Monitoring Data-Driven Prediction of Remaining Useful Life of Axle-Box Bearings for Urban Rail Transit Trains
-
摘要:
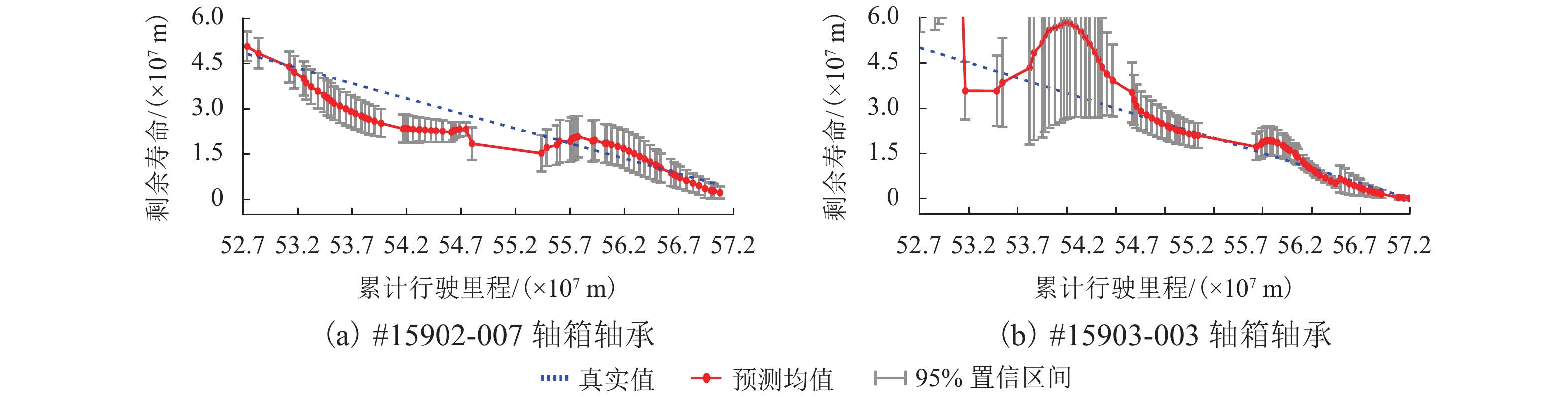
城轨列车轴箱轴承的运行工况复杂多变、外部随机干扰频繁,导致其监测数据中包含大量测量噪声乃至“脏”数据,进而制约了剩余寿命预测模型的精度. 为解决上述问题,提出了一种监测数据驱动的动态多重聚合剩余寿命预测方法. 首先,通过度量短时数据的幅值分布相似性自动识别并清洗“脏”数据;然后,将健康指标按不同时间尺度进行动态聚合,预测出各类潜在的未来退化轨迹,进而获得轴箱轴承的剩余寿命预测均值与方差;并使用现场实测数据与加速寿命实验数据对提出方法进行验证. 结果表明:所提方法能有效剔除监测数据中的空采数据和强干扰数据;剩余寿命预测均值随累计行驶里程的增加逐渐收敛到真实值,且95%置信区间越来越窄;相比于单指数预测模型和混合预测模型,提出方法的累计相对精度平均值分别提高了29.78%和27.63%,预测收敛速度平均值分别增加了10.56%和10.20%.
Abstract:The operating conditions of axle-box bearings of urban rail transit trains are complex and time-varying, and they often suffer from random external interferences. Correspondingly, the monitoring data of axle-box bearings contain a great amount of measurement noise and even abnormal data, thereby limiting the accuracy of prognostics models. To overcome the aforementioned problems, a monitoring data-driven dynamic multiple aggregation prediction method is proposed for forecasting the remaining useful life (RUL) of axle-box bearings of urban rail transit trains. In the proposed method, abnormal data are first automatically recognized and deleted by measuring the amplitude distribution similarity between signals in a short time. Then, various degradation curves can be fitted to predict the mean and variance of RUL by aggregating health indicators from different temporal scales. The proposed method is evaluated using vibration data from real monitoring systems of urban rail transit trains and accelerated degradation tests of rolling element bearings. The results show that the proposed method is able to effectively recognize the not a number (NaN) data and strong interference data, and as time goes on, the predictive RUL converges to the actual RUL gradually and the 95% confidence interval becomes narrower. Further, compared with the single exponential prognostics model and the hybrid prognostics model, the proposed method increases the mean of cumulative relative accuracy by 29.78% and 27.63% respectively, and improves the mean of convergence speed by 10.56% and 10.20% respectively.
-
表 1 提出方法与现有方法的预测性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison between the proposed method and existing prediction methods
-
[1] 中国城市轨道交通协会. 城市轨道交通2021年度统计和分析报告[R]. 北京: 中国城市轨道交通协会, 2022. [2] 裴洪,胡昌华,司小胜,等. 基于机器学习的设备剩余寿命预测方法综述[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(8): 1-13. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.001PEI Hong, HU Changhua, SI Xiaosheng, et al. Review of machine learning based remaining useful life prediction methods for equipment[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(8): 1-13. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.08.001 [3] LEI Y G, LI N P, GONTARZ S, et al. A model-based method for remaining useful life prediction of machinery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(3): 1314-1326. doi: 10.1109/TR.2016.2570568 [4] EL-TAWIL K, JAOUDE A A. Stochastic and nonlinear-based prognostic model[J]. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2013, 1(1): 66-81. [5] PAROISSIN C. Inference for the Wiener process with random initiation time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 65(1): 147-157. doi: 10.1109/TR.2015.2456056 [6] KHELIF R, CHEBEL-MORELLO B, MALINOWSKI S, et al. Direct remaining useful life estimation based on support vector regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(3): 2276-2285. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2623260 [7] WANG B, LEI Y G, LI N P, et al. Multiscale convolutional attention network for predicting remaining useful life of machinery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(8): 7496-7504. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3003649 [8] HUANG C G, HUANG H Z, LI Y F. A bidirectional LSTM prognostics method under multiple operational conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(11): 8792-8802. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2891463 [9] WANG B, LEI Y G, LI N P, et al. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(1): 401-412. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 [10] 刘德昆,李强,王曦,等. 动车组轴箱轴承基于实测载荷的寿命预测方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2016,52(22): 45-54. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.22.045LIU Dekun, LI Qiang, WANG Xi, et al. Life prediction method for EMU axle box bearings based on actual measured loadings[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(22): 45-54. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.22.045 [11] 赵珂,顾佳,姜喜民. 动车组转向架轴箱剩余寿命预测方法研究[J]. 软件,2020,41(3): 219-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6970.2020.03.052ZHAO Ke, GU Jia, JIANG Ximin. Research on prediction method of residual life of bogie axle box for multiple unit train[J]. Computer Engineering & Software, 2020, 41(3): 219-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6970.2020.03.052 [12] 吕晟. 城市轨道交通车辆走行部轴箱轴承健康评估及寿命预测系统[J]. 城市轨道交通研究,2021,24(增1): 149-153. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2021.S1.033LYU Sheng. Health assessment and life prediction system for axle box bearing of urban rail transit vehicle running gear[J]. Urban Mass Transit, 2021, 24(S1): 149-153. doi: 10.16037/j.1007-869x.2021.S1.033 [13] 刘嘉蔚,李奇,陈维荣,等. 基于核超限学习机和局部加权回归散点平滑法的PEMFC剩余使用寿命预测方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(24): 7272-7279,7500. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.181614LIU Jiawei, LI Qi, CHEN Weirong, et al. Remaining useful life prediction method of PEMFC based on kernel extreme learning machine and locally weighted scatterplot smoothing[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(24): 7272-7279,7500. doi: 10.13334/J.0258-8013.PCSEE.181614 [14] LI N P, LEI Y G, LIN J, et al. An improved exponential model for predicting remaining useful life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(12): 7762-7773. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2455055 [15] SAXENA A, CELAYA J, SAHA B, et al. Metrics for offline evaluation of prognostic performance[J]. International Journal of Prognostics and Health Management, 2021, 1(1): 2153-2648. [16] DU W L, HOU X K, WANG H C. Time-varying degradation model for remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearings under variable rotational speed[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(8): 4044.1-4044.17. doi: 10.3390/app12084044 -





 下载:
下载: