Influence of Underbody Parameters of High-Speed Trains on Aerodynamic Noise
-
摘要:
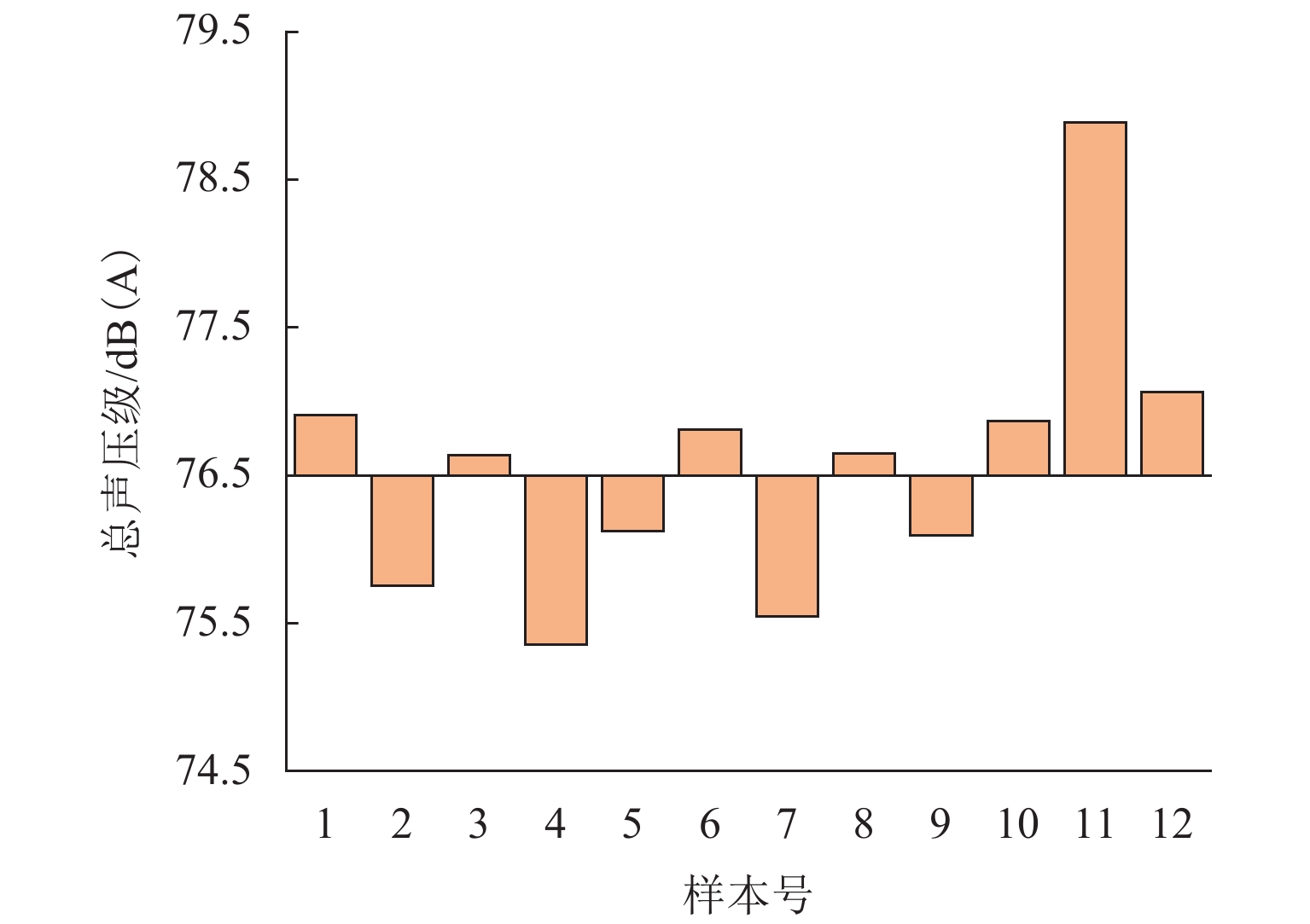
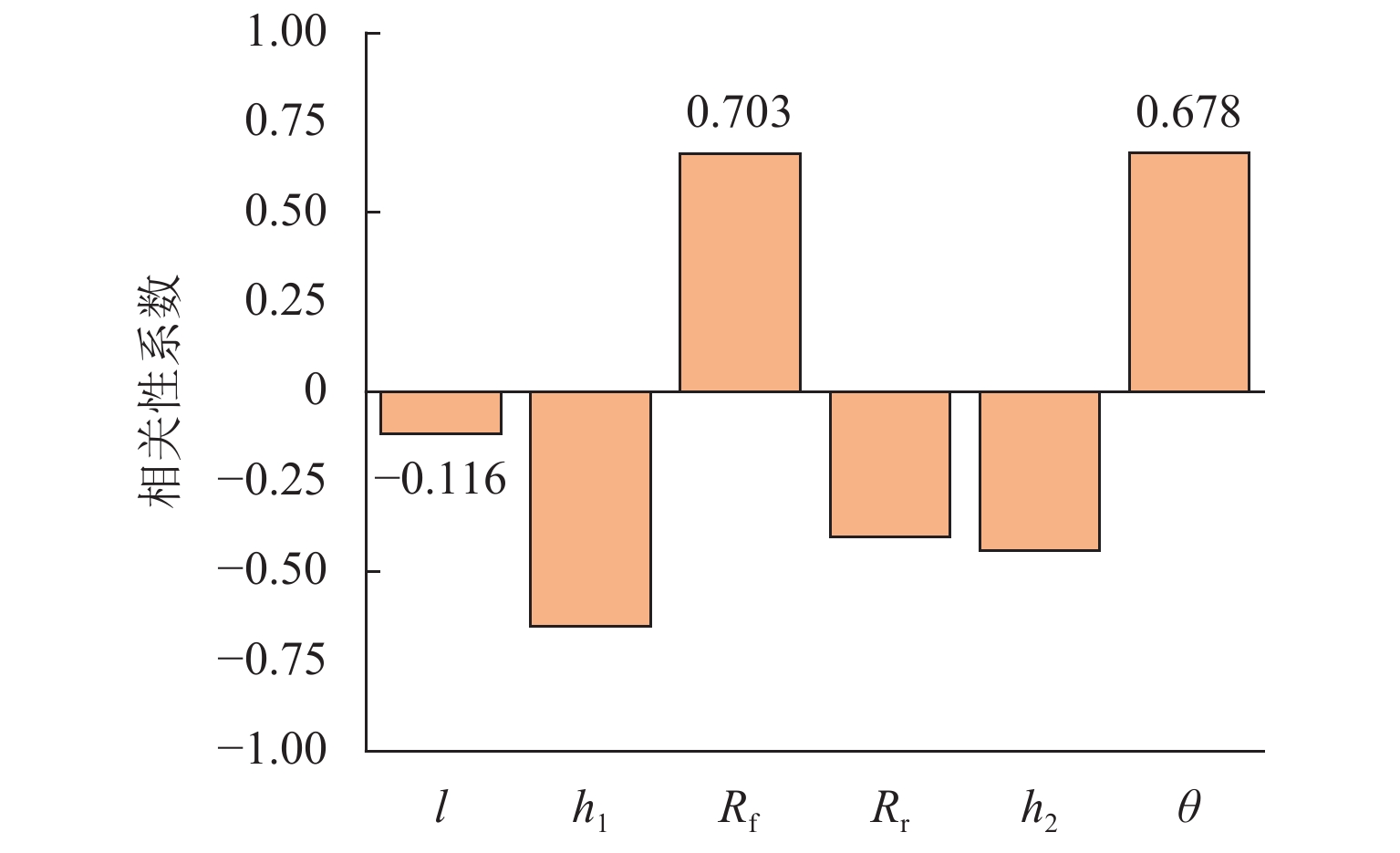
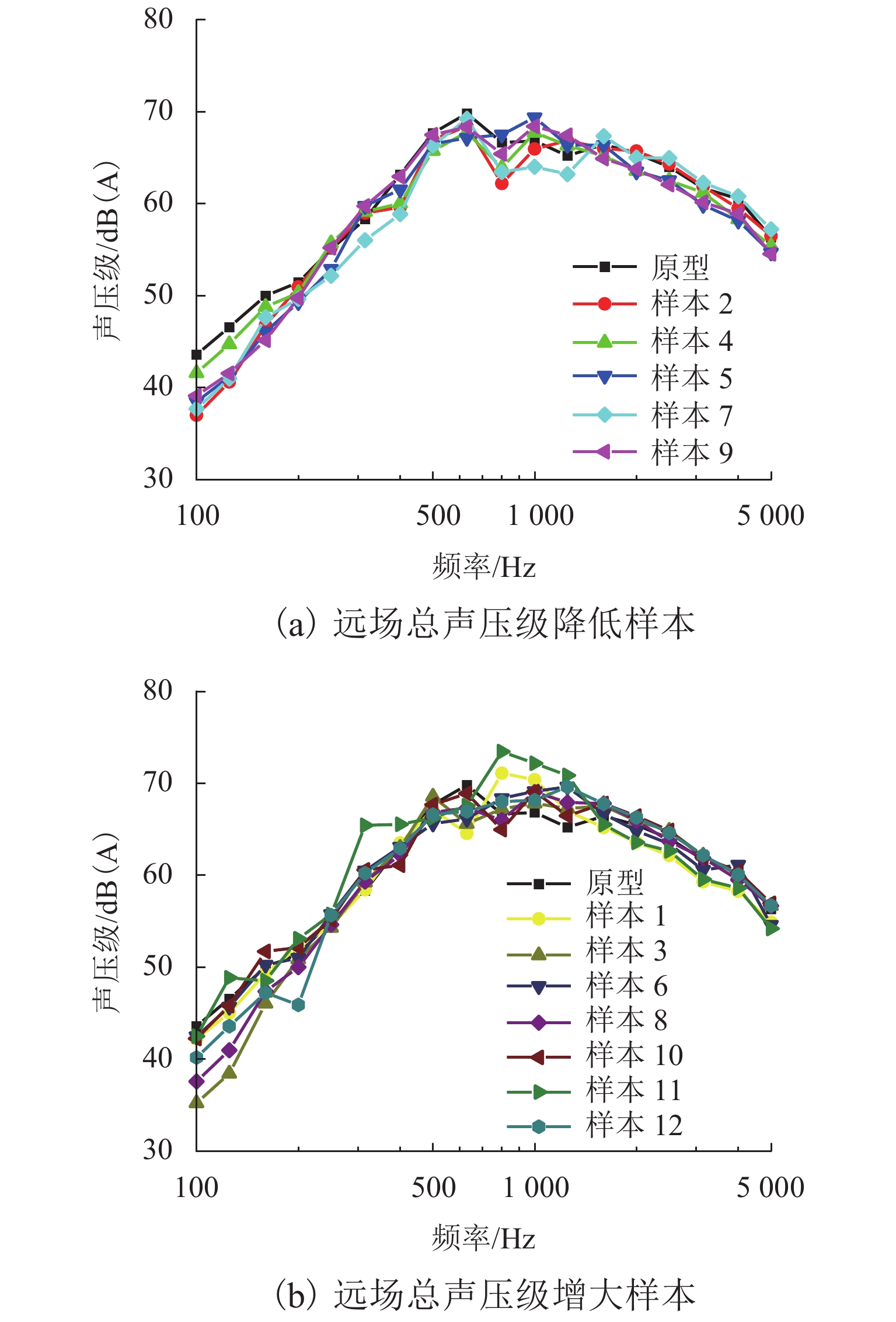
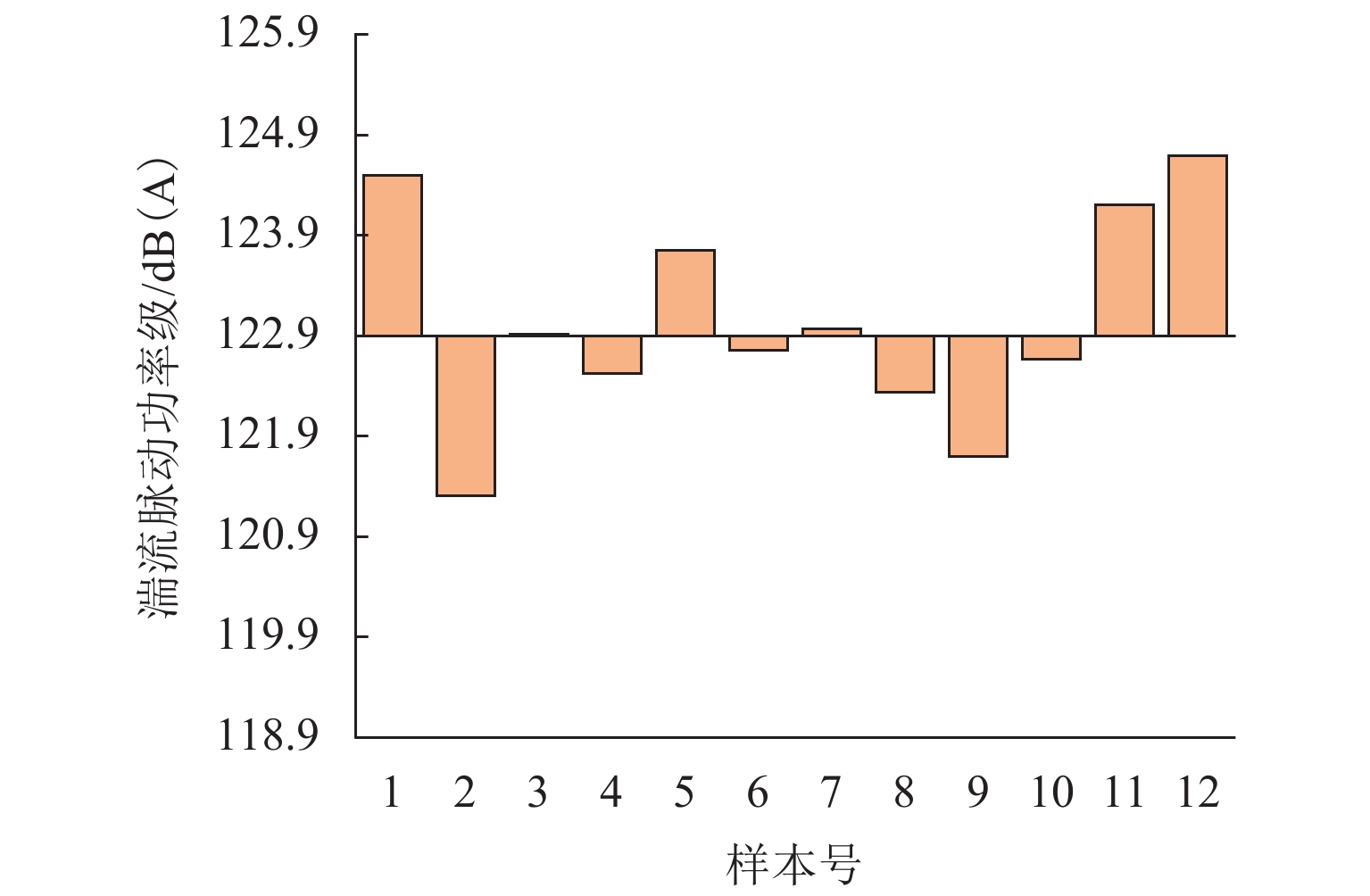
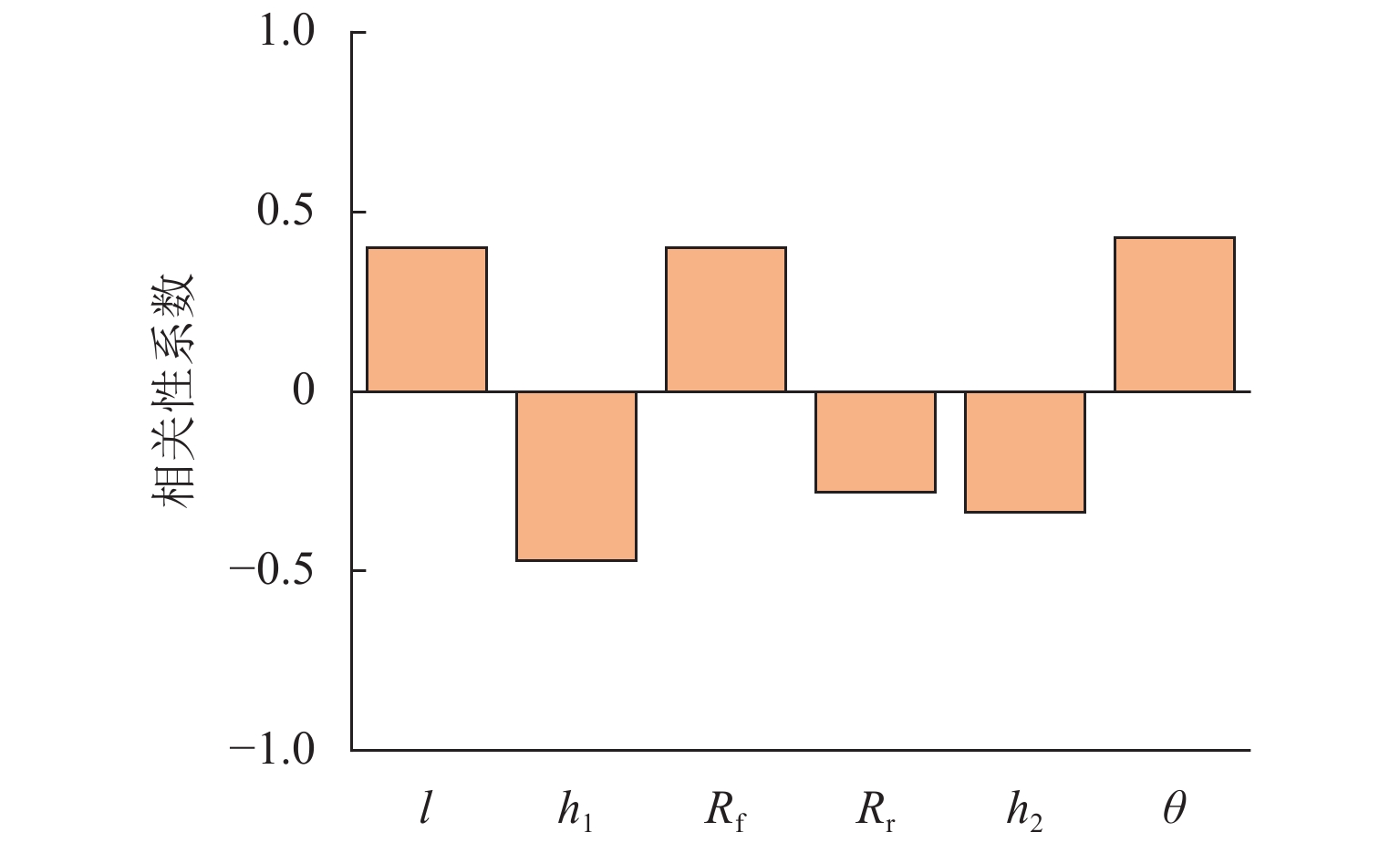
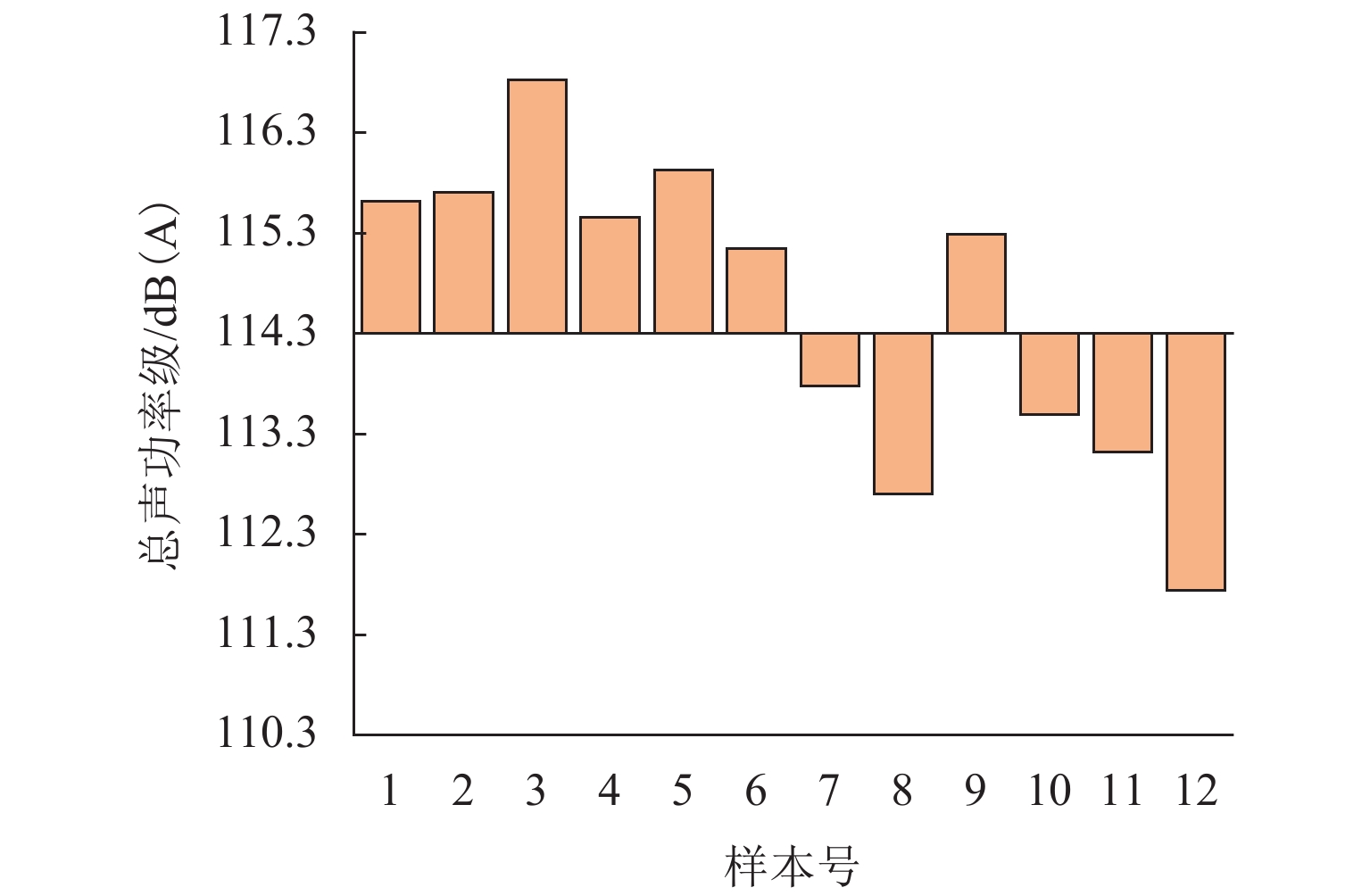
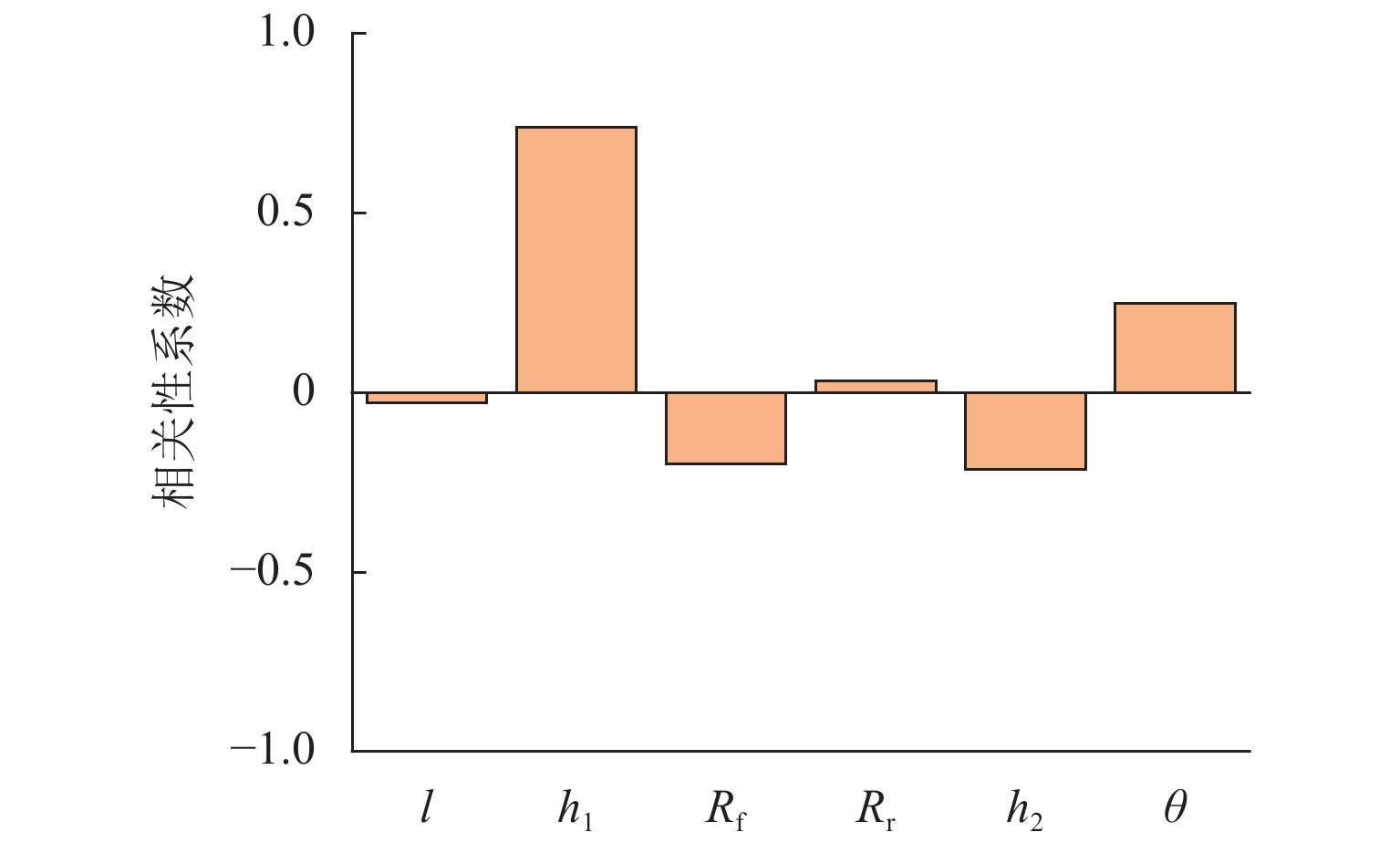
为更好地开展高速列车气动降噪设计,建立了高速列车头车第一组转向架区域的6参数模型,采用计算气动声学和拉丁超立方抽样实验所设计的方法,得到了13个参数化模型的远场气动噪声、转向架舱内湍流脉动功率级和声功率级,并分析了底部结构参数对远场和近场气动噪声的影响规律. 结果表明:底部结构参数对远场噪声影响范围为75.4~78.9 dB(A),裙板高度、排障器厚度、转向架舱后缘倒角和舱长度与远场噪声为负相关,舱前缘倒角、排障器前缘夹角与远场噪声为正相关,底部结构参数的变化主要影响中心频带315~1250 Hz间的噪声能量;排障器厚度和前缘夹角与远场噪声、舱内湍流脉动功率、声功率均为负相关;裙板高度和远场噪声、舱内湍流脉动功率级为负相关,与舱内声功率为正相关.
Abstract:In order to better perform the aerodynamic noise reduction design of high-speed trains, a 6-parametric model of the first bogie section of the high-speed train head car was established. The method designed by computational aeroacoustics and Latin hypercube sampling experiments was used, and the far-field aerodynamic noise, turbulent fluctuation power level, and acoustic power level inside the bogie cavity of 13 parametric models were obtained. The influence of underbody parameters on far-field and near-field aerodynamic noise was analyzed. The results show that the influence range of the underbody parameters on the far-field noise is 75.4–78.9 dB(A). The apron height, cowcatcher thickness, chamfer of the rear edge of the bogie cavity, and cavity length are negatively correlated with the far-field noise, while the chamfer of the leading edge of the cavity and the leading-edge included angle of the cowcatcher are positively correlated with the far-field noise. The changes in underbody parameters mainly affect the noise energy in the central frequency band of 315–1 250 Hz. The cowcatcher thickness and leading-edge included angle are negatively correlated with far-field noise, turbulent fluctuation power level, and acoustic power level inside the bogie cavity. The apron height is negatively correlated with the far-field noise and the turbulent fluctuation power level inside the bogie cavity and positively correlated with the acoustic power level inside the bogie cavity.
-
Key words:
- high-speed train /
- aerodynamic noise /
- underbody /
- parametric design /
- correlation coefficient
-
表 1 参数变化范围
Table 1. Ranges of parameters
参数 变化范围 l/mm 495~605 h1/mm 0~100 Rf/mm 0~20 Rr/mm 0~20 h2/mm 15~50 θ/(°) 95~140 表 2 高速列车底部结构参数化实验设计
Table 2. Design of experiment table of high-speed train under body parameters
样本点 l/mm h1/mm Rf/mm Rr/mm h2/mm θ/(°) 原型 535 63 0 0 28 125 1 536 64 5 6 28 127 2 534 98 3 10 40 117 3 510 99 13 18 19 136 4 596 96 2 16 42 96 5 602 93 11 14 35 113 6 578 87 10 3 20 124 7 597 84 1 5 38 101 8 503 82 4 11 40 104 9 498 79 6 17 26 110 10 590 65 18 15 49 112 11 561 33 17 1 22 133 12 566 0 19 13 35 116 表 3 网格敏感性验证
Table 3. Gird sensitivity verification
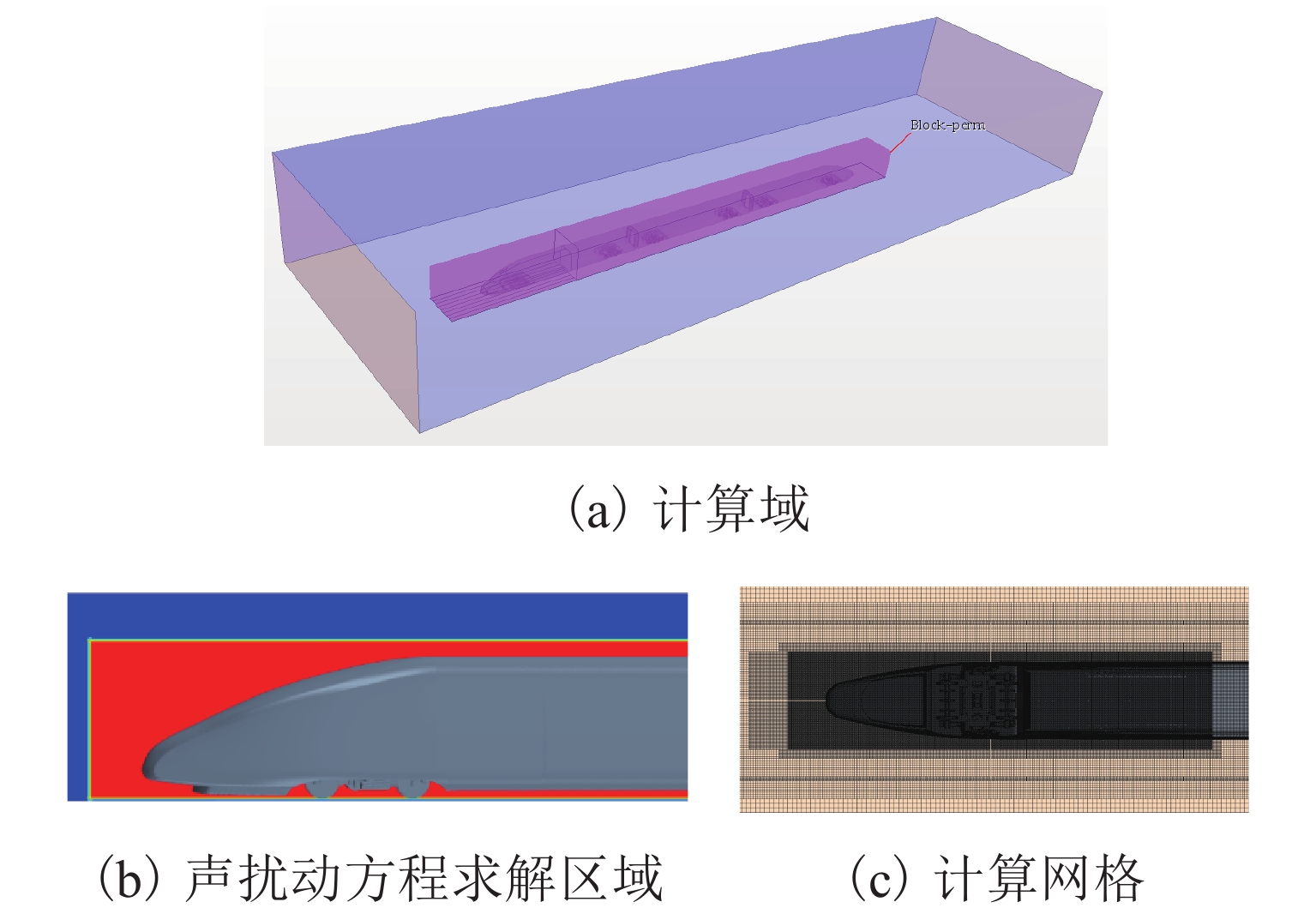
序号 网格/万 y+ x+ z+ Cd 偏差/% 1 4100 1 450 450 0.281 −1.1 2 4900 1 300 300 0.283 −0.4 3 8800 1 150 150 0.284 表 4 测点总声压级
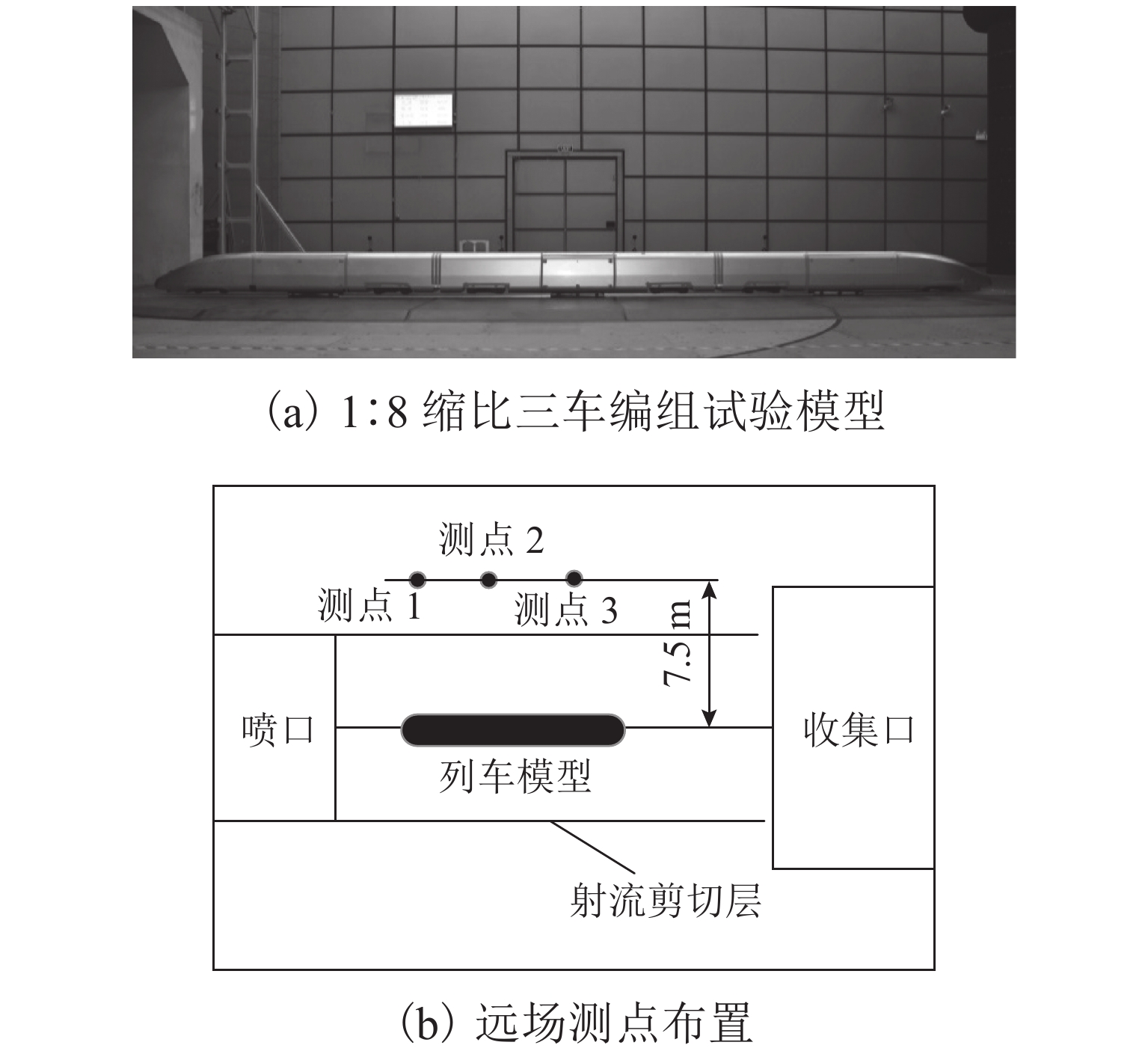
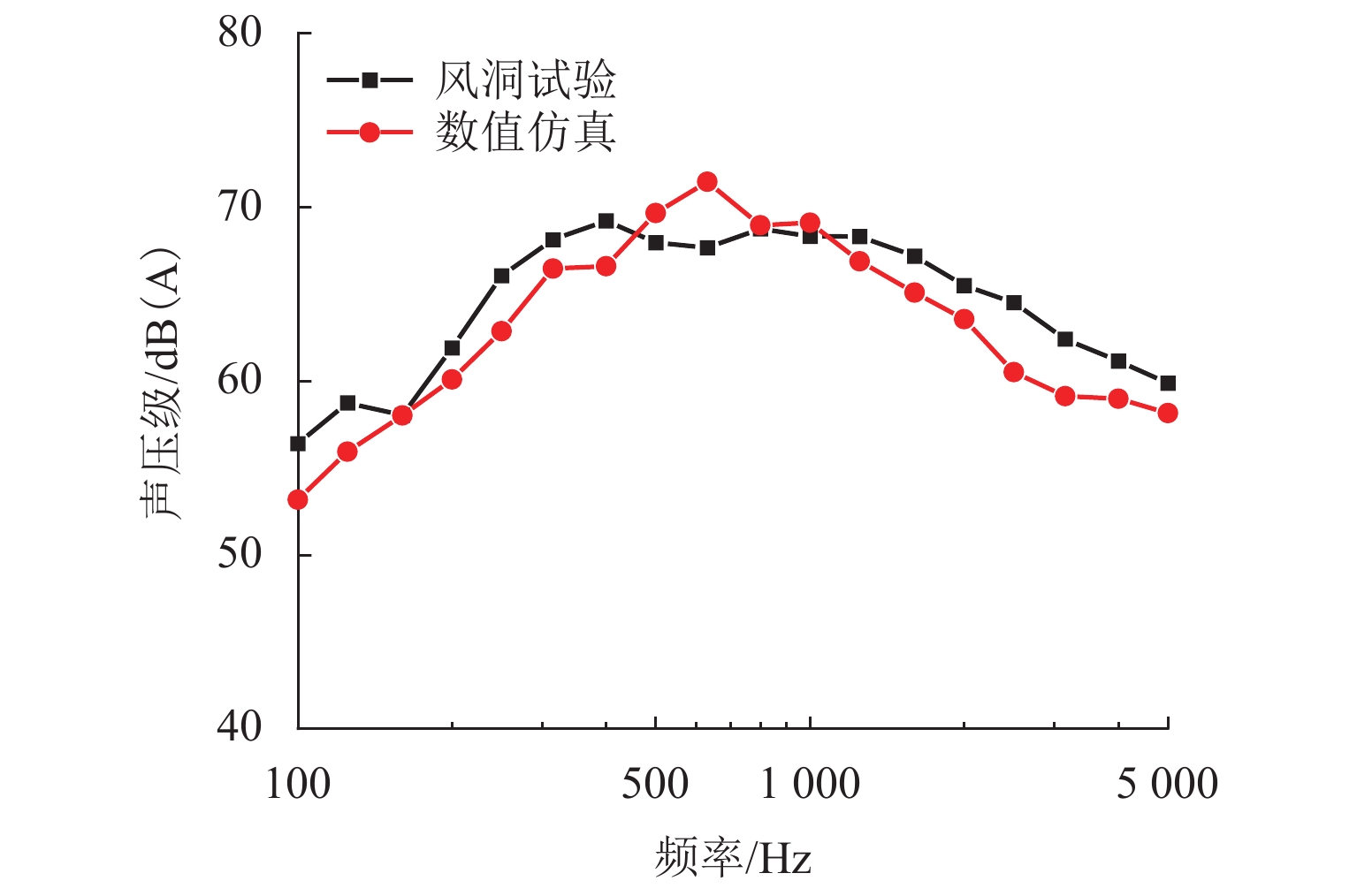
Table 4. OASPL of measureing points
dB(A) 方法 测点 1 测点 2 测点 3 数值仿真 78.5 78.4 80.6 风洞试验 78.1 78.7 78.6 -
[1] 翟婉明,赵春发. 现代轨道交通工程科技前沿与挑战[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001ZHAI Wanming, ZHAO Chunfa. Frontiers and challenges of sciences and technologies in modern railway engineering[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 209-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001 [2] 朱自未,李牧皛,成功,等. 高速列车噪声源声功率与速度的函数关系[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2020,55(2): 290-298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180023ZHU Ziwei, LI Muxiao, CHENG Gong, et al. Functional relationships between sound Powers radiated from noise sources of high-speed train and its speed[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020, 55(2): 290-298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20180023 [3] ZHANG J, XIAO X B, SHENG X Z, et al. An acoustic design procedure for controlling interior noise of high-speed trains[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2020, 168: 107419. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107419 [4] HE B, JIN X S. Investigation into external noise of a high-speed train at different speeds[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A, 2014, 15: 1019-1033. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1400307 [5] 高阳,王毅刚,王金田,等. 声学风洞中的高速列车模型气动噪声试验研究[J]. 声学技术,2013,32(6): 506-510.GAO Yang, WANG Yigang, WANG Jintian, et al. Testing study of aerodynamic noise for high speed train model in aero-acoustic wind tunnel[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2013, 32(6): 506-510. [6] 张亚东,张继业,李田. 高速列车整车气动噪声声源特性分析及降噪研究[J]. 铁道学报,2016,38(7): 40-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.07.006ZHANG Yadong, ZHANG Jiye, LI Tian. Research on aerodynamic noise source characterization and noise reduction of high-speed trains vehicle[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2016, 38(7): 40-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2016.07.006 [7] LATORRE IGLESIAS E, THOMPSON D J, SMITH M, et al. Anechoic wind tunnel tests on high-speed train bogie aerodynamic noise[J]. International Journal of Rail Transportation, 2017, 5(2): 87-109. doi: 10.1080/23248378.2016.1274685 [8] SUN Z X, ZHANG Y, YANG G W. Surrogate based optimization of aerodynamic noise for streamlined shape of high speed trains[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(2): 196-212. doi: 10.3390/app7020196 [9] 张亮,张继业,李田,等. 超高速列车流线型头型多目标优化设计[J]. 机械工程学报,2017,53(2): 106-114. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.02.106ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Jiye, LI Tian, et al. Multi-objective optimization design of the streamlined head shape of super high-speed trains[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(2): 106-114. doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.02.106 [10] 安翼,莫晃锐,刘青泉. 高速列车头型长细比对气动噪声的影响[J]. 力学学报,2017,49(5): 985-996. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-17-126AN Yi, MO Huangrui, LIU Qingquan. Study on the influence of the nose slenderness ratio of high-speed train on the aerodynamic noise[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017, 49(5): 985-996. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-17-126 [11] ZHU J Y, HU Z W, THOMPSON D J. The flow and flow-induced noise behaviour of a simplified high-speed train bogie in the cavity with and without a fairing[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2018, 232(3): 759-773. doi: 10.1177/0954409717691619 [12] 高阳,李启良,陈羽,等. 高速列车头型近场与远场噪声预测[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(1): 124-129.GAO Yang, LI Qiliang, CHEN Yu, et al. Prediction of near field and far field noise for high-speed train head shape[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2019, 47(1): 124-129. [13] 田红旗. 中国高速轨道交通空气动力学研究进展及发展思考[J]. 中国工程科学,2015,17(4): 30-41.TIAN Hongqi. Development of research on aerodynamics of high-speed rails in China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2015, 17(4): 30-41. [14] MCKAY M D, BECKMAN R J, CONOVER W J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code[J]. Technometrics, 2000, 42(1): 55-61. doi: 10.1080/00401706.2000.10485979 [15] IMAN R L, HELTON J C, CAMPBELL J E. An approach to sensitivity analysis of computer models: part I—introduction, input variable selection and preliminary variable assessment[J]. Journal of Quality Technology, 1981, 13(3): 174-183. doi: 10.1080/00224065.1981.11978748 [16] EWERT R, SCHRÖDER W. Acoustic perturbation equations based on flow decomposition via source filtering[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 188(2): 365-398. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00168-2 [17] LECOQ D, PÉZERAT C, THOMAS J H, et al. Extraction of the acoustic component of a turbulent flow exciting a plate by inverting the vibration problem[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2014, 333(12): 2505-2519. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2014.02.003 -




 下载:
下载: