Experimental of Anti-Frost Jacking Model of Grotesque Pile Foundations of Overhead Contact System Mast of Qinghai–Xizang Railway
-
摘要:
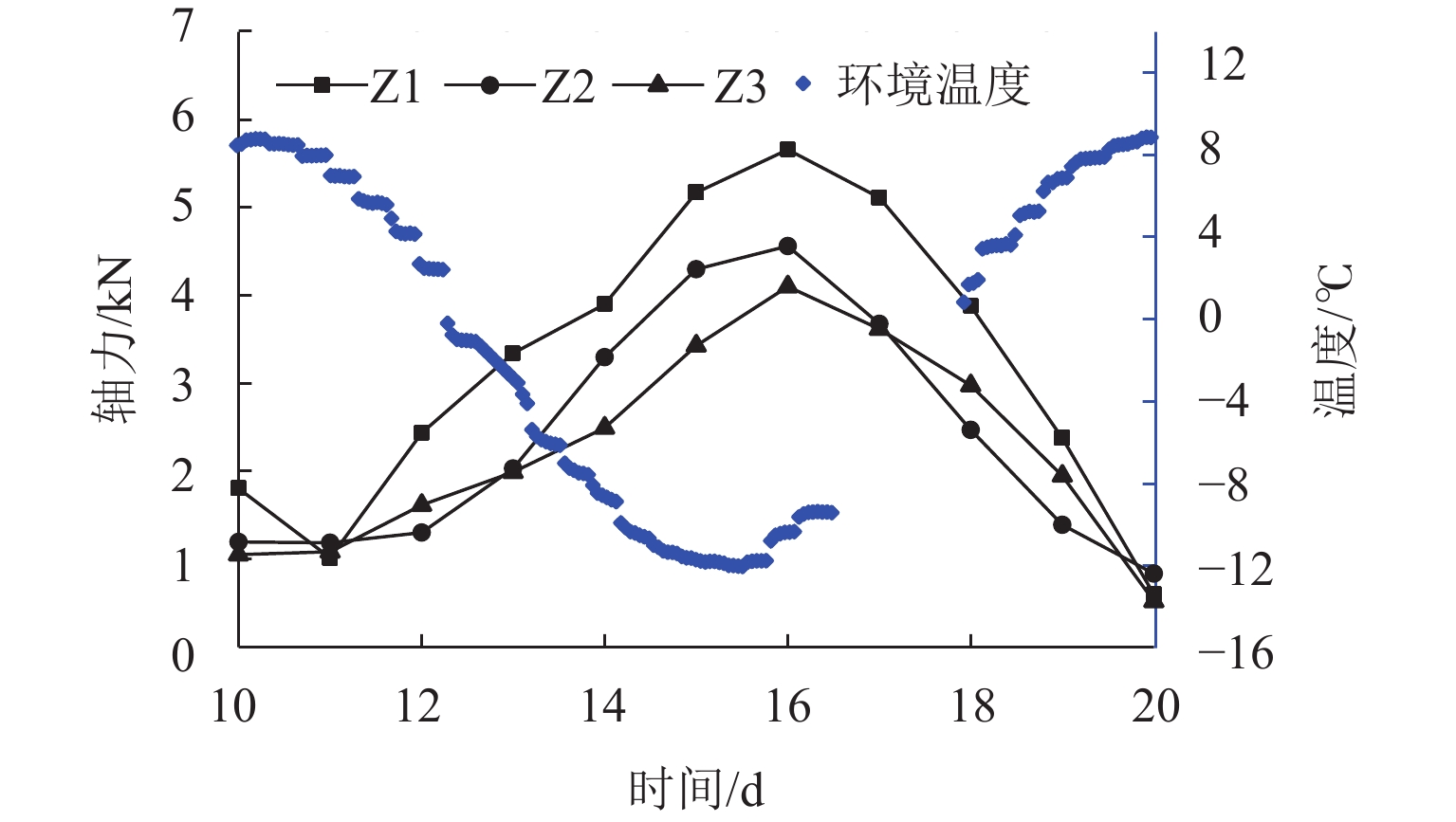
保证接触网支柱桩基础的冻拔稳定性是青藏铁路格拉段电气化改造工程建设中的关键问题之一,为研究不同截面形式桩(等截面圆形桩Z1、直锥柱形桩Z2及曲锥柱形桩Z3)的抗冻拔性能,以青藏线路基填料为试验土体,进行3个冻融循环的室内模型试验,得到冻融作用下接触网支柱桩基础的地温、桩顶位移及桩身应力的分布规律. 试验结果表明:路基体的冻结(融化)是二维冻结(融化),接触网支柱桩基础附近的冻结深度约为30 cm;路肩处土体的竖向冻胀位移为4.30 mm,Z1的竖向冻拔量为0.26 mm,Z2与Z3的竖向冻拔量分别为Z1的46%、58%,3根桩的桩顶均产生约0.1 mm的水平位移;冻结过程中桩基整体受拉,冻深附近桩身轴力最大;切向冻胀应力的最大值出现在地表附近,曲锥柱形桩切向冻胀总力最小,抗冻拔效果最好.
Abstract:One of the key problems in the construction of the electrification reconstruction project of Gela section of Qinghai−Xizang Railway is to ensure the frost jacking stability of the pile foundation of the overhead contact system mast (OCSM). In order to study the anti-frost jacking performance of piles with different sections (equal-section circular pile (Z1), straight-cone cylindrical pile (Z2), and curved-cone cylindrical pile (Z3)), the indoor model tests with three freeze-thaw cycles were carried out by using the subgrade filling materials of Qinghai-Xizang Railway as the test soil sample. The distribution laws of ground temperature, pile-top displacement, and pile body stress of the OCSM pile foundations under the influence of freezing and thawing were obtained. The test results show that the freezing (thawing) of the subgrade is two-dimensional, and the depth of freezing near the OCSM pile foundations is about 30 cm. The vertical frost-heave displacement at the subgrade shoulder is 4.30 mm, and the vertical frost jacking displacement of Z1 is 0.26 mm. In addition, the vertical frost jacking displacement of Z2 and Z3 is only 46% and 58% of Z1, respectively. The top of the three piles has a horizontal displacement of about 0.1 mm. During the freezing process, the pile is under tension as a whole, and the axial force is greatest near the depth of freezing. The maximum value of tangential frost-heave stress occurs near the ground surface. The total tangential frost-heave force of the curved-cone cylindrical pile is the smallest, with the best anti-frost jacking effect.
-
Key words:
- permafrost /
- OCSM pile foundation /
- grotesque pile /
- model test /
- freeze-thaw effect /
- frost jacking characteristics
-
表 1 不同桩型模型桩的受力对比
Table 1. Stress comparison of model piles in different shapes
桩 Zn/m S/cm2 F/kN τ/kPa Z1 0.3 518 5.66 109.3 Z2 0.3 447 4.56 106.4 Z3 0.3 427 4.01 97.7 -
[1] 汪双杰,金龙,穆柯,等. 高原冻土区公路路基病害及工程对策[J]. 中国工程科学,2017,19(6): 140-146. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2017.06.020WANG Shuangjie, JIN Long, MU Ke, et al. Distresses and countermeasures of highway subgrade in plateau permafrost regions[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2017, 19(6): 140-146. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2017.06.020 [2] 仝睿,宋二祥,赵志宏,等. 某铁路路基冻胀过程实测及 “时变覆盖效应” 分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报,2020,17(8): 1949-1956.TONG Rui, SONG Erxiang, ZHAO Zhihong, et al. Measurement of frost heave process of a railway subgrade and analysis of “time-varying canopy effect”[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(8): 1949-1956. [3] 孙兵,仇文革,周超. 饱和粘土三轴冻胀应力-应变关系试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2009,44(2): 177-180,268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.02.006SUN Bing, QIU Wenge, ZHOU Chao. Experimental investigation on triaxial frost heaving stress-strain relationship of saturated clay[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009, 44(2): 177-180,268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2009.02.006 [4] GUO L, XIE Y L, YU Q H, et al. Displacements of tower foundations in permafrost regions along the Qinghai−Tibet power transmission line[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2016, 121: 187-195. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.07.012 [5] 蒋代军,王旭,刘德仁,等. 青藏铁路多年冻土地基输电塔热棒桩基稳定性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(增2): 4258-4263. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.s2.108JIANG Daijun, WANG Xu, LIU Deren, et al. Experimental study of stability of piled foundation with thermosyphons of power transmission tower along Qinghai−Tibet railway in permafrost regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(S2): 4258-4263. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.s2.108 [6] LU J F, YIN J, SHUAI J. A model for predicting the frost-heave effect of a pile embedded in the frozen soil[J]. Cold regions science and technology, 2018, 146: 214-222. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.10.005 [7] ZHOU Y L, WANG X, NIU F, et al. Frost jacking characteristics of transmission tower pile foundations with and without thermosyphons in permafrost regions of Qinghai–Tibet plateau[J]. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering, 2021, 35(2): 04021004.1-04021004.12. [8] 王腾飞,刘建坤,邰博文,等. 螺旋桩冻拔特性的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(6): 1084-1092. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201806014WANG Tengfei, LIU Jiankun, TAI Bowen. Model tests on frost jacking behaviors of helical steel piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(6): 1084-1092. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201806014 [9] WANG T F, LIU J K, TIAN Y D. Frost jacking characteristics of screw piles by model testing[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2017, 138: 98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.03.008 [10] WANG T F, LIU J K, TAI B W, et al. Frost jacking characteristics of screw piles in seasonally frozen regions based on thermo-mechanical simulations[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2017, 91: 27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.06.018 [11] 许健,袁俊,管顺清,等. 多年冻土区锥柱基础抗拔承载性能试验研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版),2017,49(1): 70-75. doi: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2017.01.011XU Jian, YUAN Jun, GUAN Shunqing, et al. Experimental studies on the uplift bearing capacity of cone-cylindrical foundation in permafrost area[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science), 2017, 49(1): 70-75. doi: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2017.01.011 [12] 孙鑫. 寒区锥形桩切向冻胀力与抗冻拔效果研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2020. [13] 史向阳,张泽,李东庆,等. 冻融循环作用下锥柱式桩基础水热及变形动态变化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(增1): 3092-3101. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1228SHI Xiangyang, ZHANG Ze, LI Dongqing, et al. Research on dynamic variation of moisture, temperature and deformation of cone-cylindrical pile under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(S1): 3092-3101. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1228 [14] 史向阳,张泽,李东庆,等. 锥柱式桩基础明挖基坑回填土回冻过程模型试验研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2018,45(7): 125-134. doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2018.07.016SHI Xiangyang, ZHANG Ze, LI Dongqing, et al. Model test study on refreezing process of backfill in cone-cylindrical pile foundation pit[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 45(7): 125-134. doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2018.07.016 [15] 黄旭斌,周恒,狄圣杰,等. 融化和冻结状态下土及混凝土/土界面剪切特性试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2021,52(11): 4137-4147.HUANG Xubin, ZHOU Heng, DI Shengjie, et al. Experimental study on shear characteristics of soil and concrete/soil interface in thawing and freezing state[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(11): 4137-4147. [16] 黄旭斌,盛煜,黄龙,等. 单向冻结条件下扩底桩抗冻拔能力试验研究[J]. 工程科学与技术,2021,53(1): 122-131.HUANG Xubin, SHENG Yu, HUANG Long, et al. Experimental study on the anti-frost jacking ability of belled pile under unidirectional freezing condition[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2021, 53(1): 122-131. [17] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: