Capacity Optimization Configuration of Electric Vehicle Swapping-Storage Integrated Station Considering Support Ability to Grid
-
摘要:
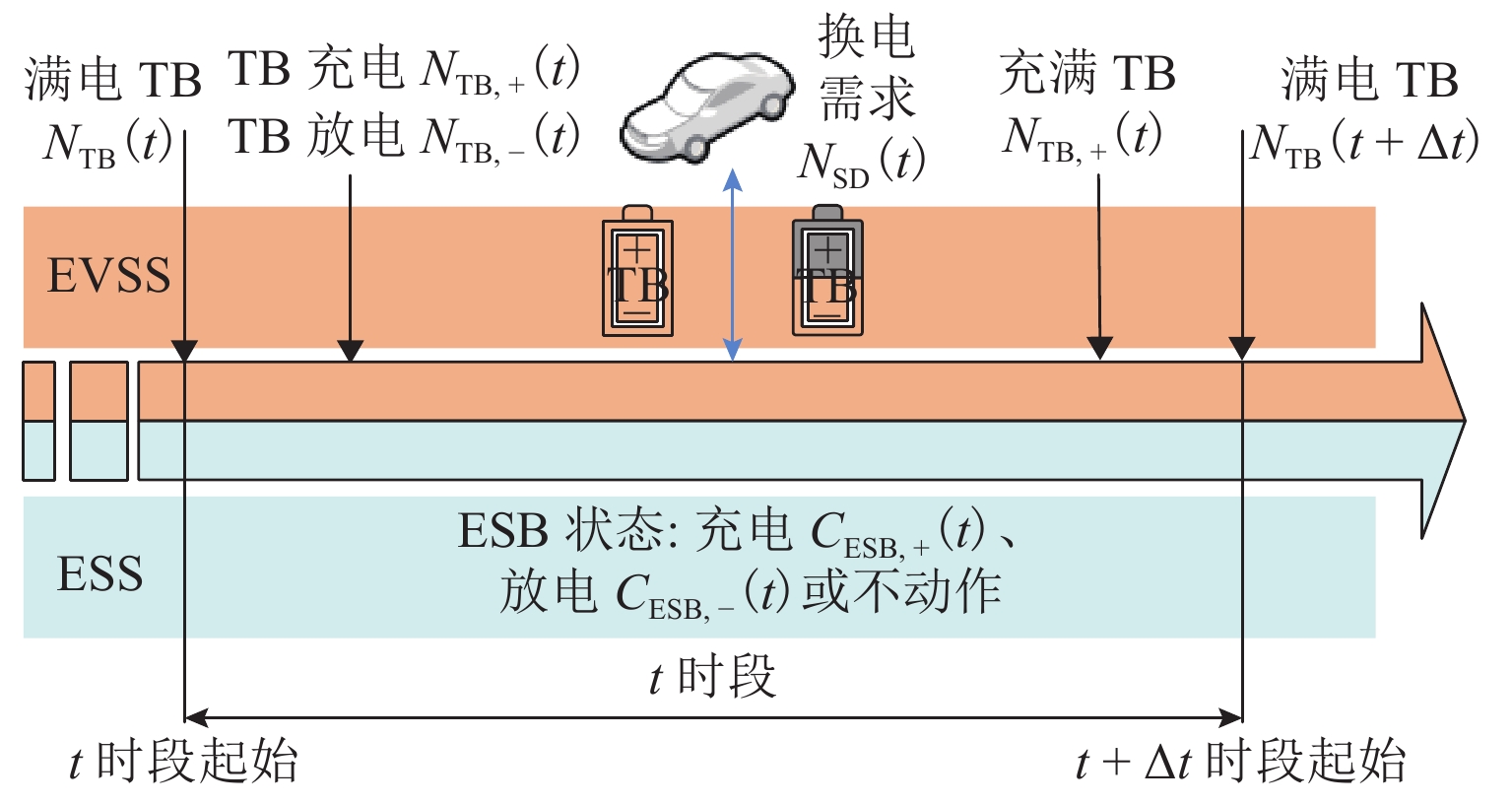
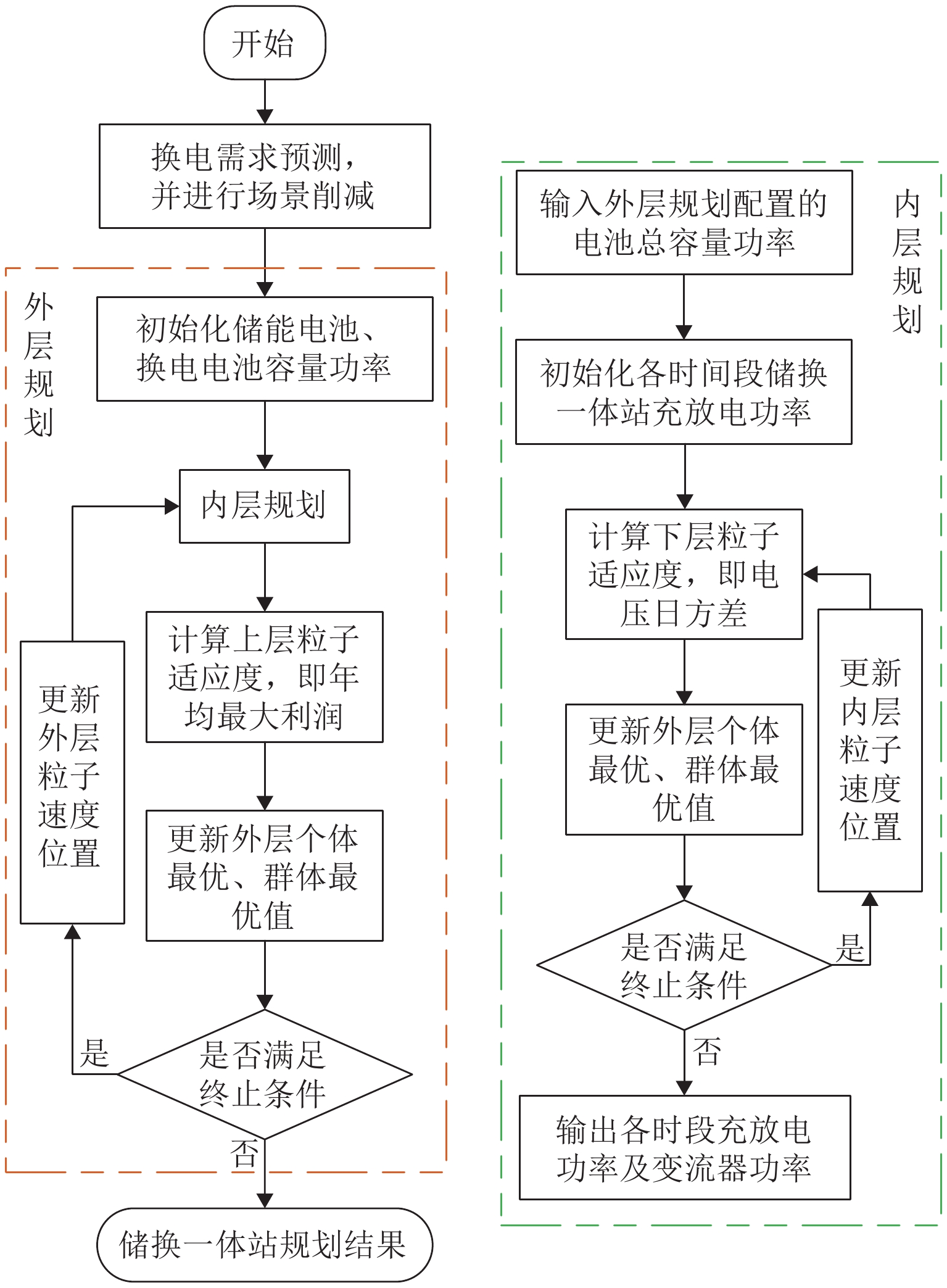
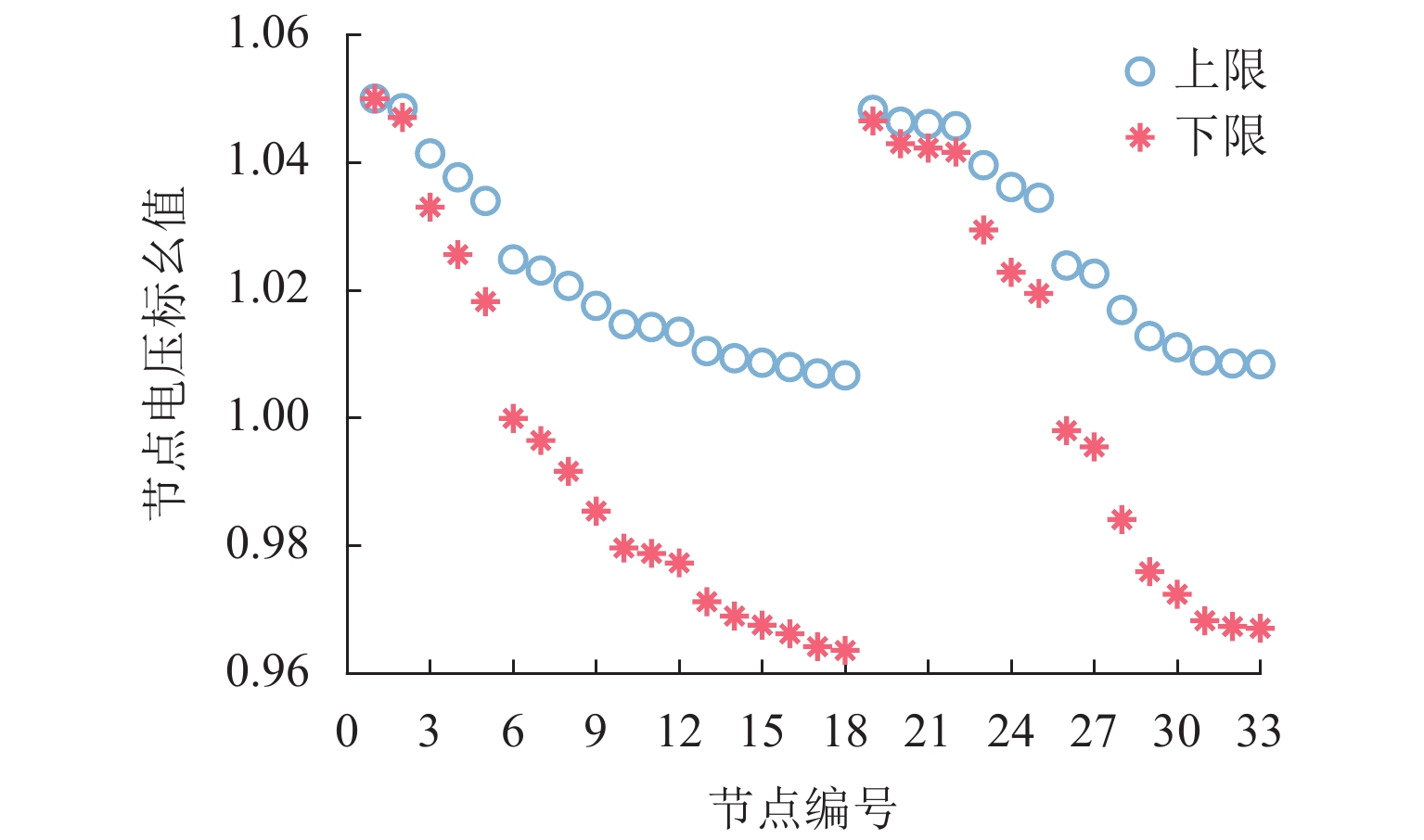
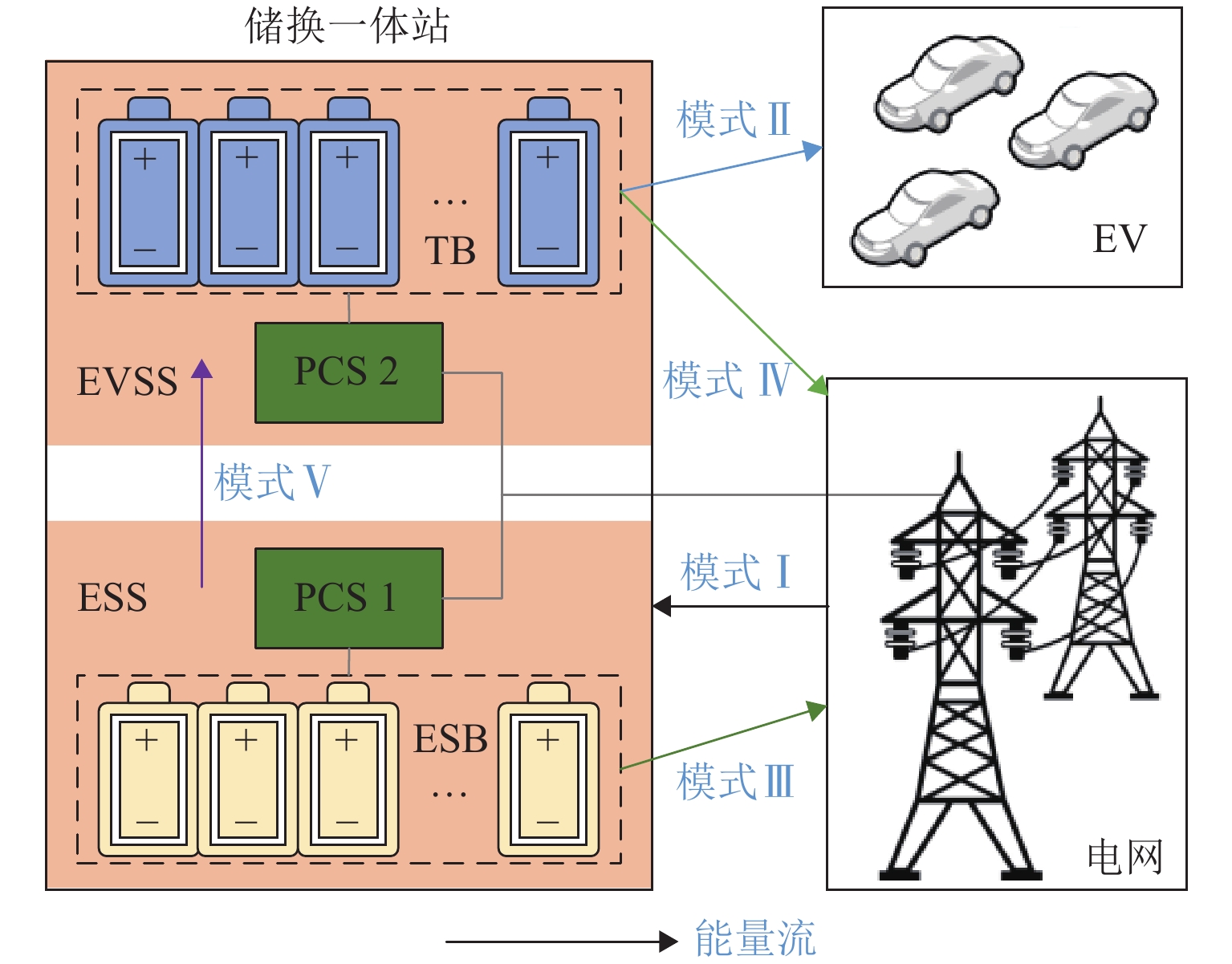
电动汽车换电站同时作为储能电站,既可实现经济获利,又兼顾电网支撑,但目前缺乏这种储换一体站的容量配置研究. 为此,本文首先分析储换一体站工作模式及电价时段,构建一体站的运行模型;然后,基于用户出行模拟,建立电动汽车换电需求预测模型;接着,建立考虑全寿命周期收益和电网支撑能力的储换一体站容量双层规划模型,外层规划以全寿命周期总收益为目标,实现储换一体站的容量规划,内层规划以对电网支撑能力为目标,实现电池组充放电行为优化,内层获得最优充放电功率并返回外层,实现储换一体站容量最优配置;最后,在 IEEE33 节点系统上验证规划模型的有效性,为储换一体站建设提供理论支撑. 研究结果表明:与其他储换一体站模式相比,储换一体站投资收益率提高 1.51%~2.26%;基于双层规划的容量优化配置方法,在保证一体站经济性的同时,能够对支撑电网电压,使电压日方差降低 20%;随着参与换电的电动汽车数量增加,一体站的经济性进一步提高.
Abstract:Electric vehicle (EV) swapping stations can achieve economic benefits while also supporting the power grid by serving as energy storage stations. However, there is currently a lack of research on the capacity configuration of such EV storage and swapping integrated stations (EVSS-IS). To this end, the working mode and tariff period of EVSS-IS were firstly analyzed to build an operational model. Then, a predictive model for EV swapping demand was developed based on user travel simulations. Next, a bi-level capacity programming model of the EVSS-IS was established, which considered life cycle benefits and grid support capacity. Specifically, the outer planning aimed at the total revenue during the whole life cycle to optimize the capacity of the EVSS-IS; the inner planning aimed at supporting the power grid and optimizing the charging and discharging behaviors; the optimal charging and discharging power from the inner layer was returned to the outer layer to realize the optimal capacity programming of the EVSS-IS. Finally, the effectiveness of the planning model was verified on the IEEE33 node system, which provided theoretical support for the construction of the EVSS-IS. The results show that the return on investment of the EVSS-IS is 1.51%–2.26% higher compared with other models; the capacity optimization allocation method based on bi-level planning can support the grid voltage while ensuring the economy of the station, resulting in a 20% reduction in the daily variance of the voltage; as the number of EVs swapping batteries increases, the economics of the EVSS-IS is further improved.
-
表 1 储换一体站参数表
Table 1. Parameters of EVSS-IS
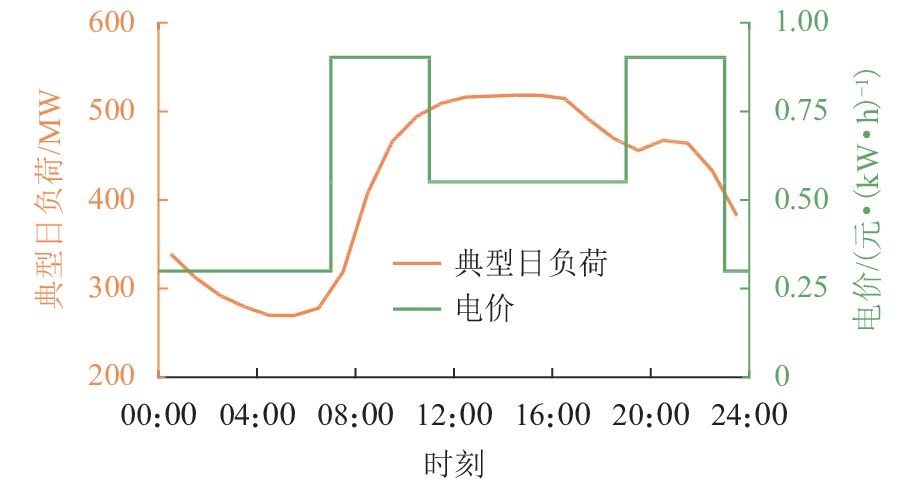
参数 数值 参数 数值 Ebat/(kW·h) 100 CES,E/(元·(kW·h)−1) 1800 CEV,E/(元·(kW·h)−1) 1280 CP/(元·kW−1) 2400 COM/(元·(kW·年)−1) 155 DEV/(元·(kW·h)−1) 1.47 DES,b/(元·(kW·h)−1) 0.15 DEV,b/(元·(kW·h)−1) 0.1 Drt/(元·年−1) 10800 $ {\eta _{\text{c}}}{\text{, }}{\eta _{\text{d}}} $ 0.9 r/% 5 N/a 15 表 2 换电需求典型聚类场景统计结果
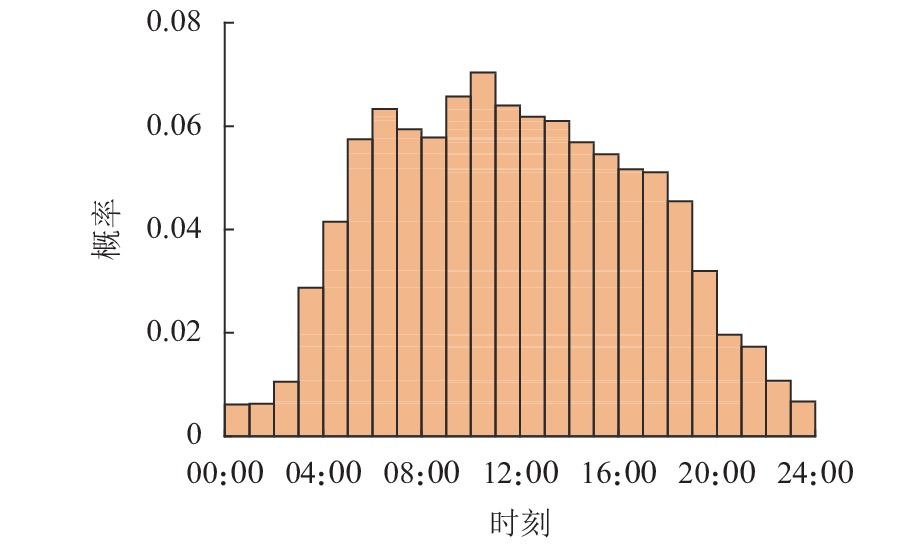
Table 2. Statistical results of demands for battery swapping on typical clustering scenarios
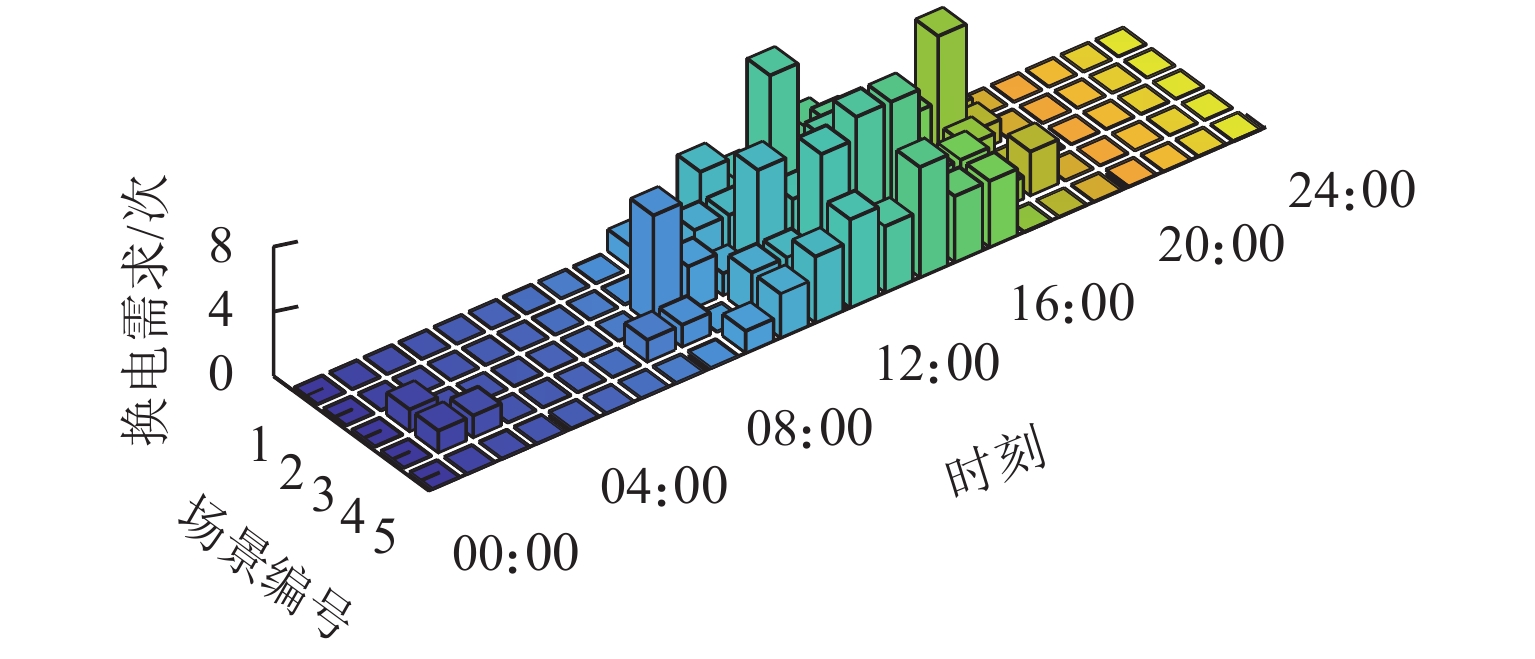
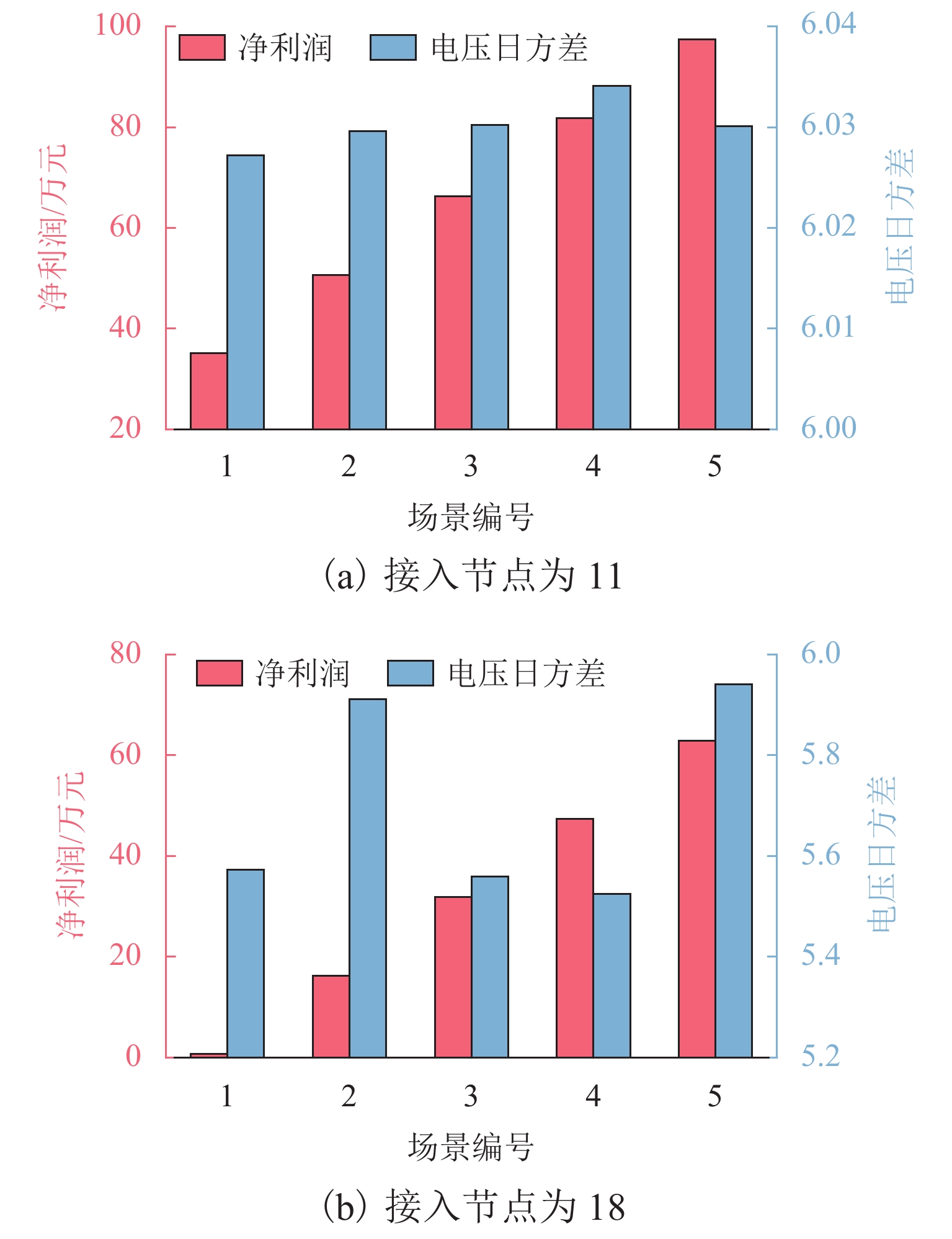
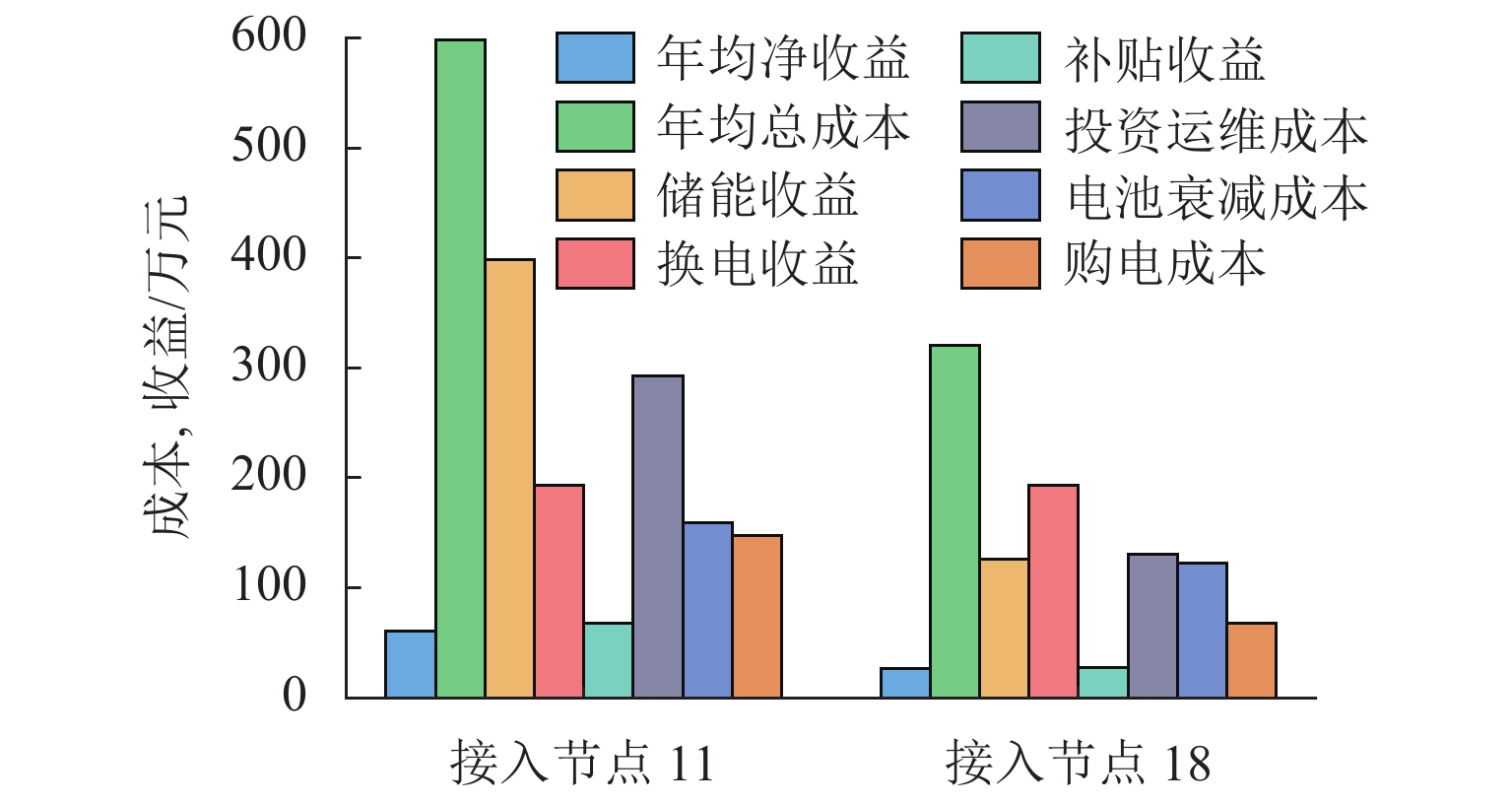
场景编号 总需求/次 概率 1 20 0.0785 2 25 0.4189 3 30 0.3265 4 35 0.1397 5 40 0.0364 表 3 接入节点为11、18时不同情景下的规划结果
Table 3. Optimization results for different scenarios with the accessing 11th, 18th nodes
接入
节点方案
编号储能容
量/(MW·h)储能功
率/MW换电容
量/(MW·h)换电功
率/MW年均净
利润/万元电压日
方差年均成
本/万元11 1 10 2.00 3.5 0.60 60.590 6.0303 598.61 2 13.5 2.70 0 0 42.961 5.3699 534.91 3 0 0 3.5 0.61 17.016 5.9595 216.55 4 10.0 2.00 3.5 0.60 53.510 5.6288 621.68 5 7.6981 18 1 2.7 0.54 3.5 0.71 26.159 5.7167 320.57 2 6.2 1.26 0 0 19.885 5.6637 245.51 3 0 0 3.5 0.73 16.318 5.9594 214.94 4 2.7 0.54 3.5 0.71 25.440 5.6904 336.27 5 7.6981 -
[1] 杨健维,杨鹤,张夏霖,等. 基于换电规则优化与车辆-电池组匹配的电动公交车充换电站充电优化策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(8): 2337-2347. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.172500YANG Jianwei, YANG He, ZHANG Xialin, et al. A charging optimization strategy on charging and swapping station for electric buses based on optimization of switching rules and matching of buses and batteries[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(8): 2337-2347. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.172500 [2] 陈丽丹,张尧,FIGUEIREDO Antonio. 电动汽车充放电负荷预测研究综述[J]. 电力系统自动化,2019,43(10): 177-191. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180814001CHEN Lidan, ZHANG Yao, FIGUEIREDO A. Overview of charging and discharging load forcasting for electric vehicles[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(10): 177-191. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180814001 [3] LI G, ZHANG X P. Modeling of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle charging demand in probabilistic power flow calculations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2012, 3(1): 492-499. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2011.2172643 [4] 杜习超,刘永民,徐则诚,等. 电动汽车随机负荷建模及对配电网节点电压分布的影响[J]. 电力自动化设备,2018,38(6): 124-130. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.06.018DU Xichao, LIU Yongmin, XU Zecheng, et al. Modeling of random load of electric vehicle and its influence on node voltage distribution of distribution network[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38(6): 124-130. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2018.06.018 [5] LYU L, YANG X R, XIANG Y, et al. Exploring high-penetration electric vehicles impact on urban power grid based on voltage stability analysis[J]. Energy, 2020, 198: 117301.1-117301.12. [6] PIMM A J, PALCZEWSKI J, MORRIS R, et al. Community energy storage: a case study in the UK using a linear programming method[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 205: 112388.1-112388.11. [7] ANEKE M, WANG M H. Energy storage technologies and real life applications—a state of the art review[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 179: 350-377. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.097 [8] YUAN H T, WEI G, ZHU L, et al. Optimal scheduling for micro-grid considering EV charging−swapping−storage integrated station[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2020, 14(6): 1127-1137. [9] 韦钢,李明,卢炜,等. 充放储一体站并网的多级阶梯电压控制分区方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2015,35(15): 3823-3831. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.15.010WEI Gang, LI Ming, LU Wei, et al. Multistage ladder voltage control partitioning method containing grid-connected charging-discharging-storage integrative station[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(15): 3823-3831. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.15.010 [10] 吴万禄,周江昕,余浩斌,等. 含充放储一体化电站的电网供电能力评估[J]. 电网技术,2018,42(4): 1266-1273. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2017.0202WU Wanlu, ZHOU Jiangxin, YU Haobin, et al. Power supply capability evaluation of power grid containing integrated charging-discharging-storage station[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(4): 1266-1273. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2017.0202 [11] ZHENG Y, DONG Z Y, XU Y, et al. Electric vehicle battery charging/swap stations in distribution systems: comparison study and optimal planning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2014, 29(1): 221-229. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2013.2278852 [12] WU H, PANG G K H, CHOY K L, et al. An optimization model for electric vehicle battery charging at a battery swapping station[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 881-895. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2758404 [13] WU C Y, GU W, XU Y L, et al. Bi-level optimization model for integrated energy system considering the thermal comfort of heat customers[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 232: 607-616. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.09.212 [14] 田梦瑶,汤波,杨秀,等. 综合考虑充电需求和配电网接纳能力的电动汽车充电站规划[J]. 电网技术,2021,45(2): 498-509. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0636TIAN Mengyao, TANG Bo, YANG Xiu, et al. Planning of electric vehicle charging stations considering charging demands and acceptance capacity of distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(2): 498-509. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0636 [15] 贾龙,胡泽春,宋永华,等. 储能和电动汽车充电站与配电网的联合规划研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2017,37(1): 73-84. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.160818JIA Long, HU Zechun, SONG Yonghua, et al. Joint planning of distribution networks with distributed energy storage systems and electric vehicle charging stations[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(1): 73-84. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.160818 [16] DING H J, HU Z C, SONG Y H. Value of the energy storage system in an electric bus fast charging station[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 630-639. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.058 [17] GARVEY S D, EAMES P C, WANG J H, et al. On generation-integrated energy storage[J]. Energy Policy, 2015, 86: 544-551. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2015.08.001 [18] NUH E, DRAGAN P, SADIK K, et al. An integrated multi-objective optimization and multi-criteria decision-making model for optimal planning of workplace charging stations[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 304: 117866.1-117866.15. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117866 [19] 何晨可,韦钢,朱兰,等. 电动汽车充换放储一体化电站选址定容[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(2): 479-489,645. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.181446HE Chenke, WEI Gang, ZHU Lan, et al. Locating and sizing of electric vehicle charging-swapping-discharging-storage integrated station[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(2): 479-489,645. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.181446 [20] 曾梦隆,韦钢,朱兰,等. 交直流配电网中电动汽车充换储一体站规划[J]. 电力系统自动化,2021,45(18): 52-60. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20210112007ZENG Menglong, WEI Gang, ZHU Lan, et al. Planning of electric vehicle charging-swapping-storage integrated station in AC/DC distribution network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(18): 52-60. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20210112007 [21] 胡代豪,郭力,刘一欣,等. 计及光储快充一体站的配电网随机-鲁棒混合优化调度[J]. 电网技术,2021,45(2): 507-519. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0838HU Daihao, GUO Li, LIU Yixin, et al. Stochastic/robust hybrid optimal dispatching of distribution networks considering fast charging stations with photovoltaic and energy storage[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(2): 507-519. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0838 [22] Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration. Summary of travel trends: 2009 national household travel survey [EB/OL]. (2011-02-28)[2022-03-13]. https://nhts.org/gov/2009/pub/stt.pdf. [23] 陈静鹏,艾芊,肖斐. 基于用户出行需求的电动汽车充电站规划[J]. 电力自动化设备,2016,36(6): 34-39. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2016.06.006CHEN Jingpeng, AI Qian, XIAO Fei. EV charging station planning based on travel demand[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2016, 36(6): 34-39. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2016.06.006 [24] HERRERA V, MILO A, GAZTAÑAGA H, et al. Adaptive energy management strategy and optimal sizing applied on a battery-supercapacitor based tramway[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 169: 831-845. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.02.079 -




 下载:
下载: