Intelligent Evaluation Method for Ball Screw Degradation State
-
摘要:
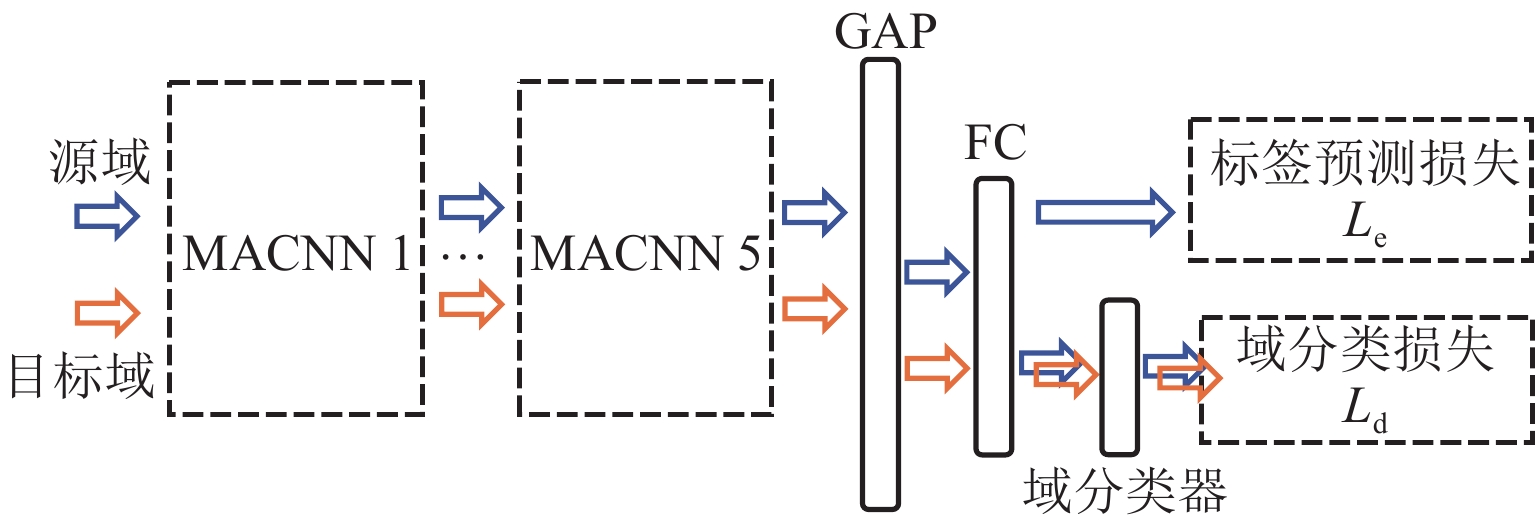
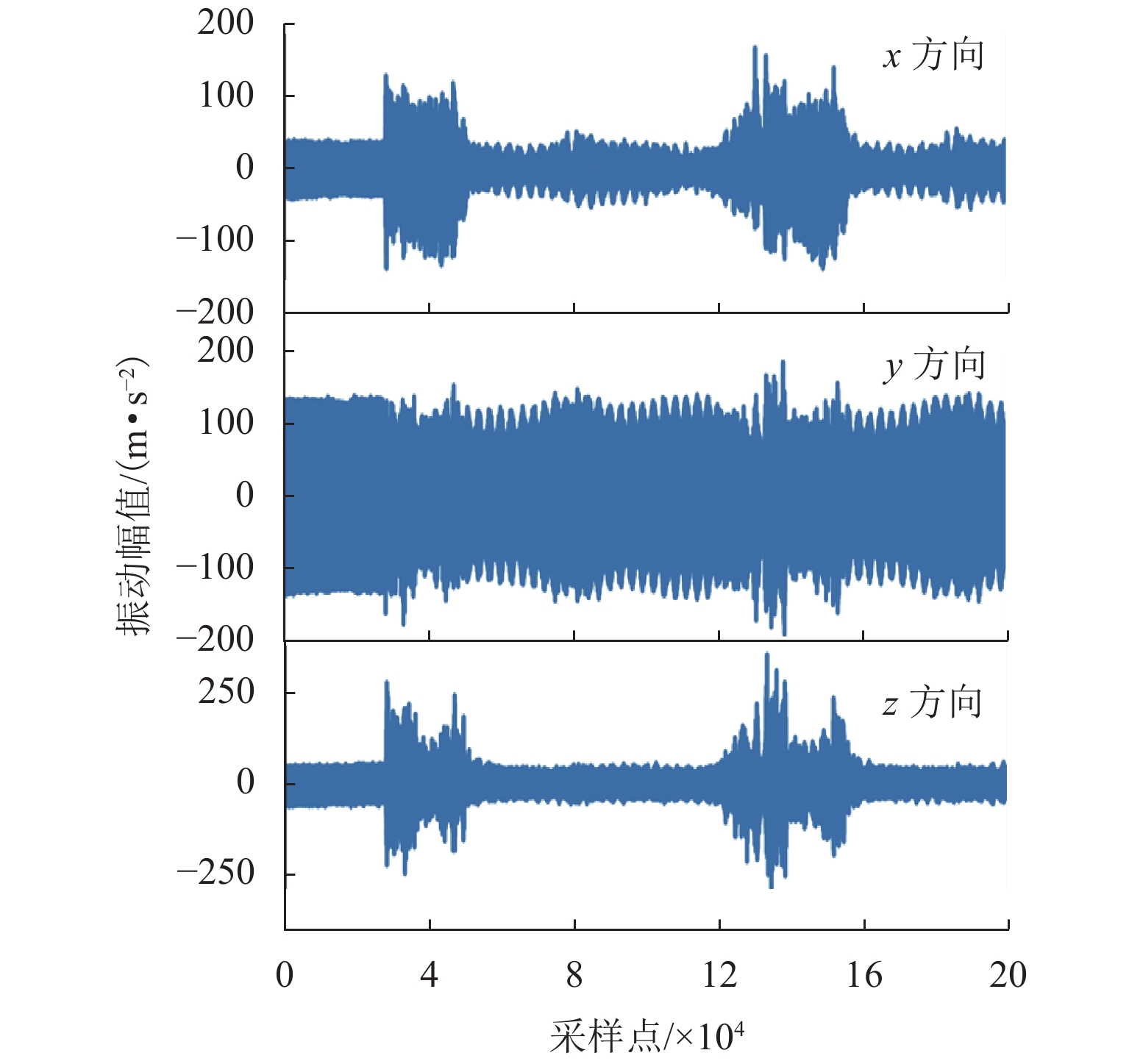
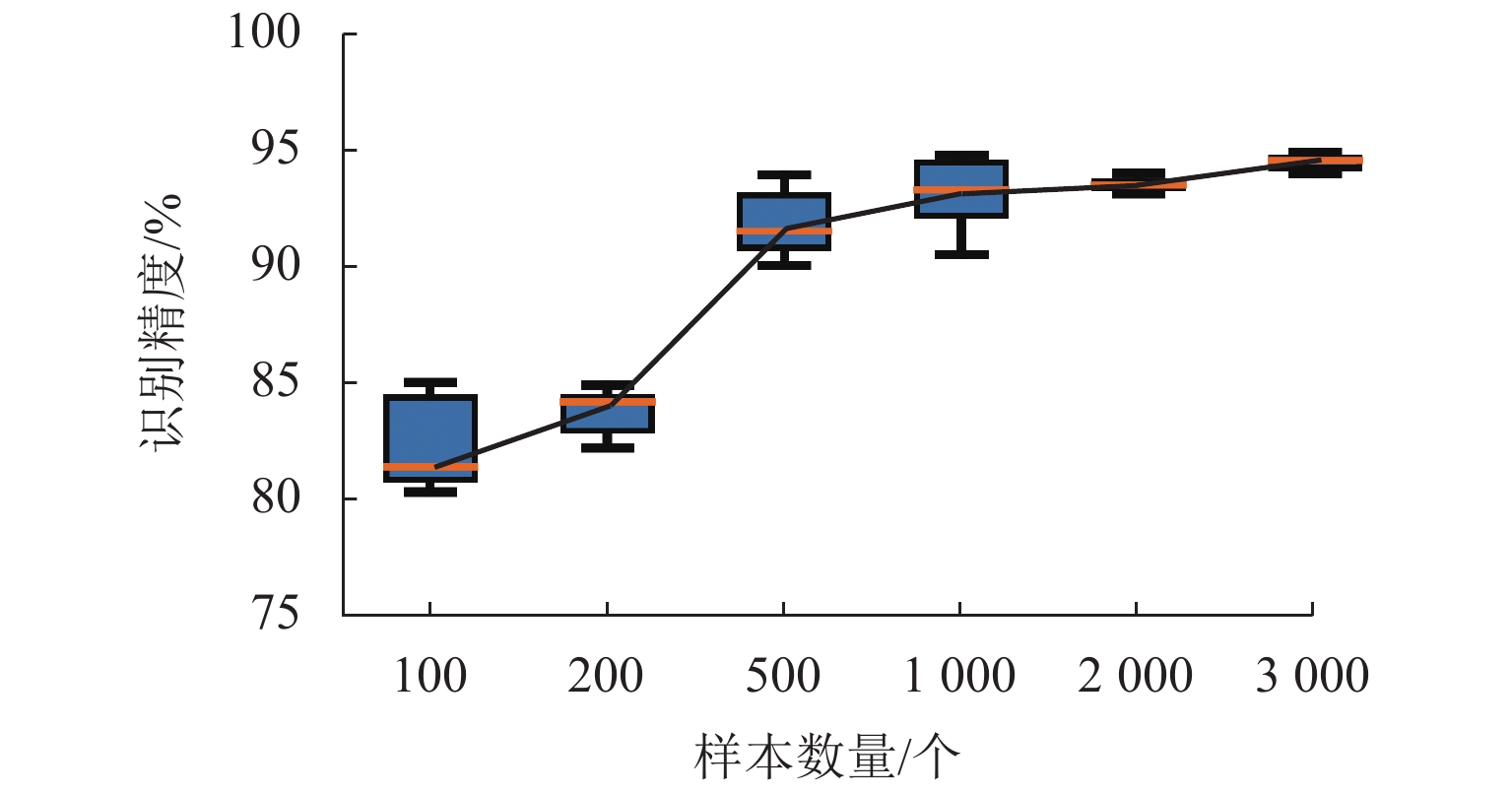
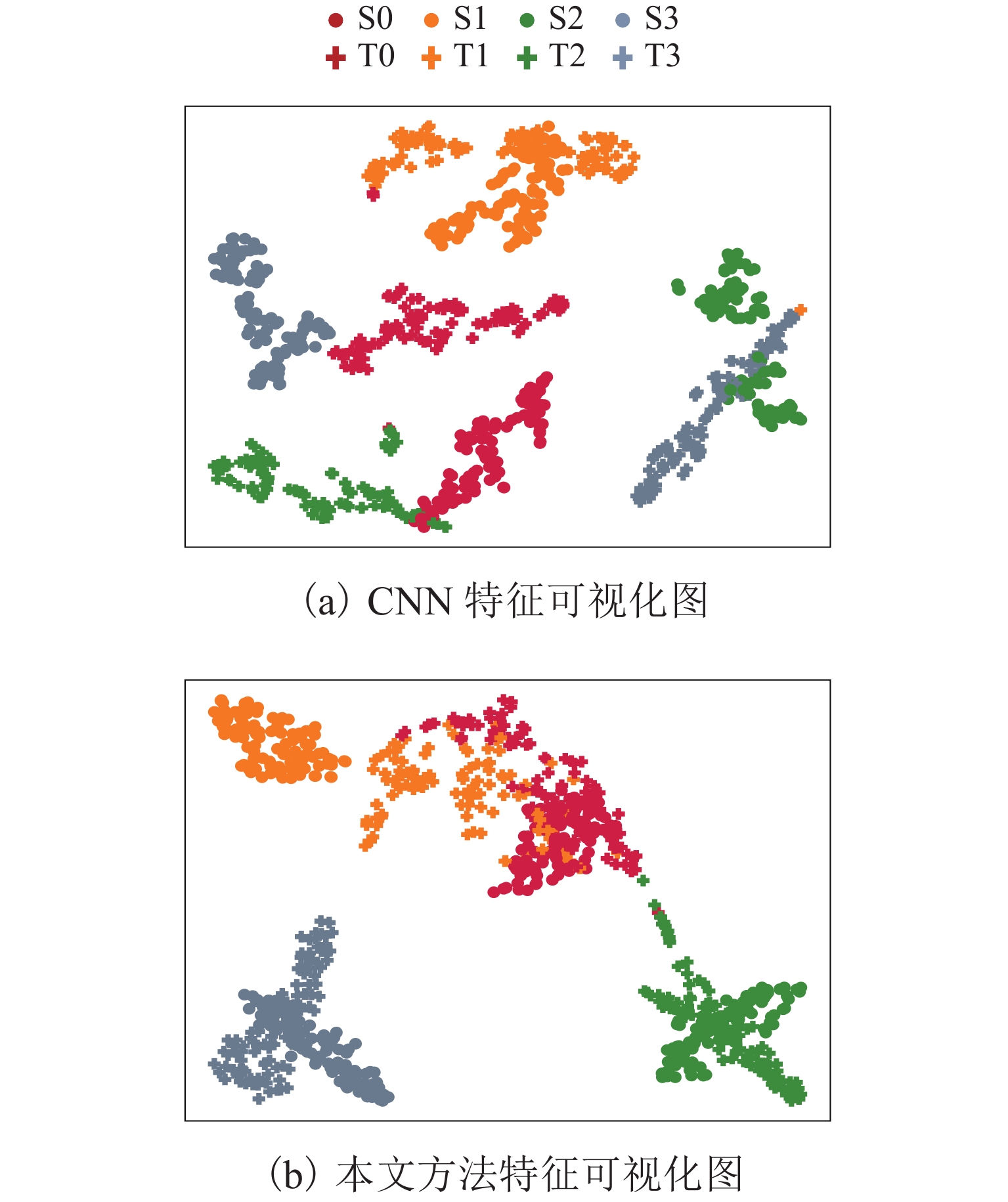
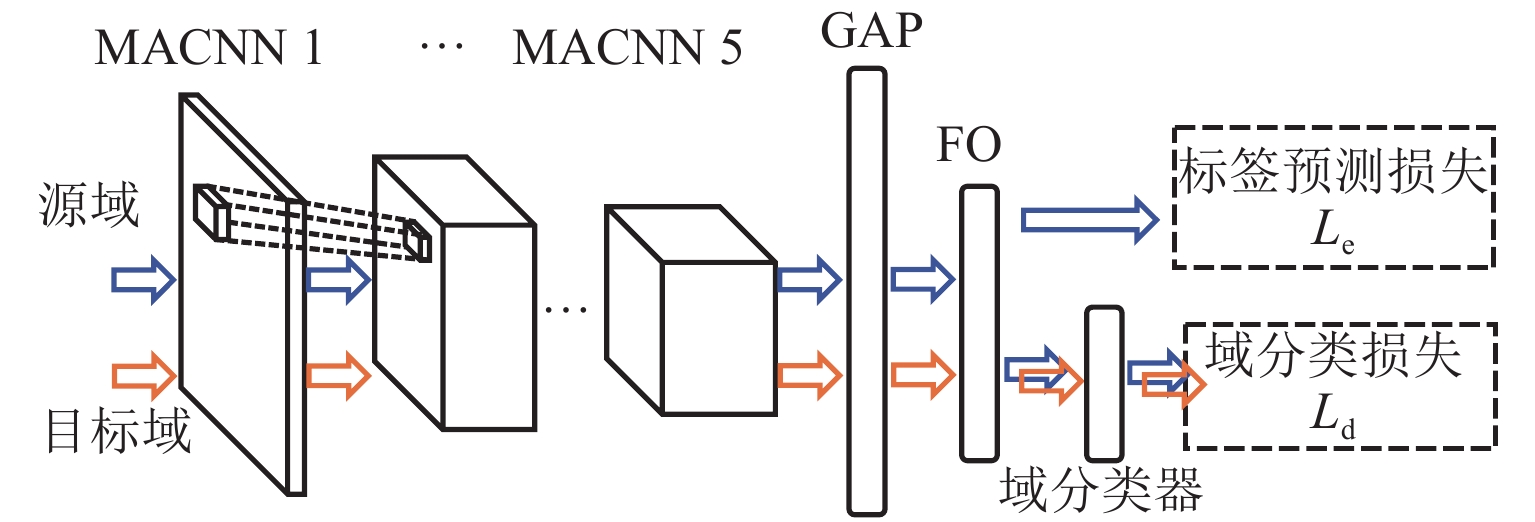
现有滚珠丝杠副退化状态评估方法通常假设已有充足且带标签的数据集,但实际工程应用中故障成本过高、获取标签难度过大,难以在特定工况下获得大量带标签数据集. 针对上述问题,提出一种基于多尺度对抗域对抗学习的智能化状态评估方法,结合注意力卷积神经网络模块和域对抗学习模块,利用不同工况下采集的传感器信号建立深度学习模型,从而自适应地学习域不变特征并实现高效的知识复用和特征迁移;利用多工况下采集的滚珠丝杠副退化信号构建试验数据集来验证方法的有效性. 研究结果表明:本文方法在6个标签缺失跨工况条件下的滚珠丝杠副退化状态识别子任务中均取得了高于89.02%的识别准确率;能够充分迁移带标签数据的关键特征,实现了标签样本缺失条件下目标工况退化状态识别.
Abstract:The existing ball screw degradation assessment method usually assumes that sufficient labeled data sets are available. However, it is difficult to obtain massive labeled data sets under practical projects due to excess failure cost and difficulty of obtaining labels. To solve the above problems, an intelligent state evaluation method based on multi-scale adversarial domain adversarial learning is proposed. Combining an attention convolution neural network module and a domain adversarial learning module, a deep learning model is established by using sensor signals collected under different working conditions, so as to learn domain invariant features adaptively and realize efficient knowledge reuse and feature migration. The experimental data sets are constructed by using the ball screw degradation signals collected under multiple working conditions to verify the effectiveness of the method. The results show that the proposed method achieves a recognition accuracy higher than 89.02% in six sub-tasks of degradation state identification of ball screw under cross-working conditions with missing labels. The proposed method can fully migrate key features with labeled data and achieve the degradation state identification of target operating conditions under missing label samples.
-
Key words:
- ball screw /
- degradation state evaluation /
- deep learning /
- domain adversarial learning
-
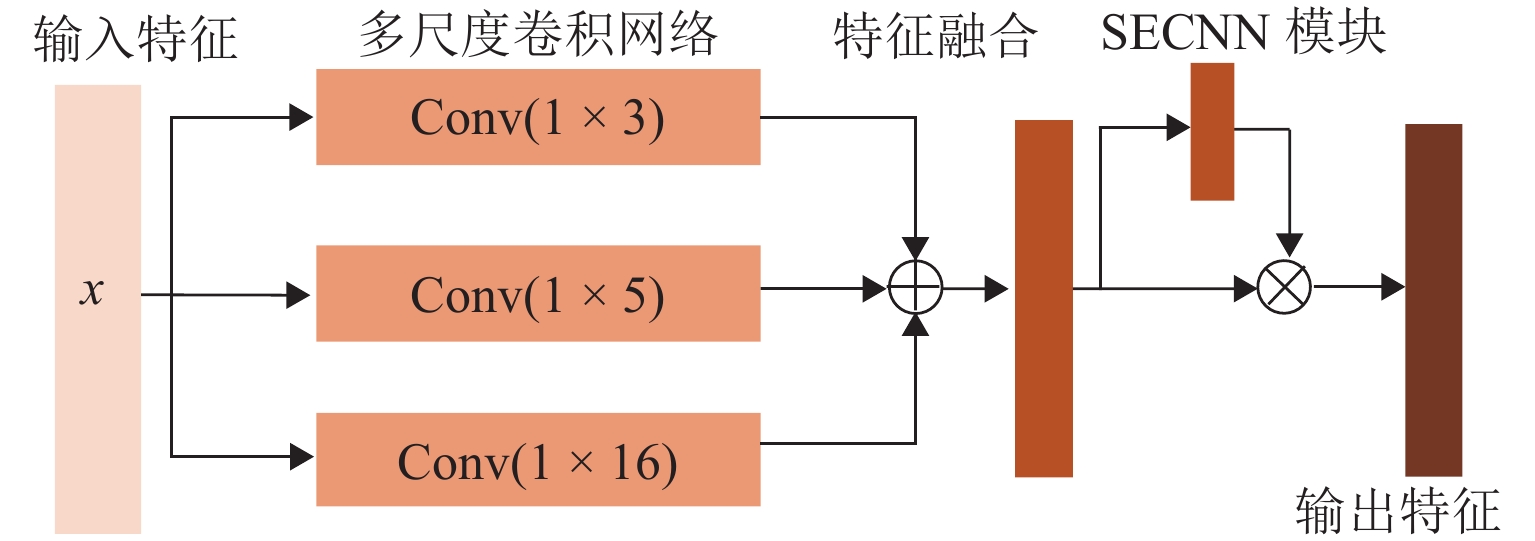
表 1 MACNN模块基础参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of the MACNN modules
模块名 卷积核大小 卷积核个数 MACNN 1 3 × 1/5 × 1/16 × 1 1 × 3 MACNN 2 3 × 1/5 × 1/16 × 1 10 × 3 MACNN 3 3 × 1/5 × 1/16 × 1 10 × 3 MACNN 4 3 × 1/5 × 1/16 × 1 10 × 3 MACNN 5 3 × 1/5 × 1/16 × 1 10 × 3 表 2 所选FFZD4010-3型滚珠丝杠副基础参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of selected FFZD4010-3 ball screw
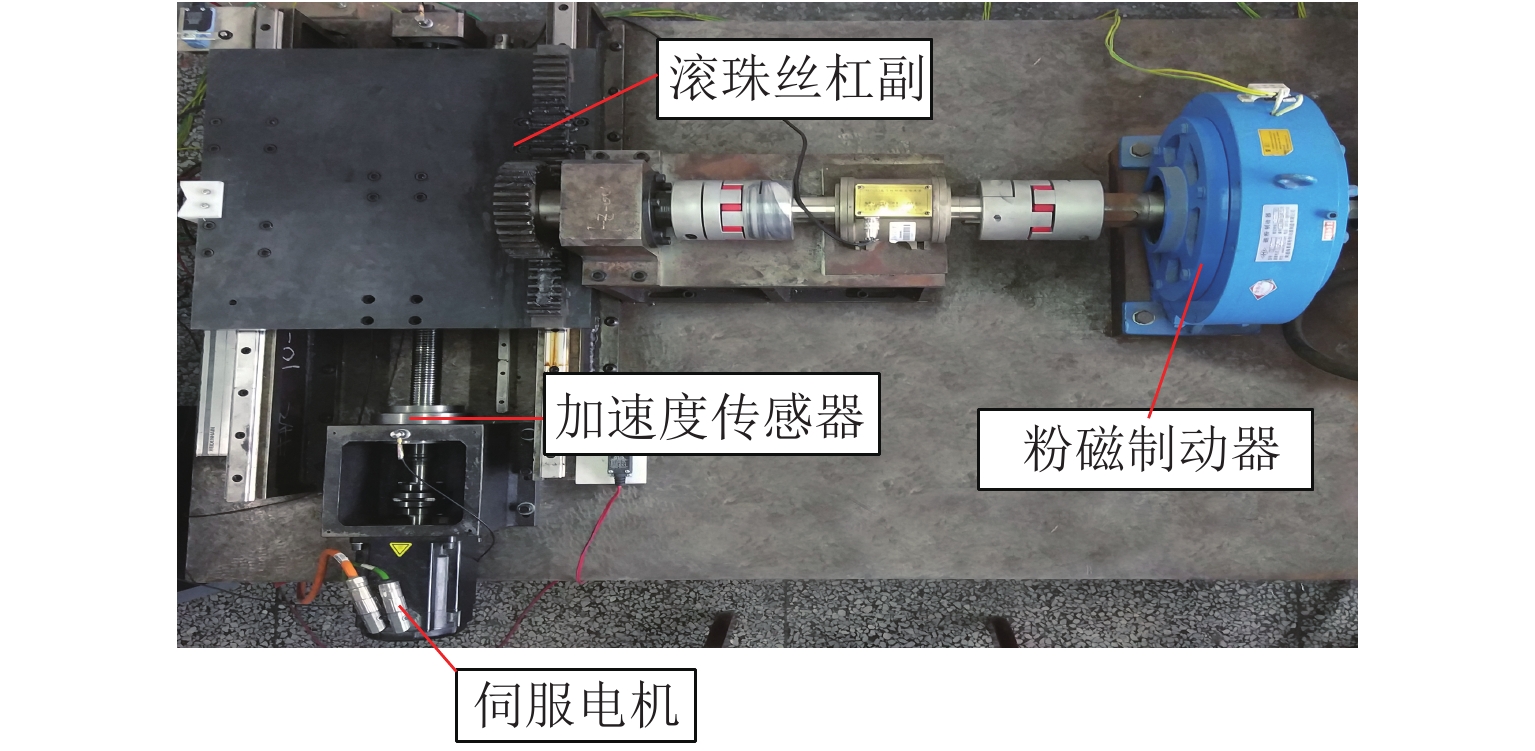
参数 取值 参数 取值 公称直径/mm 40 丝杠底径/mm 34.3 导程/mm 10 循环总圈数/圈 3 丝杠外径/mm 39.5 额定动载荷/kN 30 滚珠直径/mm 7.14 额定静载荷/kN 66.3 表 3 试验工况详细参数
Table 3. Detailed parameters of test working conditions
工况 轴向载荷/kN 丝杠转速/(r•min−1) 1 0 100 2 1 300 3 2 800 表 4 滚珠丝杠副退化状态识别试验
Table 4. Ball screw degradation state identification test
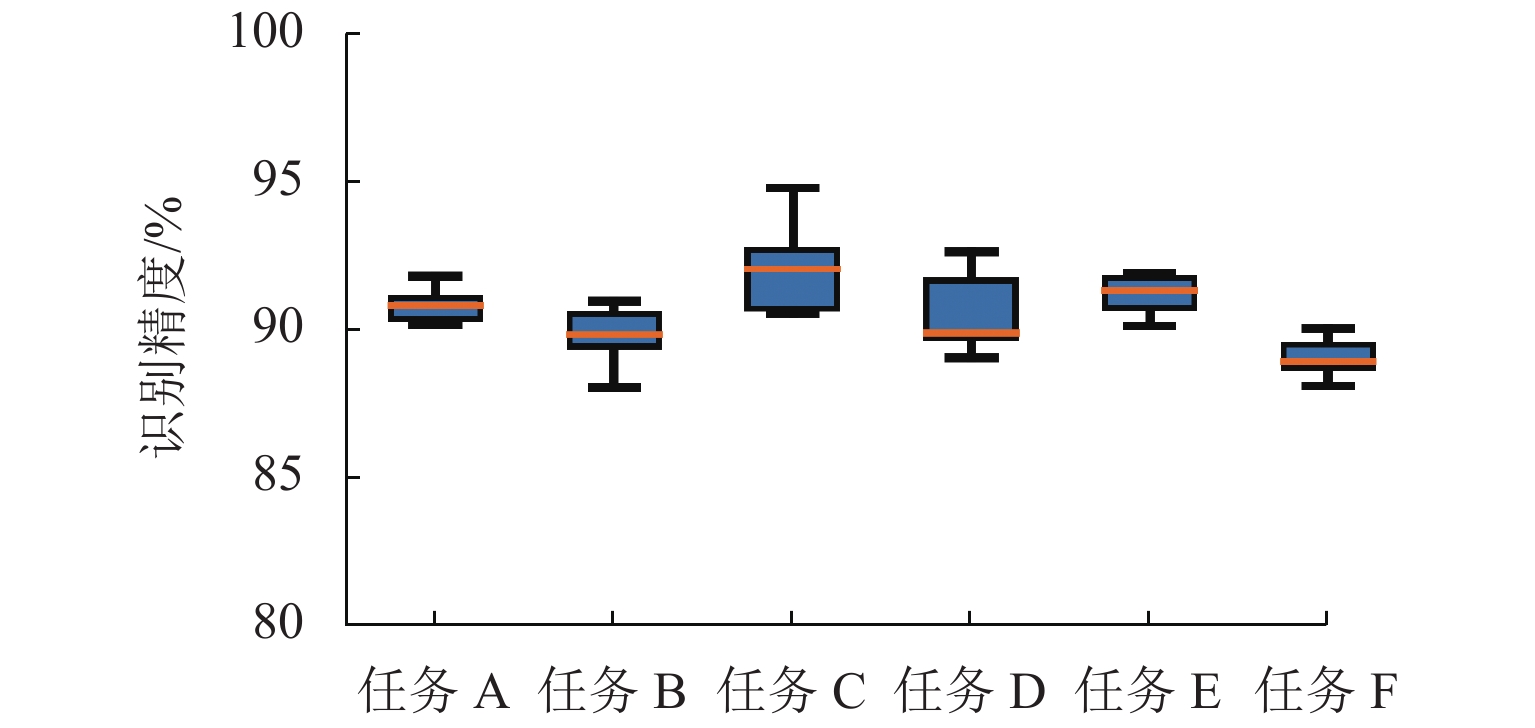
名称 详情 名称 详情 任务 A 工况 1→工况 2 任务 D 工况 2→工况 3 任务 B 工况 1→工况 3 任务 E 工况 3→工况 1 任务 C 工况 2→工况 1 任务 F 工况 3→工况 2 表 5 退化状态识别试验结果
Table 5. Results of degradation state identification tests
% 名称 识别精度 名称 识别精度 任务 A 90.76 任务 D 90.51 任务 B 89.75 任务 E 91.17 任务 C 92.13 任务 F 89.02 表 6 所提方法与对比方法的结果比较
Table 6. Comparison between the proposed method and the state-of-the-art methods
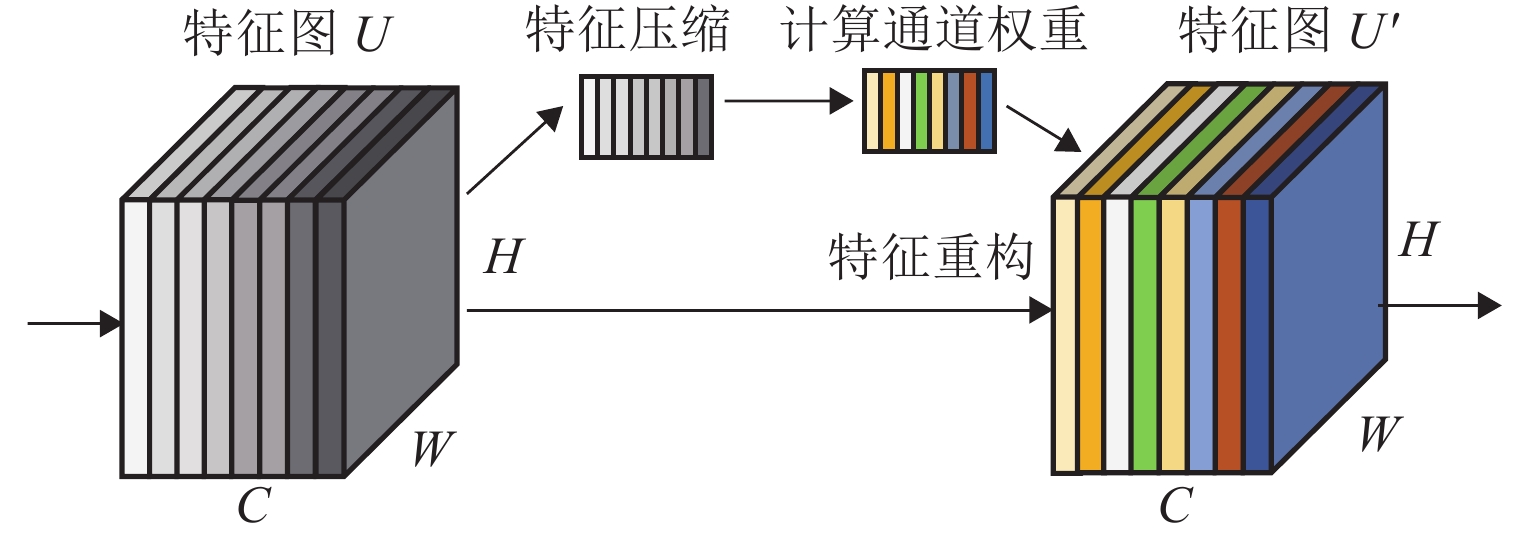
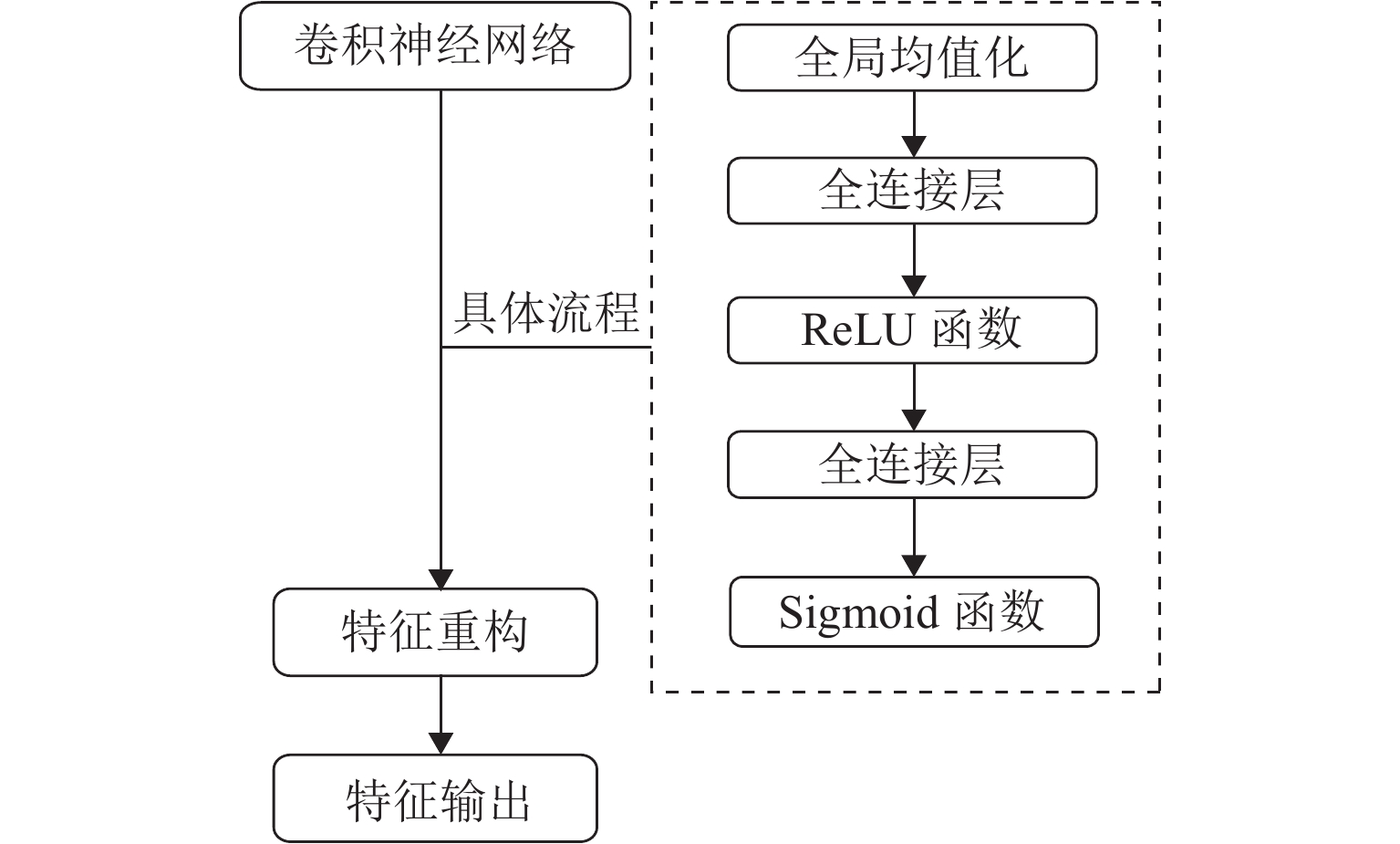
名称 识别精度/% 精度标准差 CNN 73.57 5.33 JDAN 86.24 0.70 DANN 87.26 1.47 本文所提方法 91.84 1.28 -
[1] GUO L, YU Y X, DUAN A, et al. An unsupervised feature learning based health indicator construction method for performance assessment of machines[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 167: 108573.1-108573.17. [2] GUO L, YU Y X, GAO H L, et al. Online remaining useful life prediction of milling cutters based on multisource data and feature learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(8): 5199-5208. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3118994 [3] 潘承莹,祖莉,周长光,等. 基于滚珠丝杠副滚道磨损的摩擦力矩计算与试验[J]. 振动与冲击,2021,40(24): 212-220.PAN Chengying, ZU Li, ZHOU Changguang, et al. Calculation and test of the friction torque based on the wear depth of ball screw pairs[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(24): 212-220. [4] ZHANG L, GUO L, GAO H L, et al. Instance-based ensemble deep transfer learning network: a new intelligent degradation recognition method and its application on ball screw[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 140: 106681.1-106681.14. [5] 林志斌, 高宏力, 吴昱东, 等. 基于EWT-KLD的机械密封金刚石涂层磨损声发射降噪[J/OL]. 西南交通大学学报. [2021-10-12]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20211102.1813.002.html.LIN Zhibin, GAO Hongli, WU Yudong, et al. Denoising of acoustic emission of diamond-coated mechanical seals wear based-on empirical wavelet transform and kullback-leibler divergence[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University. [2021-10-12]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1277.U.20211102.1813.002.html. [6] CHEN K, ZU L, WANG L. Prediction of preload attenuation of ball screw based on support vector machine[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 10(9): 168781401879916.1-168781401879916.10 [7] GOU J P, MA H X, OU W H, et al. A generalized mean distance-based K-nearest neighbor classifier[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2019, 115: 356-372. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.021 [8] SHORTEN C, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M, FURHT B. Deep learning applications for COVID-19[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2021, 8(1): 1-54. doi: 10.1186/s40537-020-00387-6 [9] ZHANG H, XU H, TIAN X, et al. Image fusion meets deep learning: a survey and perspective[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 76: 323-336. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.06.008 [10] VASHISHT R K, PENG Q J. Online chatter detection for milling operations using LSTM neural networks assisted by motor current signals of ball screw drives[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2021, 143(1): 011008.1-011008.15. [11] LONG X F, LI S Q, WU X W, et al. Wind turbine anomaly identification based on improved deep belief network with SCADA data[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 8810045.1-8810045.15. [12] BASIRI M E, NEMATI S, ABDAR M, et al. ABCDM: an Attention-based Bidirectional CNN-RNN Deep Model for sentiment analysis[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2021, 115: 279-294. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.08.005 [13] YU L A, ZHOU R T, TANG L, et al. A DBN-based resampling SVM ensemble learning paradigm for credit classification with imbalanced data[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 69: 192-202. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.04.049 [14] 周文宣,刘洋,邓敏强,等. 基于CAE和CNN的变工况下滚动轴承智能故障诊断研究[J]. 动力工程学报,2022,42(1): 43-48.ZHOU Wenxuan, LIU Yang, DENG Minqiang, et al. Research on intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearings under variable conditions based on CAE and CNN[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2022, 42(1): 43-48. [15] LI Y B, SONG Y, JIA L, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis by fusing domain adversarial training and maximum mean discrepancy via ensemble learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(4): 2833-2841. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3008010 [16] AZAMFAR M, LI X, LEE J. Intelligent ball screw fault diagnosis using a deep domain adaptation methodology[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2020, 151: 103932.1-103932.18. [17] ZHU Z Y, WANG L Z, PENG G L, et al. WDA: an improved Wasserstein distance-based transfer learning fault diagnosis method[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(13): 4394.1-4394.19. [18] WU L, LI C Y, CHEN Q L, et al. Deep adversarial domain adaptation network[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2020, 17(5): 106236.1-106236.10. [19] 董靖川, 谭志兰, 王太勇, 等. 结合域对抗自适应的刀具磨损预测方法[J/OL]. 机械科学与技术. [2021-10-12] https://doi.org/10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200614.DONG Jingchuan, TAN Zhilan, WANG Taiyong, et al. Tool wear prediction method combined with domain adversarial adaptation[J/OL]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering. [2021-10-12] https://doi.org/10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200614. [20] GUO L, LEI Y G, XING S B, et al. Deep convolutional transfer learning network: a new method for intelligent fault diagnosis of machines with unlabeled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(9): 7316-7325. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2877090 [21] TAN Y W, GUO L, GAO H L, et al. MiDAN: a framework for cross-domain intelligent fault diagnosis with imbalanced datasets[J]. Measurement, 2021, 183: 109834.1-109834.12. [22] 崔新明,贾宁,周洁美慧. 基于条件生成式对抗网络的情感语音生成模型[J]. 计算机系统应用,2022,31(1): 322-326.CUI Xinming, JIA Ning, ZHOU Jiemeihui. Speech generation model based on conditional generative adversarial network[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2022, 31(1): 322-326. [23] PENG D D, WANG H, LIU Z L, et al. Multibranch and multiscale CNN for fault diagnosis of wheelset bearings under strong noise and variable load condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4949-4960. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2967557 [24] HU J, SHEN L, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [25] HAN T, LIU C, YANG W G, et al. Deep transfer network with joint distribution adaptation: a new intelligent fault diagnosis framework for industry application[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 97: 269-281. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.012 -




 下载:
下载: