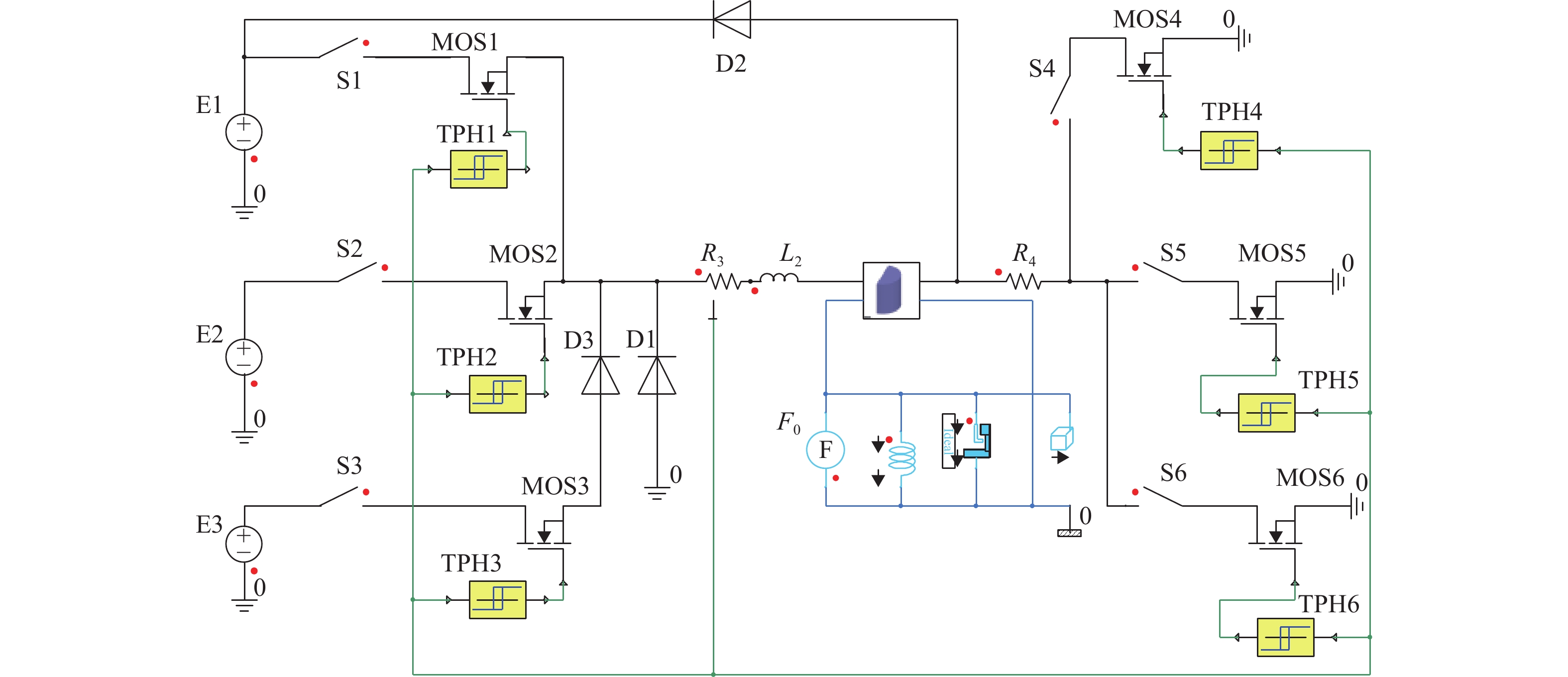
Simulation Research on Coupling Relationship Between Energy Distribution and Dynamic Response of High-Speed Solenoid Valves
-
摘要:
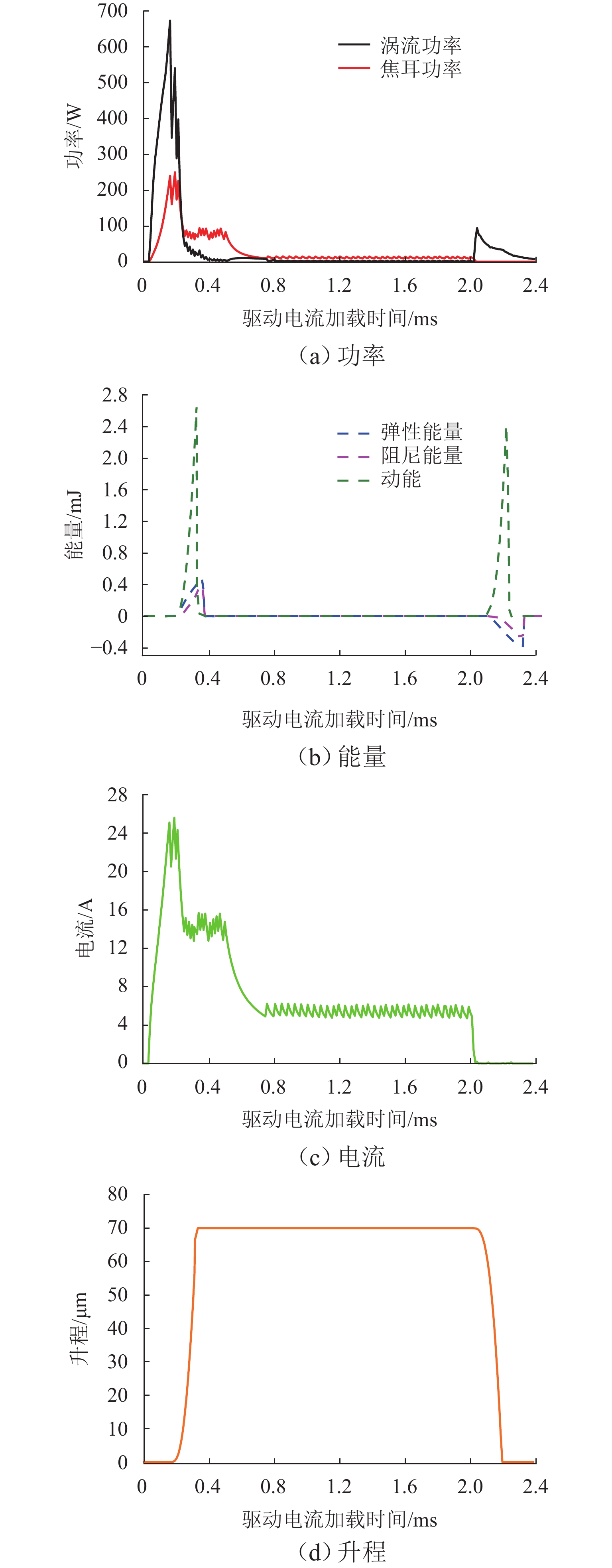
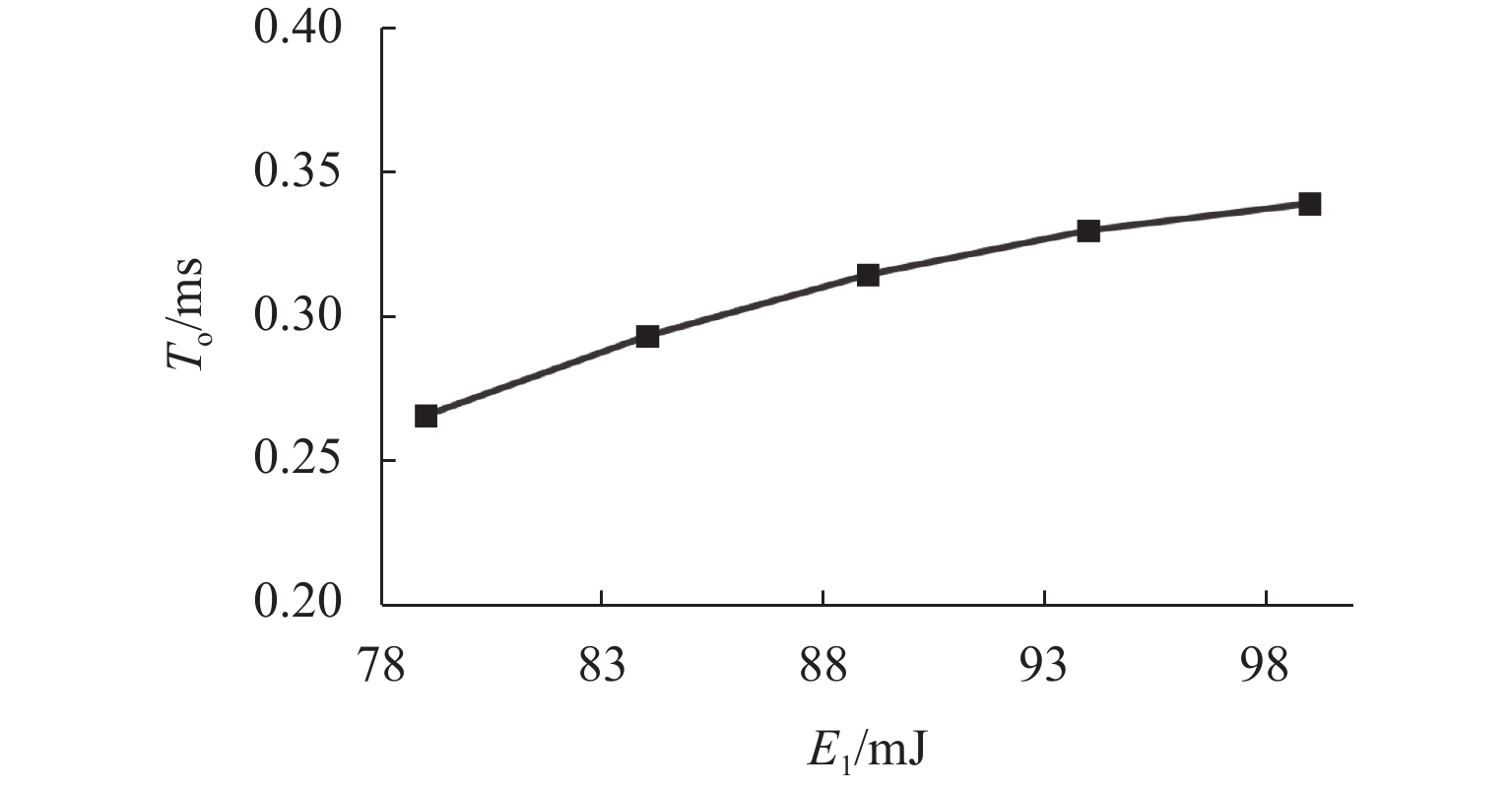
为研究高速电磁阀内部的能量分布及能量参数与动态响应之间的耦合关系,对高速电磁阀性能进行优化. 首先,基于有限元法建立高速电磁阀动态模型,并通过实验数据验证模型的准确性;其次,利用D最优实验设计方法和最小二乘法,构建以能量参数为因素的电磁阀动态响应特性响应面预测模型;最后,使用元效应分析法开展了高速电磁阀动态响应显著能量参数及参数交互作用的仿真分析. 研究结果表明:单参数中涡流能量
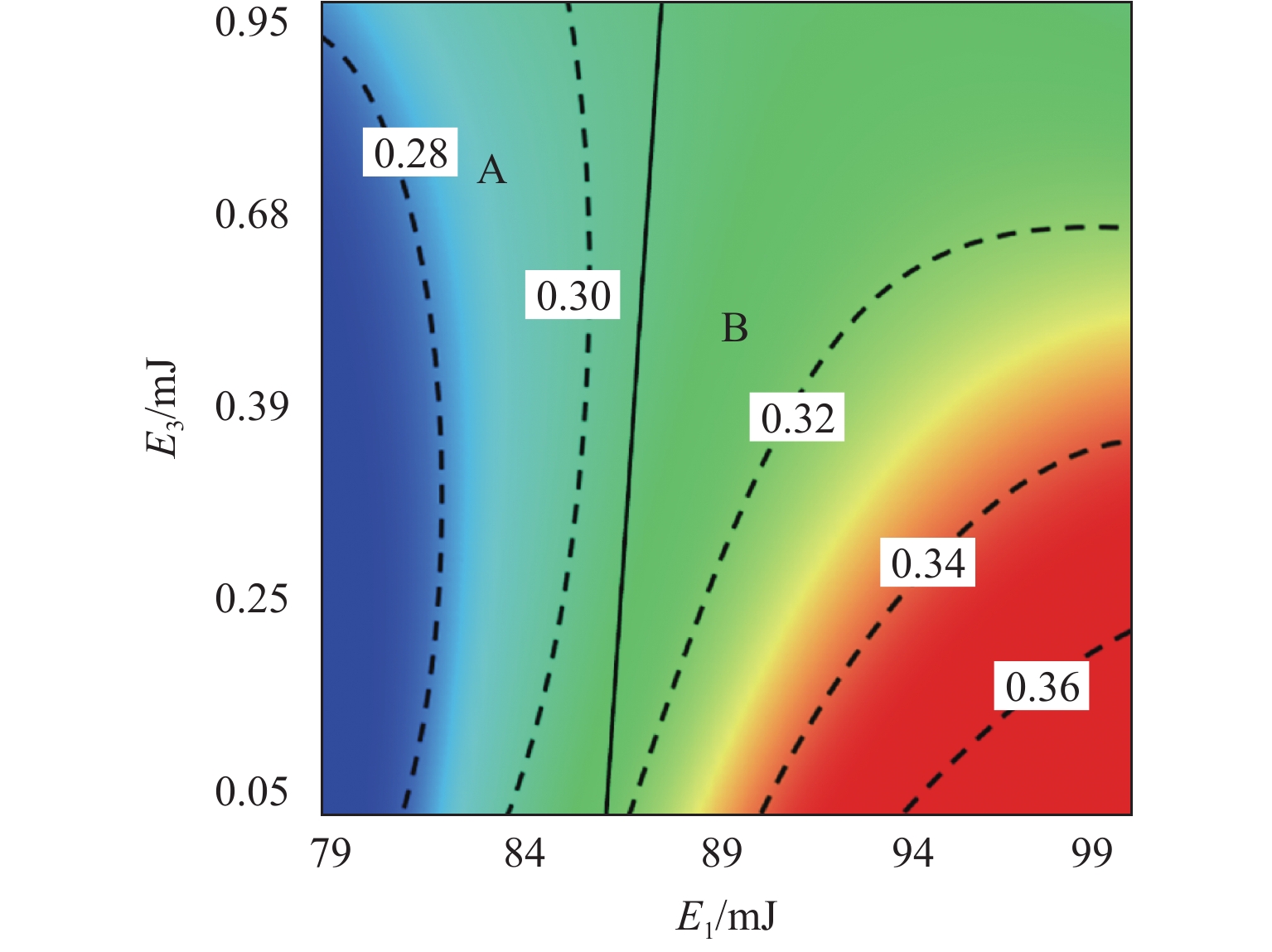
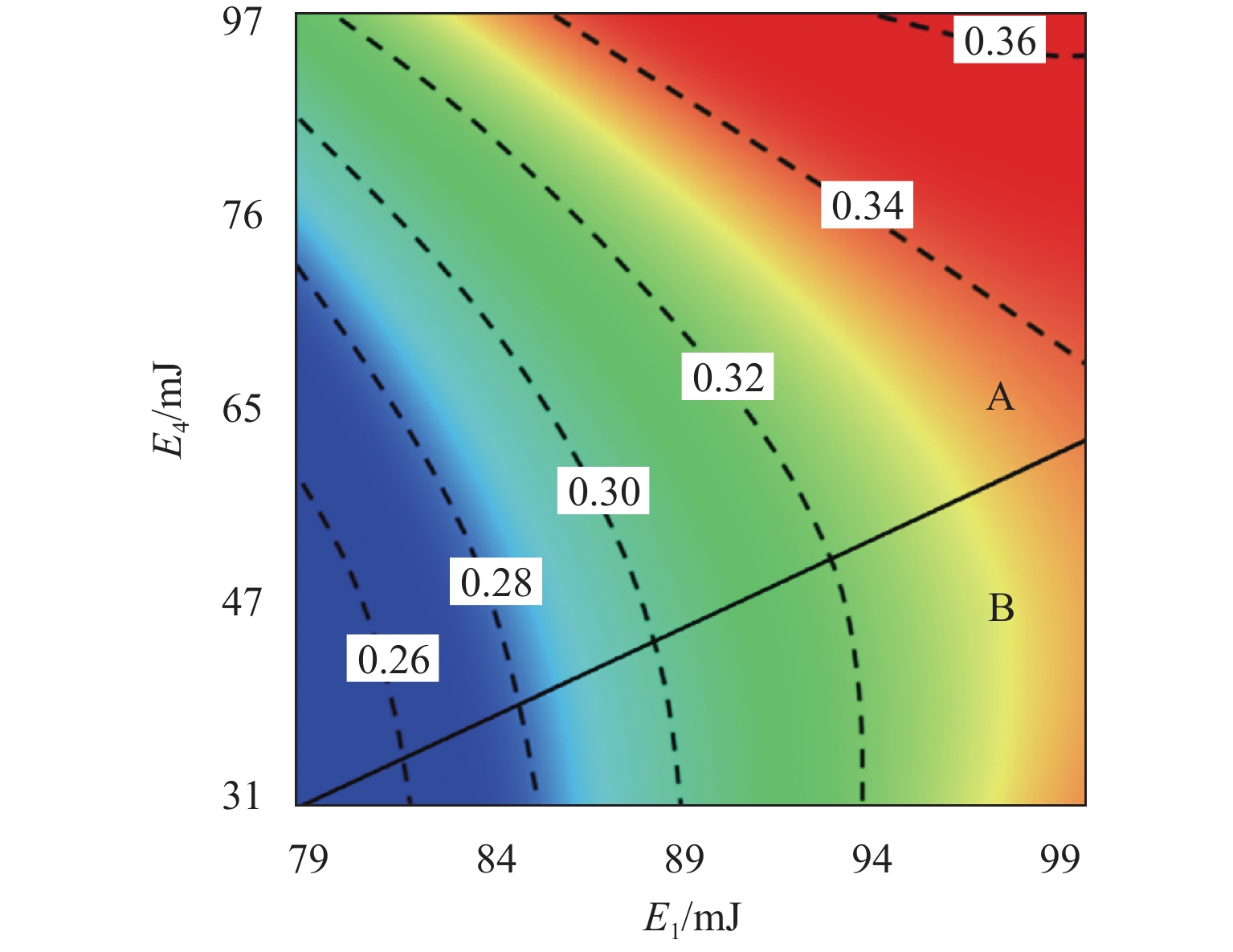
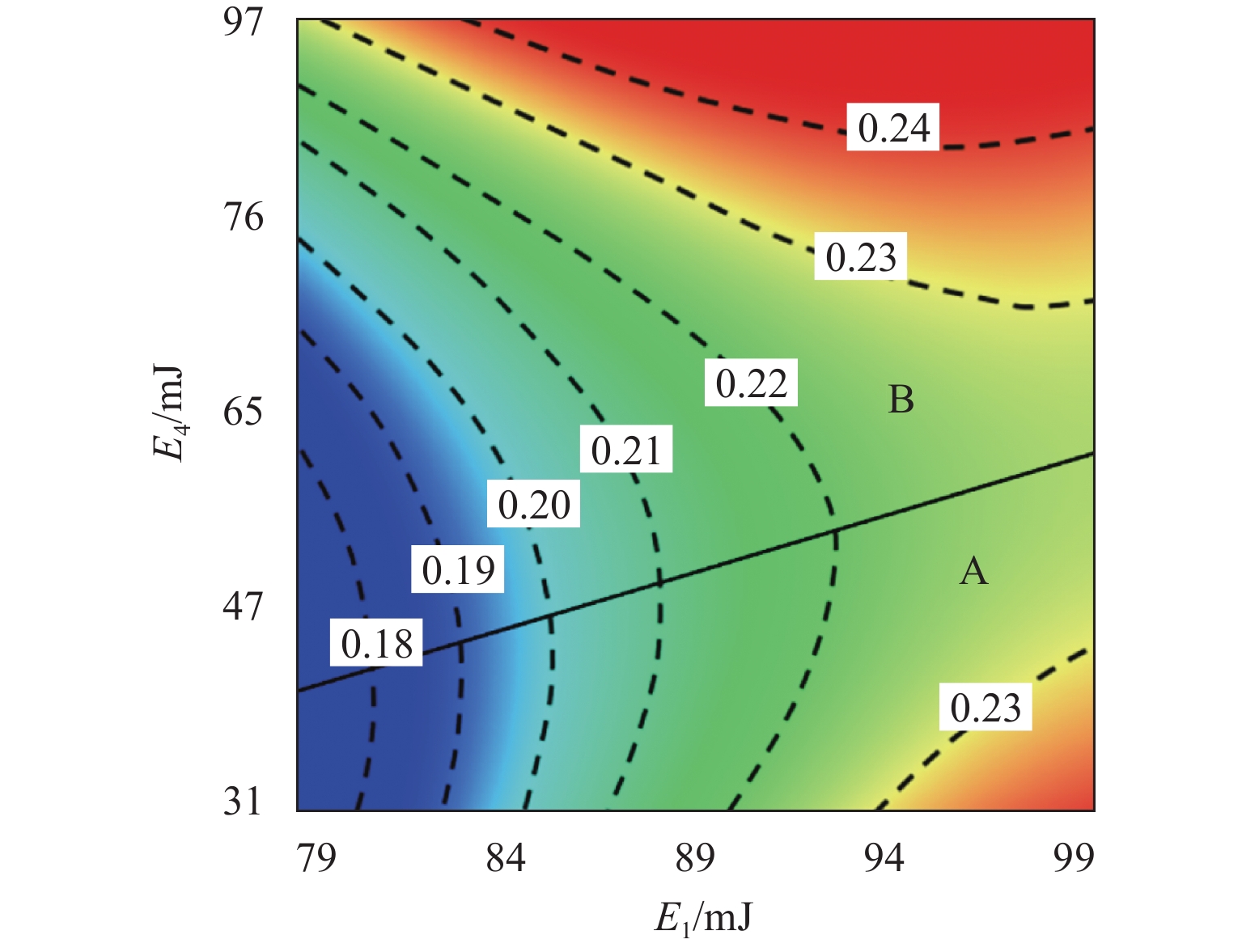
E 1是影响高速电磁阀开启响应时间T o的较敏感参数,T o随着E 1的增加相应地增加了约25%,涡流能量分别与阻尼能量(E 3)和焦耳能量(E 4)之间的交互是影响T o的高敏感参数,同时涡流能量与焦耳能量之间的交互也是影响关闭响应时间T c的高敏感参数;交互参数中起主导作用的因素会随取值范围而改变.Abstract:In order to study the energy distribution inside the high-speed solenoid valve and the coupling relationship between the energy parameters and the dynamic response, the performance of the high-speed solenoid valve was optimized. Firstly, the dynamic model of the high-speed solenoid valve was established based on the finite element method, and the accuracy of the model was validated through the experimental data. Secondly, based on the D-optimal design of experiments and the method of least squares, the response surface prediction model of the solenoid valve’s dynamic response characteristics was constructed, with the energy parameters as the factors. Finally, based on the meta-analysis method, the simulation analysis of the dynamic response of the high-speed solenoid valve with significant energy parameters and parameter interactions was carried out. The results show that the eddy energy
E 1 is the relatively sensitive parameter affecting the response time of high-speed solenoid valve openingT o among the single parameters, andT o increases by about 25% with the increase inE 1. The interaction betweenE 1 and damping energyE 3 and betweenE 1 and Joule energyE 4 is the highly sensitive parameter affectingT o, and the interaction betweenE 1 andE 4 is the highly sensitive parameter affecting the response time of closingT c. The results also find that the factors that play a dominant role in the interaction parameters change with the range of values.-
Key words:
- solenoid valve /
- energy distribution /
- dynamic response /
- response surface method /
- significant factors
-
表 1 高速电磁阀不同阶段能量分布
Table 1. Energy distribution of high-speed solenoid valves at different stages
% 能量 打开阶段 保持阶段 关闭阶段 E1 70.87 57.41 37.05 E2 3.93 17.06 19.03 E3 2.37 25.53 9.69 E4 14.56 0 0 E5 8.27 0 34.23 表 2 参数变化范围
Table 2. Parameter variation range
改变参数 基准值 变化范围 电导率/(S·mm−1) 2000 1400 ~2600 弹簧刚度/(N·mm−1) 57 47~67 阻尼系数/(N·(m·s−1)−1) 95 75~115 电阻/Ω 0.38 0.18~0.58 表 3 仿真计算矩阵
Table 3. Simulation calculation matrix
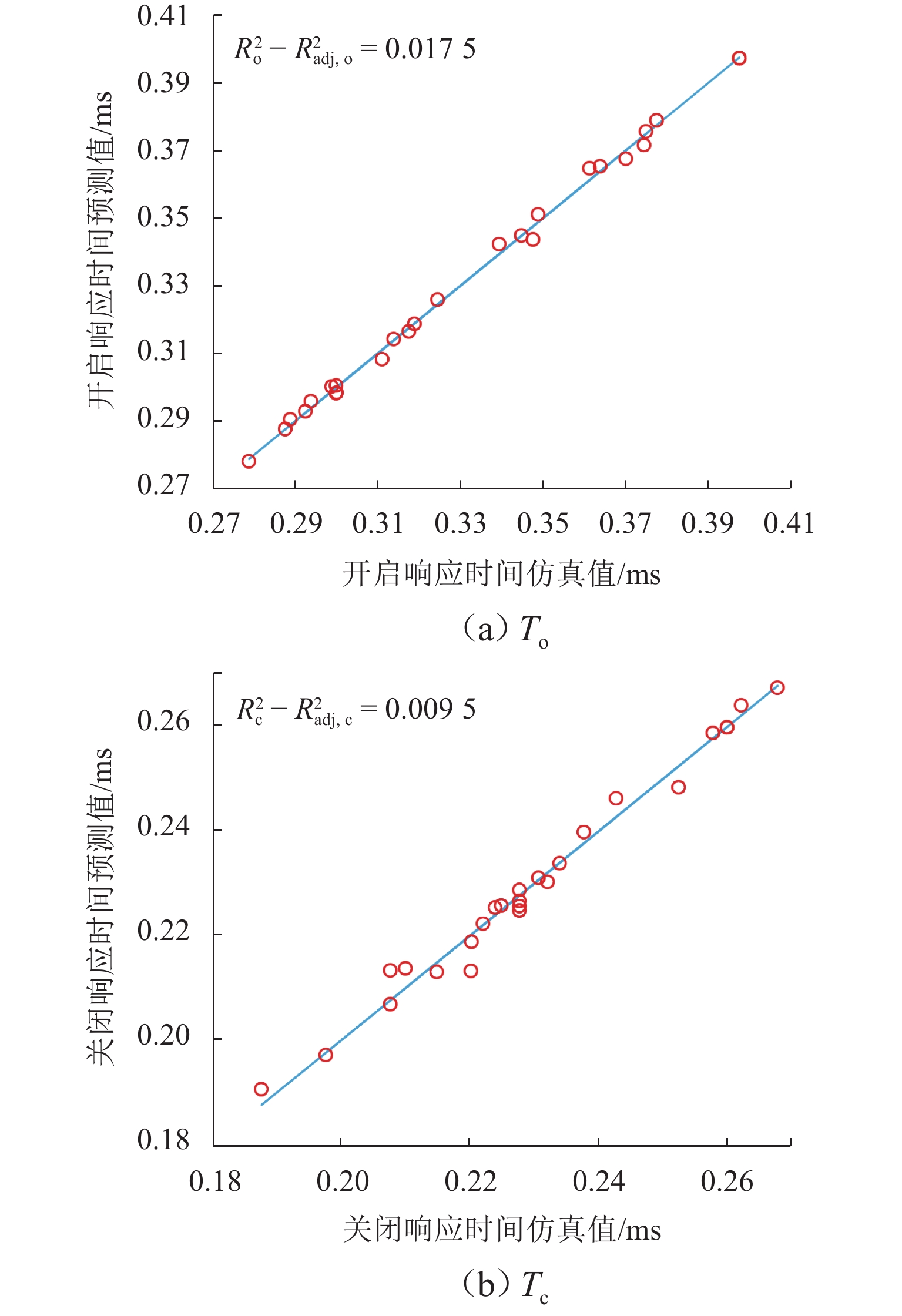
组别 E1/J E2/J E3/J E4/J To/ms Tc/ms 1 0.099 0.014 0.00044 0.033 0.32 0.22 2 0.086 0.016 0.00019 0.031 0.28 0.19 3 0.098 0.018 0.00022 0.032 0.34 0.23 4 0.090 0.018 0.00037 0.033 0.30 0.21 5 0.086 0.012 0.00095 0.031 0.29 0.22 6 0.097 0.012 0.00035 0.032 0.37 0.27 7 0.097 0.016 0.00030 0.032 0.37 0.26 8 0.086 0.018 0.00028 0.031 0.30 0.23 9 0.099 0.012 0.00028 0.049 0.34 0.22 10 0.085 0.012 0.00072 0.047 0.29 0.21 11 0.095 0.018 0.00041 0.048 0.35 0.24 12 0.092 0.014 0.00092 0.049 0.31 0.23 13 0.087 0.012 0.00053 0.077 0.30 0.21 14 0.082 0.018 0.00059 0.075 0.29 0.20 15 0.091 0.016 0.00022 0.079 0.35 0.23 16 0.095 0.014 0.00017 0.080 0.38 0.25 17 0.082 0.012 0.00079 0.075 0.31 0.23 18 0.079 0.012 0.00053 0.088 0.29 0.22 19 0.092 0.018 0.00004 0.093 0.36 0.22 20 0.092 0.012 0.00014 0.093 0.37 0.24 21 0.079 0.014 0.00057 0.088 0.30 0.21 22 0.085 0.016 0.00054 0.091 0.32 0.23 23 0.093 0.012 0.00045 0.097 0.36 0.26 24 0.079 0.018 0.00041 0.088 0.32 0.23 25 0.092 0.018 0.00006 0.093 0.40 0.26 26 0.092 0.018 0.00006 0.093 0.40 0.26 27 0.092 0.018 0.00006 0.093 0.40 0.26 28 0.092 0.018 0.00006 0.093 0.40 0.26 表 4 能量参数对响应时间的敏感程度
Table 4. Sensitivity of energy parameters to response time
参数 开启响应时间的 μ* 关闭响应时间的 μ* E1 0.096 0.056 E2 0.007 0.014 E3 0.032 0.012 E4 0.052 0.034 E1E2 0.032 0.112 E1E3 0.491 0.135 E1E4 0.249 0.253 E2E3 0.016 0.099 E2E4 0.077 0.018 E3E4 0.019 0.018 -
[1] GU Y Q, FAN L Y, ZHANG J Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization of high-speed solenoid valve for biodiesel electronic unit pump[J]. Current Chinese Science, 2022, 1(1): 38-47. [2] TAO G, CHEN H Y, J Y Y, et al. Optimal design of the magnetic field of a high-speed response solenoid valve[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2002, 129(1/2/3): 555-558. [3] WANG Q L, YANG F Y, YANG Q, et al. Experimental analysis of new high-speed powerful digital solenoid valves[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2011, 52(5): 2309-2313. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2010.12.032 [4] SUN Z Y, LI G X, WANG L, et al. Effects of structure parameters on the static electromagnetic characteristics of solenoid valve for an electronic unit pump[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 113: 119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.031 [5] ZHAO J H, WANG M L, WANG Z J, et al. Different boost voltage effects on the dynamic response and energy losses of high-speed solenoid valves[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 123: 1494-1503. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.117 [6] BREIDI F, HELMUS T, LUMKES J. The impact of peak-and-hold and reverse current solenoid driving strategies on the dynamic performance of commercial cartridge valves in a digital pump/motor[J]. International Journal of Fluid Power, 2016, 17(1): 37-47. doi: 10.1080/14399776.2015.1120138 [7] EBRAHIMI N, SCHIMPF P, JAFARI A. Design optimization of a solenoid-based electromagnetic soft actuator with permanent magnet core[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2018, 284: 276-285. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2018.10.026 [8] ZHAO J H, YUE P F, GREKHOV L, et al. Hold current effects on the power losses of high-speed solenoid valve for common-rail injector[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 128: 1579-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.09.123 [9] LAN Q, BAI Y, FAN L Y, et al. Investigation on fuel injection quantity of low-speed diesel engine fuel system based on response surface prediction model[J]. Energy, 2020, 211: 118946.1-118946.11. [10] MÄKELÄ M. Experimental design and response surface methodology in energy applications: a tutorial review[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 151: 630-640. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.09.021 [11] VITALI R. Response surface methods for high-dimensional structural design problems[M]. Florida: University of Florida, 2000: 270-289. [12] GE Q, MENENDEZ M. Extending Morris method for qualitative global sensitivity analysis of models with dependent inputs[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2017, 162: 28-39. [13] FENG K X, LU Z Z, XIAO S N. A new global sensitivity measure based on the elementary effects method[J]. Computers & Structures, 2020, 229: 106183.1-106183.12. [14] FENG K X, LU Z Z, YANG C Q. Enhanced Morris method for global sensitivity analysis: good proxy of Sobol’ index[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2019, 59(2): 373-387. doi: 10.1007/s00158-018-2071-7 -





 下载:
下载: