Non-uniform Corrosion and Load Bearing Capacity Deterioration Tests of Reinforced Concrete Beams Under Load and Chloride Salt Environment
-
摘要:
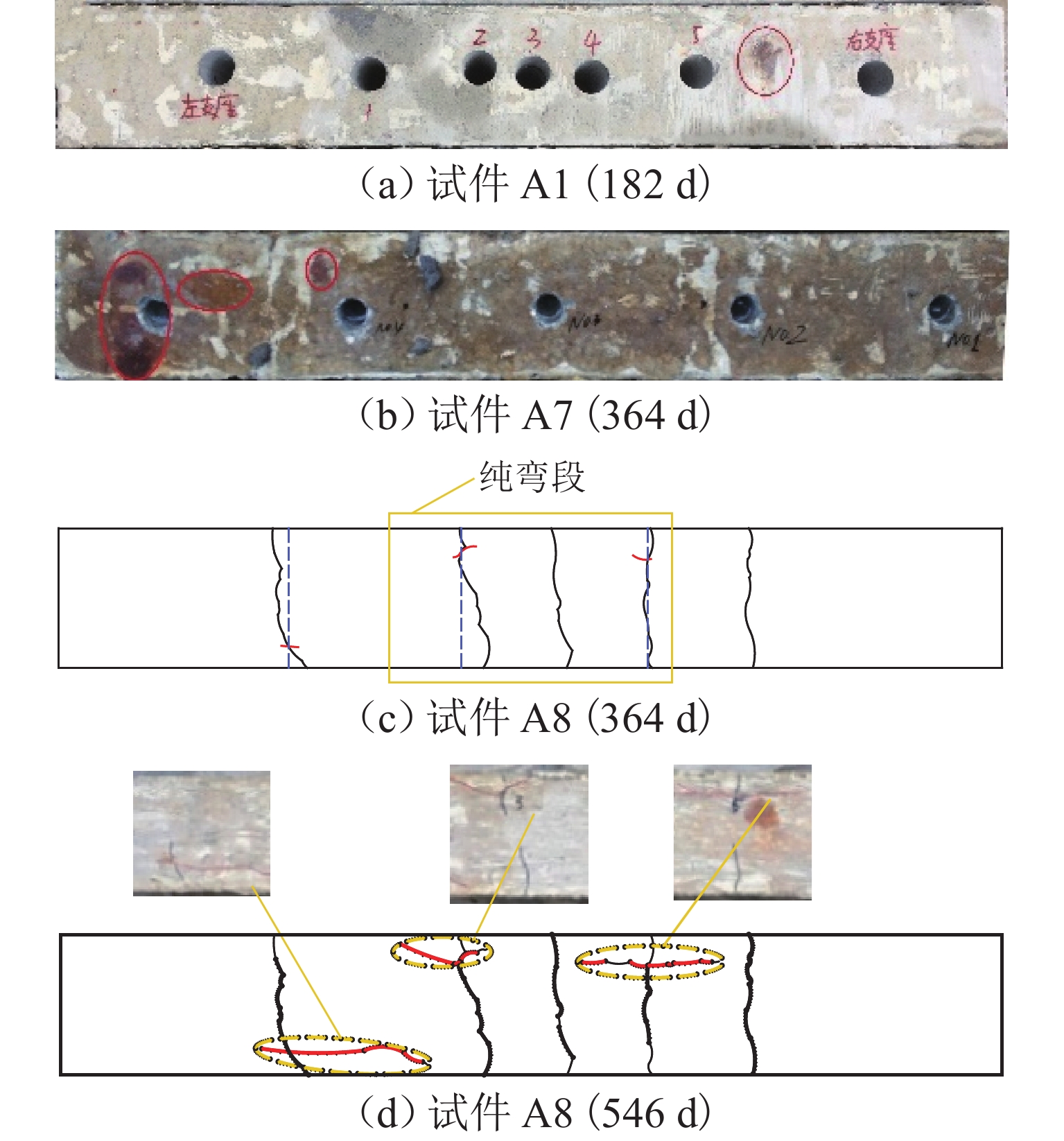
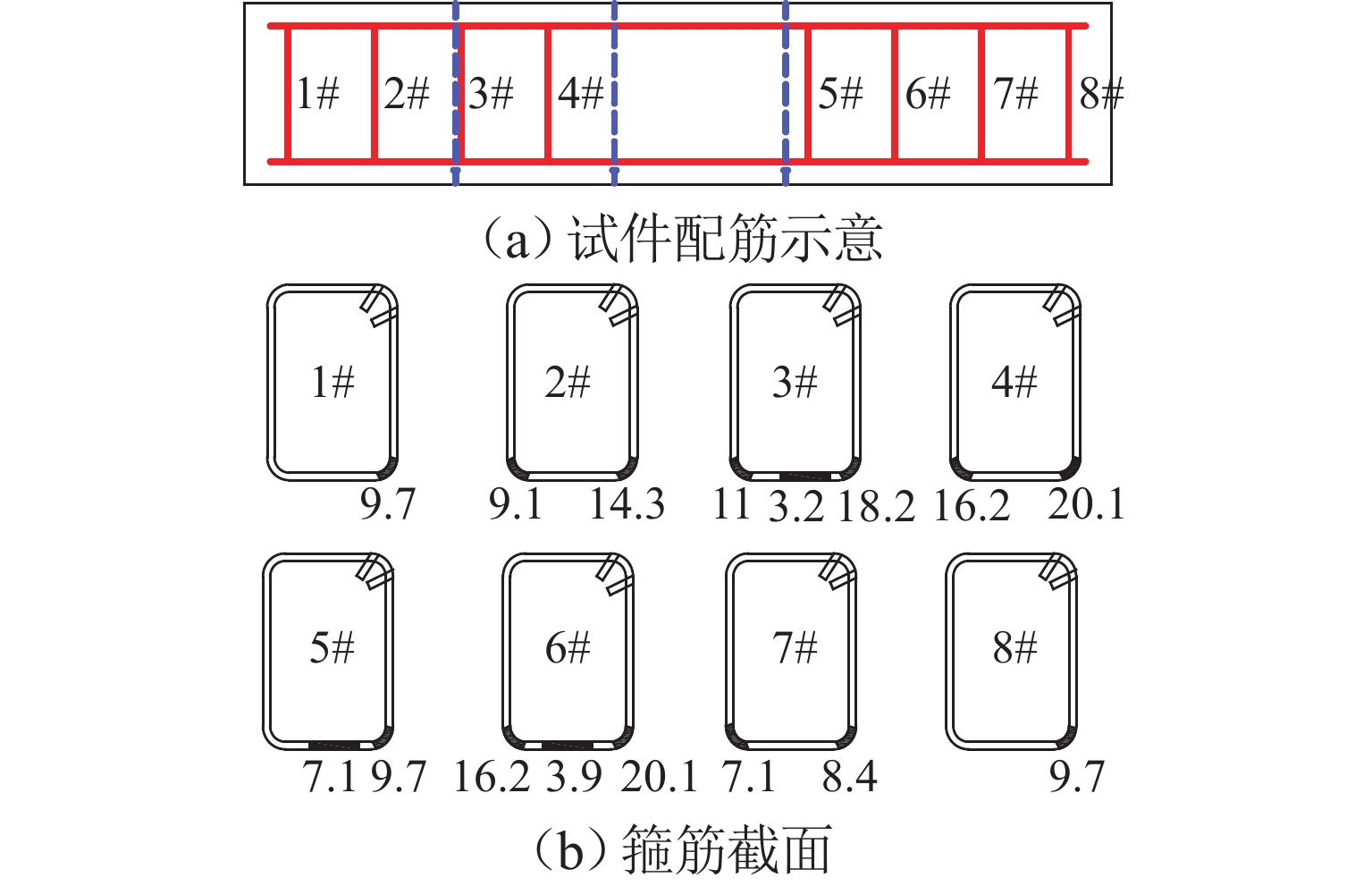
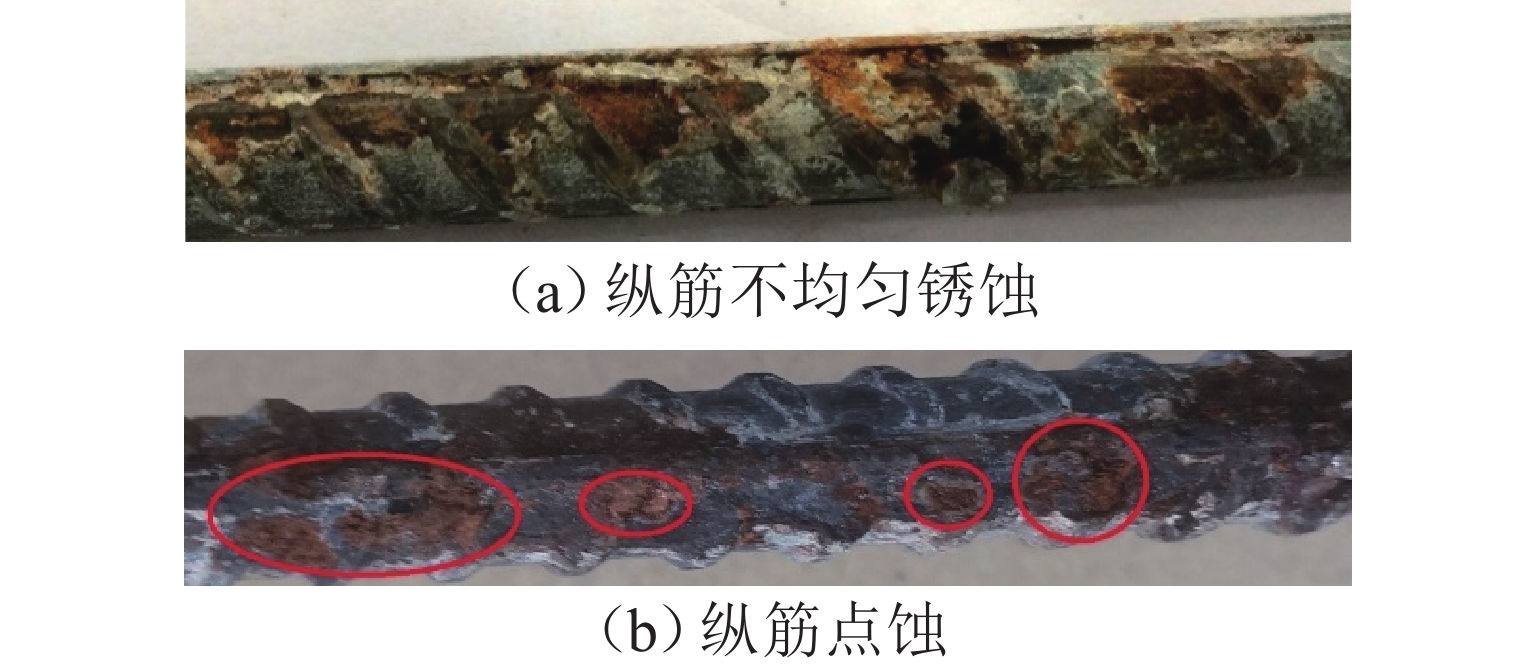
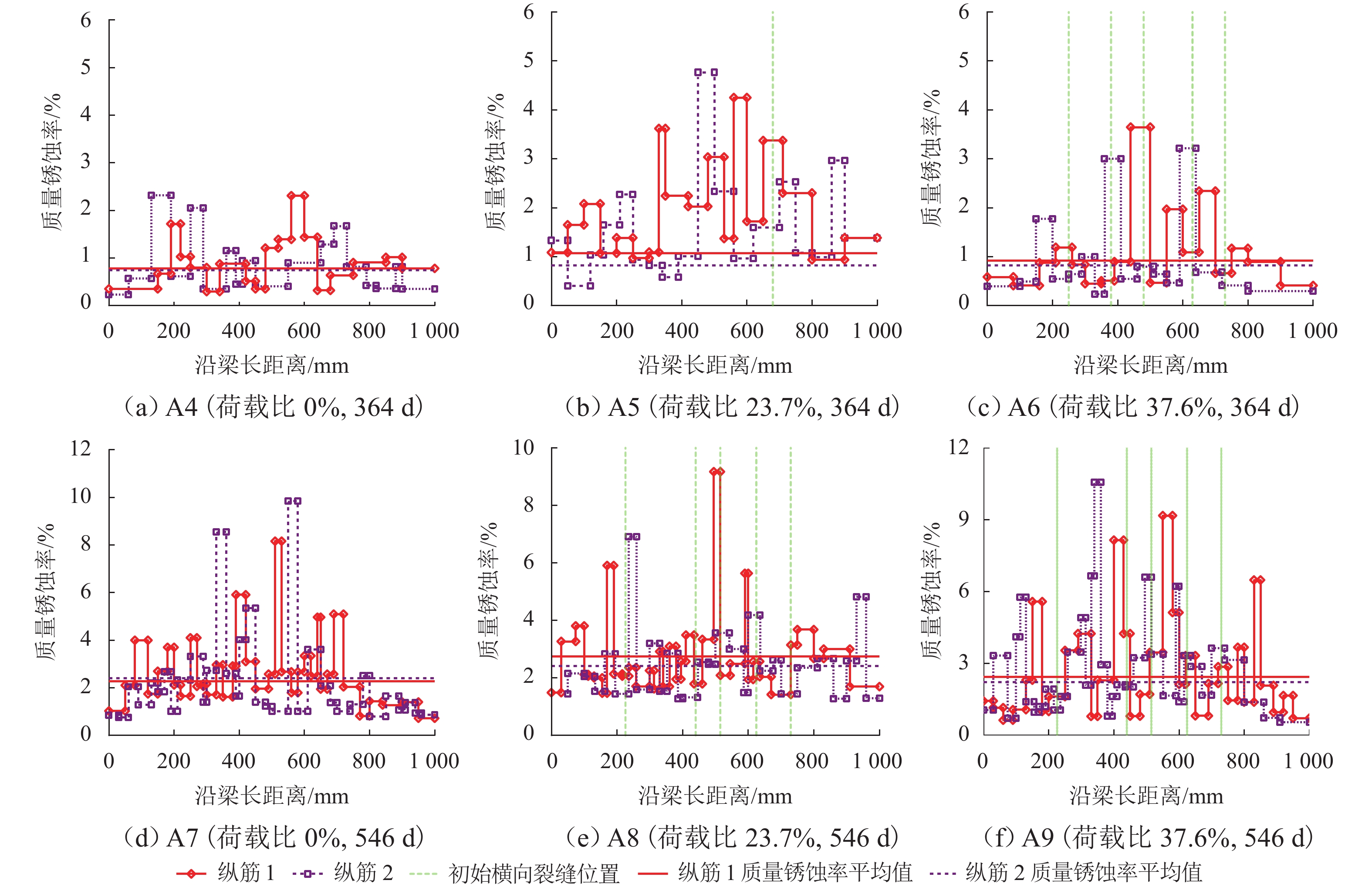
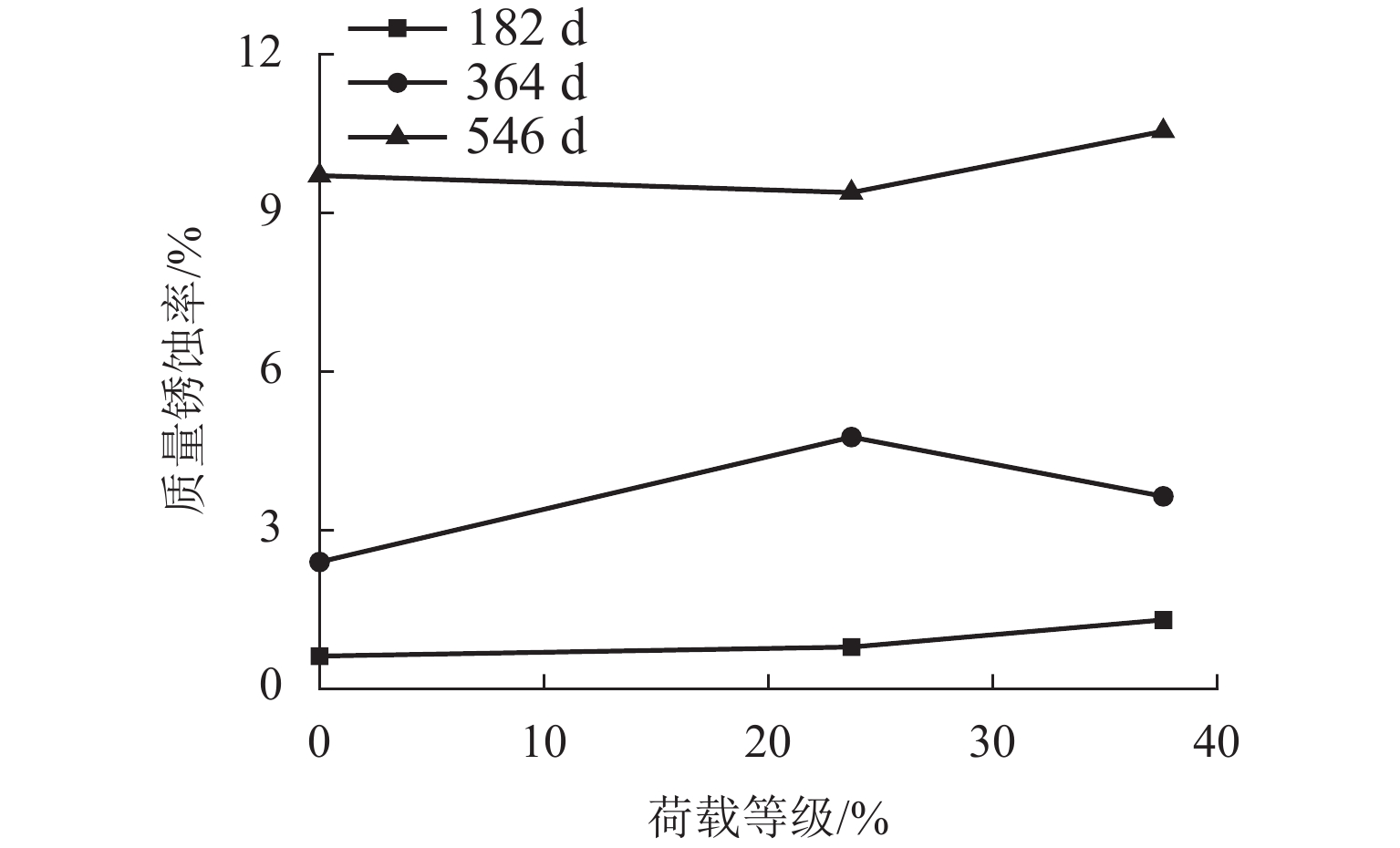
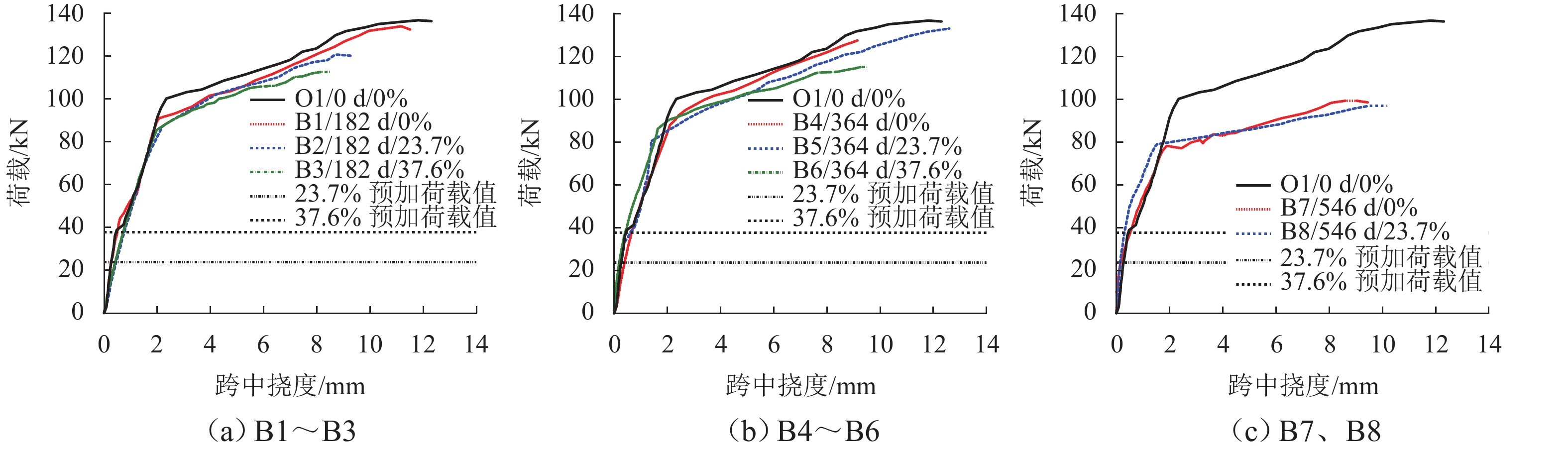
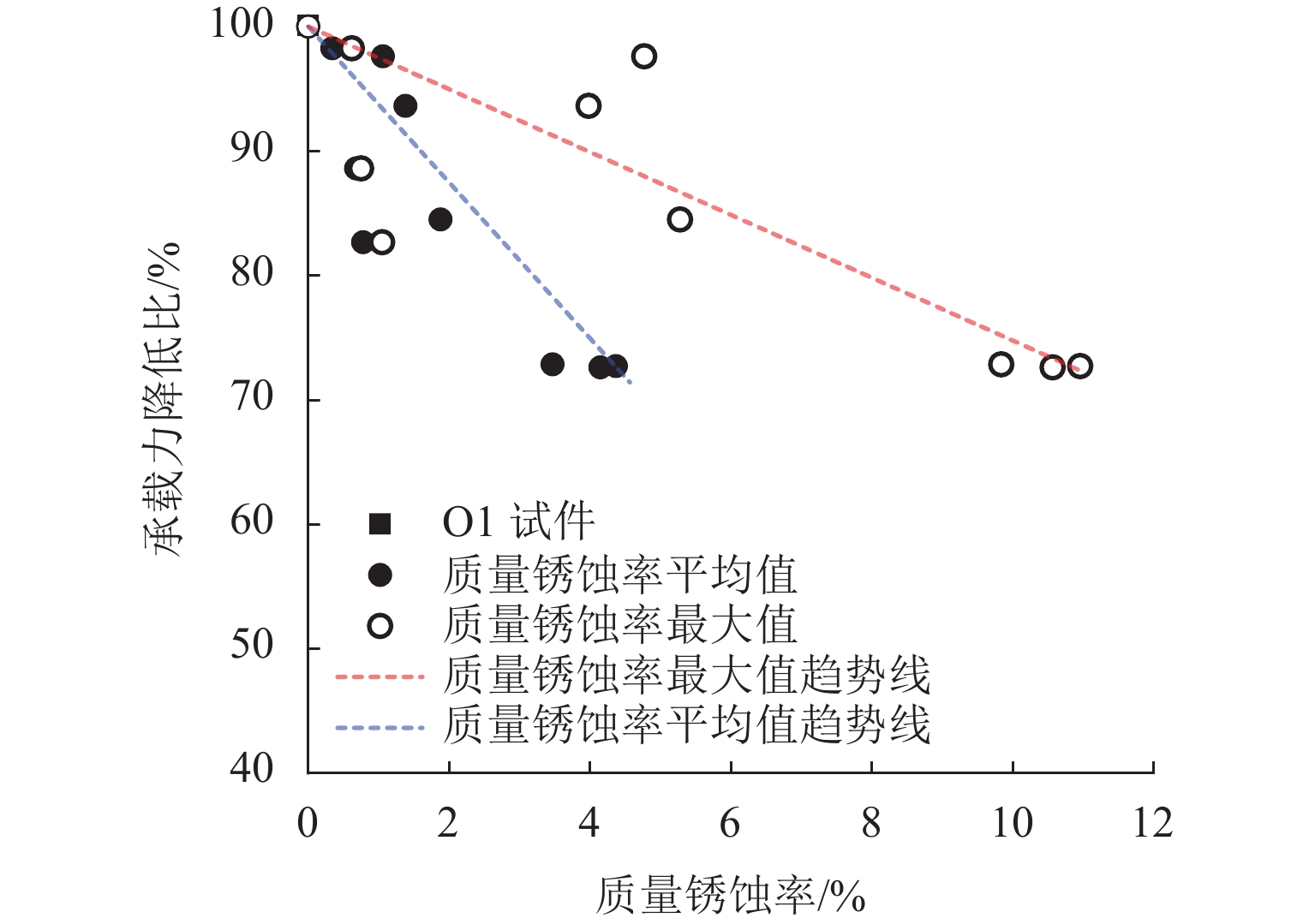
为考察持续荷载与氯盐干湿循环共同作用对钢筋混凝土(RC)梁抗弯性能的影响,先后进行19根钢筋混凝土梁的腐蚀试验和抗弯承载力试验,研究不同持续荷载等级和干湿循环天数对裂缝分布、钢筋质量锈蚀率以及受腐蚀构件受弯性能的影响,并分别总结纵筋最大和平均质量锈蚀率与承载力降低比的关系. 研究结果表明:纯弯段的钢筋锈蚀程度较高,纵筋锈蚀程度沿圆周分布不均匀;纵筋质量锈蚀率的极值点位置与初始横向裂缝的出现位置无必然关联性;纵筋最大质量锈蚀率随荷载等级和干湿循环天数的增加而增大,受干湿循环天数的影响更明显;腐蚀后梁峰值荷载呈下降趋势;当纵筋锈蚀率较小时(平均值≤3%或最大值≤6%),锈蚀率与承载力降低比的相关度较低,且最大质量锈蚀率的相关度小于平均质量锈蚀率;当纵筋锈蚀率较大时(平均值>3%或最大值>6%),质量锈蚀率与承载力降低比的相关度提高;在纵筋平均质量锈蚀率相同时,采用自然腐蚀试件的承载力降低程度高于采用外加电流腐蚀的试件.
Abstract:To explore how sustained loading and drying-wetting cycles of chloride salt affect the flexural behavior of reinforced concrete (RC) beams, the corrosion tests and flexural capacity tests of 19 RC beams were carried out at first. The effects of various sustained loading grades and drying-wetting cycle periods were studied on the crack distribution, the mass corrosion rate of longitudinal reinforcements, and the flexural behavior of corroded members. The relationship was summarized between the maximum and average mass corrosion rate of longitudinal reinforcements and the flexural bearing capacity reduction ratio. The study results show that the corrosion degree of longitudinal reinforcements was higher in the pure bending segment than in other areas, and distributed non-uniformly along the circumference of the longitudinal reinforcements. There was no noticeable correlation between the position of the extreme mass corrosion rate of longitudinal reinforcements and the occurrence position of initial transverse cracks. The maximum mass corrosion rate of longitudinal reinforcements increased with the loading grade and drying-wetting cycle period, and was more notably affected by the drying-wetting cycle period. The peak load of the beam decreased after corrosion. When the mass corrosion rate of the longitudinal reinforcements was low (average value below 3% or maximum value above 6%), the correlation between the mass corrosion rate and the reduction ratio of bearing capacity was low, and the maximum mass corrosion rate has less correlation with the reduction ratio of bearing capacity than the average mass corrosion rate. When the mass corrosion rate of longitudinal reinforcements increased (average value above 3% or maximum value above 6%), both the maximum and the average mass corrosion rates of longitudinal reinforcements had an increased correlation with the reduction ratio of bearing capacity. When the average mass corrosion rate of longitudinal reinforcements is the same, the reduction of bearing capacity of specimens with natural corrosion is higher than that of specimens with external current corrosion.
-
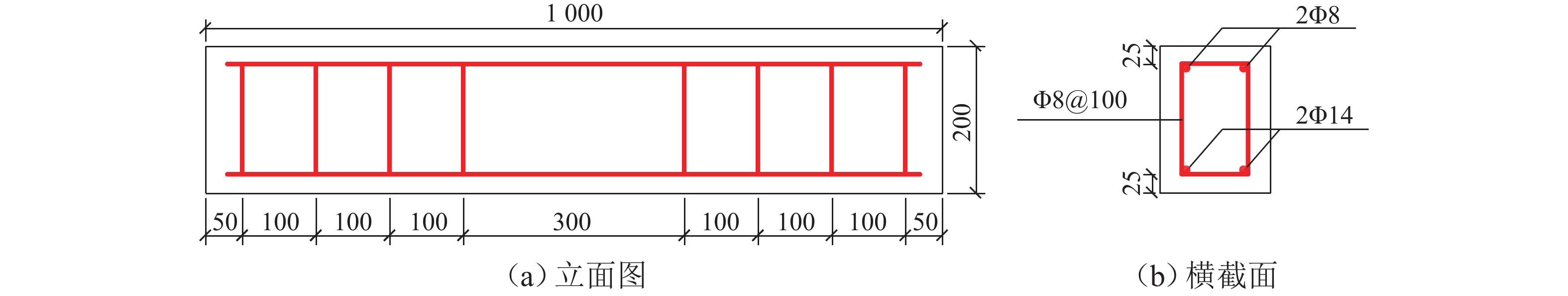
表 1 试件参数
Table 1. Specimen parameters
试件 荷载比(P/Pu)/% 干湿循环天数/d 加载方式 O1 0 0 不加载 A1 0 182 不加载 A2 23.7 182 与 B2 互锚 A3 37.6 182 与 B3 互锚 A4 0 364 不加载 A5 23.7 364 与 B5 互锚 A6 37.6 364 与 B6 互锚 A7 0 546 不加载 A8 23.7 546 与 B8 互锚 A9 37.6 546 与 B9 互锚 B1 0 182 不加载 B2 23.7 182 与 A2 互锚 B3 37.6 182 与 A3 互锚 B4 0 364 不加载 B5 23.7 364 与 A5 互锚 B6 37.6 364 与 A6 互锚 B7 0 546 不加载 B8 23.7 546 与 A8 互锚 B9 37.6 546 与 A9 互锚 表 2 混凝土组成成分
Table 2. Concrete composition
kg/m3 成分 水泥 水 天然江砂 粗骨料 配合比 455 185 755 1465 表 3 材料力学指标
Table 3. Material mechanical indexes
MPa 钢筋类型 屈服强度 极限强度 HPB300 308.2 484.9 HRB400 471.7 628.1 表 4 抗弯承载力试验结果与纵筋锈蚀程度
Table 4. Test results of flexural bearing capacity and corrosion level of reinforcements
试件
编号峰值荷载/
kN峰值荷载时
跨中挠度/mm平均质量锈蚀率/% 最大质量锈蚀率/% O1 136.22 12.31 0 0 B1 133.83 11.56 0.34 0.62 B2 120.69 9.31 0.68 0.75 B3 112.61 8.50 0.78 1.05 B4 127.54 12.29 1.38 3.98 B5 132.96 12.61 1.06 4.77 B6 115.11 9.54 1.88 5.28 B7 99.24 9.45 3.47 9.84 B8 99.03 10.19 4.37 10.96 B9 98.91 4.15 10.57 -
[1] ZHANG D F, XIONG J B, WANG S N, et al. Comparative study on the durability of pile, beam and slab reinforced concrete structure in marine environment[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 719(2): 022027.1-022027.15. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/719/2/022027 [2] 金伟良. 氯盐环境下混凝土结构耐久性理论与设计方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2011: 135-140. [3] YIN S P, HUA Y T, YU Y L. Flexural durability and chloride diffusion equation of TRC-strengthened beams under a chloride environment[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2020, 24(6): 1868-1880. doi: 10.1007/s12205-020-1640-7 [4] FRANÇOIS R, ARLIGUIE G. Influence of service cracking on reinforcement steel corrosion[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 1998, 10(1): 14-20. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(1998)10:1(14) [5] YU L W, FRANÇOIS R, DANG V H, et al. Development of chloride-induced corrosion in pre-cracked RC beams under sustained loading: effect of load-induced cracks, concrete cover, and exposure conditions[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2015, 67: 246-258. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2014.10.007 [6] 左志亮,张帆,罗赤宇,等. 缓黏结预应力混凝土梁耐久性能试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2019,52(9): 69-78.ZUO Zhiliang, ZHANG Fan, LUO Chiyu, et al. Research on durability of retard-bonded prestressed concrete beams[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2019, 52(9): 69-78. [7] LU Z H, LI H, LI W G, et al. Shear behavior degradation and failure pattern of reinforced concrete beam with chloride-induced stirrup corrosion[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2019, 22(14): 2998-3010. doi: 10.1177/1369433219855917 [8] 郭诗惠,刘炳. 锈蚀钢筋混凝土梁抗弯承载力计算与分析[J]. 建筑结构,2017,47(4): 44-48.GUO Shihui, LIU Bing. Calculation and analysis of flexural bearing capacity of corroded reinforced concrete beams[J]. Building Structure, 2017, 47(4): 44-48. [9] 何世钦,王海超,贡金鑫. 荷载与锈蚀共同作用下钢筋混凝土梁抗弯试验研究[J]. 水力发电学报,2007,26(6): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1243.2007.06.009HE Shiqin, WANG Haichao, GONG Jinxin. Study on flexural experiment of reinforced concrete beams under simultaneous service loading and corrosion[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2007, 26(6): 46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1243.2007.06.009 [10] 金伟良,王毅. 持续荷载与氯盐作用下钢筋混凝土梁力学性能试验[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2014,48(2): 221-227.JIN Weiliang, WANG Yi. Experimental study on mechanics behaviors of reinforced concrete beams under simultaneous chloride attacks and sustained load[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2014, 48(2): 221-227. [11] HE S Q, CAO Z Y, LIU W J, et al. Experimental study on long-term performance of reinforced concrete beams under a sustained load in a corrosive environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: 117288.1-117288.11. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117288 [12] YUAN Y, JI Y, SHAH S P. Comparison of two accelerated corrosion techniques for concrete structures[J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2007, 104(3): 344-347. [13] 混凝土结构设计规范:GB 50010—2010 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社,2011. [14] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard specification for portland cement: ASTM C150[S]. Pennsylvania: West Conshohocken, 2020. [15] BALLIM Y, REID J C. Reinforcement corrosion and the deflection of RC beams––an experimental critique of current test methods[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2003, 25(6): 625-632. doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00076-8 -




 下载:
下载: