Coupled Vibration Analysis of Earthquake-Wind-Vehicle-Bridge for Long-Span Bridges Considering Scouring Effect
-
摘要:
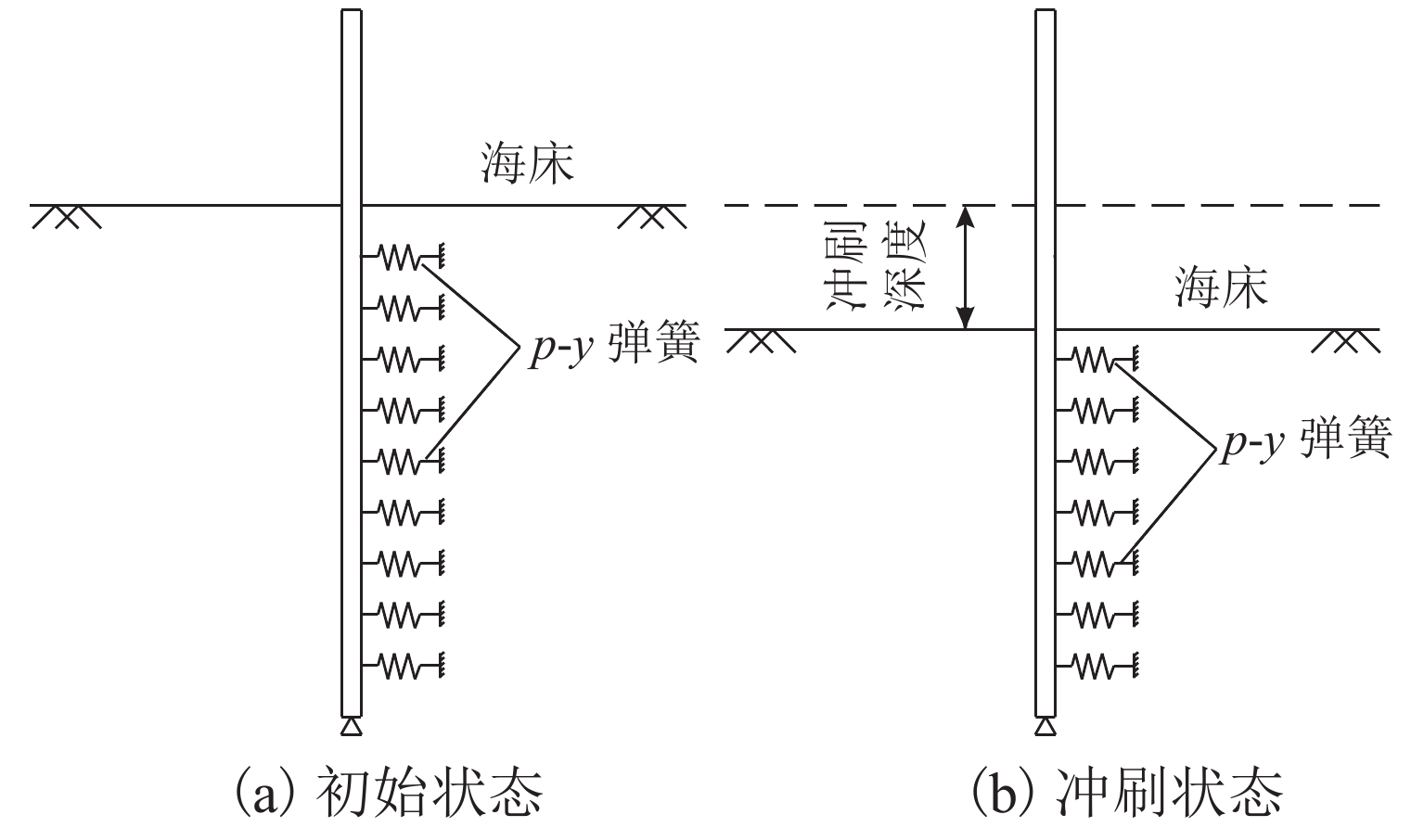
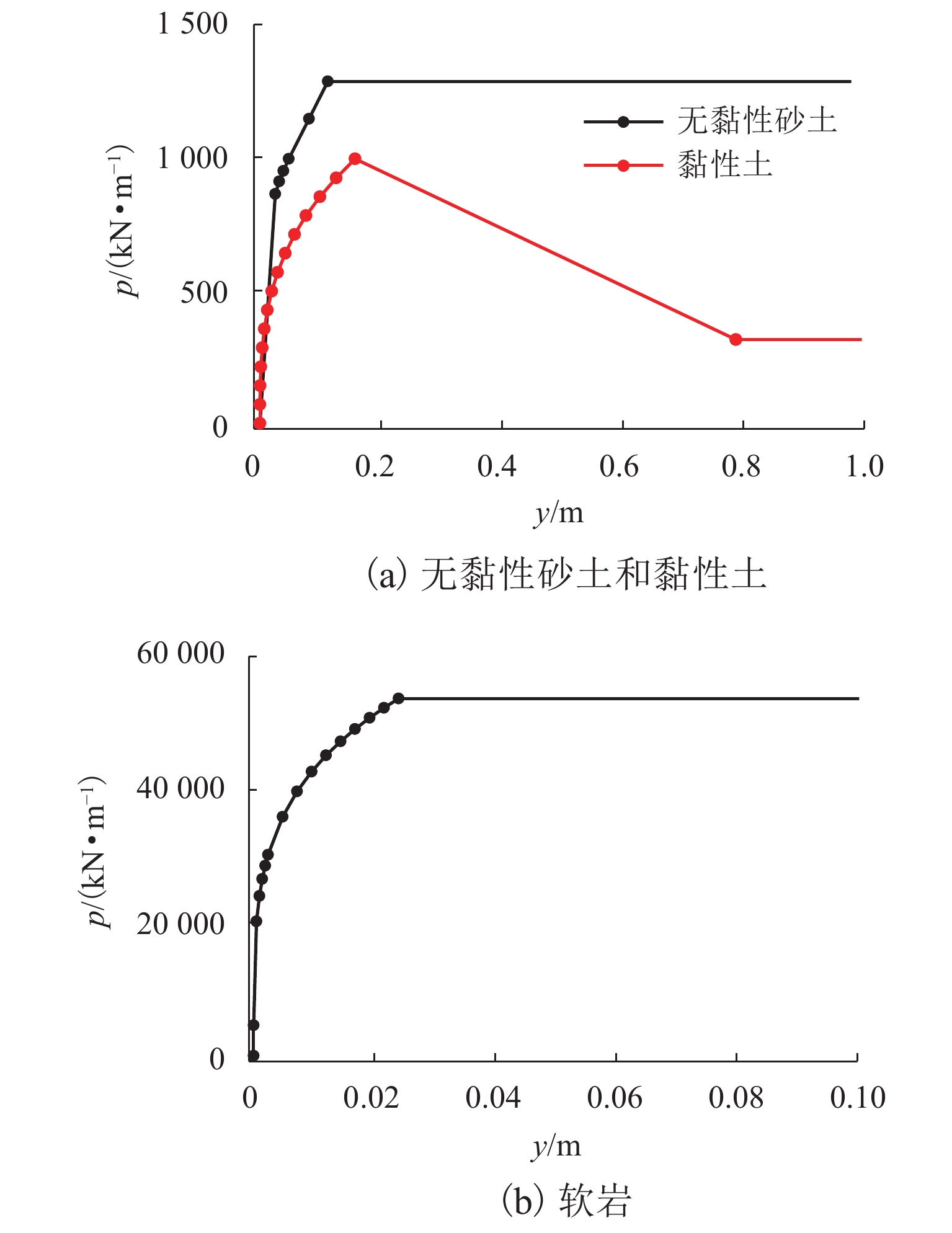
为研究冲刷效应对地震与风联合作用下大跨桥梁动力响应的影响,在已建立的地震-风-车-桥耦合振动分析模型基础上,利用
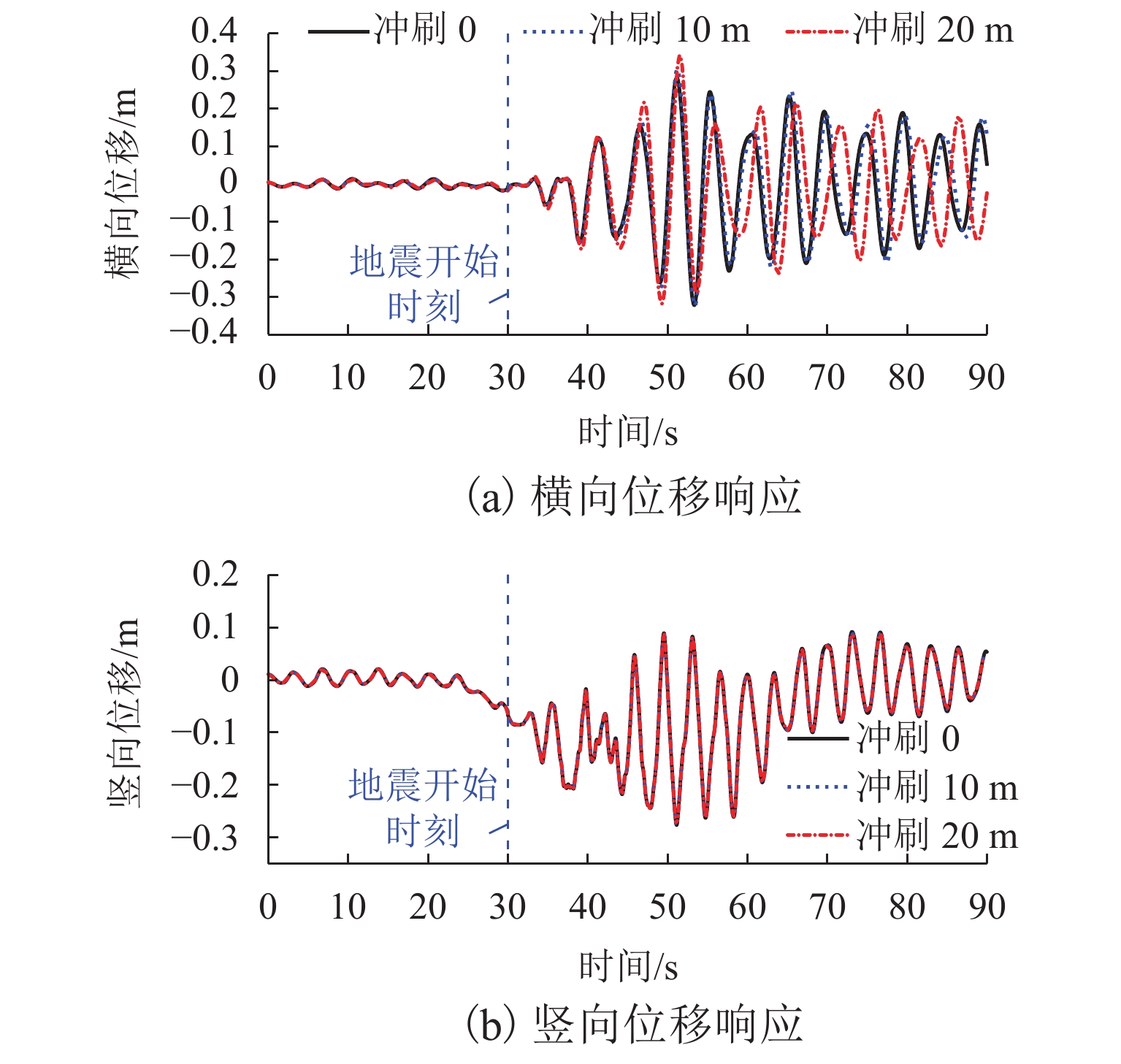
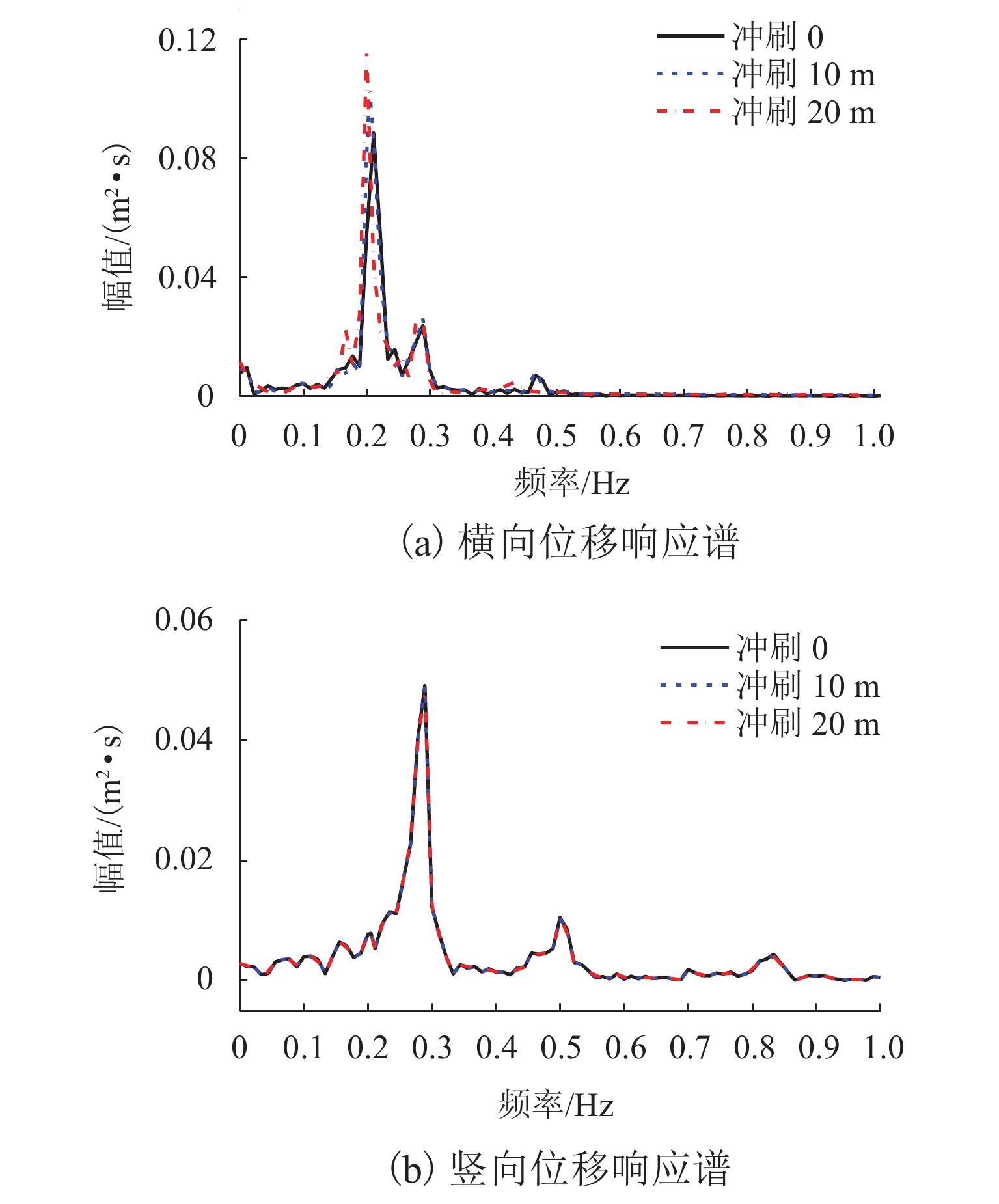
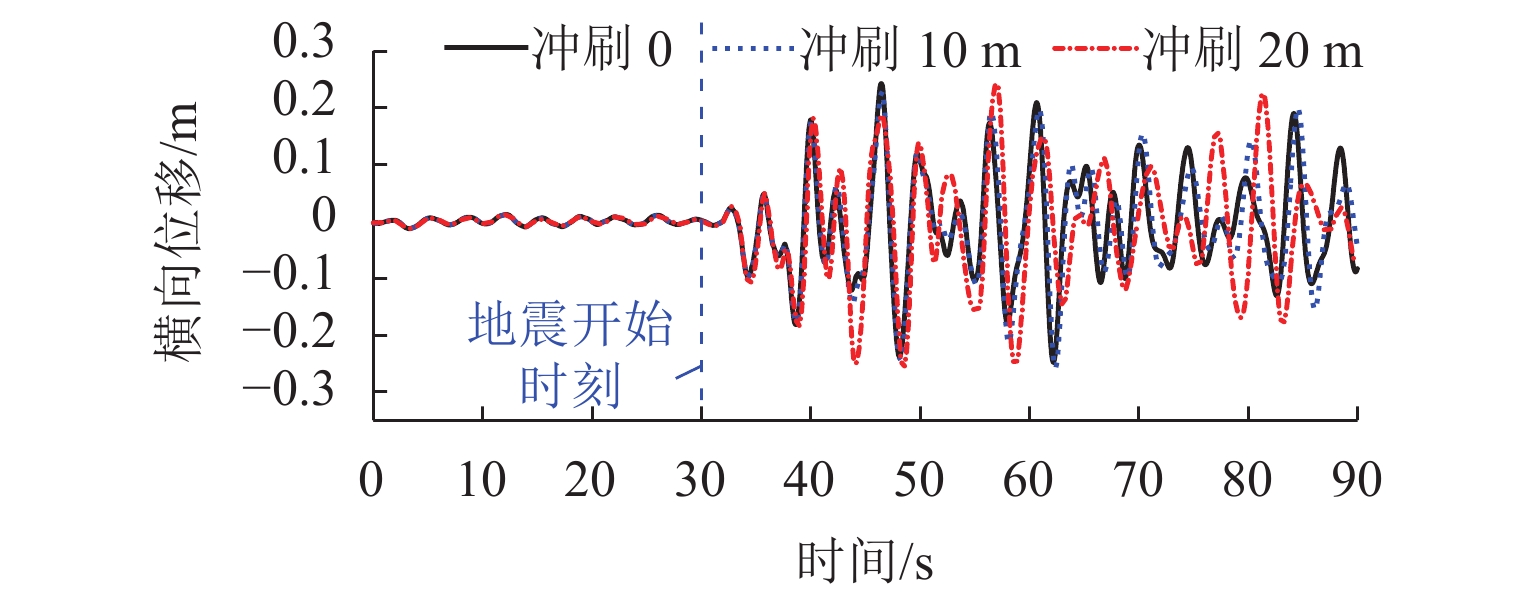
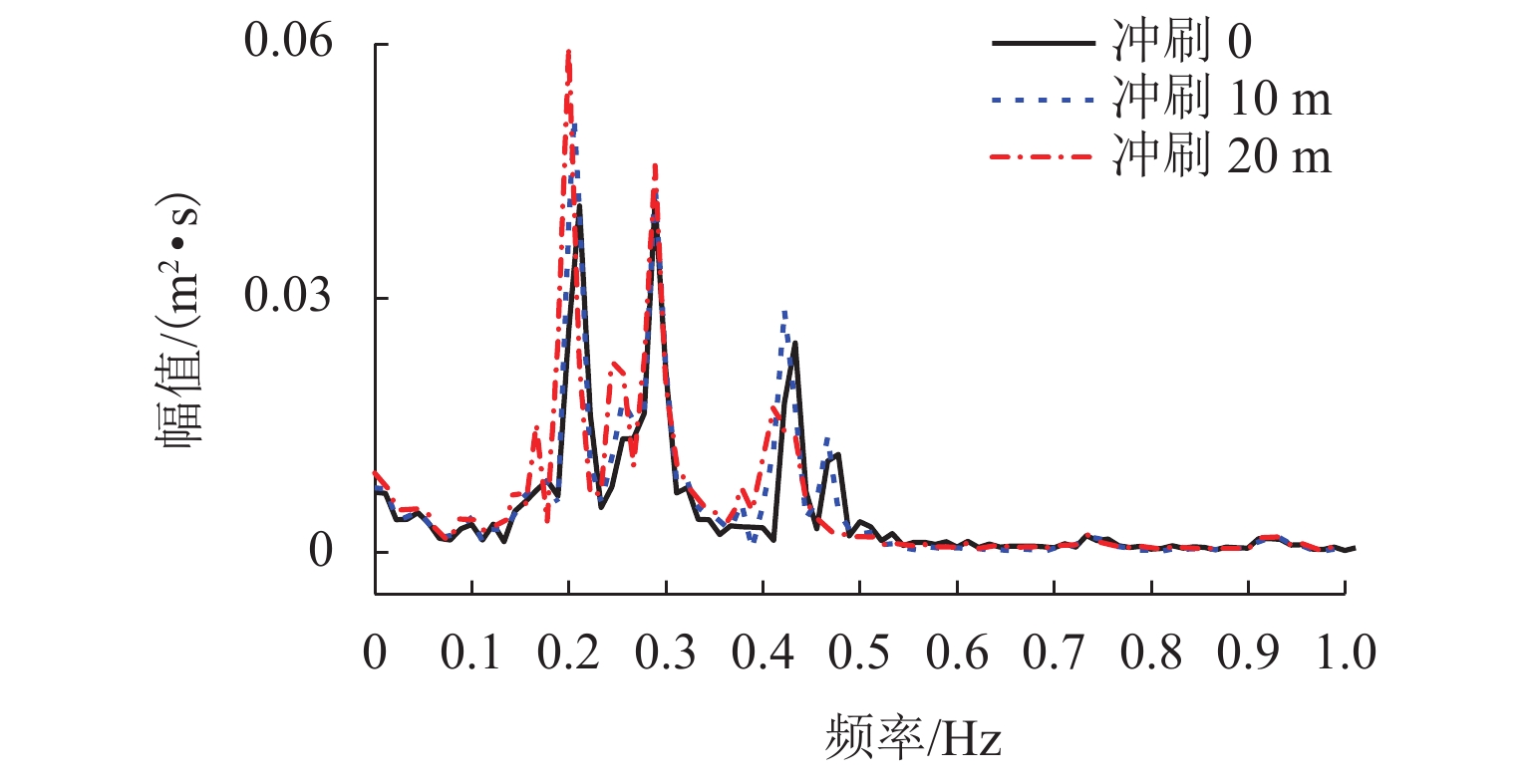
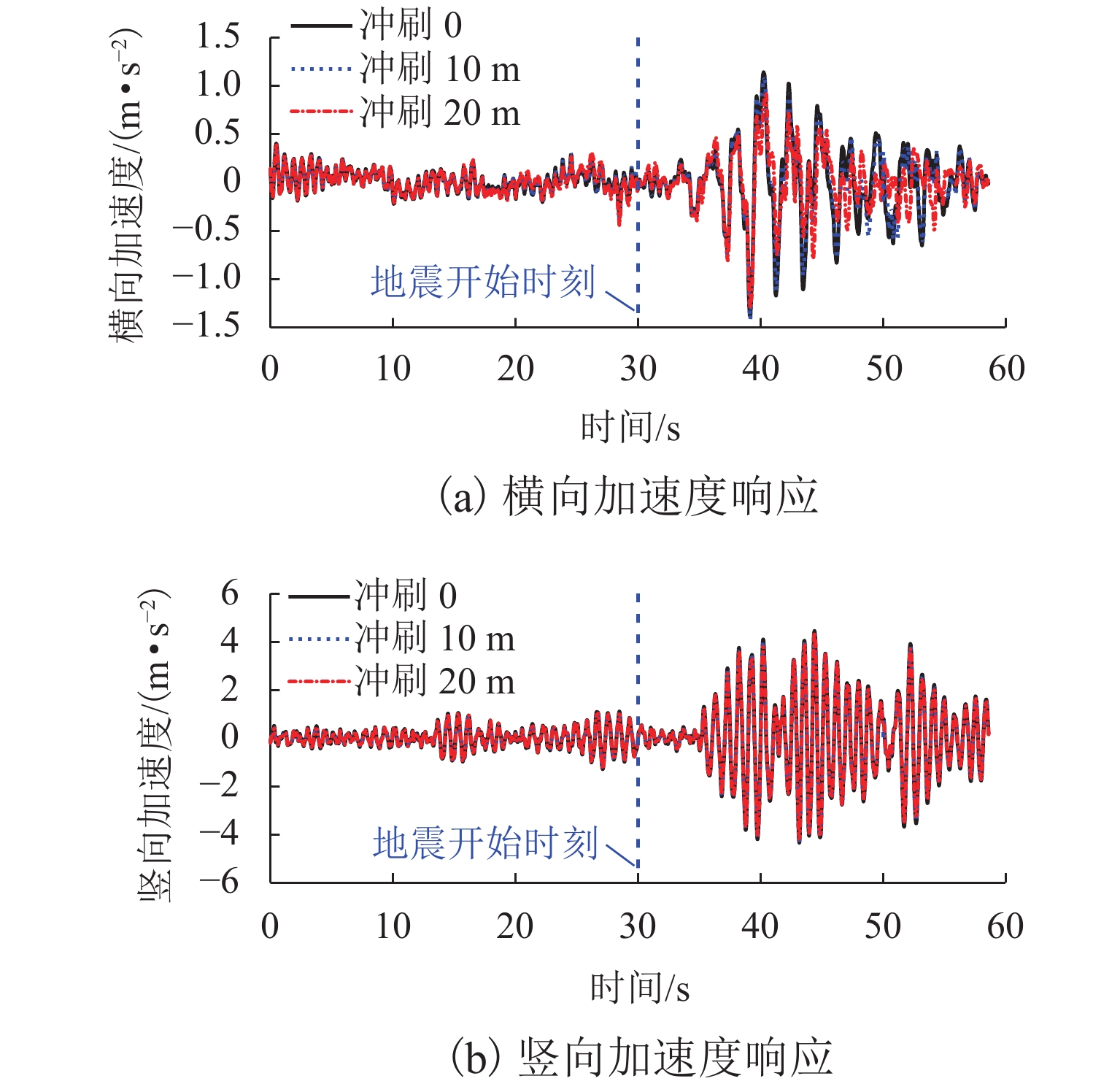
p -y 曲线(p 为土阻力,y 为变形)折减法考虑不同冲刷深度的桩土荷载-位移关系,根据桩土荷载-位移关系和冲刷深度更新桩基的侧向支撑刚度和长度,从而考虑了冲刷效应对大跨桥梁动力响应的影响,并将模型应用到江顺大桥冲刷效应的分析研究中. 研究结果表明:基础冲刷减弱了地基土对结构的侧向约束,从而降低结构的自振频率,侧向振型的自振频率最大降低6.01%;在运营车辆和风荷载作用下,基础冲刷对结构的振动响应影响很小;在地震发生后,基础冲刷会增大结构的横向振动,结构的横向位移响应极值最大增大9.1%,横向位移响应谱也相应增大,而对结构的竖向振动影响很小;基础冲刷可能减小车辆横向加速度的响应,车辆的横向加速度响应极值最大降低7.7%,对车辆的竖向振动影响很小.-
关键词:
- 冲刷效应 /
- p-y曲线 /
- 大跨桥梁 /
- 地震-风-车-桥系统 /
- 耦合振动
Abstract:In order to study the influence of the scouring effect on the dynamic response of long-span bridges under the combined action of earthquake and wind, based on the established coupled vibration analysis model of earthquake-wind-vehicle-bridge, the
p -y curve (p is the soil resistance andy is the pile displacement) reduction method was used to consider the load-displacement relationship between the piles and soil with different scour depths, and the lateral support stiffness and length of pile foundation were updated according to the load-displacement relationship and scour depth. Thus, the influence of the scouring effect on the dynamic response of long-span bridges was considered, and the model was applied to analyze the scouring effect of Jiangshun Bridge. The results show that the foundation scour weakens the lateral constraint of the foundation soil on the structure, thus reducing the natural vibration frequency of the structure, and the maximum reduction of the natural vibration frequency of lateral vibration mode is 6.01%; under the action of the operational vehicle and wind load, foundation scour has little effect on the vibration response of the structure; after the earthquake, the foundation scour increases the lateral vibration of the structure, and the maximum increase in the extreme value of the lateral displacement response of the structure is 9.1%; the lateral displacement response spectrum increases accordingly, but it has little effect on the vertical vibration of the structure; foundation scour may reduce the response of lateral acceleration of vehicles, and the maximum reduction of the extreme value of the lateral vehicle acceleration response is 7.7%, but it has little effect on the vertical vibration of vehicles. -
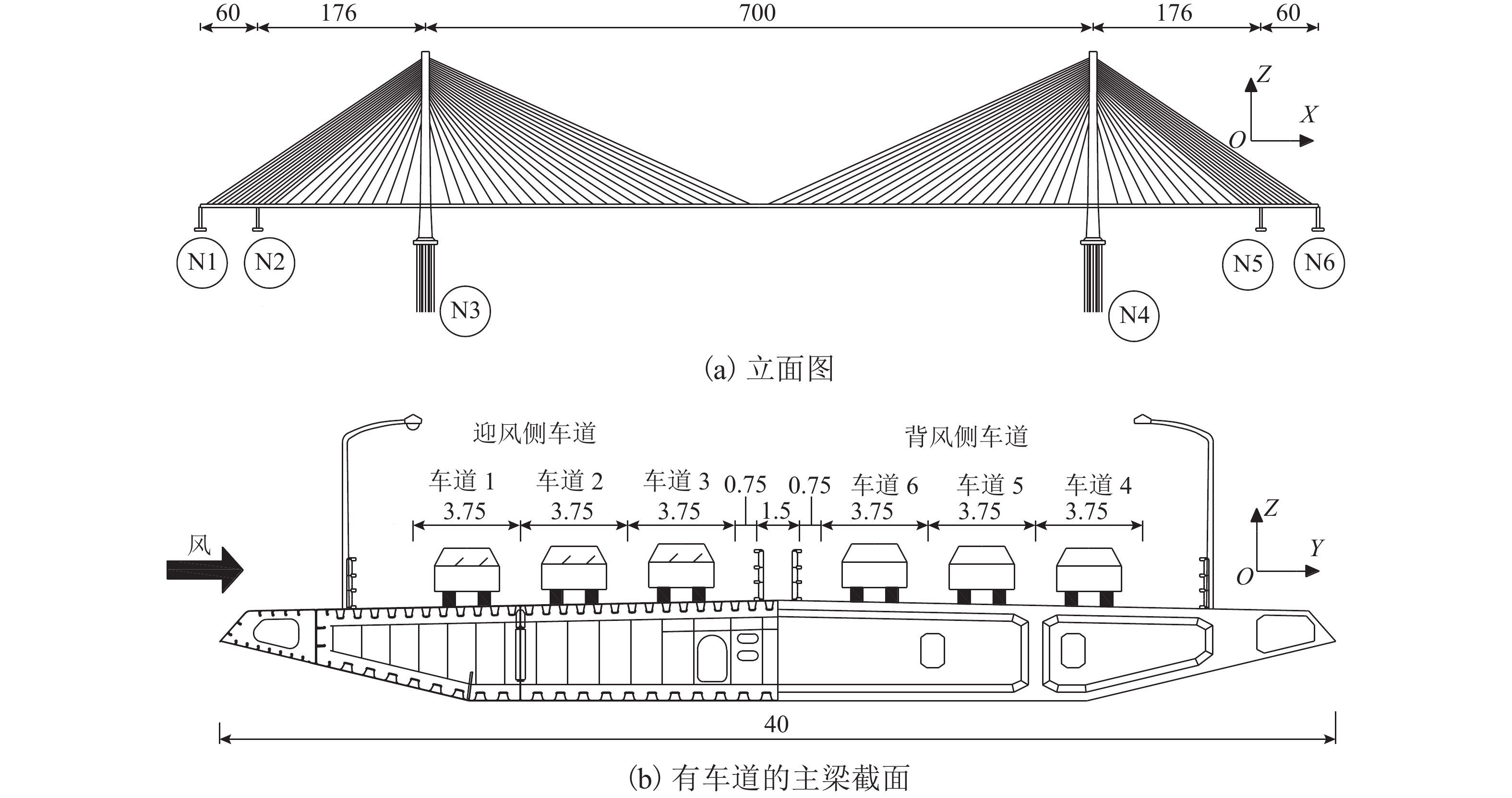
表 1 桥梁结构的前十阶自振频率和振型
Table 1. First 10 natural vibration frequencies and modes of bridge
振型数 自振频率/Hz 振型 1 0.0905 纵飘(主梁) 2 0.2029 1 阶对称侧弯(主梁、桥塔) 3 0.2572 1 阶反对称侧弯(主梁、桥塔) 4 0.2917 2 阶对称侧弯(主梁、桥塔) 5 0.2944 1 阶对称竖弯(主梁) 6 0.3331 1 阶反对称竖弯(主梁) 7 0.3450 2 阶对称竖弯(主梁) 8 0.3890 2 阶反对称竖弯(主梁) 9 0.4138 2 阶反对称侧弯(主梁、桥塔) 10 0.4274 1 阶对称扭转(主梁) 表 2 群桩基础处不同土层的物理和力学参数
Table 2. Physical and mechanical properties of different soil layers at group-pile foundation
土层 地基土
的类别土层
厚度/m重度/
(kN·m−3)排水剪切
强度/kPa内摩擦
角/(°)泊松比 弹性模量/
MPa单轴抗压
强度/MPa最大主应力为50% 的应变 应变
因子1 无黏性
砂土7.5 18 30 0.30 3 2 黏性土 10.0 20 93.8 0.35 21 0.007 3 软岩 29.5 22 0.25 7240 3.45 0.0005 表 3 不同冲刷深度时桥梁的自振频率
Table 3. Natural frequencies of the bridge under various scour depths
Hz 振型序号 冲刷深度 0 5 m 10 m 15 m 20 m 1 0.0905 0.0903 0.0902 0.0901 0.0894 2 0.2029 0.1994 0.1987 0.1984 0.1907 3 0.2572 0.2531 0.2523 0.2520 0.2428 4 0.2917 0.2912 0.2911 0.2910 0.2835 5 0.2944 0.2933 0.2928 0.2926 0.2899 6 0.3331 0.3261 0.3240 0.3229 0.2988 7 0.3450 0.3366 0.3342 0.3331 0.3138 8 0.3890 0.3860 0.3852 0.3848 0.3796 9 0.4138 0.4070 0.4058 0.4053 0.3864 10 0.4274 0.4179 0.4152 0.4139 0.3907 -
[1] WARDHANA K, HADIPRIONO F C. Analysis of recent bridge failures in the United States[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2003, 17(3): 144-150. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3828(2003)17:3(144) [2] DIAZ E E M, MORENO F N, MOHAMMADI J. Investigation of common causes of bridge collapse in Colombia[J]. Practice Periodical on Structural Design and Construction, 2009, 14(4): 194-200. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)SC.1943-5576.0000006 [3] 易仁彦,周瑞峰,黄茜. 近15年国内桥梁坍塌事故的原因和风险分析[J]. 交通科技,2015(5): 61-64.YI Renyan, ZHOU Ruifeng, HUANG Qian. Reason and risk of bridge collapse in recent 15 years[J]. Transportation Science & Technology, 2015(5): 61-64. [4] 商宇,叶爱君,王晓伟. 冲刷条件下的桩基桥梁振动台试验[J]. 中国公路学报,2017,30(12): 280-289.SHANG Yu, YE Aijun, WANG Xiaowei. Shake table test of pile supported bridge under scour condition[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(12): 280-289. [5] 梁发云,王琛,贾承岳,等. 冲刷深度对简支桥模态参数影响的模型试验[J]. 振动与冲击,2016,35(14): 145-150.LIANG Fayun, WANG Chen, JIA Chengyue, et al. Model test on the influence of scour depth on modal parameters of simply supported bridge[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(14): 145-150. [6] 熊文,邹晨,叶见曙. 基于动力特性识别的桥墩冲刷状态分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2017,30(5): 89-96.XIONG Wen, ZOU Chen, YE Jianshu. Condition assessment of bridge scour by tracing dynamic performances of bridges[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(5): 89-96. [7] CHEN C C, WU W H, SHIH F, et al. Scour evaluation for foundation of a cable-stayed bridge based on ambient vibration measurements of superstructure[J]. NDT & E International, 2014, 66: 16-27. [8] BAO T, LIU Z L, BIRD K. Influence of soil characteristics on natural frequency-based bridge scour detection[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 446: 195-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.01.040 [9] MALEKJAFARIAN A, PRENDERGAST L J, OBRIEN E. Use of mode shape ratios for pier scour monitoring in two-span integral bridges under changing environmental conditions[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2020, 47(8): 962-973. doi: 10.1139/cjce-2018-0800 [10] KHAN M A, MCCRUM D P, PRENDERGAST L J, et al. Laboratory investigation of a bridge scour monitoring method using decentralized modal analysis[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2021, 20(6): 3327-3341. doi: 10.1177/1475921720985122 [11] 李克冰,张楠,方翔宇,等. 考虑河流冲刷作用的车桥耦合系统动力分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2014,33(19): 40-47,73.LI Kebing, ZHANG Nan, FANG Xiangyu, et al. Dynamic analysis of a vehicle-bridge coupled system considering river scouring[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(19): 40-47,73. [12] KONG X, CAI C S. Scour effect on bridge and vehicle responses under bridge-vehicle-wave interaction[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(4): 04015083.1-04015083.16. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000868 [13] WANG Z H, DUEÑAS -OSORIO L, PADGETT J E. Influence of scour effects on the seismic response of reinforced concrete bridges[J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 76: 202-214. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.06.026 [14] 杨婷婷,李岩,林雪琦. 基于车辆制动激励和小波包能量分析的连续梁桥基础冲刷识别方法[J]. 中国公路学报,2021,34(4): 51-60.YANG Tingting, LI Yan, LIN Xueqi. Foundation scour identification method based on vehicle braking excitation and wavelet packet energy analysis for continuous beam bridges[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(4): 51-60. [15] 李岩,张振浩,林国伟,等. 基础冲刷对多种车激作用下桥梁动力行为的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2021,53(9): 17-25.LI Yan, ZHANG Zhenhao, LIN Guowei, et al. Scour effect on dynamic performance of bridges under excitations of vehicles with various driving conditions[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021, 53(9): 17-25. [16] WEI K, HE H F, ZHANG J R, et al. An endurance time method-based fragility analysis framework for cable stayed bridge systems under scour and earthquake[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 232: 109128.1-109128.12. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109128 [17] REESE L C. LPILE Plus 3.0: A program for the analysis of piles and drilled shafts under lateral loads[CP]. Austin: Ensoft, 1997. [18] LI W, IGOE D, GAVIN K. Evaluation of CPT-based p-y models for laterally loaded piles in siliceous sand[J]. Géotechnique Letters, 2014, 4(2): 110-117. [19] YANG K J, LI Q X, WANG F Y. Behavior of pile groups under lateral load[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 1991, 5(2): 235-244. [20] 谢耀峰. 横向承载群桩性状及承载力研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,1996,18(6): 39-45.XIE Yaofeng. Behavior and bearing capacity of laterally loaded pile groups[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1996, 18(6): 39-45. [21] ZHU J, ZHANG W, WU M X. Coupled dynamic analysis of the vehicle-bridge-wind-wave system[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2018, 23(8): 04018054.1-04018054.17. [22] BAKER C J. A simplified analysis of various types of wind-induced road vehicle accidents[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1986, 22(1): 69-85. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(86)90012-7 [23] LI Y L, QIANG S Z, LIAO H L, et al. Dynamics of wind-rail vehicle-bridge systems[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2005, 93: 483-507. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2005.04.001 [24] LÉGER P, IDÉ I M, PAULTRE P. Multiple-support seismic analysis of large structures[J]. Computers & Structures, 1990, 36(6): 1153-1158. [25] HAN Y, LIU S, HU J X, et al. Experimental study on aerodynamic derivatives of a bridge cross-section under different traffic flows[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2014, 133: 250-262. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2014.08.003 [26] HAN Y, HU J X, CAI C S, et al. Experimental and numerical studies of aerodynamic forces on vehicles and bridges[J]. Wind and Structures, 2013, 17(2): 163-184. doi: 10.12989/was.2013.17.2.163 [27] American Association of State Highway Transportation Officials (AASHTO). Guide specifications for bridges vulnerable to coastal storms[S]. Washington D. C.: IHS Markit, 2008. -




 下载:
下载: