Method for Compressing Departure Tracking Interval of High-Speed Trains Based on Pre-departure Strategy
-
摘要:
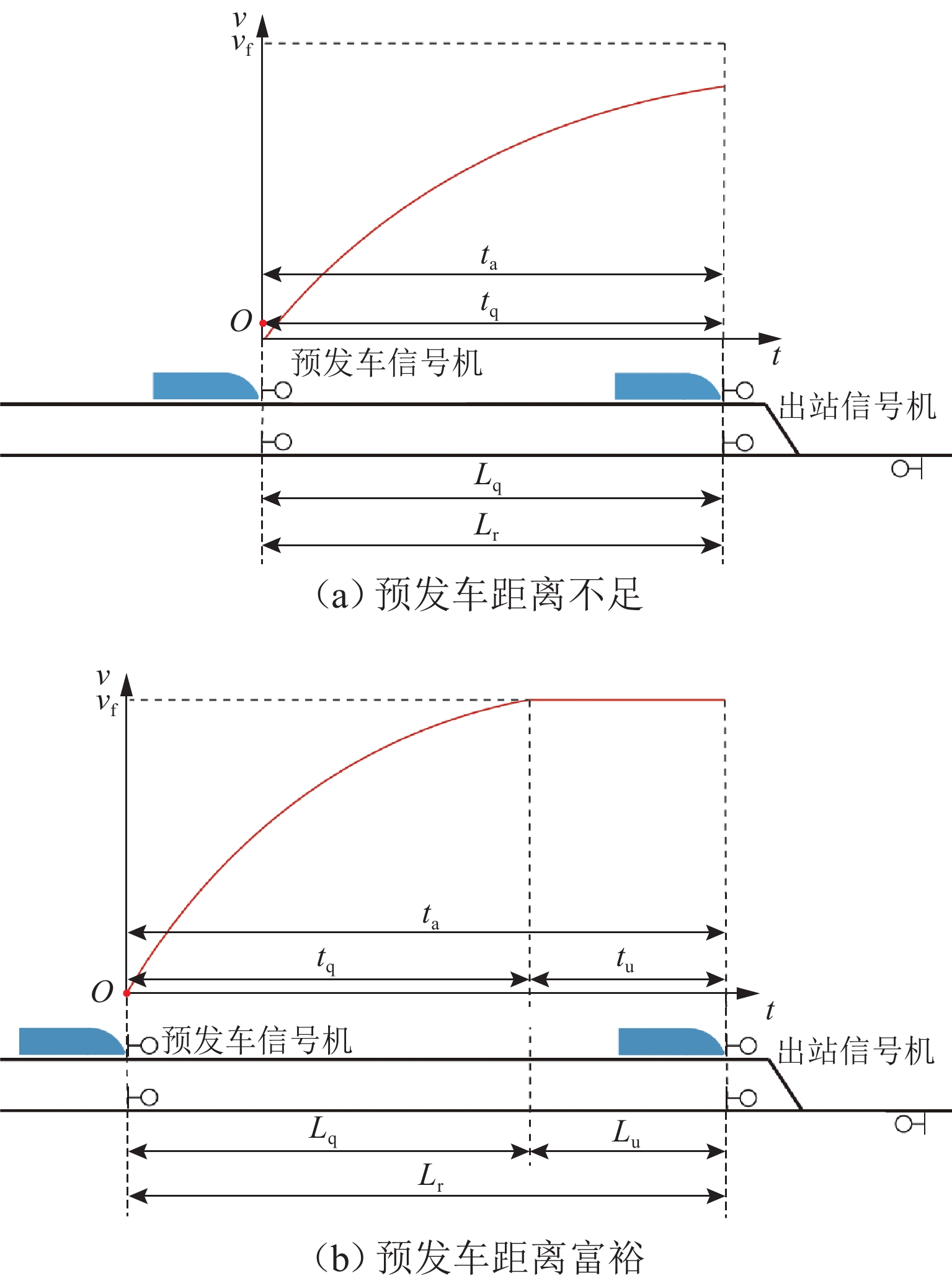
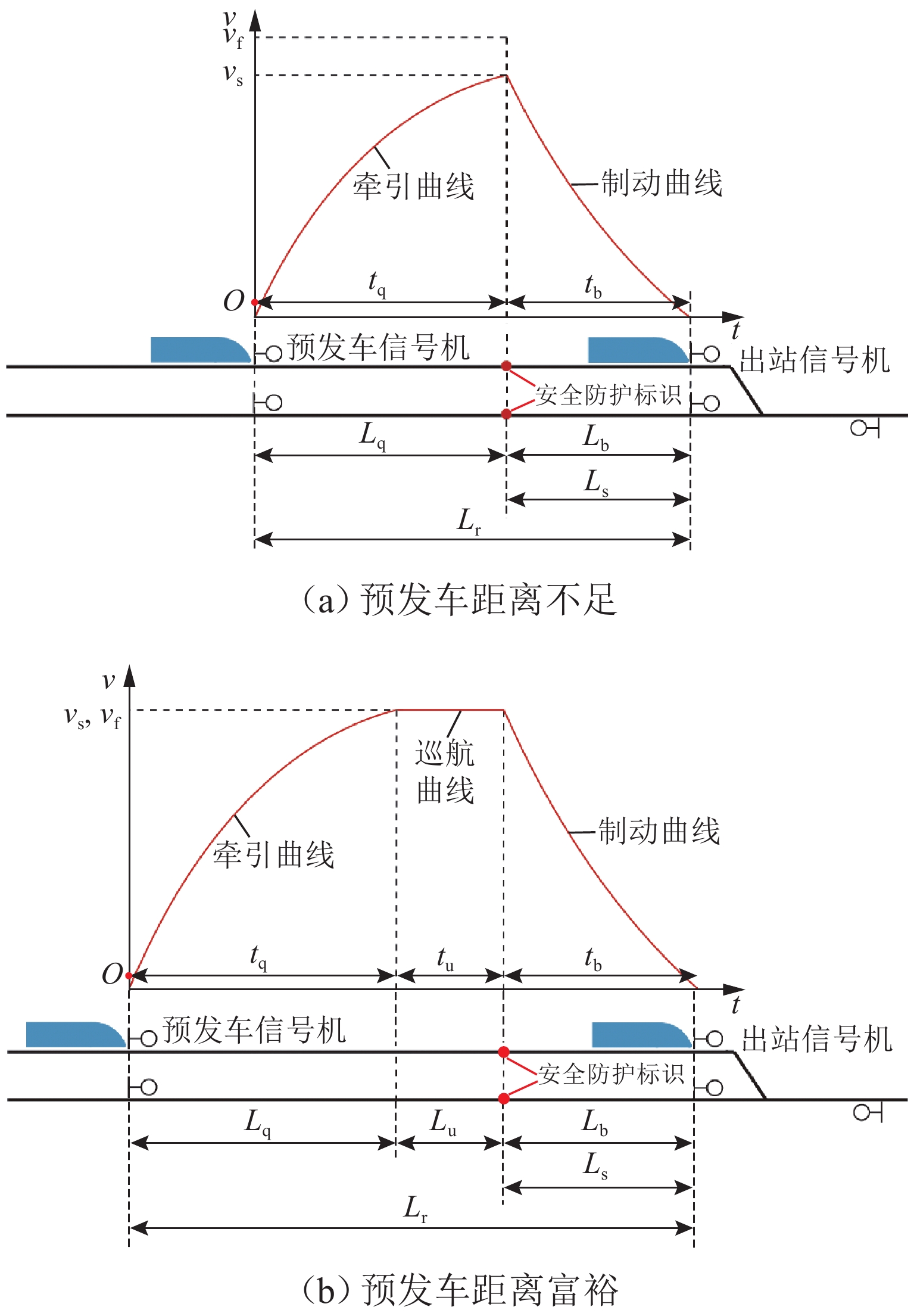
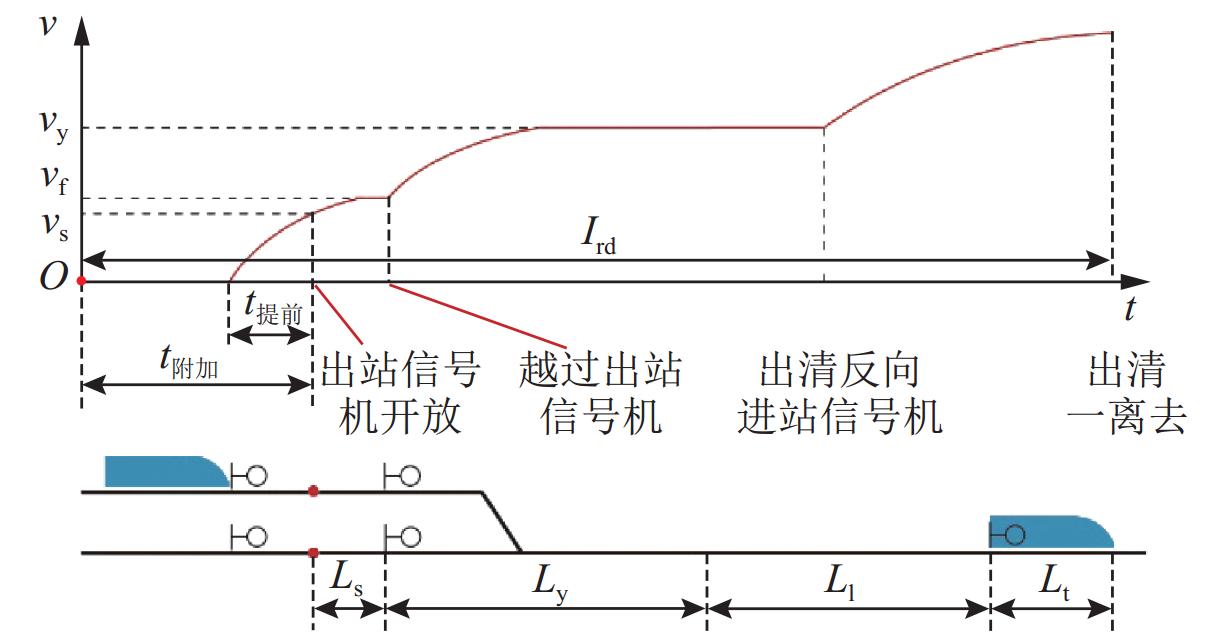
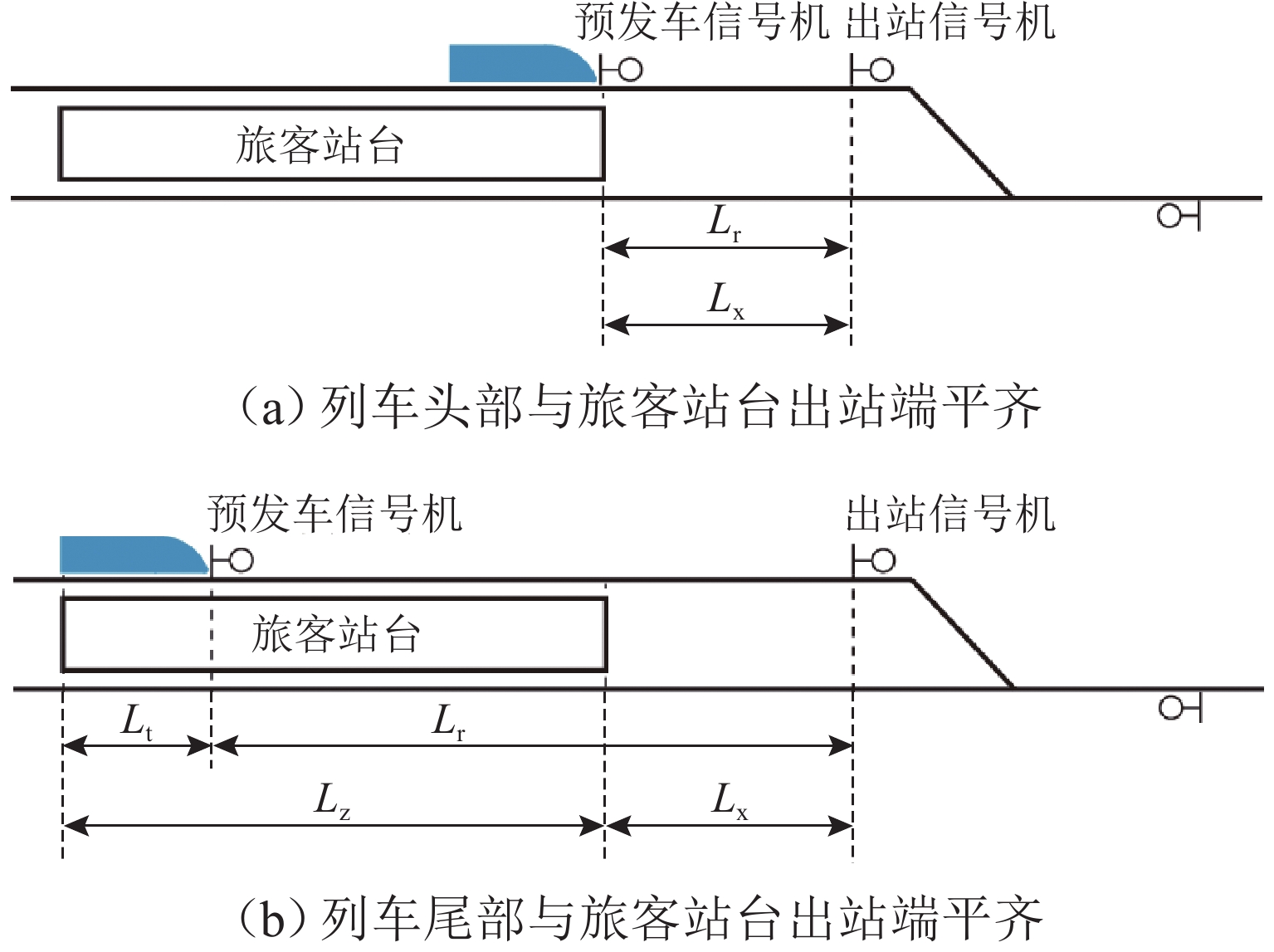
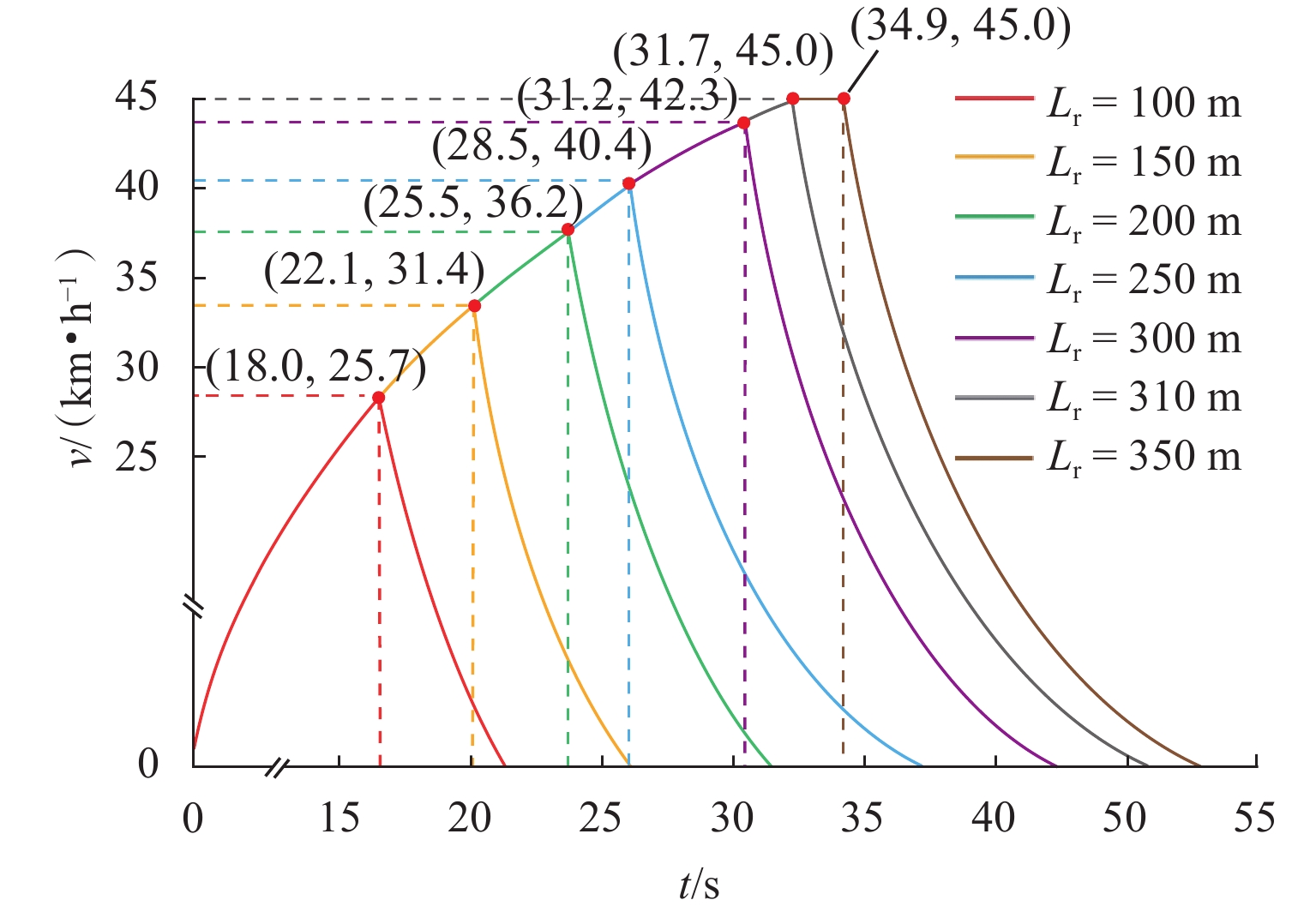
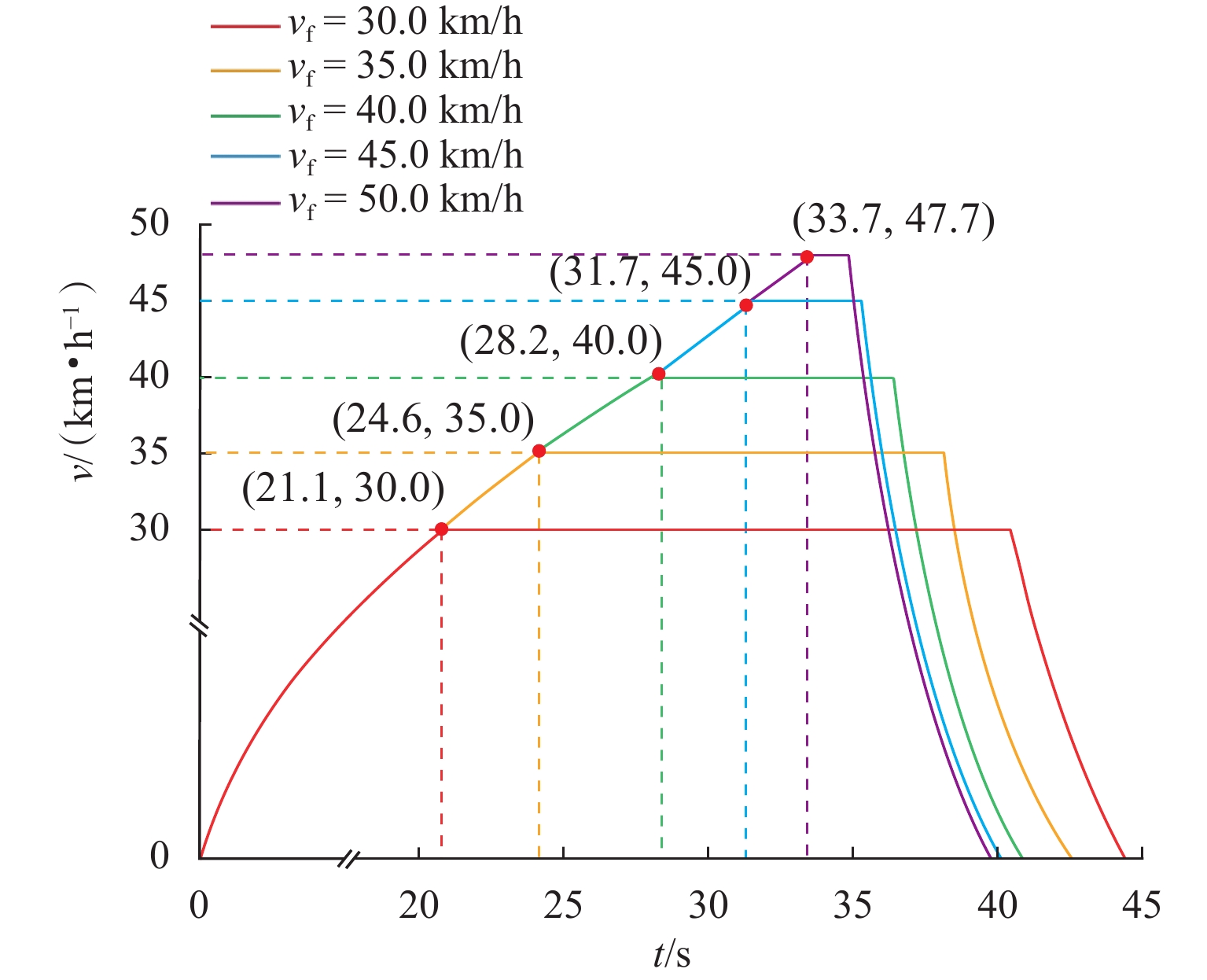
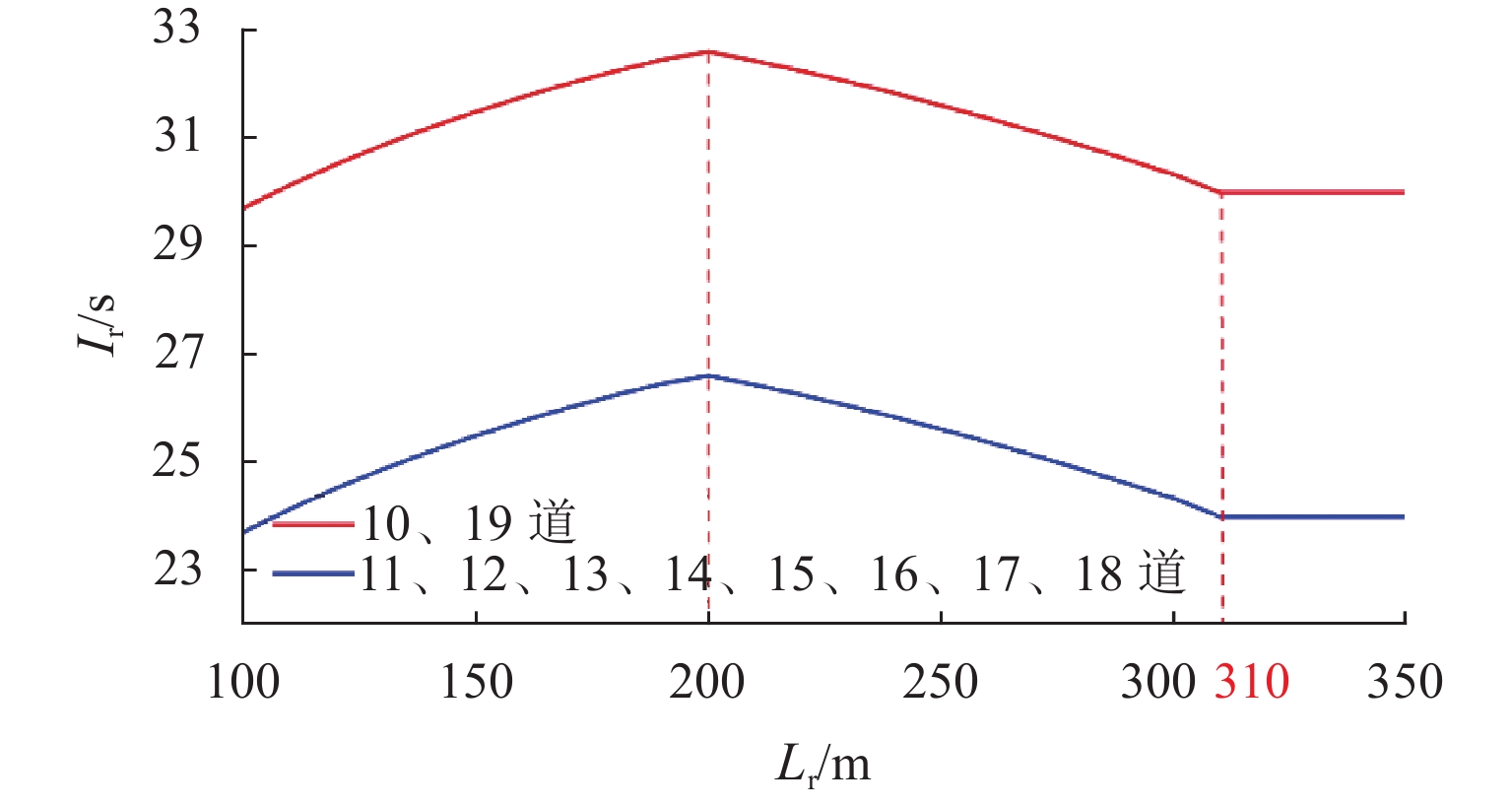
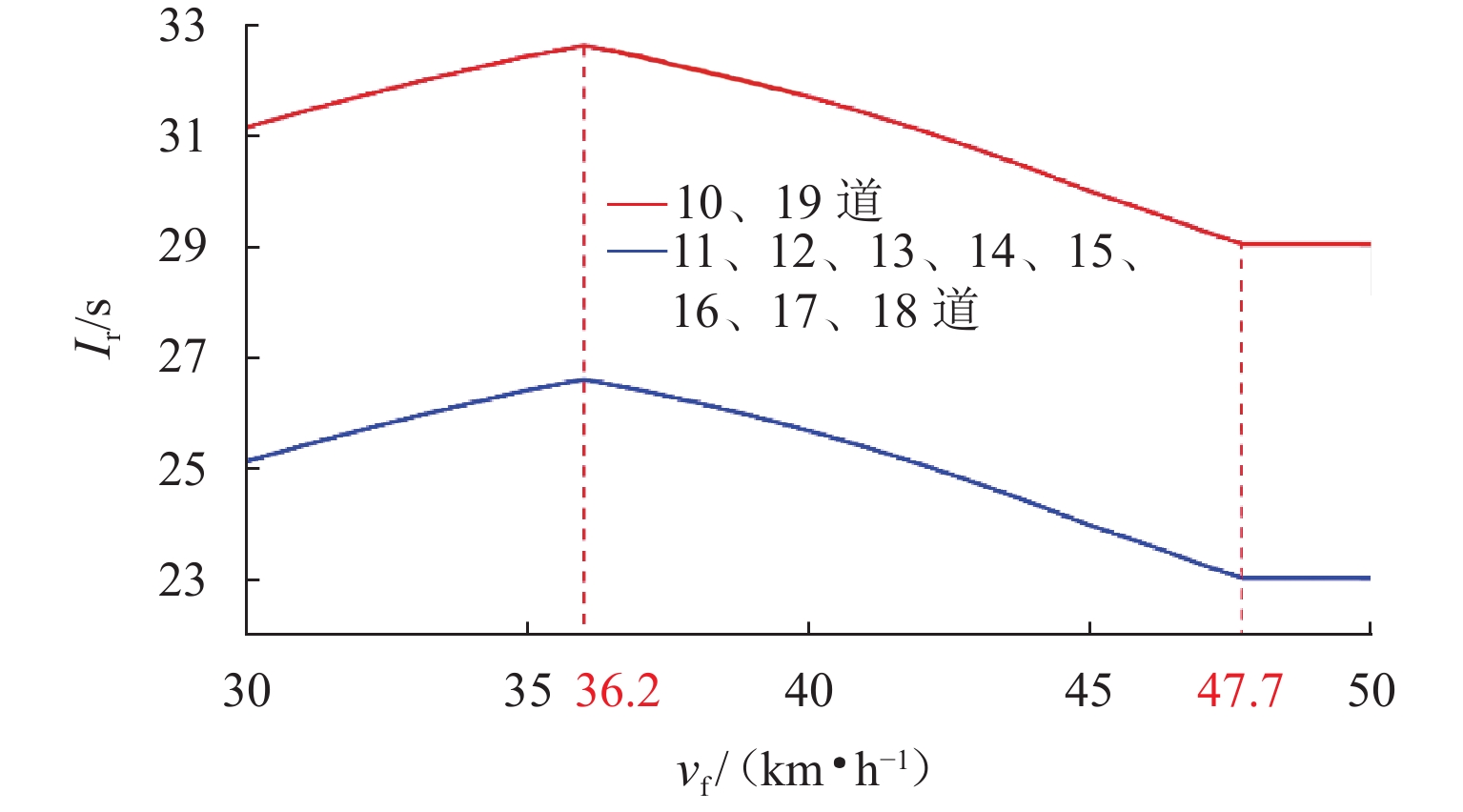
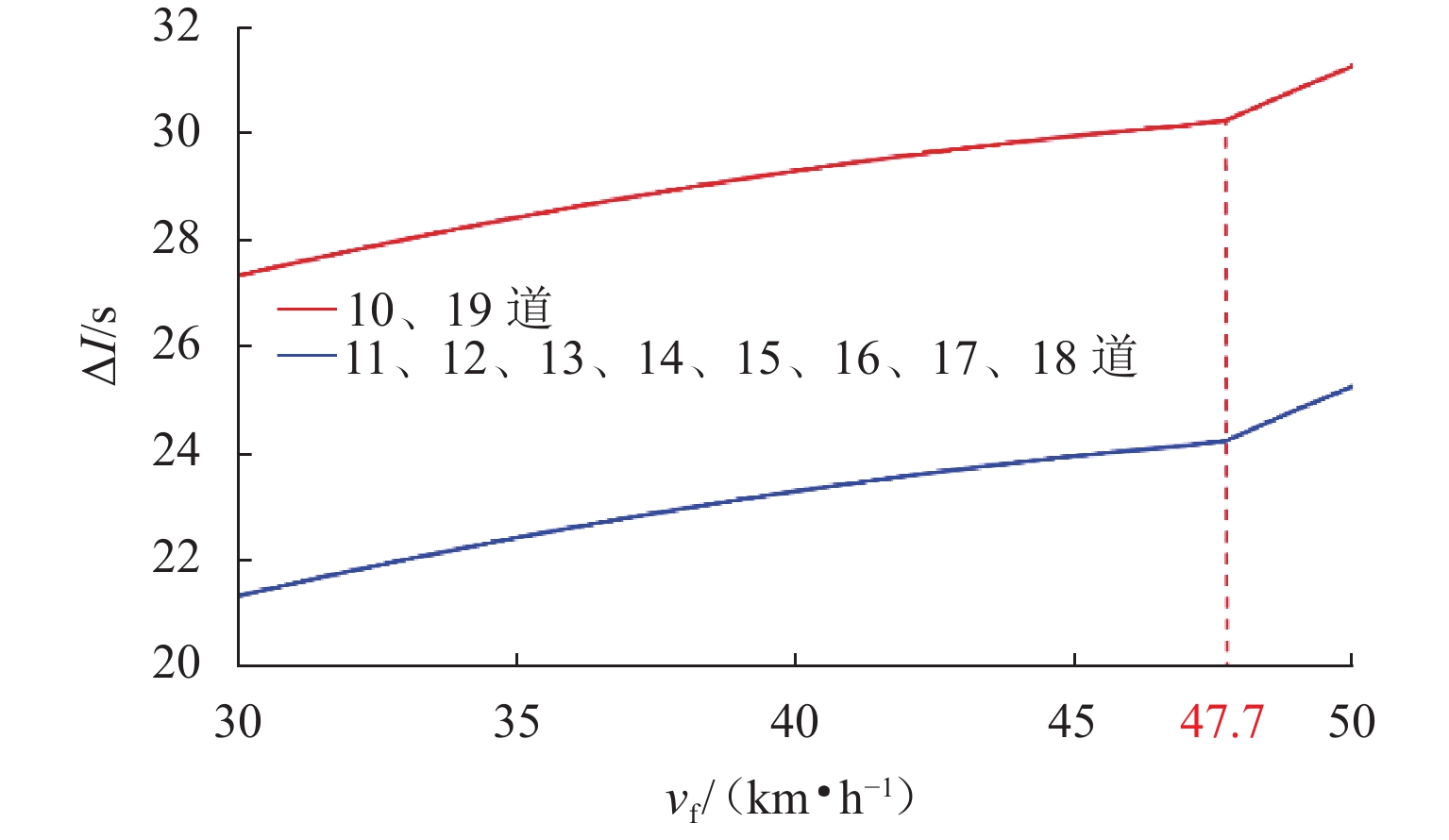
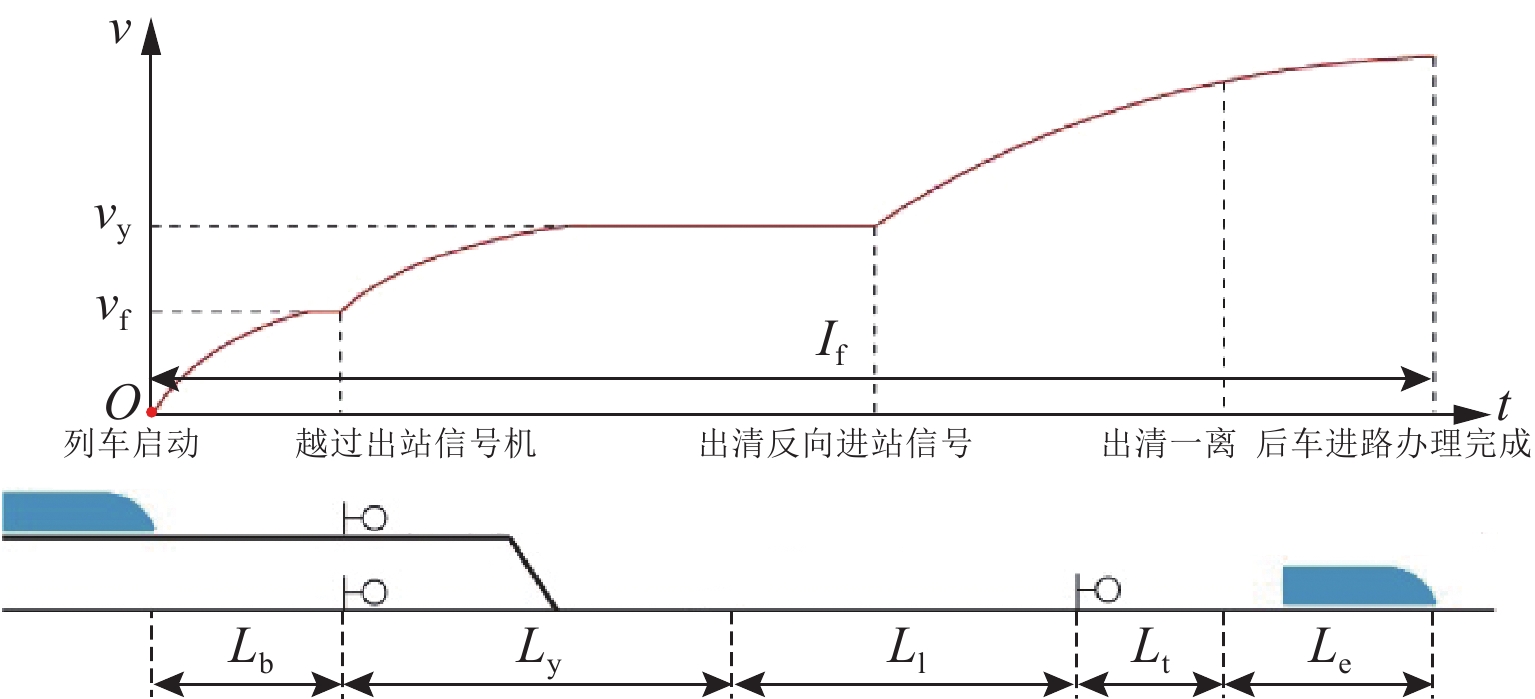
出发追踪间隔时间是限制列车实现3 min追踪运行的主要瓶颈之一,压缩出发追踪间隔时间可有效提高线路通过能力. 首先,分析高速列车出发追踪运行过程,提出在出站信号机内侧一定距离设置预发车信号机,使列车在出站信号机开放时具有一定初速度且剩余出站距离缩短;并设计预发车过程的“故障导向安全”原则以确保列车不冒进出站信号机;然后,在分析影响压缩出发追踪间隔时间因素的基础上,研究不同预发车方案下的列车控车模式曲线;最后,以上海虹桥站高速场为例进行仿真验证. 研究表明:该方法能压缩列车出发追踪间隔时间,压缩效果随预发车距离的增大呈现先上升后下降的趋势;在到发线有效长可提供200 m预发车距离时,最大可压缩列车出发追踪间隔时间26 s以上.
Abstract:The departure tracking interval is one of the main bottlenecks that limit the 3-minute tracking operation of trains, and compressing the departure tracking interval can effectively improve line capacity. The departure tracking process of high-speed trains was first analyzed, and a pre-departure annunciator was set at a certain distance inside the outbound annunciator, making the train have a certain initial speed and shortening the remaining outbound distance when the outbound annunciator was open. At the same time, the principle of “failure-oriented safety” for the pre-departure process was put forward to ensure that the train did not cross the outbound annunciator. Then, based on the analysis of factors affecting the compression of departure tracking interval, the curves of train control mode under different pre-departure schemes were studied. Finally, the high-speed yard of Shanghai Hongqiao Station was studied, and the results show that the departure tracking interval can be compressed by the proposed method. The compression effect increases first and then decreases with the increase in the pre-departure distance, and the maximum compressible departure tracking interval can be more than 26 s if the pre-departure distance reaches 200 m of the effective lengths of the arrival-departure track.
-
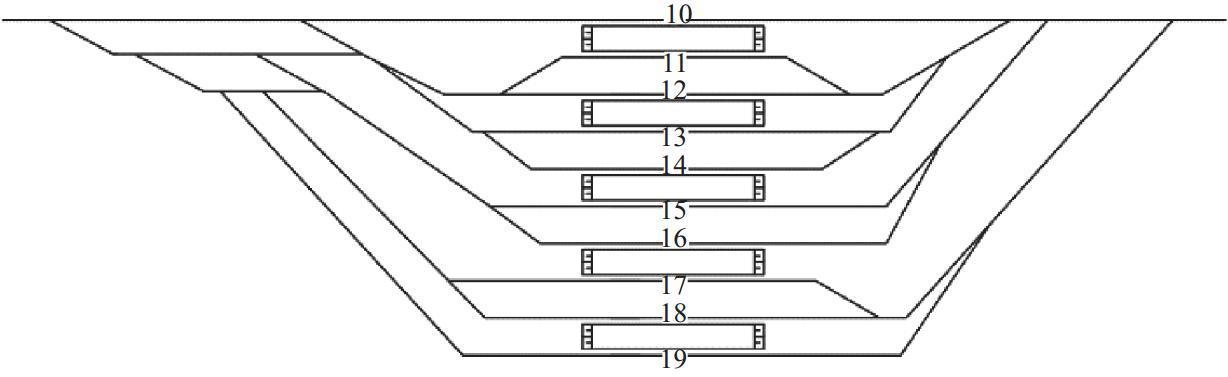
表 1 相关参数
Table 1. Related parameters
股道 发车进路
长度/m$ {L}_{{\mathrm{b}}} $/m $ {t}_{{\mathrm{e}}} $/s $ {v}_{{\mathrm{f}}} $/
(km•h−1)$ {v}_{{\mathrm{y}}} $/
(km•h−1)10 2607 290 51.0 45.0 80.0 11 2903 215 12 2903 215 13 2871 215 14 2871 215 15 2879 215 16 2879 215 17 2936 215 18 2936 215 19 2551 290 -
[1] 胡志垚. 进路分段办理压缩大型客站发车追踪间隔时间[J]. 交通科技与经济,2018,20(3): 23-27,65.HU Zhiyao. Compressing departure tracking interval of large passenger railway station with departure route subsection[J]. Technology & Economy in Areas of Communications, 2018, 20(3): 23-27,65. [2] SHANGGUAN W, YAN X H, CAI B G, et al. Multiobjective optimization for train speed trajectory in CTCS high-speed railway with hybrid evolutionary algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(4): 2215-2225. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2402160 [3] YAN X H, CAI B G, NING B, et al. Moving horizon optimization of dynamic trajectory planning for high-speed train operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(5): 1258-1270. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2015.2499254 [4] GAO S L, ZHENG Y S. Adjustment of train interval time based on dynamic programming algorithm[C]// 2018 IEEE International Conference of Intelligent Robotic and Control Engineering (IRCE). Lanzhou: IEEE, 2018: 106-110. [5] WAGTER W. Block sections around stations under ETCS: the effect of the block layout on the headways at stations[D]. Enschede:Enschede University of Twente, 2019. [6] VIGNALI V, CUPPI F, LANTIERI C, et al. A methodology for the design of sections block length on ETCS L2 railway networks[J]. Journal of Rail Transport Planning & Management, 2020, 13: 100160.1-100160.22. [7] 田长海,张守帅,张岳松,等. 高速铁路列车追踪间隔时间研究[J]. 铁道学报,2015,37(10): 1-6.TIAN Changhai, ZHANG Shoushuai, ZHANG Yuesong, et al. Study on the train headway on automatic block sections of high speed railway[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(10): 1-6. [8] 彭其渊,王超宇,鲁工圆. 基于到发线运用方案的列车到达追踪间隔时间压缩方法及仿真研究[J]. 中国铁道科学,2020,41(2): 131-138.PENG Qiyuan, WANG Chaoyu, LU Gongyuan. Compression method and simulation of train arrival interval based on utilization of arrival-departure track[J]. China Railway Science, 2020, 41(2): 131-138. [9] 鲁工圆,沈子力,彭其渊,等. 基于区间速度控制的列车到达追踪间隔时间压缩方法研究[J]. 铁道学报,2021,43(1): 19-27.LU Gongyuan, SHEN Zili, PENG Qiyuan, et al. Compressing arrival interval of high-speed trains by speed control within railway section[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(1): 19-27. [10] 鲁工圆,王超宇,沈子力,等. 面向追踪间隔压缩的高速铁路列车运行时空轨迹优化[J]. 铁道学报,2021,43(7): 10-18.LU Gongyuan, WANG Chaoyu, SHEN Zili, et al. Headway compression oriented space-time trajectory optimization for high-speed railway trains[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2021, 43(7): 10-18. [11] TAKAGI R. Synchronisation control of trains on the railway track controlled by the moving block signalling system[J]. IET Electrical Systems in Transportation, 2012, 2(3): 130-138. doi: 10.1049/iet-est.2011.0053 [12] 张婷. 通过提高列车出站速度压缩高速铁路列车发车追踪间隔时间[J]. 价值工程,2018,37(3): 34-36.ZHANG Ting. Compress the tracing interval of high-speed railway trains by increasing train outbound speed[J]. Value Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 34-36. [13] 聂英杰,胡志垚. 京沪高速铁路北京南站发车追踪间隔研究[J]. 铁道运输与经济,2018,40(11): 28-31.NIE Yingjie, HU Zhiyao. A study on departure headway interval of Beijing South Railway Station of Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway[J]. Railway Transport and Economy, 2018, 40(11): 28-31. [14] 朱子轩. 高速铁路列车追踪间隔时间压缩策略仿真分析研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学,2019. [15] 张岳松,田长海,姜昕良,等. 高速铁路列车间隔时间的计算方法[J]. 中国铁道科学,2013,34(5): 120-125.ZHANG Yuesong, TIAN Changhai, JIANG Xinliang, et al. Calculation method for train headway of high speed railway[J]. China Railway Science, 2013, 34(5): 120-125. [16] 中国铁路总公司. CRH系列动车组操作规则:TG/JW105—2015[S]. 北京: 中国铁路总公司,2015. [17] 赵博. 高铁车站出站信号机与停车标设置方案探讨[J]. 铁道工程学报,2018,35(10): 69-72.ZHAO Bo. Research on the setting scheme of starting signal and train stop sign on high speed railway station[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2018, 35(10): 69-72. -




 下载:
下载: