Traffic Speed Prediction in Merging Zone of Urban Expressway Based on Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network
-
摘要:
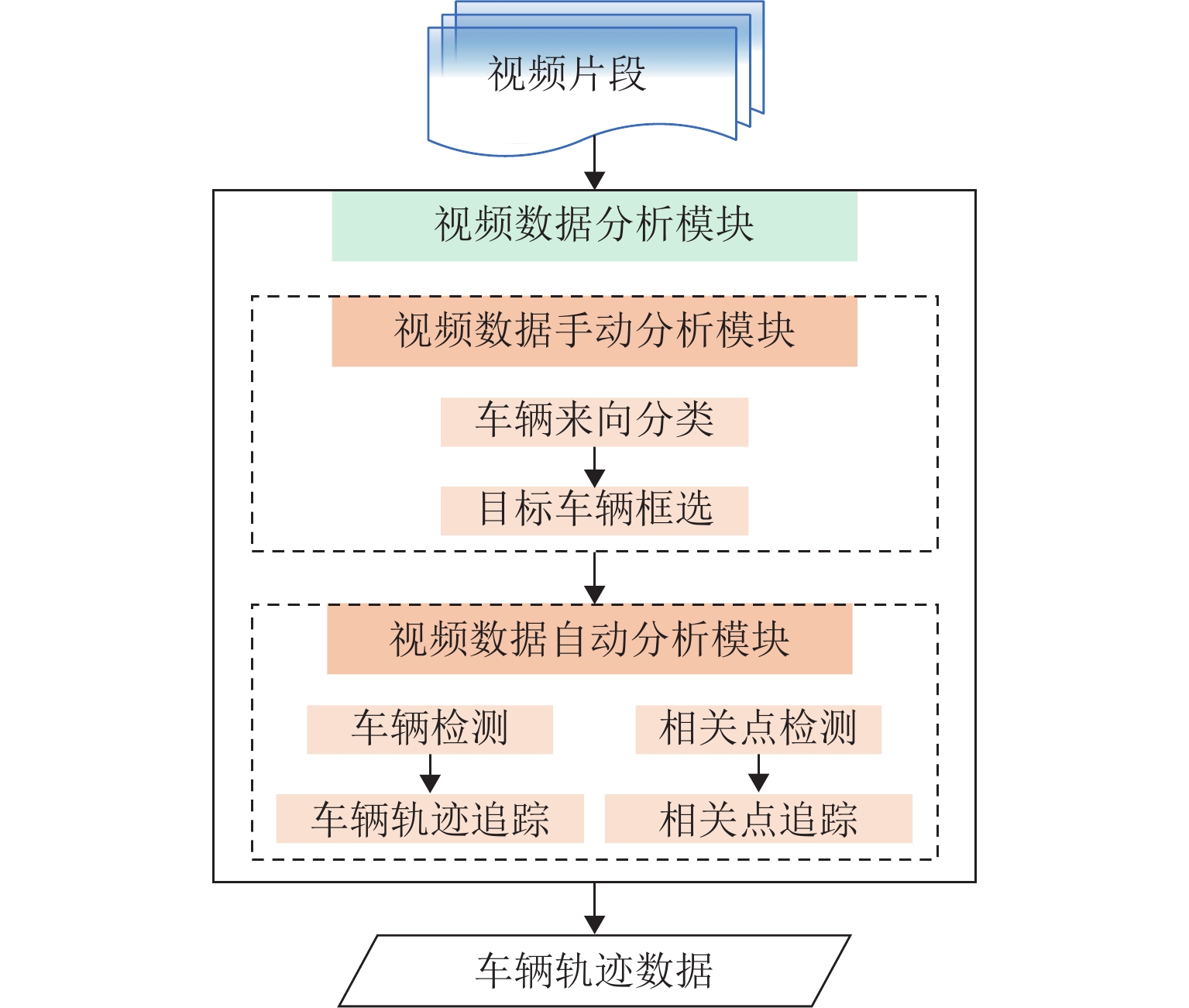
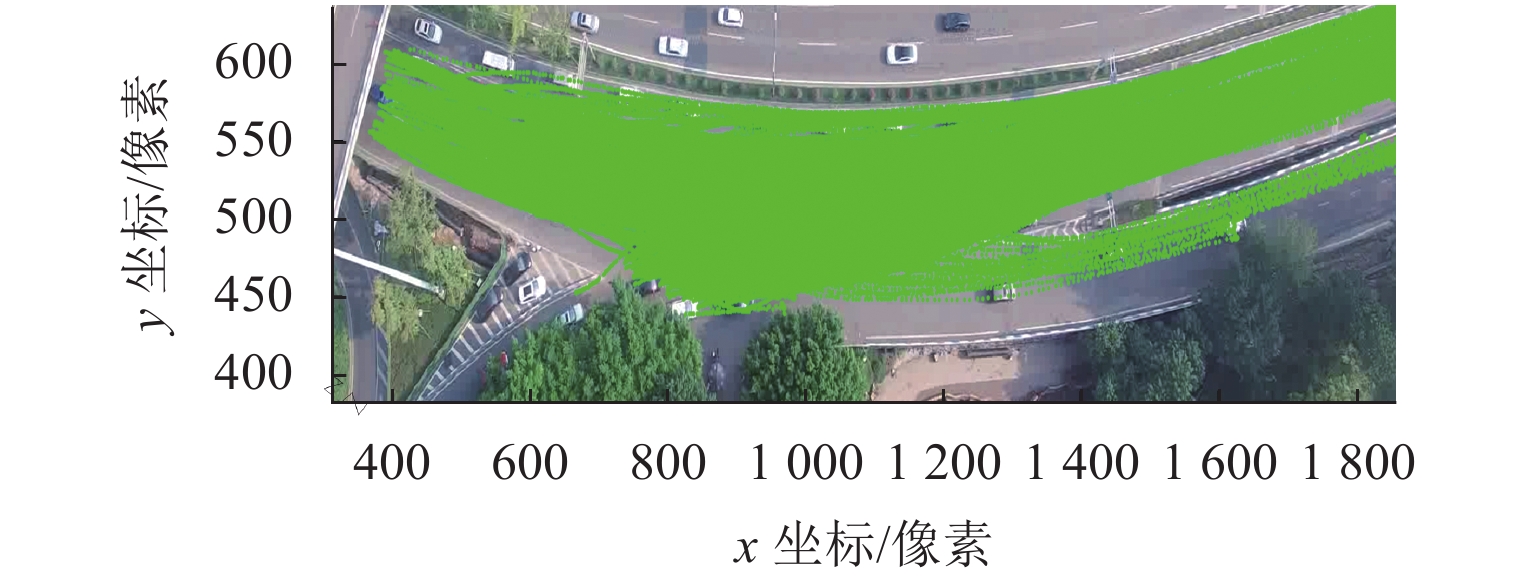
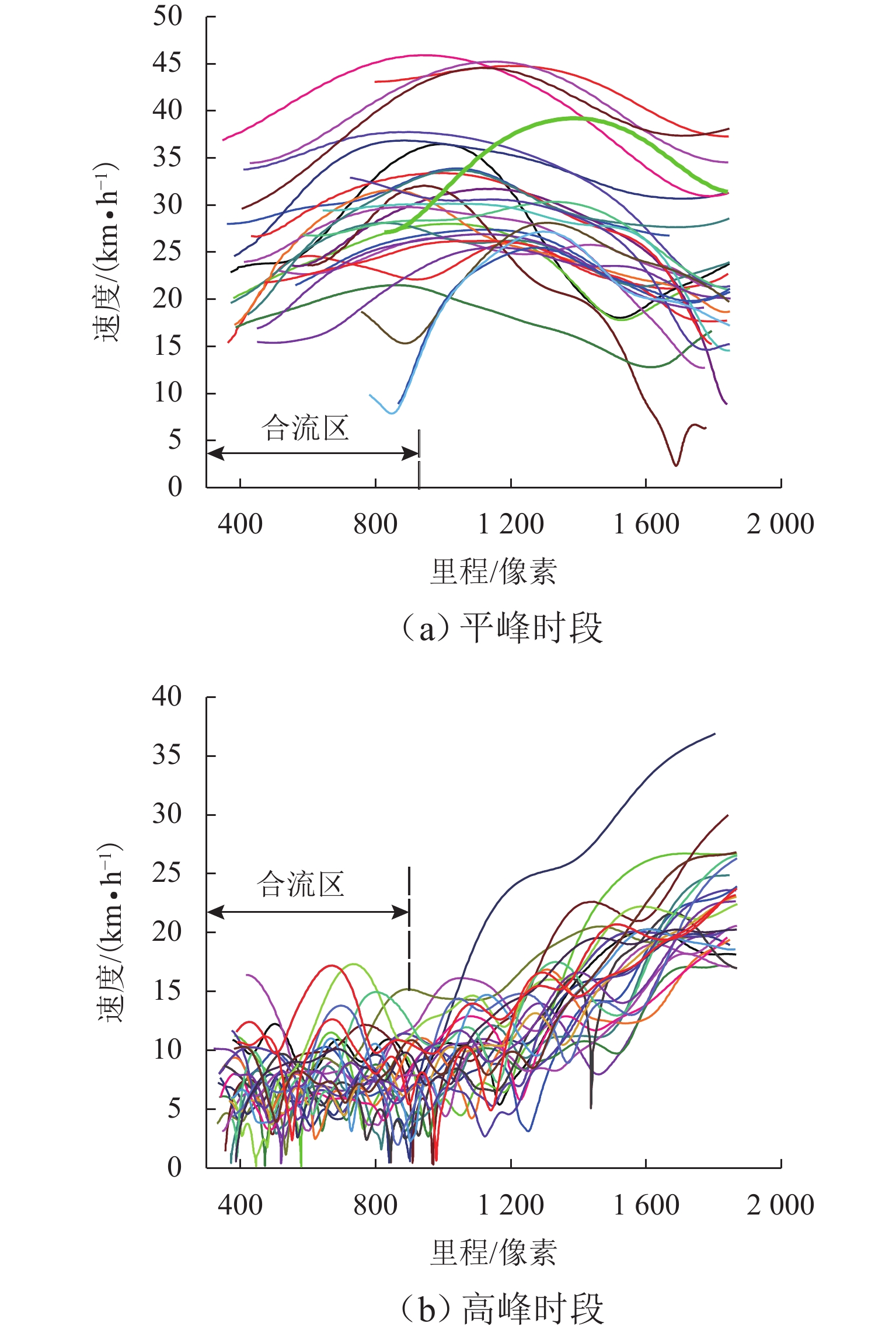
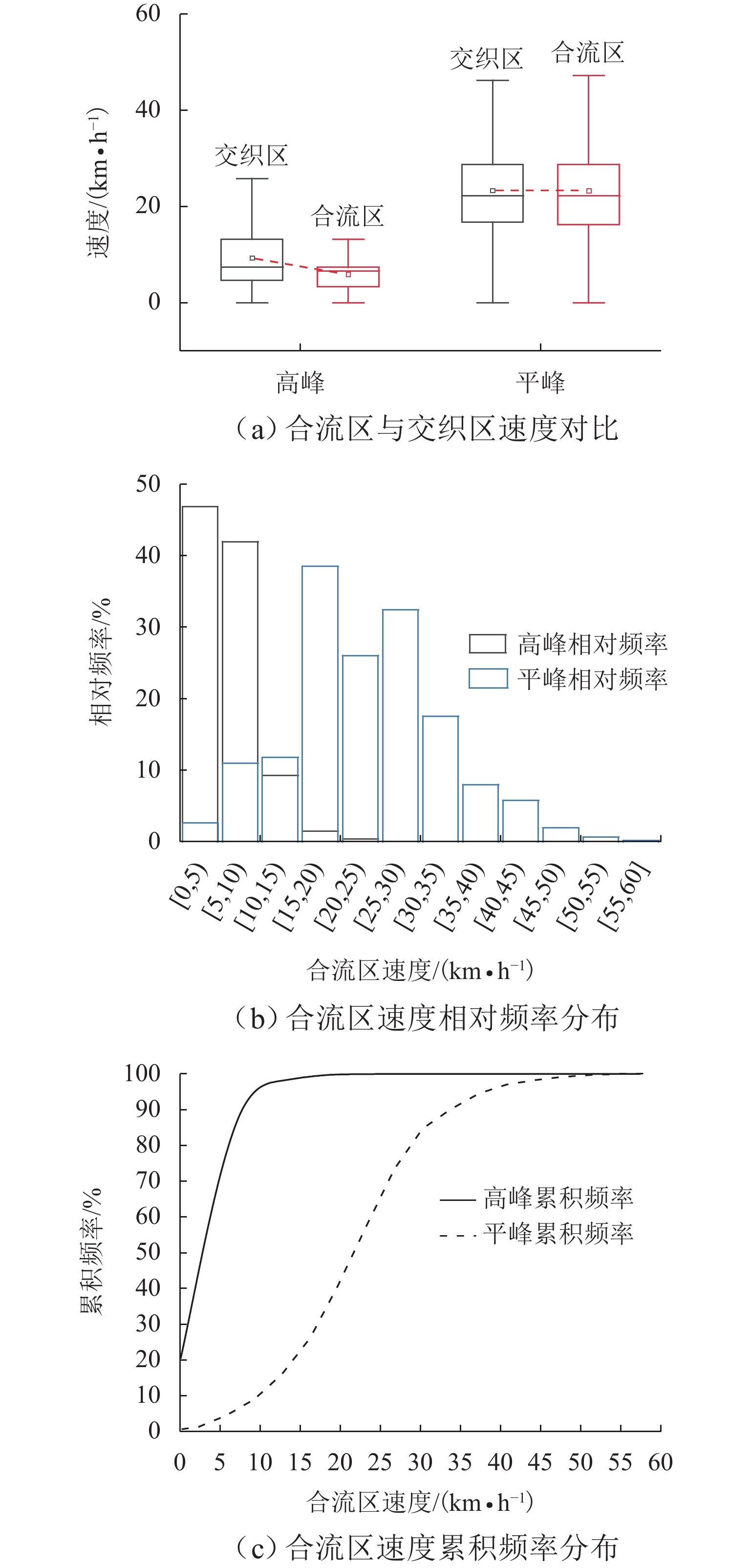
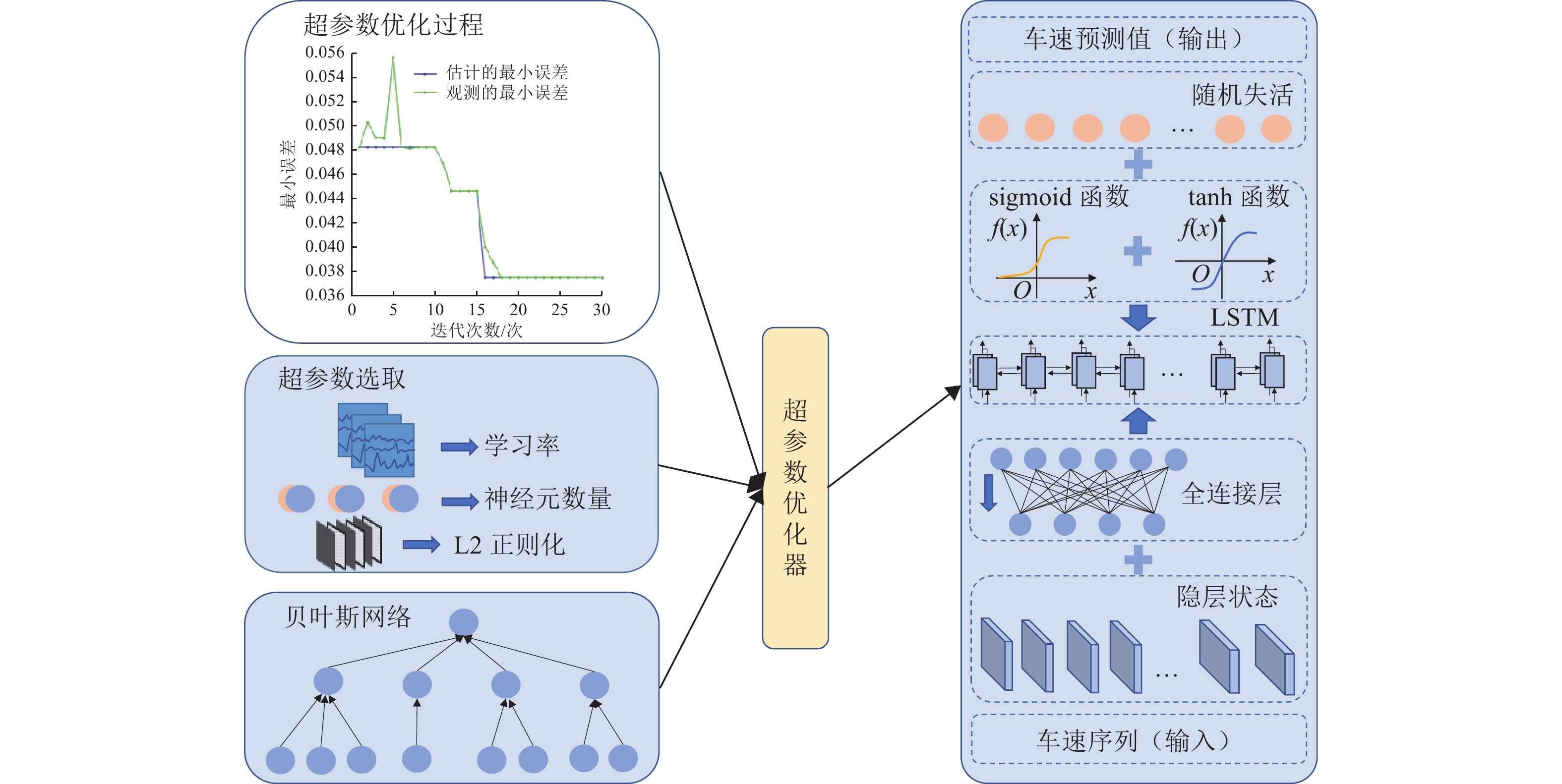
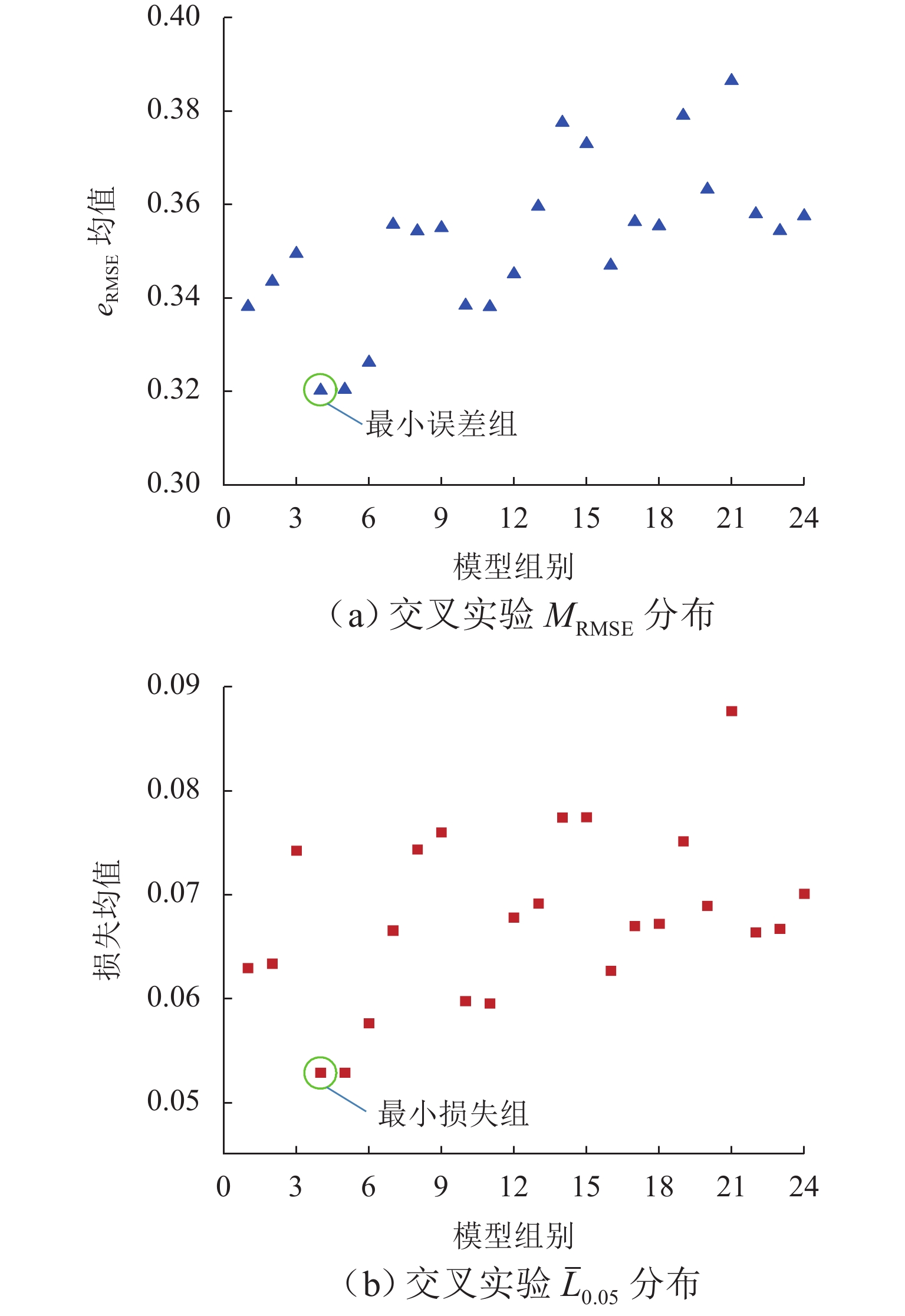
非典型复杂场景微观交通参数的准确预测是保证车路协同系统(IVICS)稳定运行的前提. 为解决IVICS条件下合流区高峰时段瓶颈现象所致的车速分布紊乱而不易预测的问题,首先,基于无人机高空视频,从广域视角提取交织区高峰时段全样本高精度车辆轨迹数据;然后,考虑双向长短期记忆网络(bidirectional long short-term memory,Bi-LSTM)时间较长且人工设置训练参数对模型预测性能影响较大,提出基于贝叶斯超参数(bayesian hyperparameters optimization,BHO)优化的BHO-Bi-LSTM 车速预测集成模型;最后,构建经典多元线性回归车速预测模型、Bi-LSTM车速预测模型作对比. 结果表明:BHO-Bi-LSTM模型表现最优,拟合优度、秩相关度分别为91.05%、94.87%,误差均值、误差的标准差、均方误差、均方根误差、归一化均方根误差分别为
0.056 1 、0.455 6 、0.210 6 、0.458 9 、0.078 5 ,有效改善了合流区高峰时段车速特性复杂而导致不易预测的缺陷.Abstract:Accurate prediction of microscopic traffic parameters in atypical complex scenes is a prerequisite to ensure stable operation of the intelligent vehicle infrastructure cooperative systems (IVICS). To solve the problem of vehicle speed distribution disorder and difficulty in prediction caused by bottleneck phenomenon during peak hours in the merging area under IVICS conditions, First, using the UAV video, the full-sample high-precision vehicle trajectory data of the intertwined area during peak hours are extracted from a wide-area view. Then, as bidirectional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) networks cost long time and affect the prediction performance of the model when training parameters are manually set, a BHO-Bi-LSTM (bayesian hyperparameter optimization bidirectional long short-term memory) integrated vehicle speed prediction model based on Bayesian hyperparameters optimization is proposed. Finally, the classical multiple linear regression model and Bi-LSTM model of vehicle speed prediction are constructed for comparison. The results show that the BHO-Bi-LSTM model outperforms other models, with a goodness-of-fit and rank correlation of 91.05% and 94.87%, respectively, and error mean, error standard deviation, mean square error, root mean square error, and normalized root mean square error of
0.0561 ,0.4556 ,0.2106 ,0.4589 , and0.0785 , respectively, which can overcome the disadvantage in prediction of complicated traffic speeds during peak hours.-
Key words:
- traffic engineering /
- speed prediction /
- multiple weaving area /
- trajectory data /
- Bayesian optimization
-
表 1 模型总体评价指标对比
Table 1. Comparison of overall model evaluation indicators
模型 R2 $\mu $ estD eMSE eRMSE eNRMSE rs 多元线性回归[22]
(模型Ⅰ)0.7980 0.001 7 1.659 5 2.754 2 1.659 6 0.269 0 0.844 0 Bi-LSTM[23]
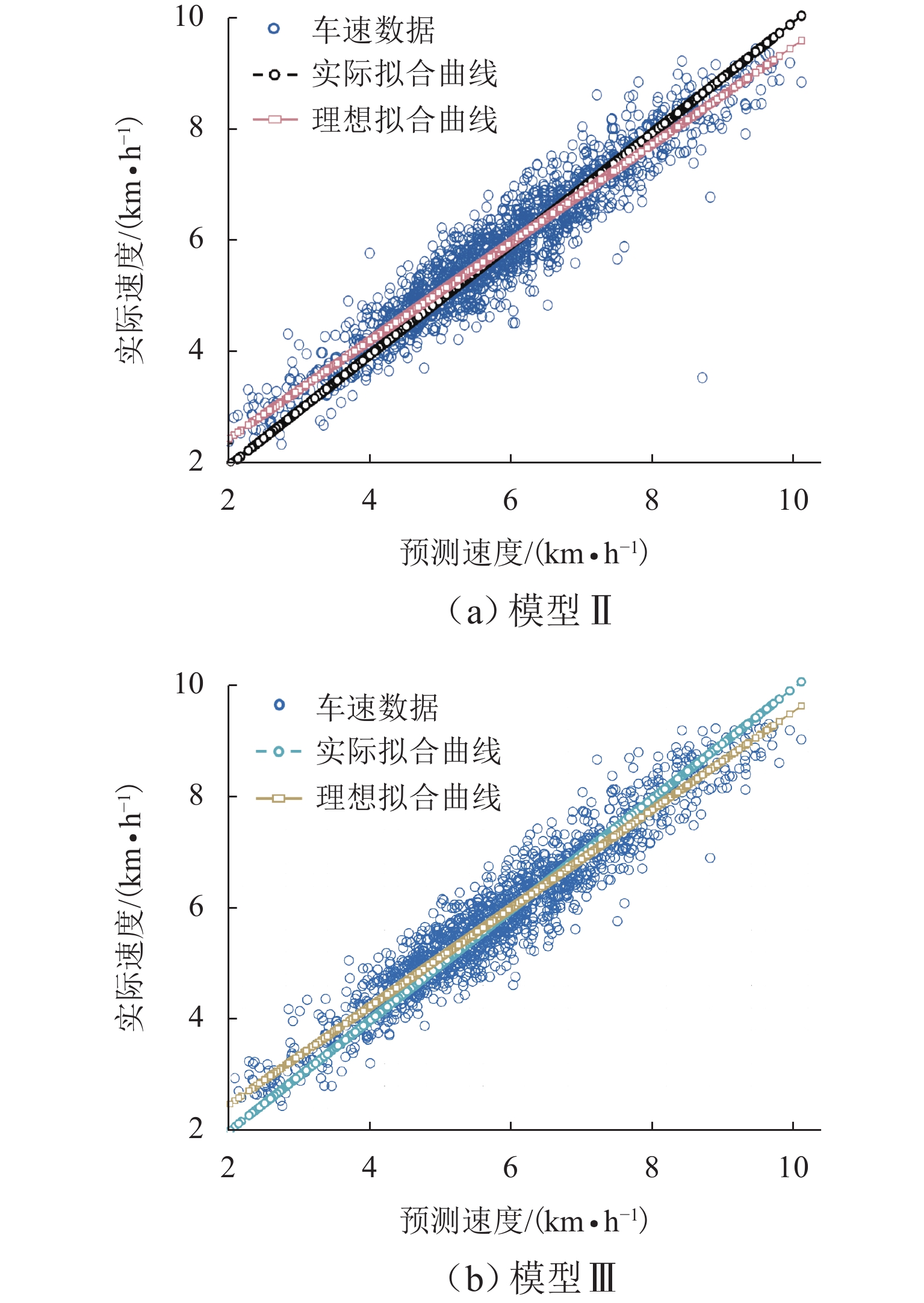
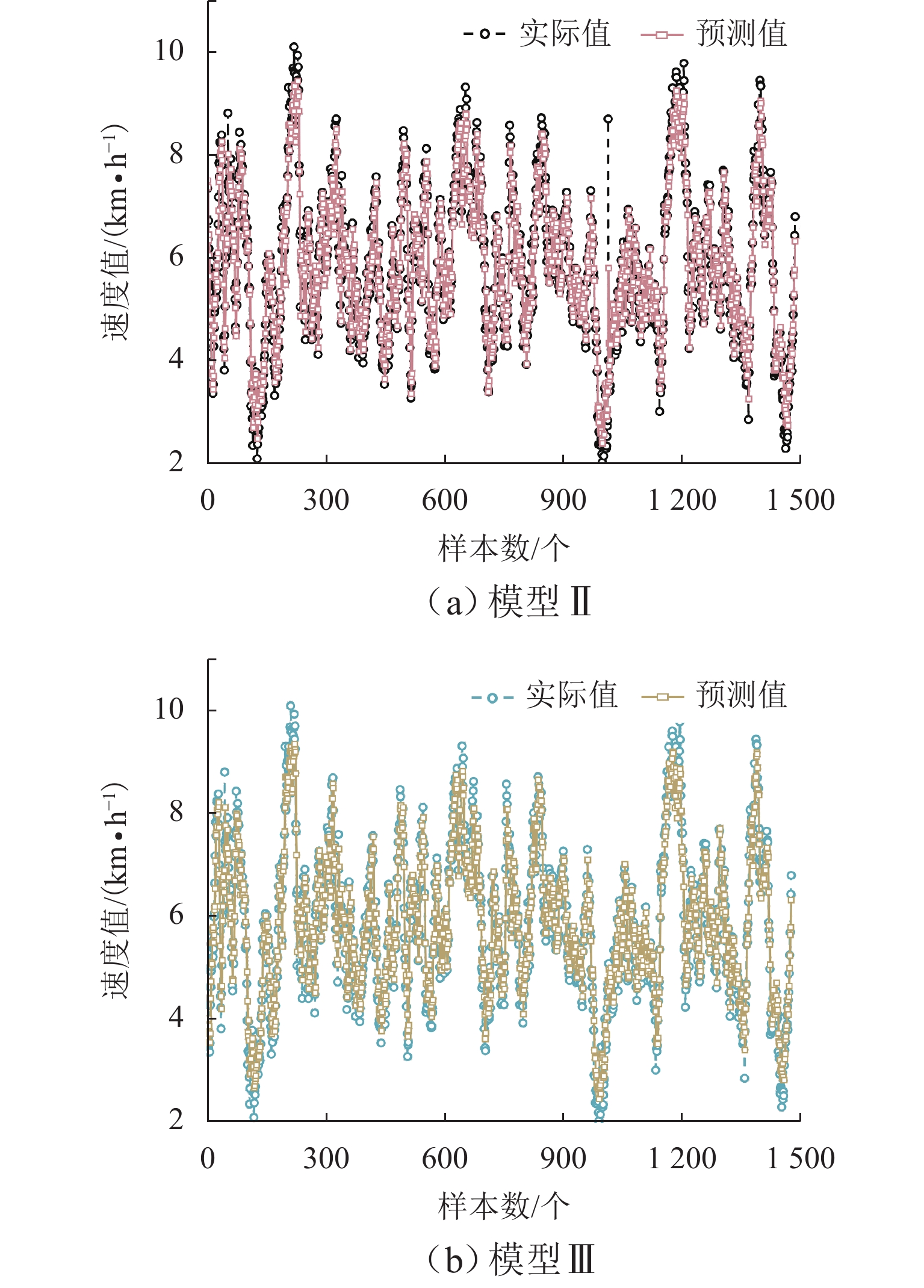
(模型Ⅱ)0.8882 −0.005 3 0.471 1 0.221 8 0.470 9 0.080 6 0.945 3 BHO-Bi-LSTM
(模型Ⅲ)0.9105 0.056 1 0.455 6 0.210 6 0.458 9 0.078 5 0.948 7 模型Ⅲ对比模型Ⅰ
(提升或下降比例)+ 0.1125
(↑14.10%)+ 0.054 4
(↓3 200%)−1.203 9
(↑72.55%)−2.543 6
(↑92.35%)−1.200 7
(↑72.35%)−0.190 5
(↑70.82%)+ 0.1047
(↑12.35%)模型Ⅲ对比模型Ⅱ
(提升或下降比例)0.2230
(↑3.80%)+ 0.061 4
(↓1158.49%)−0.015 5
(↑3.29%)−0.011 2
(↑5.05%)−0.012 0
(↑2.548%)−0.002 1
(↑2.605%)+ 0.0034
(↑0.40%)注:黑体加粗表示最优指标 -
[1] 朱洁玉,马艳丽. 合流区域多车交互风险实时评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版),2022,52(7):1574-1578.ZHU Jieyu, MA Yanli. Risk assessment method in real-time of multi-vehicle interaction at themerging area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022,52(7):1574-1578. [2] 阎莹,盛彦婷,袁华智,等. 高速公路出入口区域行车风险评价及车速控制[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2011,11(2): 90-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2011.02.015YAN Ying, SHENG Yanting, YUAN Huazhi, et al. Driving risk evaluation and speed control in passageway areas of freeway[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2011, 11(2): 90-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1637.2011.02.015 [3] 贺正冰,徐瑞康,谢东繁,等. 数据驱动跟驰模型综述[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(5): 102-113.HE Zhengbing, XU Ruikang, XIE Dongfan, et al. A review of data-driven car-following models[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(5): 102-113. [4] 徐进,曾粤. 高速条件下隧道出入口行驶速度特性[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(4): 197-209.XU Jin, ZENG Yue. Characteristics of driving speed at tunnel entrance and exit at high speed[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(4): 197-209. [5] Williams B M, Hoel L A. Modeling and forecasting vehicular traffic flow as a seasonal ARIMA process: Theoretical basis and empirical results[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2003, 129(6): 664-672. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2003)129:6(664) [6] Yang J S. A study of travel time modeling via time series analysis[C]//Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Conference on Control Applications, 2005. Toronto: IEEE, 2005:855-860. [7] MIR Z H, FILALI F. An adaptive Kalman filter based traffic prediction algorithm for urban road network[C]//2016 12th International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT). Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2016:1-6. [8] YAO B, CHEN C, CAO Q, et al. Short-term traffic speed prediction for an urban corridor[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 32(2): 154-169. doi: 10.1111/mice.12221 [9] 陈孟,干可,李凯,等. 基于实时多模态时空数据的时空图卷积网络精准鲁棒交通流预测模型[J]. 公路交通科技,2021,38(8): 134-139,158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.08.018CHEN Meng, GAN Ke, LI Kai, et al. A spatial-temporal graph convolutional network model for accurate and robust traffic flow prediction based on real-time multimodal spatial-temporal data[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2021, 38(8): 134-139,158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.08.018 [10] ZHAO Z, CHEN W, WU X, et al. LSTM network: a deep learning approach for short-term traffic forecast[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2017, 11(2): 68-75. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2016.0208 [11] XU Y, KONG Q J, KLETTE R, et al. Accurate and interpretable bayesian mars for traffic flow prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(6): 2457-2469. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2014.2315794 [12] ZHENG L, YANG J, CHEN L, et al. Dynamic spatial-temporal feature optimization with ERI big data for short-term traffic flow prediction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 412: 339-350. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.038 [13] Peng Y, Xiang W. Short-term traffic volume prediction using GA-BP based on wavelet denoising and phase space reconstruction[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 549: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2019.123913 [14] 李桃迎,王婷,张羽琪. 考虑多特征的高速公路交通流预测模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(3): 101-111.LI Taoying, WANG Ting, ZHANG Yuqi. Highway traffic flow prediction model considering multi-features[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(3): 101-111. [15] 陈华伟,邵毅明,敖谷昌,等. 面向在线地图的GCN-LSTM神经网络速度预测[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2021,21(4):183-196.CHEN Huawei, SHAO Yiming, AO Guchang, et al. On-line map oriented GCN-LSTM neural network speed prediction[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2021,21(4):183-196. [16] LI T, NI A, ZHANG C, et al. Short-term traffic congestion prediction with Conv-BiLSTM considering spatio-temporal features[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2021, 14(14): 1978-1986. [17] BERGSTRA J , BENGGIO Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2012,13(1):281-305. [18] JIA W, CHEN X Y, et al. Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning models based on bayesian optimization[J]. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology,2019, 17(1):26-40. [19] 崔佳旭,杨博. 贝叶斯优化方法和应用综述[J]. 软件学报,2018,29(10): 3068-3090.CUI Jiaxu, YANG Bo. Survey on bayesian optimization methodology and applications[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(10): 3068-3090. [20] SHAHRIARI B , SWERSKY K , WANG Z , et al. Taking the human out of the loop: a review of bayesian optimization[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE,2015,104(1):148-175. [21] 徐进, 陈莹, 张晓波, 等. 回头曲线路段的轨迹曲率特性和汽车过弯方式[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2021,56(06):1143-1152.XU Jin, CHEN Ying, ZHANG Xiaobo, et al. Longitudinal acceleration performance of passenger cars on complex mountain highways[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2021,56(06):1143-1152. [22] 朱云波, 夏玉兰, 王玥然, 等. 基于生态驾驶的道路合流区车辆运行状态估计[J]. 北京工业大学学报,2023,49(7):785-791.ZHU Yunbo, XIA Yulan, WANG Yueran, et al. Estimation of vehicle operating states in merging areas of roads based on eco-driving[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2023,49(7):785-791. [23] 秦雅琴, 夏玉兰, 钱正富, 等. 微观轨迹信息驱动的Bi-LSTM合流区车速预测[J]. 重庆大学学报,2023,46(4):120-128.QIN Yaqin, XIA Yulan, QIAN Zhengfu, et al. Bi-LSTM merging area speed prediction driven by microscopic trajectory information[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2023,46(4):120-128. -





 下载:
下载: