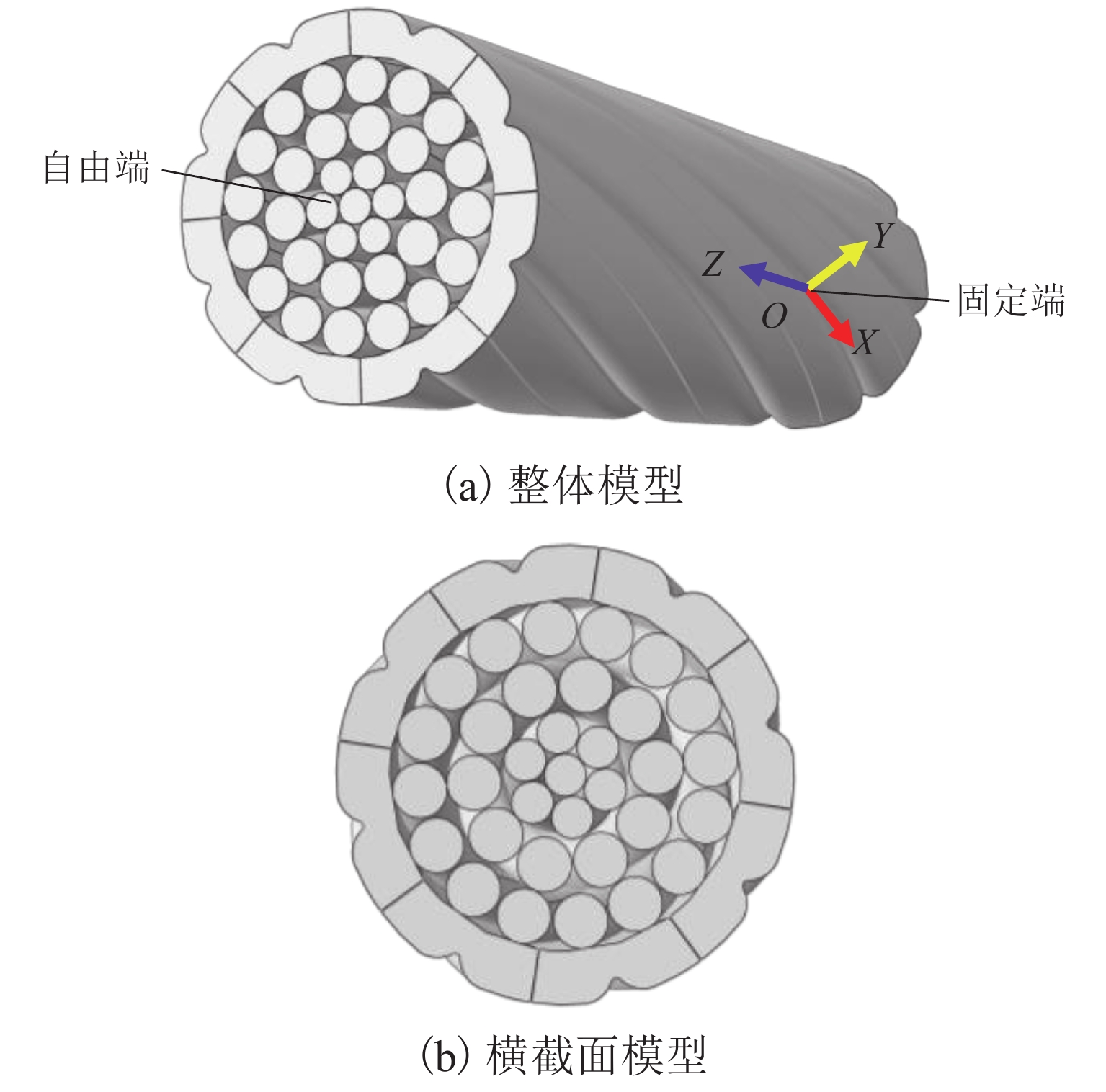
Mechanical Characteristics of Low-Wind-Pressure Catenary Positive Feeder in Gale Area of Lanzhou‒Urumuqi High-Speed Railway
-
摘要:
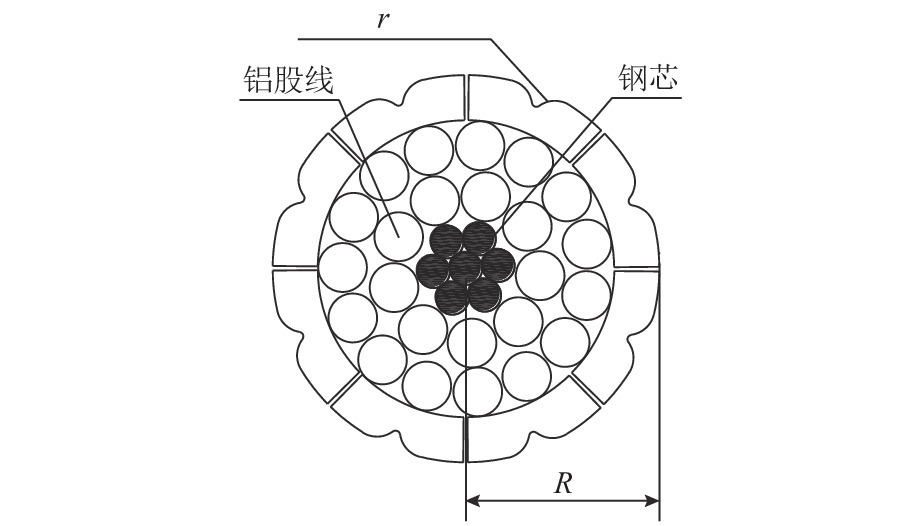
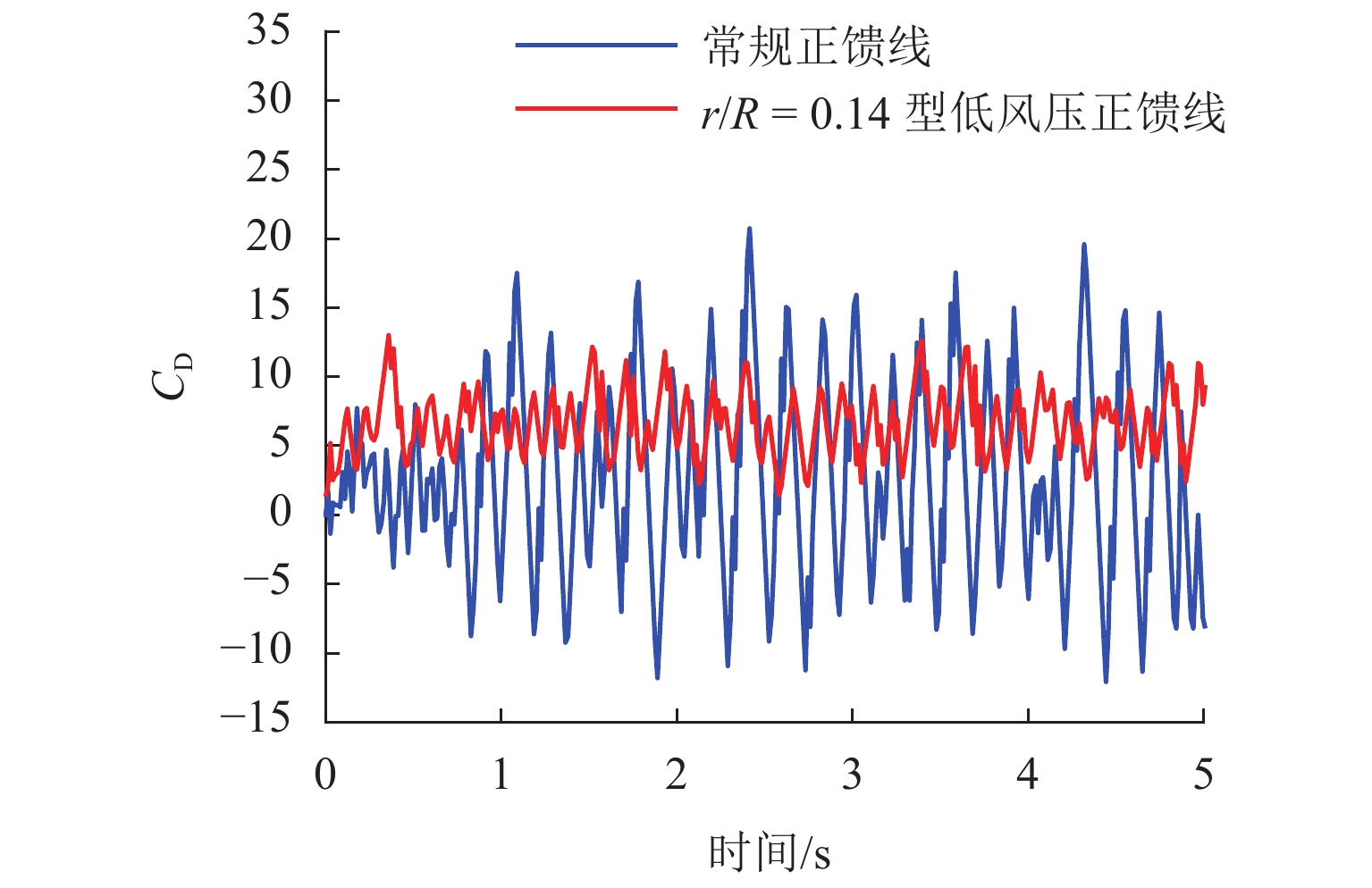
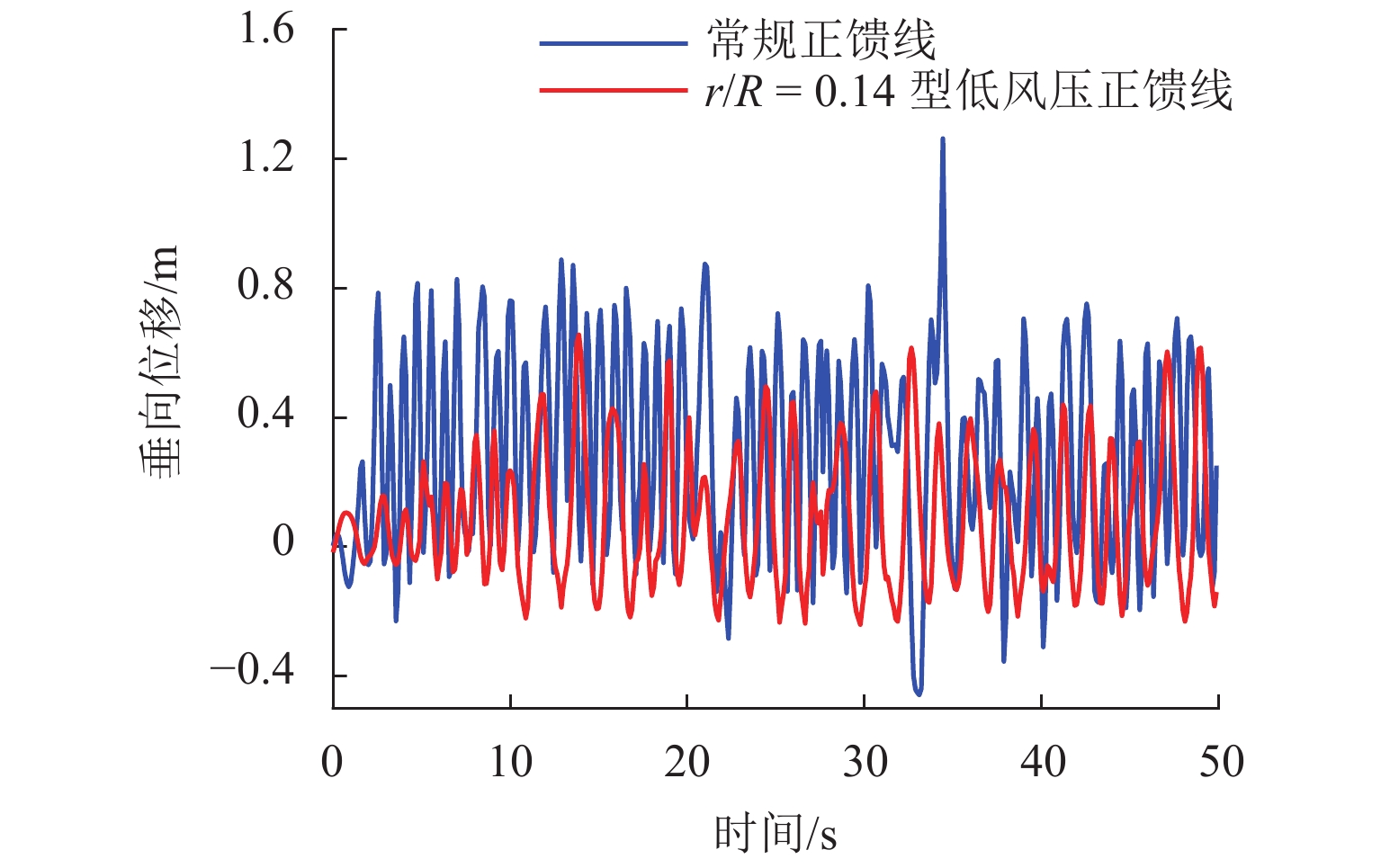
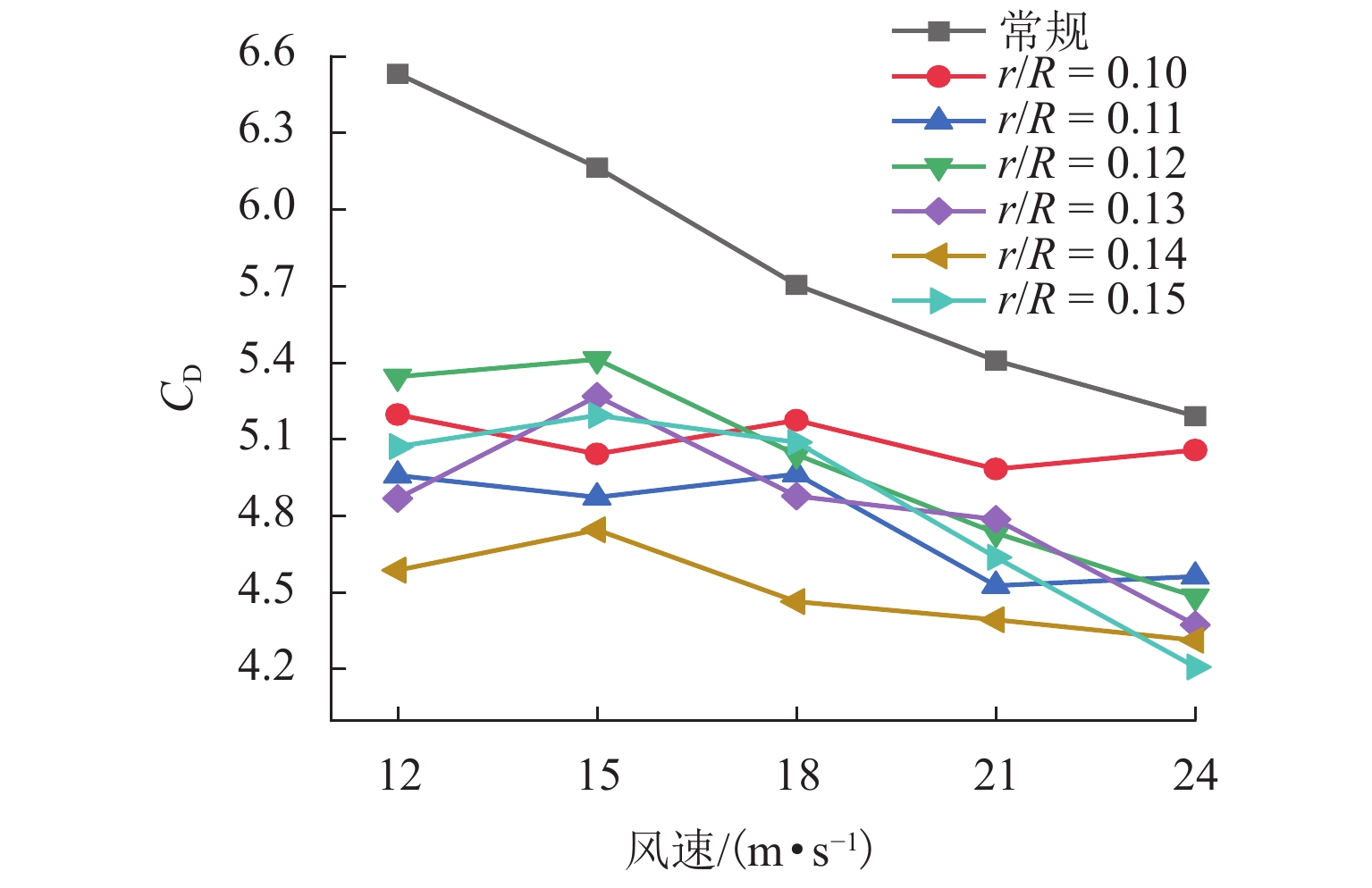
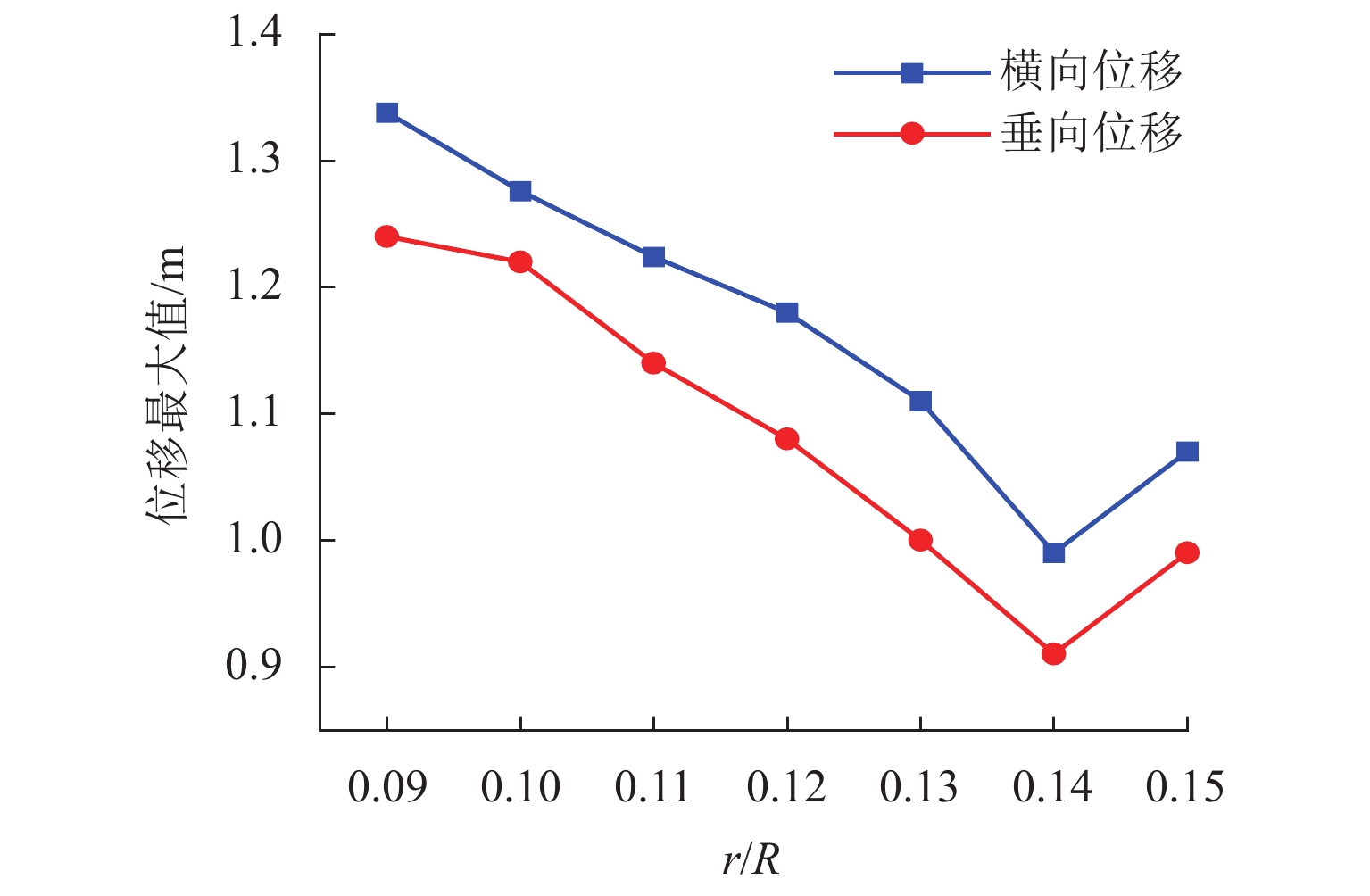
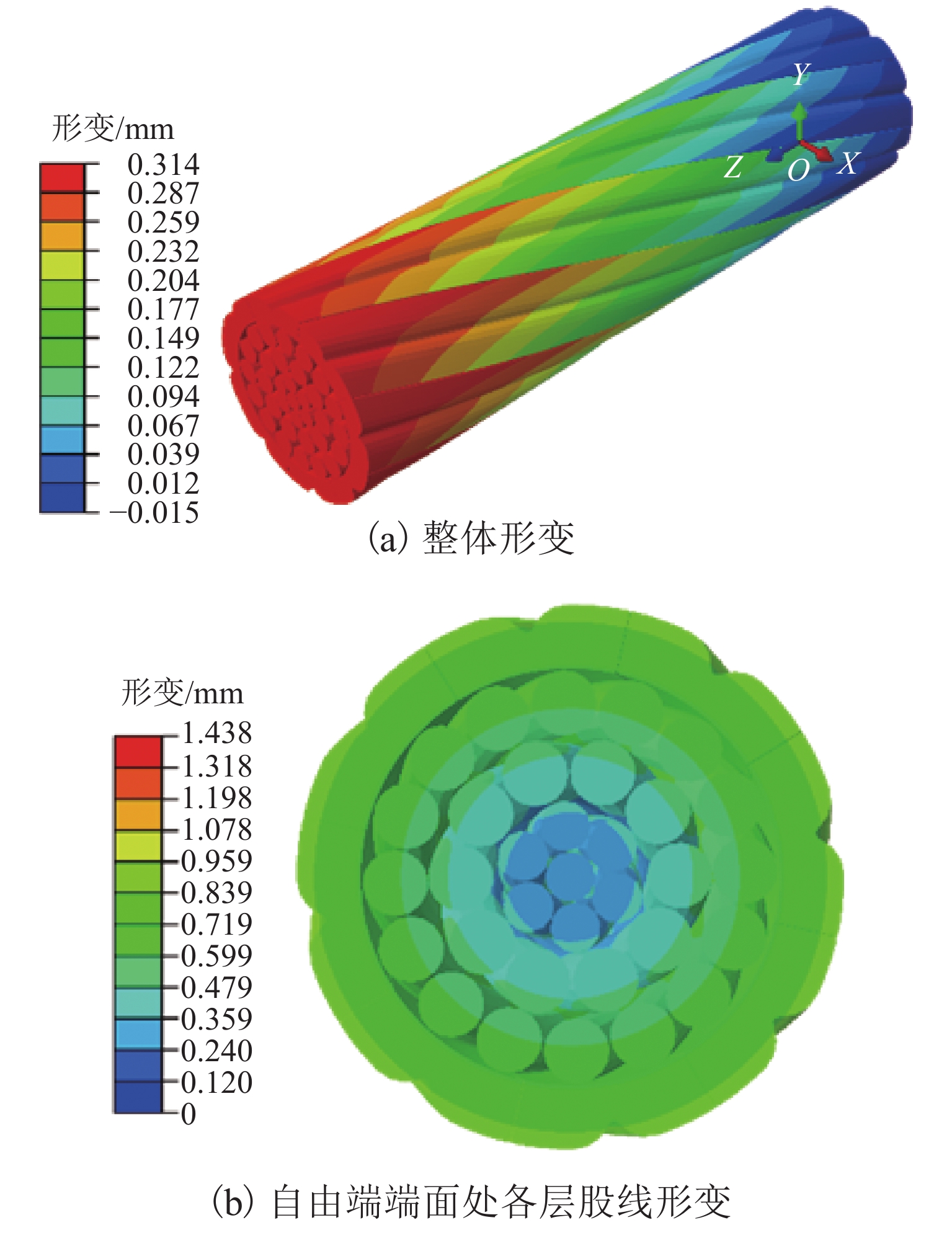
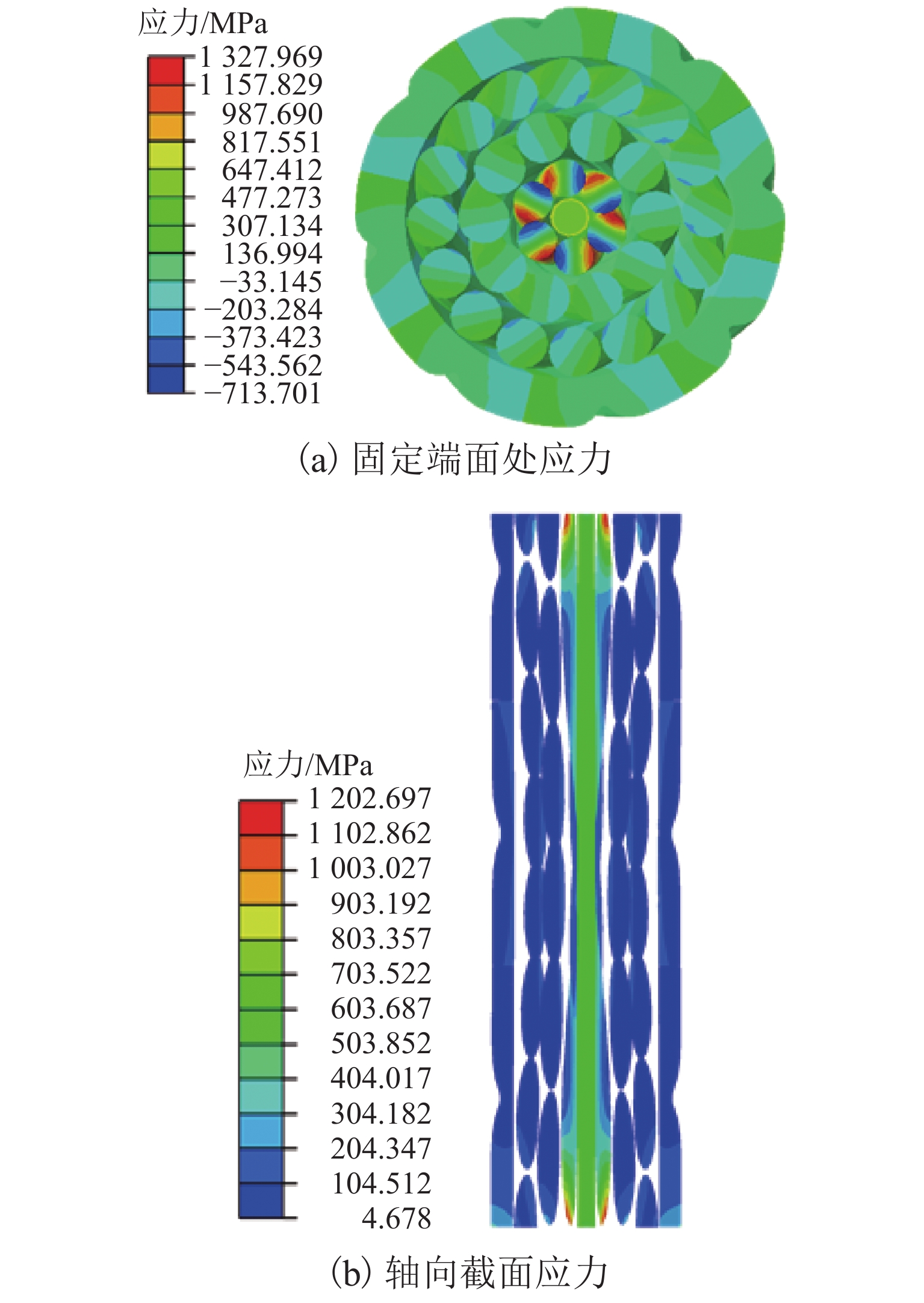
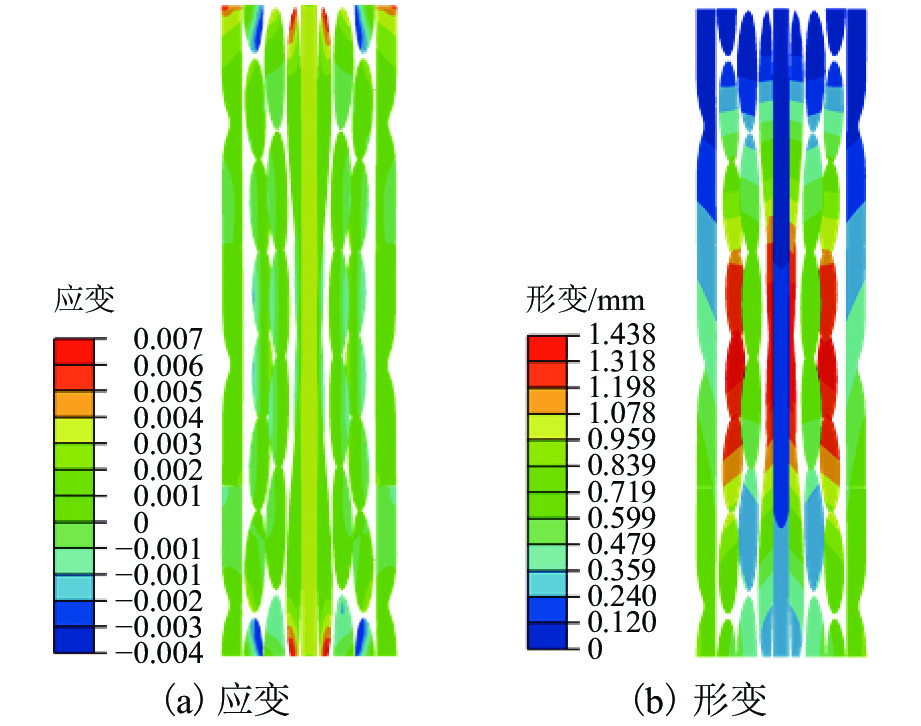
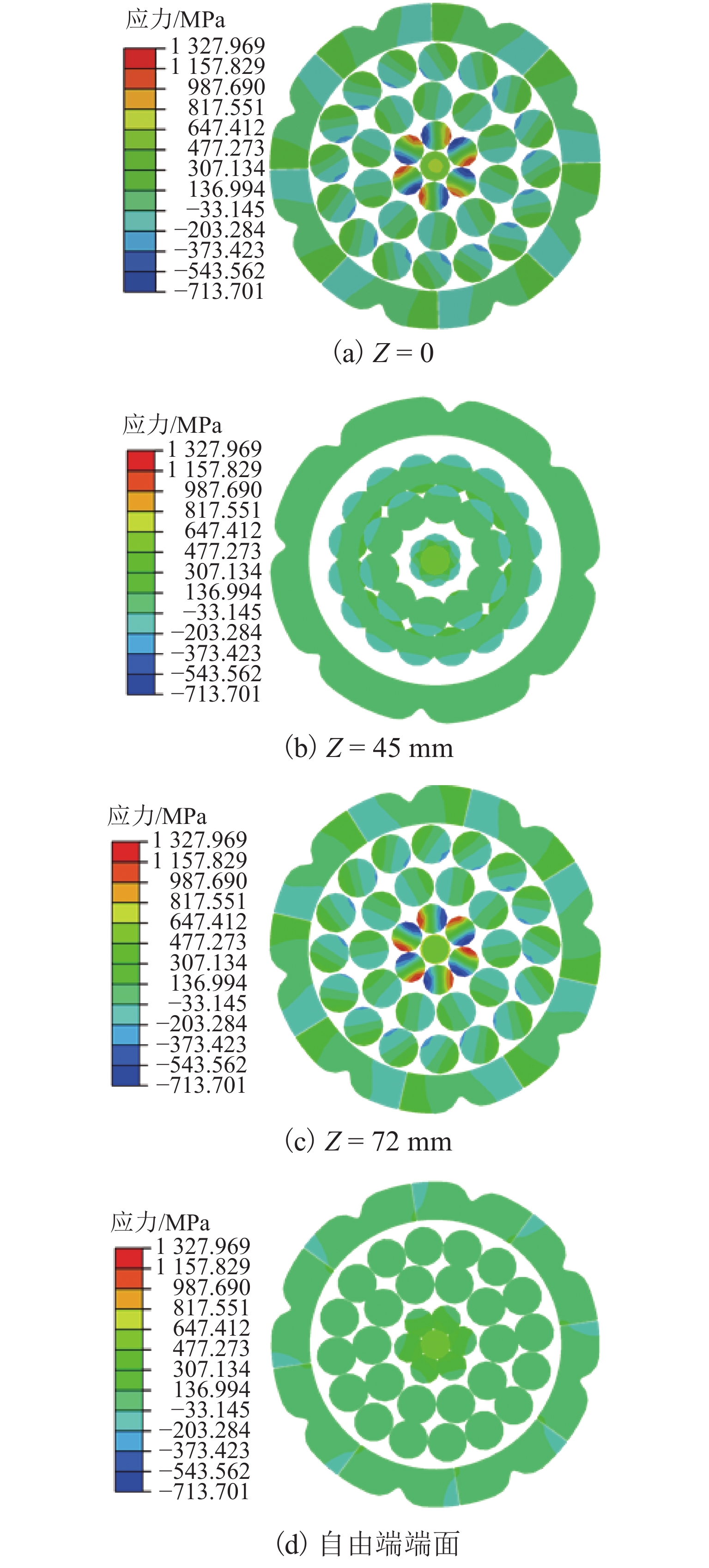
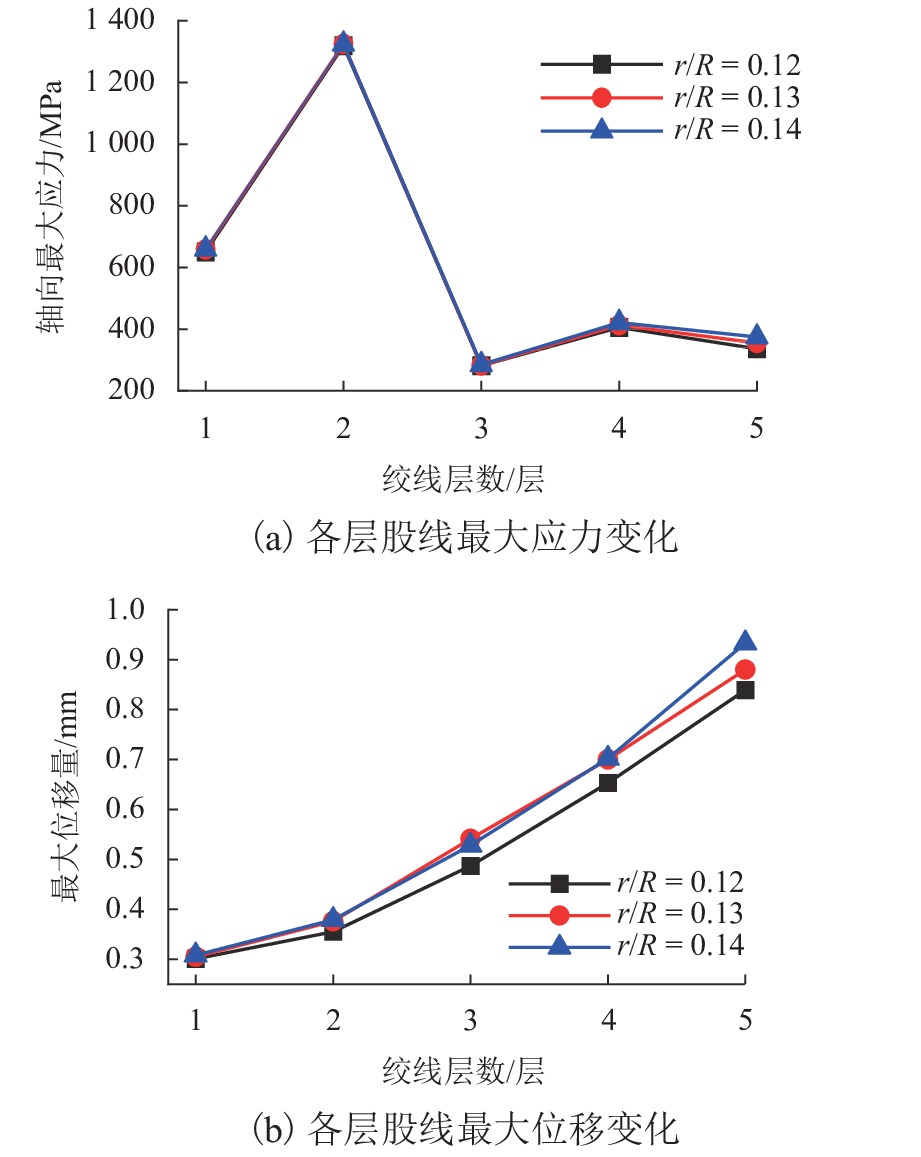
为抑制兰新高铁大风区正馈线舞动,保证列车安全运行, 首先,设计新型低风压正馈线,仿真获取常规正馈线和低风压正馈线在不同风载荷下的气动力参数和舞动幅值,并进行对比分析;其次,对防舞效果较佳的3种低风压正馈线建立三维有限元模型,并施加拉伸载荷,模拟正馈线舞动时的受力情况;最后,分析低风压正馈线形变及应力变化. 结果表明:低风压正馈线自由端形变量远大于固定端,铝股线形变量大于钢股线,且越往外层,股线形变量越大;在绞线制造时可以考虑将钢层和铝层交替绞合,以平衡绞线的导电性和刚性. 在股线相互接触的位置出现了应力集中,应力集中位置与股线绞合方向相同;在绞线制造时,可以考虑在股线表面覆缓冲层,以减缓正馈线舞动时股线之间的振荡冲击,并延长正馈线的使用寿命;低风压正馈线模型的凹槽小圆弧半径与常规正馈线半径的比值越大,最外层铝股线的形变越大,正馈线舞动时越容易断股;在低风压正馈线选型时应该综合考虑,平衡防舞有效性与使用寿命.
Abstract:In order to restrain the galloping amplitude of the positive feeder in the gale area of the Lanzhou‒Urumuqi high-speed railway and ensure the safe operation of the train, firstly, a novel type of low-wind-pressure catenary positive feeder was designed, and the aerodynamic parameters and galloping amplitude of the conventional catenary positive feeder and the low-wind-pressure catenary positive feeder under different wind loads were simulated and compared. Then, a three-dimensional finite element model of the low-wind-pressure catenary positive feeders with the three better anti-galloping effects was established and tensile loads were applied to simulate the stress condition of the positive feeder when the positive feeders were galloping. Finally, the deformation and variation stress of the low-wind-pressure catenary positive feeder were analyzed. The results show that, the deformation of the free end of the catenary positive feeder is much larger than that of the fixed end, the deformation of the aluminum strand layer is larger than that of the steel strand layer, and the further to the outer layer, the larger the strand deformation, twining alternately steel and aluminum layers can be considered in the feeder manufacturing to balance the electroconductibility and rigidity. The stress concentration occurs at the location where the strands squeezing with each other, and the stress concentration position is the same as the direction of the strand twining with each other. A buffer layer should be considered on the surface of the strands during the positive feeder manufacturing, to mitigate oscillatory shock between the strands when the positive feeder galloping, and to prolong the service life of the positive feeder. The larger the ratio of the groove radius of the low-wind-pressure catenary positive feeder to the radius of the conventional feeder, the greater the deformation of the outermost aluminum strands, the strands are more likely to break when the positive feeder is galloping. Therefore, the type selection of low wind pressure positive feeder should be comprehensively considered to balance the anti-galloping effectiveness and the service life.
-
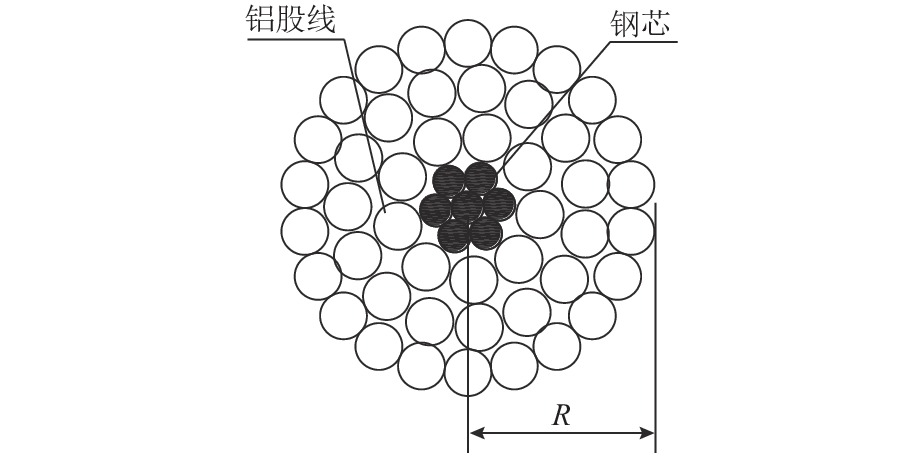
表 1 常规正馈线结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of conventional positive feeder
材料 层数 股数/股 直径/mm 节径/mm 节距/mm 绞向 钢 最内层 1 2.22 次内层 6 2.22 21 139.86 左 铝 次外层 10 2.85 13 160.68 右 邻外层 16 2.85 12 216.72 左 最外层 22 2.85 11 261.36 右 表 2 常规正馈线各层股线轴向张力
Table 2. Axial tension of each layer of conventional positive feeder
kN 材料 层数 理论值 仿真值 误差 钢 最内层 5.963 5.921 0.242 次内层 7.839 7.818 0.221 铝 次外层 3.956 3.651 0.305 邻外层 5.045 4.889 0.156 最外层 3.383 3.112 0.271 -
[1] 孟祥连,李鲲,谢胜波,等. 兰新高铁大风区风况特征及防风工程设计分区[J]. 中国沙漠,2018,38(5): 972-977.MENG Xianglian, LI Kun, XIE Shengbo, et al. Strong wind environmental characteristics and countermeasures according to engineering divisions along a high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(5): 972-977. [2] 刘志刚,宋洋,刘煜铖. 电气化高速铁路接触网微风振动特性[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2015,50(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.01.001LIU Zhigang, SONG Yang, LIU Yucheng. Aeolian vibration characteristics of electrified high-speed railway catenary[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015, 50(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2015.01.001 [3] 姚远,赵文彬,卢武,等. 多风速段下低风阻导线抗风能力实验分析及导线截面结构参数优化[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2021,49(21): 97-106. doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.201629YAO Yuan, ZHAO Wenbin, LU Wu, et al. Wind resistance test and optimal design of cross-sectional structure of a drag-reduced conductor at multiple wind speed levels[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(21): 97-106. doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.201629 [4] 吴明埝,缪姚军,张军,等. 低风压导线流场仿真设计及应用[J]. 电线电缆,2020(5): 10-14,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6901.2020.05.003WU Mingnian, MIAO Yaojun, ZHANG Jun, et al. Flow field simulation design and application of drag reduced conductor[J]. Wire & Cable, 2020(5): 10-14,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6901.2020.05.003 [5] 段旭东,韩宇,陆春阳,等. 低风压导线与常规导线对比分析[J]. 电气工程学报,2019,14(4): 66-71. doi: 10.11985/2019.04.010DUAN Xudong, HAN Yu, LU Chunyang, et al. Comparative analysis of low wind pressure conductor and conventional conductor[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2019, 14(4): 66-71. doi: 10.11985/2019.04.010 [6] 刘鹏. 输电线路低风阻导线结构设计与研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2017. [7] LÉVESQUE F, GOUDREAU S, CLOUTIER L, et al. Finite element model of the contact between a vibrating conductor and a suspension clamp[J]. Tribology International, 2011, 44(9): 1014-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2011.04.006 [8] PALO A. Transmission line reference book: wind induced conductor motion[M]. California: Electric Power Research Institute, 1979. [9] 周超,陈作,李力,等. 基于有限元的低风压导线结构分析[J]. 图学学报,2018,39(1): 129-135. doi: 10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2018010129ZHOU Chao, CHEN Zuo, LI Li, et al. Analysis of low-wind-pressure conductor based on finite element[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2018, 39(1): 129-135. doi: 10.11996/JG.j.2095-302X.2018010129 [10] 刘阳,徐凯,郜宁,等. 强风区高压输电线路铝线夹疲劳断裂机制研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版),2020,53(2): 176-182. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2020-02-012LIU Yang, XU Kai, GAO Ning, et al. Fatigue fracture mechanism of aluminum terminal connector for high voltage transmission line in strong wind area[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2020, 53(2): 176-182. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2020-02-012 [11] 司伟杰. 输电导线微风振动损伤机理及检测技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安工程大学, 2018. [12] 仝步升. 架空输电线路微风振动监测与疲劳损伤计算[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2013. [13] 林建华,曾伟. 架空导线用钢芯铝绞线张力分层特性研究[J]. 电线电缆,2015(4): 30-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6901.2015.04.007LIN Jianhua, ZENG Wei. Research on aluminum conductor steel reinforced tension layered characteristics of overhead conductors[J]. Wire & Cable, 2015(4): 30-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6901.2015.04.007 [14] HONG K J, DER KIUREGHIAN A, SACKMAN J L. Bending behavior of helically wrapped cables[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2005, 131(5): 500-511. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2005)131:5(500) [15] 祝贺, 袁鸣, 郭鑫. 温度影响下碳纤维导线分层力学特性有限元分析[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报, (2022-03-31)[2022-06-02]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C45S0n9fL2suRadTyEVl2pW9UrhTDCdPD65IXe8xbsrGOBqwsuR8VxuP2PPs0V1tYS7DplaisN5YfIkYT3ZQRt-9&uniplatform=NZKPT [16] 丁亮亮. 架空输电导线热应力分析与微风振动疲劳寿命研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2019: 52-60. [17] 黄欲成,陈池,汪峰,等. 大跨越架空输电导线钢芯铝股应力分布特性研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(4): 76-81. doi: 10.13393/j.cnki.issn.1672-948X.2016.04.016HUANG Yucheng, CHEN Chi, WANG Feng, et al. Stress distribution characteristics of steel core and aluminum strand of large span overhead transmission line[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University. (Natural Sciences), 2016, 38(4): 76-81. doi: 10.13393/j.cnki.issn.1672-948X.2016.04.016 [18] 段一锋,马行驰,高磊,等. 钢芯铝绞线微动损伤机理及防护措施的研究进展[J]. 材料导报,2018,32(增1): 37-40.DUAN Yifeng, MA Xingchi, GAO Lei, et al. Research on fretting damage mechanism and protective measures of aluminum cable steel reinforced[J]. Materials Review, 2018, 32(S1): 37-40. -




 下载:
下载: