Calculation of Collaborative Power Flow for Urban Rail Traction Power Supply System with Bidirectional Converter Device
-
摘要:
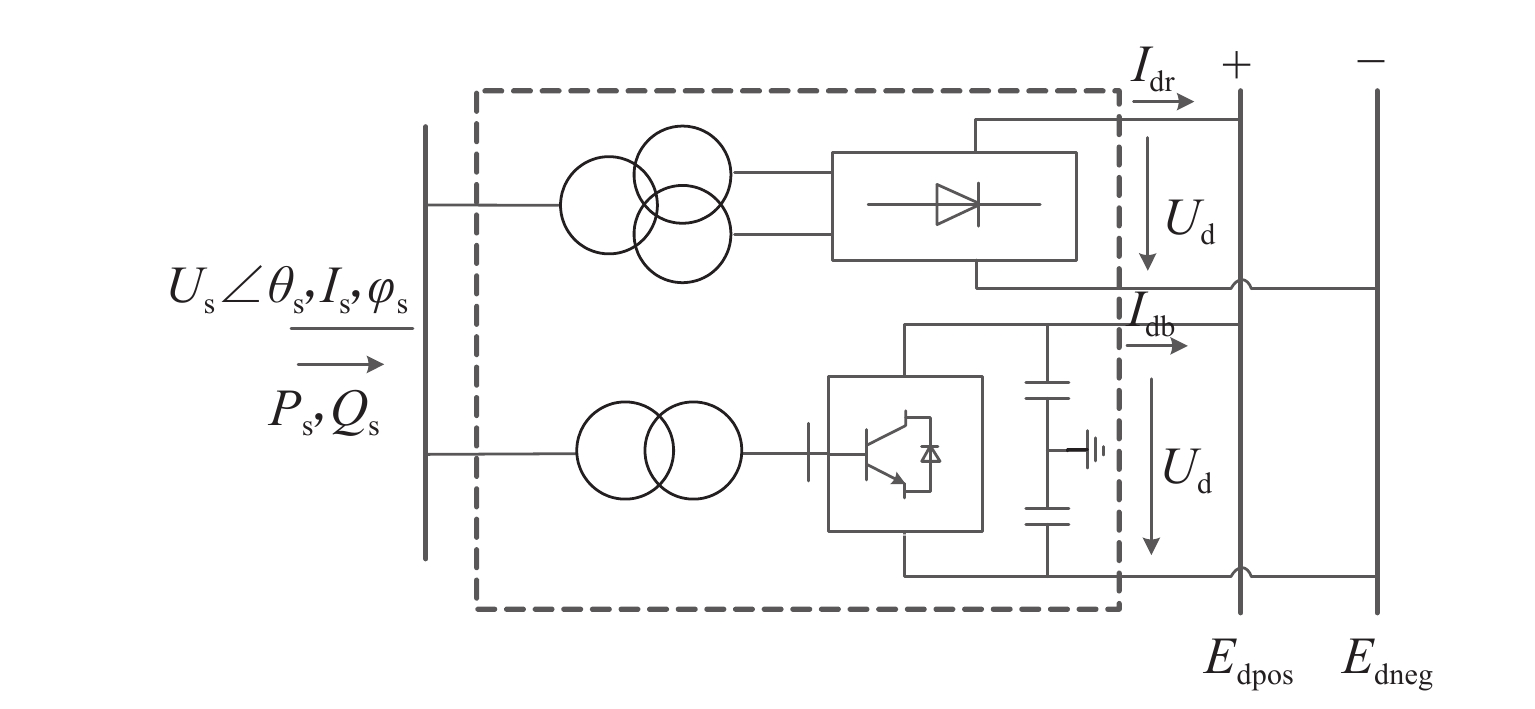
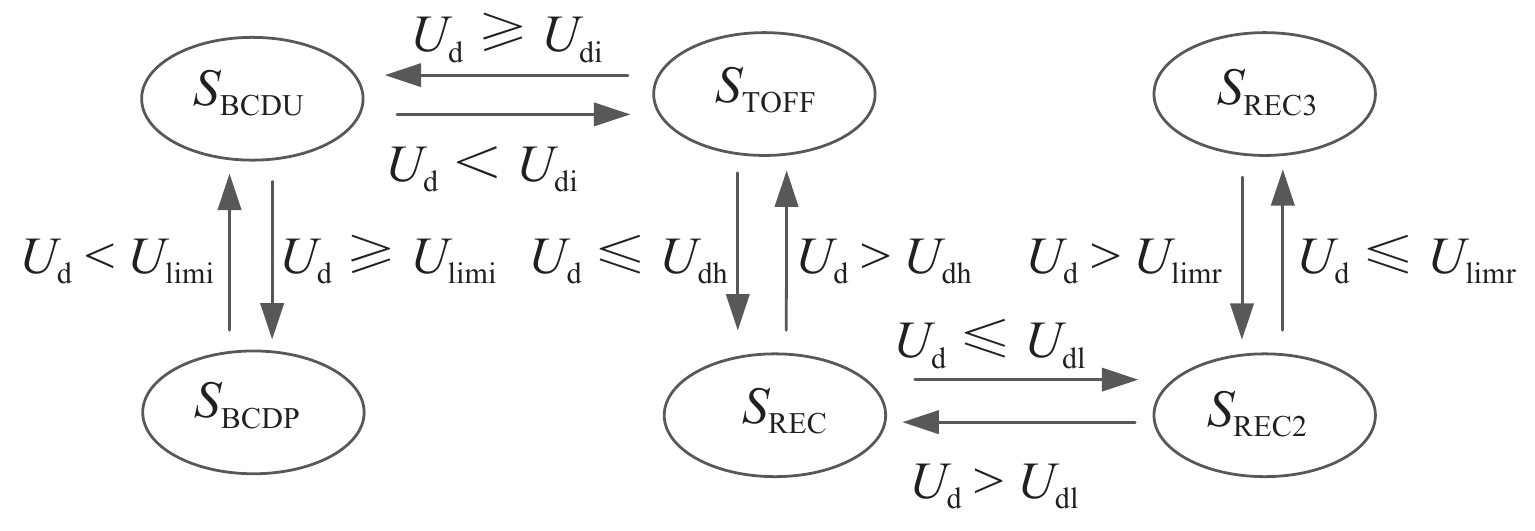
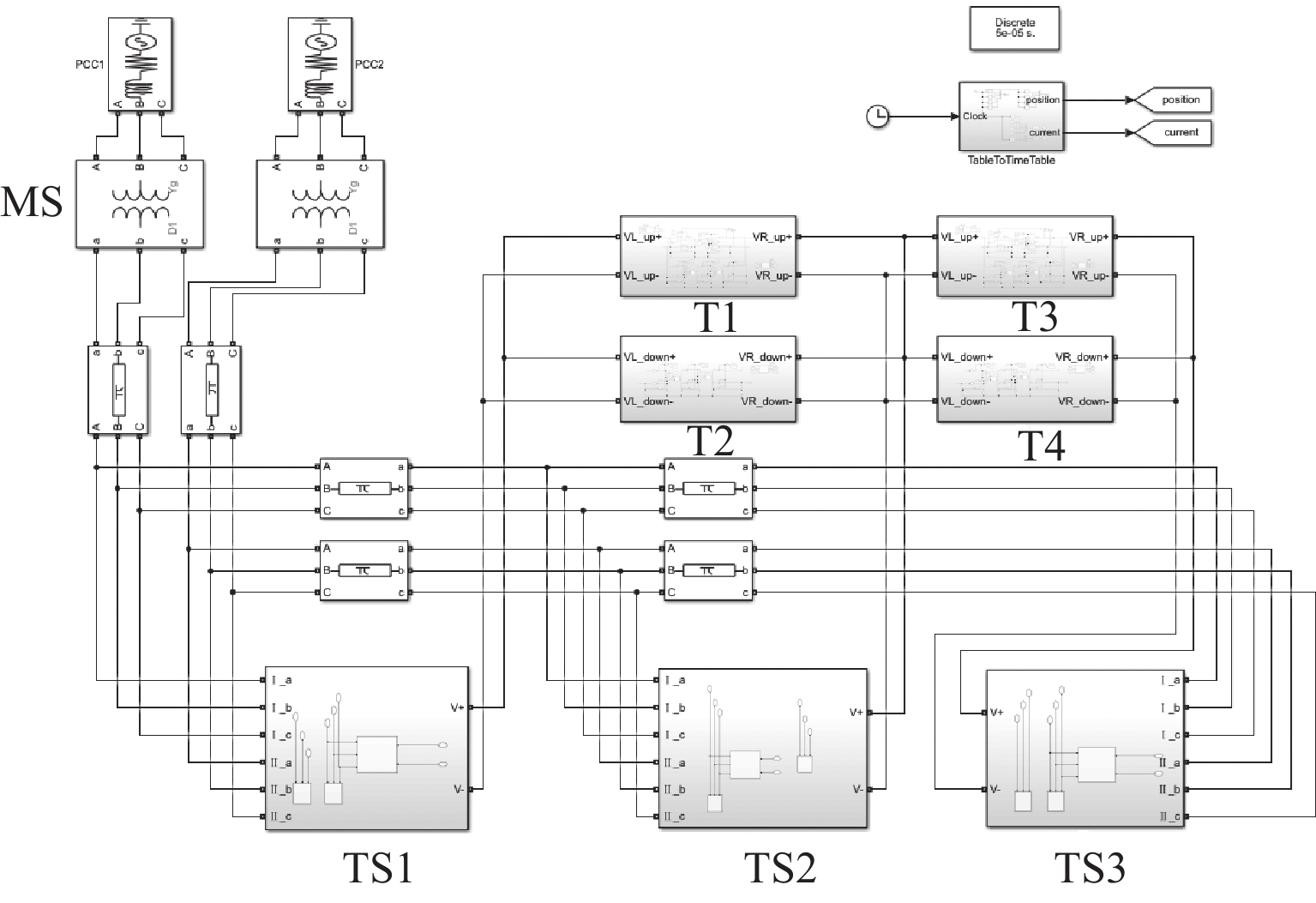
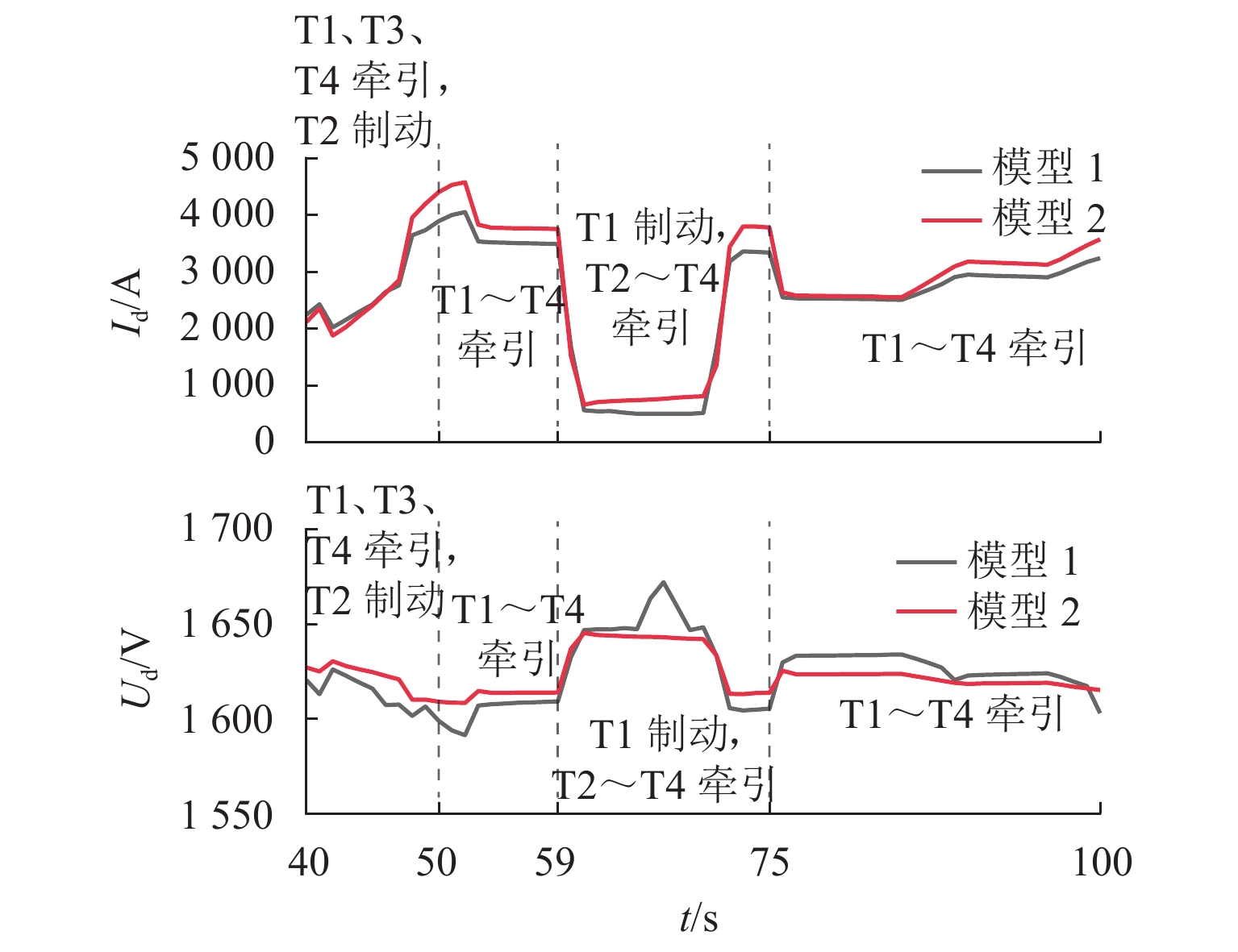
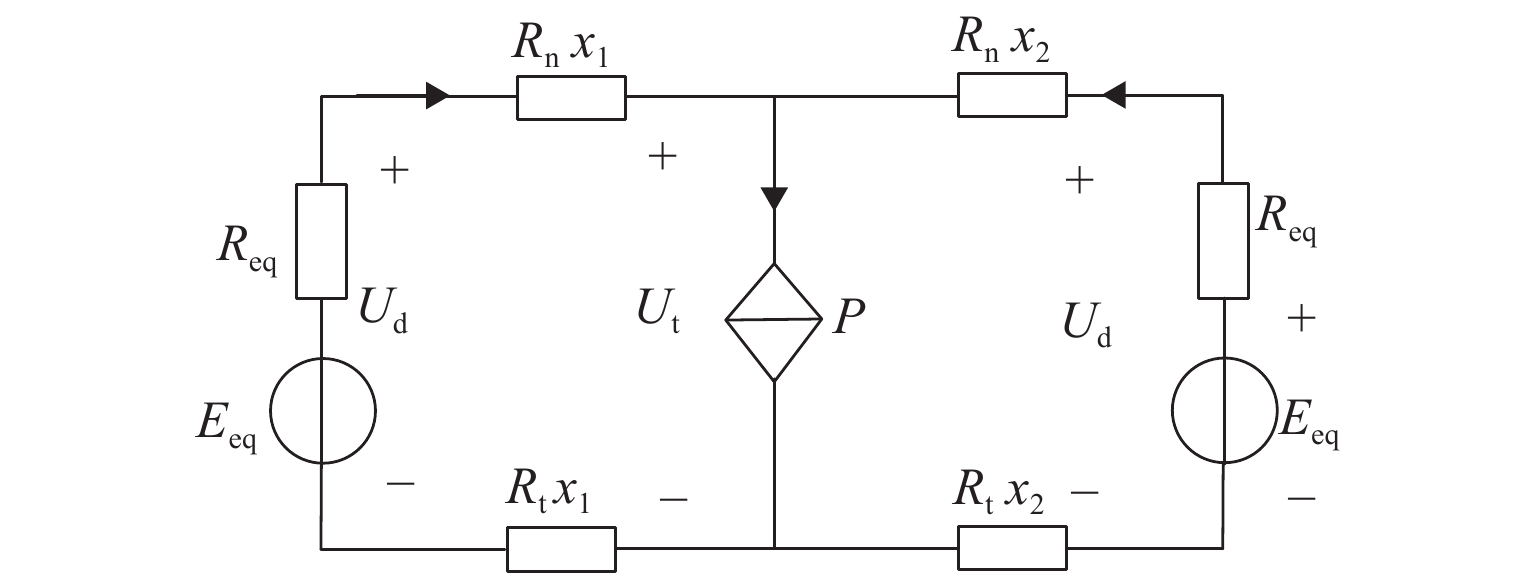
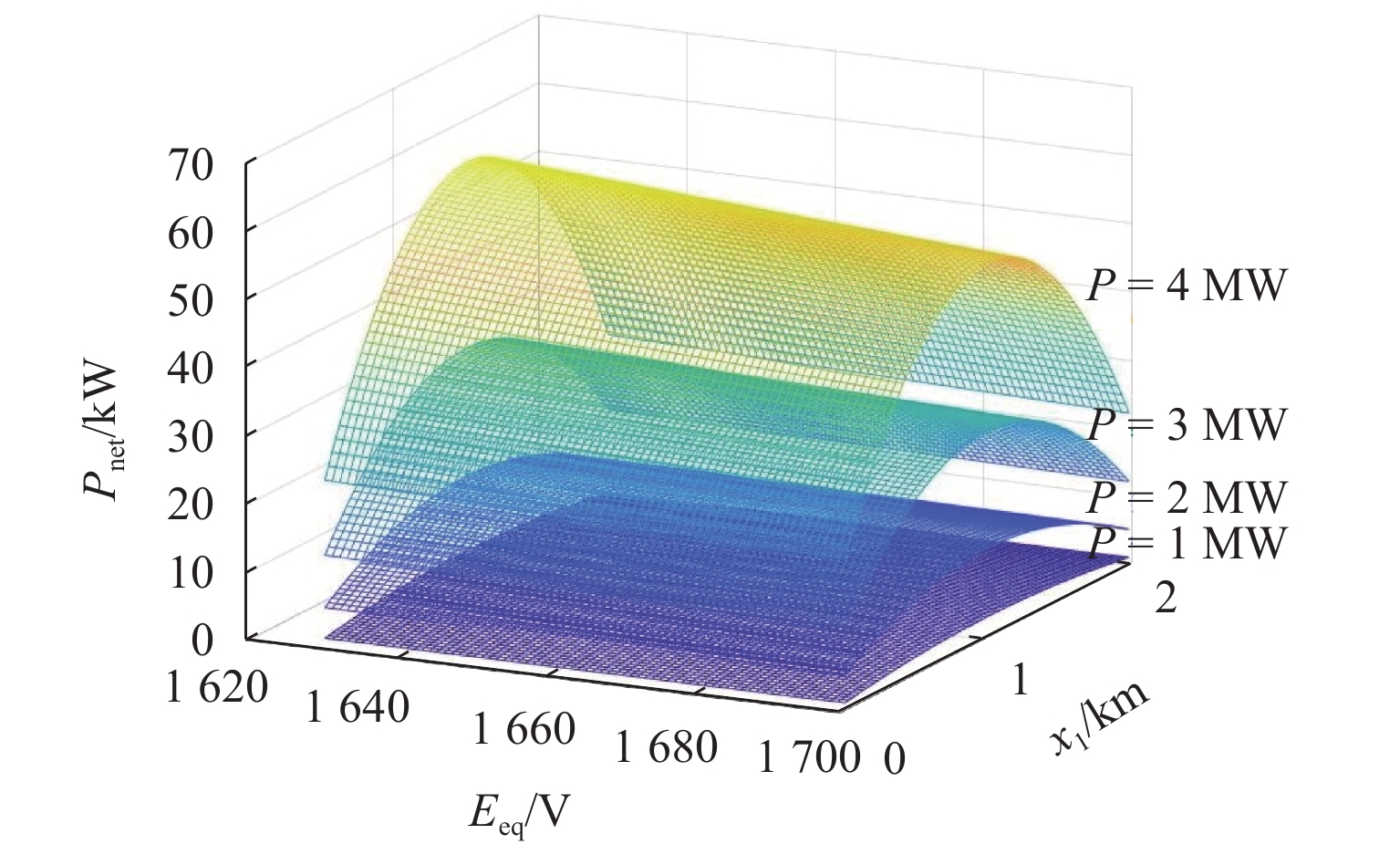
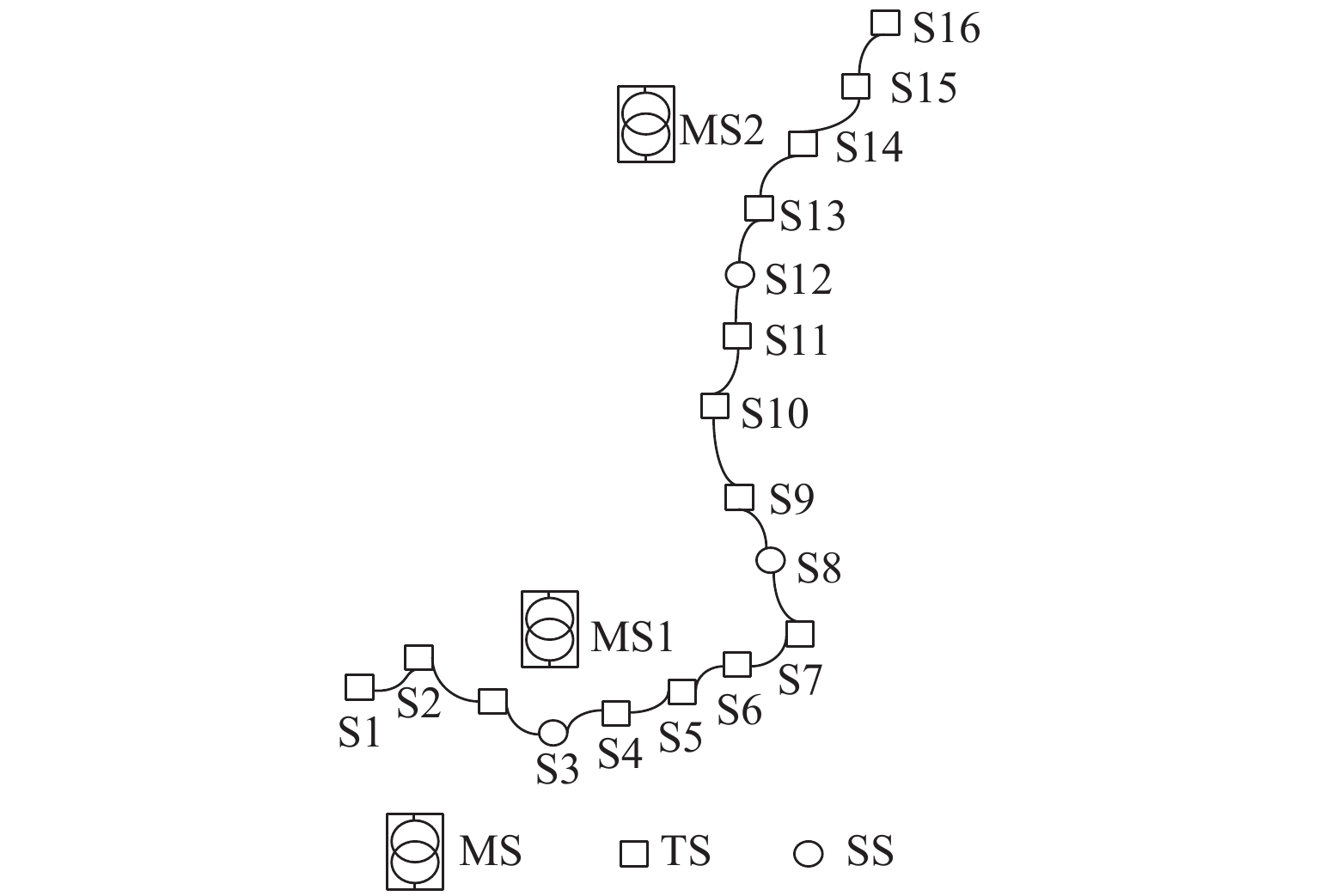
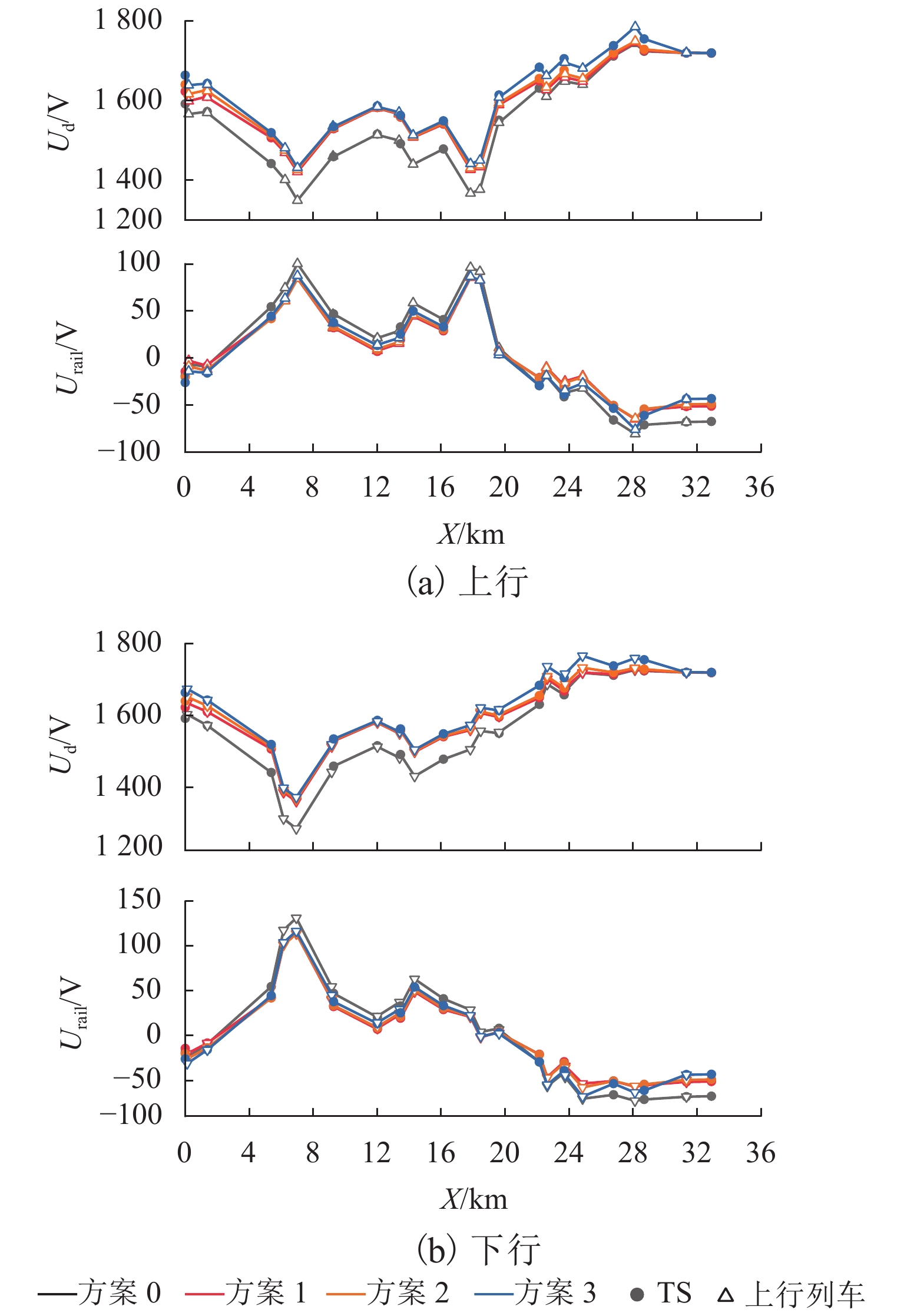
双向变流装置可以有效抑制牵引变电所直流侧网压的波动, 减小跨区间传输的电流,限制钢轨电位. 鉴于电双向变流装置与整流机组的协同控制策略会对城轨牵引供电系统潮流产生直接影响,提出双向变流装置与24 脉波整流机组协同供电的方案,分析该方案下牵引变电所的综合输出外特性;建立计及换流装置精确有功损耗的牵引变电所供电计算模型,并提出考虑滞环比较的多状态切换控制策略,实现含双向变流装置的城轨牵引供电系统协同供电潮流计算;通过与Simulink仿真结果对比,验证算法的有效性及准确性. 以某地铁工程为例进行仿真,仿真结果表明:协同供电方案下,牵引网网压上升,全线上、下行钢轨电位最大值分别降低12.6%~15.6%、14.7%~17.5%,直流牵引供电系统损耗、系统综合成本最多可分别降低9.7%、1.17%;随着双向变流装置整流启动电压增大,部分牵引变电所的整流/逆变功率增大,直流牵引供电系统损耗先升高后降低,但钢轨电位变化不大. 在实际工程中,双向变流装置的逆变启动电压一定时,适当提高其整流启动电压可以获得更佳的节能效果.
Abstract:The bidirectional converter device can effectively inhibit the fluctuation of the DC-side grid voltage at traction substation, reduce the current transmitted between regions, and limit the rail potential. As the collaborative control strategy of the bidirectional converter and rectifier unit will directly affect the power flow of urban rail traction power supply system, a coordinated power supply scheme composed of a bidirectional converter device and a 24-pulse rectifier is proposed, and the comprehensive output characteristics of traction substation with this scheme are analyzed. The power supply calculation model of traction substation is established, allowing for the accurate active power loss of converter device, and a multi-state switching control strategy with hysteresis comparison is proposed to calculate the cooperative power flow for urban rail traction power supply system with a bidirectional converter device. Compared with Simulink simulation results, the effectiveness and accuracy of the algorithm are verified. In the simulation of a subway project, under the collaborative power supply scheme, when the traction network pressure increases, the maximum rail potential decreases by 12.6%–15.6% and 14.7%–17.5% up and down the whole line, respectively. The loss of DC traction power supply system and the overall cost of the system can be reduced by 9.7% and 1.17% at most. As the rectifier starting voltage of the bidirectional converter device increases, the rectifier/inverter power of some traction substations increases, and the loss of DC traction power supply system increases first and then decreases, but the rail potential changes little. In practice, when the inverter starting voltage of the bidirectional converter is fixed, increasing the rectifier starting voltage appropriately can achieve better energy saving.
-
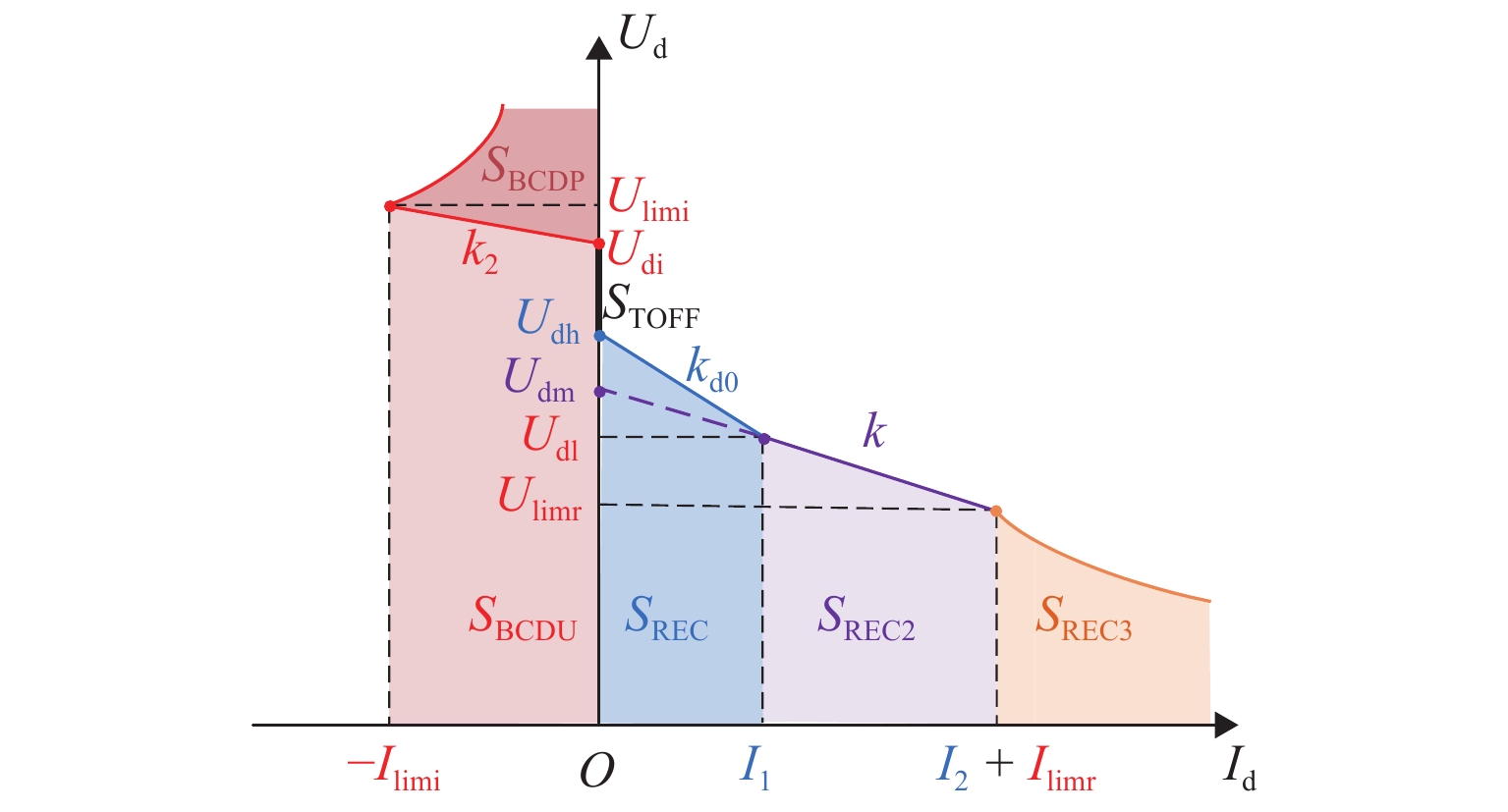
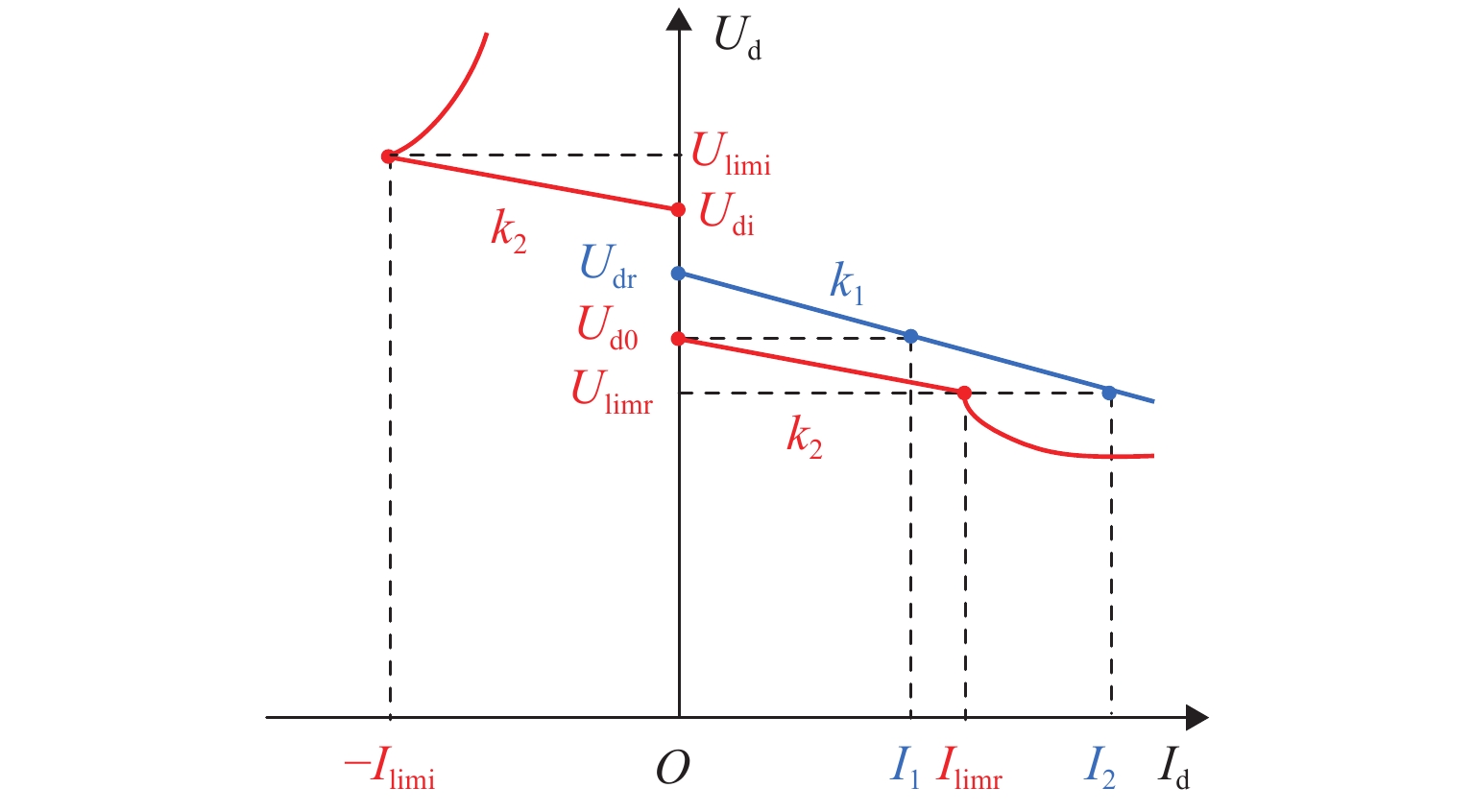
表 1 Ud0 与k2选取
Table 1. Selection of Ud0 and k2
k2/k1 Ud0/Udr 1 − δV 1 1 + δV 1−δk 方案 1 方案 2 方案 3 1 方案 4 方案 5 方案 6 1 + δk 方案 7 方案 8 方案 9 表 2 仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters
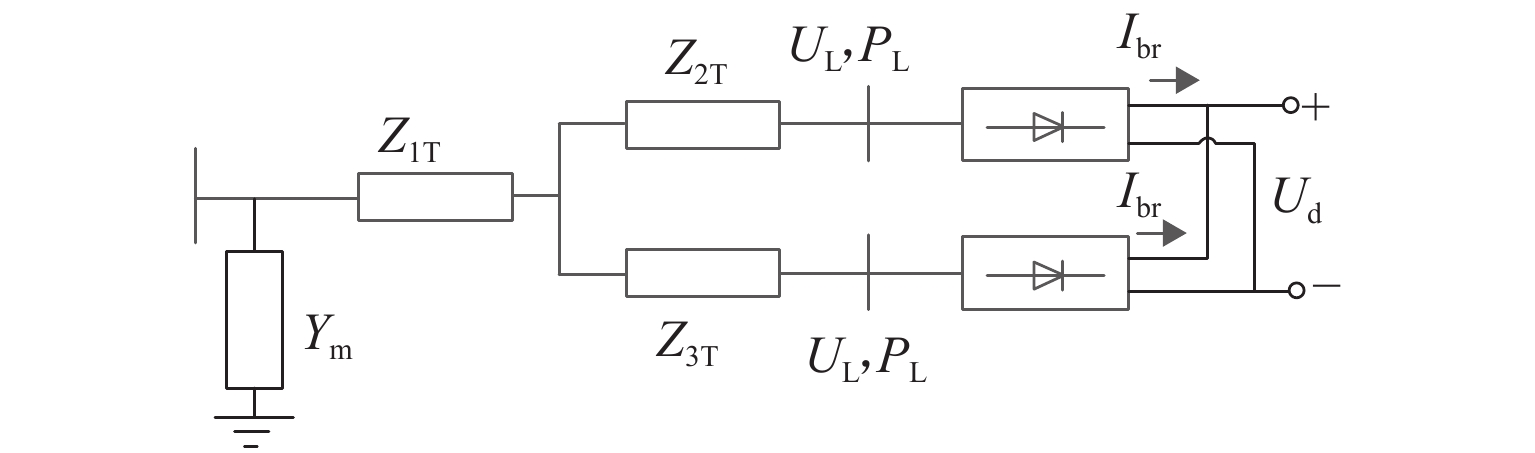
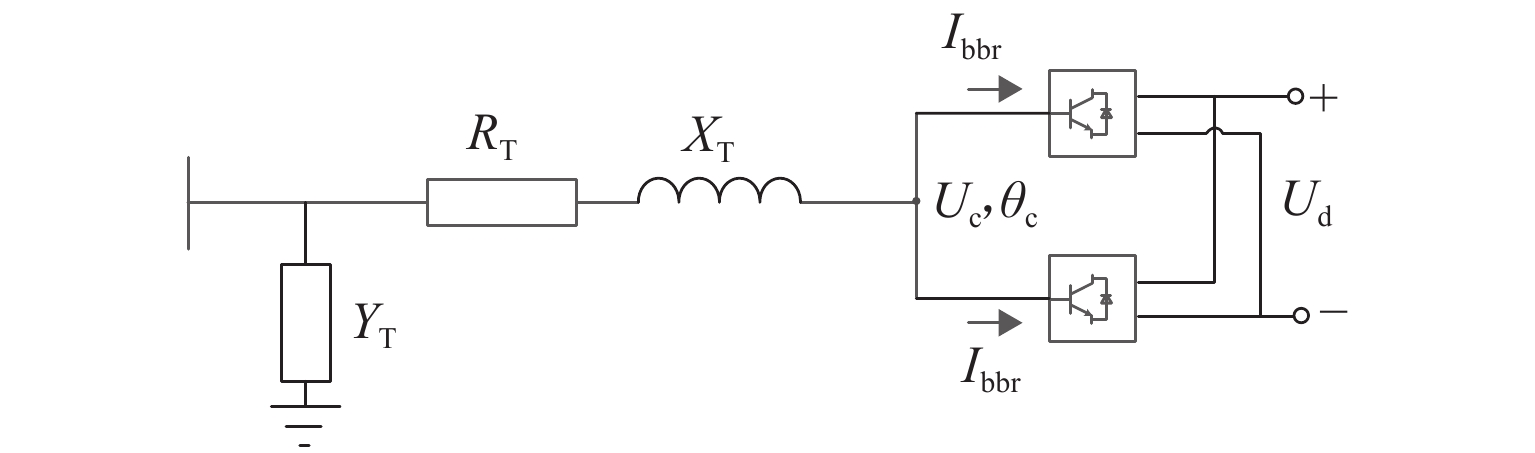
仿真参数 数值 仿真参数 数值 Udr/V 1 664 nb 6 Udi/V 1720 VF/V 1.322 Uon /V 1790 Rn/(Ω·km−1) 0.0172 SB/kW 2 000 Rt/(Ω·km−1) 0.02 SR/kW 3 000 ηs 0.25 SN/kW 1 000 np 4 VN/V 1 500 ns 1 δV/% 2 δk/% 40 表 3 变压器铭牌参数
Table 3. Nameplate parameters of transformer
变压器 短路损耗/kW 空载损耗/kW 穿越阻抗/% 空载电流/% 额定容量/
(MV•A)半穿越阻抗/% 整流变压器 21.544 4.407 7.67 0.256 3.0 6.38 BCD 27.000 6.670 6.00 0.300 2.5 表 4 Pnet与Pdevice对比
Table 4. Comparison of Pnet and Pdevice
kW 控制方案 Pnet Pdevice 模型 1 模型 2 模型 1 模型 2 方案 0 965.941 948.997 78.367 82.017 方案 1 839.404 858.485 129.585 140.863 方案 2 791.650 765.166 156.914 168.105 方案 3 763.240 740.965 186.323 194.123 方案 4 864.456 876.991 131.281 135.308 方案 5 795.564 801.213 147.300 147.922 方案 6 774.569 782.603 159.613 175.122 方案 7 881.667 867.185 127.999 134.818 方案 8 824.344 832.667 138.419 140.062 方案 9 790.304 784.278 152.234 156.016 表 5 工程算例行车组织
Table 5. Traffic organization of cases
发车对
数/对初期运营时
每天持续时间/h近期运营时
每天持续时间/h8 14 3 10 4 11 18 + 9 0 4 表 6 综合成本参数
Table 6. Overall cost parameters
参数 取值 参数 取值 BCD pc/万元 80 EFS pc/万元 40 cmt/元 1000 Y/年 10 N/个 14 Ey/(元·(kW·h−1)−1) 0.75 表 7 算例综合成本
Table 7. Overall costs of cases
万元 控制方案 F(SB,Udi,Udh,k2) 控制方案 F(SB,Udi,Udh,k2) 方案 0 88234.25 方案 5 90123.28 方案 1 89834.89 方案 6 87200.14 方案 2 91338.15 方案 7 89812.72 方案 3 87969.00 方案 8 89235.79 方案 4 89815.68 方案 9 87446.19 -
[1] 刘洋. 城市轨道交通全自动运行模式下的车地无线综合通信网络方案分析[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2019,22(12): 22-25.LIU Yang. Analysis of train/ground wireless communication under full automatic operation mode of urban rail transit[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2019, 22(12): 22-25. [2] 陈昕,杨立新,王财华,等. 双向变流技术在轨道交通牵引供电系统中的应用[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2022,25(8): 145-148,152.CHEN Xin, YANG Lixin, WANG Caihua, et al. Engineering application of bidirectional converter technology in rail transit traction power supply system[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2022, 25(8): 145-148,152. [3] SONG S Y, MCCANN R, JANG G S. Cost-based adaptive droop control strategy for VSC-MTDC system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36(1): 659-669. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2020.3003589 [4] 吴红斌,杨超,陈煜,等. 基于电压源型换流器的多端直流配电网潮流计算[J]. 电力系统自动化,2018,42(11): 79-85,93.WU Hongbin, YANG Chao, CHEN Yu, et al. VSC based power flow calculation of multi-terminal DC distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(11): 79-85,93. [5] 王学奎,彭春华,孙惠娟. 考虑VSC控制策略的交直流混合电网潮流计算[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2023,43(10): 3731-3741.WANG Xuekui, PENG Chunhua, SUN Huijuan. Power flow calculation of AC/DC hybrid power grid considering VSC control strategy[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(10): 3731-3741. [6] ZHANG G, QIAN J L, ZHANG X Y. Application of a high-power reversible converter in a hybrid traction power supply system[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(3): 7030282.1-7030282.19. [7] 徐金平,杜贵府,朱纪法,等. 城市轨道交通双向变流式牵引供电系统的应用[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2020,23(1): 179-182.XV Jinping, DU Guifu, ZHU Jifa, et al. Application of bidirectional converter traction power supply system in urban rail transit[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2020, 23(1): 179-182. [8] 张戬,刘炜,周瑞兵,等. 基于双向变流装置的城市轨道牵引供电系统潮流计算[J]. 中国铁道科学,2020,41(1): 92-98.ZHANG Jian, LIU Wei, ZHOU Ruibing, et al. Power flow of traction power supply system for urban rail transit based on bidirectional converter device[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(1): 92-98. [9] ZHANG J, LIU W, TIAN Z B, et al. Modelling, simulating and parameter designing for traction power system with bidirectional converter devices[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2022, 16(1): 110-122. [10] HAO F J, ZHANG G, CHEN J, et al. Optimal voltage regulation and power sharing in traction power systems with reversible converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35(4): 2726-2735. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2020.2968108 [11] 田胜利. 城轨1500 V 24脉波整流二极管配置分析[J]. 都市快轨交通,2005(1): 31-33. [12] 刘飞,熊晓琪,查鹏程,等. 直流配电网网架结构与分布式光伏多目标协同优化[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(12): 3754-3765.LIU Fei, XIONG Xiaoqi, ZHA Pengcheng, et al. Multi-objective collaborative optimization for DC distribution network configuration and distributed photovoltaic[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(12): 3754-3765. [13] 刘炜,张扬鑫,张戬,等. 考虑牵引所多运行状态的城轨交直流供电计算[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(6): 1163-1170.LIU Wei, ZHANG Yangxin, ZHANG Jian, et al. Calculation of urban rail AC/DC power supply with traction substation in multi-operation modes[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(6): 1163-1170. [14] 刘炜,吴拓剑,禹皓元,等. 直流牵引供电系统地面储能装置建模与仿真分析[J]. 电工技术学报,2020,35(19): 4207-4215.LIU Wei, WU Tuojian, YU Haoyuan, et al. Modeling and simulation of way-side energy storage devices in DC traction power supply system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(19): 4207-4215. [15] 诸斐琴,杨中平,林飞,等. 城轨交通牵引供电系统参数与储能系统容量配置综合优化[J]. 电工技术学报,2019,34(3): 579-588.ZHU Feiqin, YANG Zhongping, LIN Fei, et al. Synthetic optimization of traction power parameters and energy storage systems in urban rail transit[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(3): 579-588. [16] 杜贵府,张栋梁,王崇林,等. 直流牵引供电系统电流跨区间传输对钢轨电位影响[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(11): 129-139.DU Guifu, ZHANG Dongliang, WANG Chonglin, et al. Effect of traction current transmission among power sections on rail potential in DC mass transit system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(11): 129-139. -




 下载:
下载: