5G Antenna Parameter Planning for Intelligent Marshalling Station Based on Machine Learning Algorithm
-
摘要:
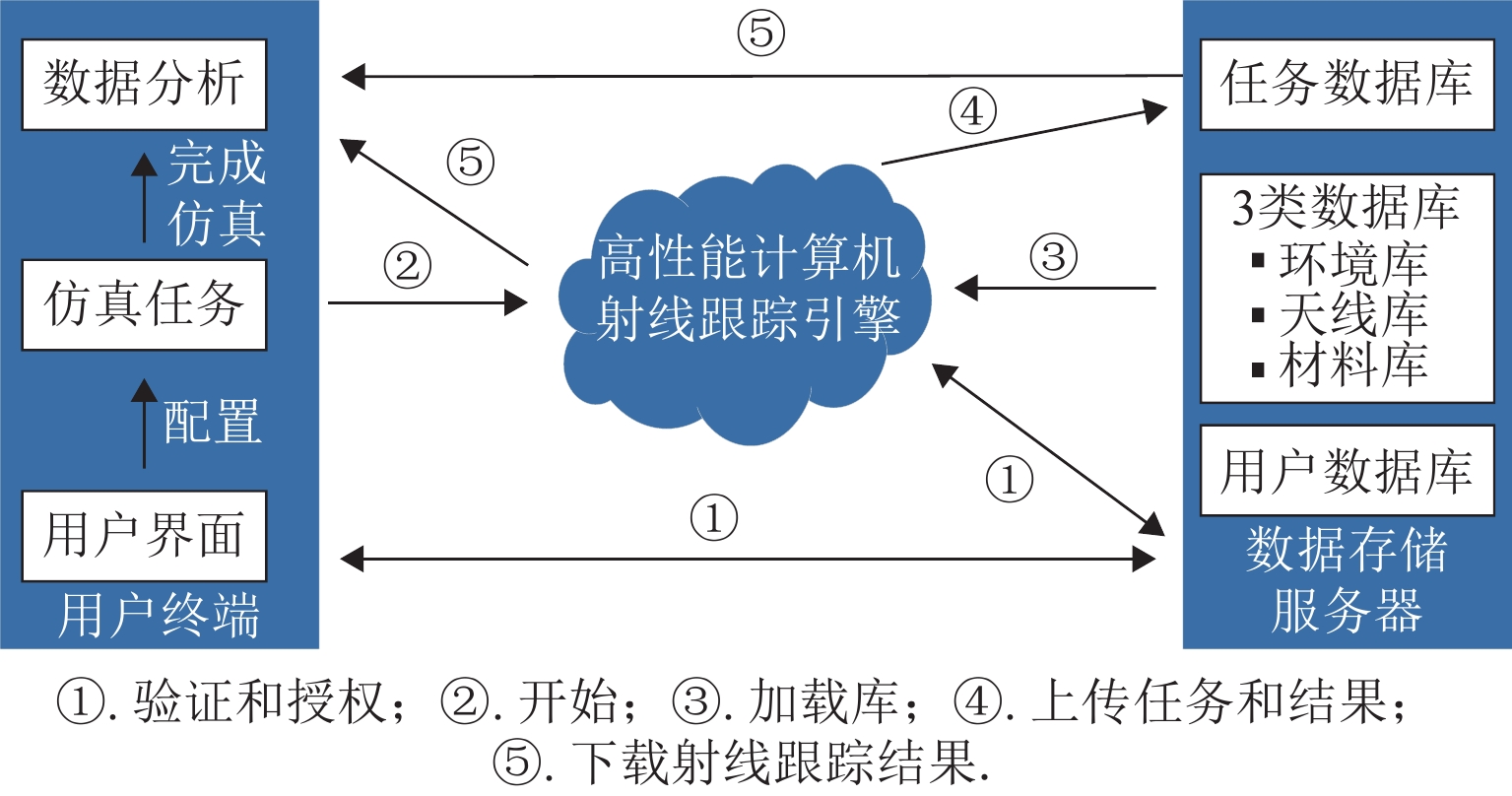
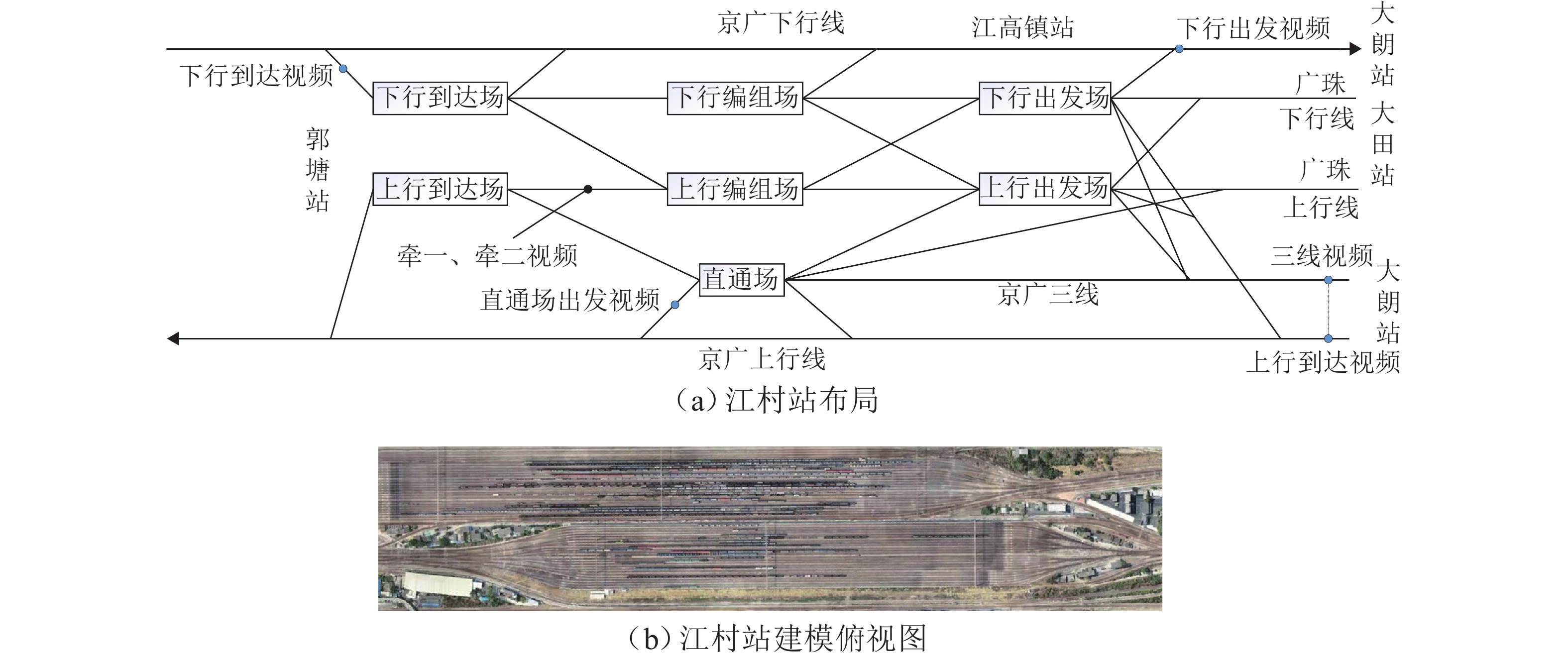
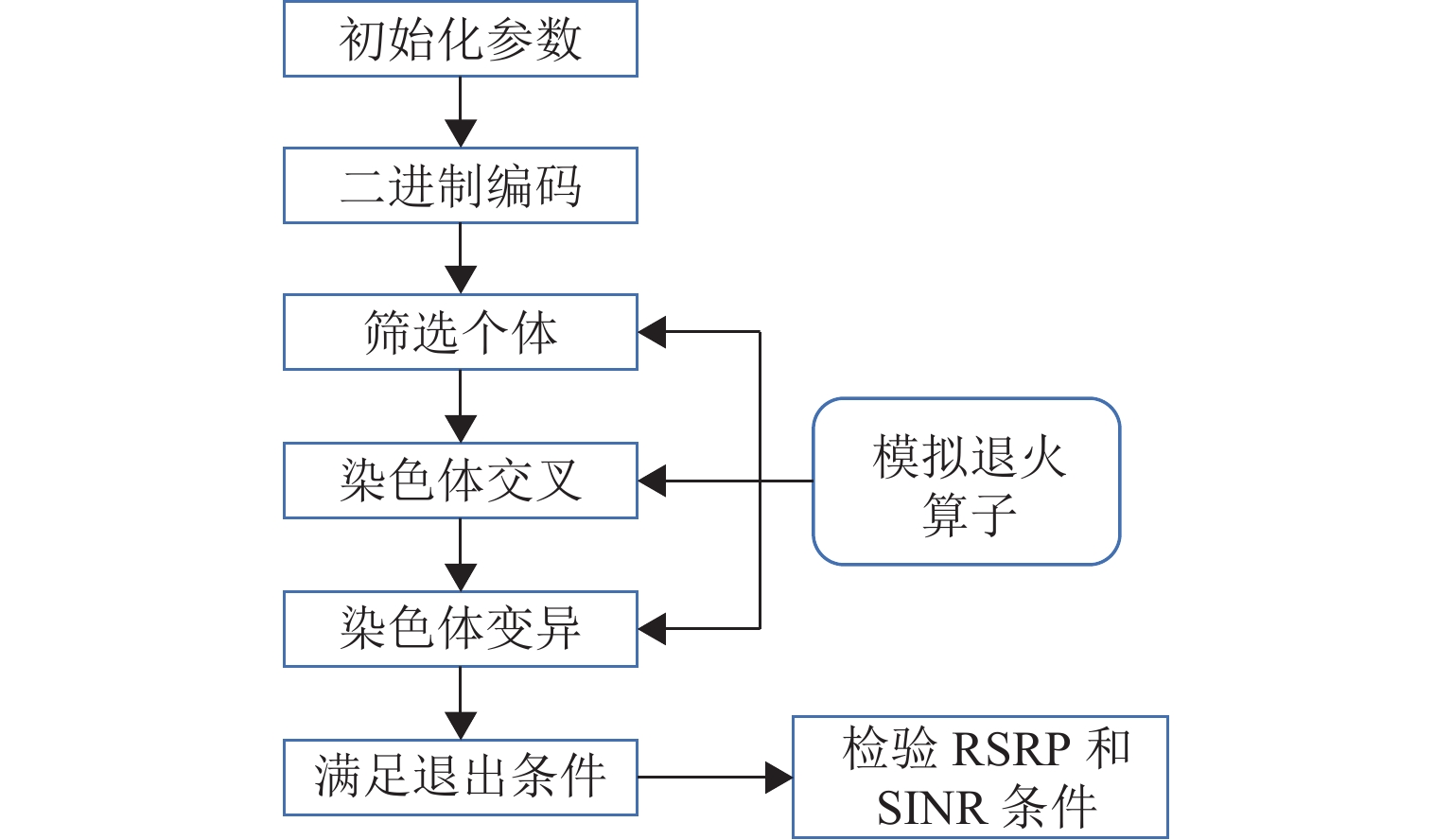
第5代移动通信技术(5G)具有连接速率高与系统容量大等优势,是编组站通信系统向未来演进的重要支撑. 为解决所涉及天线参数规划技术面临计算量大、效率和准确性难以兼顾的难题,基于CloudRT射线跟踪平台仿真场景信号覆盖情况,综合考虑通信基站天线角度选取及功率优化问题,提出一种基于机器学习算法的规划方法. 首先,基于重叠复杂度和聚类算法对天线角度参数聚类,并对聚类结果进行评估;其次,根据天线增益与角度的关系设计优化算法,简化天线角度参数组合的筛选过程;最后,在遗传算法中引入模拟退火算子求解最优功率组合,以江村编组站为场景进行验证. 研究结果表明:本文方法所得总功率比遍历算法高5.6 dB,所用时间为遍历算法的13.5%,同时实现了准确性和高效性,有望应用到未来高铁和编组站的5G系统中.
Abstract:The 5th generation mobile communication technology (5G) has advantages such as a high connection rate and large system capacity, which can support the development of marshalling station communication systems. However, the 5G antenna parameter planning is challenging due to the large amount of calculation, and it is difficult to achieve both high efficiency and accuracy simultaneously. Therefore, Based on the CloudRT ray-tracing (RT) platform, the signal coverage scenario was simulated. By considering the problem of angle selection and power optimization of communication base station antenna, a planning method based on a machine learning algorithm was proposed. Firstly, based on the overlap complexity and the clustering algorithm, the antenna angle parameters were clustered, and the clustering results were evaluated. Secondly, according to the relationship between antenna gain and angle, the optimization algorithm was designed to simplify the selection process of antenna angle parameter combinations. Finally, the simulated annealing operator was introduced into the genetic algorithm to solve the optimal power combination, and Jiangcun Marshalling Station was taken as the scenario for verification. The results indicate that the total power derived by the proposed method is 5.6 dB higher than that of the traversal algorithm, and the time required is only 13.5% of the traversal algorithm. It achieves high efficiency and accuracy simultaneously, which is expected to be applied to the 5G system of high-speed railways and marshalling stations.
-
Key words:
- 5G /
- marshalling station /
- machine learning /
- clustering algorithm /
- hybrid genetic algorithm
-
表 1 基站和天线配置
Table 1. Configuration of base stations and antennas
参数 配置 中心频率/GHz 2.1 天线增益/dBi 19 基站高度/m 15 车载接收天线位置 沿部分铁轨间隔 20 m 撒点 车载接收天线高度/m 4.57 子载波带宽/kHz 15 表 2 2.1 GHz材料电磁参数
Table 2. Electromagnetic parameters of materials at 2.1 GHz
材料 介电常数实部 损耗角正切 金属 1.00 1000000.00 地砖 1.83 0.31 红砖 1.44 0.11 木材 1.28 0.01 表 3 各聚类方法结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of results of each clustering algorithm
聚类方法 聚类簇数/个 C 值 KNA-DBSCAN 19 2.0077 × 107K-means ++ 27 1.5512 × 107层次聚类 23 2.1164 × 106表 4 功率优化初始化参数取值
Table 4. Initialized parameter configuration for power optimization
参数 取值 NS/个 216 Td/次 200 pm 0.4 pc 0.03 t 100 表 5 混合遗传算法和遍历算法得出的天线参数
Table 5. Antenna parameters derived from hybrid genetic algorithm and traversal algorithm
组号 1 号天线 2 号天线 3 号天线 总功率/dBm 角度组合 发射功率/dBm 角度组合 发射功率/dBm 角度组合 发射功率/dBm 1 (0°,4°) −4 (180°,5°) 18 (120°,3°) 2 18.1 2 (0°,4°) −11 (180°,5°) 18 (120°,2°) −7 20.0 3 (0°,5°) 1 (60°,5°) 22 (60°,1°) 7 22.2 4 (0°,4°) −3 (180°,5°) 18 (300°,1°) −8 18.0 5 (0°,4°) −8 (180°,5°) 18 (300°,2°) 0 18.1 6 (0°,5°) 8 (60°,5°) 22 (60°,1°) 4 22.2 7 (0°,4°) −9 (180°,5°) 18 (60°,1°) 0 18.1 8 (0°,5°) 0 (60°,5°) 22 (60°,1°) 4 22.1 9 (0°,4°) −3 (180°,5°) 18 (300°,1°) −8 18.0 10 (0°,4°) −6 (180°,5°) 24 (120°,2°) −5 24.0 遍历算法 (240°,5°) −6 (300°,5°) 16 (180°,1°) −6 16.1 表 6 本文方法所需时间表
Table 6. Time required for proposed algorithm
算法 本文方法所需时间 K-means ++ 算法 1 h 52 min 层次聚类算法 1 h 15 min DBSCAN 算法 20 min 求 R 值算法 < 1 min 基于 R 值的筛选 < 1 min 混合遗传算法 6 h 29 min 总时间 9 h 56 min 表 7 江村编组站5G基站信息表
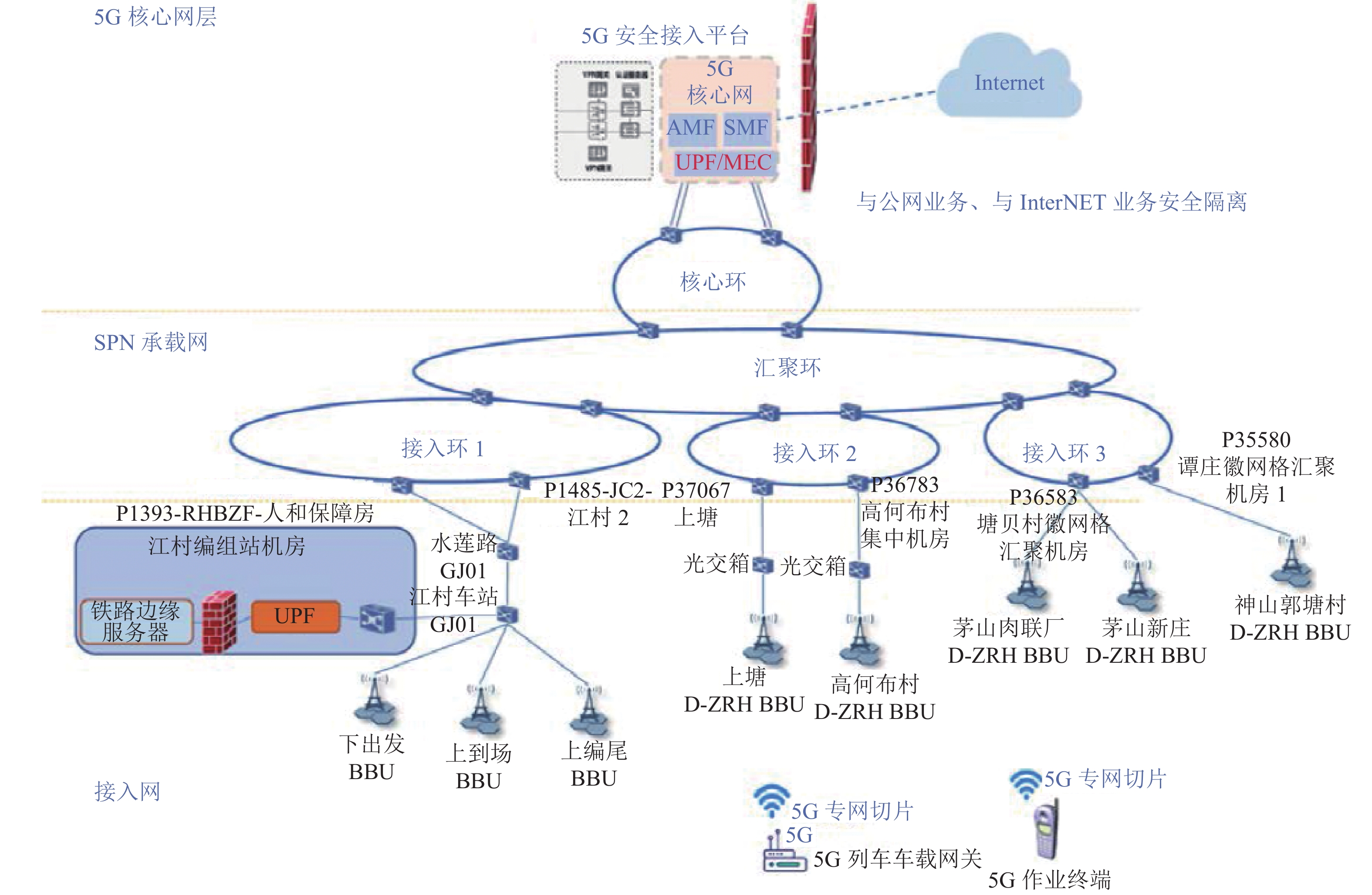
Table 7. Configurations of 5G base stations at Jiangcun Marshalling Station
站点名称 小区名称 高度/
(°)水平角/
(°)俯仰角/
(°)广州白云区江村
车站上编尾D-ZRH-1 39 80 6 D-ZRH-2 39 190 6 D-ZRH-3 39 320 6 广州白云区江村
车站下出发D-ZRH-1 24 30 6 D-ZRH-2 24 130 6 D-ZRH-3 24 240 6 D-ZRH-4 24 320 6 广州白云区江村
车站上到场D-ZRH-1 21 60 3 D-ZRH-2 21 190 3 D-ZRH-3 21 290 6 表 8 覆盖情况
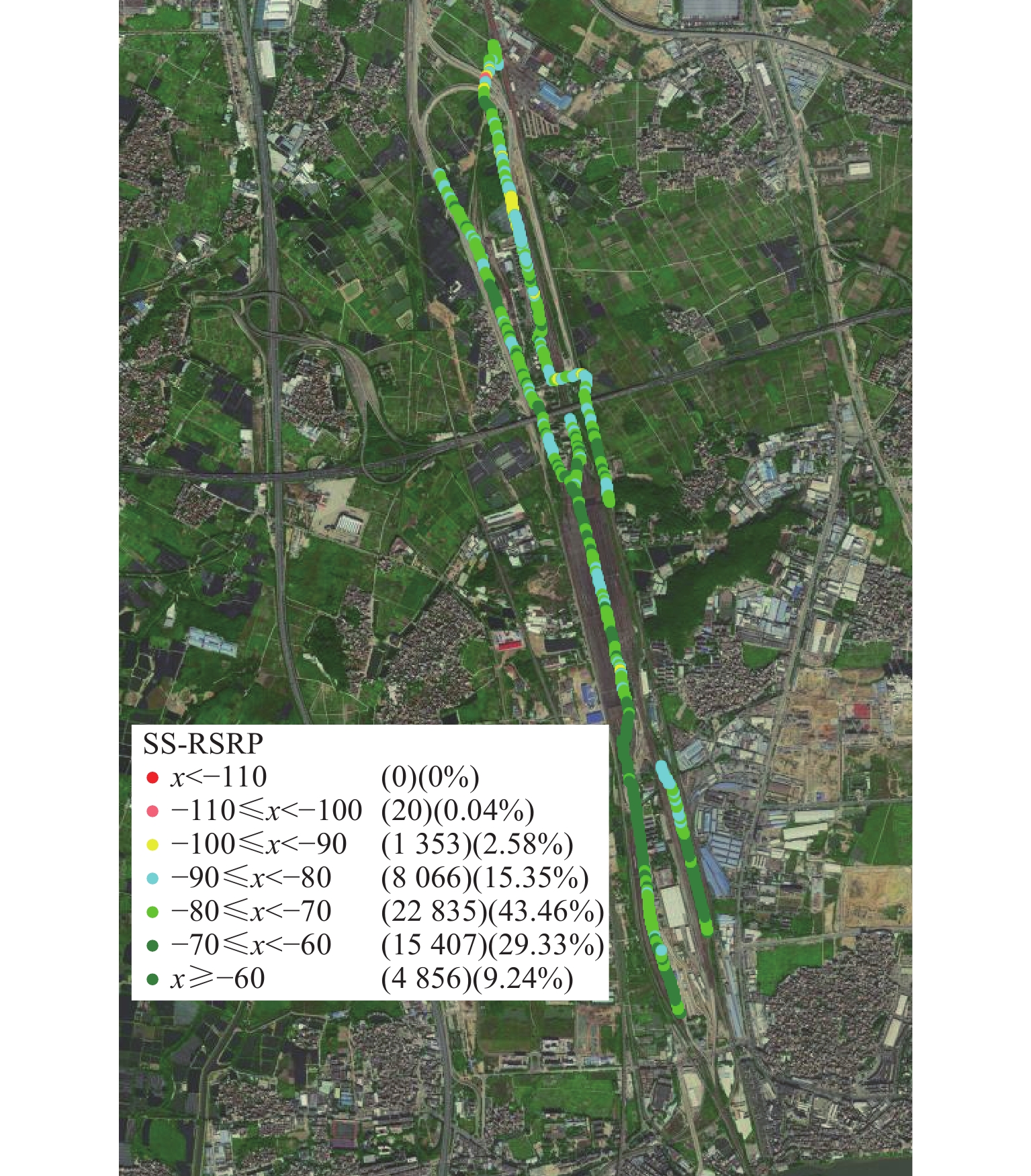
Table 8. Coverage situation
参数 配置 覆盖率/% 98.87 平均 RSRP 值/dBm −73.36 平均 SINR 值/dB 12.43 -
[1] AI B, MOLISCH A F, RUPP M, et al. 5G key technologies for smart railways[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(6): 856-893. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.2988595 [2] HE R S, AI B, WANG G P, et al. High-speed railway communications: from GSM-R to LTE-R[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2016, 11(3): 49-58. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2016.2564446 [3] 中国国家铁路集团. 新时代交通强国铁路先行规划纲要:铁发改[2020]129号[A/OL]. (2020-08-13)[2022-04-12]. http://www.china-railway.com.cn/xwzx/rdzt/ghgy/gyqw/202008/t20200812_107636.html. [4] 熊嘉阳,沈志云. 中国高铁永葆工程领跑[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(4): 711-719.XIONG Jiayang, SHEN Zhiyun. Permanent world-leading position of high-speed railways in China in Engineering [J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(4):711-719. [5] 杨焱,钟章队. 铁路编组站GSM-R分层覆盖系统及其干扰共存分析[J]. 铁道学报,2014,36(12): 40-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.12.007YANG Yan, ZHONG Zhangdui. Analysis on interference co-existence of GSM-R hierarchical coverage system in marshalling yards[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2014, 36(12): 40-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2014.12.007 [6] KASEM F, HASKOU A, DAWY Z. On antenna parameters self optimization in LTE cellular networks[C]//2013 Third International Conference on Communications and Information Technology (ICCIT). Beirut: IEEE, 2013: 44-48. [7] 朱思峰,陈国强,张新刚,等. 多目标优化量子免疫算法求解基站选址问题[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(1): 49-53.ZHU Sifeng, CHEN Guoqiang, ZHANG Xingang, et al. Multi-objective optimization quantum immune algorithm for solving base stations location planning problem[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(1): 49-53. [8] 蔡佳祺,万海斌,孙友明,等. 基于人工蜂群算法的基站天线方位角与下倾角自优化方法[J]. 电信科学,2021,37(1): 69-75. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2021006CAI Jiaqi, WAN Haibin, SUN Youming, et al. Artificial bee colony algorithm based self-optimization of base station antenna azimuth and down-tilt angles[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2021, 37(1): 69-75. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2021006 [9] ZHU F S, CAI W W, WANG Z G, et al. AI-empowered propagation prediction and optimization for reconfigurable wireless networks[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2022, 2022: 9901960.1-9901960.10. [10] 胡津铭. 基于能效的无线通信网络资源分配算法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学,2018. [11] 田春明,杨安,叶乐,等. 基于贝叶斯算法的天线端到端优化[J]. 系统工程与电子技术,2021,43(12): 3413-3419. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.12.01TIAN Chunming, YANG An, YE Le, et al. End-to-end antenna optimization based on Bayesian optimization algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3413-3419. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.12.01 [12] RAJ N. Indoor RSSI prediction using machine learning for wireless networks[C]//2021 International Conference on Communication Systems & Networks (COMSNETS). Bangalore: IEEE, 2021: 9352852.1-9352852.3. [13] 唐苏文,陈明. 基于改进粒子群算法的分布式天线系统跨层功率分配方案[J]. 高技术通讯,2010,20(2): 138-142. [14] 侯雄文. 浅析DBSCAN算法中参数设置问题的研究[J]. 科教导刊-电子版(下旬),2017(10): 266-277. [15] 北京乾径科技有限公司. CloudRT高性能云计算射线跟踪仿真平台[EB/OL]. [2021-09-23]. http://cn.raytracer.cloud. [16] HE D P, AI B, GUAN K, et al. The design and applications of high-performance ray-tracing simulation platform for 5G and beyond wireless communications: a tutorial[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(1): 10-27. [17] 中国移动通信. 4G网络高速铁路覆盖技术需求[EB/OL]. (2016-06-03)[2022-02-13]. https://max.book118.com/html/2016/0603/44748063.shtm. -




 下载:
下载: