Short-Period Error Suppression Method of PCB-Based Inductive Linear Displacement Sensor
-
摘要:
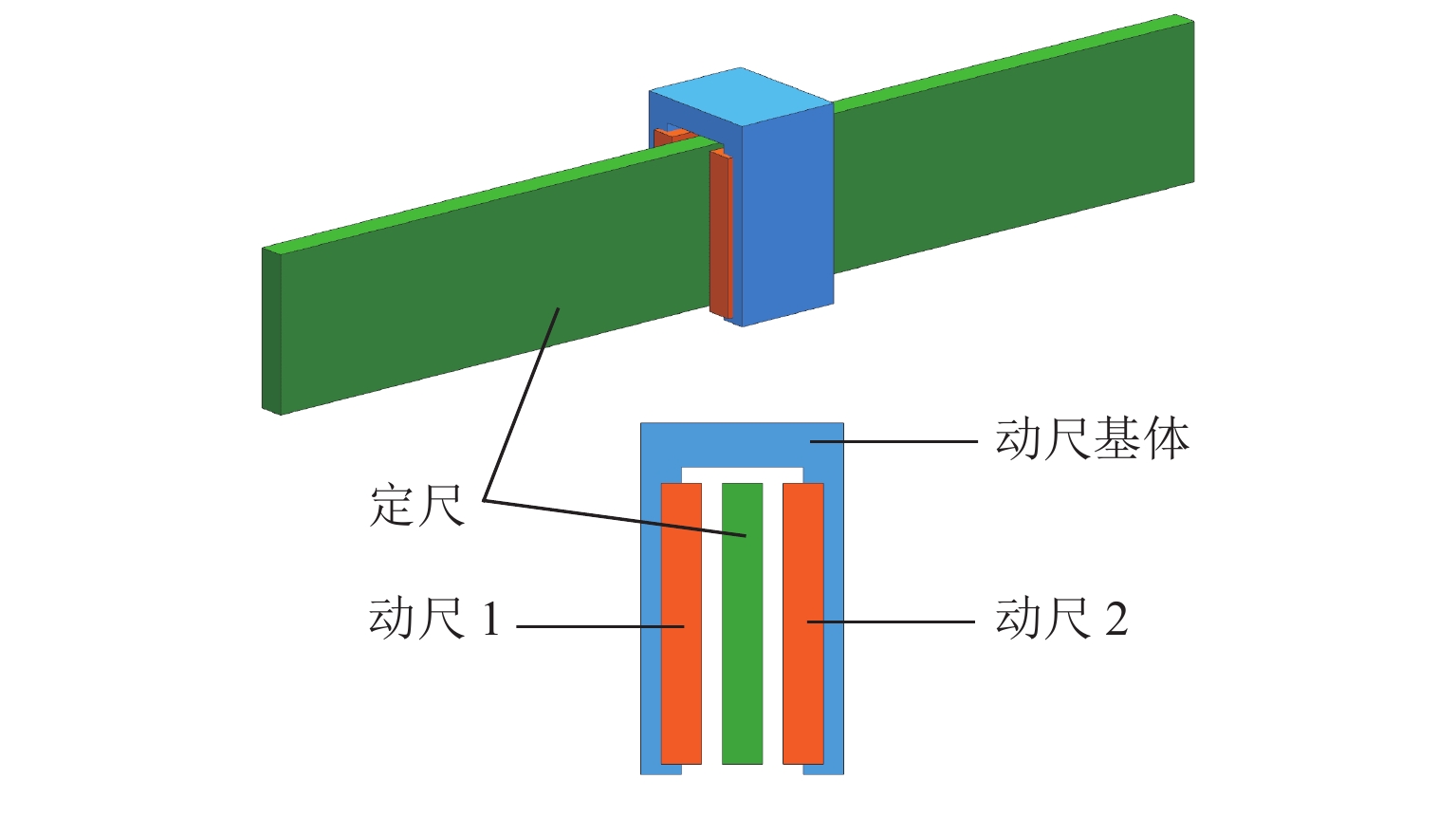
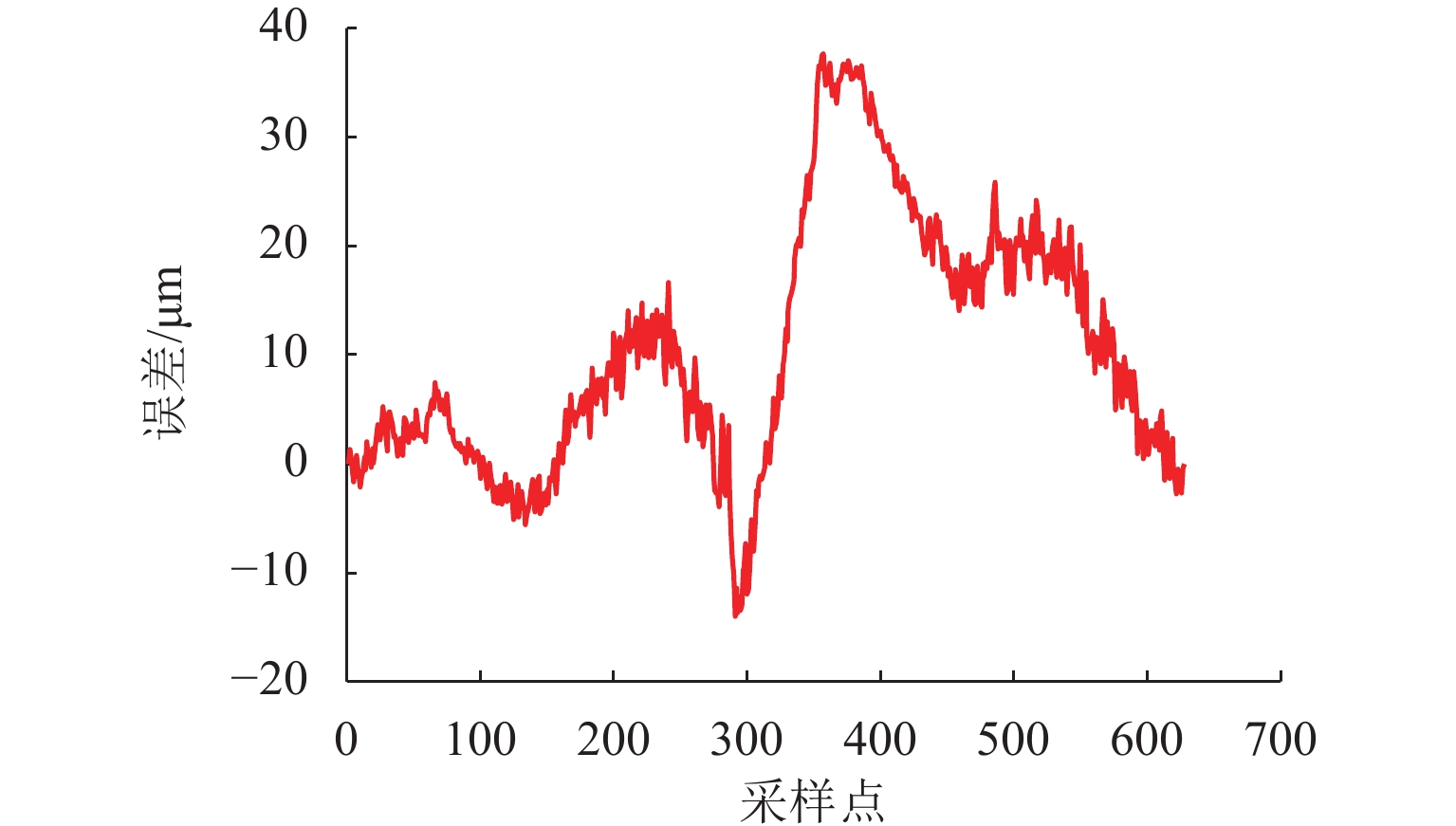
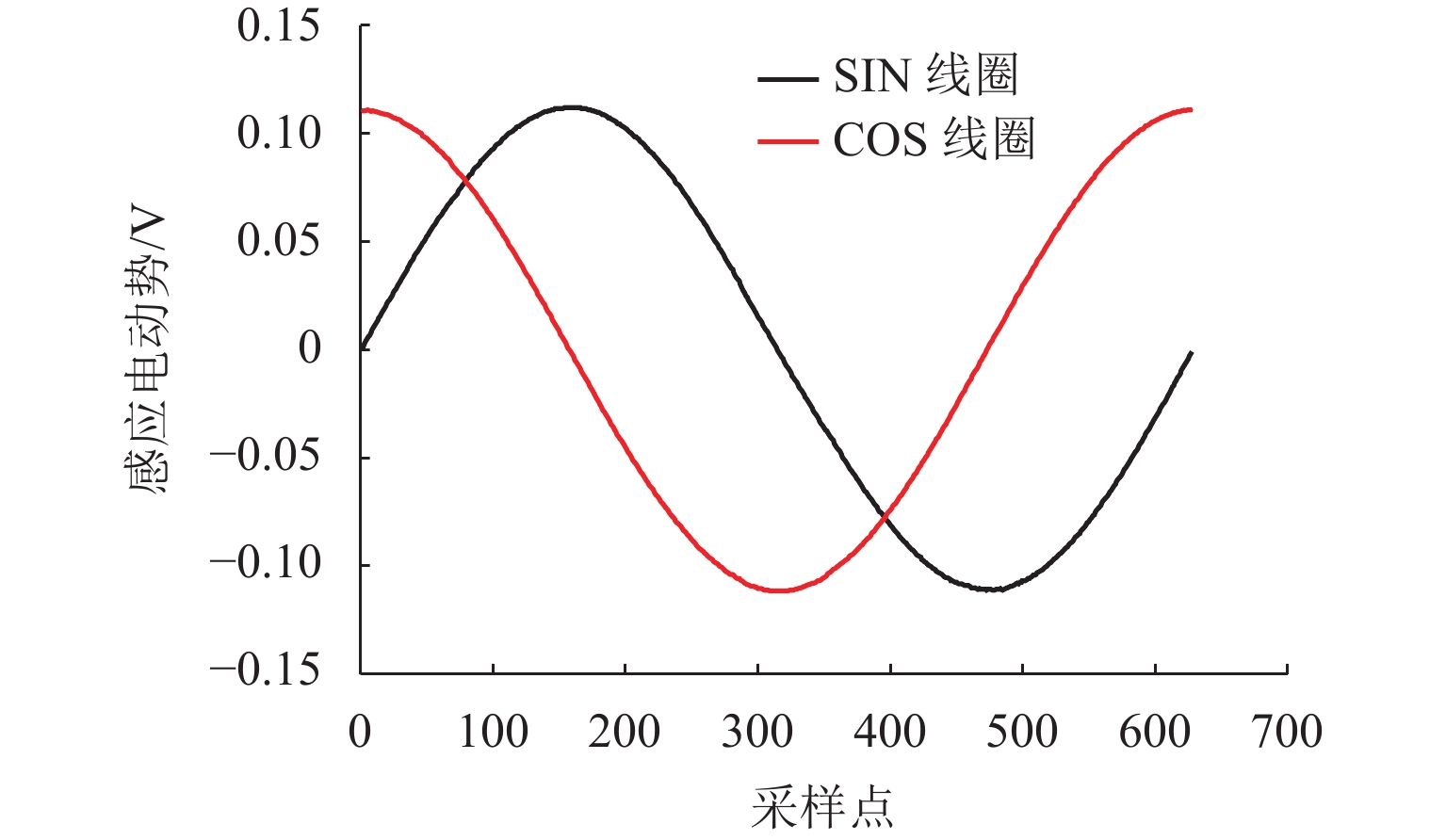
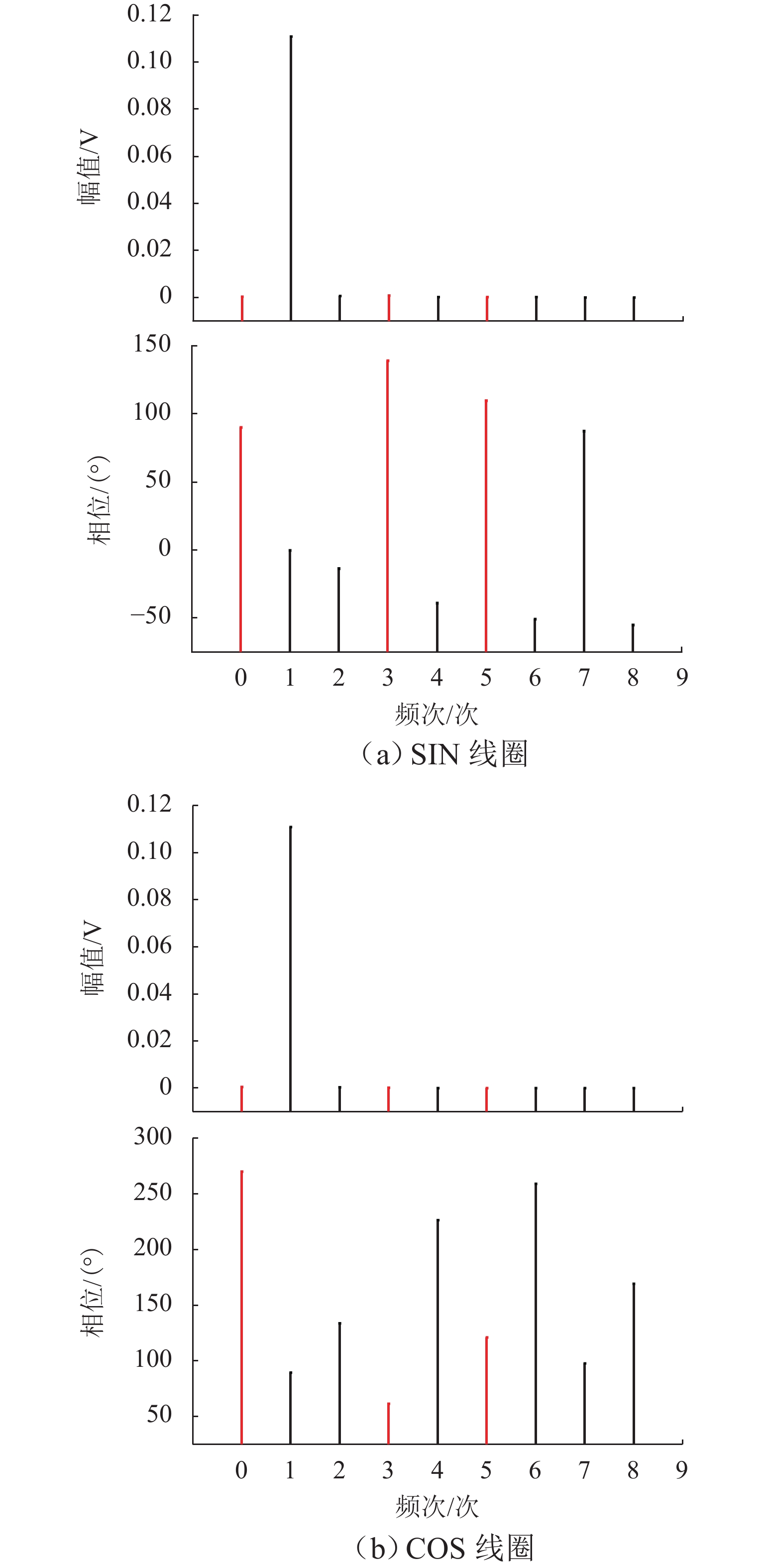
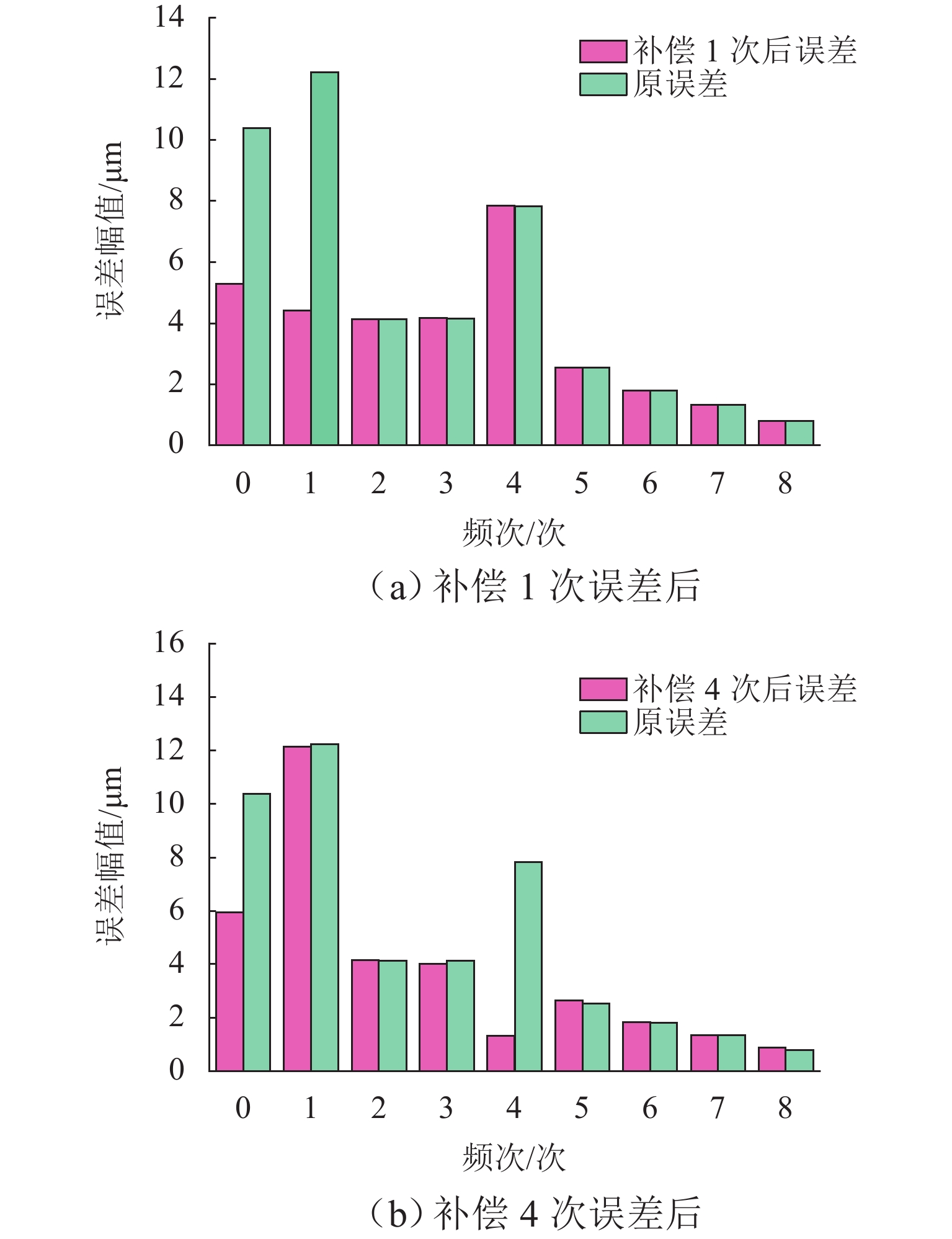
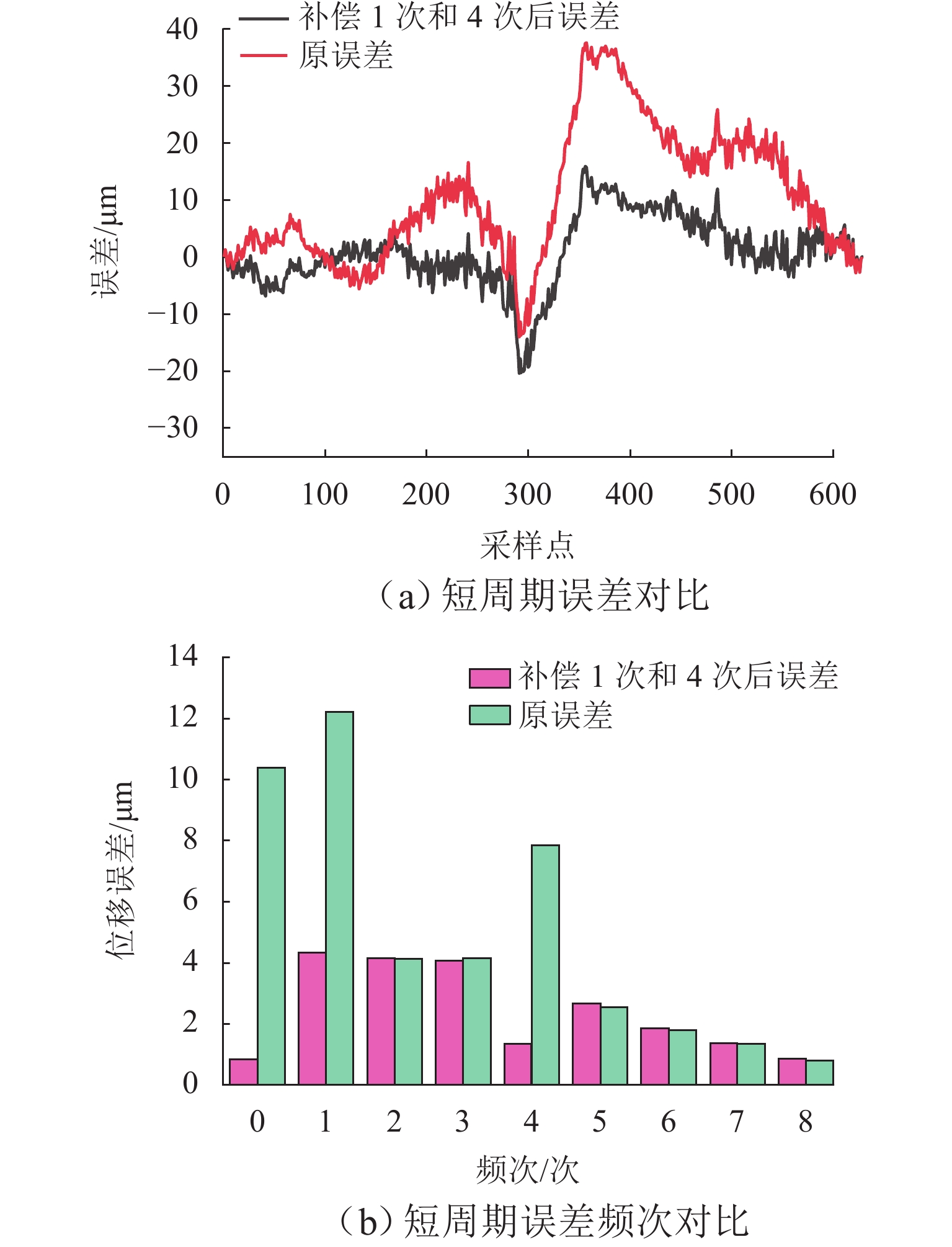
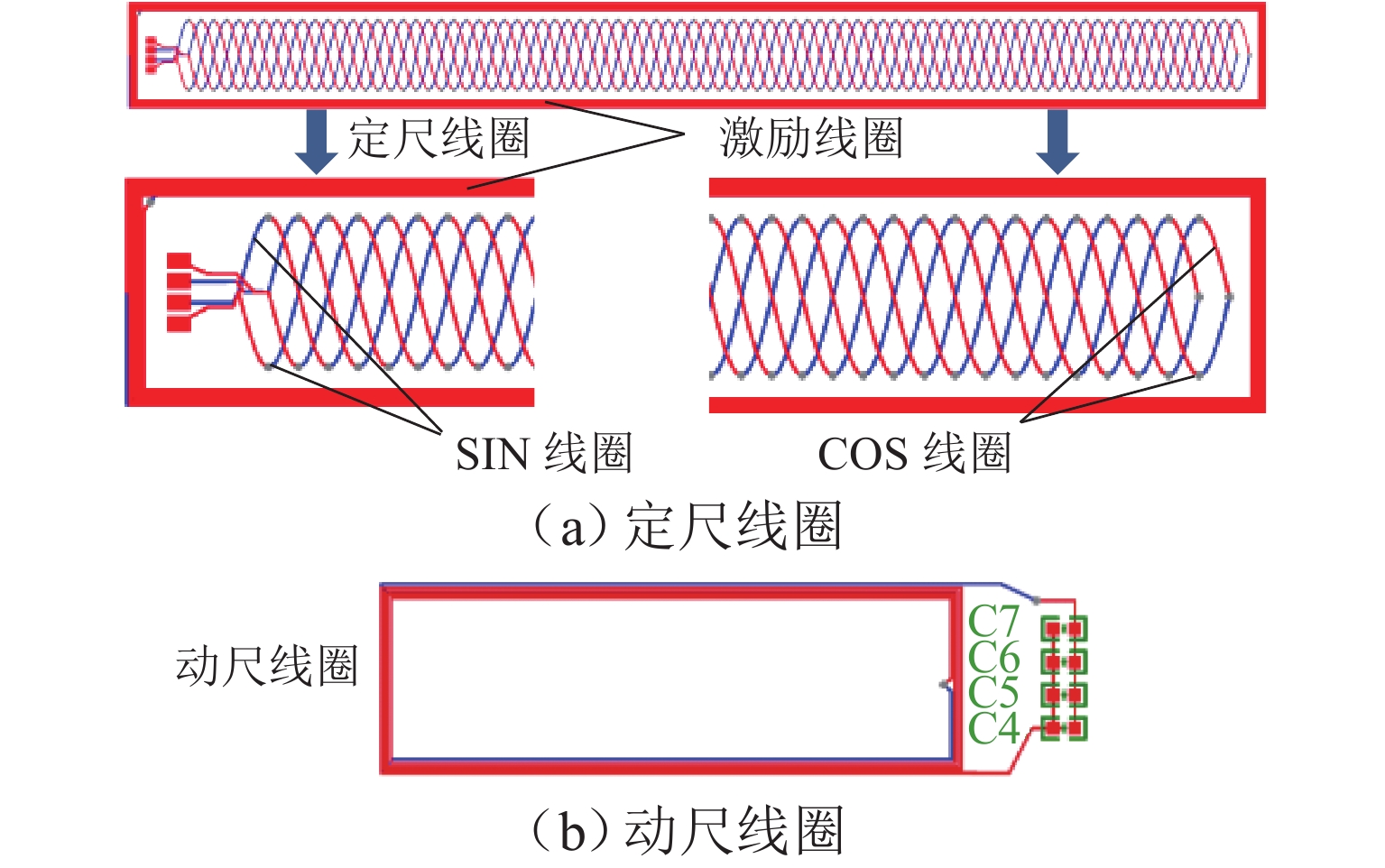
在直线位移测量中,基于PCB (printed circuit board)工艺的新型电磁感应式位移传感器因具有较大栅距,在制造、装配等工艺环节易导致短周期误差. 在所导致的短周期误差类型中,1次和4次误差是PCB型电磁感应式直线位移传感器中最常见的短周期误差. 为减小测量过程中产生的1次和4次误差,本文从输出信号出发,针对此2种误差的产生机理开展研究,并提出一种不依赖外部基准的误差自我修正方法. 首先,从理论层面分析短周期1次和4次误差的来源,以及2种误差与传感器原始SIN (sine)和COS (cosine)信号的函数关系;然后,建立基于传感器原始SIN和COS信号特征的短周期误差函数模型,并根据本文传感器样机的实测数据计算出误差函数模型中1次和4次误差的相应参数;最后,将1次和4次误差模型用于传感器样机的误差补偿. 研究结果表明:补偿后的样机实验结果显示误差峰值由51.6 μm减小到36.2 μm,其中,短周期1次误差减小了约64.5%,短周期4次误差减小了约83.0%.
Abstract:In the linear displacement measurement, the printed circuit board (PCB)-based new inductive displacement sensors is easy to lead to short-period errors in manufacturing, assembly, and other process links because of its large pitch. Among the types of short-period errors caused, the first-order and fourth-order errors are the most common short-period errors in PCB-based inductive linear displacement sensors. Therefore, in order to reduce the first-order and fourth-order errors, the generation mechanism of these two kinds of errors was first studied from the output signals, and then an error self-correction method that did not depend on external reference was proposed. Firstly, the sources of short-period first-order and fourth-order errors and the functions of the two errors with the original sine (SIN) and cosine (COS) signals of the sensor were analyzed theoretically. Then, a short-period error function model based on the characteristics of the original SIN and COS signals of the sensor was established, and the corresponding parameters of the first-order and fourth-order errors in the error function model were calculated based on the measured data of the sensor prototype. Finally, the first-order and fourth-order error models were used for the error compensation of the sensor prototype. The results of prototype experiments show that the peak-to-peak value of the error after compensation is reduced from 51.6 μm to 36.2 μm. The short-period first-order error is reduced by about 64.5%, and the short-period fourth-order error is reduced by about 83.0%.
-
Key words:
- sensor /
- linear displacement /
- induction /
- error suppression /
- self-correction
-
表 1 误差函数
Table 1. Error functions
误差频次/次 误差函数 1 $0.008\;3\sin \left( { - \dfrac{ { { {2\text{π} } }x} }{L} - 0.665} \right)$ 4 $0.006\;7\sin \left( {4 \times \dfrac{ { { {2\text{π} } }x} }{L} + 5.568} \right)$ -
[1] 高宏力,孙弋,郭亮,等. 机械加工质量预测研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(1): 120-141.GAO hongli, SUN yi, GUO liang, et al. Research status and development trend of machining quality prediction[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(1): 120-141. [2] 彭珍瑞,张楠,殷红,等. 基于频响函数的动车组构架传感器优化布置[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(2): 402-407,414.PENG Zhenrui, ZHANG Nan, YIN Hong, et al. Optimal sensor placement of EMU frame based on frequency response function[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(2): 402-407,414. [3] 魏正杰,张迪,吴冠豪. 用于精密位移测量的微型光栅传感器开发[J]. 光子学报,2021,50(9): 9-19.WEI Zhengjie, ZHANG Di, WU Guanhao. Development of miniature optical encoder for precise displacement measurement[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(9): 9-19. [4] 张周强,周玲,郭忠超,等. 基于电驱动纳米光栅的结构设计及仿真分析[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(21): 58-64.ZHANG Zhouqiang, ZHOU Ling, GUO Zhongchao, et al. Structure design and simulation analysis based on electrically driven nanograting[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(21): 58-64. [5] 王亮亮,商正君,郑立新,等. 基于激光干涉仪对天文底片扫描仪气浮式运动平台的性能测试[J]. 计算机测量与控制,2021,29(12): 79-83. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2021.12.015WANG Liangliang, SHANG Zhengjun, ZHENG Lixin, et al. Performance test of air-bearing motion platform applied by astronomical plates digitizer based on laser interferometer[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2021, 29(12): 79-83. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2021.12.015 [6] 朱记全,许候杰. 基于激光干涉仪测量内径千分尺示值误差方法的探讨[J]. 精密制造与自动化,2021(4): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-962X.2021.4.jmzzyzdh202104014ZHU Jiquan, XU Houjie. Discussion on the method of measuring the indication error of inside micrometer based on laser interferometer[J]. Precise Manufacturing & Automation, 2021(4): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-962X.2021.4.jmzzyzdh202104014 [7] ANIL KUMAR A S, ANANDAN N, GEORGE B, et al. Improved capacitive sensor for combined angular and linear displacement sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(22): 10253-10261. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2929538 [8] ZENG T, LU Y F, LIU Y M, et al. A capacitive sensor for the measurement of departure from the vertical movement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(2): 458-466. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2015.2490806 [9] LIU X K, HUANG R, YU Z C, et al. A high-accuracy capacitive absolute time-grating linear displacement sensor based on a multi-stage composite method[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 8969-8978. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054165 [10] 孟瑶,周启武,郑方燕,等. 纳米时栅的电气参数与误差特性研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2019,33(6): 65-71.MENG Yao, ZHOU Qiwu, ZHENG Fangyan, et al. Study on electrical parameters and error characteristics of nanometer time-grating[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2019, 33(6): 65-71. [11] 杨帆. 绝对式光栅尺可靠性研究与误差分析[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2021. [12] 王璐钰,李玉琼,蔡榕. 空间激光干涉仪激光抖动噪声抑制研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6): 1426-1434.WANG Luyu, LI Yuqiong, CAI Rong. Noise suppression of laser jitter in space laser interferometer[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1426-1434. [13] NIHTIANOV S. Reactive sub-nanometer displacement sensors: advantages and limitations[C]//2013 Africon. Pointe aux Piments, Mauritius. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2014: 1-6. [14] 荣锋,韩信,郭翠娟. 基于电涡流传感器的微位移测量系统的设计[J]. 仪表技术与传感器,2020(9): 12-18.RONG Feng, HAN Xin, GUO Cuijuan. Design of micro-displacement measurement system based on eddy current sensor[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2020(9): 12-18. [15] 田敏,范青. 浅析电涡流位移传感器低温环境下输出的特性[J]. 仪器仪表标准化与计量,2021(4): 46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5611.2021.04.022TIAN Min, FAN Qing. Analysis of the output characteristics of eddy current displacement sensor in low temperature environment[J]. Instrument Standardization & Metrology, 2021(4): 46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5611.2021.04.022 [16] 朱巧荣,张卫平. “直线式感应同步器—鉴相型系统”原理仿真实验CAI[J]. 机床与液压,2001,29(3): 102.ZHU Qiaorong, ZHANG Weiping. CAI of principle simulation experiment of “linear inductosyn-phase discrimination system”[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2001, 29(3): 102. [17] 曾乐乐. 直线式感应同步器[J]. 科技风,2018(34): 144. doi: 10.19392/j.cnki.1671-7341.201834127ZENG Leyue. Linear inductosyn[J]. Technology Wind, 2018(34): 144. doi: 10.19392/j.cnki.1671-7341.201834127 [18] 柏受军,杨元园,王鸣,等. 基于ADμC845的LVDT位移传感器非线性补偿[J]. 传感技术学报,2013,26(4): 541-544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2013.04.020BAI Shoujun, YANG Yuanyuan, WANG Ming, et al. Nonlinear compensation of LVDT displacement sensor based on ADμC845[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2013, 26(4): 541-544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2013.04.020 [19] 郁明辉,李鹏,刘肖肖. 双余度LVDT位移传感器输出电压线性度研究[J]. 电子测量技术,2020,43(2): 26-32. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.1903331YU Minghui, LI Peng, LIU Xiaoxiao. Research on linearity of output voltage of double redundancy LVDT displacement sensor[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2020, 43(2): 26-32. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.1903331 [20] ASCHENBRENNER B, ZAGAR B G. Analysis and validation of a planar high-frequency contactless absolute inductive position sensor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(3): 768-775. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2348631 [21] TANG Q F, WU L, CHEN X H, et al. An inductive linear displacement sensor based on planar coils[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(13): 5256-5264. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2839730 [22] 高文政,石洪,汤其富. 平面磁场式绝对角度传感器的误差产生机理与抑制方法研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2021,35(6): 113-121.GAO Wenzheng, SHI Hong, TANG Qifu. Study on the error production mechanism and suppression methods of the planar inductive absolute angle sensor[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2021, 35(6): 113-121. [23] 刘洋,武亮,彭东林,等. 平面线圈型时栅传感器及动尺姿态误差特性分析[J]. 仪表技术与传感器,2020(11): 21-27,32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2020.11.005LIU Yang, WU Liang, PENG Donglin, et al. Analysis of attitude error characteristics of planar coil time grating sensor and moving ruler[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2020(11): 21-27,32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2020.11.005 [24] BABU A, GEORGE B. Design and development of a new non-contact inductive displacement sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(3): 976-984. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2780835 [25] 翁道纛,汤其富,彭东林,等. 一种互补耦合型电磁感应式直线位移传感器的研究[J]. 传感技术学报,2019,32(7): 996-1002. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2019.07.007WENG Daodao, TANG Qifu, PENG Donglin, et al. Research on a linear inductive displacement sensor with complementary coupling structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2019, 32(7): 996-1002. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2019.07.007 [26] SANDRA K R, ANIL KUMAR A S, GEORGE B, et al. A linear differential inductive displacement sensor with dual planar coils[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(2): 457-464. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2877209 [27] GU X Y, TANG Q F, PENG D L, et al. An inductive linear displacement sensor with bilateral sensing units[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(1): 296-305. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3014674 [28] ZHAO J, LI M, PENG S, et al. An inductive linear displacement sensor with complementary resonant coupling units[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(22): 25659-25667. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3118839 -




 下载:
下载: