Integrated Heterogeneous Traffic Flow Model of Bus and Autonomous Vehicle Platoon
-
摘要:
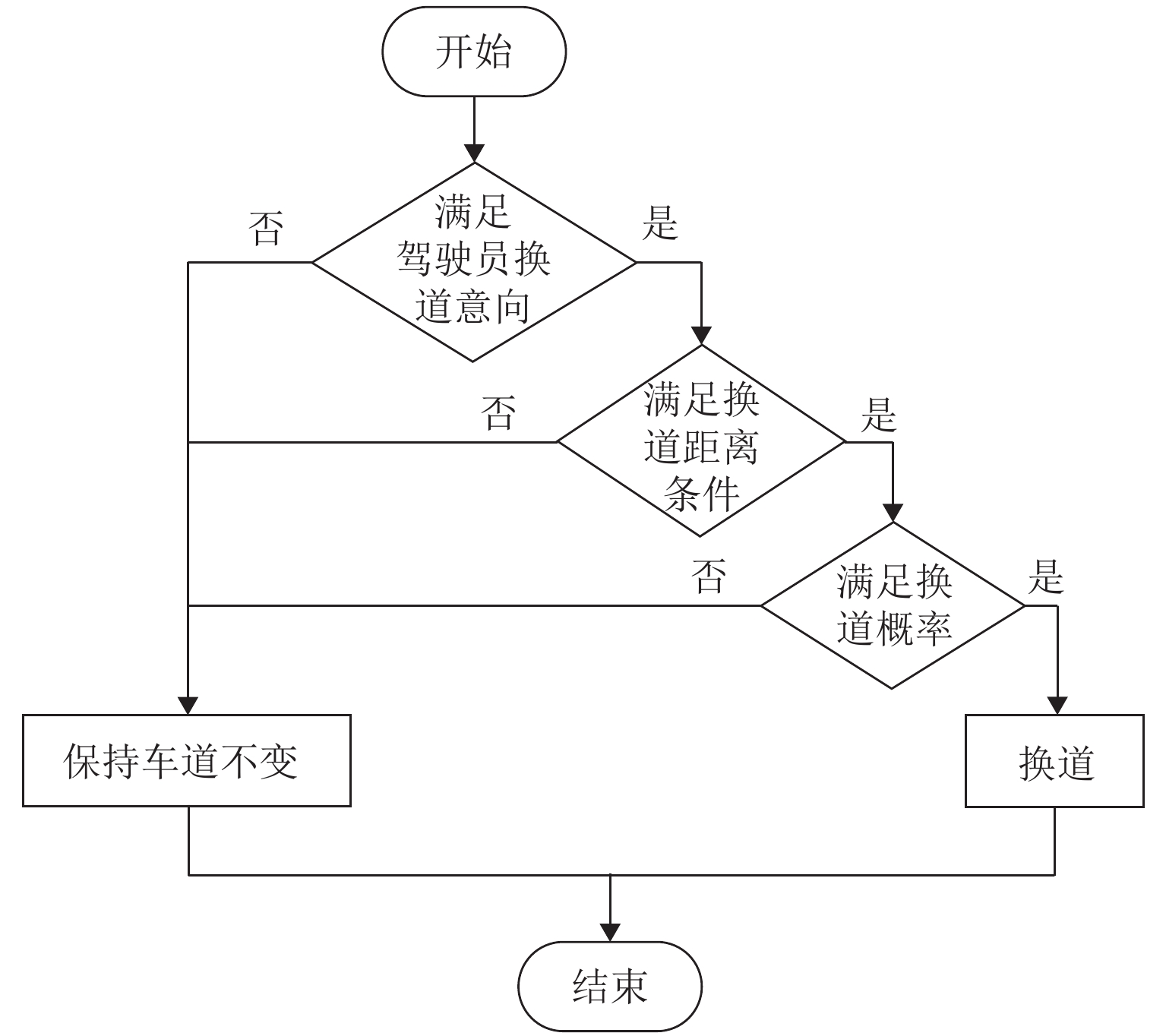
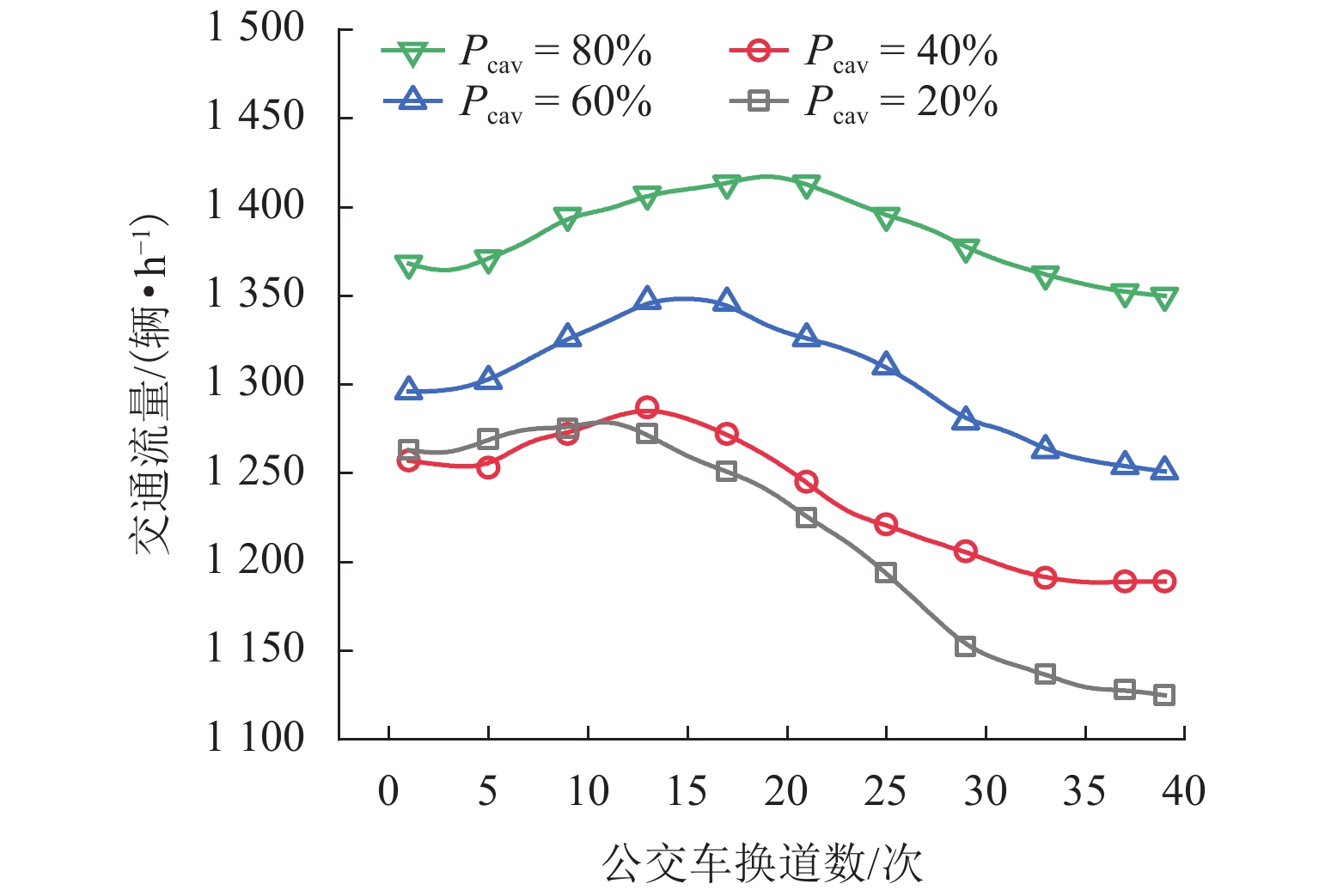
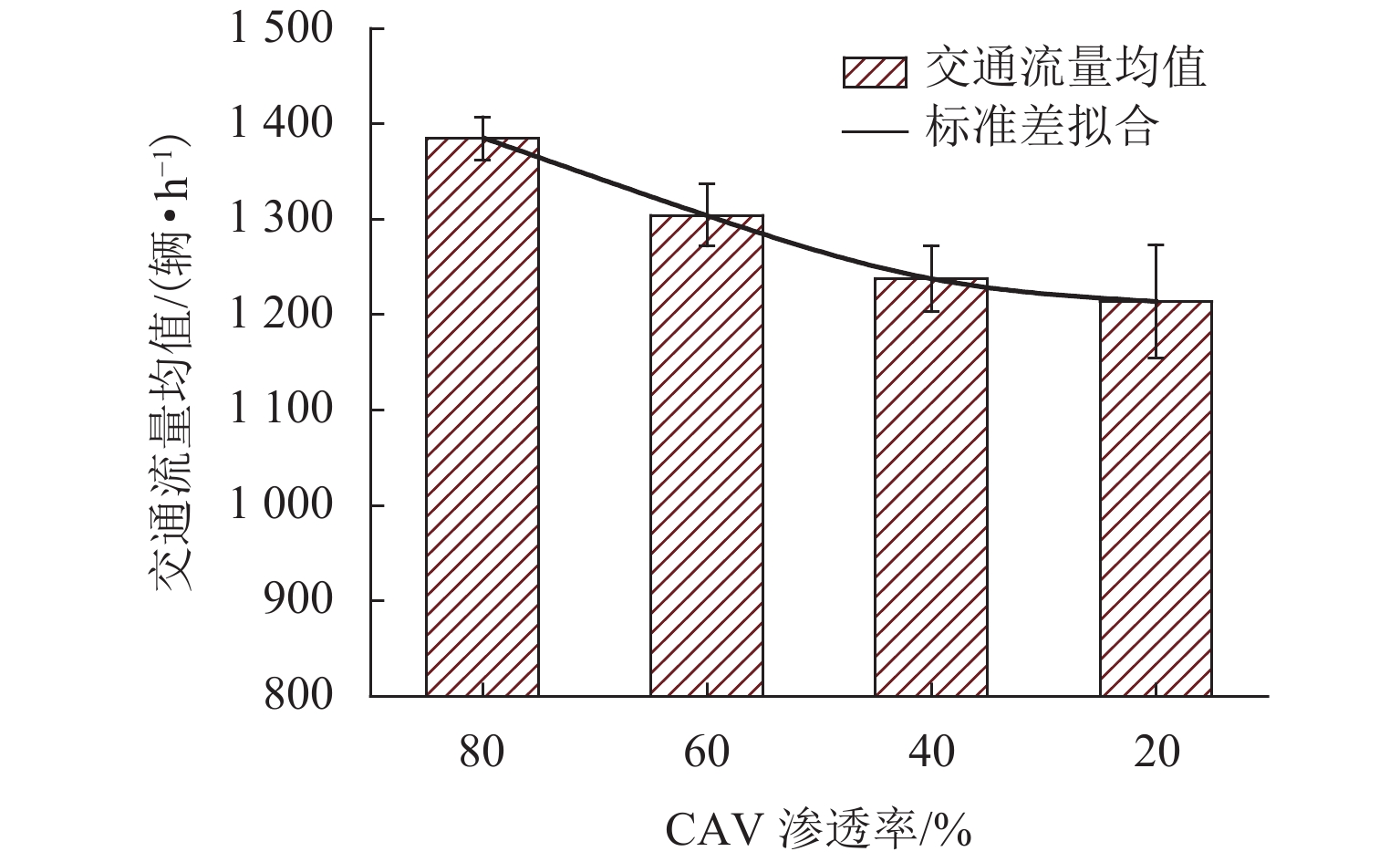
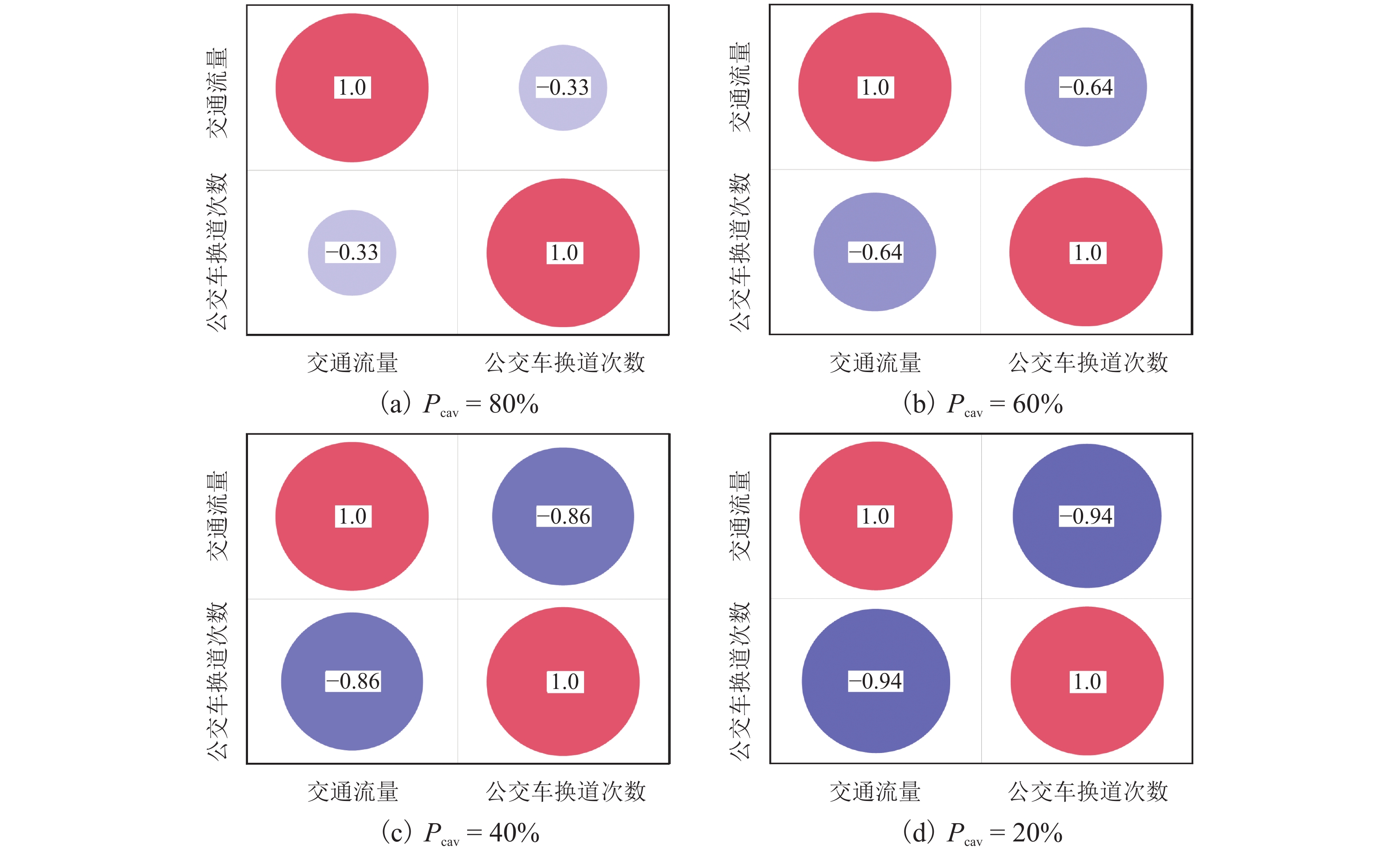
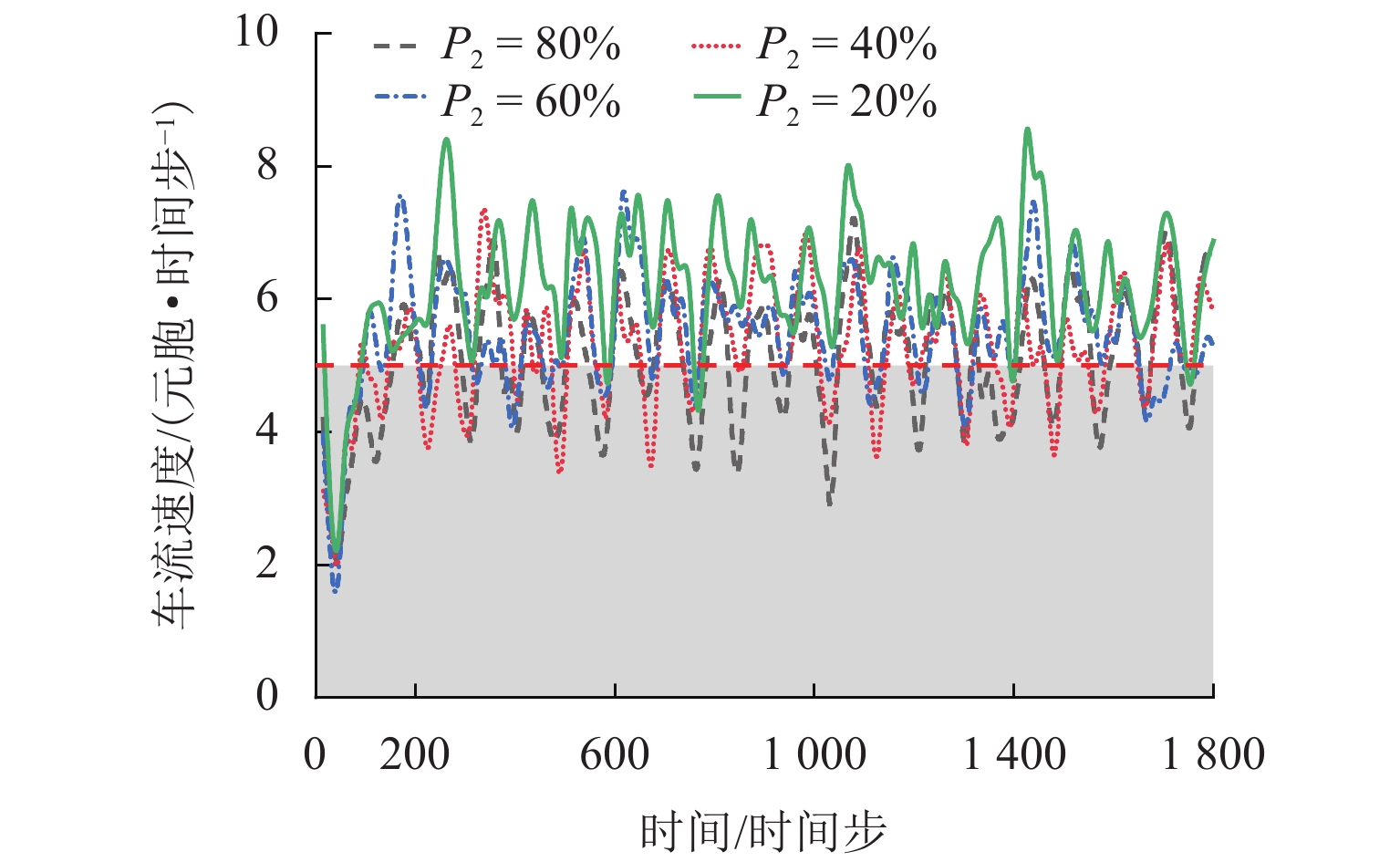
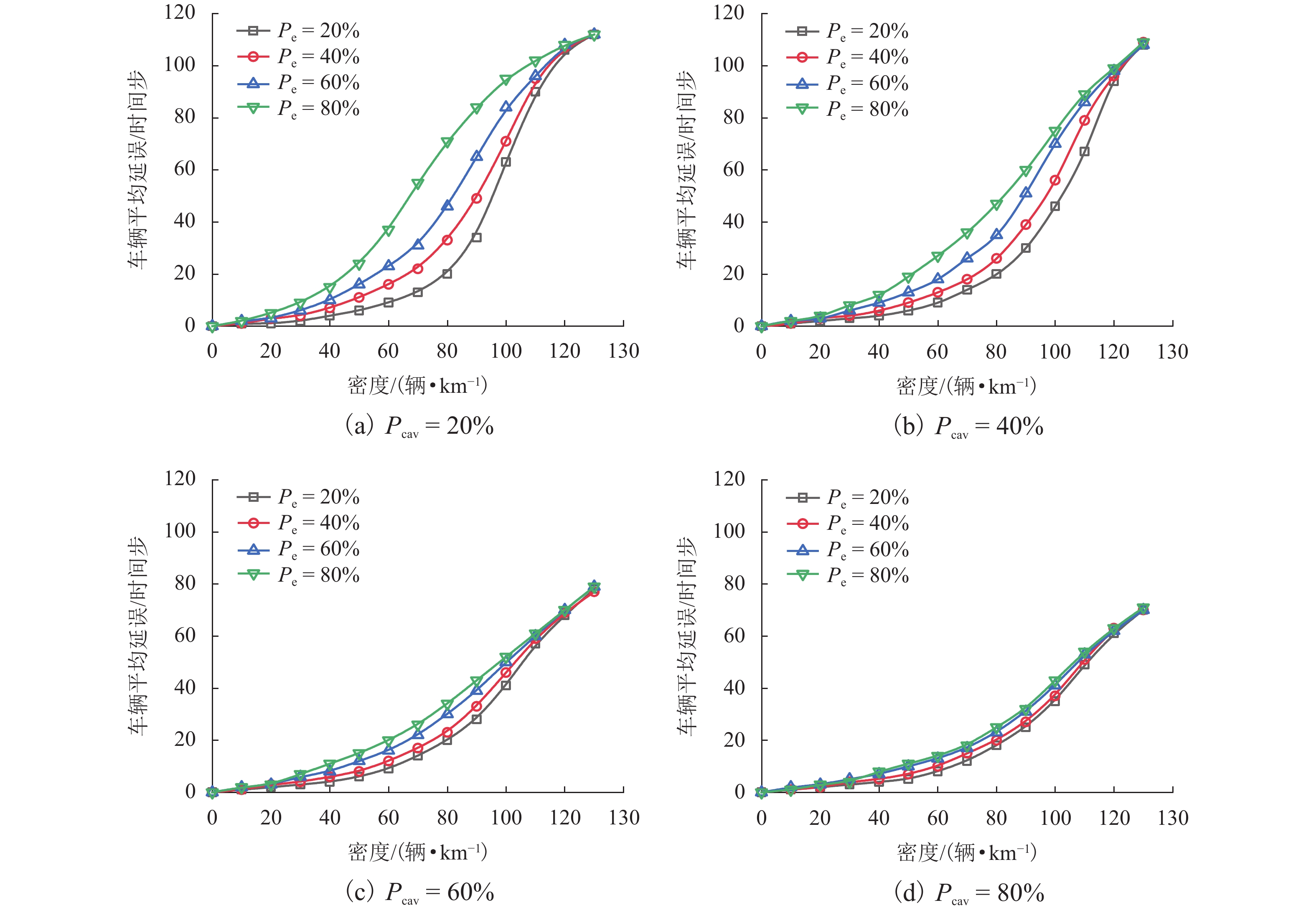
为研究网联自动驾驶车(connected autonomous vehicle, CAV)和人工驾驶车(human-pilot vehicle, HPV)所组成的异质交通流特性及公交车驾驶行为对环境的影响,首先,分析异质交通流中的4种跟驰模式:人工驾驶小汽车跟驰、人工驾驶公交车跟驰、自适应巡航控制(adaptive cruise control, ACC)跟驰和协同自适应巡航控制(cooperative adaptive cruise control, CACC)跟驰;接着,基于各跟驰模型的特点,构建车辆跟驰和换道的元胞自动机模型,综合考虑CAV车队特性、驾驶员与CAV各自反应时间特性以及HPV加塞特性,并利用跟驰模式判断参数融合不同跟驰模式特性,实现统一的模型表达;最后,仿真分析不同CAV渗透率下CAV排队强度及公交车换道行为对交通流的影响. 结果表明:在一定的CAV渗透率下,促使CAV形成队列比单纯提高CAV渗透率更能有效提升道路通行效率;适量的公交换道有助于充分利用道路通行能力,过多的公交换道则会妨碍正常交通,公交换道对交通流造成的通行效率衰减随CAV渗透率的增大而减小;同步流状态下,人工驾驶小汽车执行率与道路通行效率呈负相关关系;而在堵塞流状态下,人工驾驶小汽车执行率对通行效率影响甚微.
Abstract:In order to investigate the heterogeneous traffic flow characteristics formed by the combination of connected autonomous vehicles (CAVs) and human-pilot vehicles (HPVs), as well as the impact of bus driving behavior on this environment, four following modes in heterogeneous traffic flow are initially analyzed: human-pilot car following, human-pilot bus following, adaptive cruise control (ACC) following, and cooperative adaptive cruise control (CACC) following. Subsequently, based on the characteristics of each following model, a cellular automaton model for vehicle following and lane-changing is constructed, which comprehensively considers the characteristics of CAV platoons, the response time characteristics of drivers and CAVs, and the cutting-in behavior of HPVs. By setting the following mode judgment parameters, different following mode characteristics are integrated to achieve a unified model representation. Lastly, through simulation experiments, the queuing intensity of CAVs at different penetration rates and the impact of bus lane-changing behavior on traffic flow are analyzed. The results indicate that promoting CAVs to form platoons at a certain penetration rate is more effective in improving road traffic efficiency than merely increasing the CAV penetration rate; a moderate amount of bus lane-changing contributes to the full utilization of road traffic capacity, while excessive bus lane-changing hinders normal traffic. The traffic efficiency attenuation caused by bus lane-changing decreases as the CAV penetration rate increases; under synchronized flow conditions, the execution rate of human-pilot cars is negatively correlated with road traffic efficiency; however, under congested flow conditions, the impact of human-pilot car execution rate on traffic efficiency is negligible.
-
表 1 参数说明
Table 1. Parameter descriptions
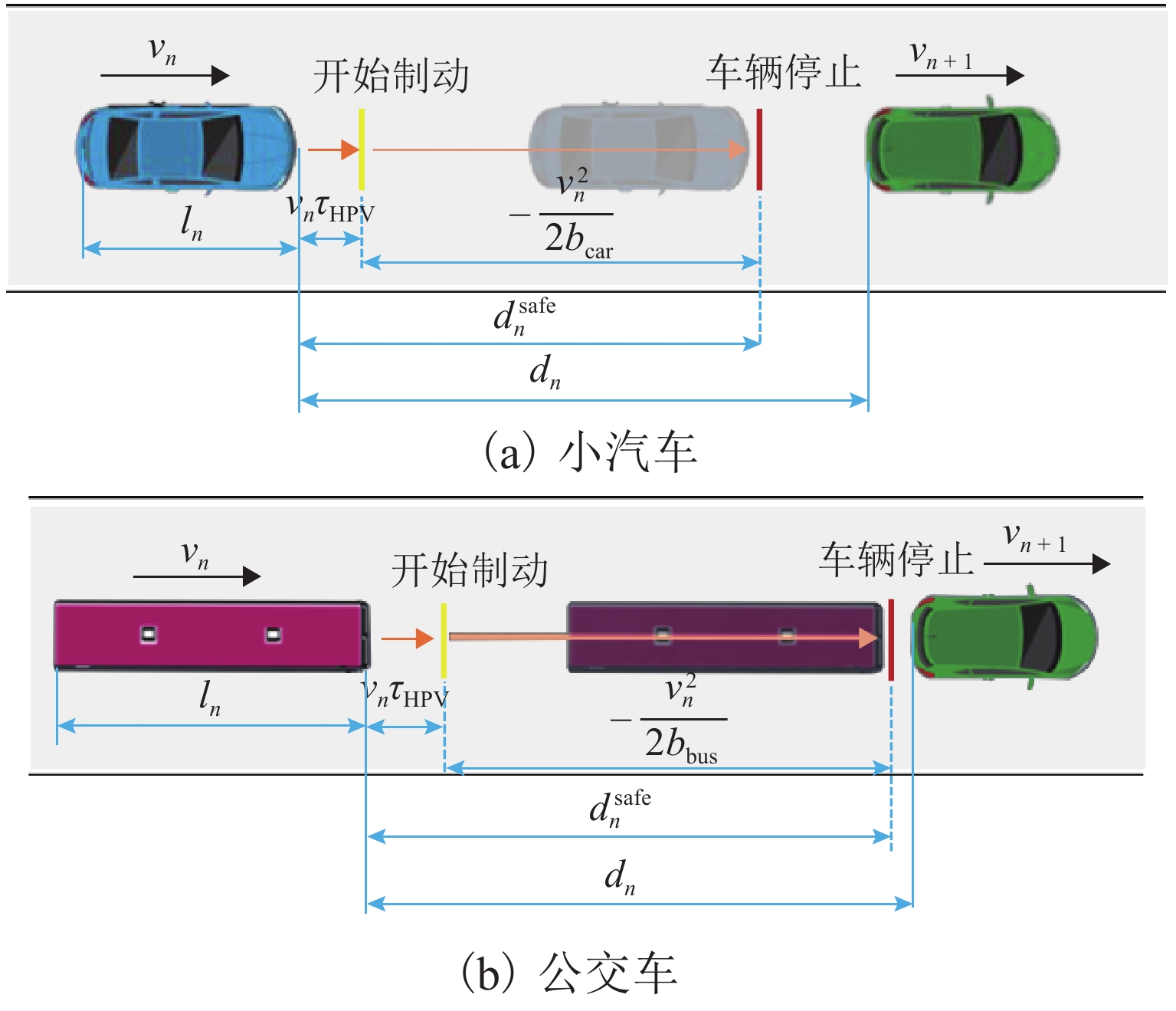
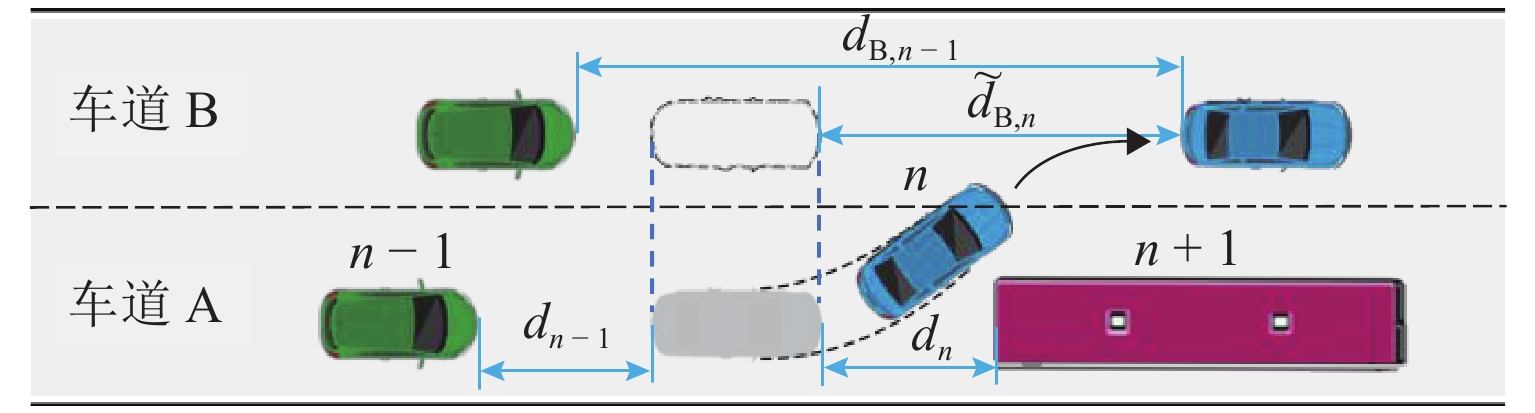
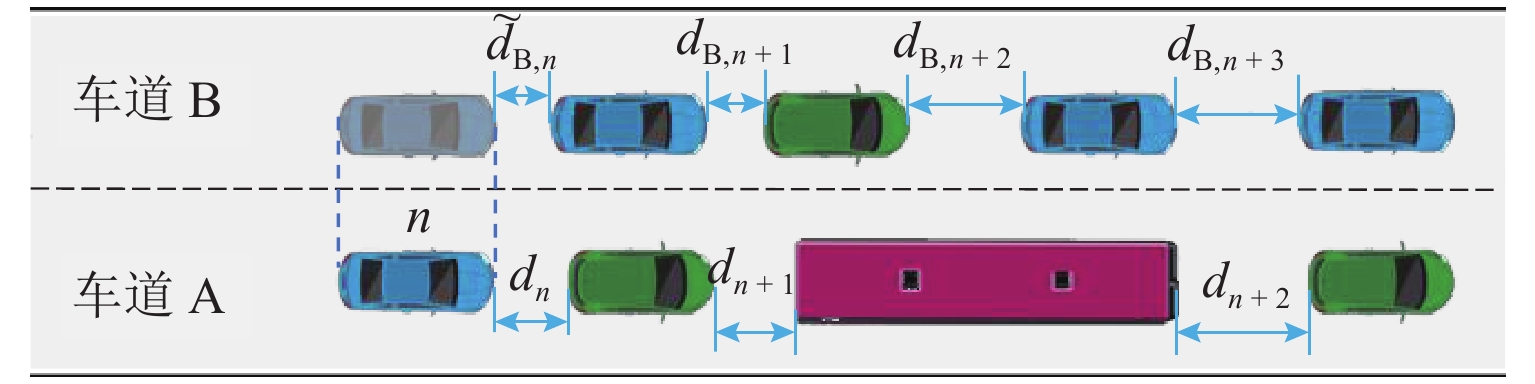
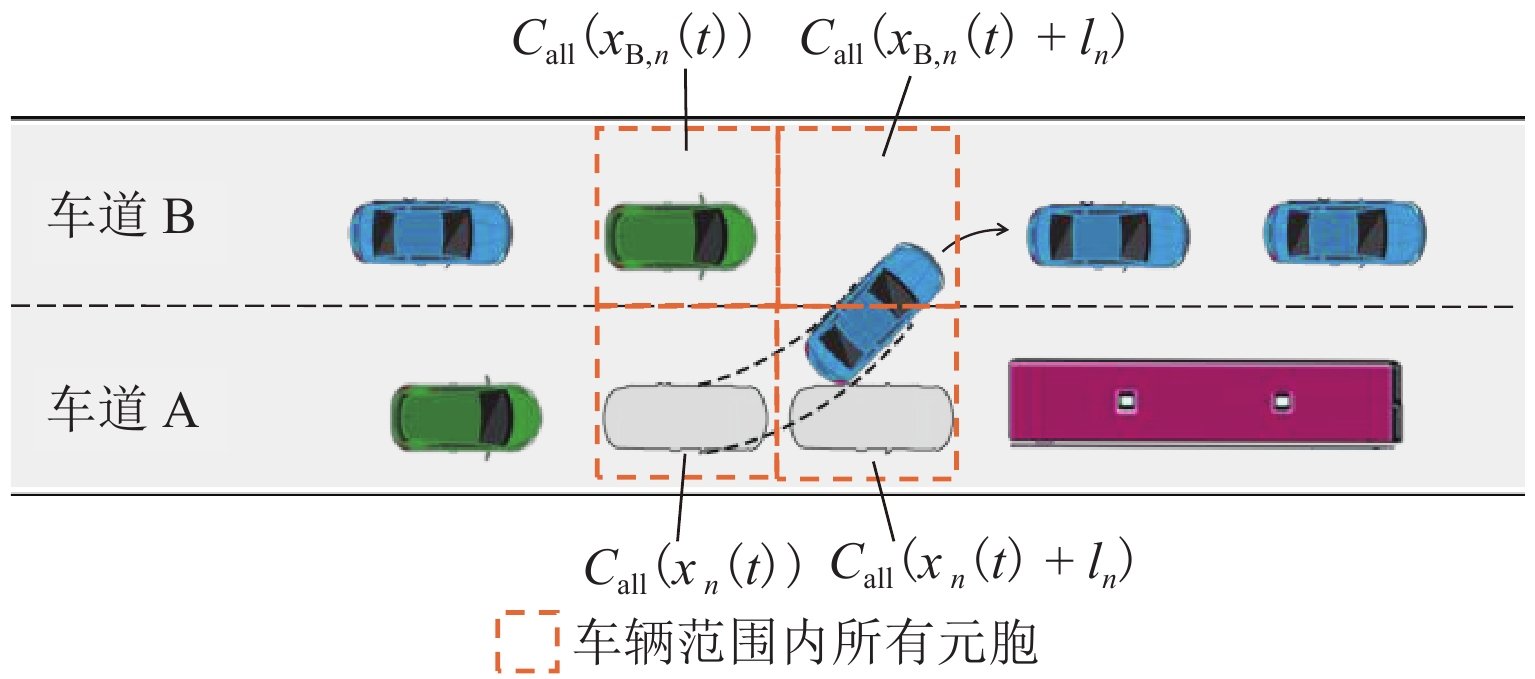
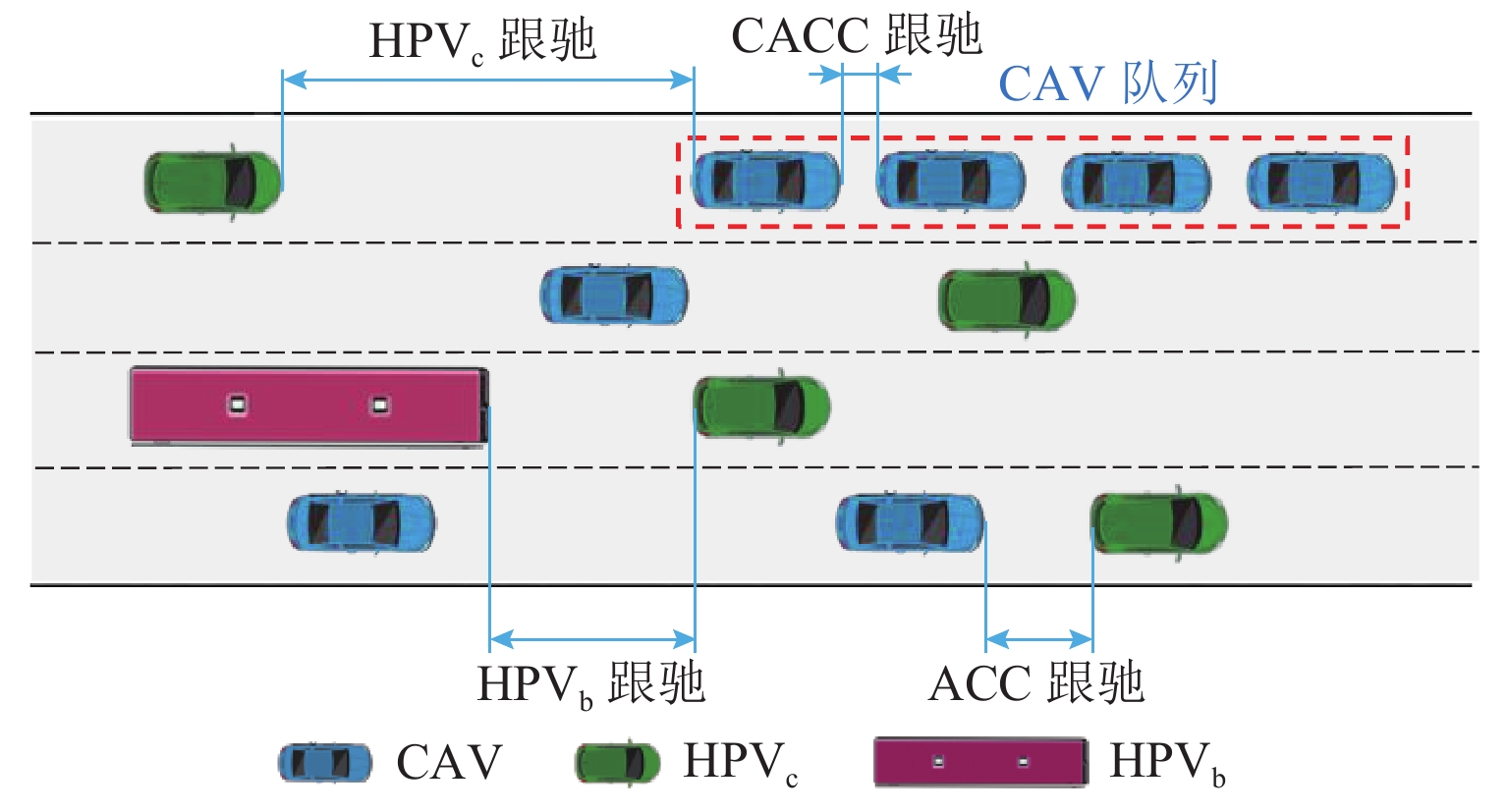
参数符号 参数说明 $ {\alpha _n} $ ${\alpha _n} \in \left\{ {0,1} \right\}$,1 表示 ACC 跟驰模式,0 表示非ACC 跟驰模式 $ {\beta _n} $ $ {\beta _n} \in \left\{ {0,1} \right\}$,1 表示 CACC 跟驰模式,0 表示非 CACC 跟驰模式 $ {\gamma _n} $ $ {\gamma _n} \in \left\{ {0,1} \right\}$,1 表示 HPVc 跟驰模式,0 表示非HPVc 跟驰模式跟驰 Ωn ${\varOmega _n} \in \left\{ {0,1} \right\}$,1 表示 HPVb 跟驰模式,0 表示非HPVb 跟驰模式跟驰 $ {v_n}\left( t \right) $ 时刻 t 车辆 n 的速度,n+1为前车,n−1为后车 $ {x_n}\left( t \right) $ 时刻 t 车辆 n 的位置,n+1为前车,n−1为后车 ${ v_{ {\rm{B} },n + 1}( t)}$ 时刻 t 车辆 n 在车道 B 前车速度 $ {d_n} $ 车辆 n 与前车车间距 $ d_n^{{\text{safe}}} $ 车辆 n 的安全车距 $ {a_n} $ 车辆 n 的加速度 $ \Delta t $ 仿真实验时间步长 $ {\tau _j} $ 人类驾驶员与自动驾驶车的反应时间,$j\in ${HPV,CAV} $v_n^{{\rm{\max }}}$ 车辆 n 的最大速度 $ {b_i} $ $ i \in \{ {\text{car,bus} }\}$,依次表示小汽车(car)与公交车(bus)的最大减速度 ${m_{\rm{A} } } ( {m_{\rm{B} } }) $ 在 CAV 通信范围内车道 A (车道 B)能获取信息的前方车辆数 ${m_{{\rm{\max }}} }$ CAV 通信范围内可获取间隔为安全距离的最大前方车辆数$ ({m_{{\rm{A}}}},m_{\rm{B}} \leqslant {m_{\max }}) $ ${\tilde d_{{\rm{B}},n} }$ 车道 B 上车辆 n 对应相同位置车头与前车车距 $ {d_{{\rm{B}},n + m}} $ 在车道 B 上车辆 n 前方第 m 辆车与其前车间的车距 $ C\left( x \right) $ $ x$位置所在元胞状态,0 表示有车,1 表示无车 $ {l_n} $ 车辆 n 的长度 ${l_{\rm{c}}}$ 元胞长度 $ O $ CAV 排队强度 $ {q_n} $ 车辆 n 占用元胞数 ${p_{ {\text{random} } } }$ 随机慢化概率 ${p_{\rm{g}}}$ 车辆换道产生加塞情况概率 表 2 仿真参数设置
Table 2. Simulation parameter setting
参数符号 仿真值 $a_n/(元胞{\text{•}}时间步^{-2})$ $ {a_{{\text{car}}}} = 2 $,$ {a_{{\text{bus}}}} = 1 $ $ {\tau _{{\text{HPV}}}}/{\rm{s}} $ 1.5 ${\tau _{ {\text{CAV} } } } /{\rm{s}}$ 0.5 ${b_{ {\text{car} } } } $/(元胞·时间步−2) −4 $ {b_{{\text{bus}}}} $/(元胞·时间步−2) −3 $ {m_{\max }} $ 50 $ {p_{{\text{random}}}} $,${p_{ {\rm{g} } } }$ 0.5 -
[1] 徐志刚,李金龙,赵祥模,等. 智能公路发展现状与关键技术[J]. 中国公路学报,2019,32(8): 1-24. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.08.001XU Zhigang, LI Jinlong, ZHAO Xiangmo, et al. A review on intelligent road and its related key technologies[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(8): 1-24. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2019.08.001 [2] 李克强,戴一凡,李升波,等. 智能网联汽车(ICV)技术的发展现状及趋势[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报,2017,8(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2017.01.001LI Keqiang, DAI Yifan, LI Shengbo, et al. State-of-the-art and technical trends of intelligent and connected vehicles[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2017, 8(1): 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2017.01.001 [3] DONG C Q, CHEN X W, DONG H B, et al. Research on intelligent vehicle infrastructure cooperative system based on Zigbee[C]//The 5th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS). Liverpool: IEEE, 2019: 1337-1343. [4] RIOS-TORRES J, MALIKOPOULOS A A. A survey on the coordination of connected and automated vehicles at intersections and merging at highway on-ramps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 18(5): 1066-1077. [5] LEE H, SONG T, YOON Y, et al. Development of a longitudinal control algorithm based on V2V communication for ensuring takeover time of autonomous vehicle[J]. Journal of Auto-Vehicle Safety Association, 2020, 12(1): 15-25. [6] WANG W S, LIANG J, PAN C F, et al. NLS based hierarchical anti-disturbance controller for vehicle platoons with time-varying parameter uncertainties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(11): 21062-21073. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3178731 [7] FAKHRMOOSAVI F, SAEDI R, ZOCKAIE A, et al. Impacts of connected and autonomous vehicles on traffic flow with heterogeneous drivers spatially distributed over large-scale networks[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of The Transportation Research Board, 2020, 2674(10): 817-830. doi: 10.1177/0361198120940997 [8] TALEBPOUR A, MAHMASSANI H S, HAMDAR S H. Modeling lane-changing behavior in a connected environment: a game theory approach[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2015, 7: 420-440. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2015.06.022 [9] SALA M, SORIGUERA F. Capacity of a freeway lane with platoons of autonomous vehicles mixed with regular traffic[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2021, 147: 116-131. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2021.03.010 [10] ZHOU Y J, ZHU H B, GUO M M, et al. Impact of CACC vehicles’ cooperative driving strategy on mixed four-lane highway traffic flow[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 540: 122721.1-122721.13. [11] LI S K, LIU R H, YANG L X, et al. Robust dynamic bus controls considering delay disturbances and passenger demand uncertainty[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2019, 123: 88-109. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2019.03.019 [12] YANG S J, SI C W, ZHI H Y, et al. A cellular automata model for mixed traffic flow considering the driving behavior of connected automated vehicle platoons[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2021, 582: 126262.1-126262.18. [13] CHEN J Z, LIANG H, LI J, et al. A novel distributed cooperative approach for mixed platoon consisting of connected and automated vehicles and human-driven vehicles[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2021, 573: 125939.1-125939.17. [14] 李霞,汪一戈,崔洪军,等. 智能网联环境下复杂异质交通流稳定性解析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(6): 114-120. doi: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2020.06.015LI Xia, WANG Yige, CUI Hongjun, et al. Stability analysis of complex heterogeneous traffic flow under connected and autonomous environment[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(6): 114-120. doi: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2020.06.015 [15] GIPPS P G. A behavioural car-following model for computer simulation[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 1981, 15(2): 105-111. doi: 10.1016/0191-2615(81)90037-0 [16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 车库建筑设计规范: JGJ 100—2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015. [17] KERNER B S. Introduction[M]//Introduction to modern traffic flow theory and control. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 1-6. -




 下载:
下载: