1999,19(8): 49-53. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.1999.08.011GAO Houlei, JIANG Shifang, HE Jiali. Study on new type of current differential protection for transmission lines[J]. Processings of the CSEE, 1999, 19(8): 49-53. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.1999.08.011 [14] 刘凯,李幼仪,伊沃布林西奇,等. 自适应线路差动保护新原理[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(13): 3440-3450,3363. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.151054LIU Kai, LI Youyi, BRNCIC Ivo, et al. A novel adaptive differential line protection principle[J]. Processings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(13): 3440-3450,3363. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.151054 [15] 伍叶凯,邹东霞. 电容电流对差动保护的影响及补偿方案[J]. 继电器,1997,25(4): 4-8.WU Yekai, ZOU Dongxia. The influence of capacitance current to differential protection and compensation scheme[J]. Relay, 1997, 25(4): 4-8. [16] 刘天琪, 邱晓燕. 电力系统分析理论[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017. [17] 贺家李, 李承丽, 董新洲, 等. 电力系统继电保护原理[M]. 5版. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2018. [18] 马庆安, 董昭德, 郭凯. 电气化铁路牵引网短路电流计算[C]//中国铁道学会自动化委员会. 中国铁道学会电气化委员会2017年年会及新技术研讨会论文集. 北京: 《电气化铁道》编辑部, 2017: 125-129. -




 下载:
下载: