Simulation Analysis on Influence of Congestion Propagation on Operation of Carsharing Systems
-
摘要:
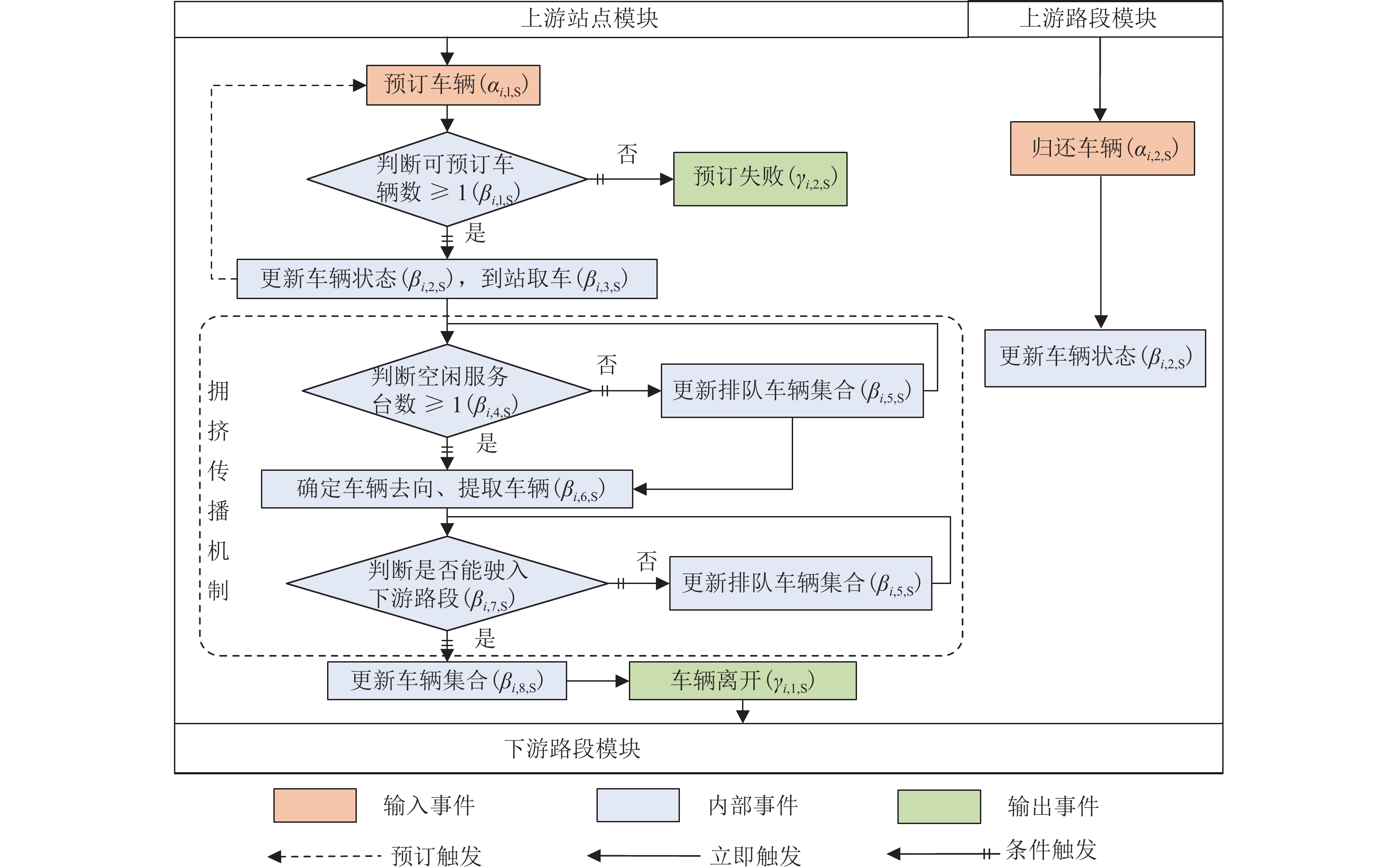
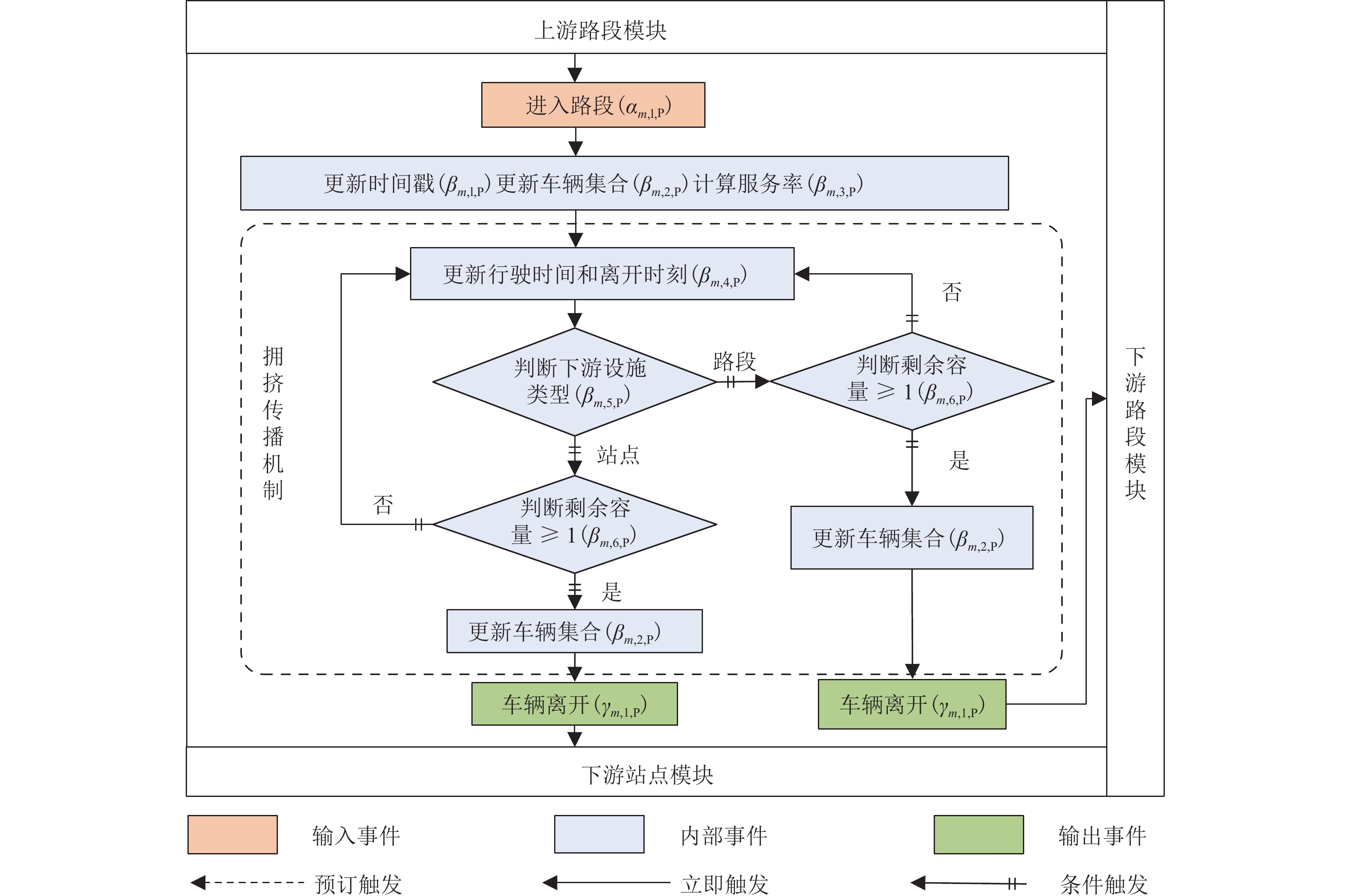
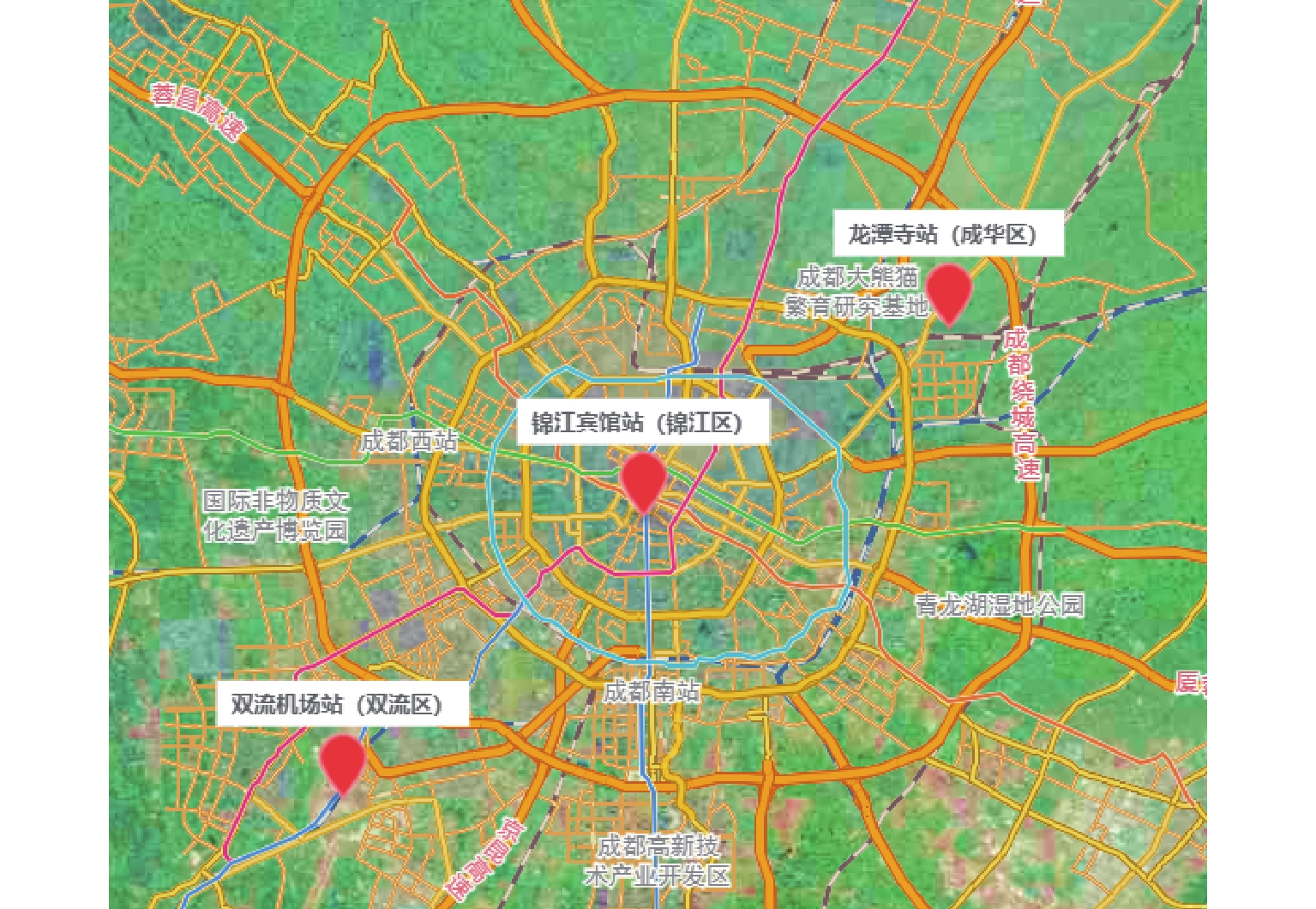
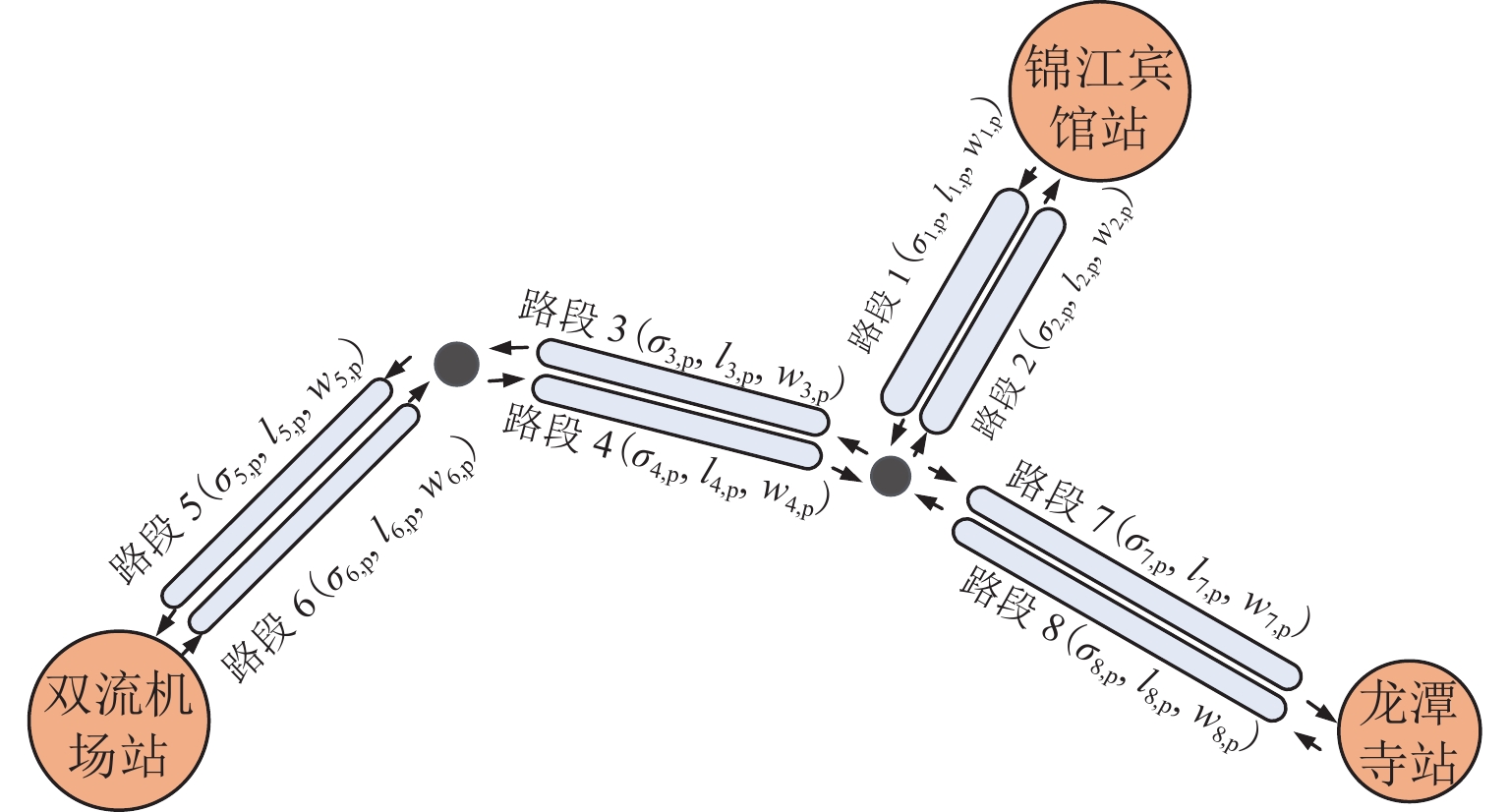
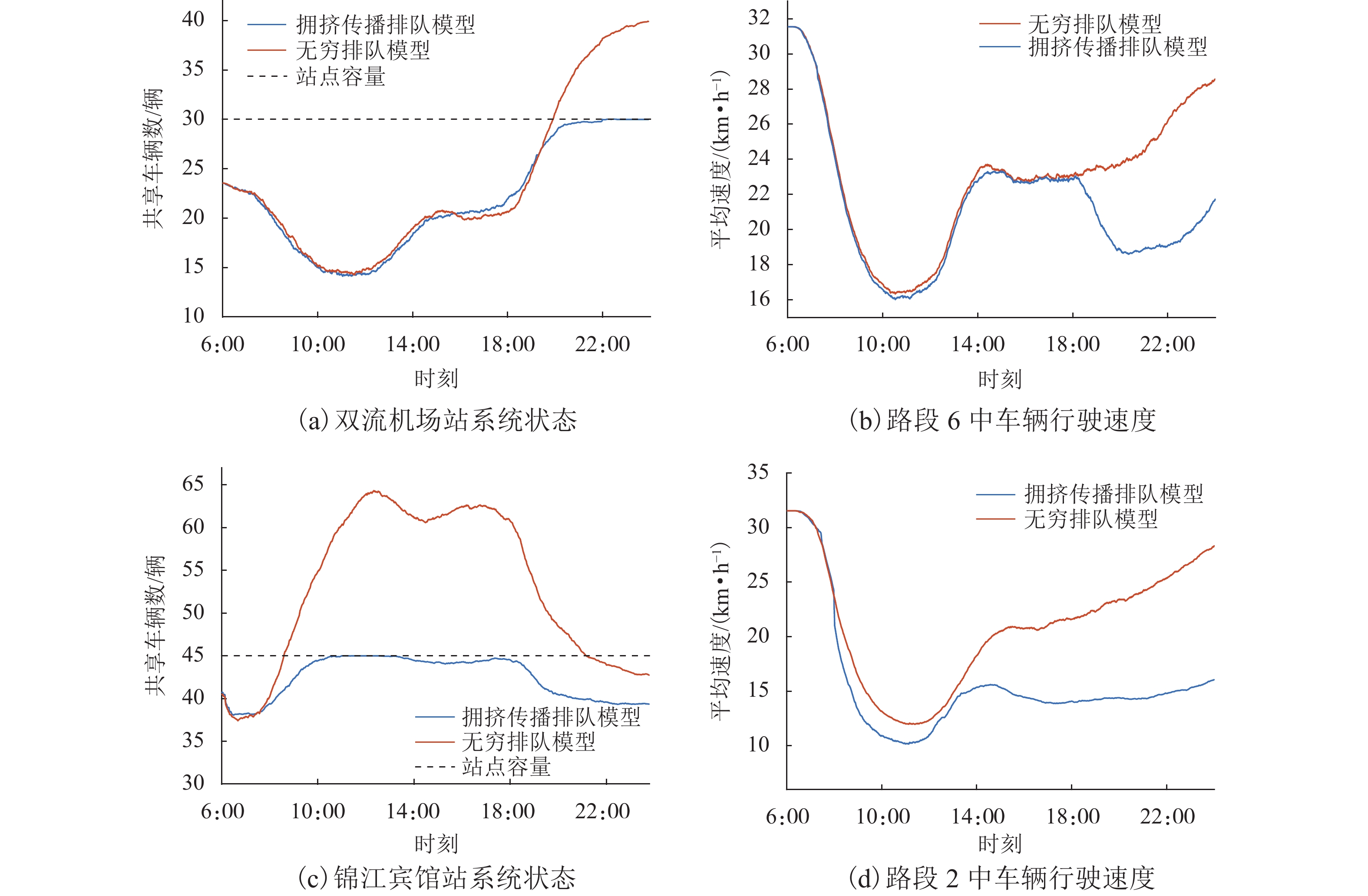
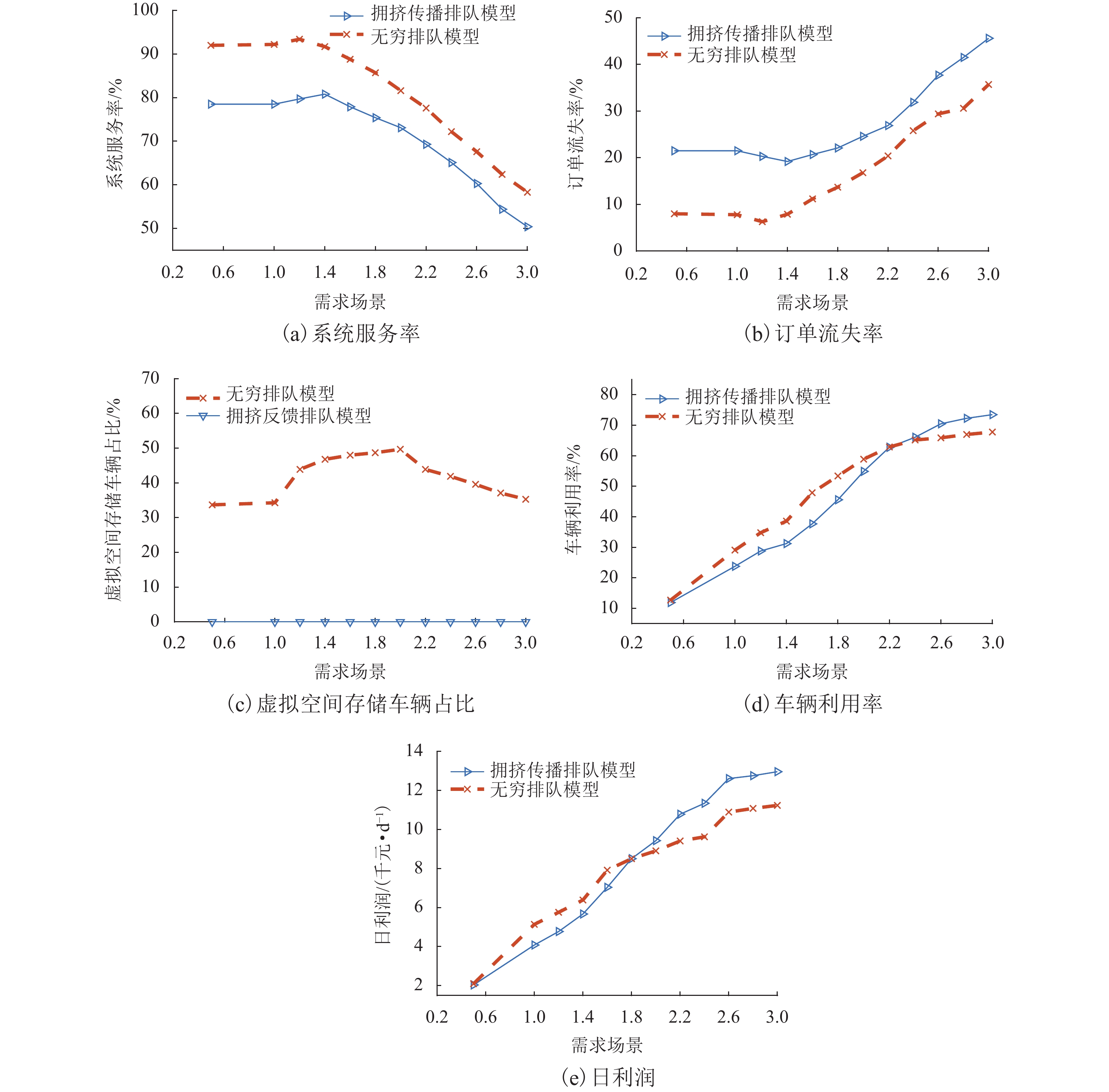
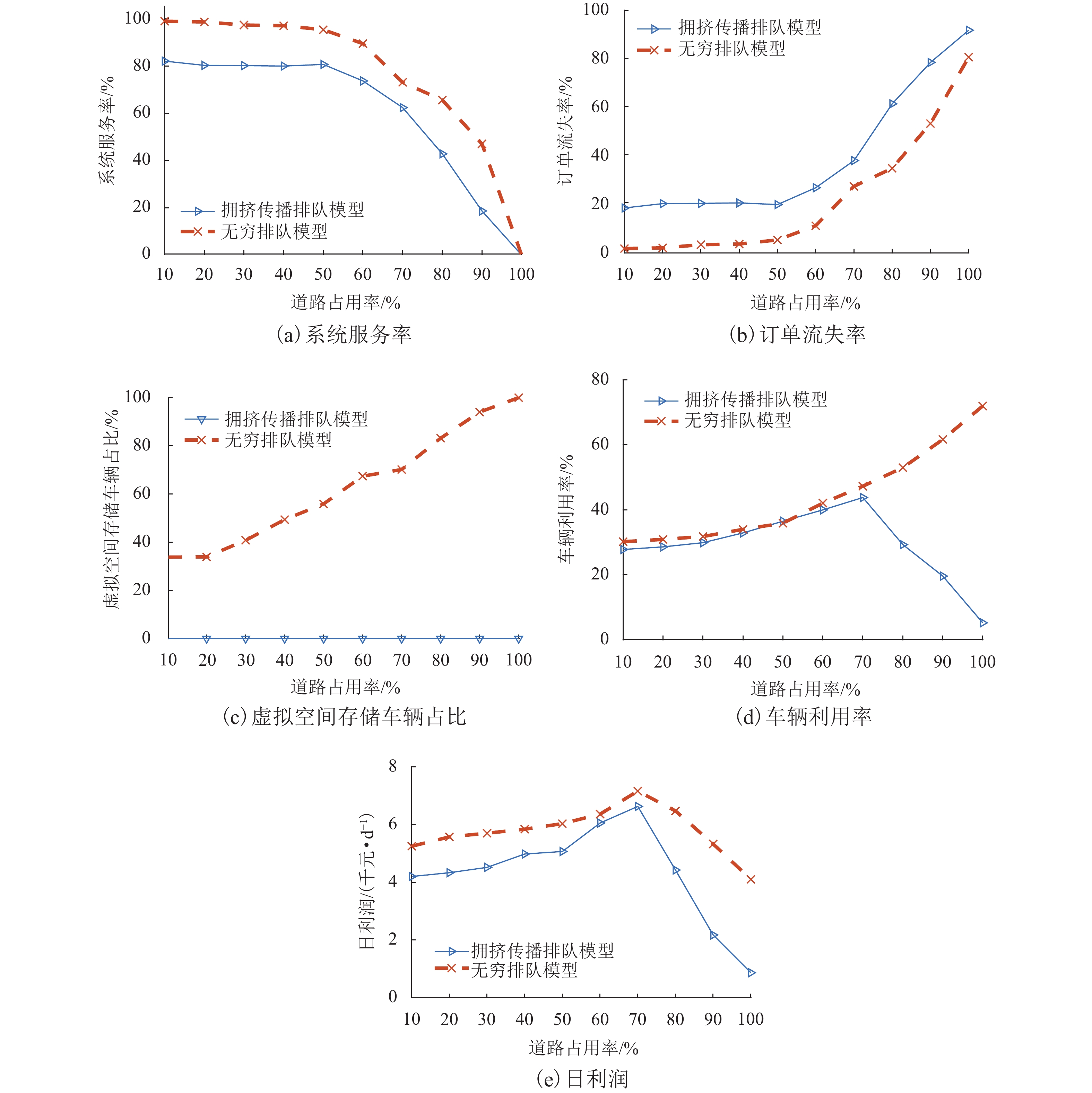
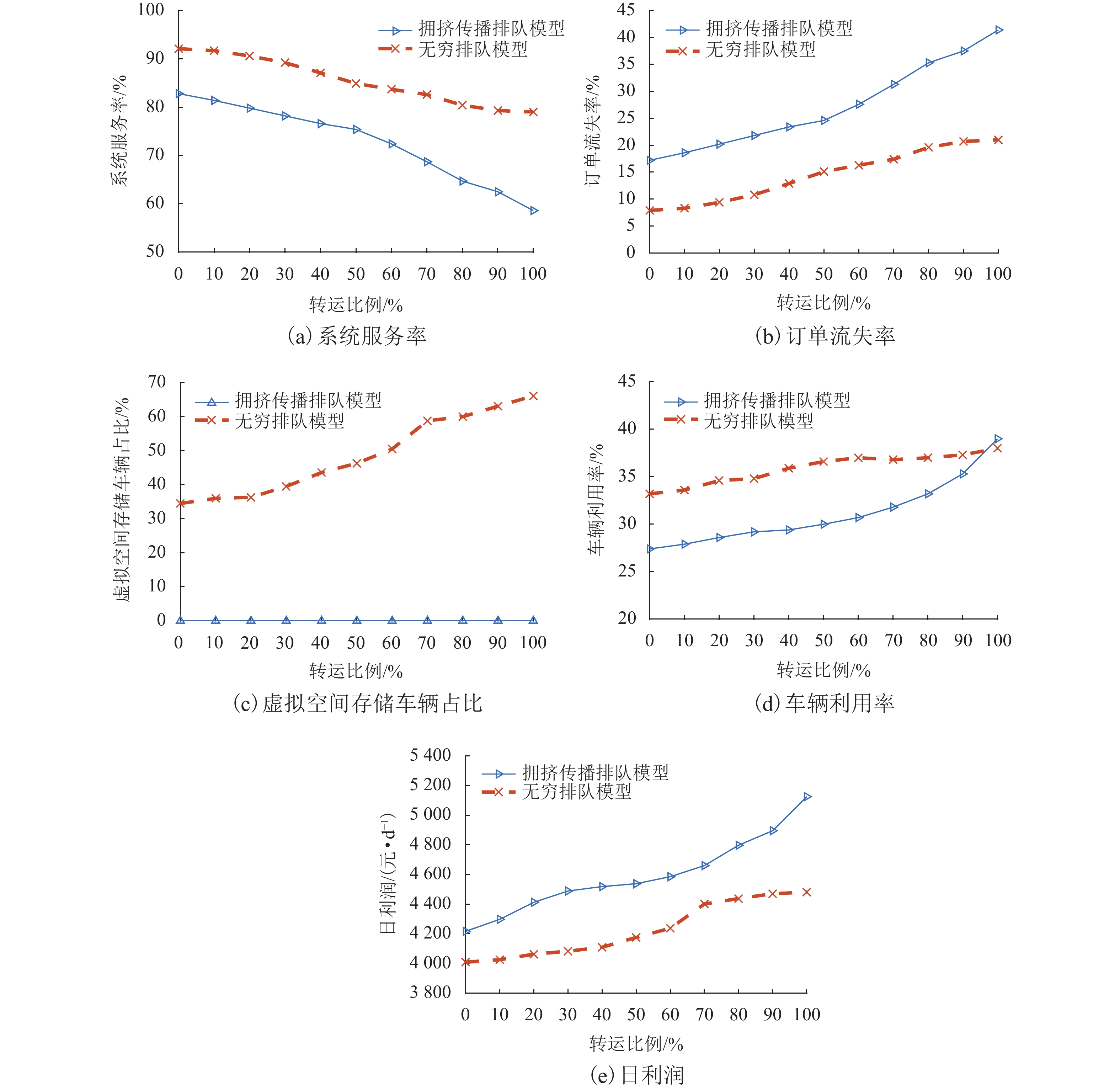
随着共享汽车渗透率的不断增加,站点、路段层面的车辆溢出和拥挤传播现象日趋严重. 为刻画拥挤传播对汽车共享系统运行的影响机理,首先,搭建具有时变性和状态相关性的汽车共享系统排队网络;其次,基于C# 语言和O2DES离散事件仿真框架,提出并设计考虑车路交互影响和拥挤传播现象的汽车共享系统仿真模型,分析动态随机环境下站点与路段层面的拥挤传播现象对汽车共享系统运行的影响;最后,以成都市三站点的小规模汽车共享系统为例,在不同转运比例、需求和道路拥堵场景下,将该模型与引入虚拟空间的无穷排队模型进行对比分析. 研究结果表明:站点和路段层面的拥挤传播现象会导致系统服务率下降9.3%~16.9%,相比无穷排队模型,考虑拥挤传播现象的排队模型更能反映汽车共享系统的实际运营过程;当路网的道路占用率为70% (路网处于中度拥堵)时,考虑拥挤传播现象的汽车共享系统可实现最大收益;汽车共享系统的引入会为道路资源的动态分配带来新变化,当公共交通转向汽车共享系统的用户占比超过70%时,路网拥堵加剧,不利于汽车共享系统的有效运营和可持续发展.
Abstract:With the increasing penetration of carsharing, vehicle overflow and congestion propagation at the level of station and path tend to be serious. In order to describe the influence mechanism of congestion propagation on the operation of carsharing systems, firstly, a queuing network of the carsharing system is built with time-varying and state-dependence properties. Secondly, based on C# language and O2DES framework of discrete event simulation, a simulation model of the carsharing system under dynamic stochastic environment is proposed, which allows for the influence of vehicle–road interaction and congestion propagation. The influence of congestion propagation on the operation of the carsharing system is analyzed in terms of the station and path levels. Finally, a small-scale carsharing system, i.e., three stations in Chengdu, is exemplified. The proposed model and the infinite queuing model in virtual space are compared and analyzed under different transfer ratios, demands and road congestion scenarios. The results show that congestion propagation at the stations and paths will decline the system service rate by 9.3%–16.9%. Compared with the infinite queuing model, the proposed model can better reflect the actual operation of the carsharing system because of considering congestion propagation. When the occupancy rate of the road network reaches 70% (the road network is in moderate congestion), the proposed carsharing system can achieve maximum benefits. The introduction of the carsharing system will bring new changes to the dynamic allocation of road resources. When the proportion of users from public transportation to the carsharing system exceeds 70%, it will intensify the congestion of the road network, which is not conducive to the effective operation and sustainable development of the carsharing system.
-
表 1 速度模型标准点取值
Table 1. Representative point values of velocity model
相对密度 平均行驶速度/(km•min−1) ${\text{ } }{f_{m,{\text{p} } } }(t){\text{ = } }0$ ${v_{m,0,{\text{p} } } } = 1.00$ ${f_{m,{\text{p} } } }(t) = {b_{m,1,{\text{p} } } }(t){\text{ = } }0.1$ ${v_{m,1,{\text{p} } } } = 0.55$ ${f_{m,{\text{p} } } }(t) = {b_{m,2,{\text{p} } } }(t){\text{ = } }0.2$ ${v_{m,2,{\text{p} } } } = 0.40$ 表 2 两种排队模型的性能指标求解结果
Table 2. Solved performance indicators of two queuing models
模型 系统服务率/% 车辆利用率/% 虚拟空间
存储车辆
占比率/%订单流失率/% 利润/
(元•d−1)拥挤传播
排队模型78.50 23.78 0 21.50 4081.50 无穷排队模型 91.33 31.09 34.28 8.67 5139.60 -
[1] YE J H, WANG D G, LI X, et al. Assessing one-way carsharing’s impacts on vehicle ownership: evidence from Shanghai with an international comparison[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2021, 150: 16-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2021.05.012 [2] 张淼,惠英,汪鸣泉. 汽车共享对城市温室气体排放的影响[J]. 中国人口 · 资源与环境,2012,22(9): 48-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2012.09.008ZHANG Miao, HUI Ying, WANG Mingquan. Urban greenhouse gas emission of car sharing[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2012, 22(9): 48-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2012.09.008 [3] XU M, MENG Q, LIU ZY. Electric vehicle fleet size and trip pricing for one-way carsharing services considering vehicle relocation and personnel assignment[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2018, 111: 60-82. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2018.03.001 [4] BAPTISTA P, MELO S, ROLIM C. Car sharing systems as a sustainable transport policy: a case Study from Lisbon, Portugal[M]//ATTARD M, SHIFTAN Y. Transport and Sustainability. [S.l.]: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2015: 205-227. [5] NANSUBUGA B, KOWALKOWSKI C. Carsharing: a systematic literature review and research agenda[J]. Journal of Service Management, 2021, 32(6): 55-91. doi: 10.1108/JOSM-10-2020-0344 [6] 曹可心,邓羽. 城市共享汽车分布的时空演变及影响因素研究:以北京市主城区为例[J]. 地理科学,2021,41(10): 1792-1801.CAO Kexin, DENG Yu. Spatial-temporal characteristics and impacting factors of carsharing in Beijing[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2021, 41(10): 1792-1801. [7] 伊二妮. 基于排队论的汽车共享服务系统车辆配置优化研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2018. [8] EFTHYMIOU D, ANTONIOU C, WADDELL P. Factors affecting the adoption of vehicle sharing systems by young drivers[J]. Transport Policy, 2013, 29: 64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2013.04.009 [9] 刘向,洪林,王宁,等. 基于时空消耗的共享汽车拥堵治理效用研究[J]. 汽车工程学报,2020,10(5): 335-341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2020.05.04LIU Xiang, HONG Lin, WANG Ning, et al. Research on the effect of car-sharing on traffic congestion management based on spatiotemporal consumption[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2020, 10(5): 335-341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2020.05.04 [10] 高永,安健,全宇翔. 网络约租车对出行方式选择及交通运行的影响[J]. 城市交通,2016,14(5): 1-8. doi: 10.13813/j.cn11-5141/u.2016.0501GAO Yong, AN Jian, QUAN Yuxiang. The impact of APP-based car sharing on travel mode shift and transportation operation performance[J]. Urban Transport of China, 2016, 14(5): 1-8. doi: 10.13813/j.cn11-5141/u.2016.0501 [11] 张三省,苏倩,张俊青. 基于系统动力学的网约车政策对城市交通的影响研究[J]. 天津大学学报(社会科学版),2019,21(6): 494-502.ZHANG Sanxing, SU Qian, ZHANG Junqing. Analysis of the influence of ride-hailing policy on urban traffic based on system dynamics[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Social Sciences), 2019, 21(6): 494-502. [12] ZHAO M, LI X, YIN J, et al. An integrated framework for electric vehicle rebalancing and staff relocation in one-way carsharing systems: model formulation and Lagrangian relaxation-based solution approach[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2018, 117: 542-572. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2018.09.014 [13] HU L, LIU Y. Joint design of parking capacities and fleet size for one-way station-based carsharing systems with road congestion constraints[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2016, 93: 268-299. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2016.07.021 [14] DENG Y H, CARDIN M A. Integrating operational decisions into the planning of one-way vehicle-sharing systems under uncertainty[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 86: 407-424. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2017.11.018 [15] KASPI M, RAVIV T, TZUR M. Parking reservation policies in one-way vehicle sharing systems[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2014, 62: 35-50. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2014.01.006 [16] 马舒予,胡路,吴佳媛,等. 共享电动汽车系统车队规模与停车泊位数优化[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报,2022,20(3): 31-42.MA Shuyu, HU Lu, WU Jiayuan, et al. Fleet size and parking capacity optimization of electric carsharing system[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2022, 20(3): 31-42. [17] 蒋阳升,李衍,李皓,等. 基于模块化仿真的共享汽车联合调度优化[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2023,58(1): 74-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210083JIANG Yangsheng, LI Yan, LI Hao, et al. Optimization for joint relocation of carsharing based on modular simulation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023, 58(1): 74-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20210083 [18] PARK S, YU W. Analysis of system parameters for one-way carsharing systems[J]. Transportation Letters: the International Journal of Transportation Research, 2021,14(3): 1-11. [19] LI H B, ZHU Y C, CHEN Y X, et al. The object-oriented discrete event simulation modeling: a case study on aircraft spare part management[C]//2015 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC). Huntington Beach: IEEE, 2015: 3514-3525. [20] LI H B, ZHOU C H, LEE B K, et al. Capacity planning for mega container terminals with multi-objective and multi-fidelity simulation optimization[J]. IISE Transactions, 2017, 49(9): 849-862. doi: 10.1080/24725854.2017.1318229 [21] 张维戈,陈连福,黄彧,等. M/G/K排队模型在电动出租汽车充电站排队系统中的应用[J]. 电网技术,2015,39(3): 724-729. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2015.03.021ZHANG Weige, CHEN Lianfu, HUANG Yu, et al. Application of M/G/K queuing model in queuing system of electric taxi charging station[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39(3): 724-729. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2015.03.021 [22] 李仕鹏. 基于排队论的汽车共享优化设计[D]. 杭州: 杭州电子科技大学, 2013. [23] KENDALL D G. Stochastic processes occurring in the theory of queues and their analysis by the method of the imbedded Markov chain[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1953, 24(3): 338-354 [24] ZEIGLER B P, PRAEHOFER H, KIM T G. Theory of modeling and simulation: integrating discrete event and continuous complex dynamic systems[M]. 2nd edition. Pittsburgh: Academic Press, 2000: 4-5. [25] HU L, ZHAO B, ZHU J X, et al. Two time-varying and state-dependent fluid queuing models for traffic circulation systems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 275(3): 997-1019. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.01.020 -




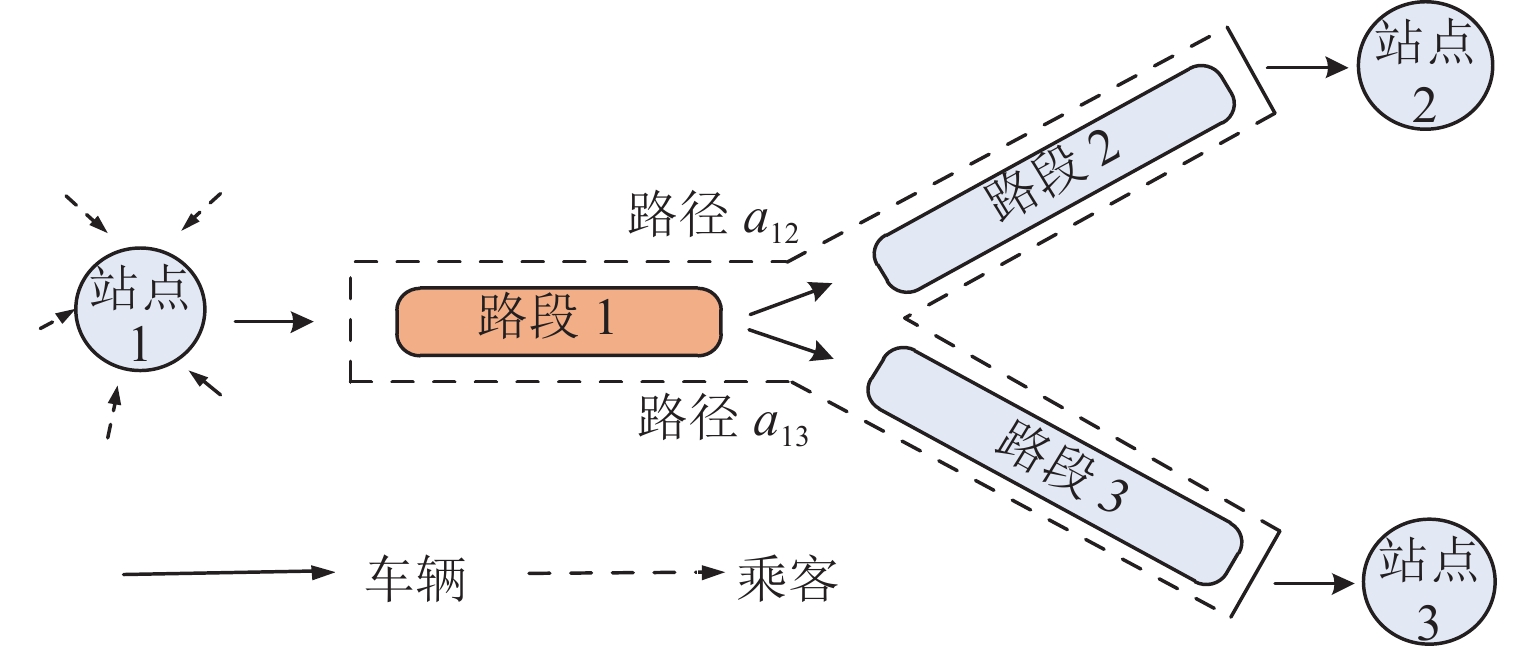
 下载:
下载: