Lightweight Detection of Railway Object Intrusion Based on Spectral Pooling and Shuffled-Convolutional Block Attention Module Enhancement
-
摘要:
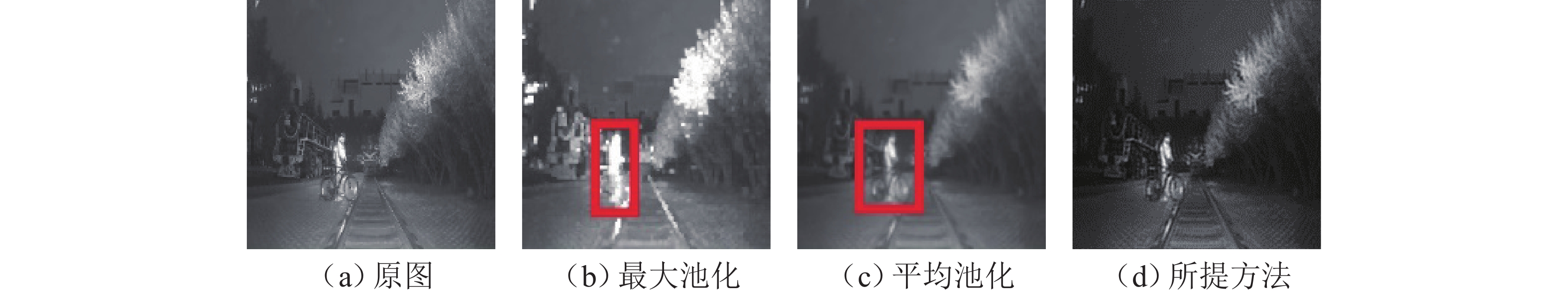
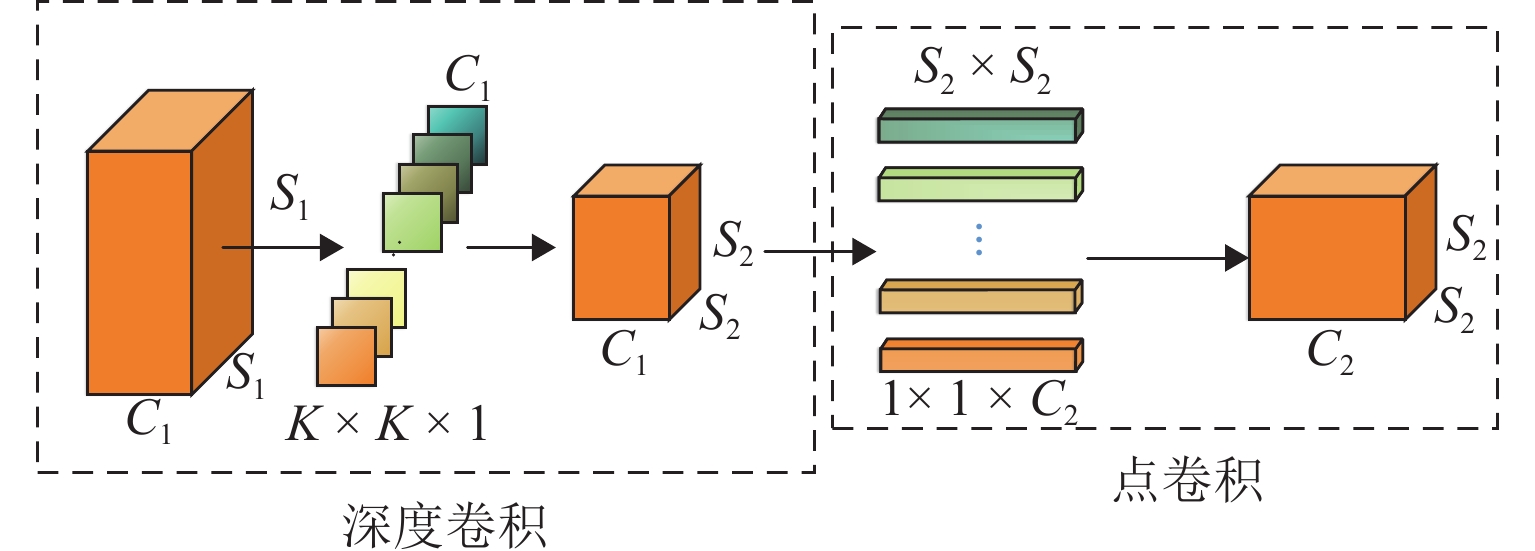
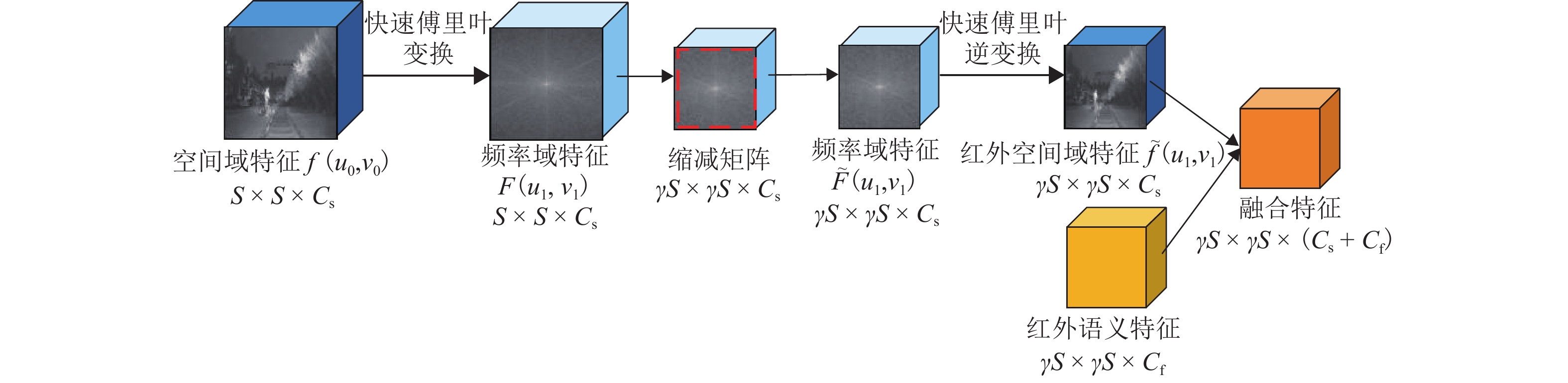
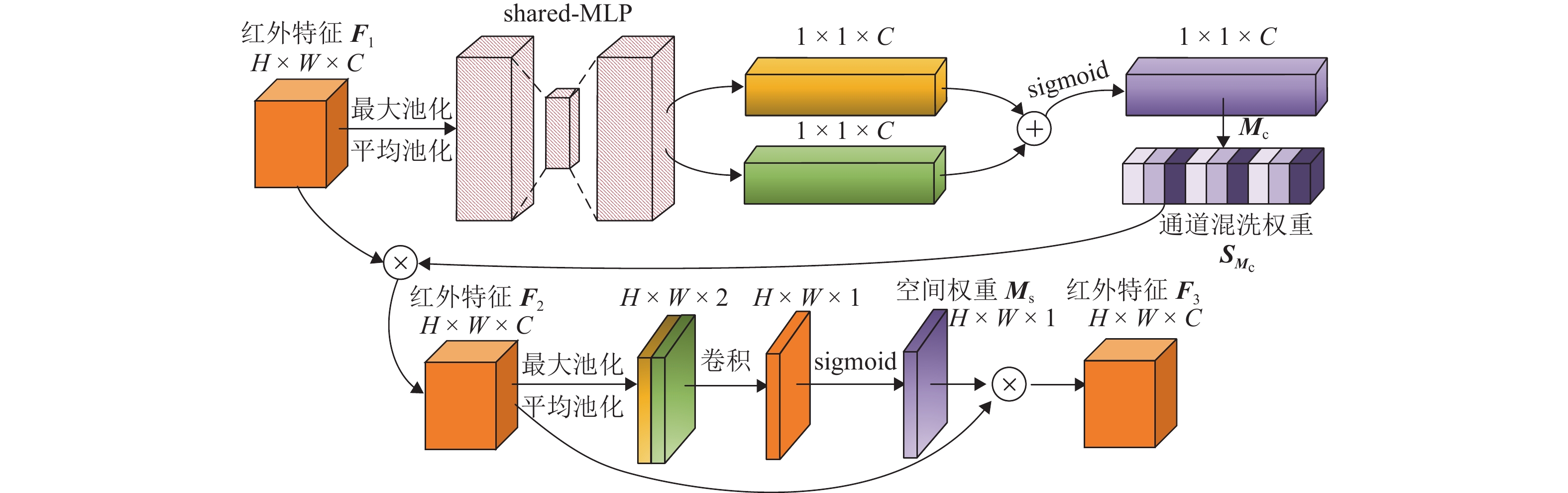
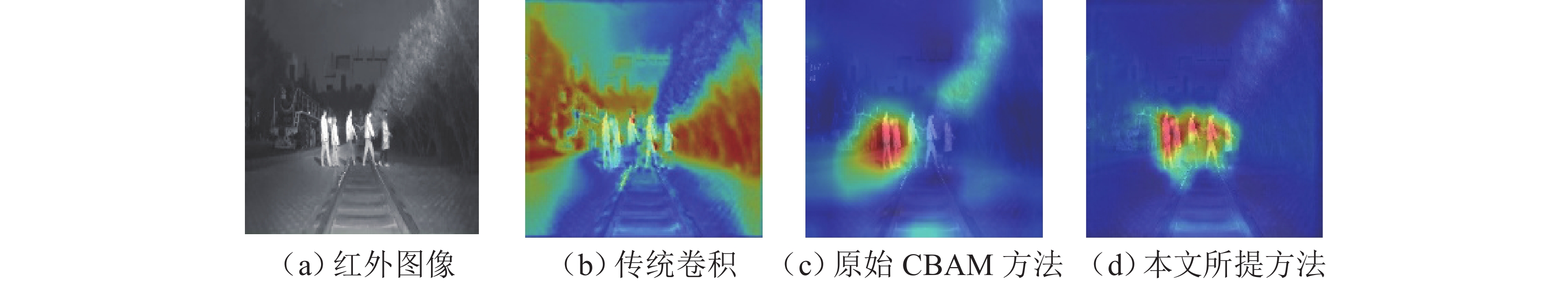
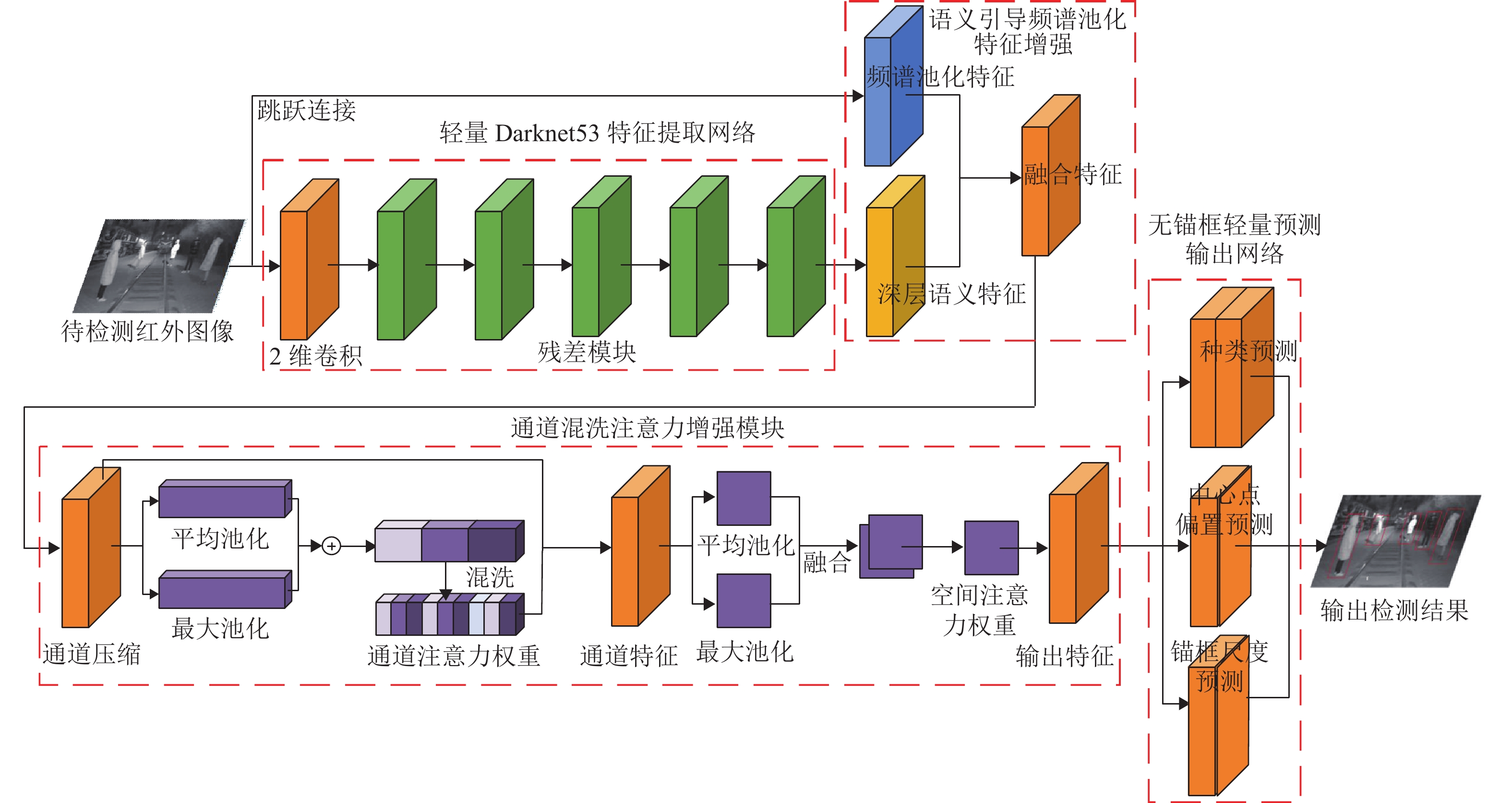
针对红外弱光环境下铁路异物侵限检测时存在检测精度低、难以实现轻量化实时检测等问题,提出一种注意力增强的轻量化铁路异物检测方法. 首先,采用深度可分离卷积改进Darknet53特征提取网络,轻量化提取红外弱光场景下的铁路异物特征;其次,利用语义引导的红外频谱池化进行特征增强,提升红外图像下采样的特征质量;然后,提出混洗注意力机制(shuffled-convolutional block attention module, shuffled-CBAM),实现对关键红外目标的特征提取与融合,提高网络对红外目标检测的精度;最后,采用无锚框轻量化网络完成铁路异物侵限检测输出,克服锚框检测非极大值抑制操作实时性差的缺点,减小计算量的同时提高检测效率. 实验结果表明:所提轻量化模型具有较高检测精度,同较改进前模型尺寸减小179.01 MB,检测速率提升至39 帧/s,为YOLOv4方法的3.9倍;相较于对比检测方法,本文所提方法能够快速精确地检测出红外铁路异物.
Abstract:In infrared low-light scenes, railway object intrusion detection faces low detection accuracy, and it is difficult to achieve lightweight real-time detection. Therefore, a lightweight detection method of railway object intrusion based on convolutional block attention module (CBAM) enhancement was proposed. Firstly, the Darknet53 feature extraction network was improved by deep separable convolution to achieve lightweight extraction of railway object intrusion characteristics in infrared low-light scenes. Secondly, semantic-guided infrared spectral pooling was used for feature enhancement to improve the feature quality of infrared image downsampling. Then, a shuffled-CBAM was proposed to achieve feature extraction and fusion of key infrared targets and improve the accuracy of infrared target detection. Finally, the lightweight anchor-free network was used to predict the output result of railway object intrusion, overcoming the deficiency of poor real-time performance due to non-maximum value suppression operation with anchor frame detection, and it reduced calculation load and speeded up the detection efficiency. The experimental results show that the lightweight model has higher detection accuracy, and the size of the model is reduced by 179.01 MB after the improvement. The detection rate is increased to 39 frames/s, which is 3.9 times that of the YOLOv4 method. Compared with other detection methods, the proposed method can detect infrared railway object intrusion quickly and accurately.
-
表 1 不同异物检测方法性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different object intrusion detection methods
表 2 所提方法分类性能实验
Table 2. Experiments on classification performance of proposed method
异物种类 准确率/% 召回率/% F1-Score 自行车 99.36 97.74 0.9854 铁路 93.83 93.91 0.9387 行人 83.16 83.67 0.8341 卡车 76.45 79.26 0.7783 汽车 77.86 77.21 0.7753 石块 70.47 70.53 0.7050 -
[1] TIAN R L, SHI H M, GUO B Q, et al. Multi-scale object detection for high-speed railway clearance intrusion[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(4): 3511-3526. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02534-9 [2] CHEN J B, TALLEY J, KELLY K F. Infrared object classification with a hybrid optical convolution neural network[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(25): G224-G231. doi: 10.1364/AO.427973 [3] 刘可佳,马荣生,唐子木,等. 采用优化卷积神经网络的红外目标识别系统[J]. 光学精密工程,2021,29(4): 822-831. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212904.0822LIU Kejia, MA Rongsheng, TANG Zimu, et al. Design of infrared target recognition system with optimized convolutional neural network[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(4): 822-831. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212904.0822 [4] LI Y S, LI Z Z, ZHANG C, et al. Infrared maritime dim small target detection based on spatiotemporal cues and directional morphological filtering[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2021, 115: 103657.1-103657.19. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2021.103657 [5] LI Q, NIE J Y, QU S C. A small target detection algorithm in infrared image by combining multi-response fusion and local contrast enhancement[J]. Optik, 2021, 241: 166919.1-166919.12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166919 [6] HAN J H, LIU C Y, LIU Y C, et al. Infrared small target detection utilizing the enhanced closest-mean background estimation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 645-662. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3038442 [7] FAN M M, TIAN S Q, LIU K, et al. Infrared small target detection based on region proposal and CNN classifier[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2021, 15(8): 1927-1936. doi: 10.1007/s11760-021-01936-z [8] 李淼,林再平,樊建鹏,等. 基于深度时空卷积神经网络的点目标检测(英文)[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2021,40(1): 122-132. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2021.01.017LI Miao, LIN Zaiping, FAN Jianpeng, et al. Point target detection based on deep spatial-temporal convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2021, 40(1): 122-132. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2021.01.017 [9] DU J M, LU H Z, HU M F, et al. CNN-based infrared dim small target detection algorithm using target-oriented shallow-deep features and effective small anchor[J]. IET Image Processing, 2021, 15(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12001 [10] LI Y D, LIU Y, DONG H, et al. Intrusion detection of railway clearance from infrared images using generative adversarial networks[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 40(3): 3931-3943. [11] GUO F, QIAN Y, SHI Y F. Real-time railroad track components inspection based on the improved YOLOv4 framework[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 125: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103596 [12] ZOU W, YIN G D, LIU H J, et al. Low-observable Target detection method for autonomous vehicles based on multi-modal feature fusion[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(9): 1114-1125. [13] MENG L, SUN X Y, ZHAO B, et al. An identification method of high-speed railway sign based on convolutional neural network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 518-530. [14] 吴双忱,左峥嵘. 基于深度卷积神经网络的红外小目标检测[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2019,38(3): 371-380. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2019.03.019WU Shuangchen, ZUO Zhengrong. Small target detection in infrared images using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2019, 38(3): 371-380. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2019.03.019 [15] LI Y D, DONG H, LI H G, et al. Multi-block SSD based on small object detection for UAV railway scene surveillance[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2020, 33(6): 1747-1755. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.02.024 [16] HSIEH C C, LIN Y W, TSAI L H, et al. Offline deep-learning-based defective track fastener detection and inspection system[J]. Sensors and Materials, 2020, 32(10): 3429.1-3429.14. doi: 10.18494/SAM.2020.2921 [17] LIU S W, YU L, ZHANG D K. An efficient method for high-speed railway dropper fault detection based on depthwise separable convolution[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 135678-135688. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2942079 [18] ZHOU A R, XIE W X, PEI J H. Background modeling in the Fourier domain for maritime infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(8): 2634-2649. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2922036 [19] 李恒超,刘香莲,刘鹏,等. 基于多尺度感知的密集人群计数网络[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2024,59(5): 1176-1183,1214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220823LI Hengchao , LIU Xianglian , LIU Peng , et al. Dense crowd counting network based on multi-scale perception[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2024, 59(5): 1176-1183,1214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20220823 [20] YANG K, CHANG S L, TIAN Z X, et al. Automatic polyp detection and segmentation using shuffle efficient channel attention network[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2022, 61(1): 917-926. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2021.04.072 [21] CHEN Y W, SONG B, ZENG Y, et al. A deep learning-based approach for fault diagnosis of current-carrying ring in catenary system[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(33): 23725-23737. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-06280-4 [22] ZHOU X, WANG D, KRAHENBUHL P. Objects as points[J]. Applied Physics Reviews, 2019, 1904: 07850.1-07850.12. -




 下载:
下载: