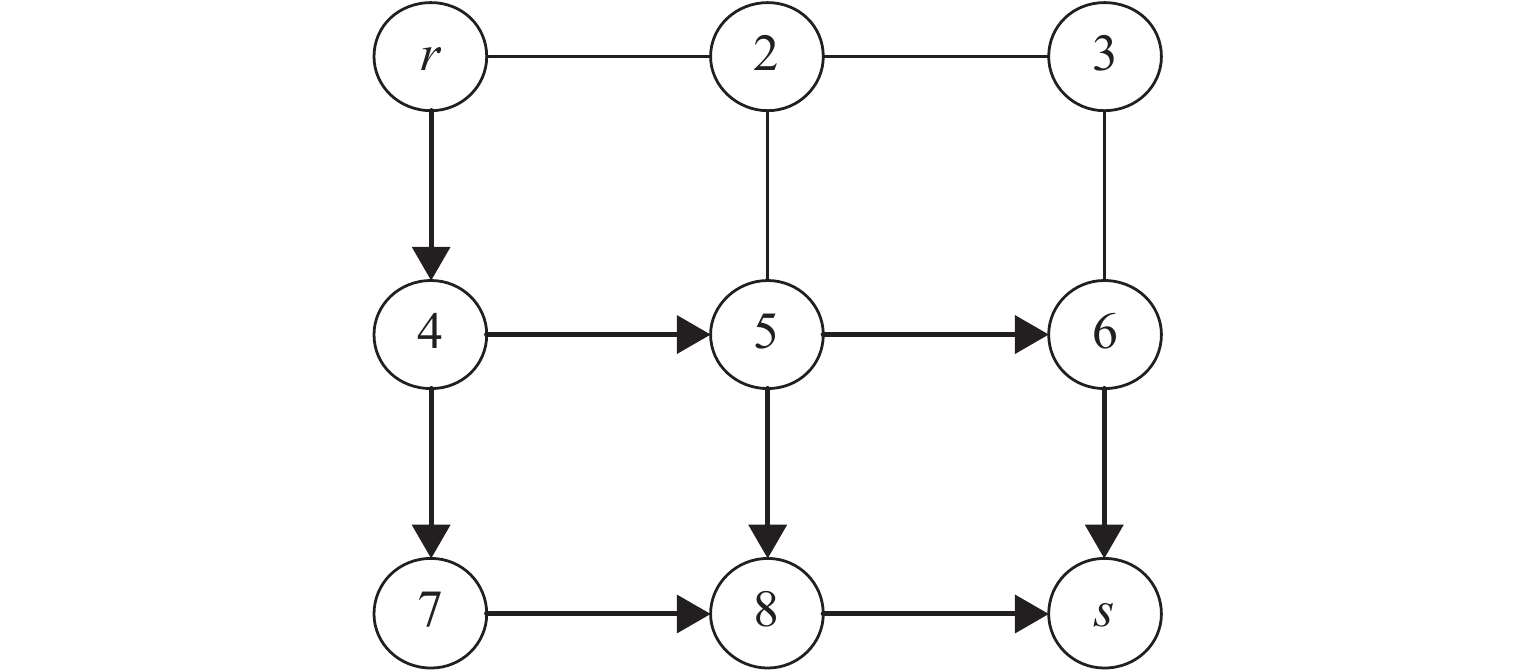
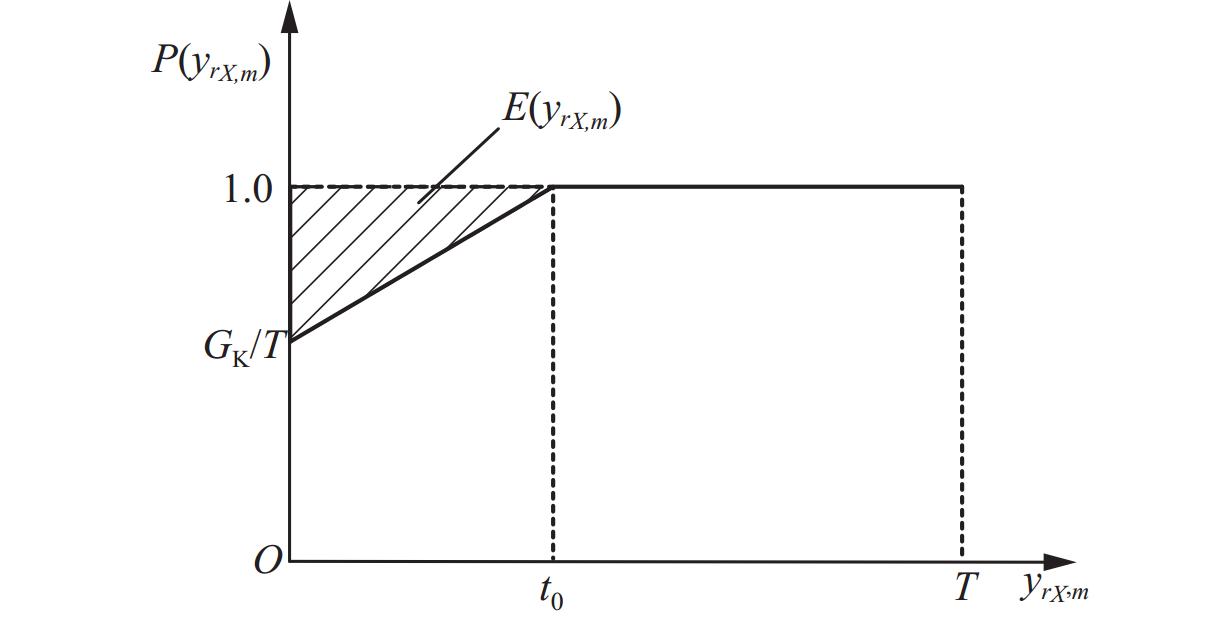
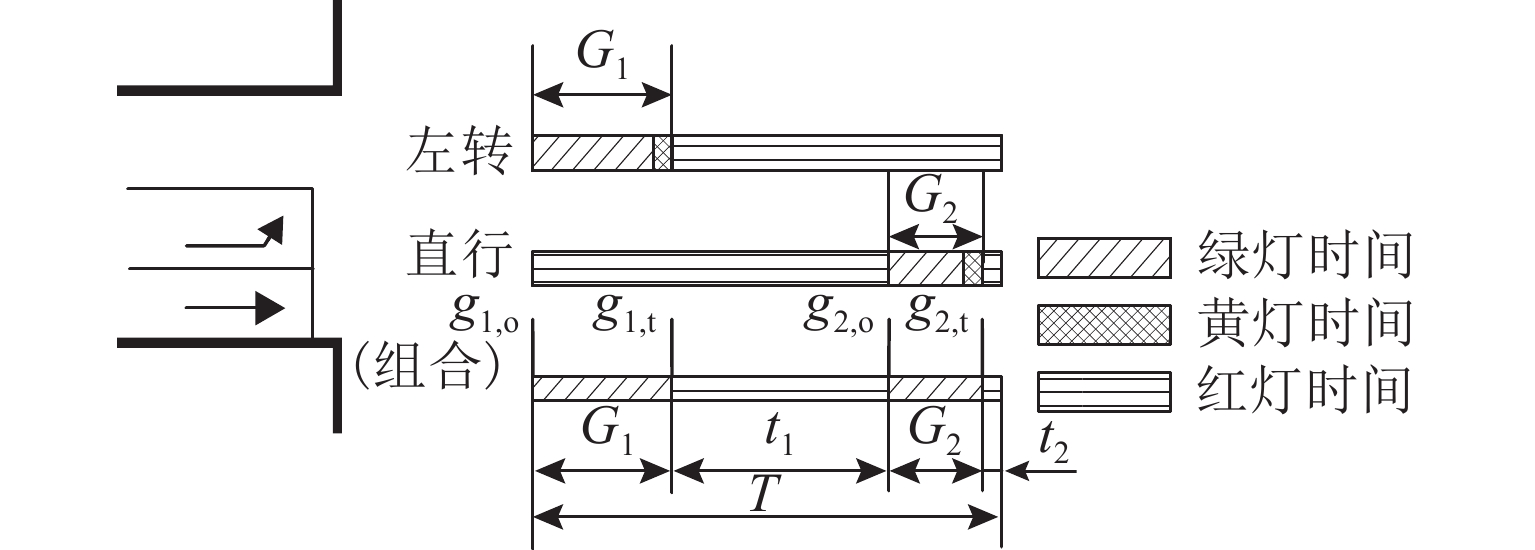
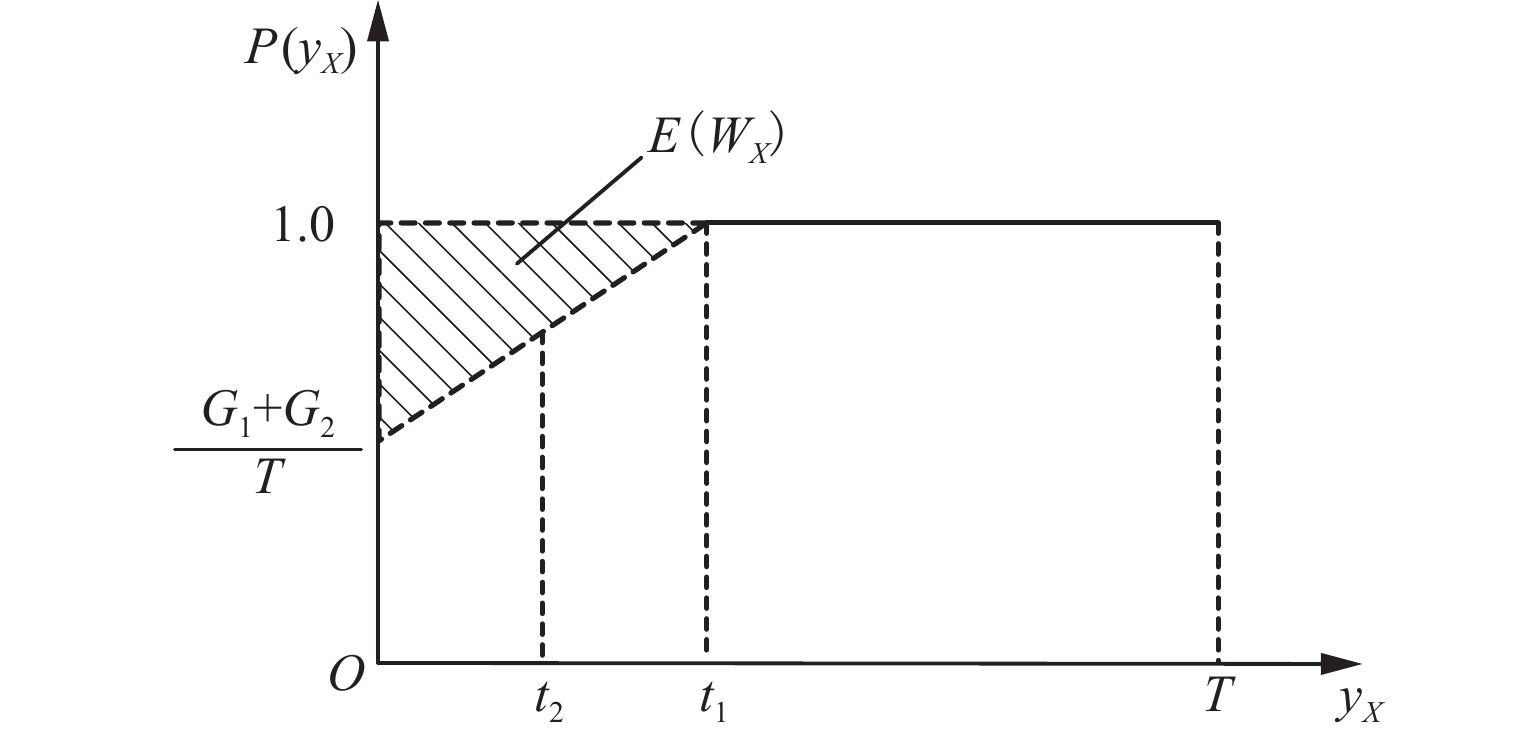
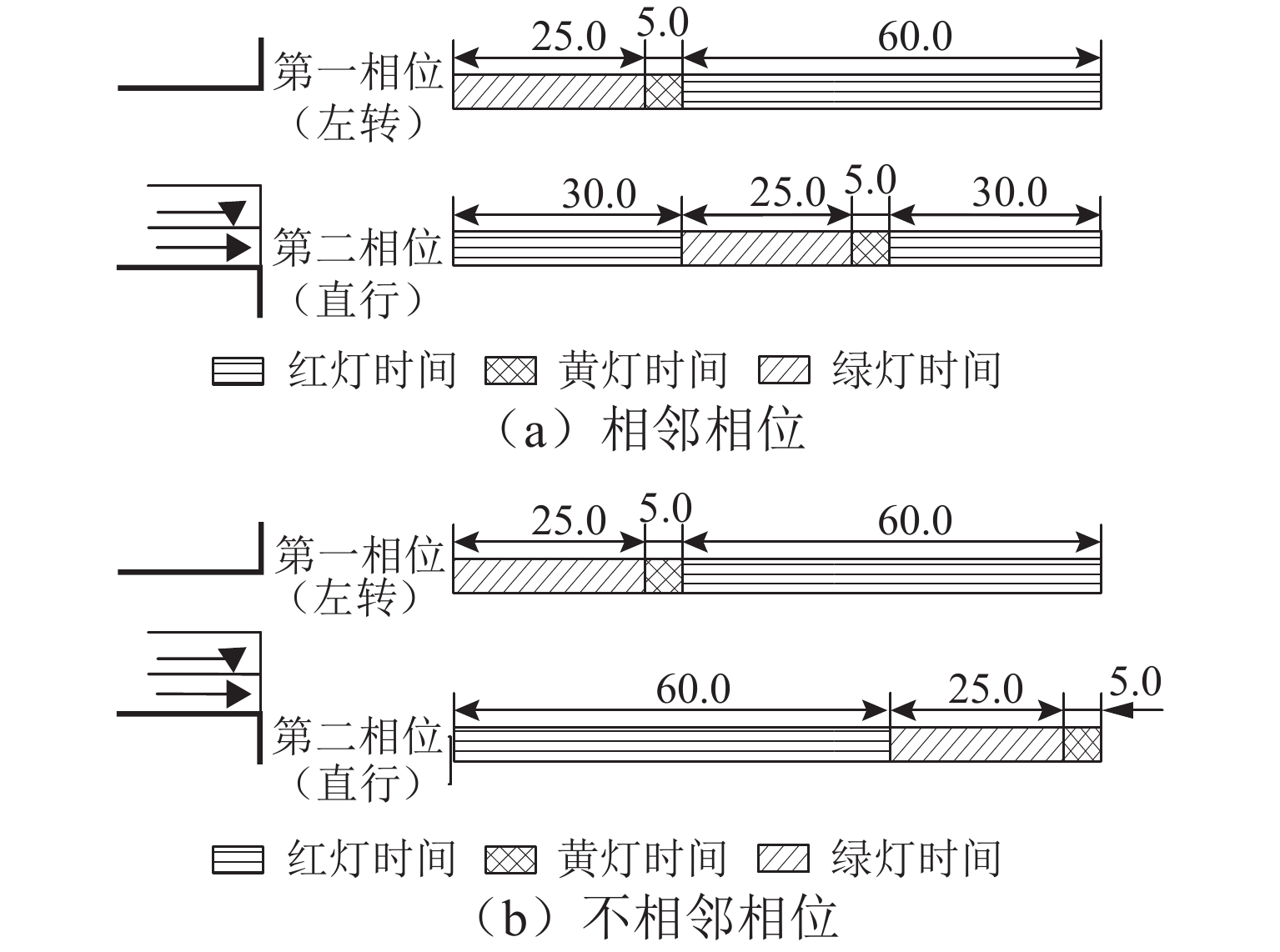
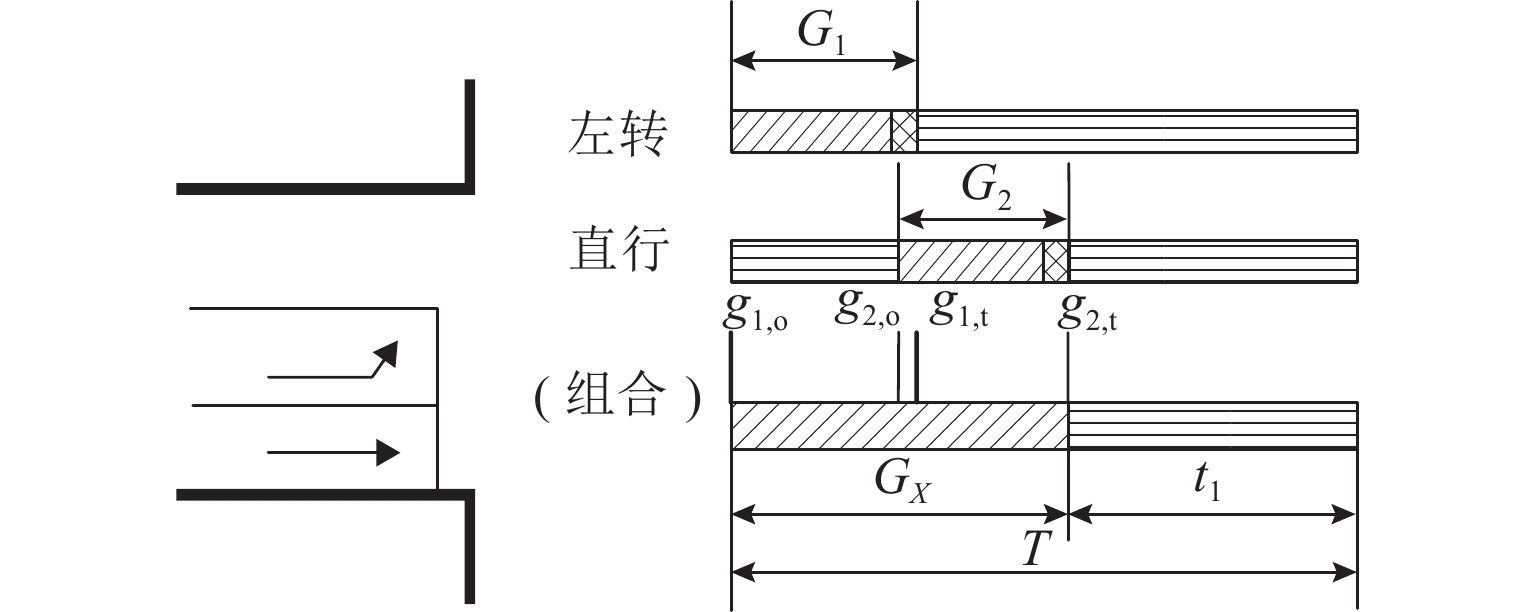
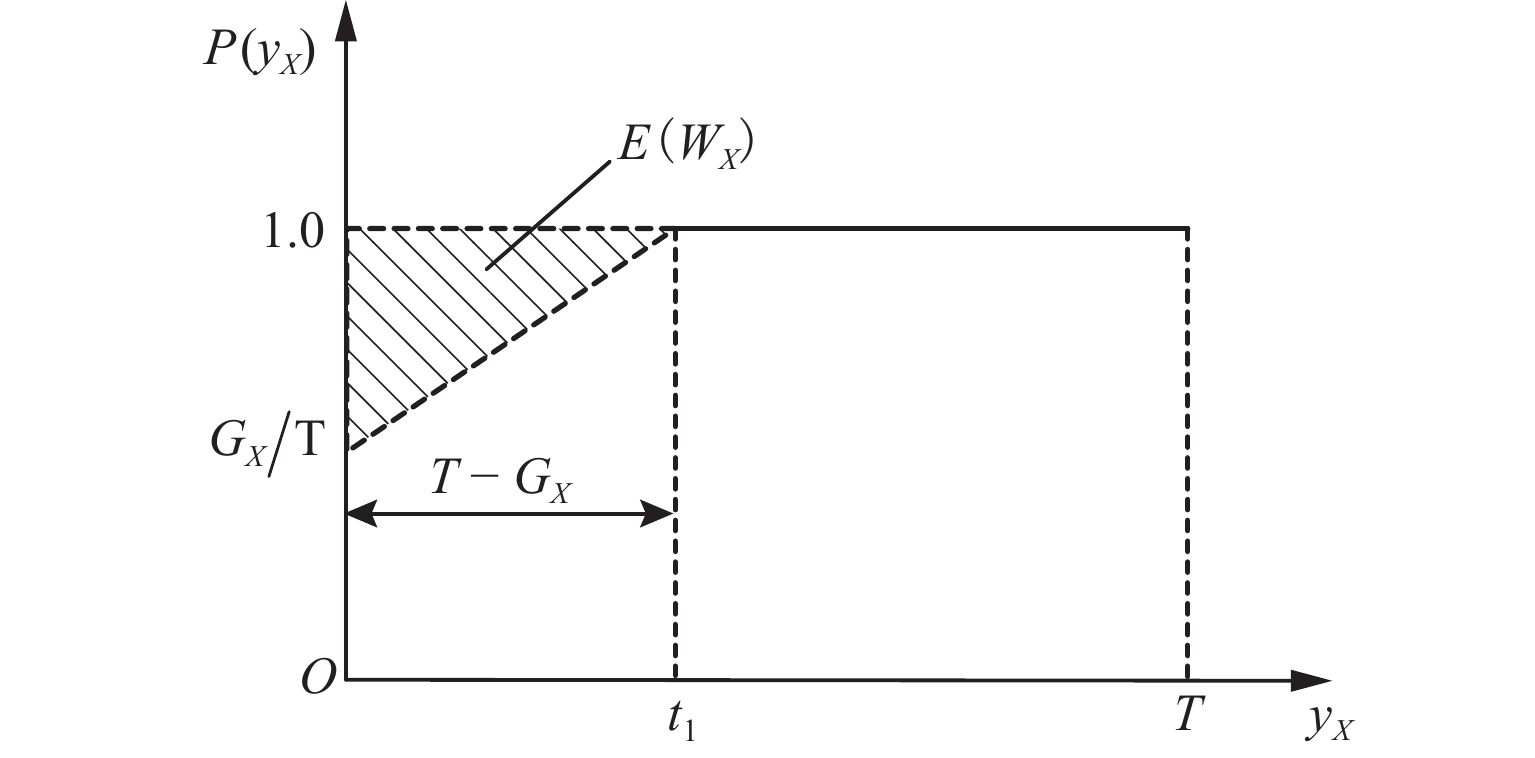
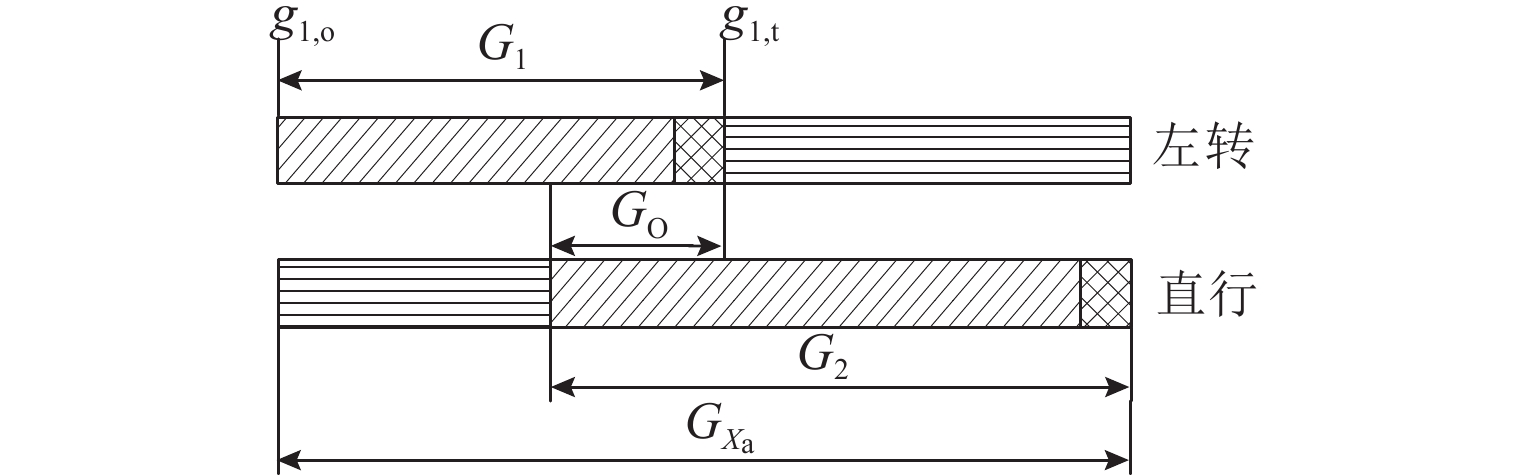
Hyperpath Searching Algorithm Method Based on Signal Delay at Intersections
-
摘要:
城市道路中交叉口信号周期性变化会导致车辆出行的不确定延误,为降低车辆在交叉口处产生的信号延误,以路段旅行时间和交叉口期望延误最小为优化目标,提出一种改进的超路径规划方法. 首先,根据车辆到达交叉口的概率分布函数,推导出车辆在信号交叉口的期望等待时间和转向比例计算公式;其次,引入标号设定算法构建高性能超路径规划方法;最后,将改进的超路径规划方法应用于南京新街口区域的路网,通过最优超路径集合分析证实其适用性. 研究表明:与最短路出行策略相比,车辆遵循基于超路径规划方法的出行策略,在行进过程时从最优超路径集合中选择变换的行驶路线可降低67.1%的交叉口信号延误和22.3%的总旅行时间;此外,超路径出行策略可优化路网中的出行结构,缓解交通拥堵,实现流量均衡.
Abstract:The periodic change of intersection signals in urban road systems leads to the uncertain delay of vehicle travel. In order to reduce the delays of vehicles at signal-controlled intersections, an improved hyperpath searching algorithm was proposed with the minimization of travel time on the road segments and the expected delay at the intersections as the optimization goal. First, according to the probability distribution function of vehicles arriving at the intersection, the expected waiting time and the turning movement proportion were derived. Then, the high-performance hyperpath searching algorithm was developed with the introduction of the label setting algorithm. Finally, the improved hyperpath searching algorithm was applied to the road network at Xinjiekou area, Nanjing, and the optimal hyperpath set was used to evaluate the applicability of the algorithm. The results show that compared with the shortest path strategy, hyperpath searching algorithm reduces the intersection delay and the total travel time by 67.1% and 22.3%, respectively as drivers shift to a driving route in the optimal hyperpath set. Furthermore, the hyperpath-based strategy can optimize the trip distribution in the road network, alleviating traffic congestion and contributing to flow equilibrium.
-
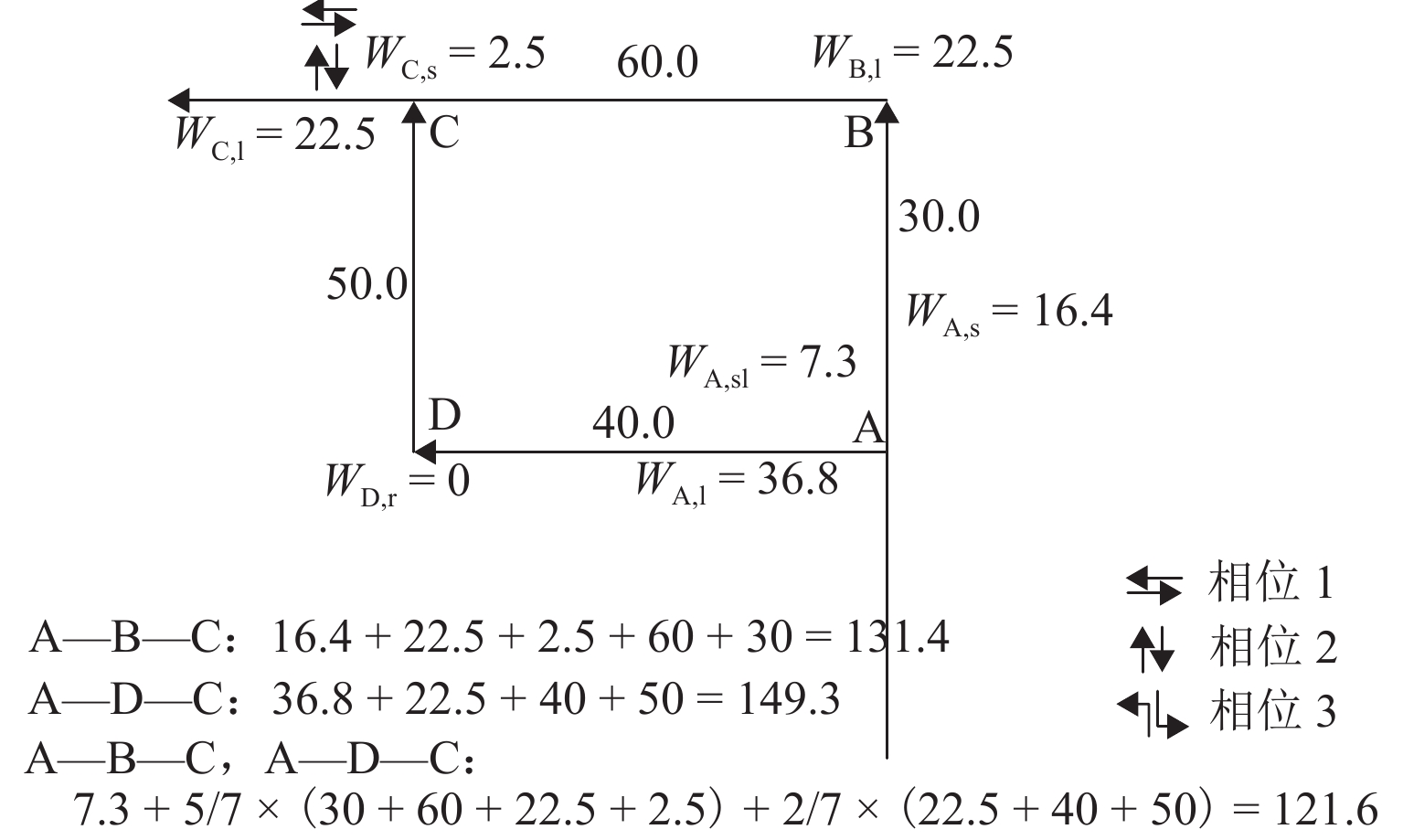
表 1 信号配时变化对超路径集合元素的影响
Table 1. Influence of signal timing on hyperpath set
序号 交叉口 周期/s 相位 1/s 相位 2/s 相位 3/s 路径 1
时间/s路径 2
时间/s组合
期望/s最优超
路径1 A 110 40 50 20 131.4 149.3 121.6 A—B—C, A—D—C C 80 60 20 0 2 A 150 80 20 50 202.6 127.1 130.1 A—D—C C 120 30 90 0 3 A 47 12 15 20 124.4 138.8 125.1 A—B—C C 110 95 15 0 表 2 参数定义
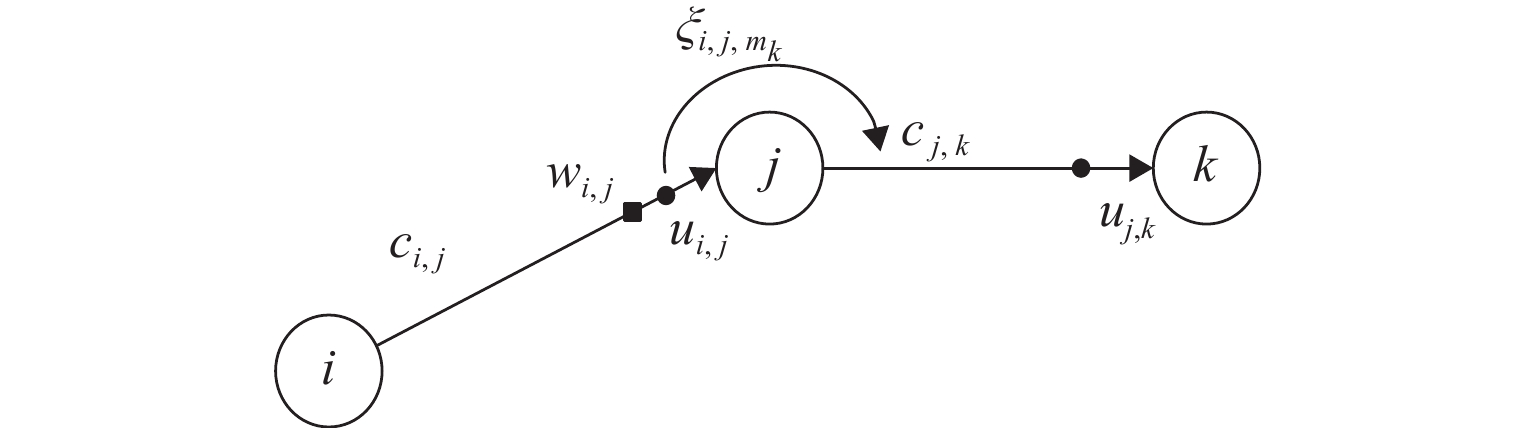
Table 2. Parameters definition
符号 含义 $ G(N,A) $ 有向网络图,其中N、A分别为网络中的节点集合、路段集合 ${\varGamma ^ - }(i)$ 流入节点$i$的路段集合 ${\varGamma ^ + }(i)$ 流出节点$i$的路段集合 j 节点 i 的下游节点标号 k 节点 j 的下游节点标号 s 终点 r 起点 ${m_k}$ 转向节点 k 的转向行为 H 超路径的路段集合 ${M_{i,j}}$ 进口道$(i,j)$处,属于超路径的转向行为集合 $u_{i,j}$ 进口道$(i,j)$到终点的期望旅行时间 $ p\{ (j,k)|i\} $ 由节点 i 转向路段$ j—k $时,节点$ j$被选择的概率 $ p\{ k|j\} $ 由节点 j 转向节点 k 时,节点 k 被选择的概率 $ {P_{ {i,j} }} $ 在节点i处,路段$ i—j $被选择的概率 $c_{i,j}$ 路段$ i—j $的旅行时间 $ \xi_{i,j,m_k} $ 从节点 i 经过节点 j 转向节点 k 的期望延误时间 $ w_{i,j} $ 进口道为$ \left(i,j\right) $时,在节点 j 处的组合延误期望值 注:$\displaystyle \sum\nolimits_{(i,j) \in {\varGamma ^ + }(i)} {P_{{i,j} }} = 1 $. 表 3 路径选择概率
Table 3. Path choice probability
路径 路径走行路段 路径被选择
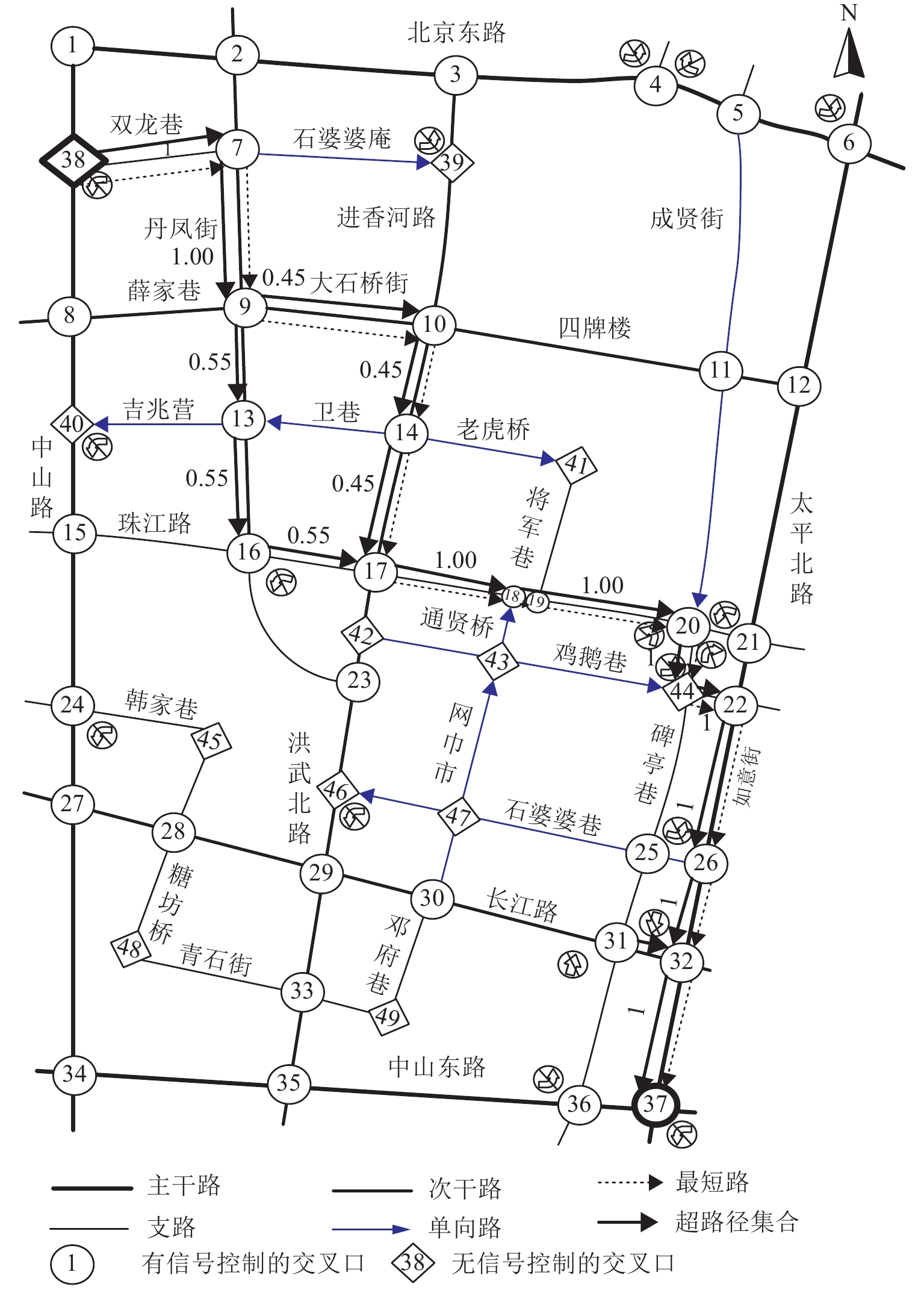
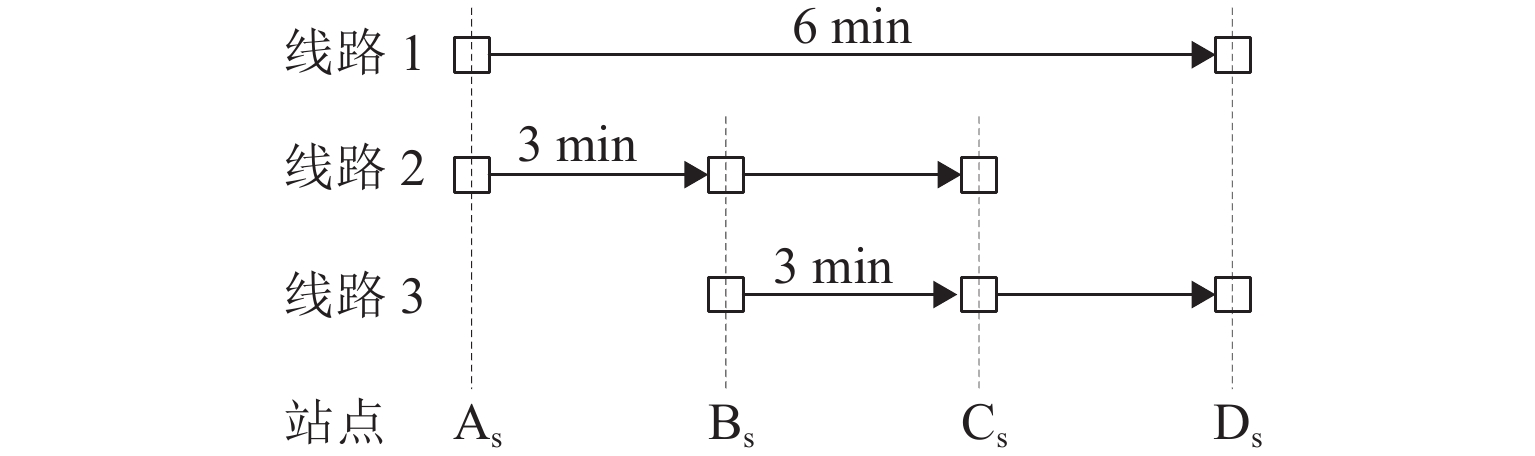
概率路径 1 38—7—9—10—14—17—18—
19—20—44—22—26—32—370.45 路径 2 38—7—9—13—16—17—18—
19—20—44—22—26—32—370.55 表 4 两种路径出行策略对比
Table 4. Comparison between two routing strategies
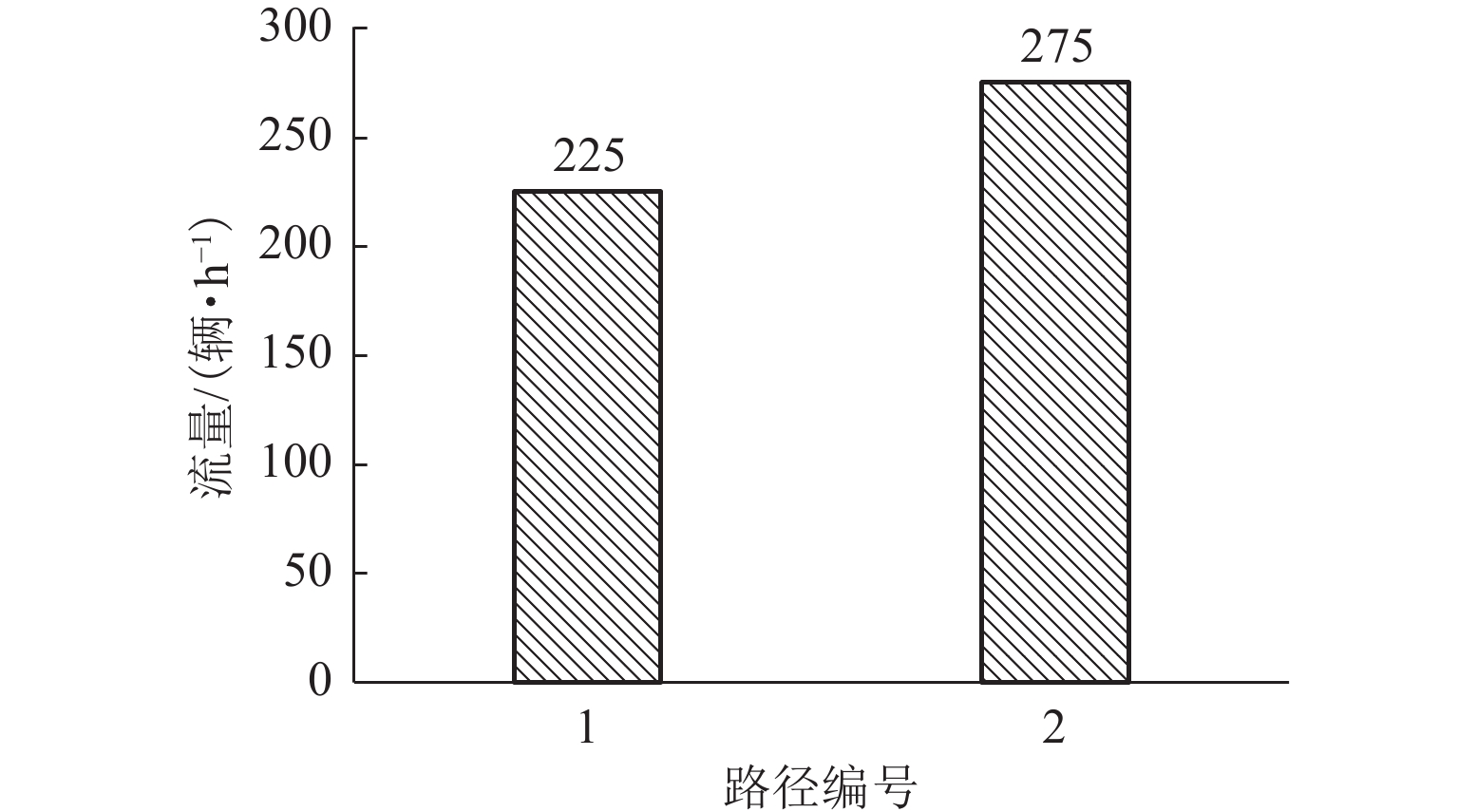
出行策略 路径 总旅行时间/s 总旅行时间降低率/% 总延误时间/s 总延误时间降低率/% 最短路 路径 1 1 010.0 317.0 超路径 路径 1 或路径 2 784.8 22.3 104.2 67.1 表 5 进口道(7,9)的相关参数
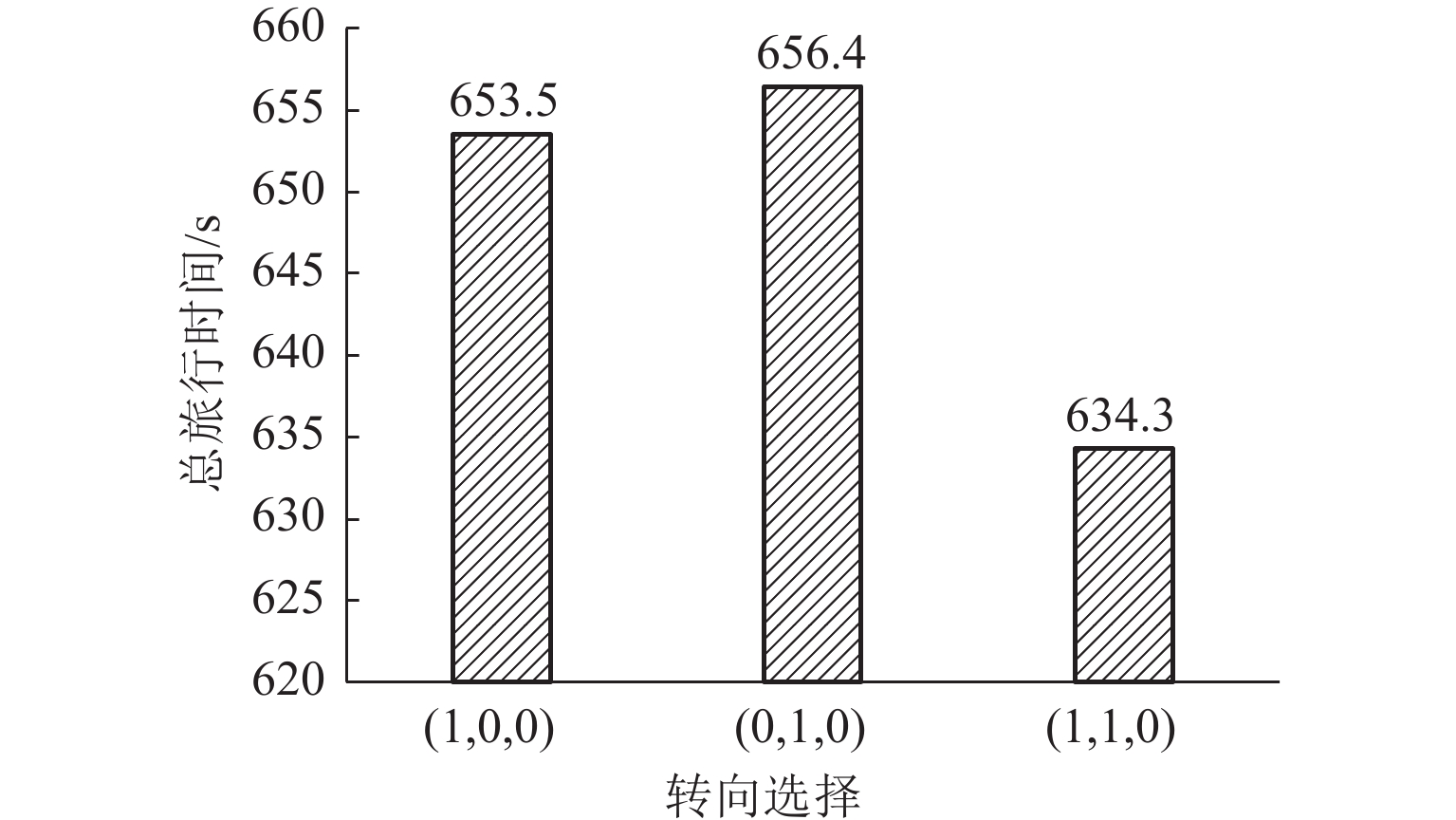
Table 5. Related parameters of entrance (7,9)
下游路段 转向行为 距终点的总旅行时间/s 路段旅行时间/s 延误时间/s 选择概率/% 组合延误时间/s 组合总旅行时间/s 9—10 左转 555.3 79.0 22.1 45 8.5 655.2 9—13 直行 582.3 52.0 19.2 55 表 6 进口道(19,20)的相关参数
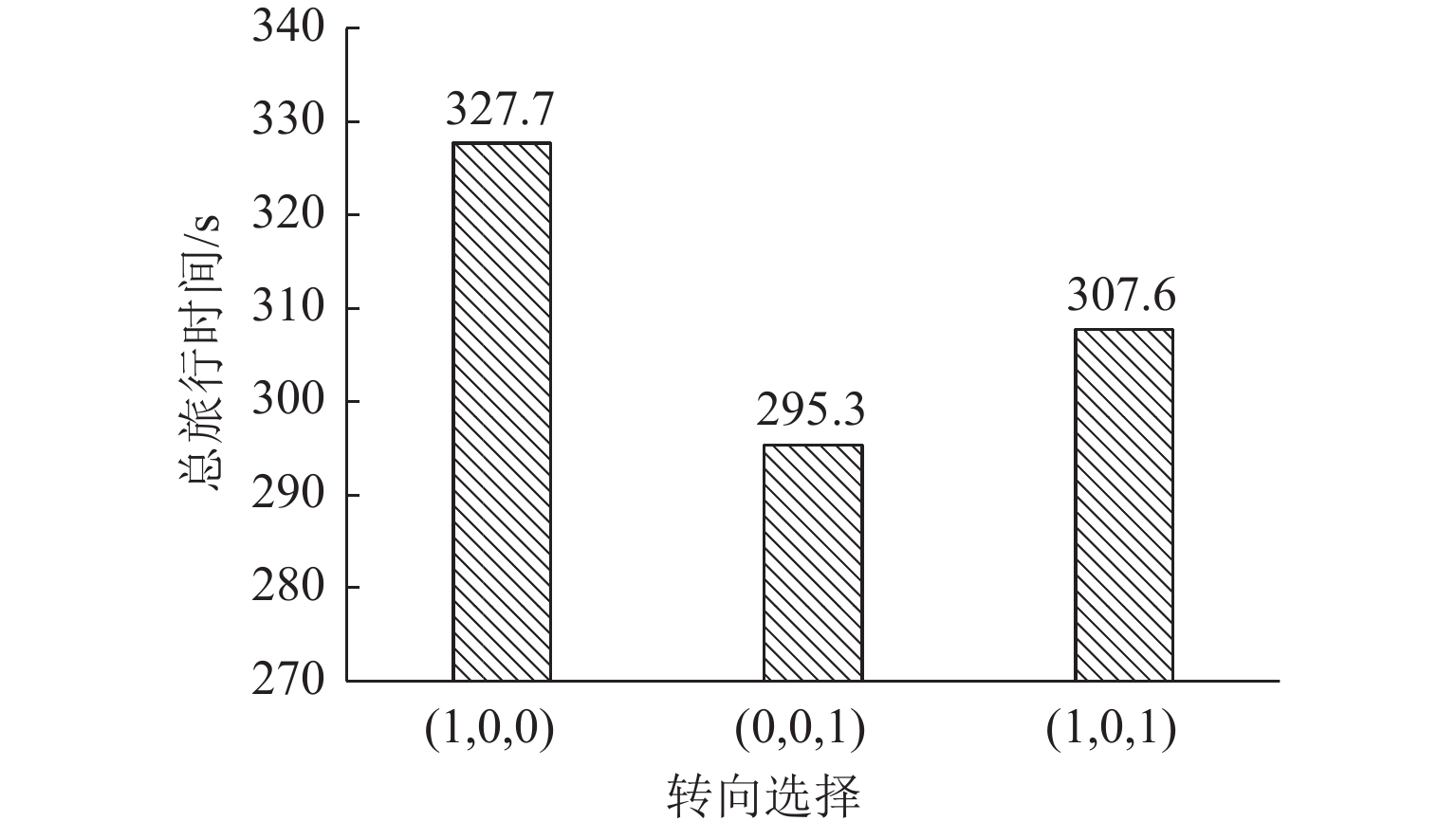
Table 6. Related parameters of entrance (19,20)
下游路段 转向行为 距终点的总旅行时间/s 路段旅行时间/s 延误时间/s 选择概率/% 组合延误时间/s 组合总旅行时间/s 20—21 直转 283.6 13.0 31.1 13.8 0 307.6 20—44 右转 255.3 40.0 0 86.2 -
[1] 王芬芬. 合理的多路径算法研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2017. [2] 段征宇,雷曾翔,孙硕,等. 随机时变车辆路径问题的多目标鲁棒优化方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2019,54(3): 565-572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170617DUAN Zhengyu, LEI Zengxiang, SUN Shuo, et al. Multi-objective robust optimisation method for stochastic time-dependent vehicle routing problem[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(3): 565-572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20170617 [3] HOFFMAN W, PAVLEY R. A method for the solution of the N th best path problem[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1959, 6(4): 506-514. doi: 10.1145/320998.321004 [4] 刘辉平. 基于路网的路径规划问题研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学,2018. [5] DROSOU M, PITOURA E. Search result diversification[J]. ACM SIGMOD Record, 2010, 39(1): 41-47. doi: 10.1145/1860702.1860709 [6] YEN J Y. Finding the K shortest loopless paths in a network[J]. Management Science, 1971, 17(11): 712-716. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.17.11.712 [7] TORRIERI D. Algorithms for finding an optimal set of short disjoint paths in a communication network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1992, 40(11): 1698-1702. doi: 10.1109/26.179933 [8] YALLOUZ J, ROTTENSTREICH O, BABARCZI P, et al. Minimum-weight link-disjoint node-“somewhat disjoint” paths[J]. ACM Transactions on Networking, 2018, 26(3): 1110-1122. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2018.2823912 [9] GOMES T, CRAVEIRINHA J. Efficient calculation of the most reliable pair of link disjoint paths in telecommunication networks[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 181(3): 1055-1064. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2006.03.005 [10] GOMES T, MARTINS L, FERREIRA S, et al. Algorithms for determining a node-disjoint path pair visiting specified nodes[J]. Optical Switching and Networking, 2017, 23: 189-204. doi: 10.1016/j.osn.2016.05.002 [11] 倪明放,高石云,马峰,等. 多约束最短链路不相交路径的启发式算法[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,14(1): 79-83.NI Mingfang, GAO Shiyun, MA Feng, et al. Heuristic algorithm for multi-constrained shortest link-disjoint paths[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 14(1): 79-83. [12] LAI C N. Optimal node-disjoint paths in folded hypercubes[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2021, 147: 100-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2020.09.005 [13] 周加全. 基于改进遗传算法路径规划问题的研究[J]. 微型电脑应用,2021,37(11): 1-3,8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-757X.2021.11.002ZHOU Jiaquan. Research of path planning problem based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Microcomputer Applications, 2021, 37(11): 1-3,8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-757X.2021.11.002 [14] SPIESS H, FLORIAN M. Optimal strategies: a new assignment model for transit networks[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 1989, 23(2): 83-102. doi: 10.1016/0191-2615(89)90034-9 [15] BELL M G H. Hyperstar: a multi-path Astar algorithm for risk averse vehicle navigation[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2009, 43(1): 97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2008.05.010 [16] MA J S, FUKUDA D, SCHMÖCKER J D. Faster hyperpath generating algorithms for vehicle navigation[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2013, 9(10): 925-948. doi: 10.1080/18128602.2012.719165 [17] 高明霞,贺国光. 考虑交叉口延误和转向限制的弧标号最短路径算法[J]. 兰州交通大学学报,2011,30(6): 111-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2011.06.026GAO Mingxia, HE Guoguang. An arc labeling algorithm for shortest path problem considering turn penalties and prohibitions at intersections[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2011, 30(6): 111-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2011.06.026 [18] JU Z Y, DU M Q. Hyperpath searching algorithm considering delay at intersection and its application in CVIS for vehicle navigation[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2022, 2022: 2304097.1-2304097.15. [19] 杜牧青,程琳. 考虑交叉口转向延误的最短路径拍卖算法[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(2): 249-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.02.015DU Muqing, CHENG Lin. Auction algorithm for shortest paths in road networks considering delays for intersection movements[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(2): 249-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.02.015 [20] ZILIASKOPOULOS A K, MAHMASSANI H S. A note on least time path computation considering delays and prohibitions for intersection movements[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 1996, 30(5): 359-367. doi: 10.1016/0191-2615(96)00001-X [21] 任刚. 交通管制下的交通分配算法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学,2003. [22] 卢顺达,程琳,邵娟. 转向延误和路段容量双约束下的用户均衡模型及算法研究[J]. 道路交通与安全,2017,17(6): 19-24.LU Shunda, CHENG Lin, SHAO Juan. Research on user equilibrium model and algorithm with turning delays and link capacity[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2017, 17(6): 19-24. [23] 李晓红. 城市干线交通信号协调优化控制及仿真[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学,2007. -




 下载:
下载: